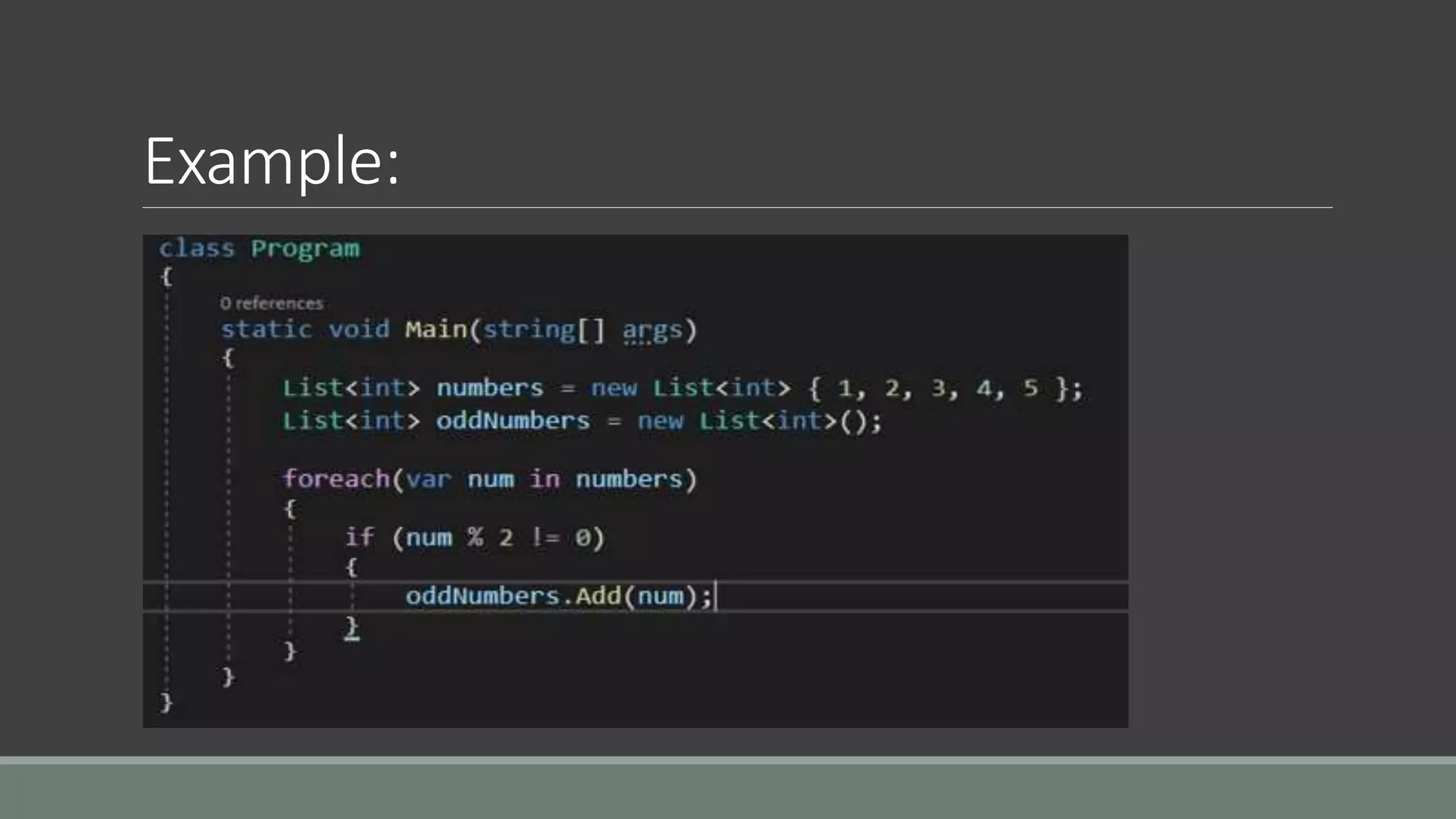
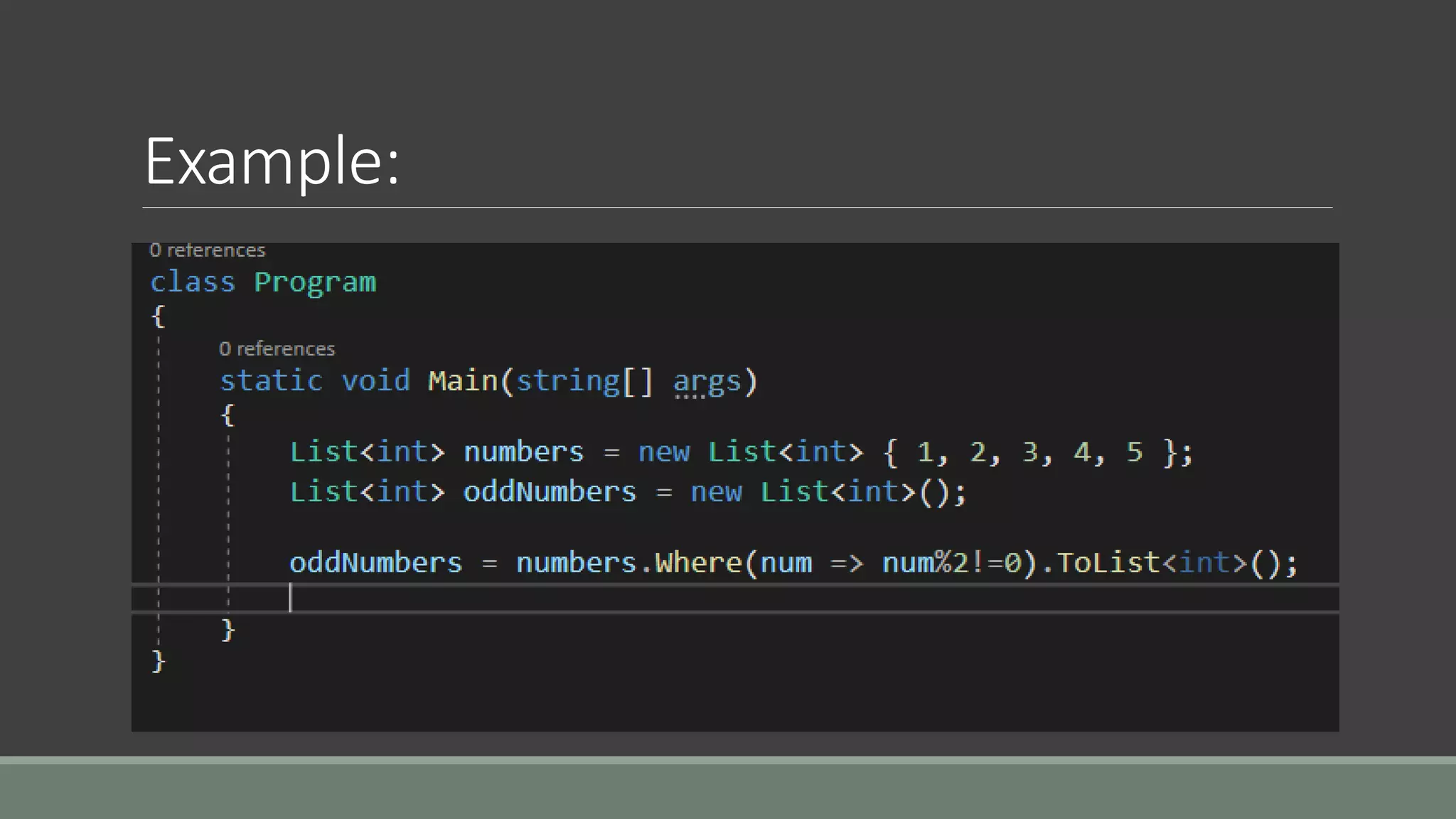
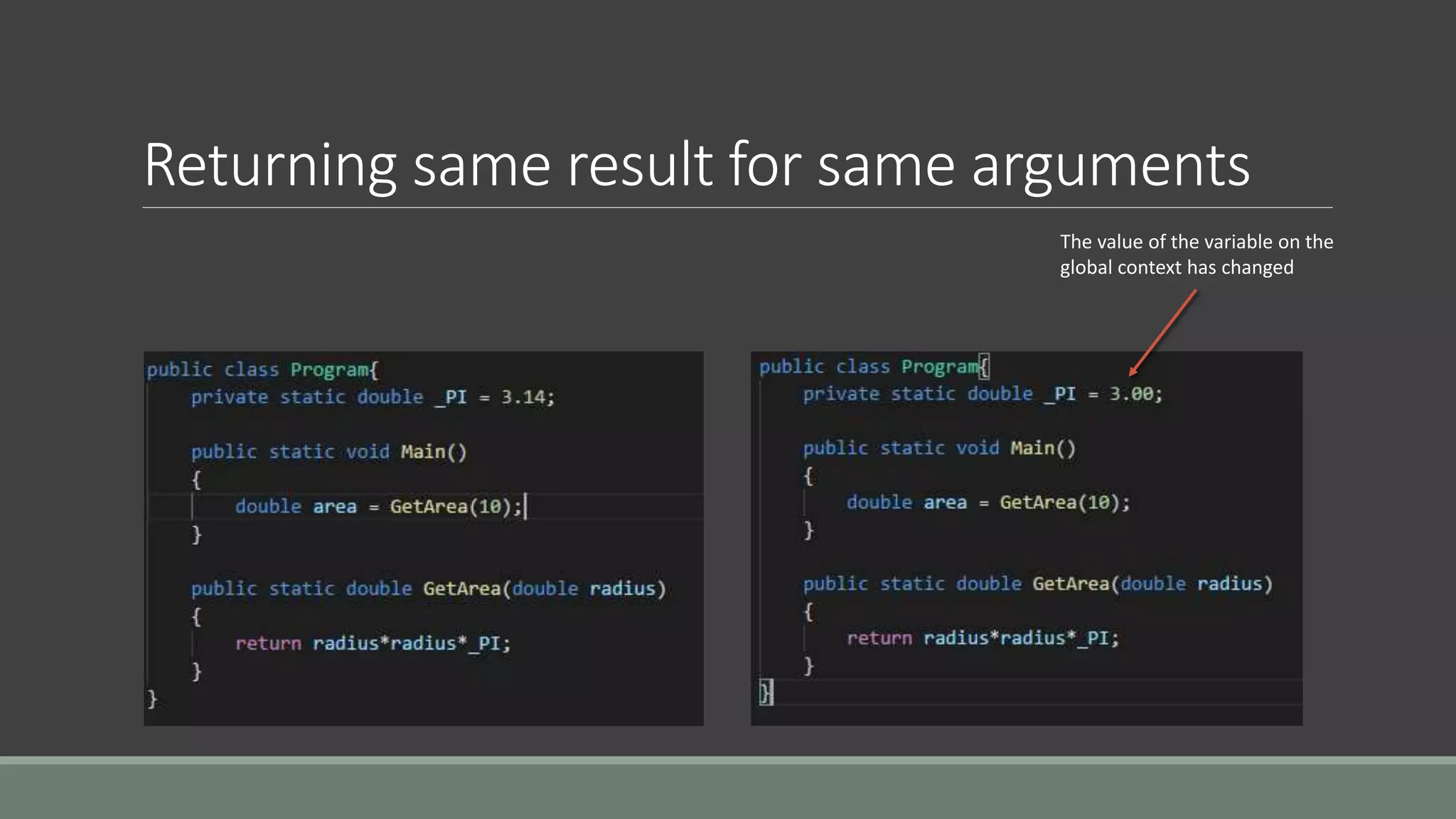
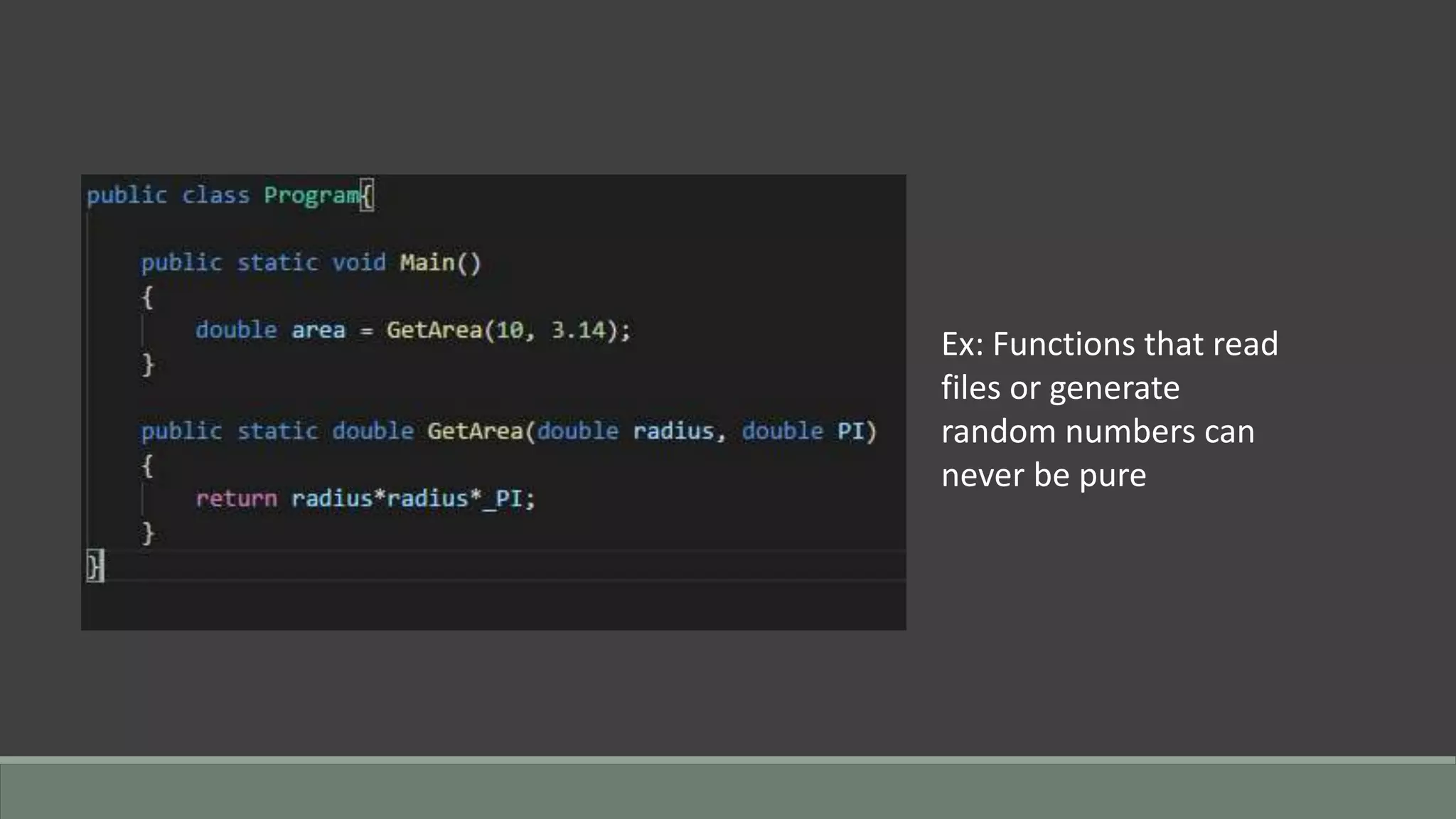
