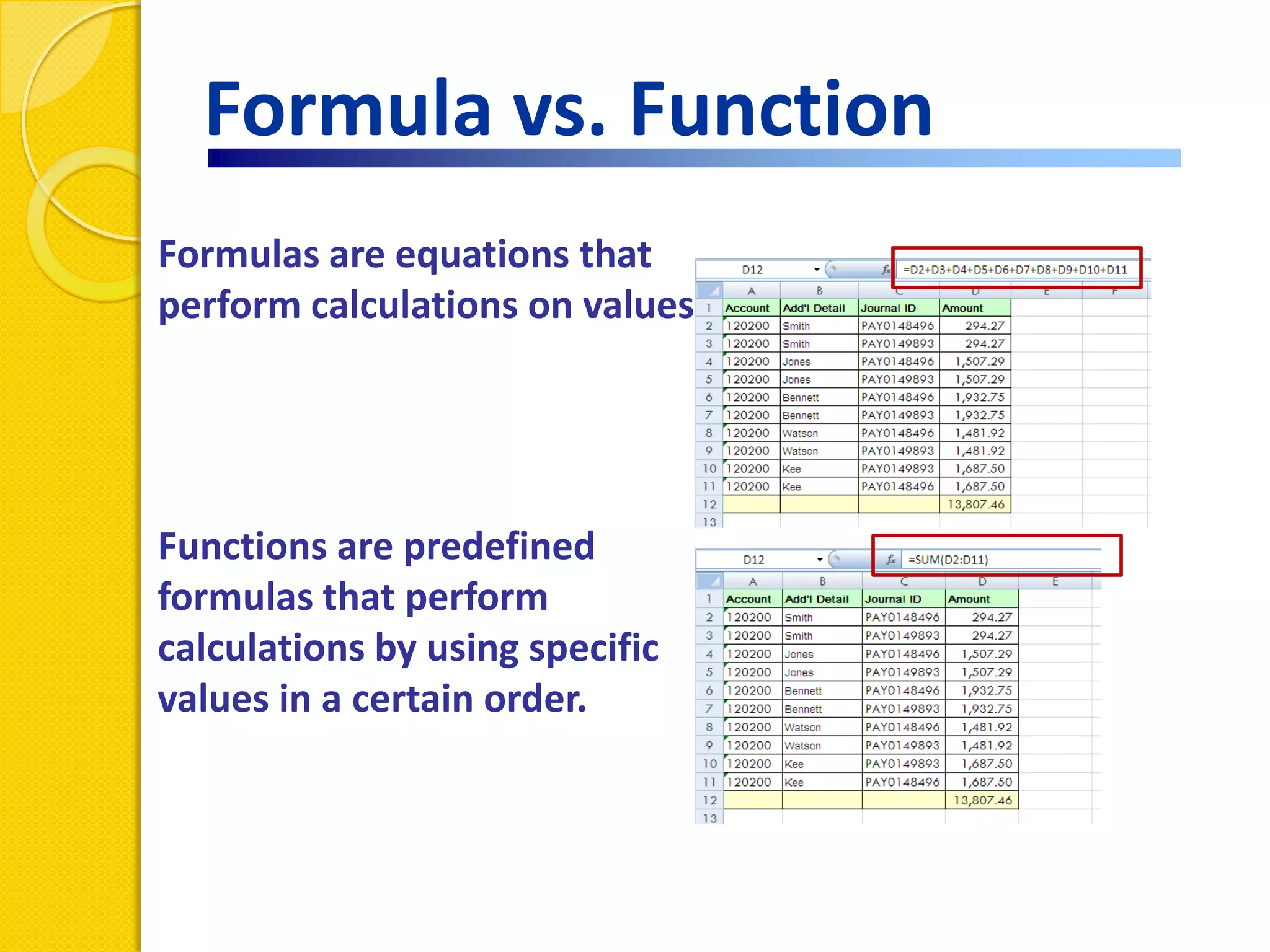
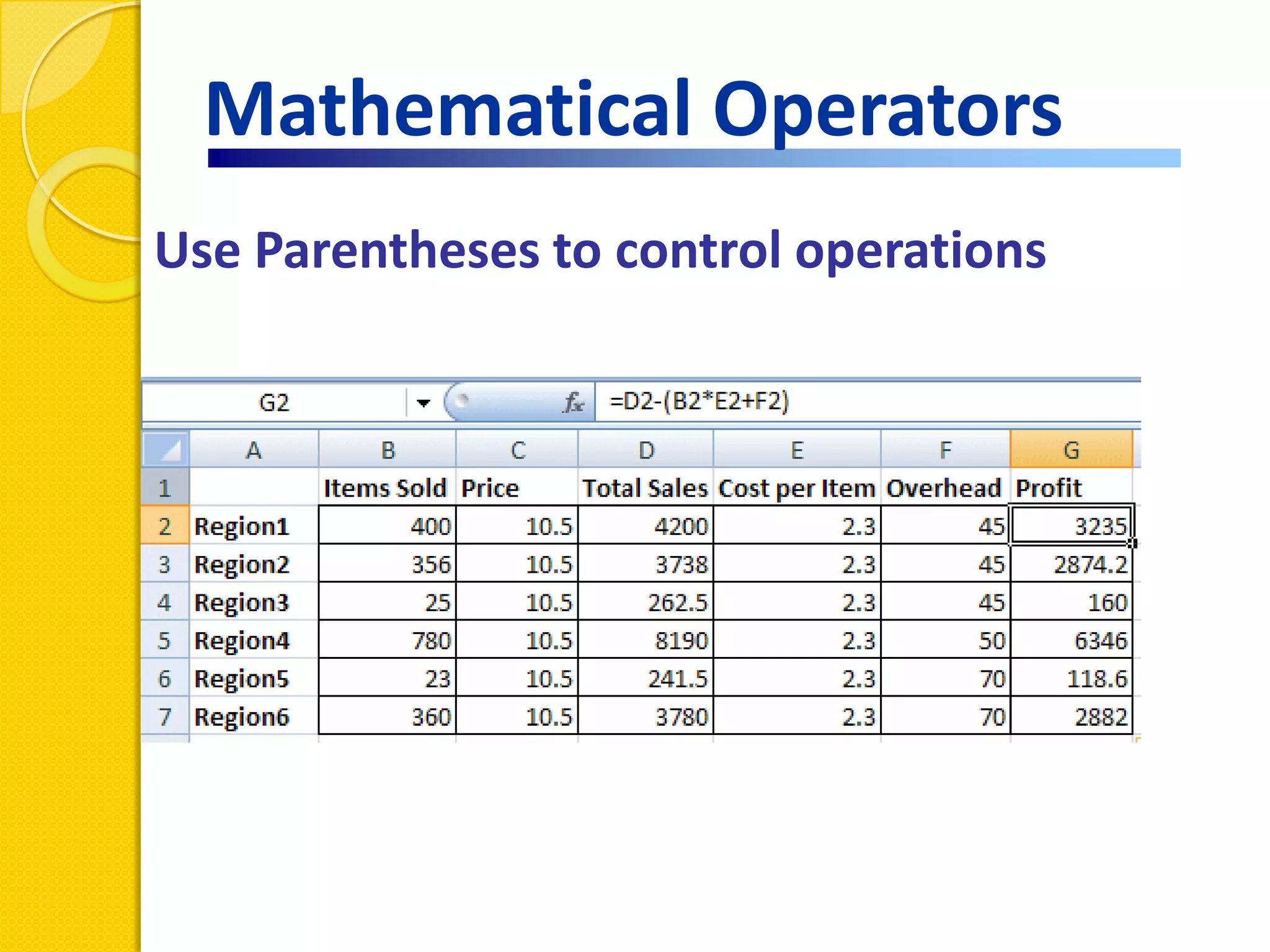
