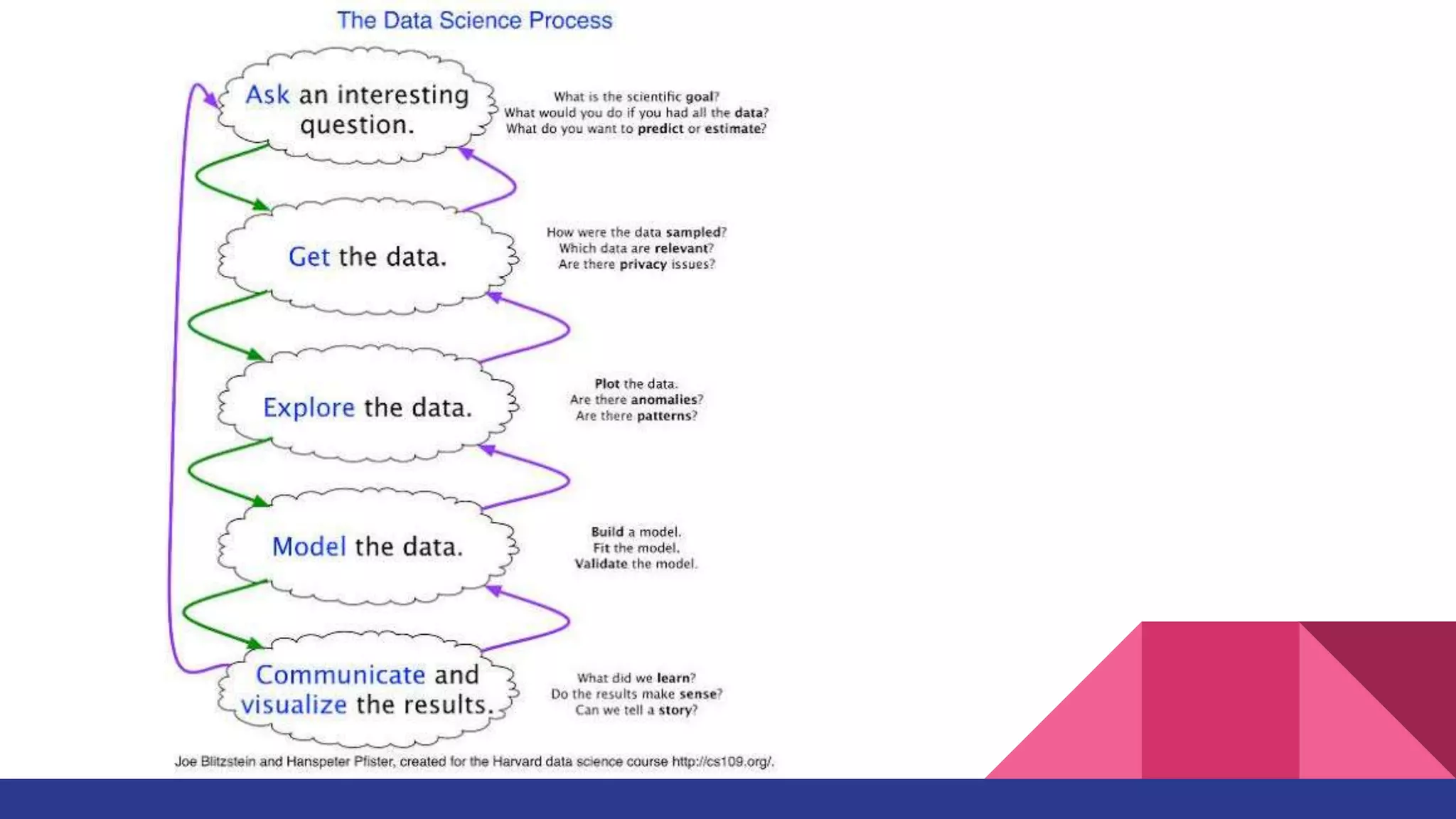
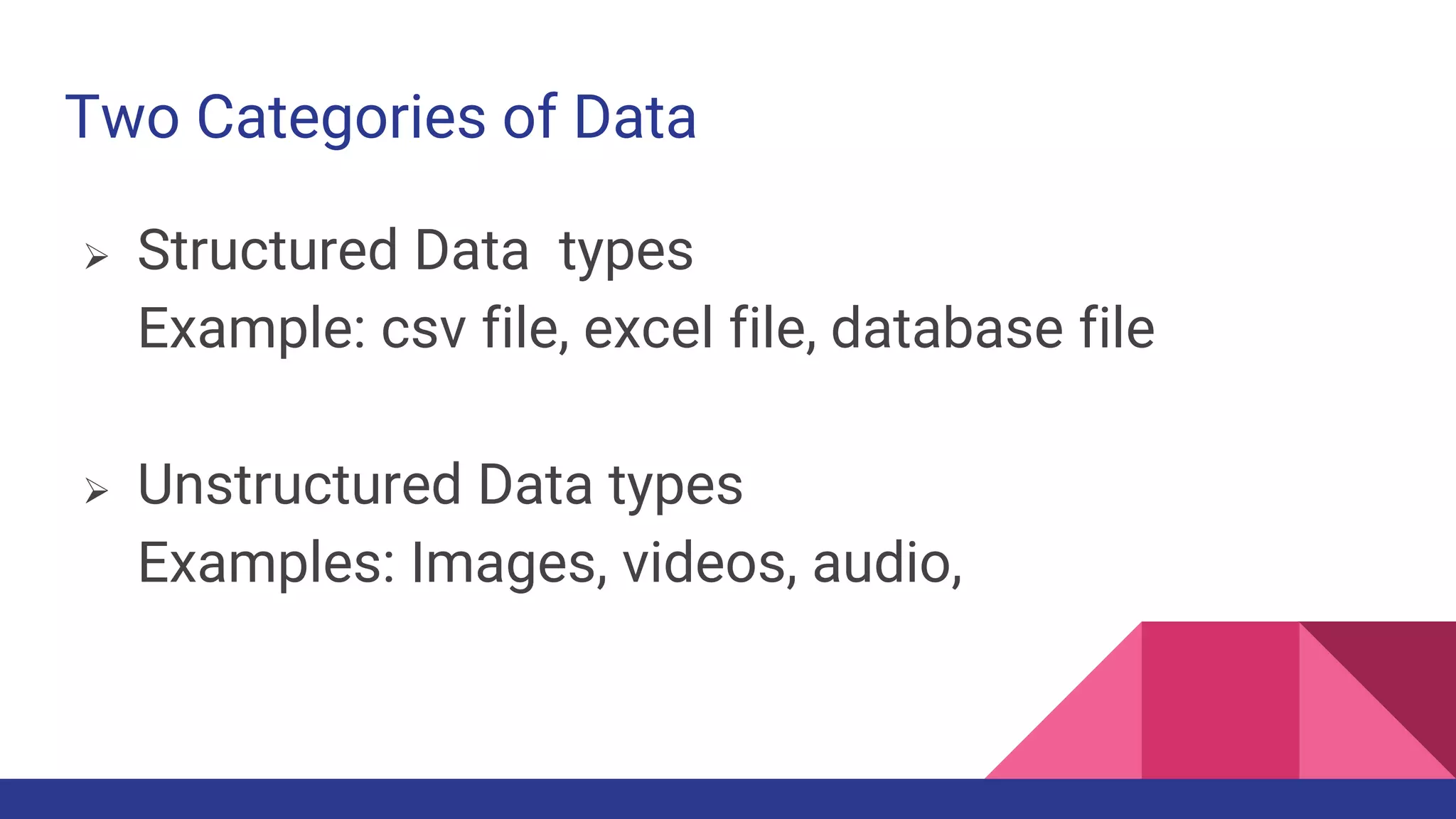
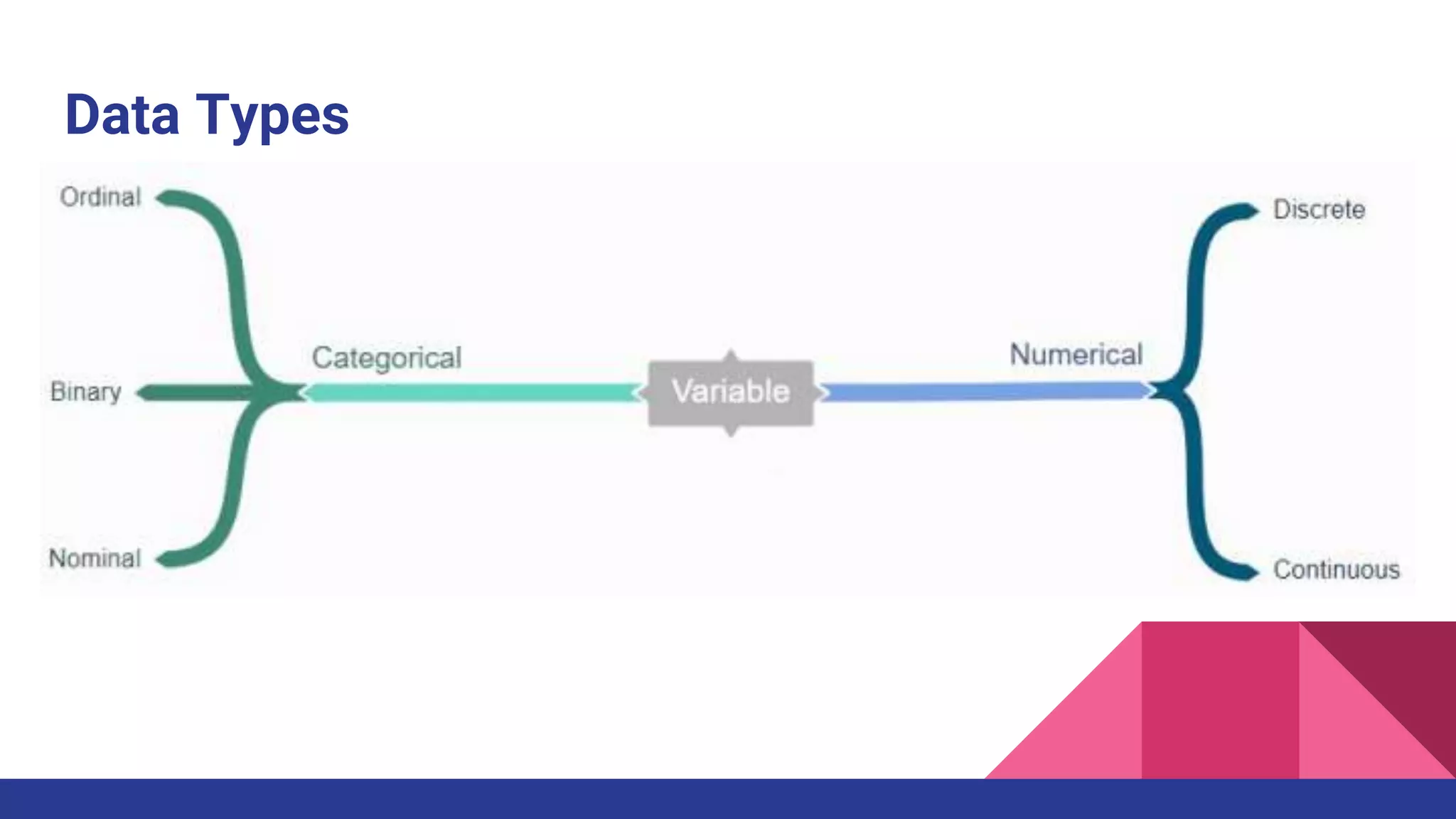
