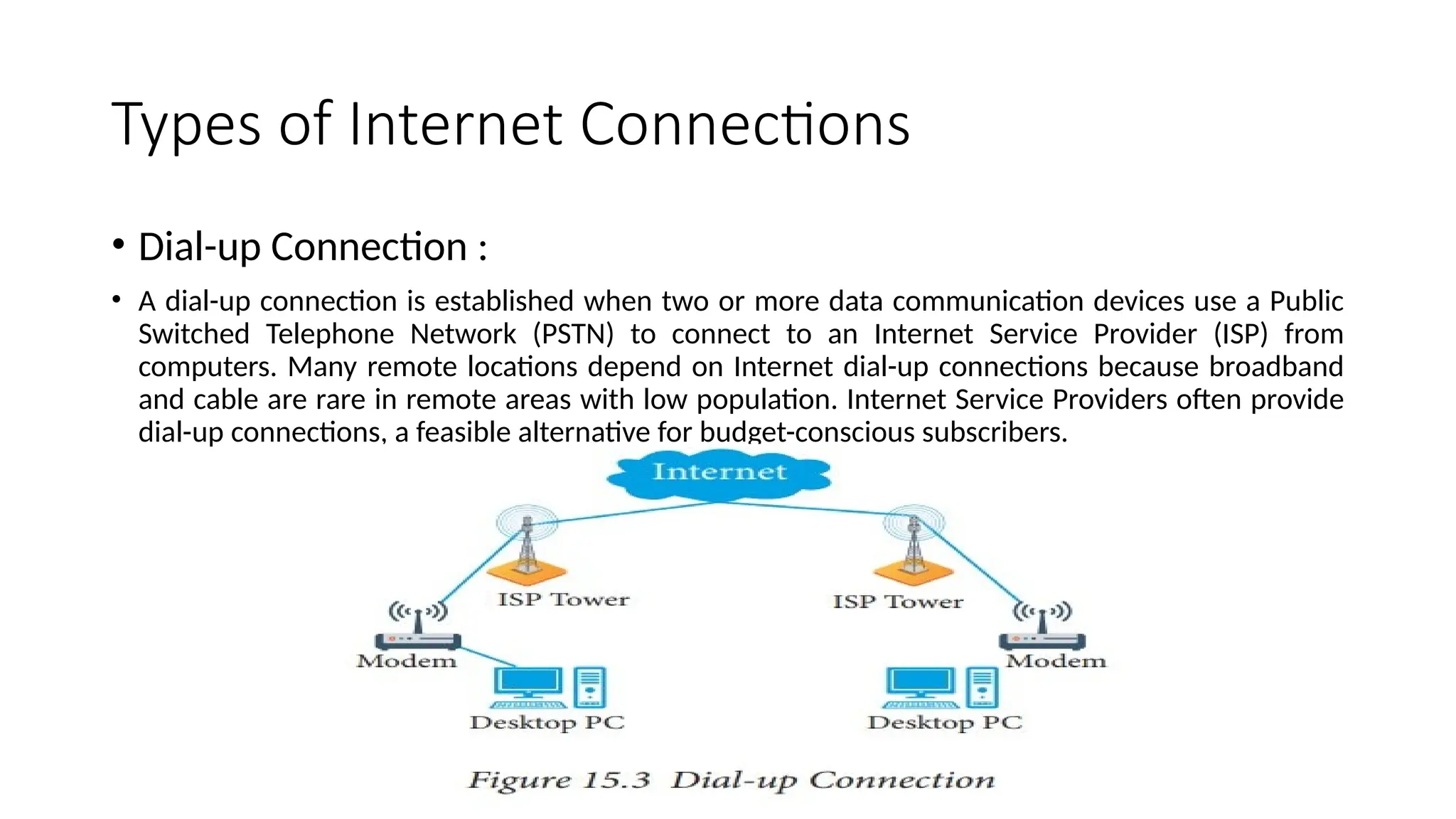
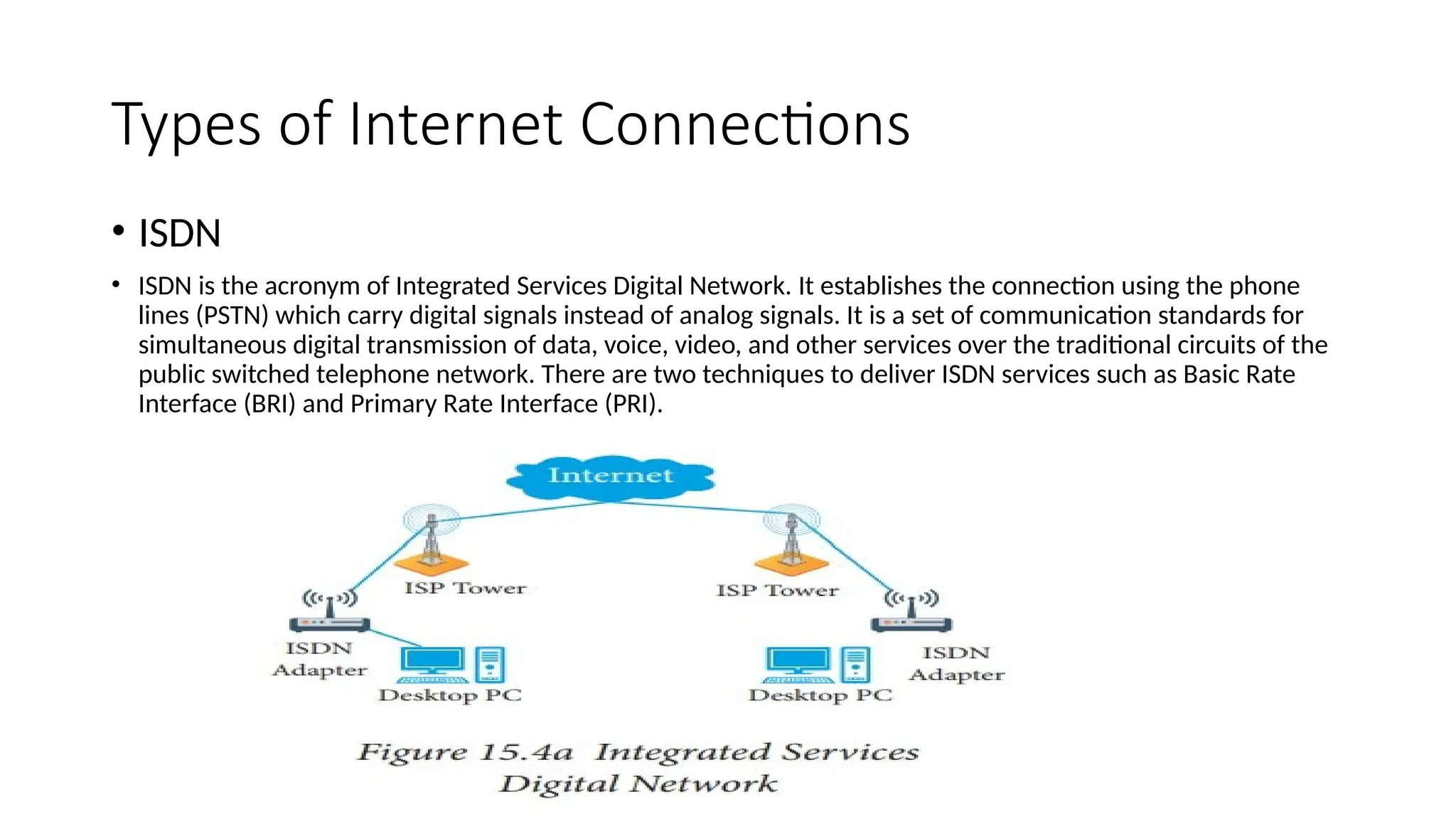
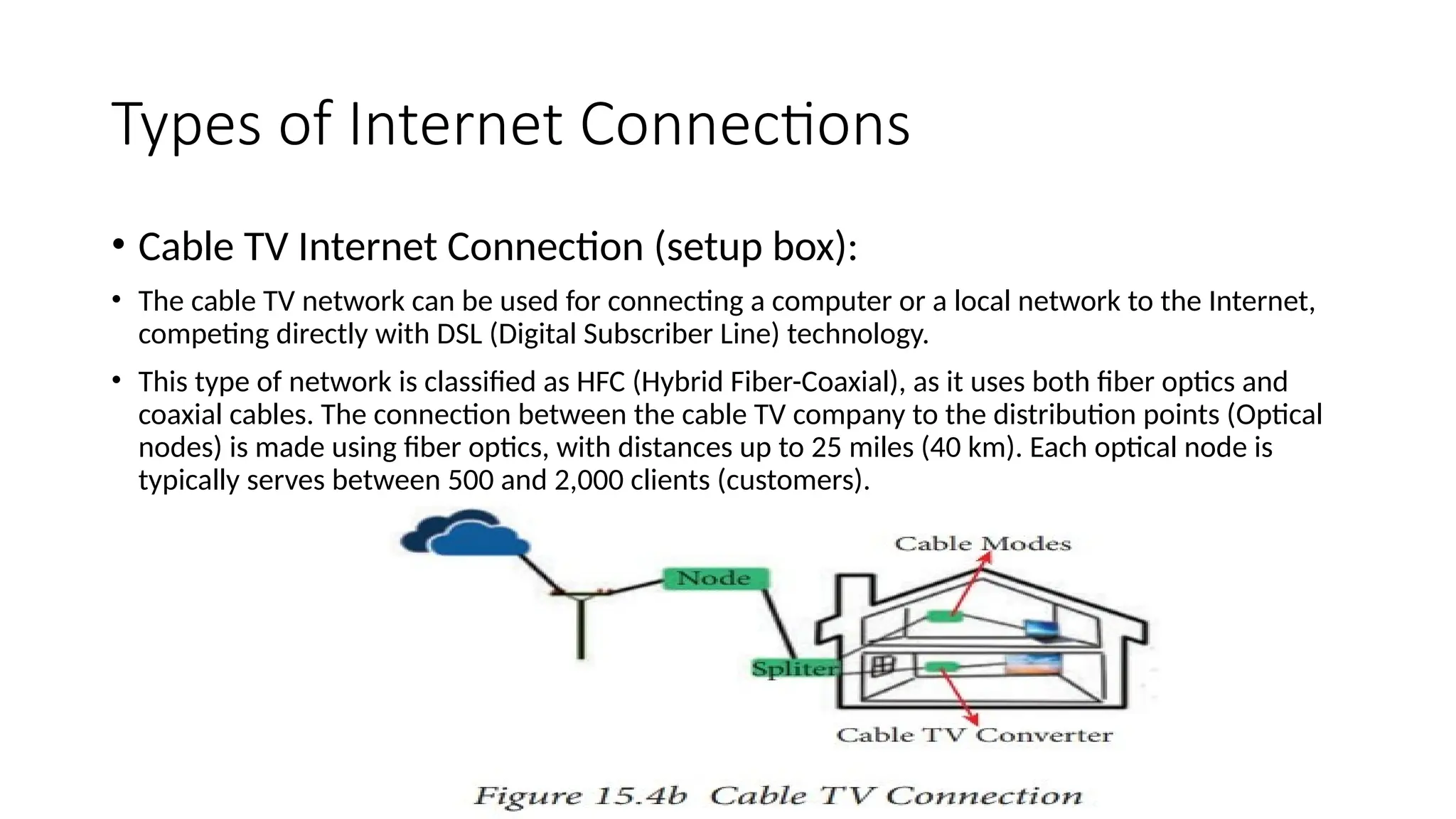