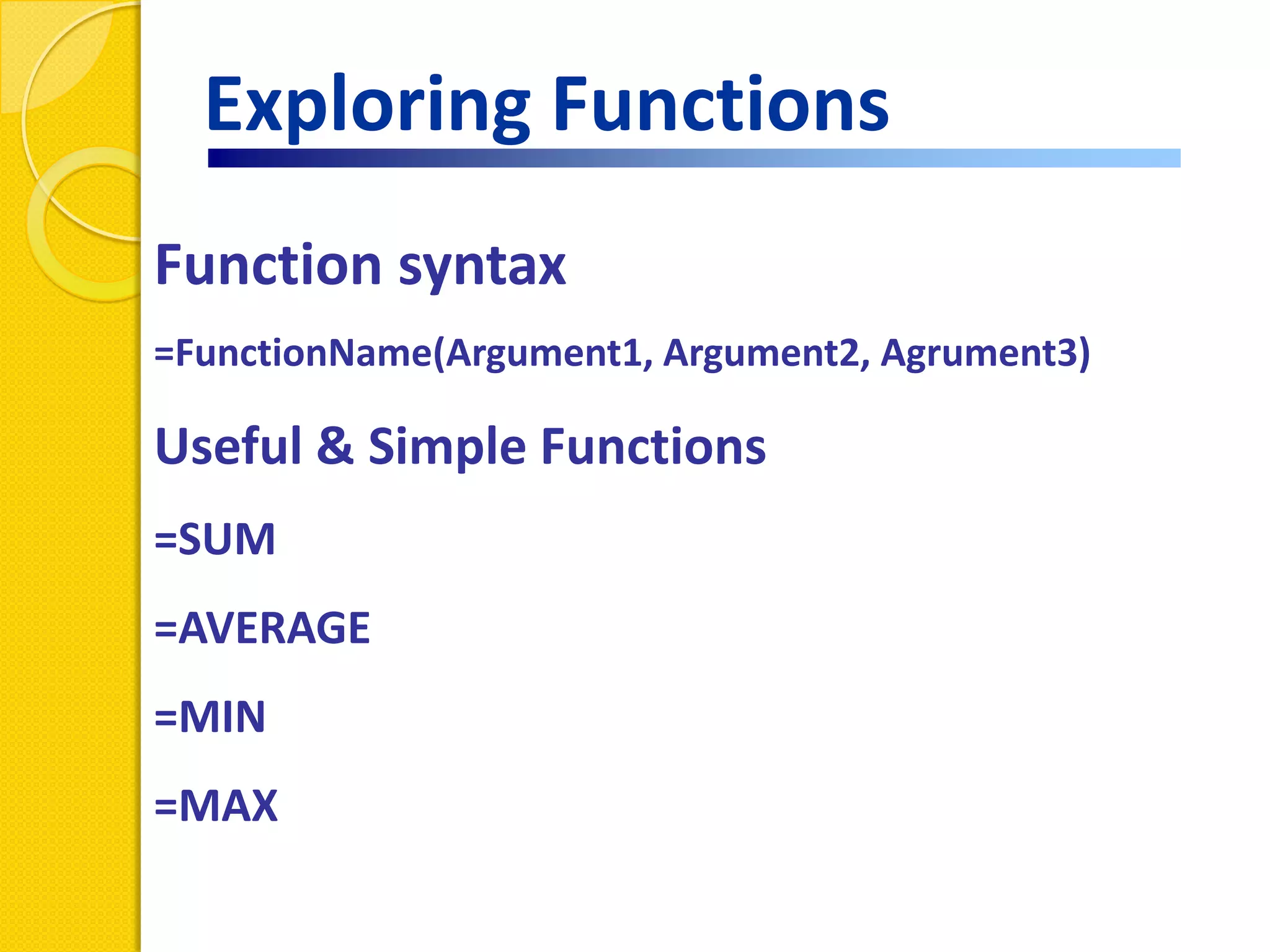
