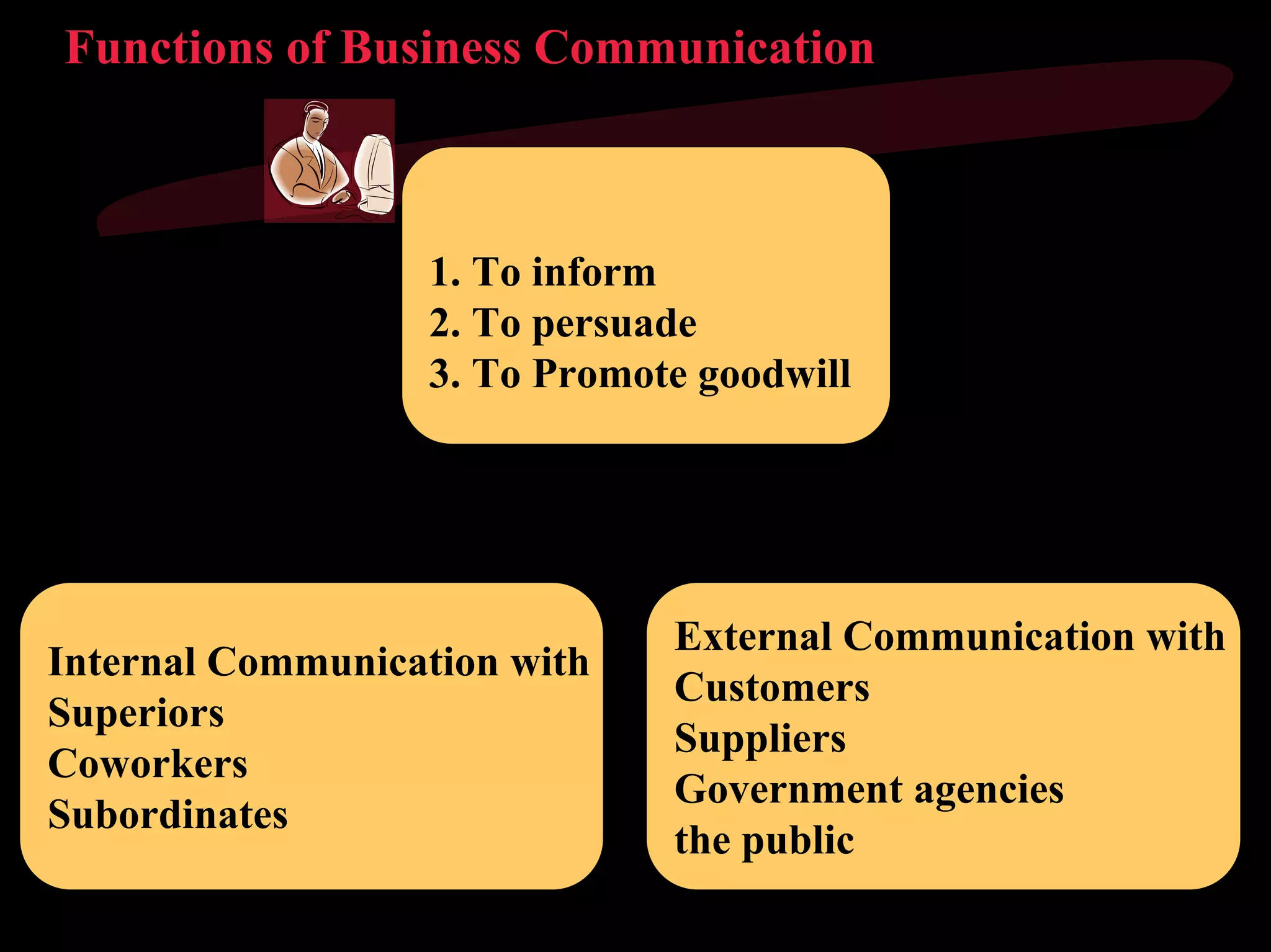
The document discusses the functions of communication. It describes communication as the process through which organizations emerge and evolve. The main functions of communication are information and persuasion. Communication serves important roles in decision making, control, and helping organizations adapt to their environment. Good leaders need to be good communicators to share vision, inspire, motivate, and pass information.