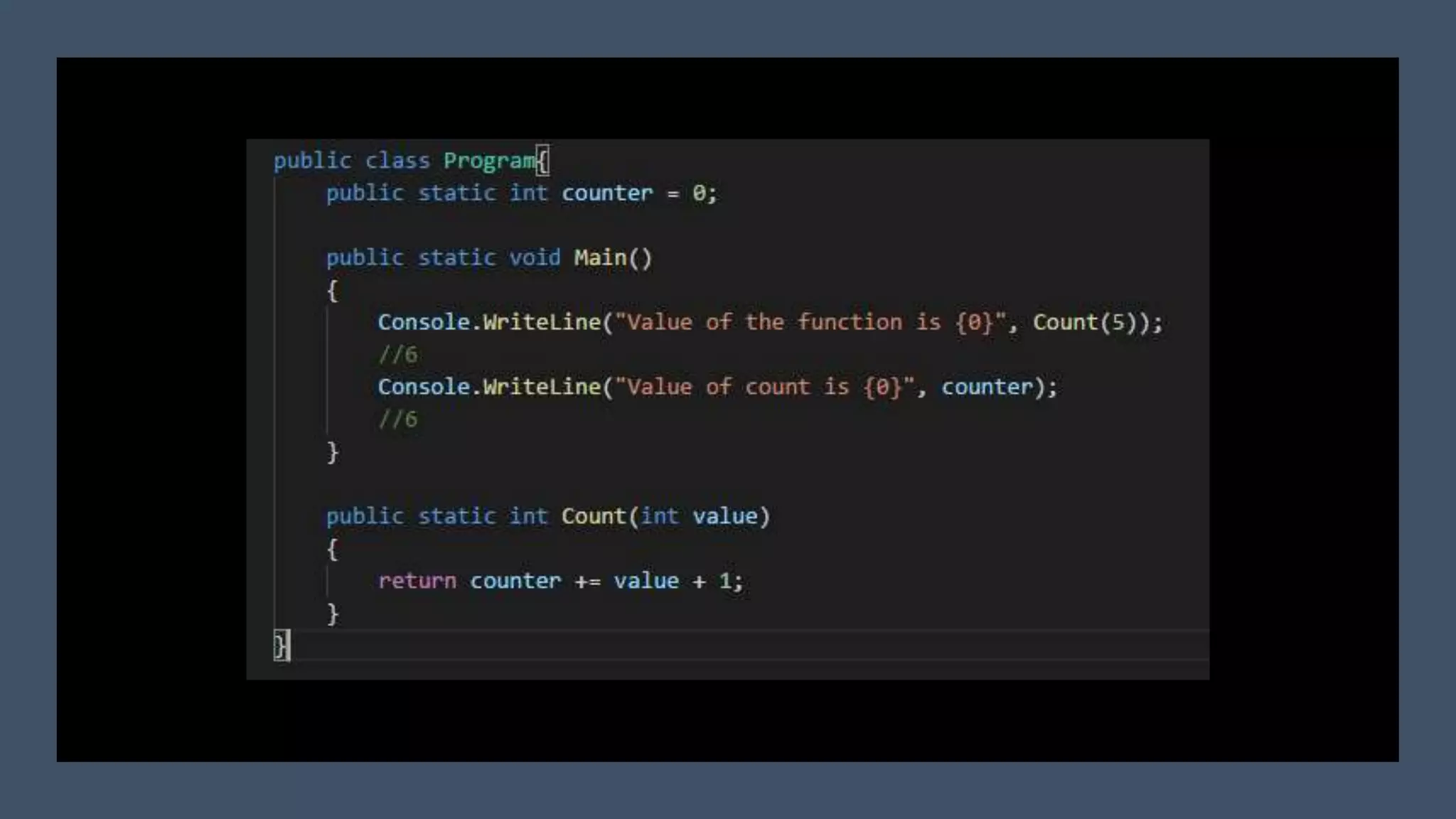
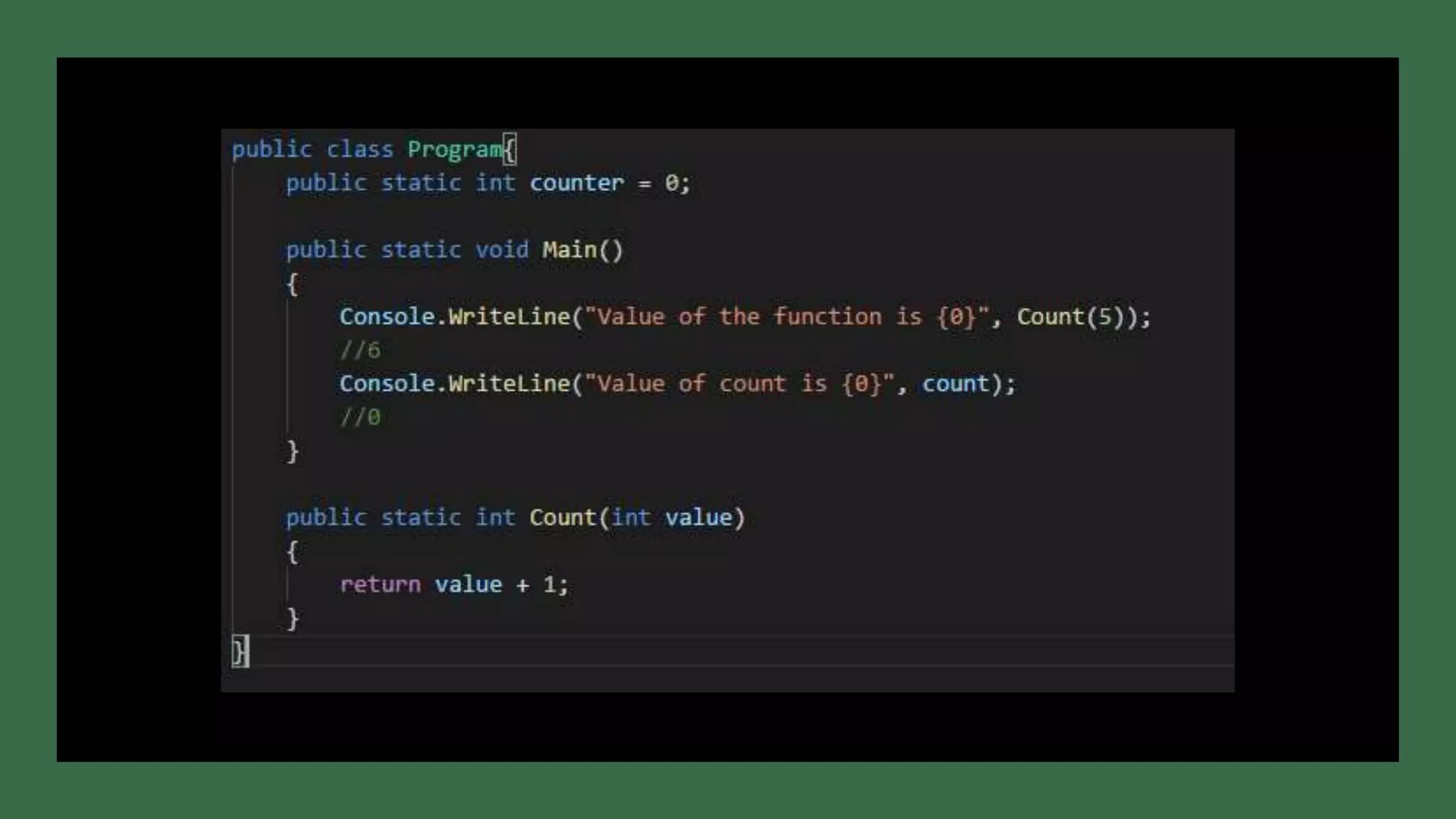
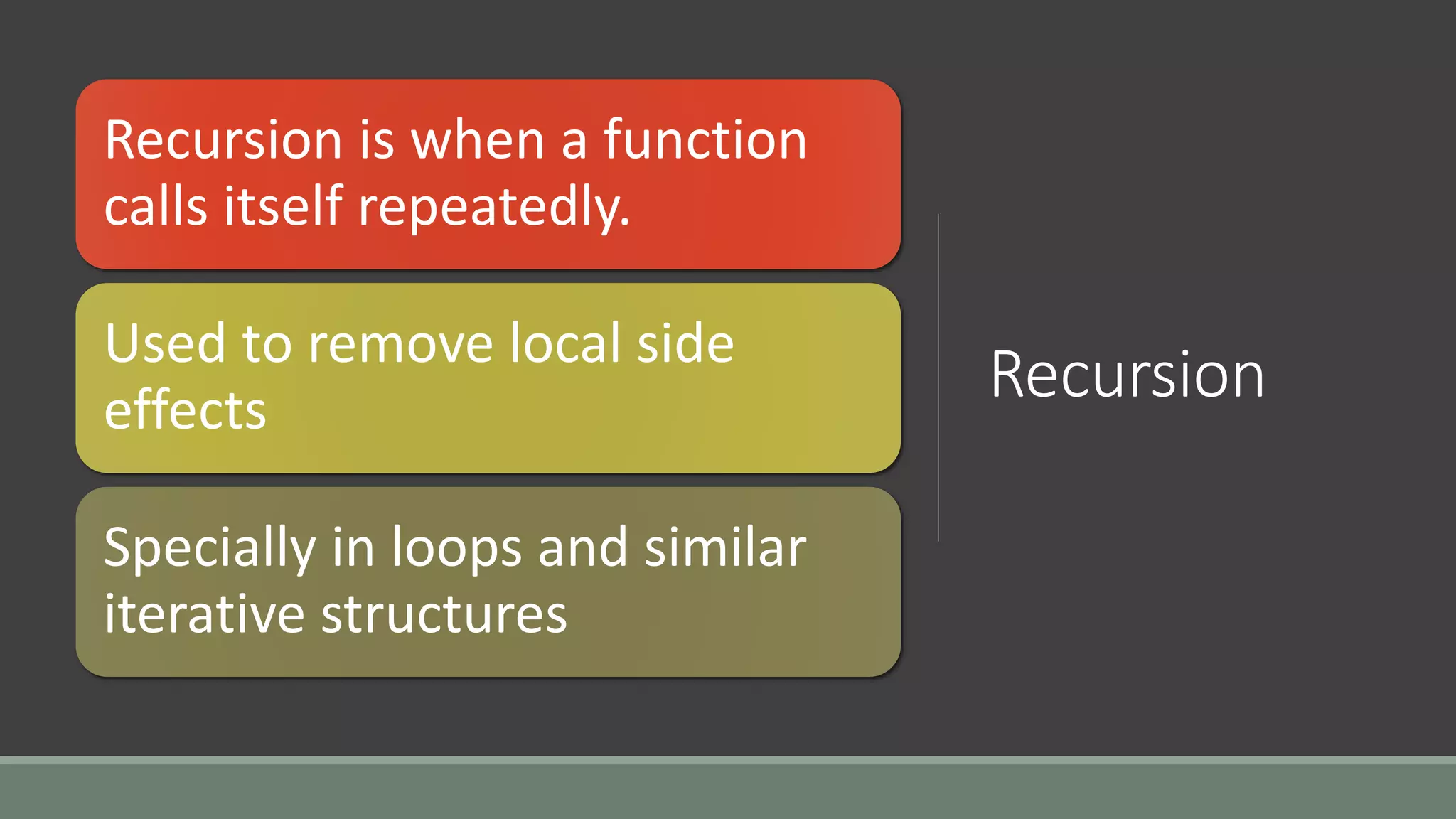
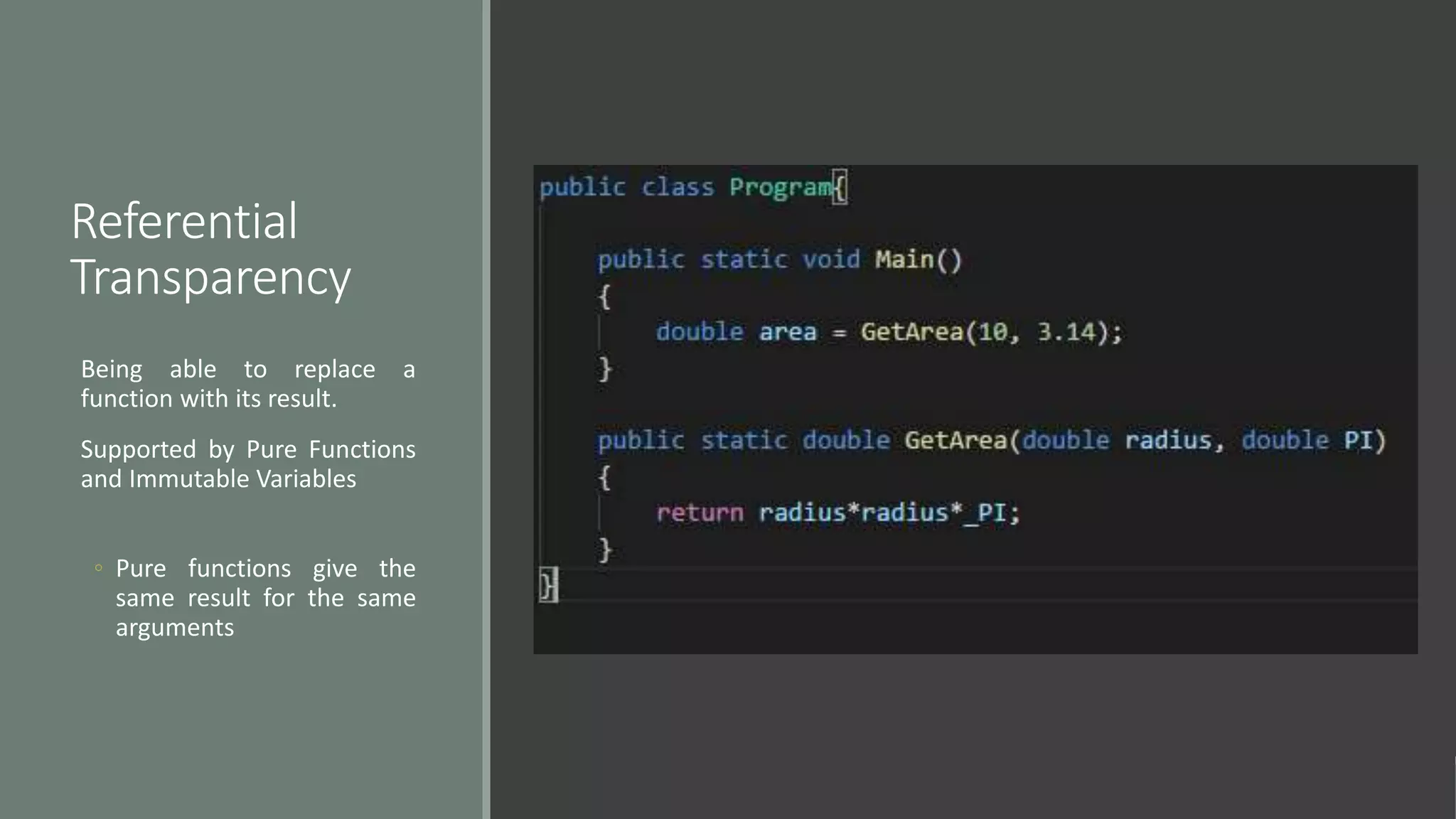
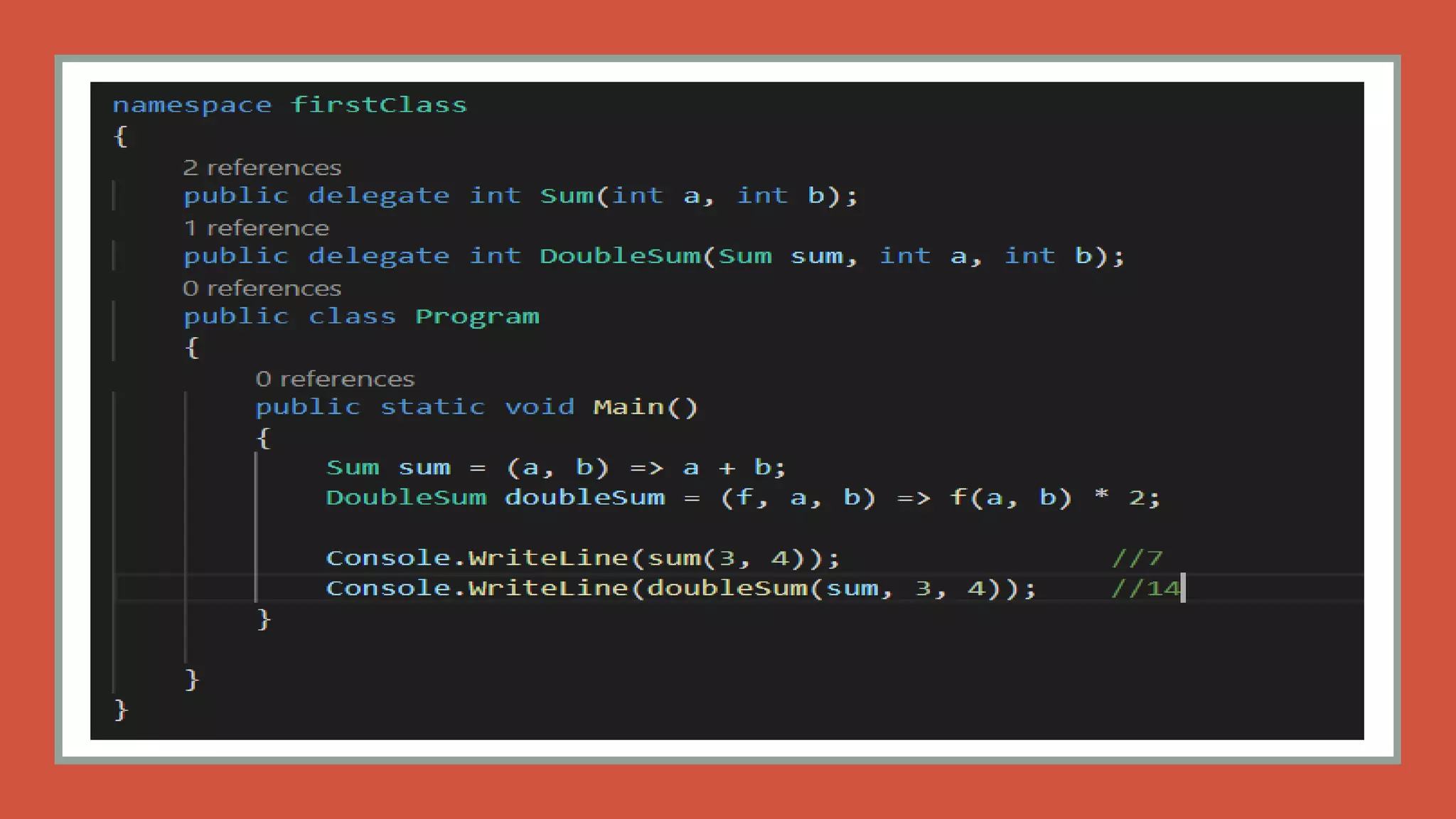