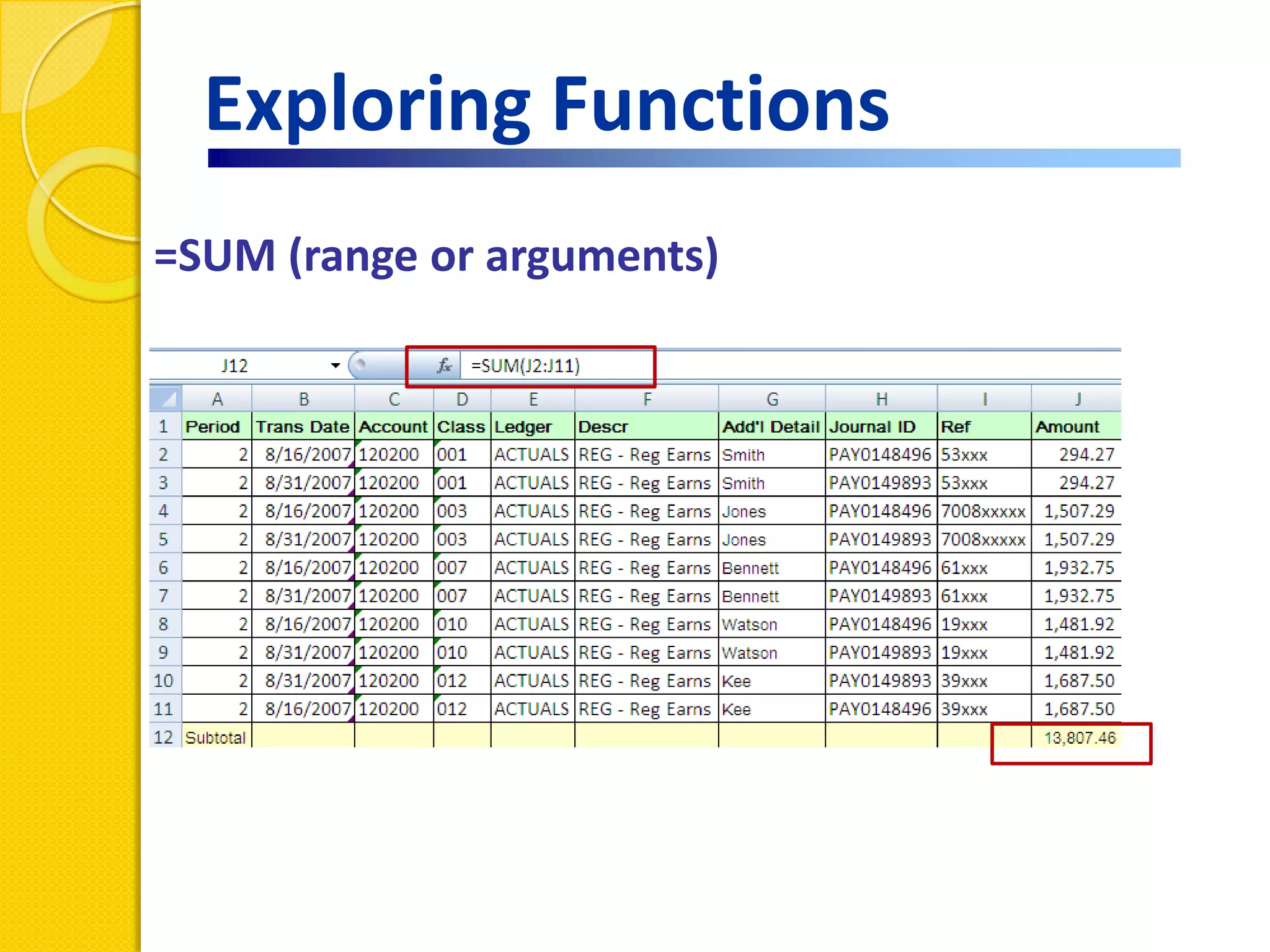