Fundamentals of Computers and Information System:
Basics of Computers: Hardware, Input/Output Devices
Storage Devices & Memory
System & Application Software
Compilers, Interpreters, Assemblers
Computer Languages: Levels, Features
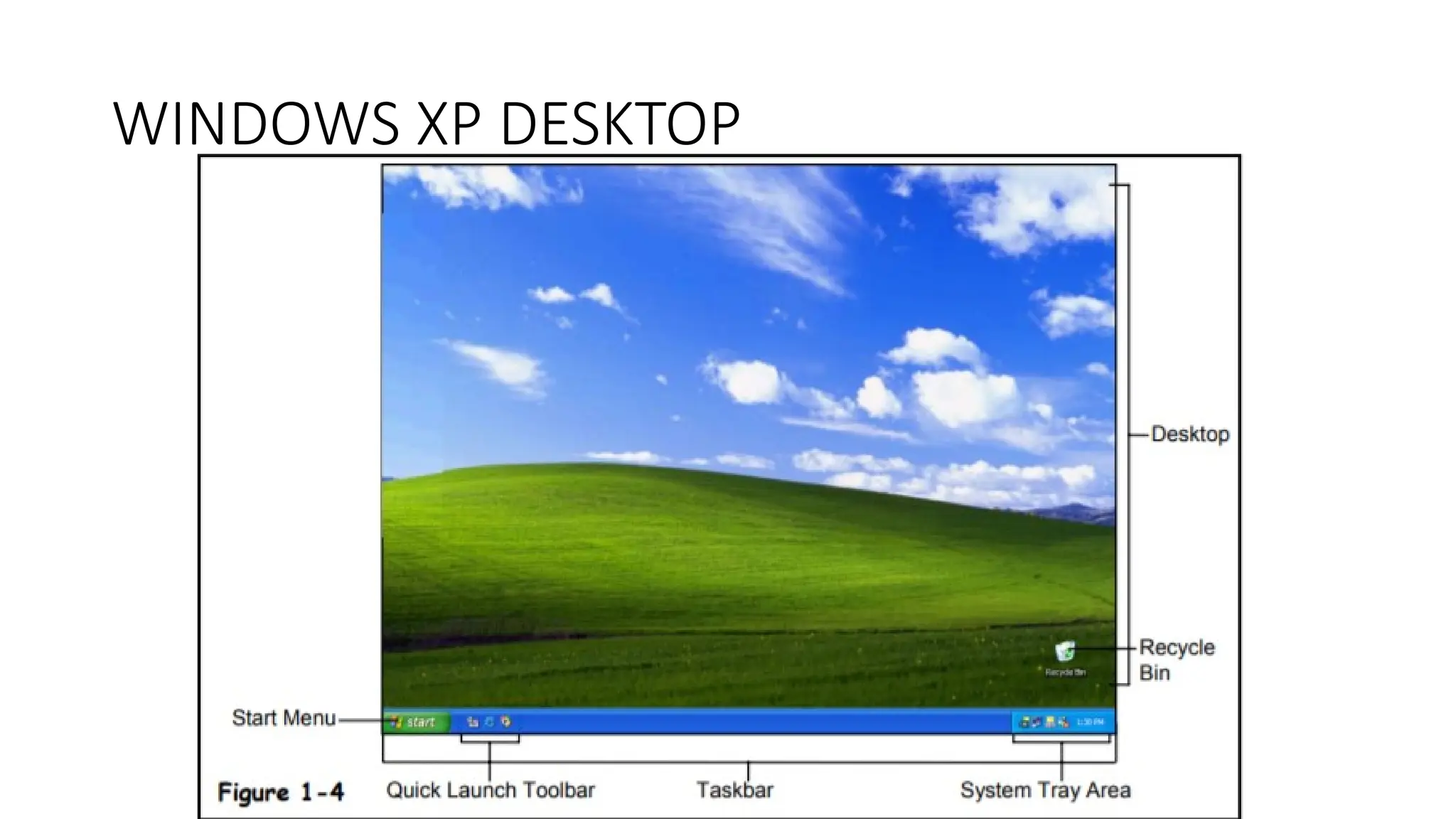
Internet Concepts & Services, OS basics (Windows XP)