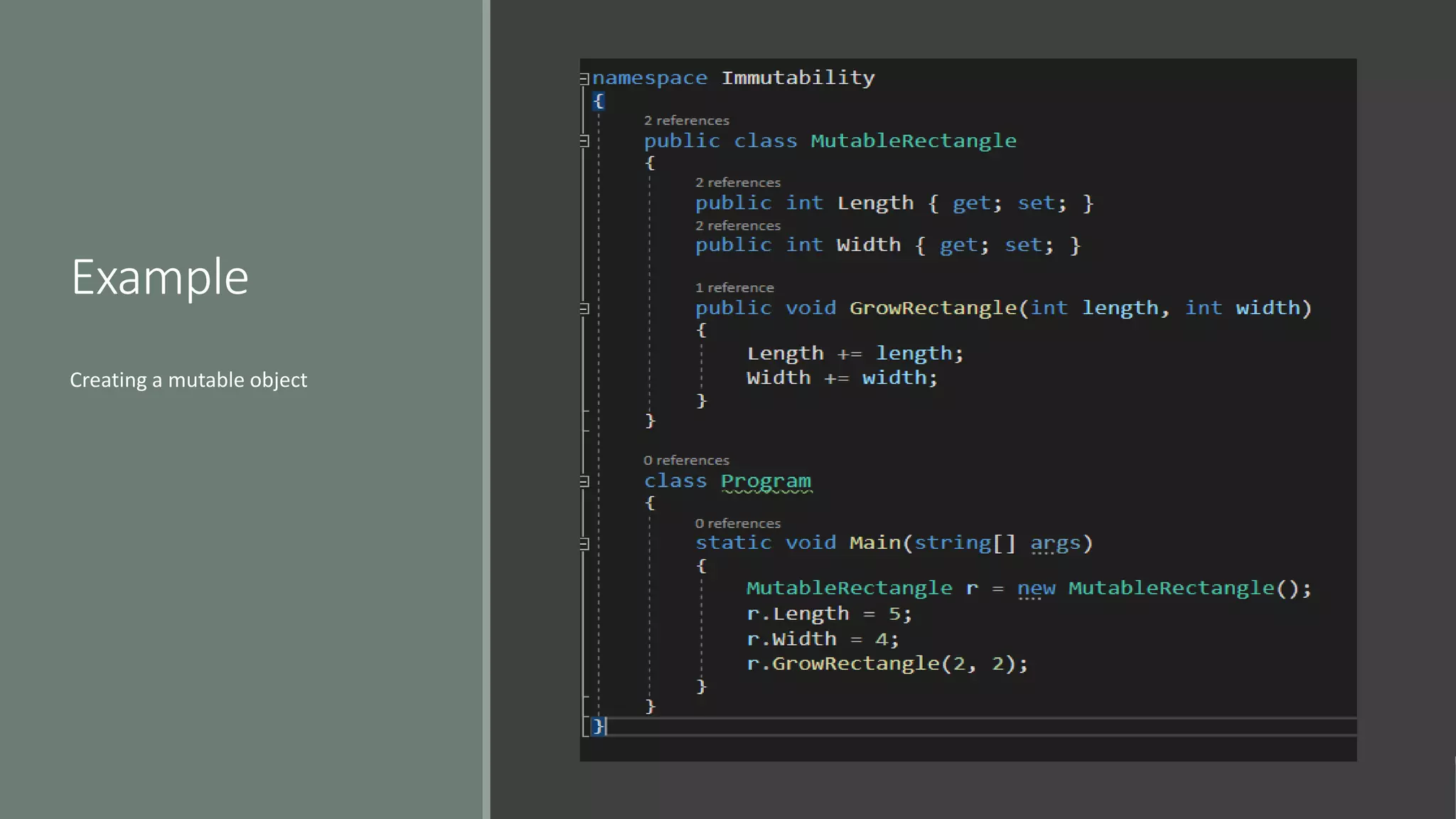
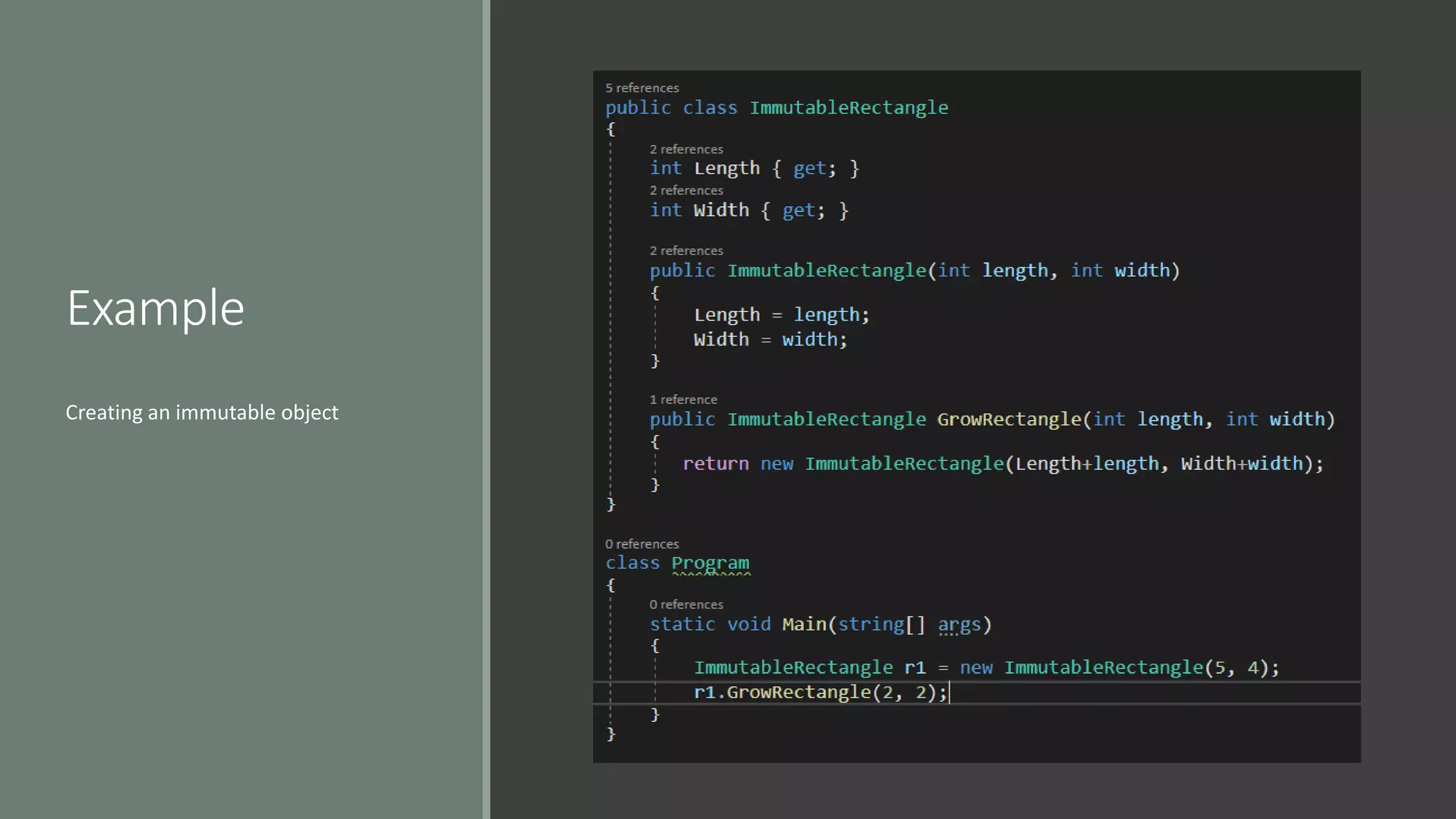
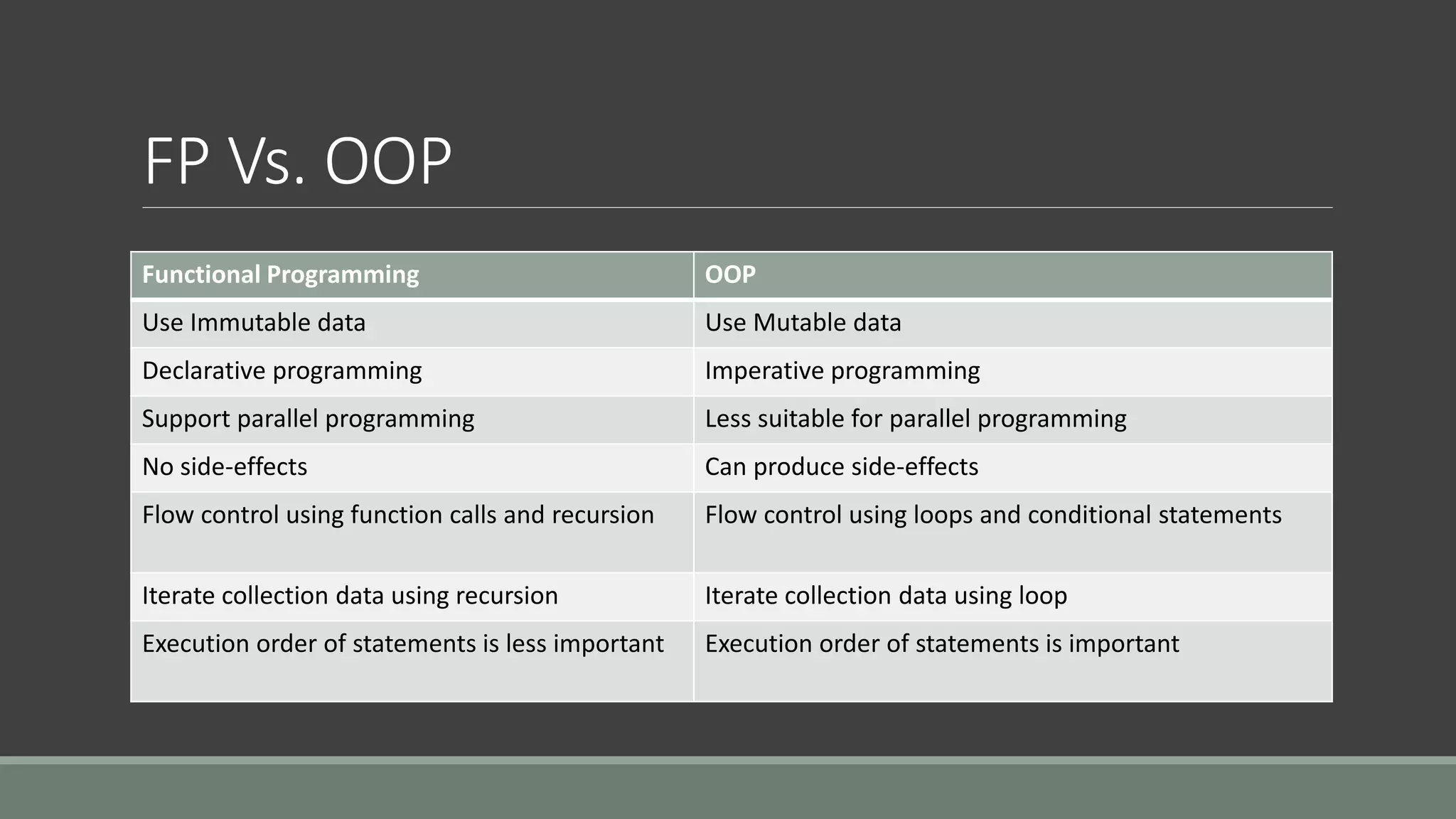
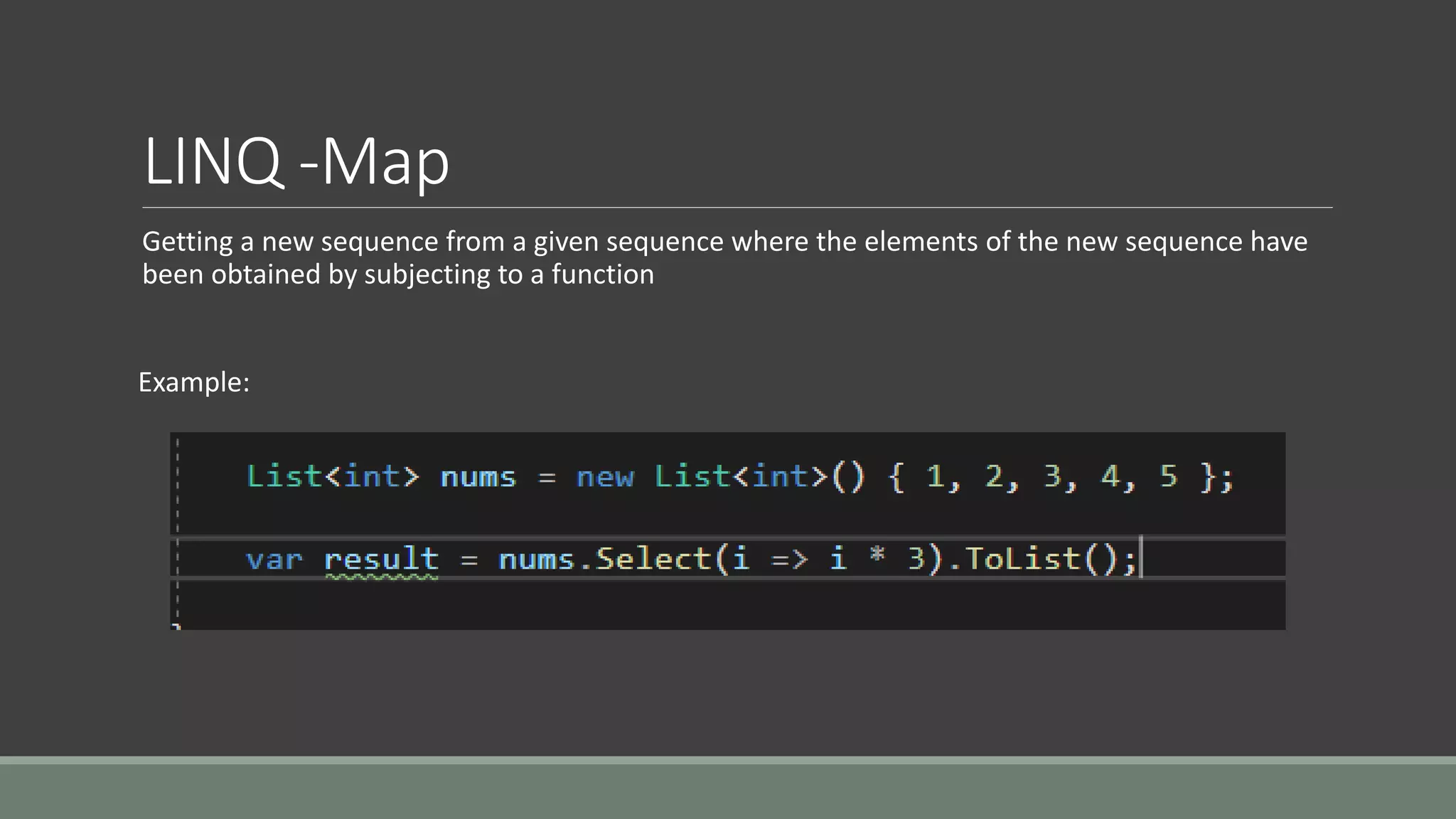