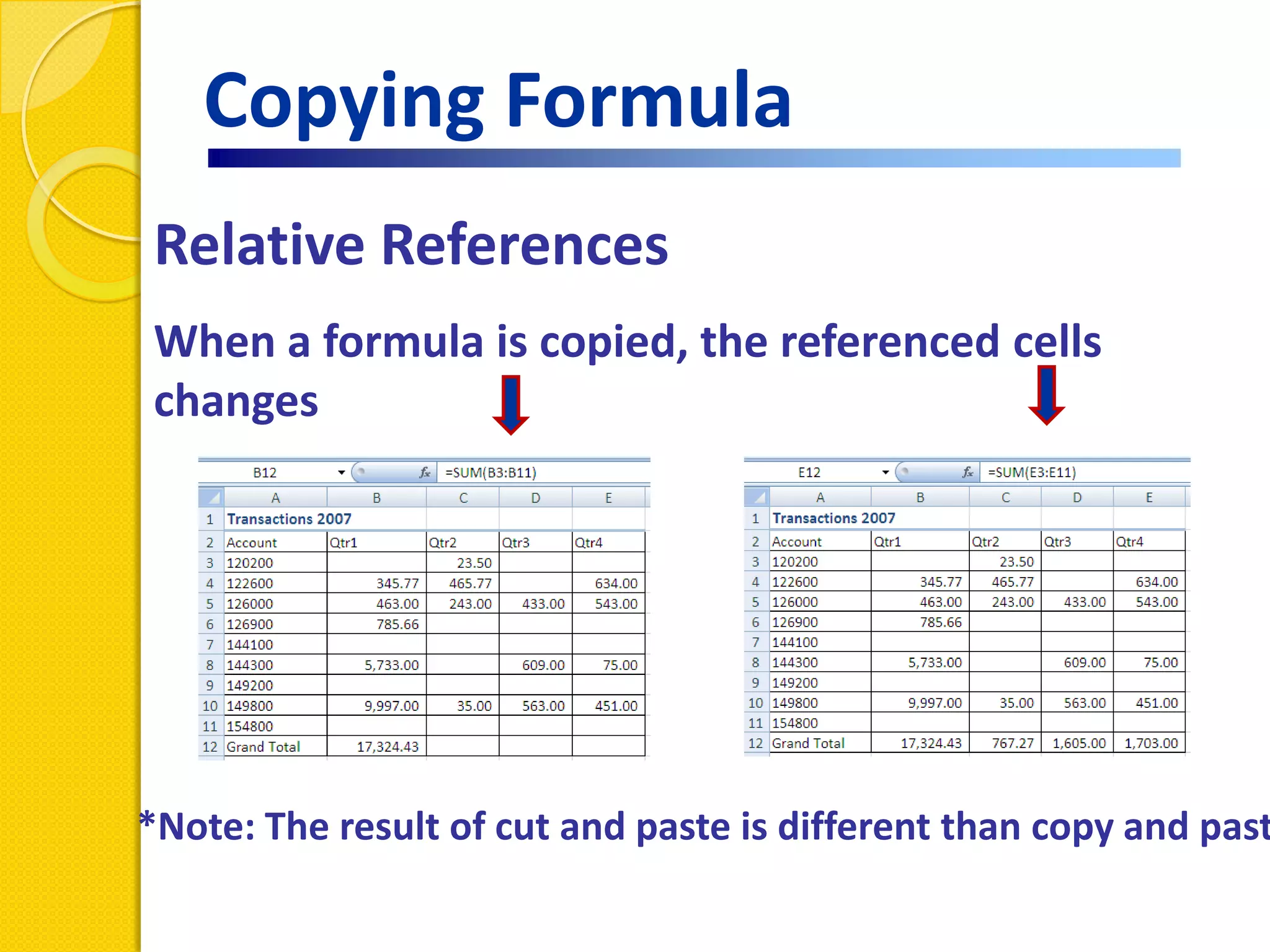
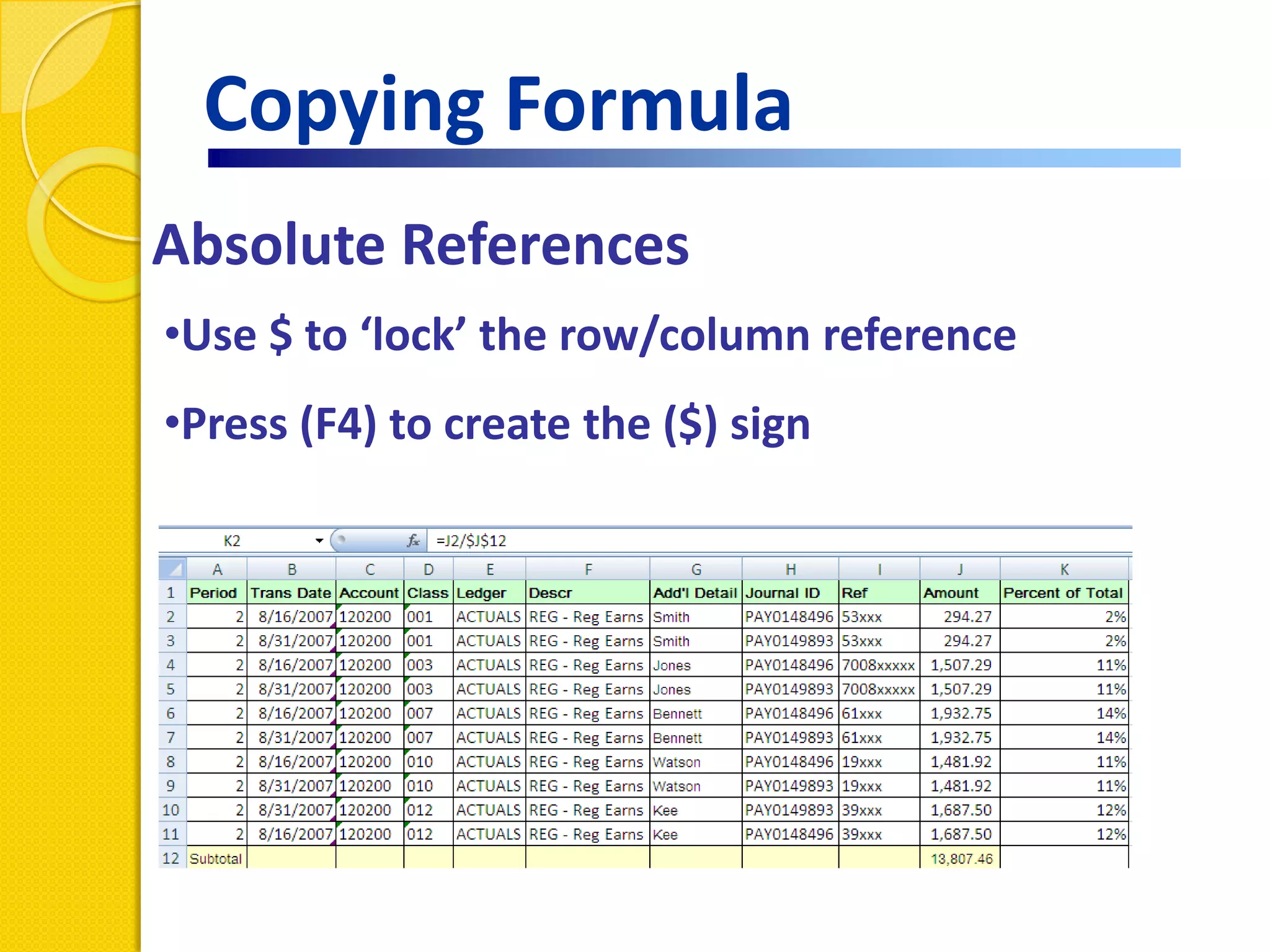