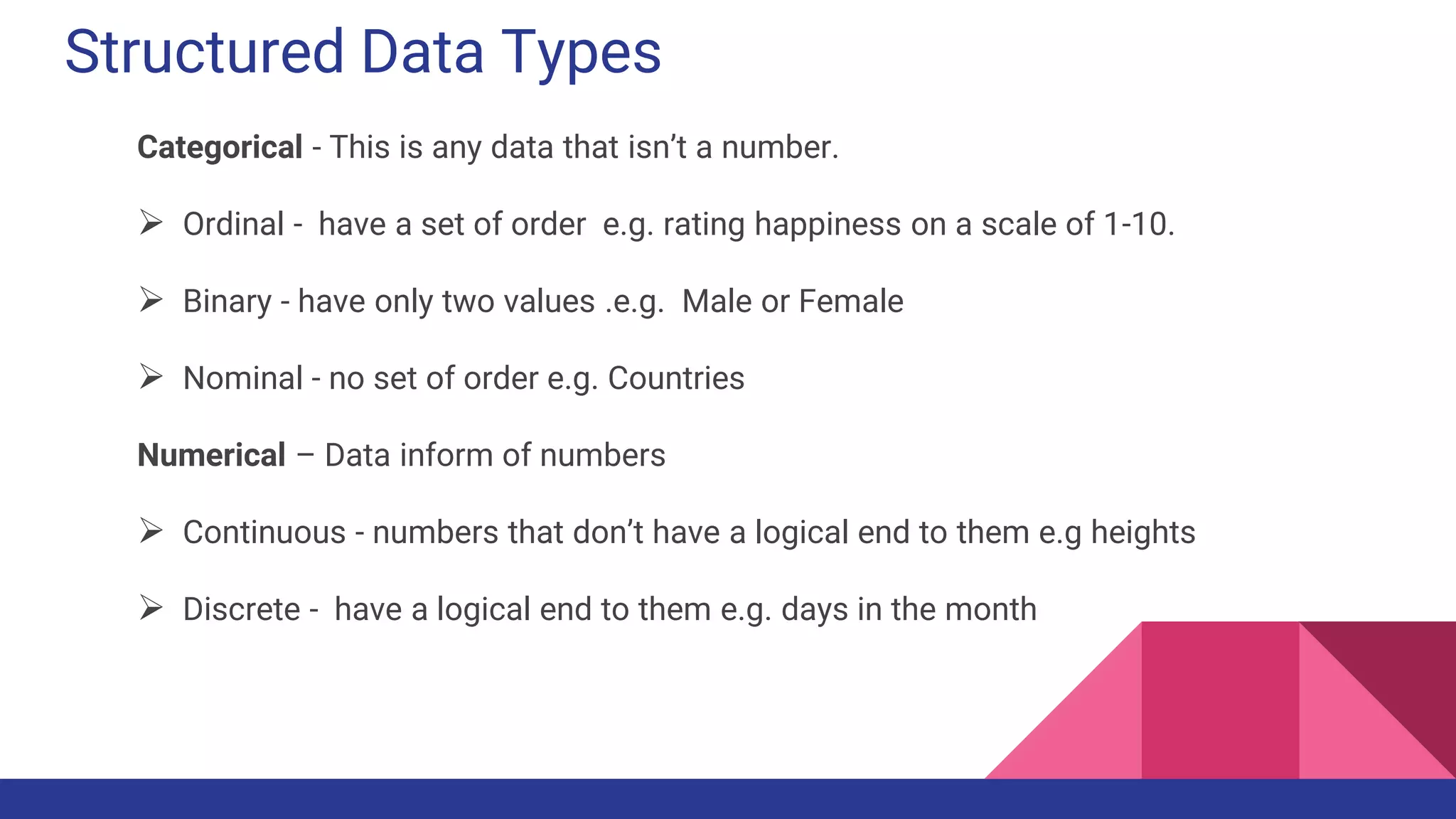
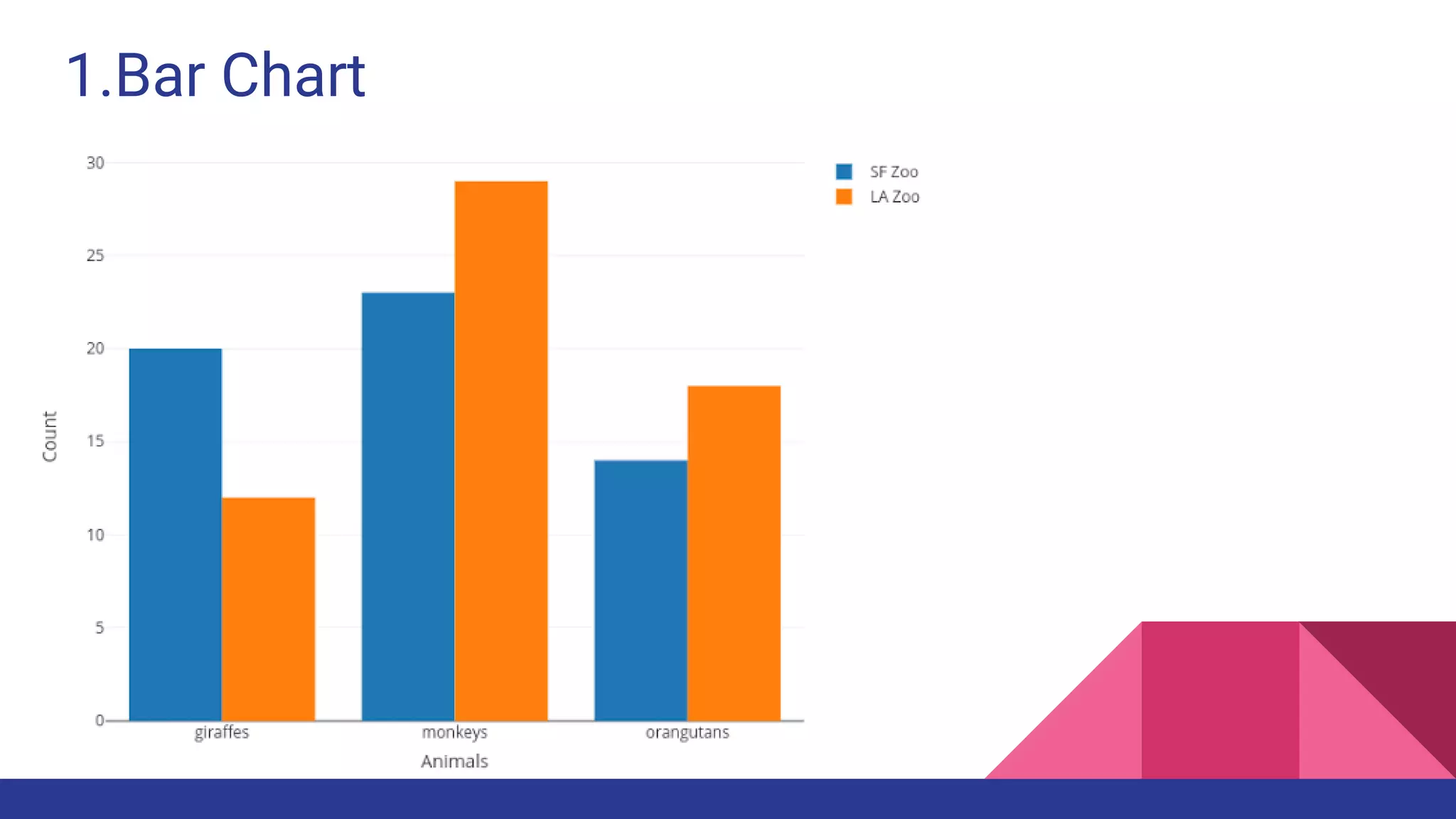
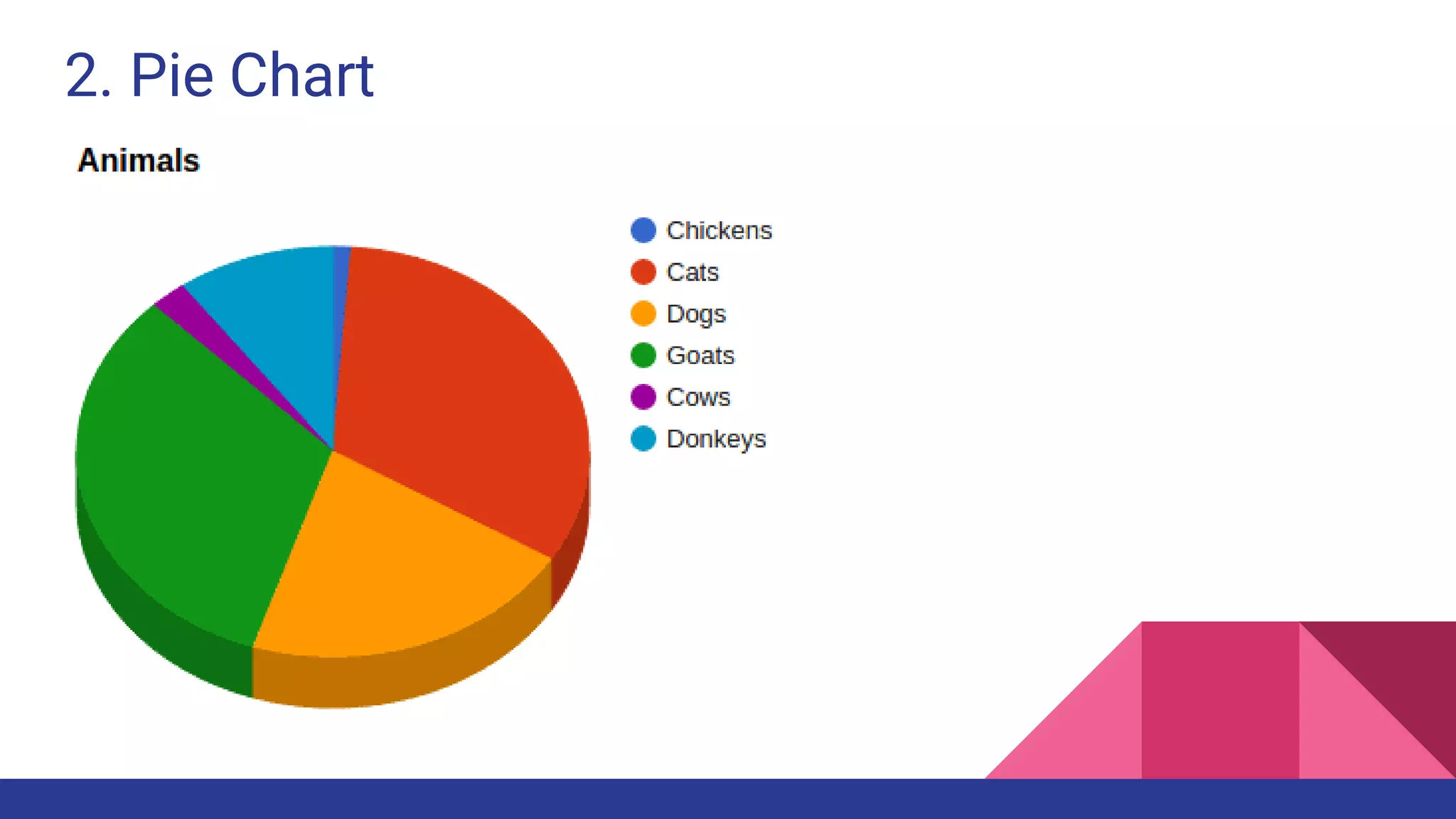
