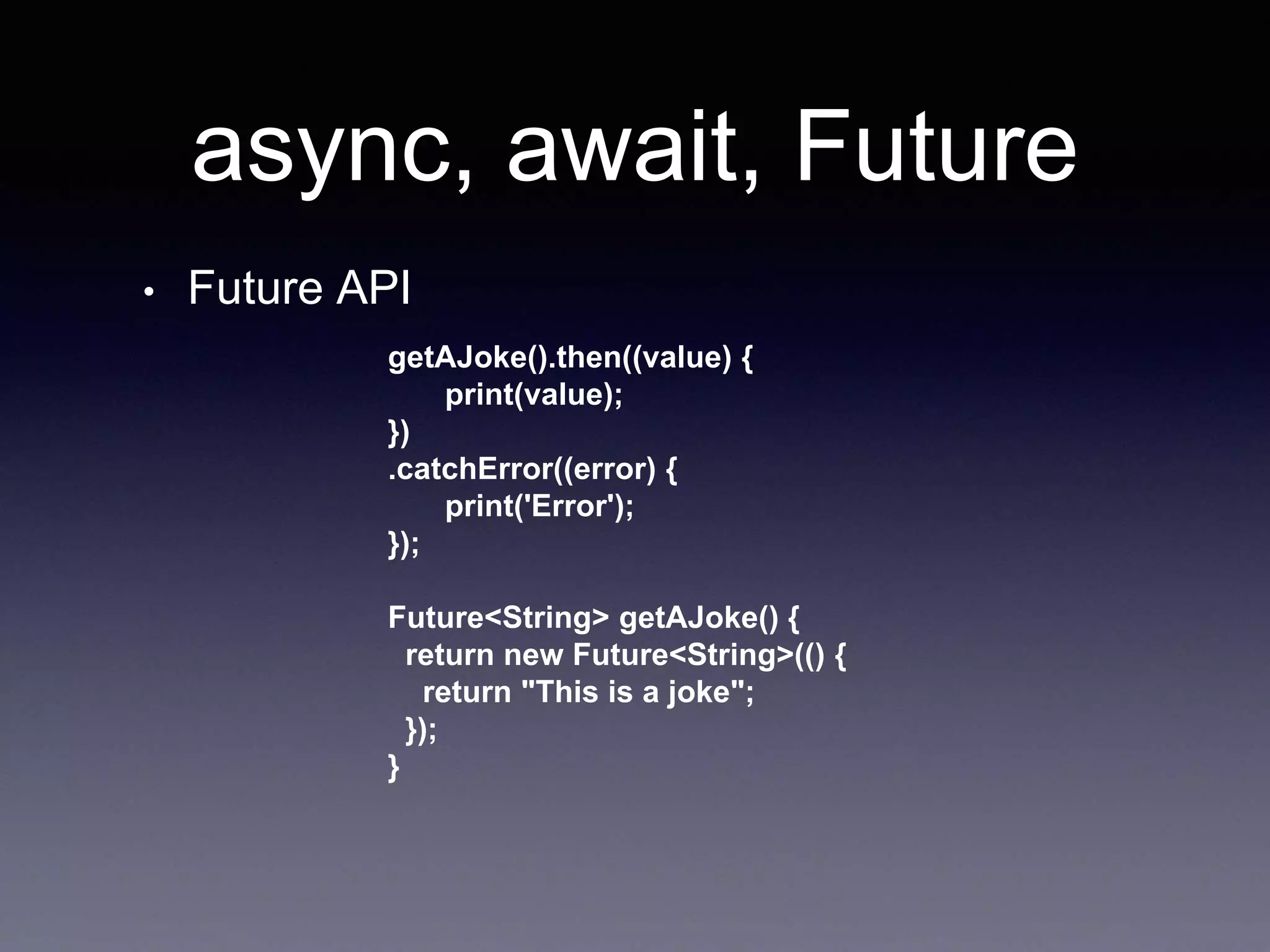
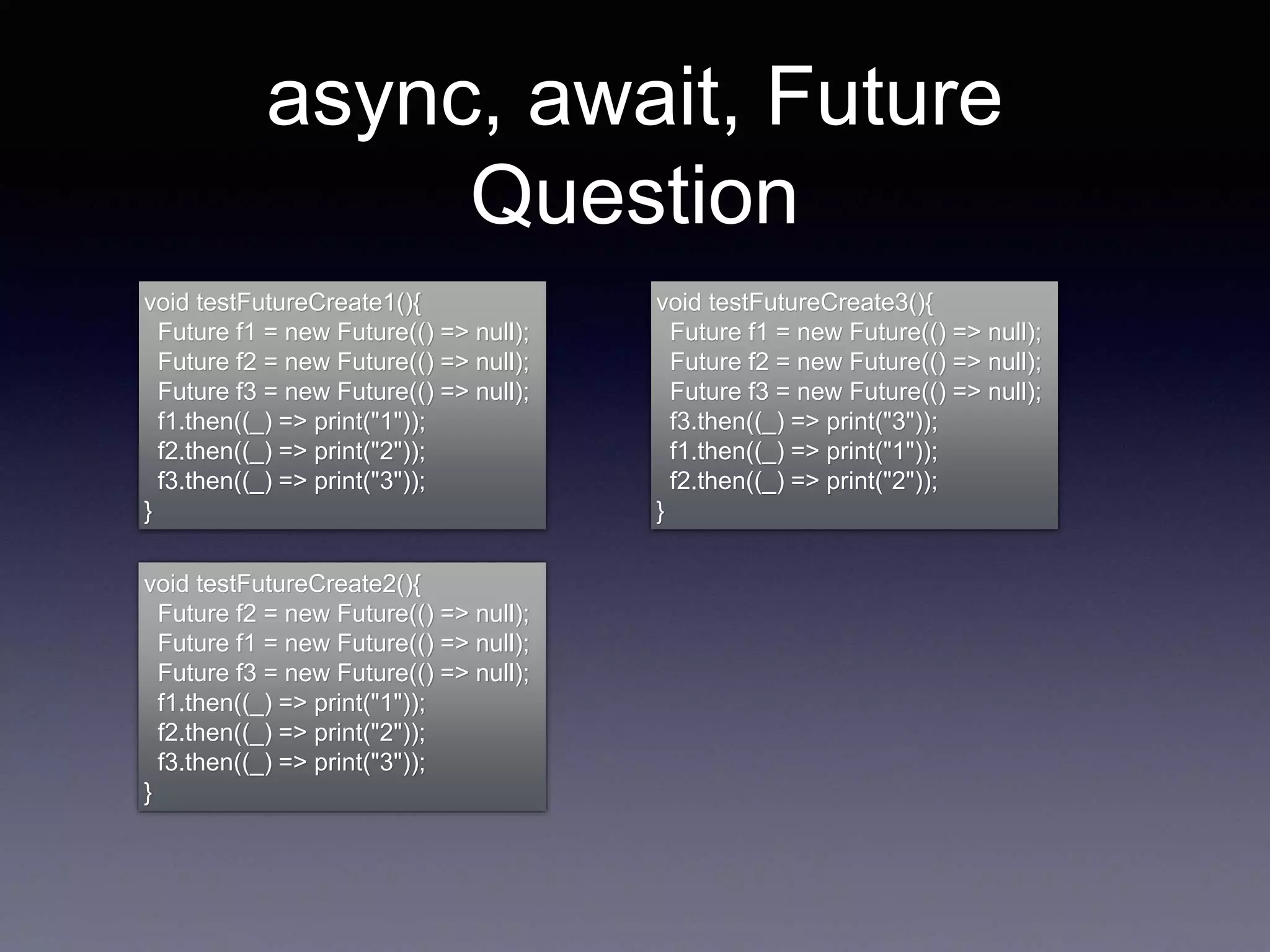
The document discusses various Flutter widgets including BottomNavigationBar, Row, Column, Stack, Expanded, and Padding. It explains how to use these widgets to layout apps and position elements. It also covers asynchronous programming concepts like async/await and Futures and how they are used to handle asynchronous code in Dart. Key topics are future chaining with then/catch, async functions, and awaiting Futures. The document ends with questions about Futures and print order.



![Row / Column
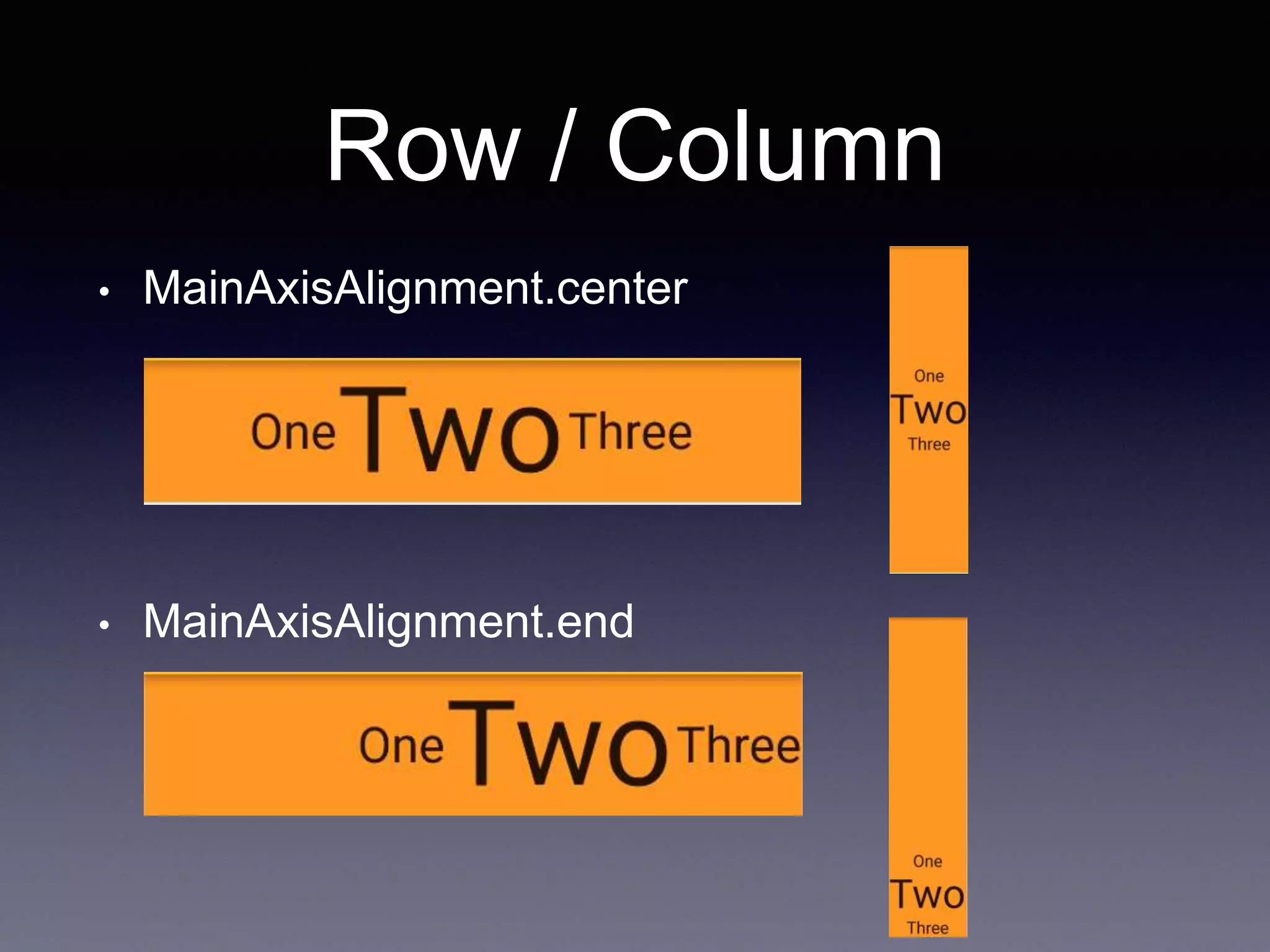