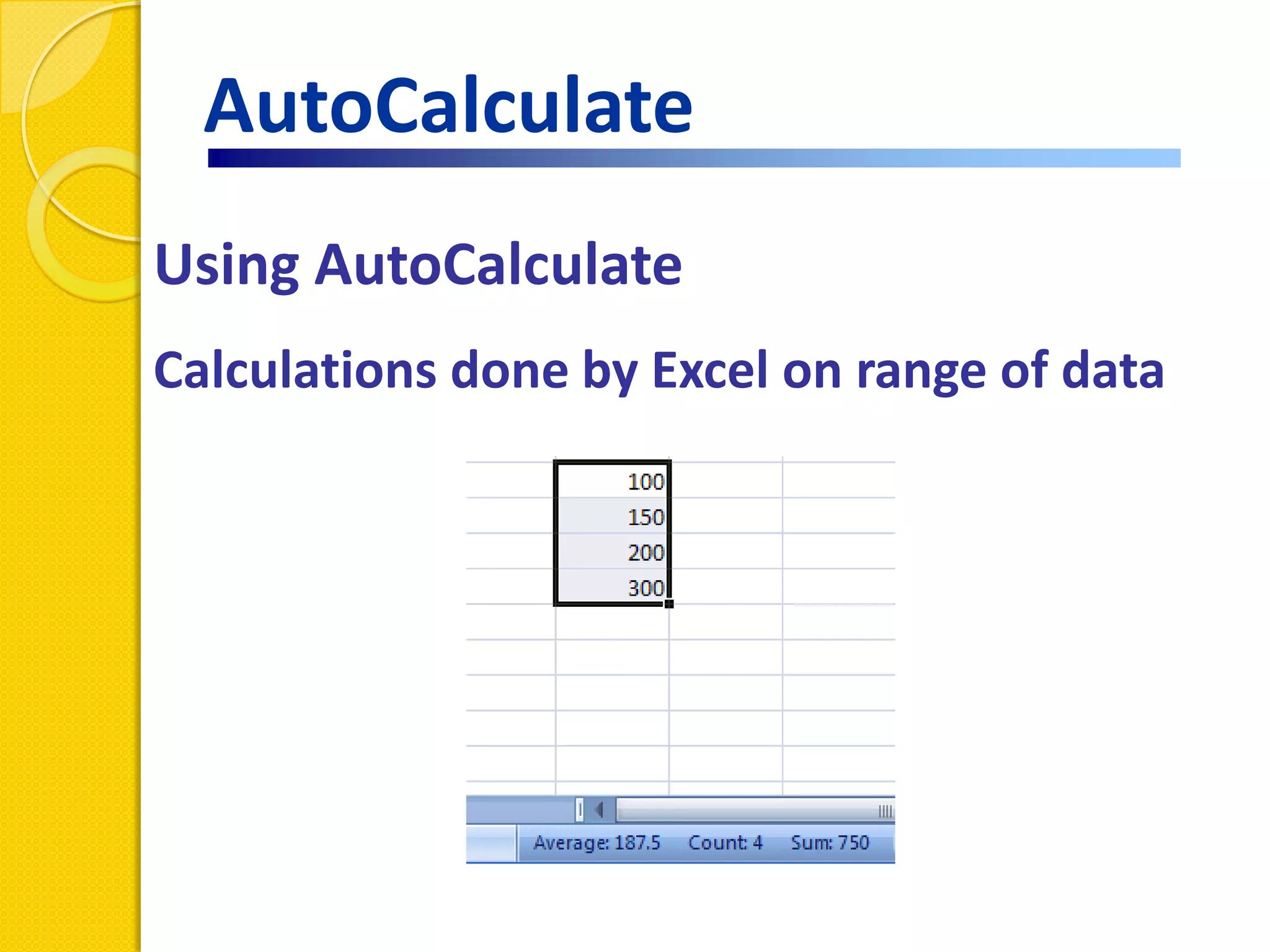
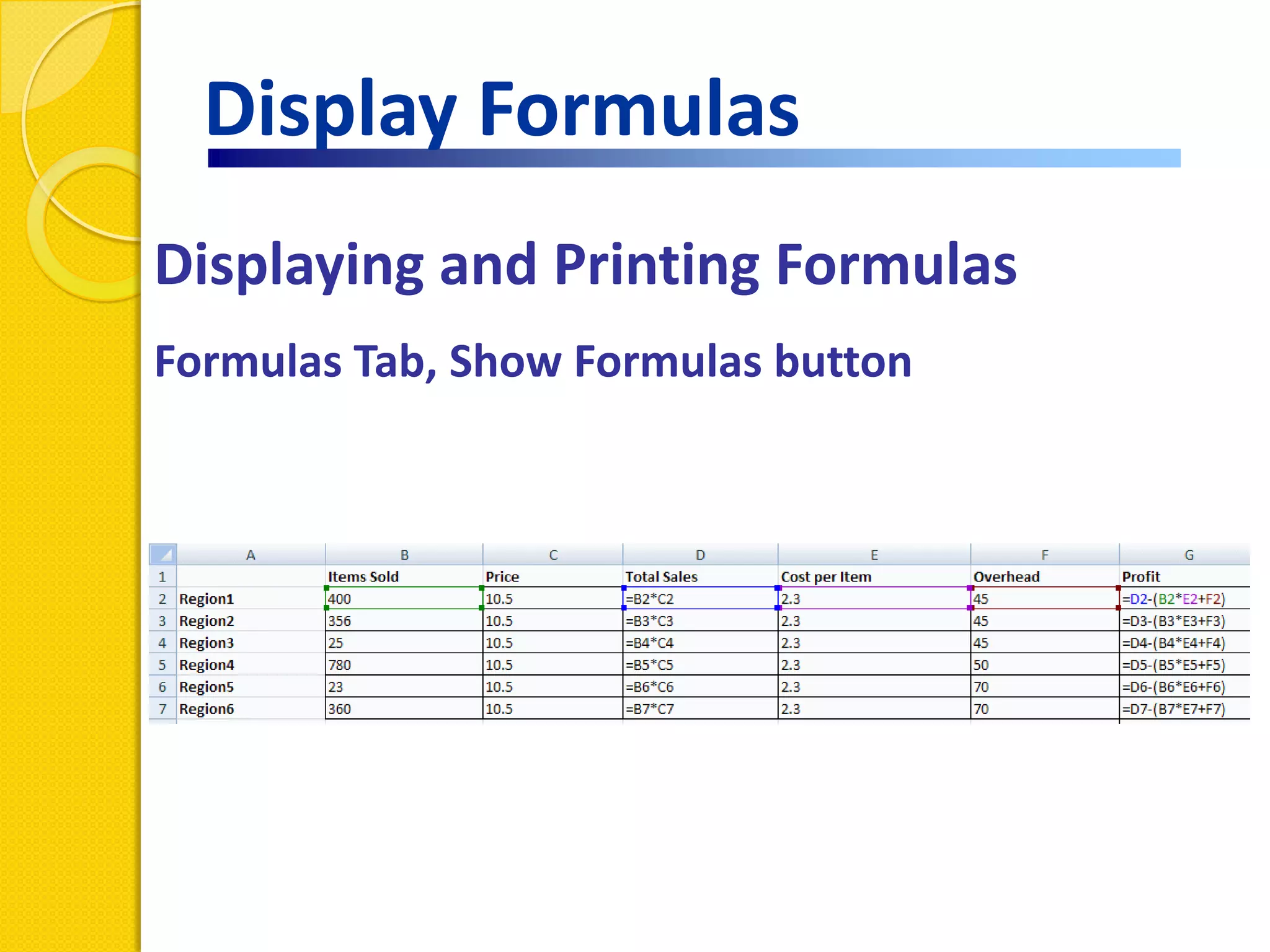