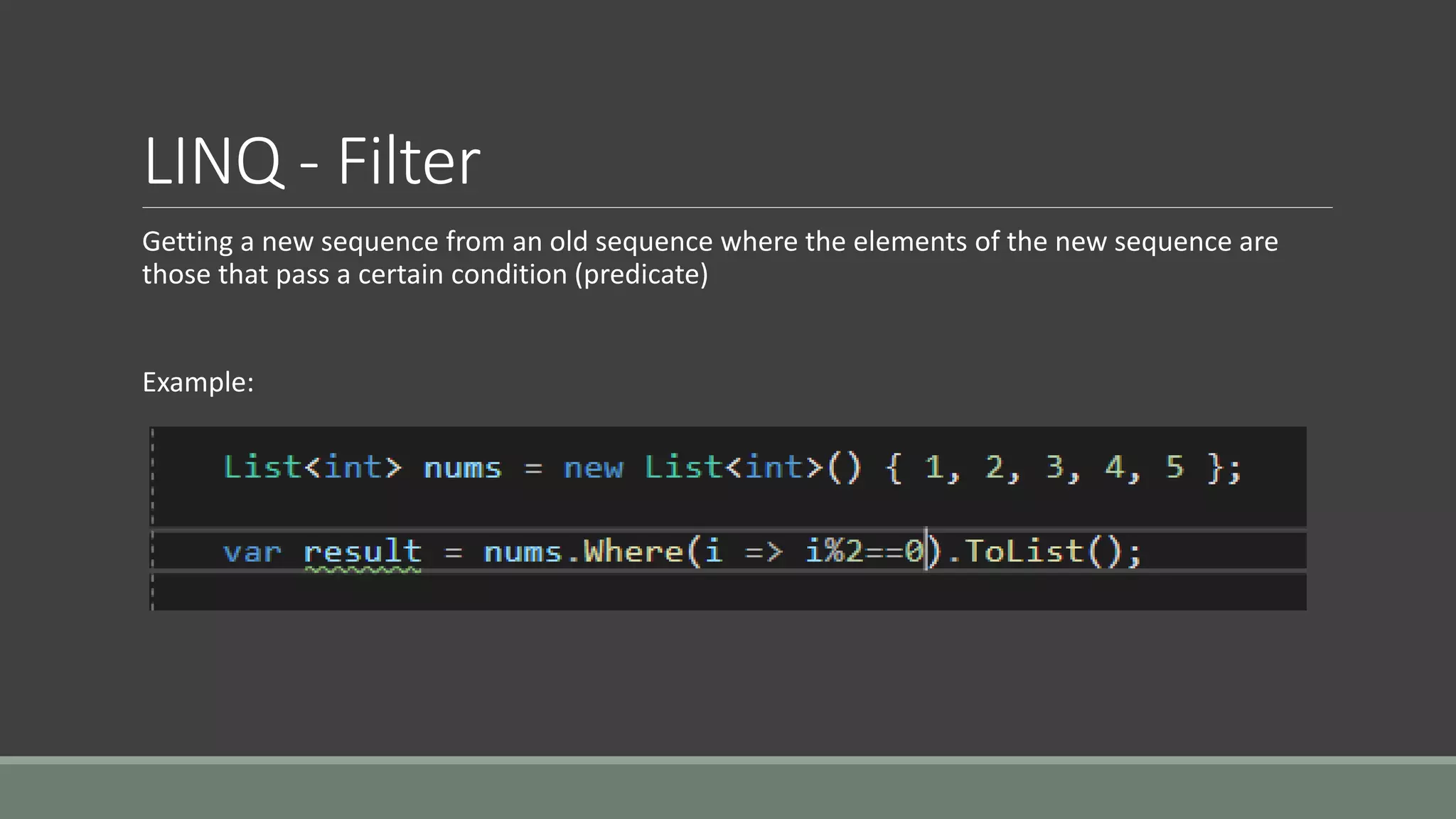
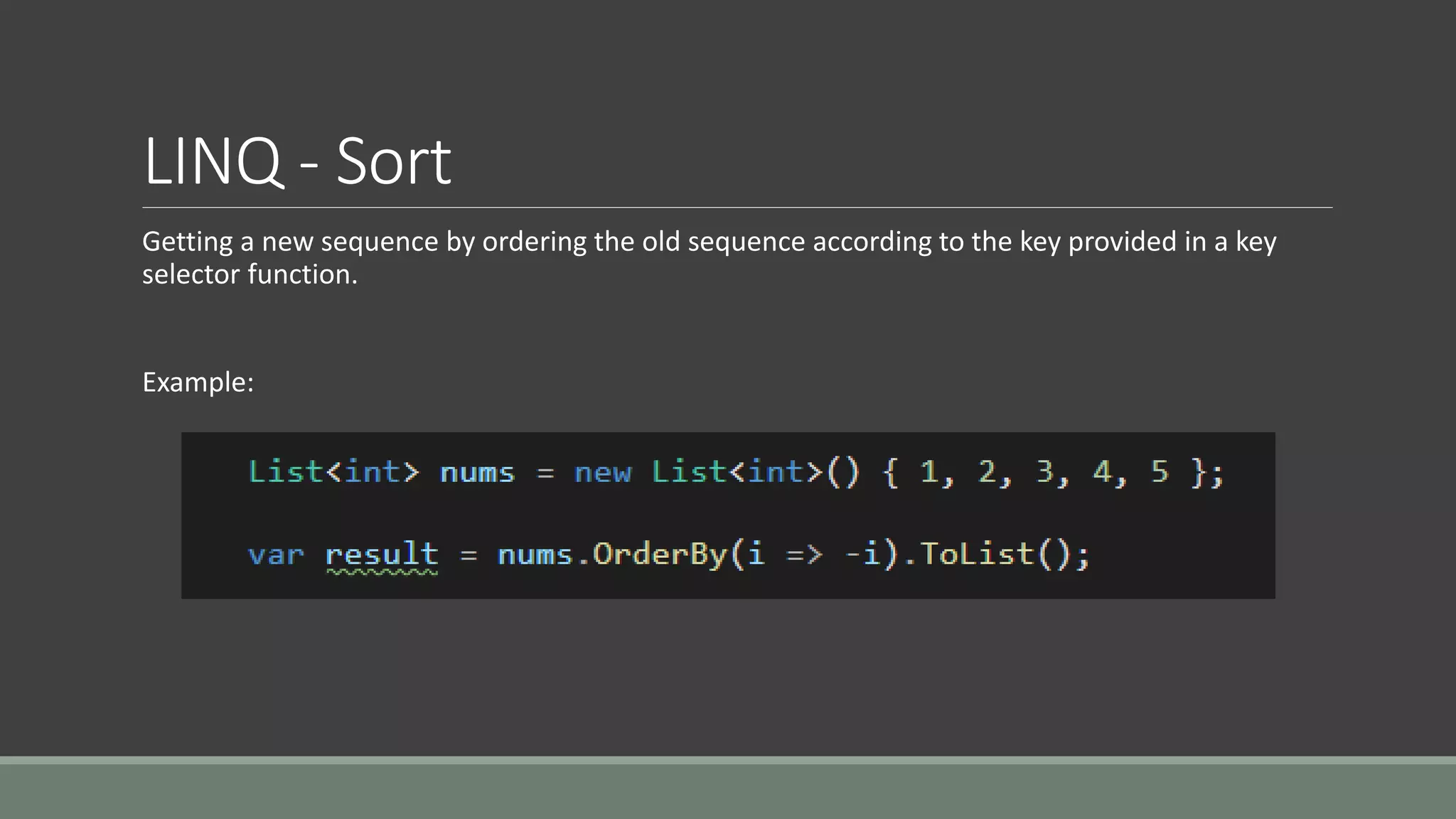
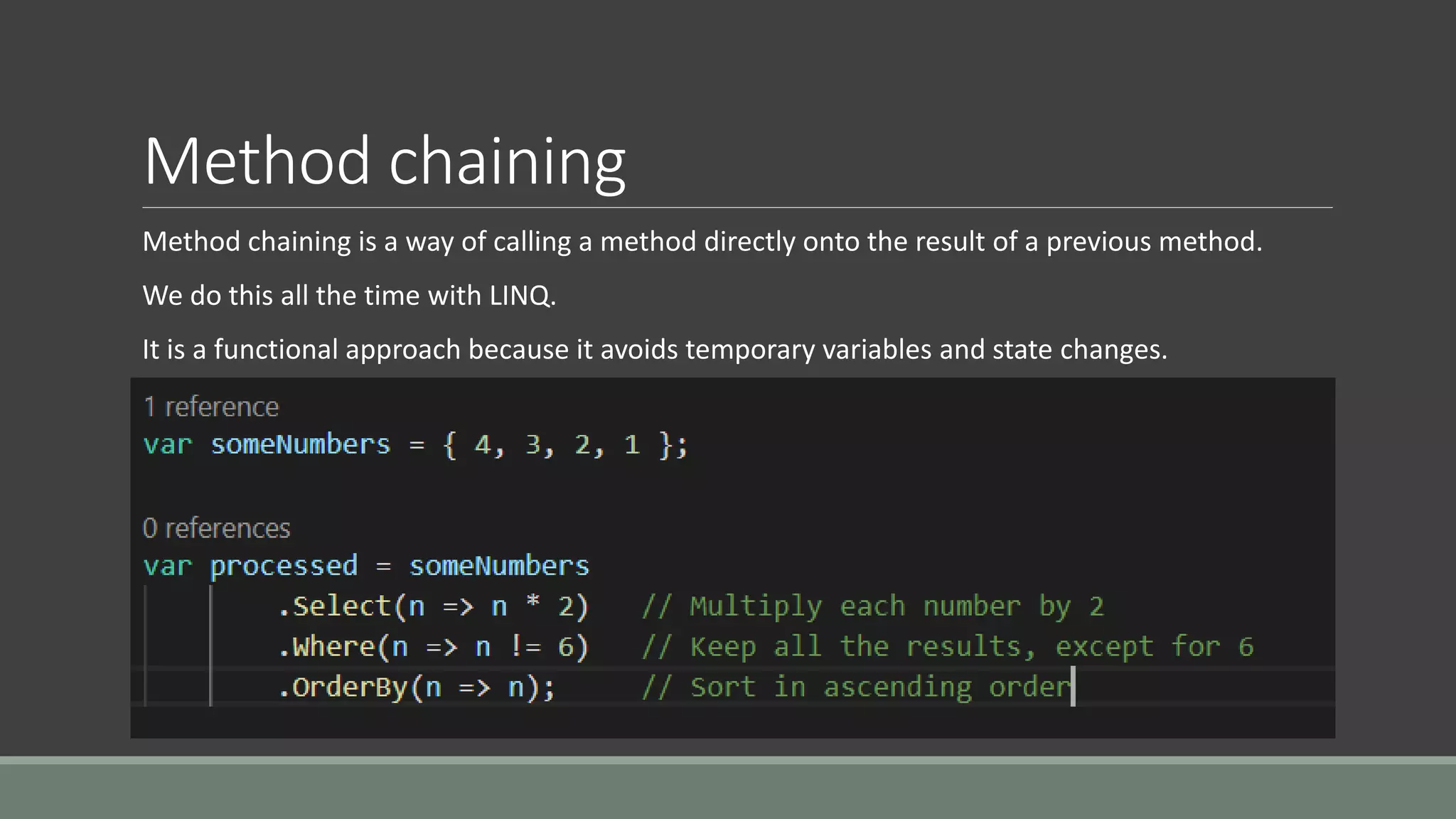
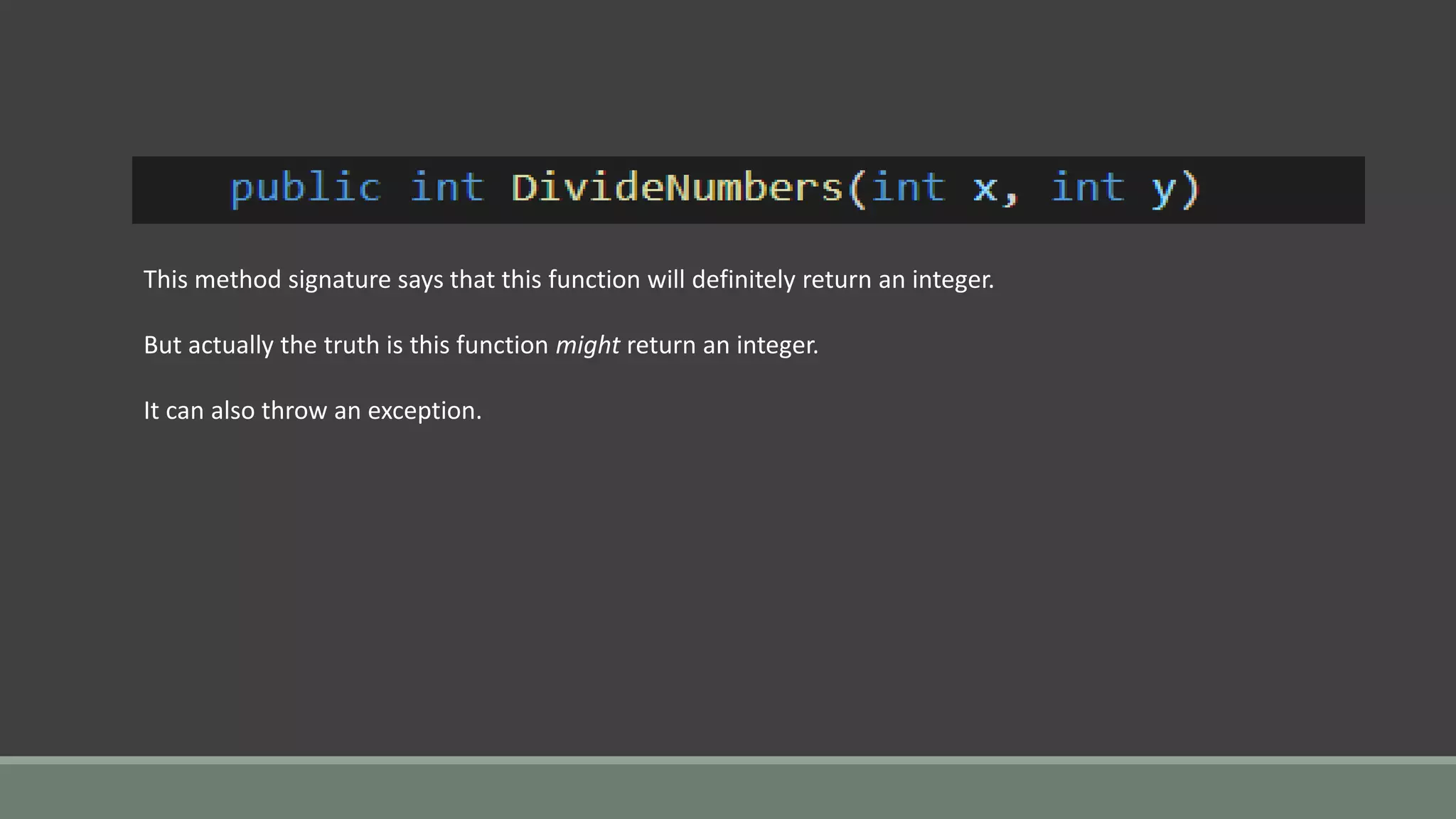