• MainAxisAlignment.start
Row /*or Column*/(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
Text("One", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 28.0),),
Text("Two", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 68.0),),
Text("Three", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 28.0),)
],
),](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flutter3-190314033850/75/Flutter-3-5-2048.jpg)
![Row / Column
• MainAxisAlignment.start
Row /*or Column*/(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
Text("One", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 28.0),),
Text("Two", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 68.0),),
Text("Three", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 28.0),)
],
),](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flutter3-190314033850/75/Flutter-3-6-2048.jpg)
![Row / Column
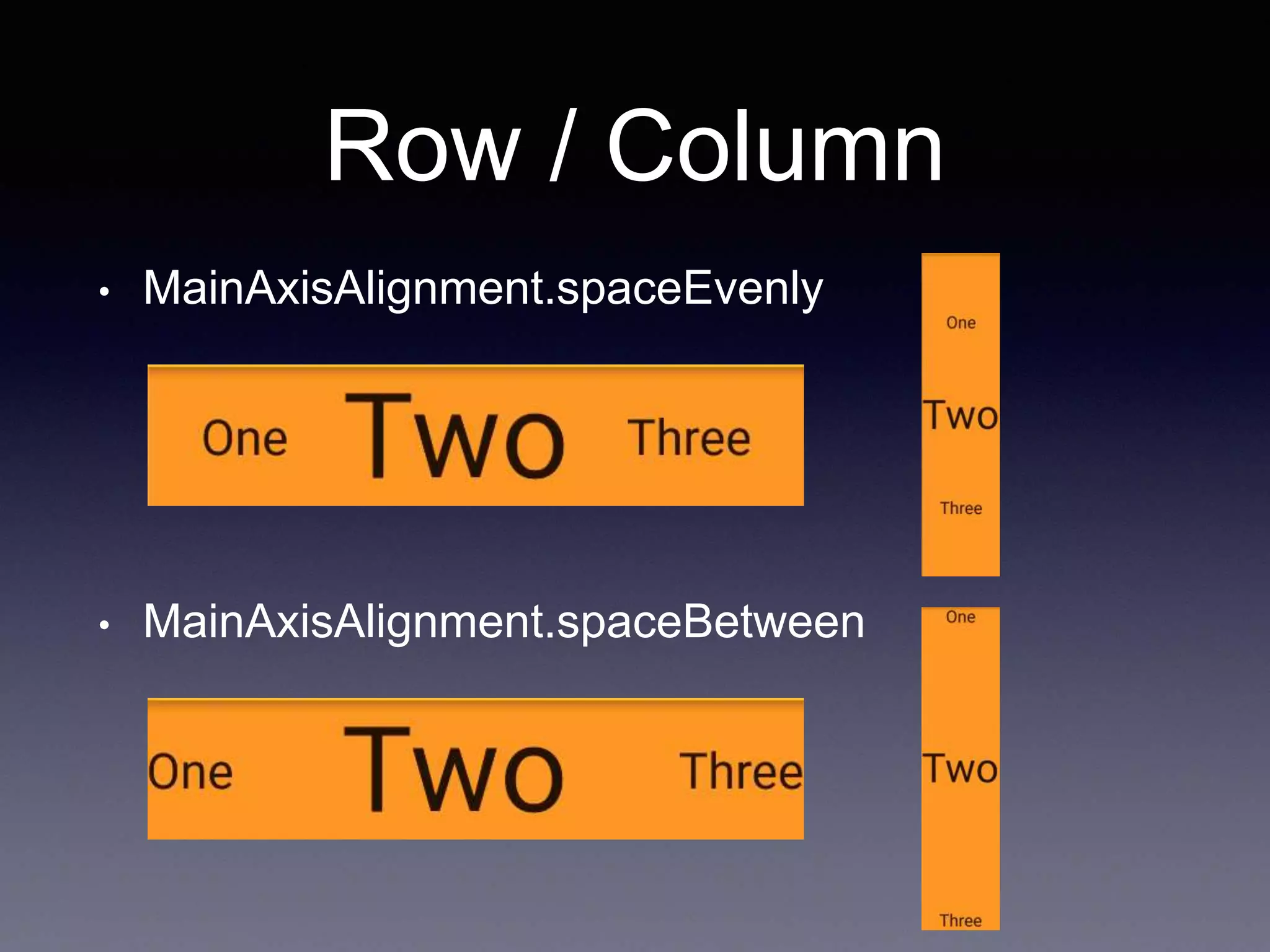
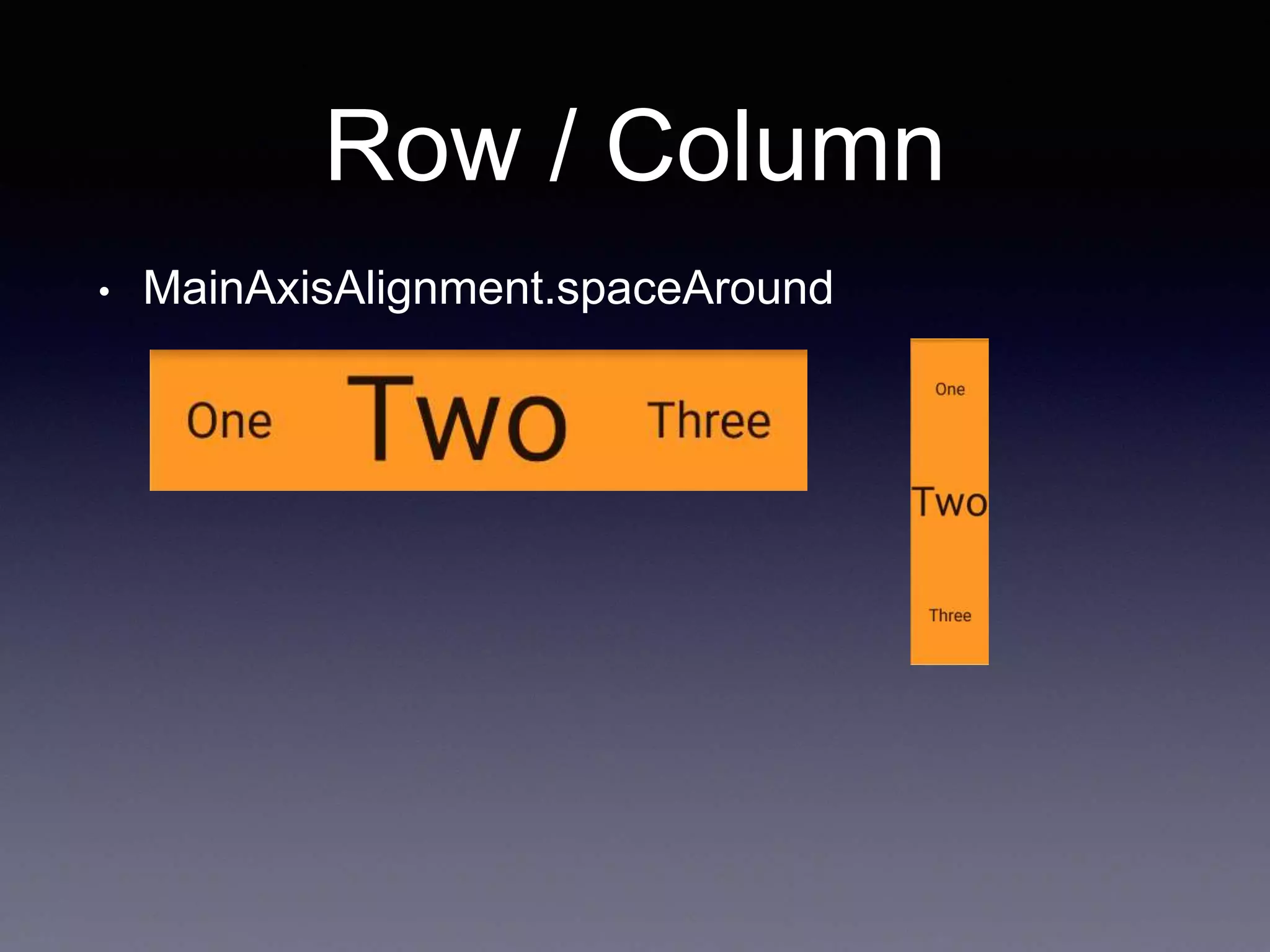
• MainAxisSize.min
Row /*or Column*/(
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.min,
children: <Widget>[
Text("One", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 28.0),),
Text("Two", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 68.0),),