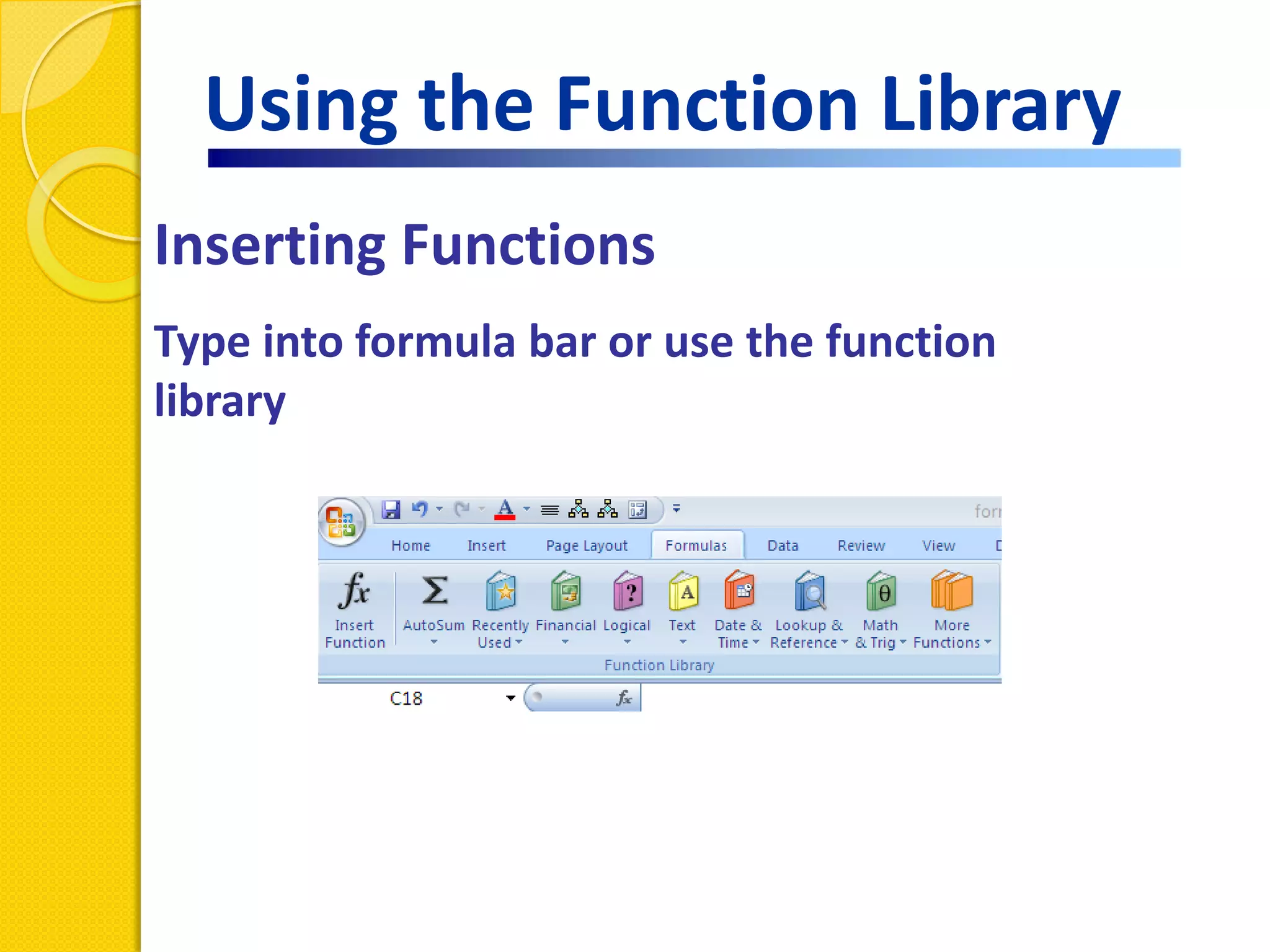