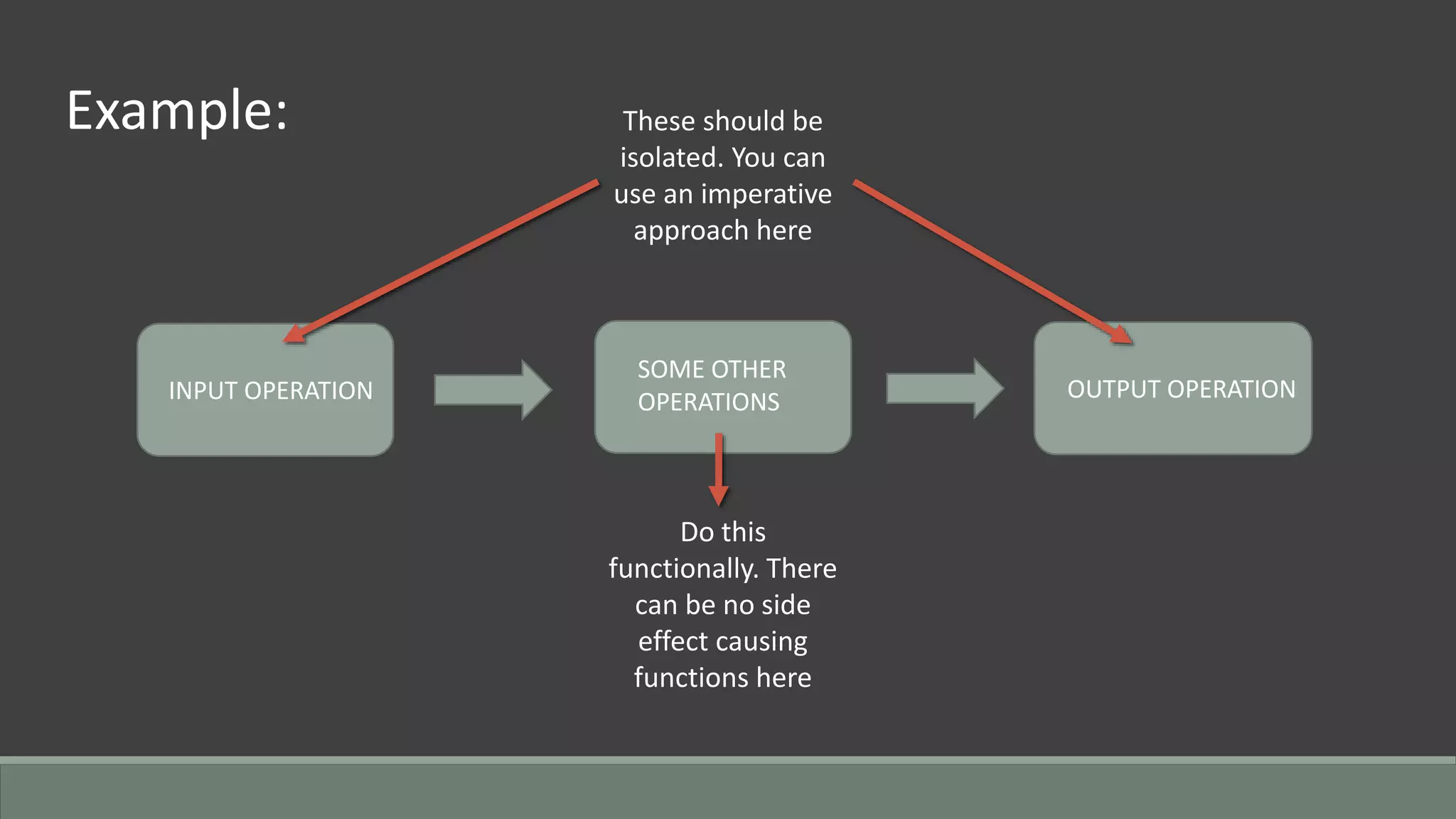
This document discusses functional programming. It begins by stating that functional programming popularity has increased, with languages like F#, Haskell, Scala, Erlang and Elixir gaining popularity. Even OOP languages like C# and Java have incorporated some functional features. The document then covers key concepts of functional programming like pure functions, immutability, higher order functions and referential transparency. It discusses how C# supports a multi-paradigm approach, combining functional programming with imperative programming. Finally, it notes that functional programming is trending due to benefits for concurrency and parallel processing.