Text("Three", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 28.0),)
],
),](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flutter3-190314033850/75/Flutter-3-10-2048.jpg)
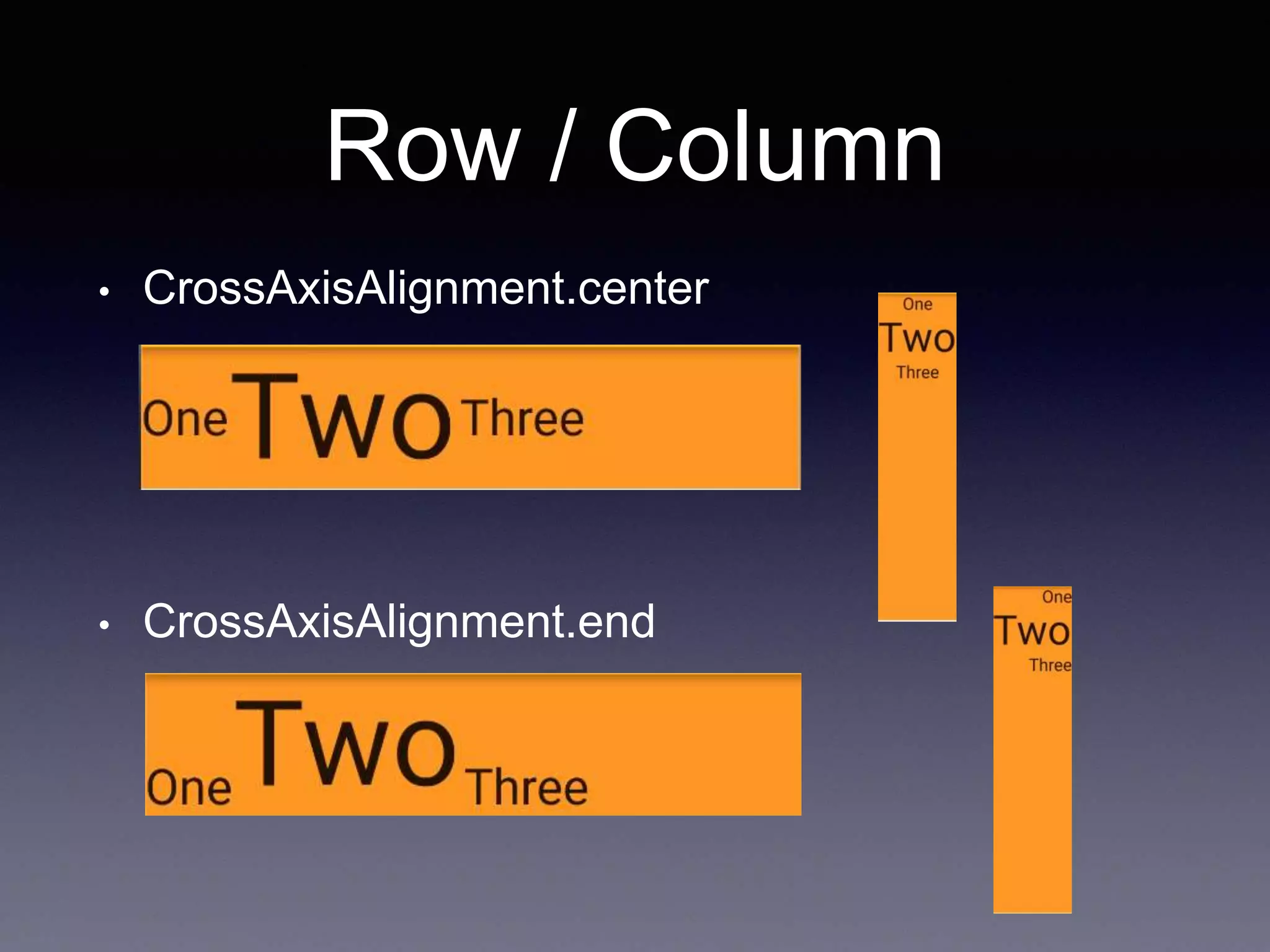
![Row / Column
• CrossAxisAlignment.start
Row /*or Column*/(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
Text("One", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 28.0),),
Text("Two", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 68.0),),
Text("Three", style: TextStyle(fontSize: 28.0),)
],
),](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flutter3-190314033850/75/Flutter-3-11-2048.jpg)