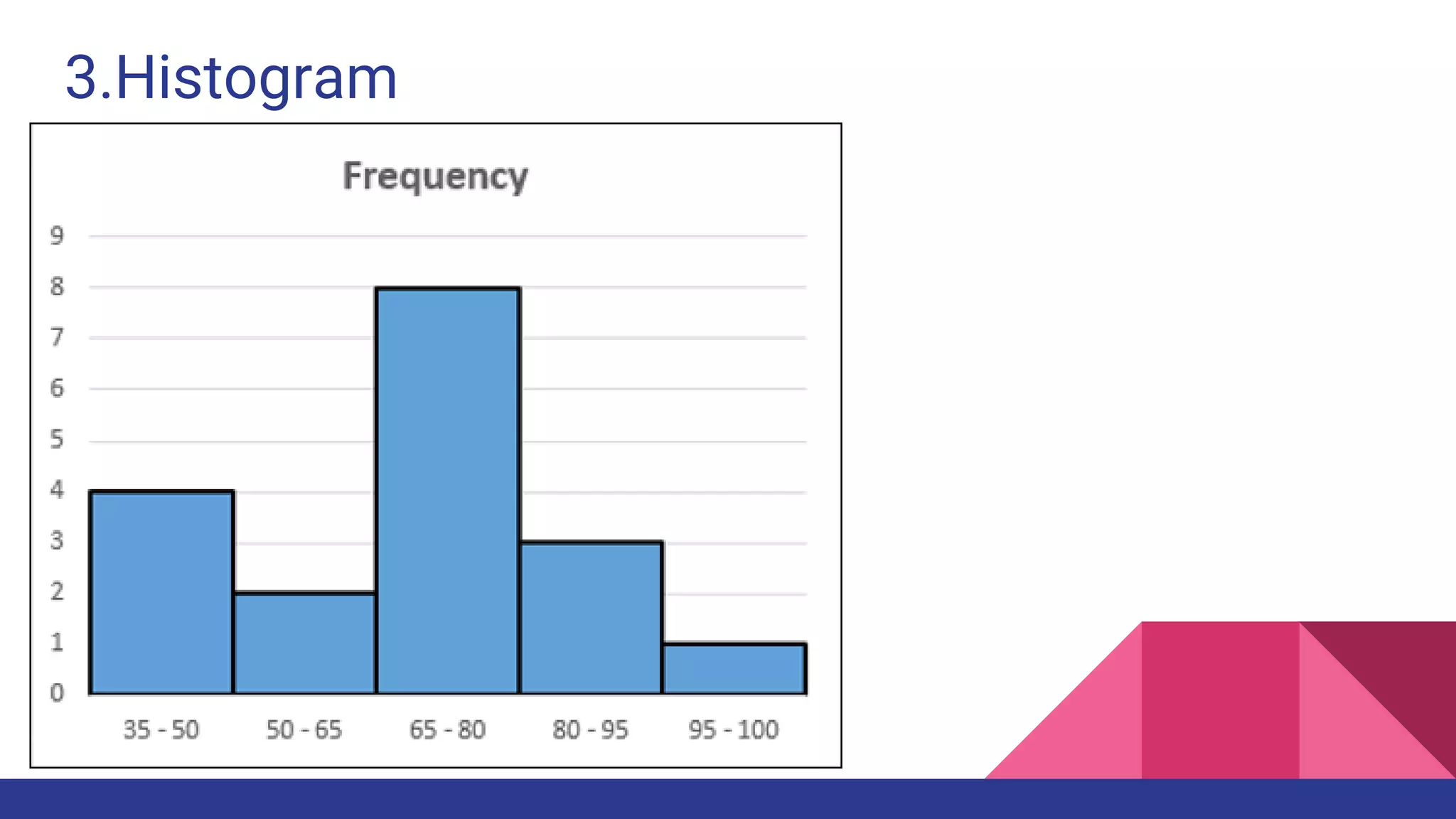
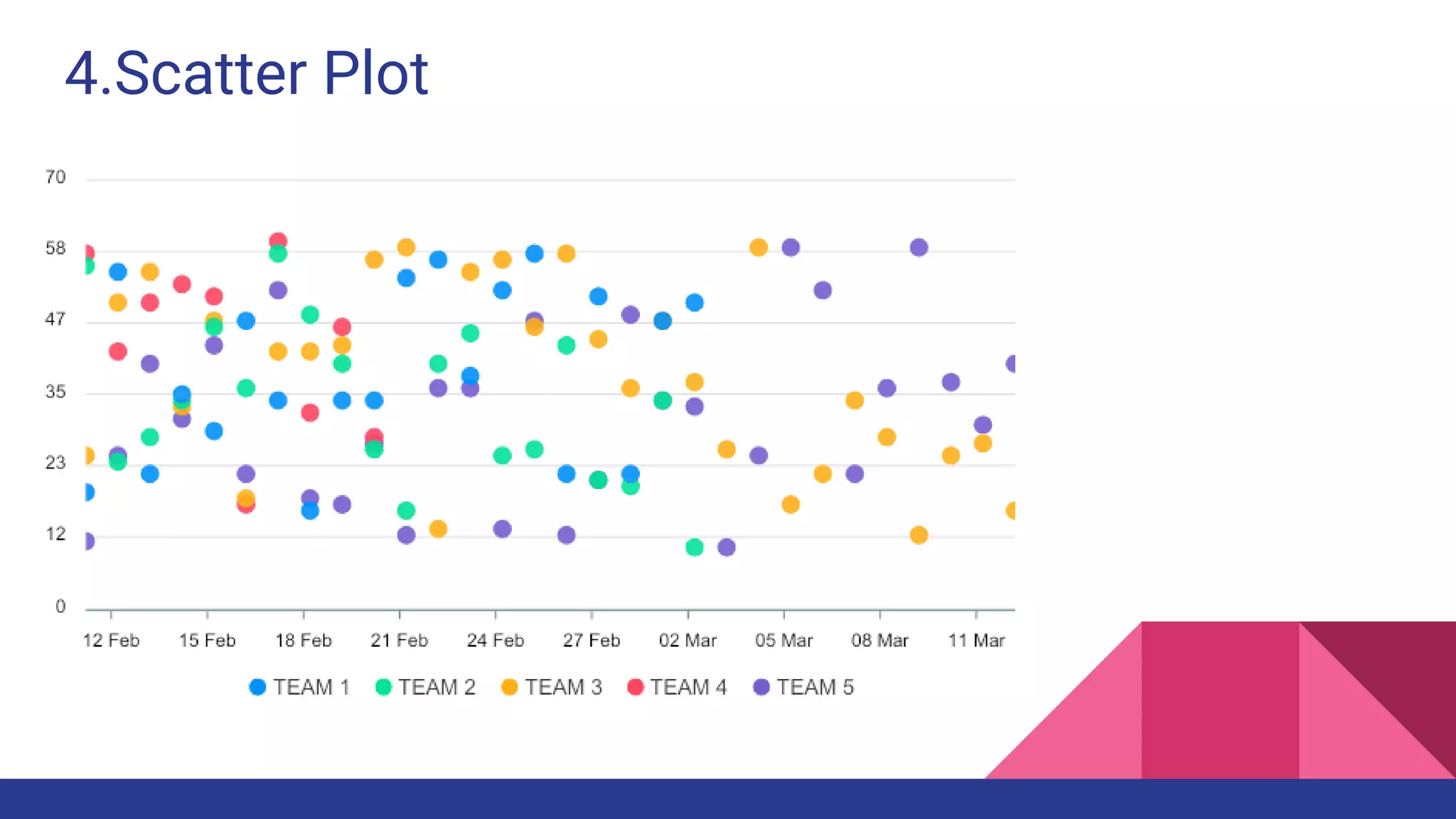
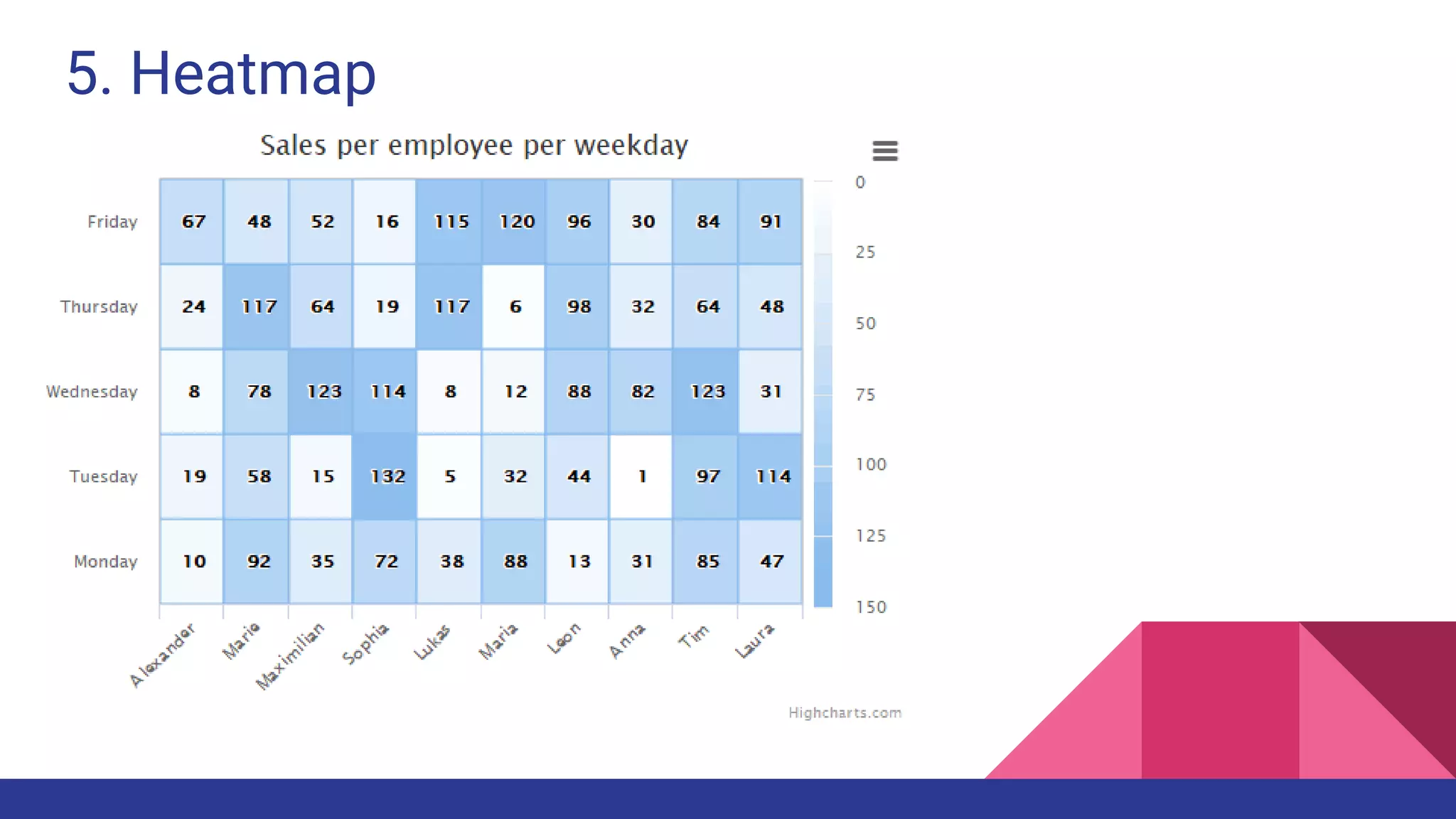