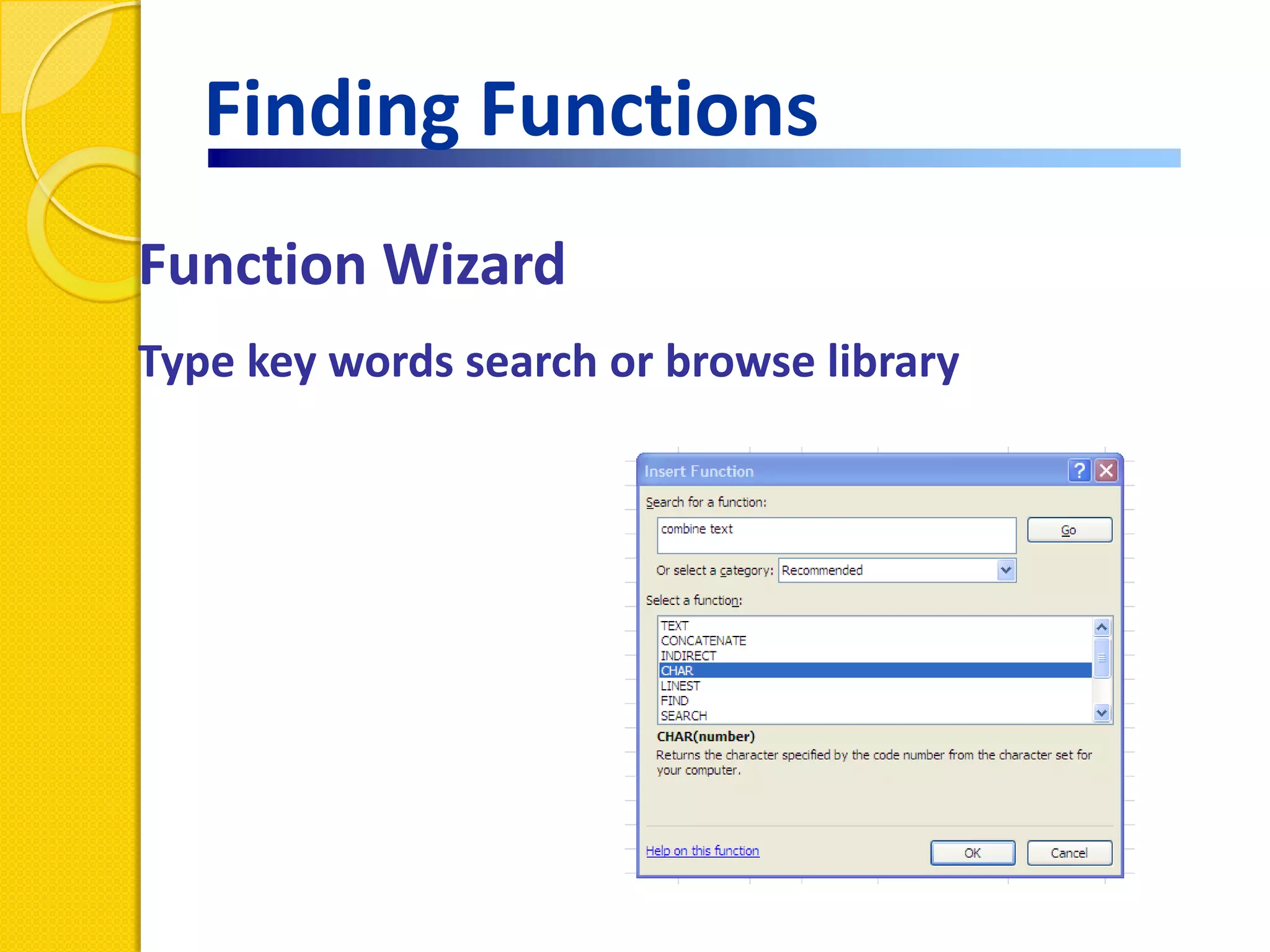