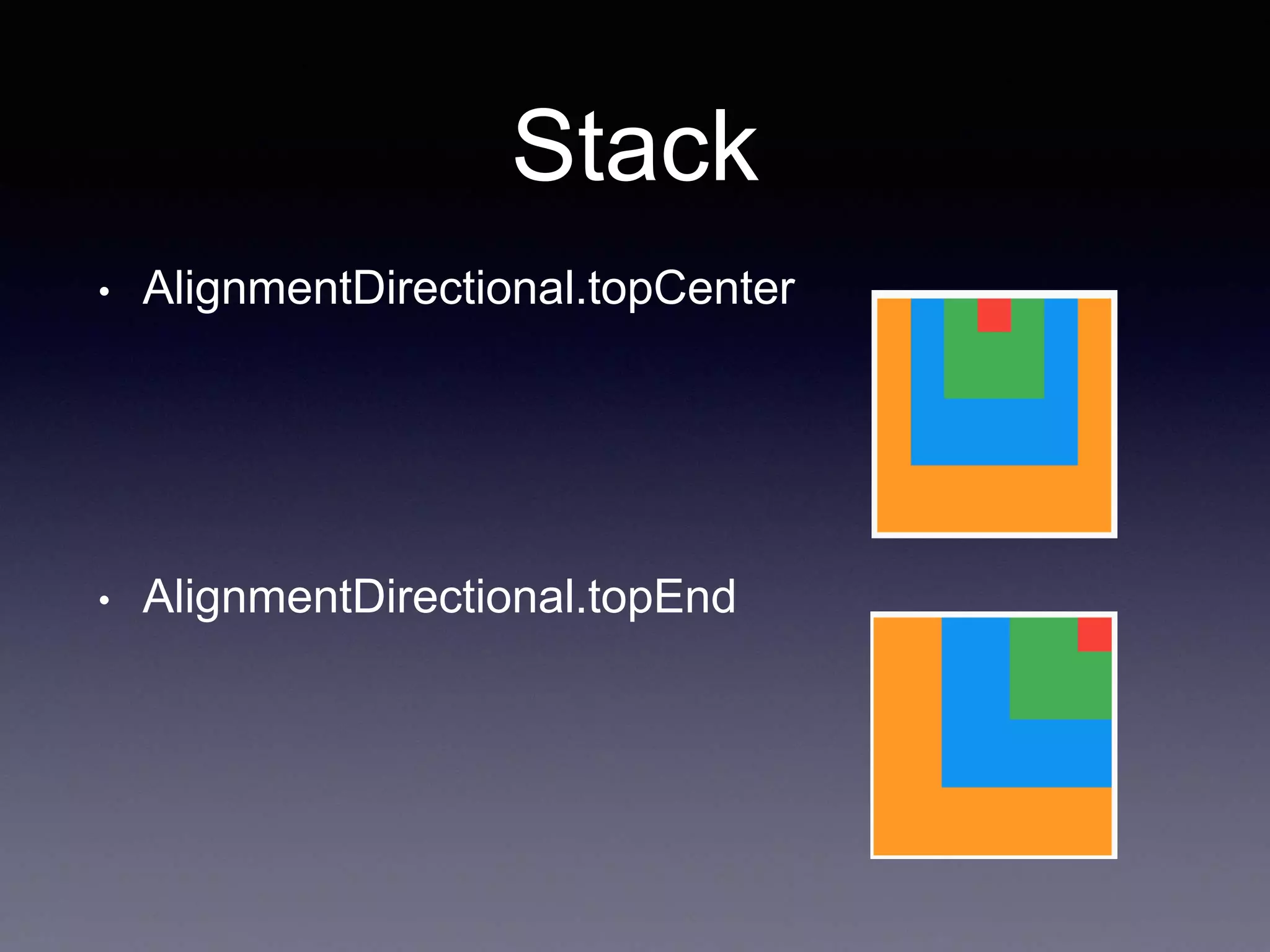
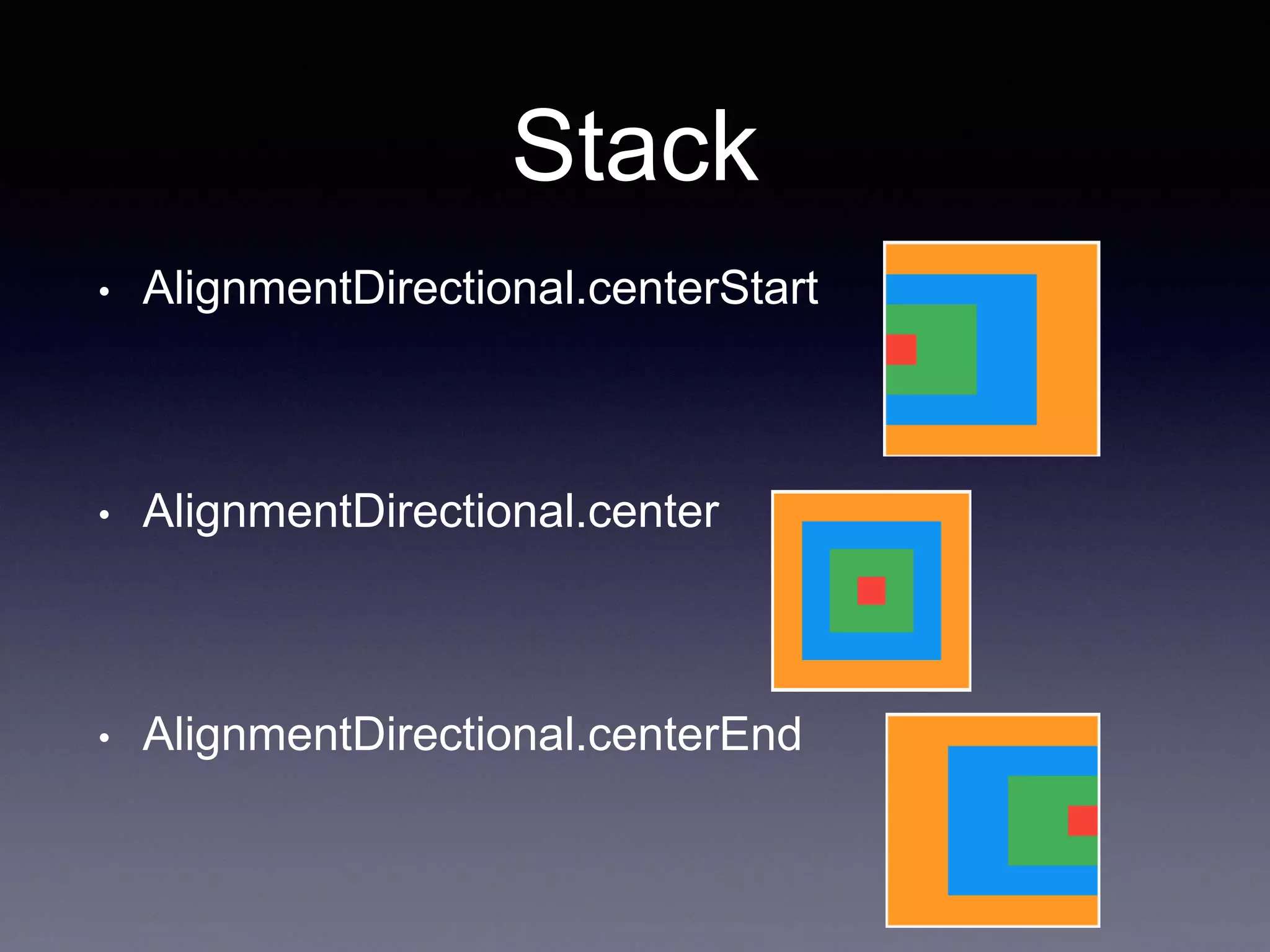
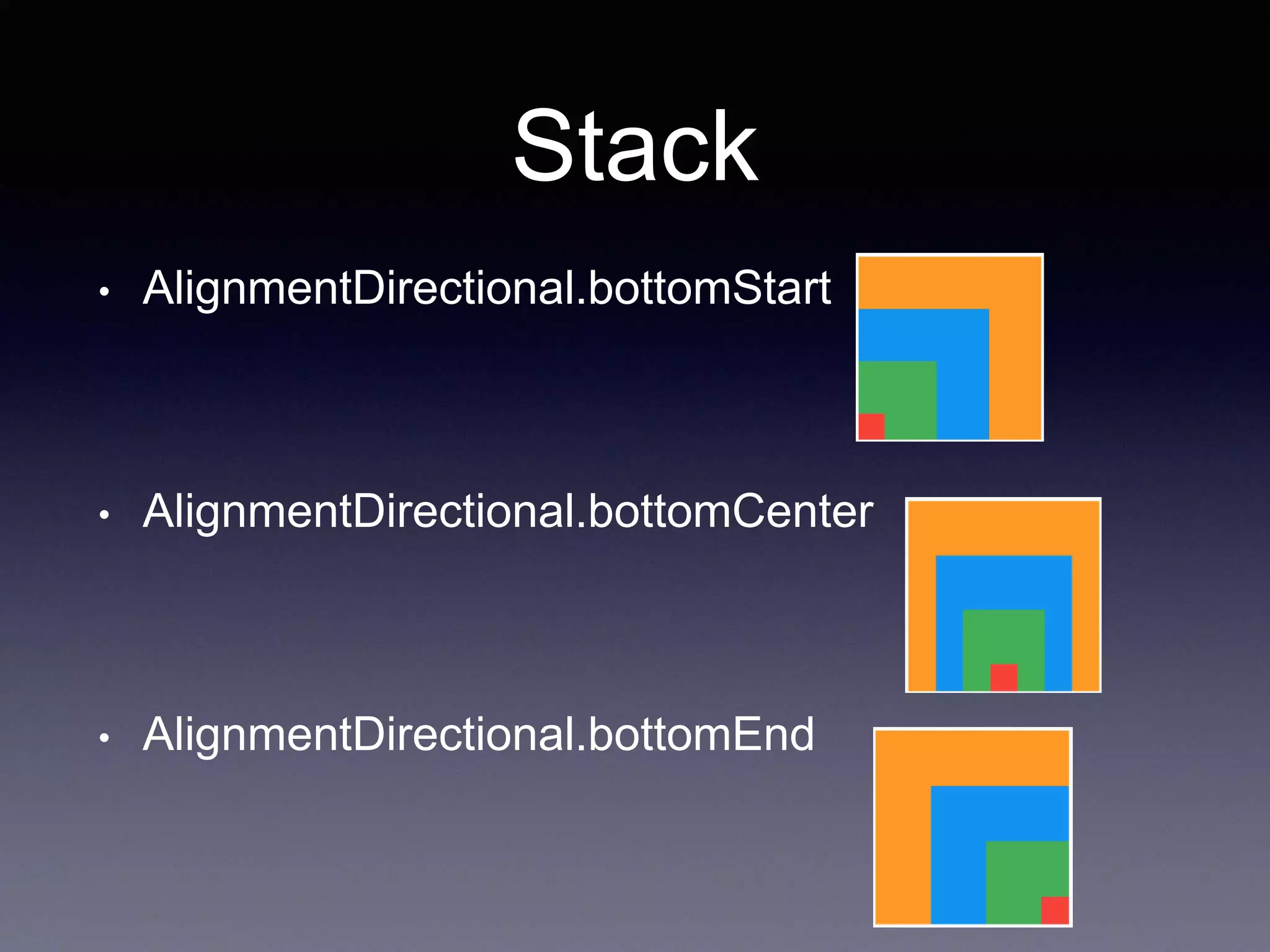
![Stack
• A widget that positions its children relative to the
edges of its box.
Stack(
children: <Widget>[
alignment: AlignmentDirectional.topStart,
Container(color: Colors.orange, width: 350, height: 350,),
Container(color: Colors.blue, width: 250, height: 250,),
Container(color: Colors.green, width: 150, height: 150,),
Container(color: Colors.red, width: 50, height: 50,),
],
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flutter3-190314033850/75/Flutter-3-14-2048.jpg)