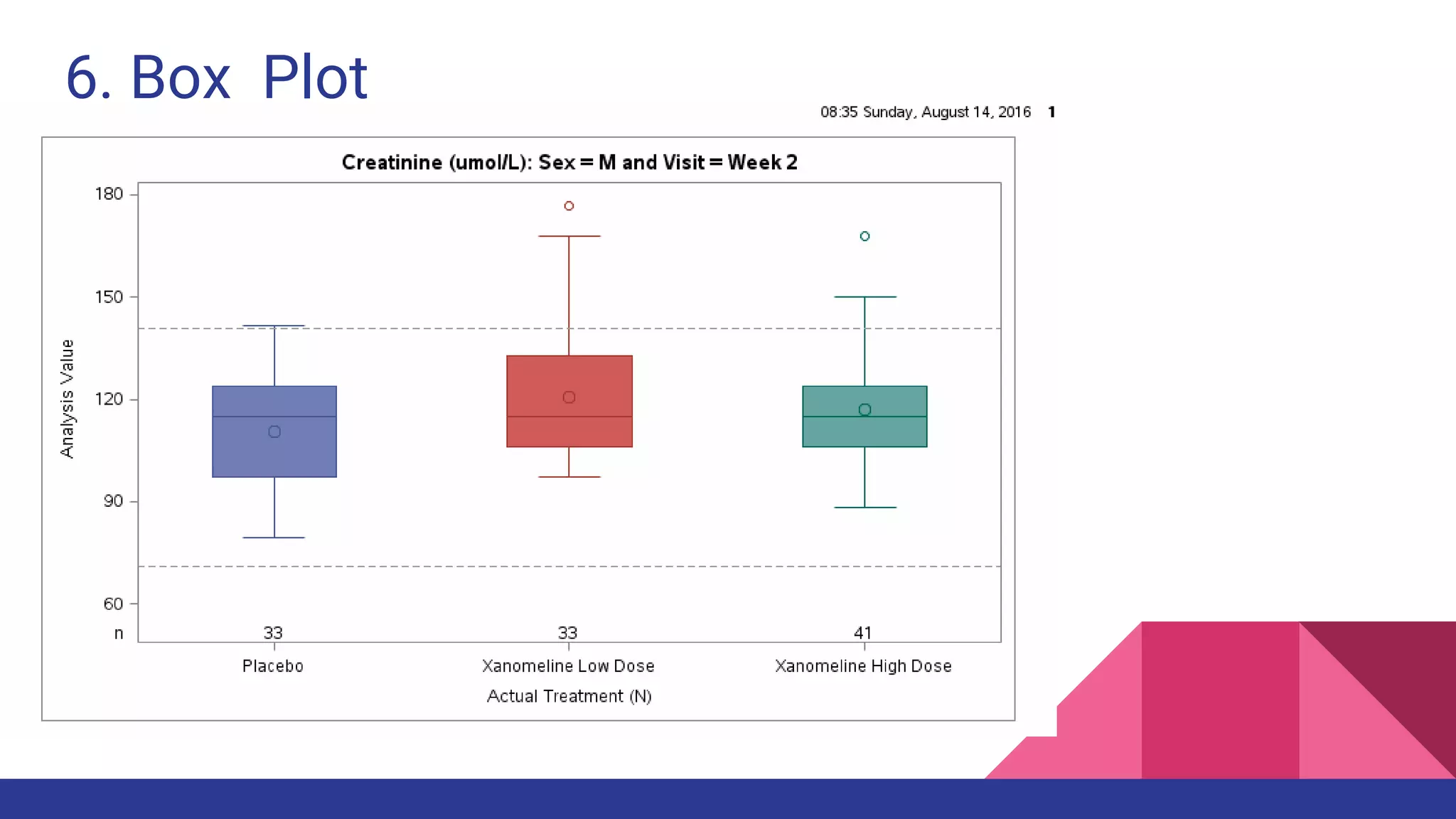
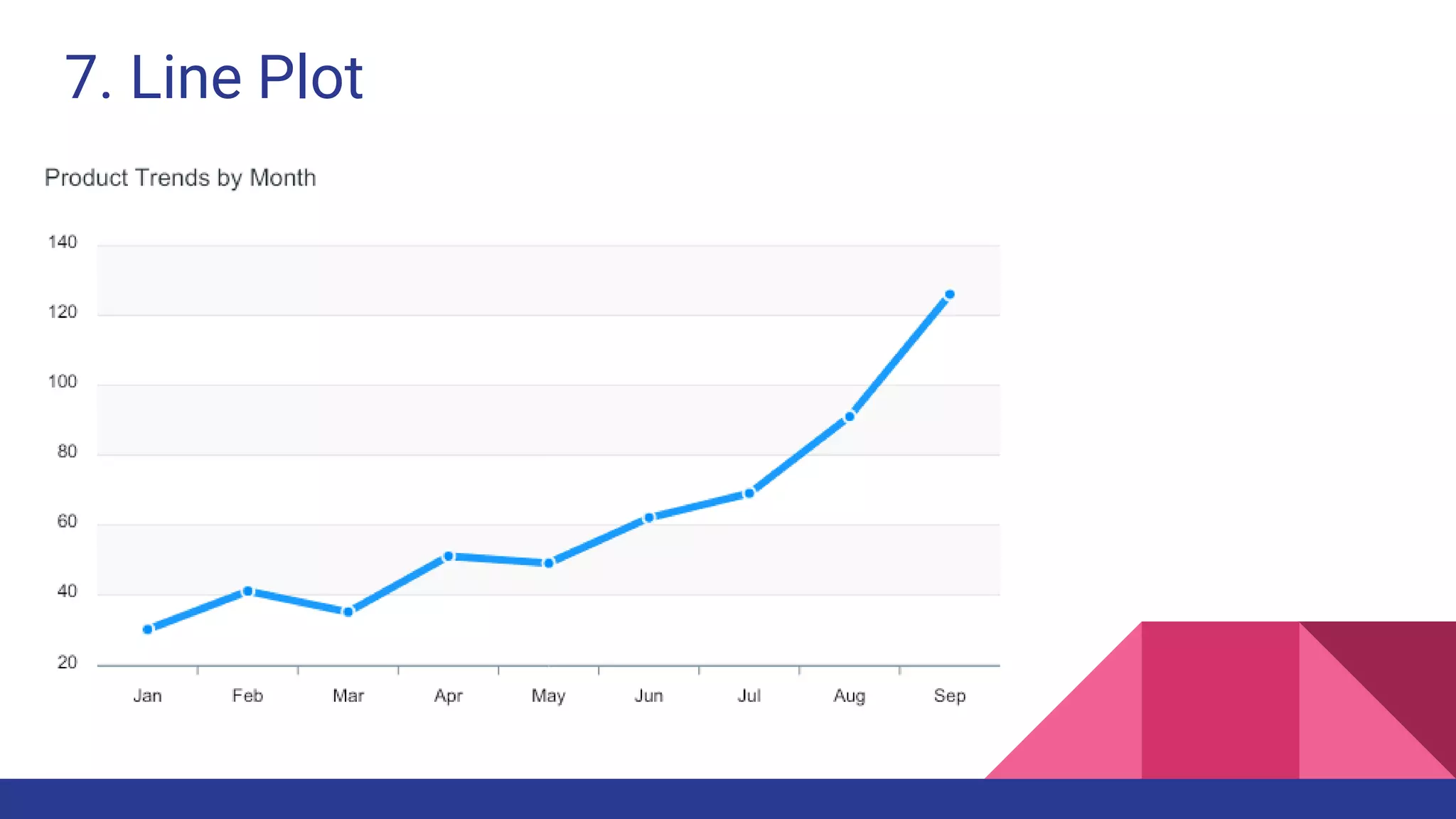
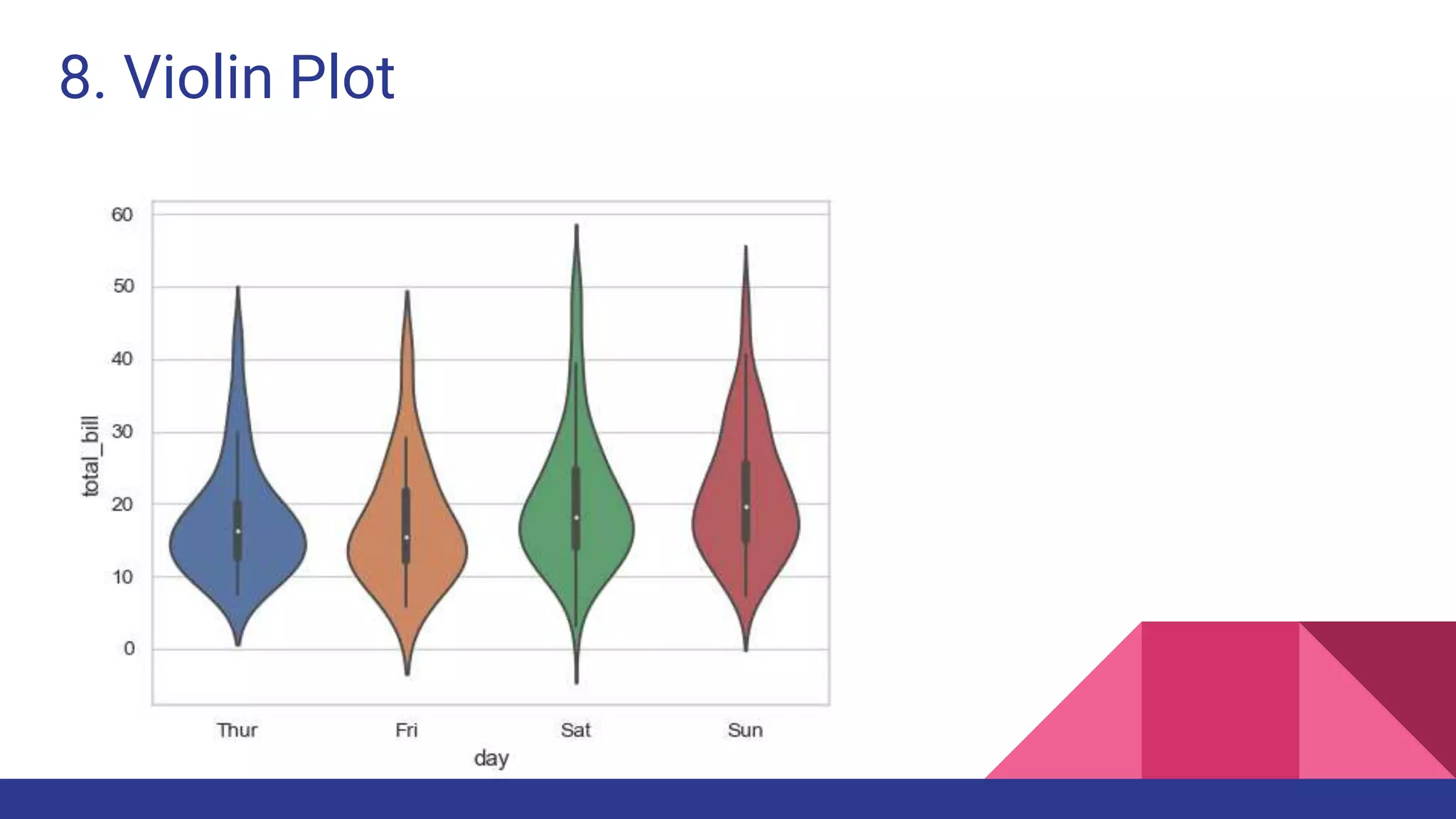
The document discusses Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA), emphasizing its significance in identifying important variables, testing hypotheses, and ensuring data quality. It covers data types, distinguishing between structured and unstructured data, and categorizes various types of data such as categorical and numerical. Additionally, it lists Python packages for creating different types of graphs to visualize data effectively.