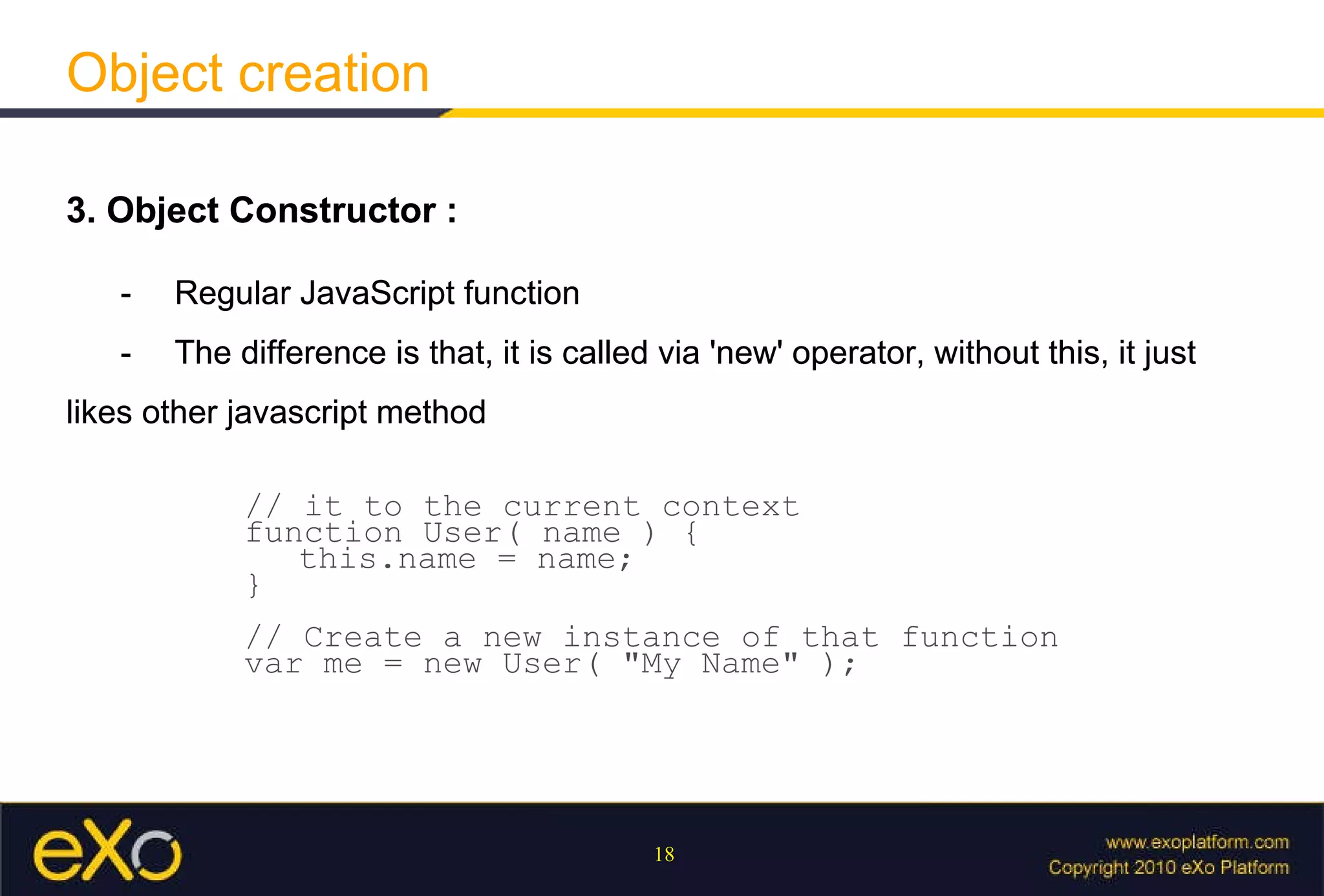
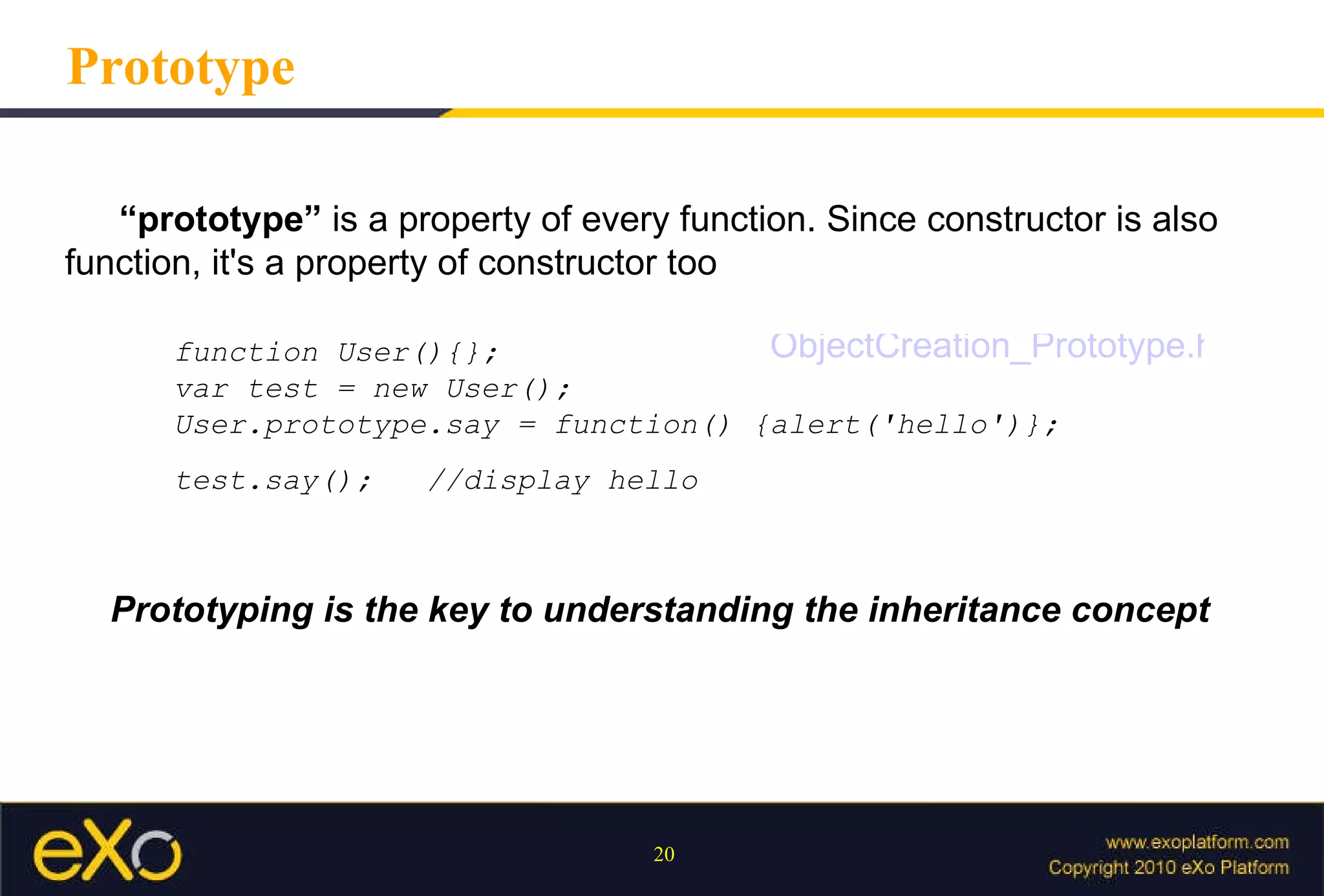
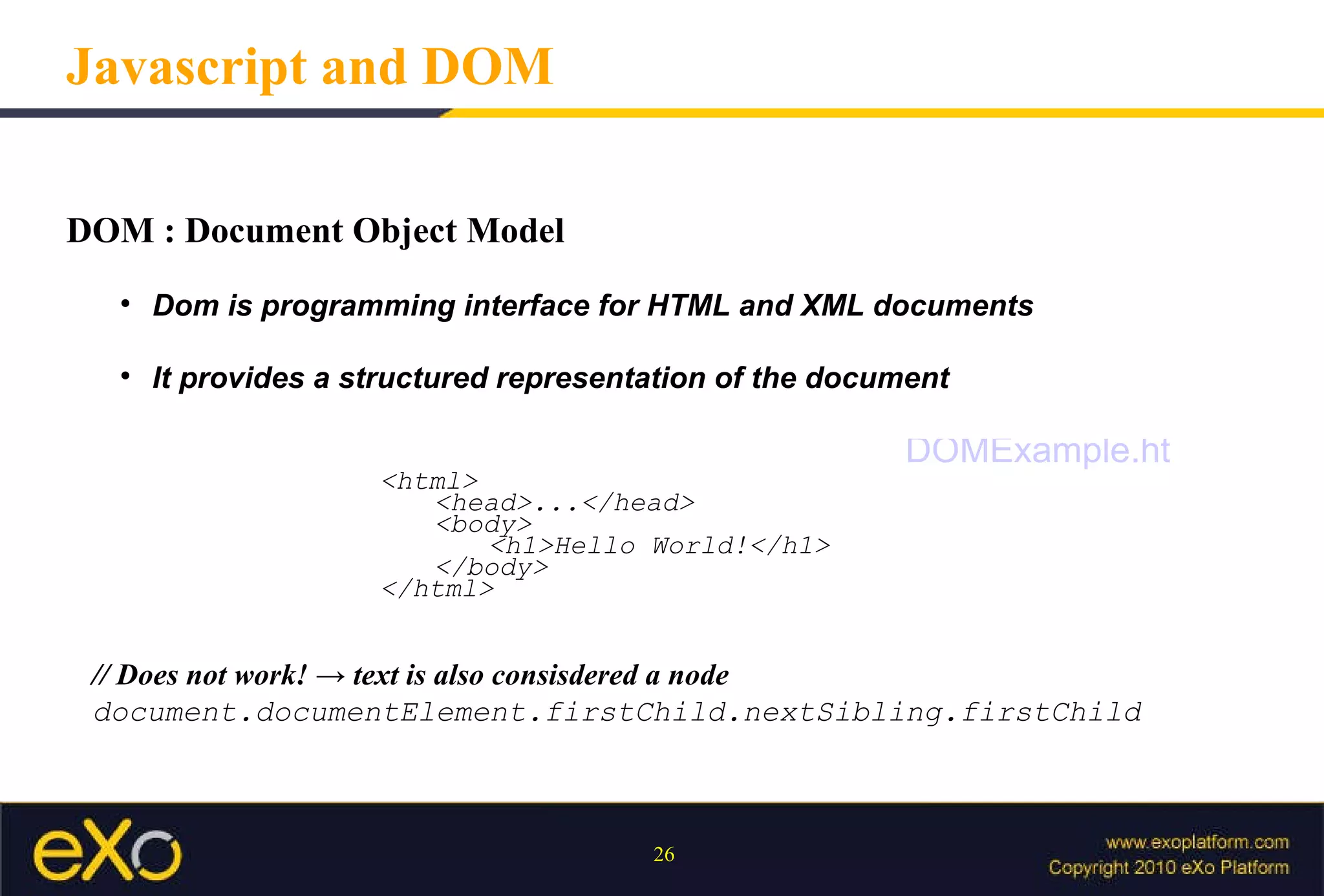
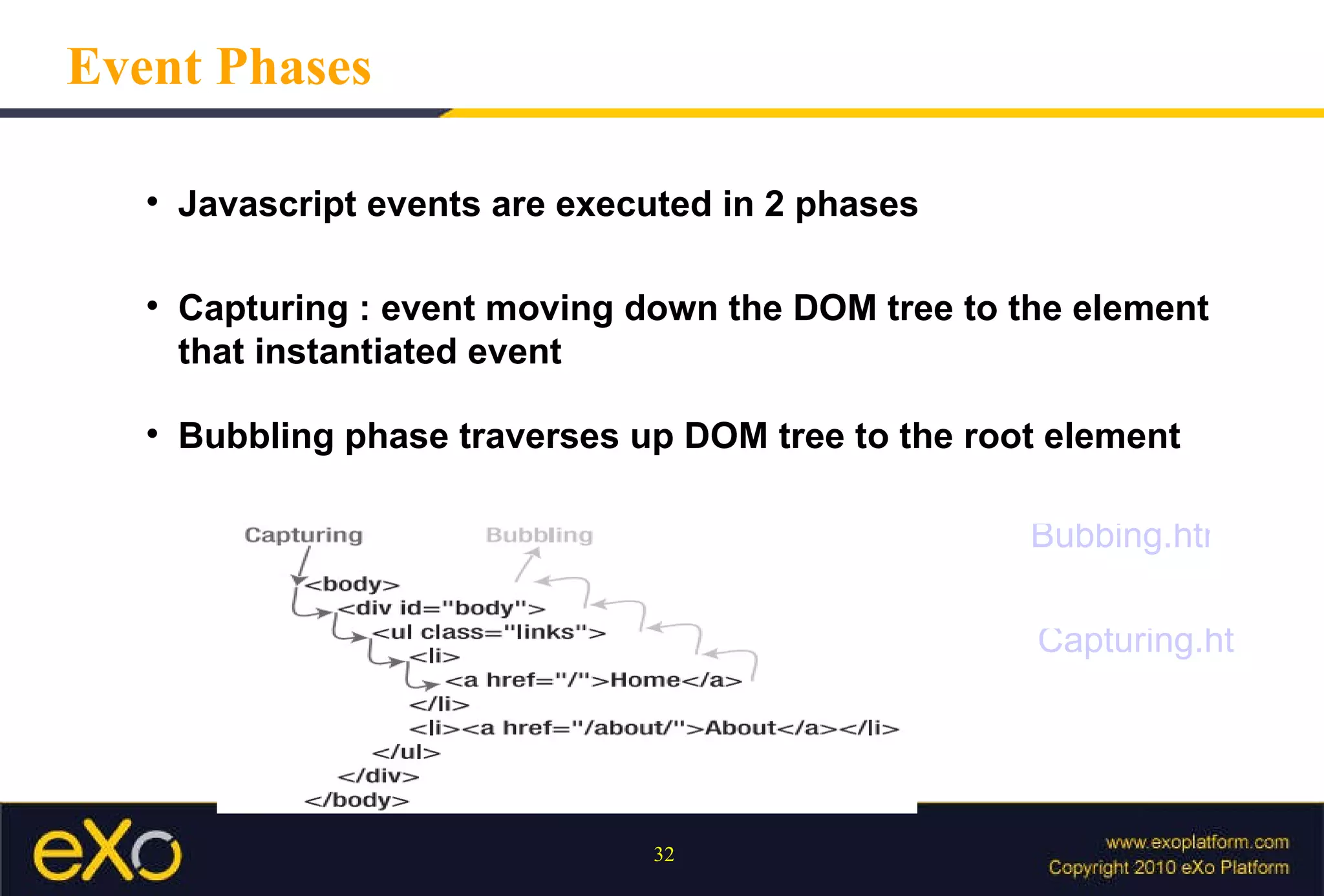