![Stack
• Use the Positioned widget to position Flutter
widgets in a Stack
Stack(
children: <Widget>[
Container(color: Colors.orange, width: 350, height: 350,),
Positioned(left: 20.0, child: Container(color: Colors.blue, width: 150,
height: 150,)),
Positioned(left:20.0, top:190.0,child: Container(color: Colors.green,
width: 150, height: 150,)),
Positioned(left:190.0,child: Container(color: Colors.red, width: 150,
height: 150,)),
],),
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flutter3-190314033850/75/Flutter-3-18-2048.jpg)
![Stack Question
Stack(
children: <Widget>[
alignment: AlignmentDirectional.topStart,
Container(color: Colors.orange, width: 150, height: 150,),
Container(color: Colors.blue, width: 150, height: 150,),
Container(color: Colors.green, width: 150, height: 150,),
Container(color: Colors.red, width: 150, height: 150,),
],
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flutter3-190314033850/75/Flutter-3-19-2048.jpg)
![Expanded
• distributing space between multiple items
Row(
children: <Widget>[
Expanded(
child: Container(
decoration: const BoxDecoration(color: Colors.red),
),
flex: 3,
),
Expanded(
child: Container(
decoration: const BoxDecoration(color: Colors.green),
),
flex: 2,
),
Expanded(
child: Container(
decoration: const BoxDecoration(color: Colors.blue),
),
flex: 1,
),
],
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flutter3-190314033850/75/Flutter-3-20-2048.jpg)
![Expanded Question
Column(
children: <Widget>[
Expanded(
child: Container(
decoration: const BoxDecoration(color: Colors.red),
),
),
Expanded(
child: Container(
decoration: const BoxDecoration(color: Colors.green),
),
),
Expanded(
child: Container(
decoration: const BoxDecoration(color: Colors.blue),
),
),
],
)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flutter3-190314033850/75/Flutter-3-21-2048.jpg)