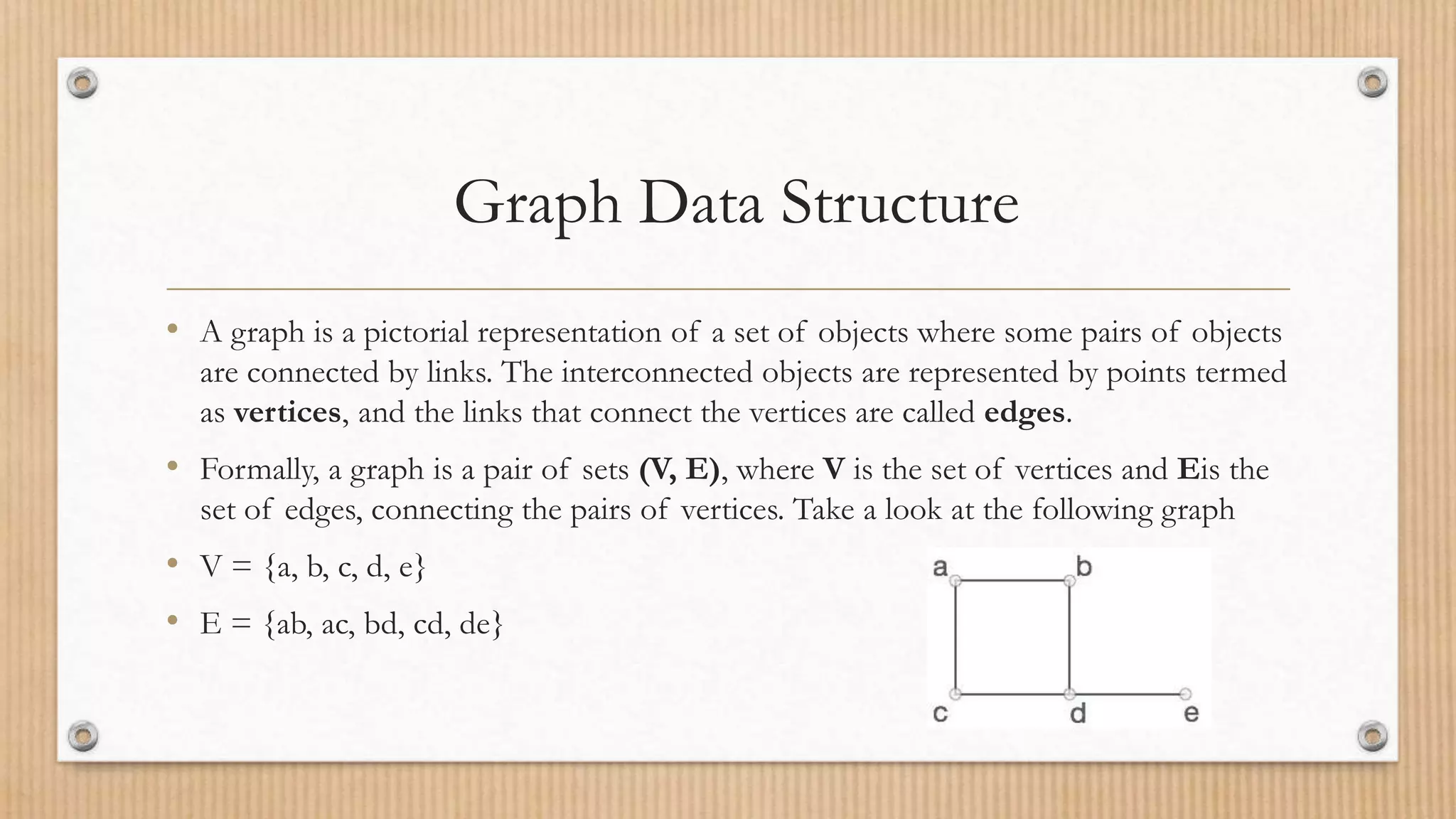
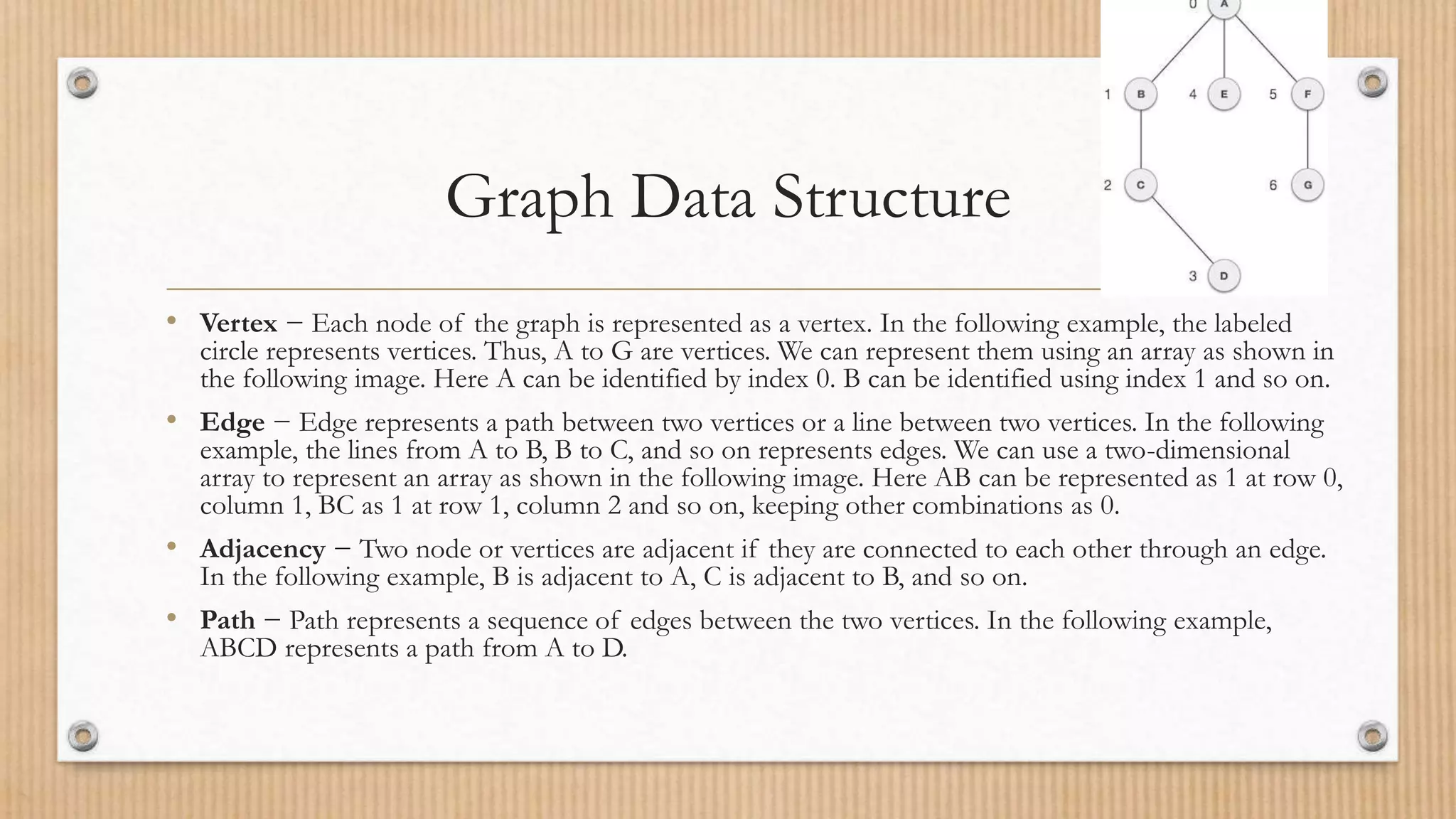
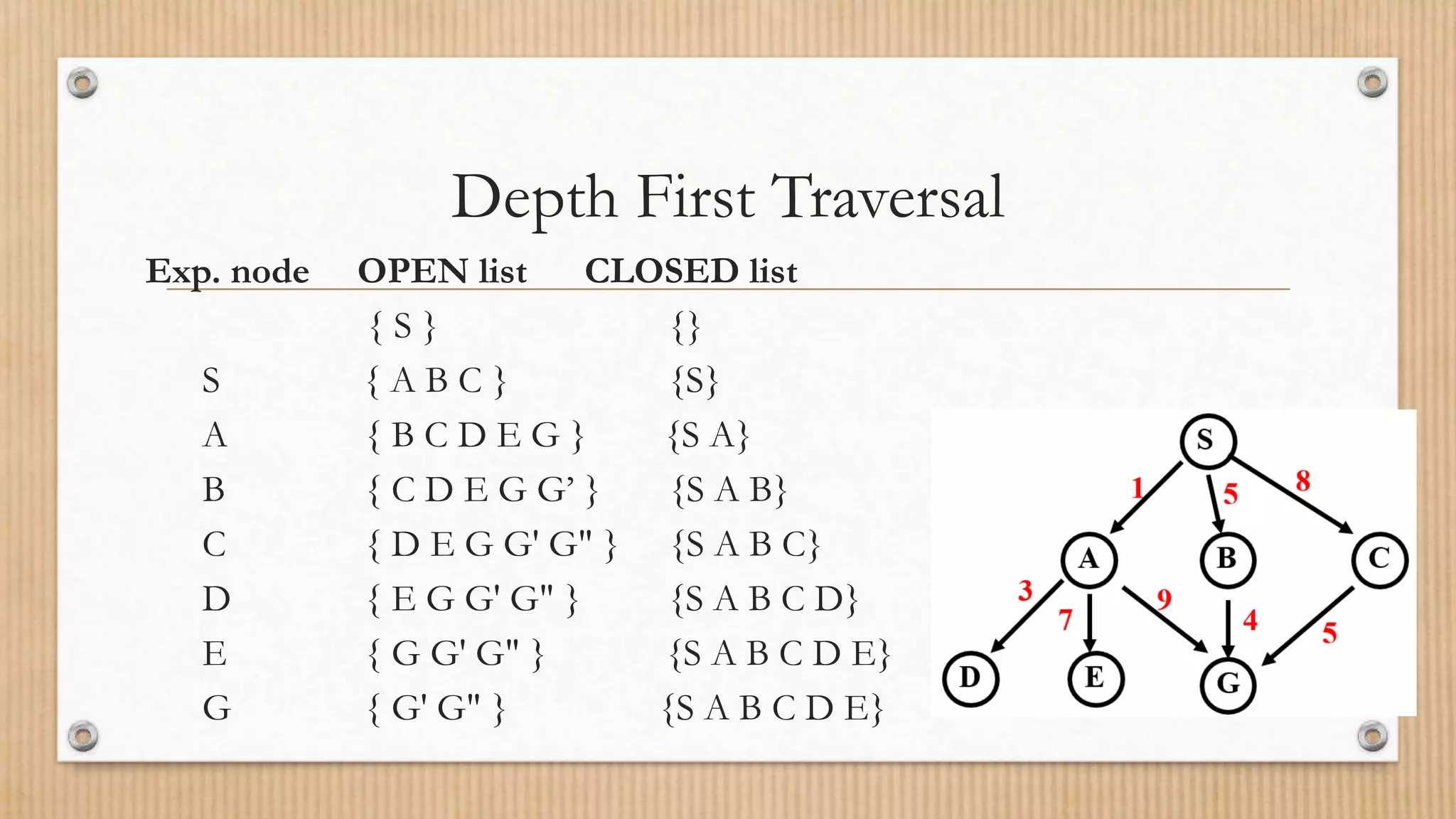
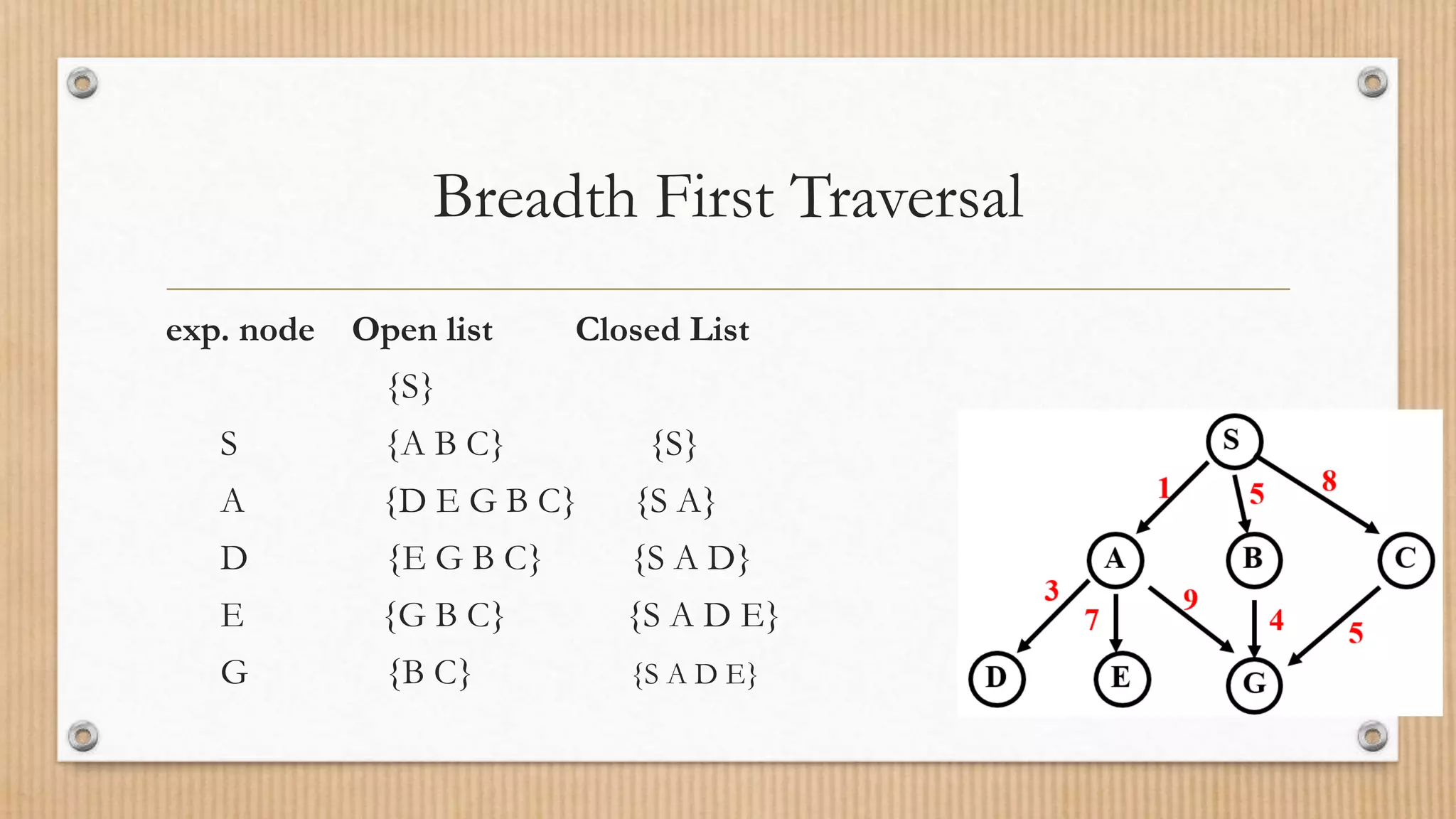
The document explains the concept of a graph as a collection of vertices and edges, illustrating how they relate through pairs of connected objects. It covers key terms such as vertices, edges, adjacency, and paths, and introduces graph traversal algorithms like Depth First Search (DFS) and Breadth First Search (BFS). Both traversal methods are detailed with examples of their respective open and closed lists during search operations.