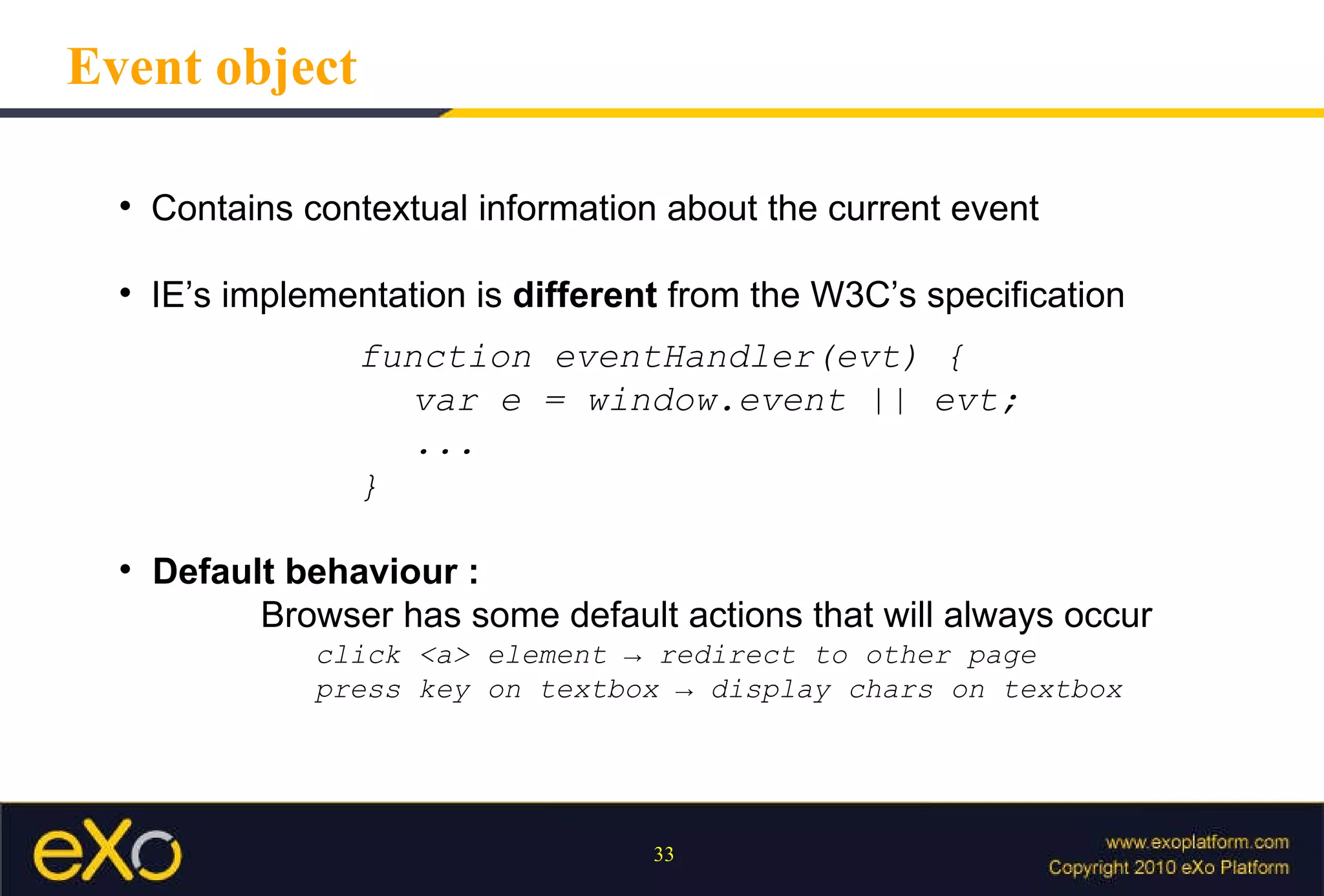
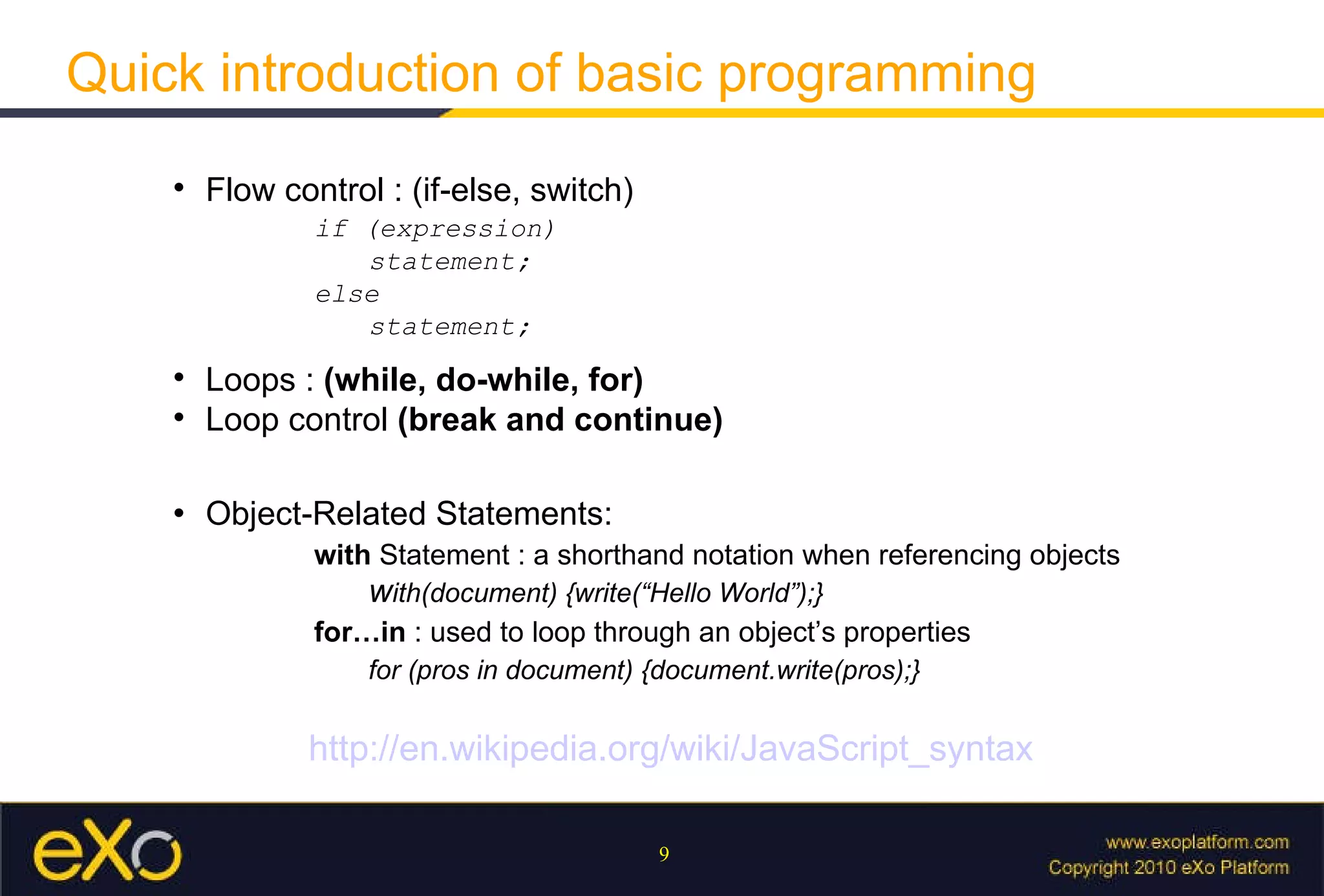
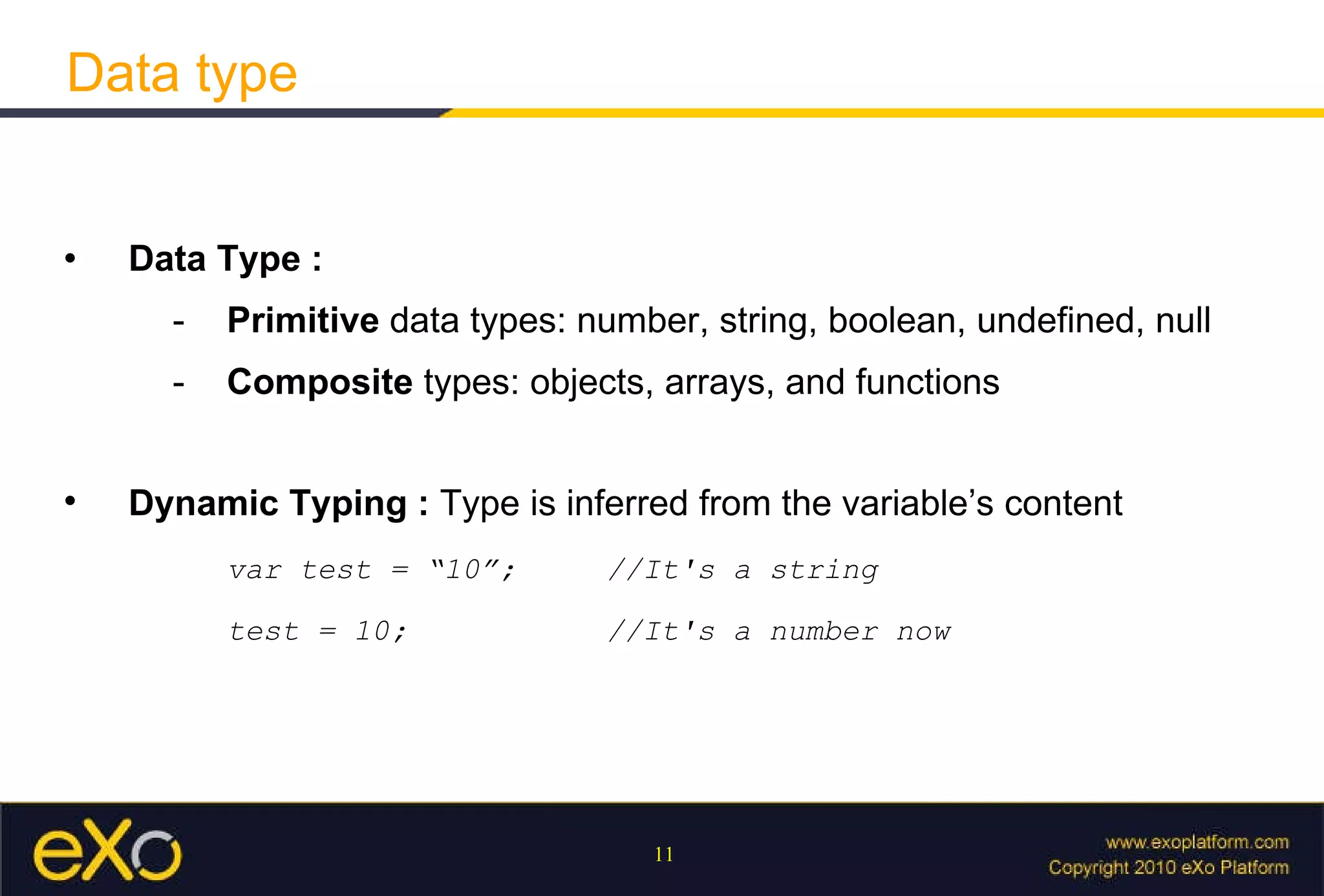
Javascript allows interactive content on web pages and control of the browser and document. It is an interpreted scripting language that is cross-platform but support varies. Javascript can provide interactive content, control document appearance and content, and interact with the user through event handlers.










![Functions Function creation syntax : function Add(x, y) { var sum = x + y; return sum; } var test = new Function(“alert('test')”); var test = function() {alert('test')}; How to deal with arguments : length property arguments [] property FunctionCreation.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javascripttraining-100625101736-phpapp01/75/eXo-SEA-JavaScript-Introduction-Training-13-2048.jpg)