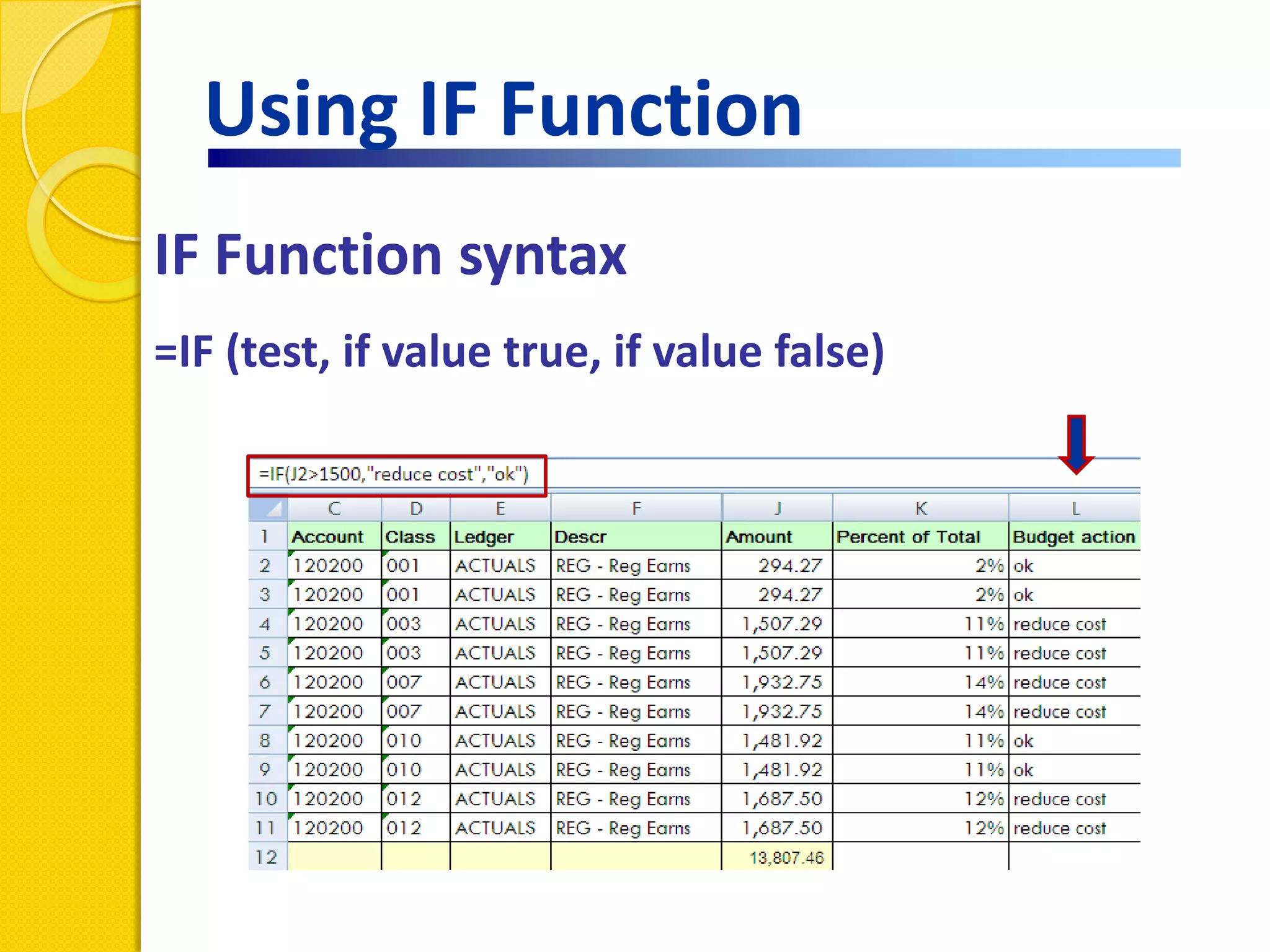
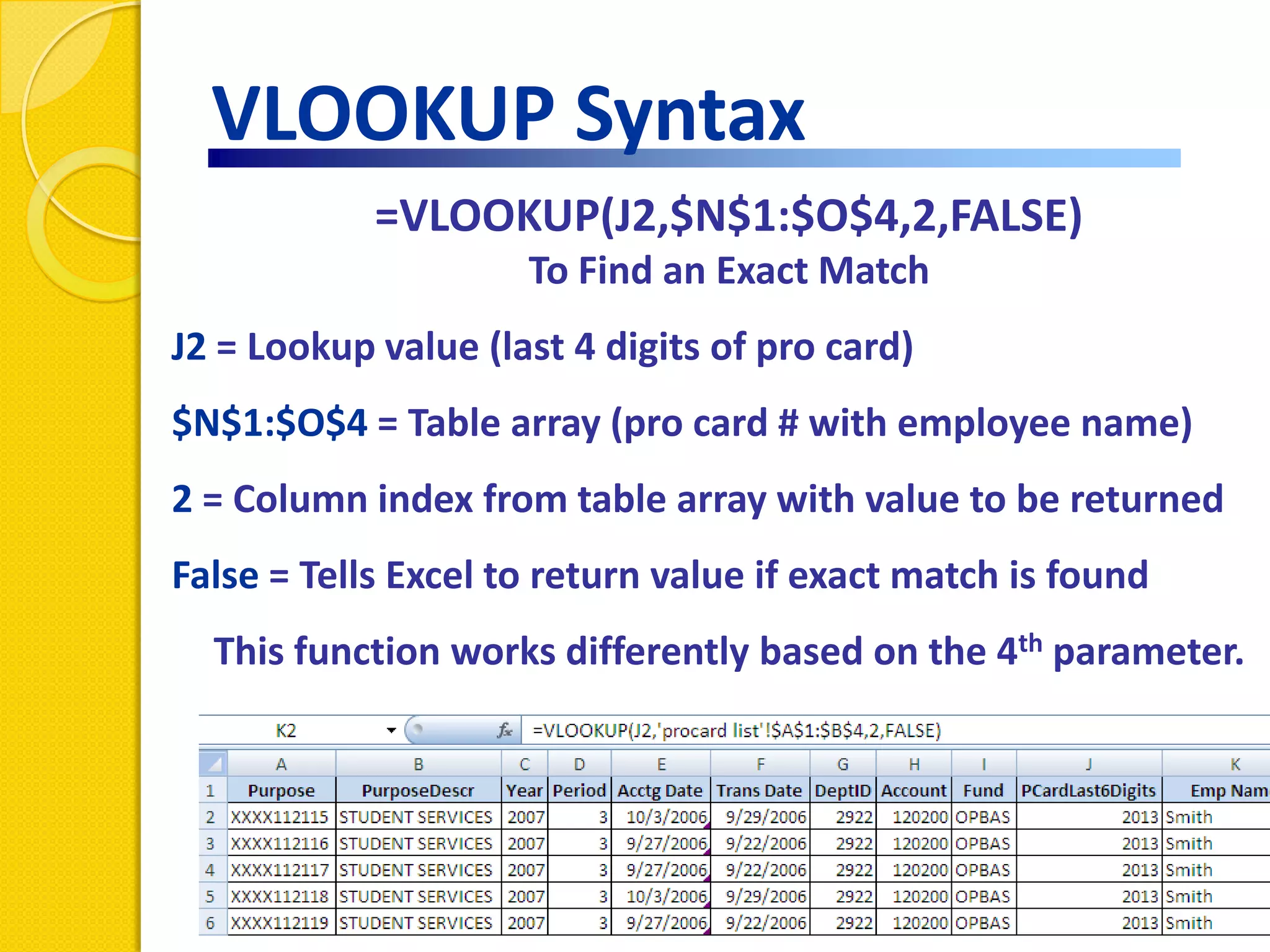
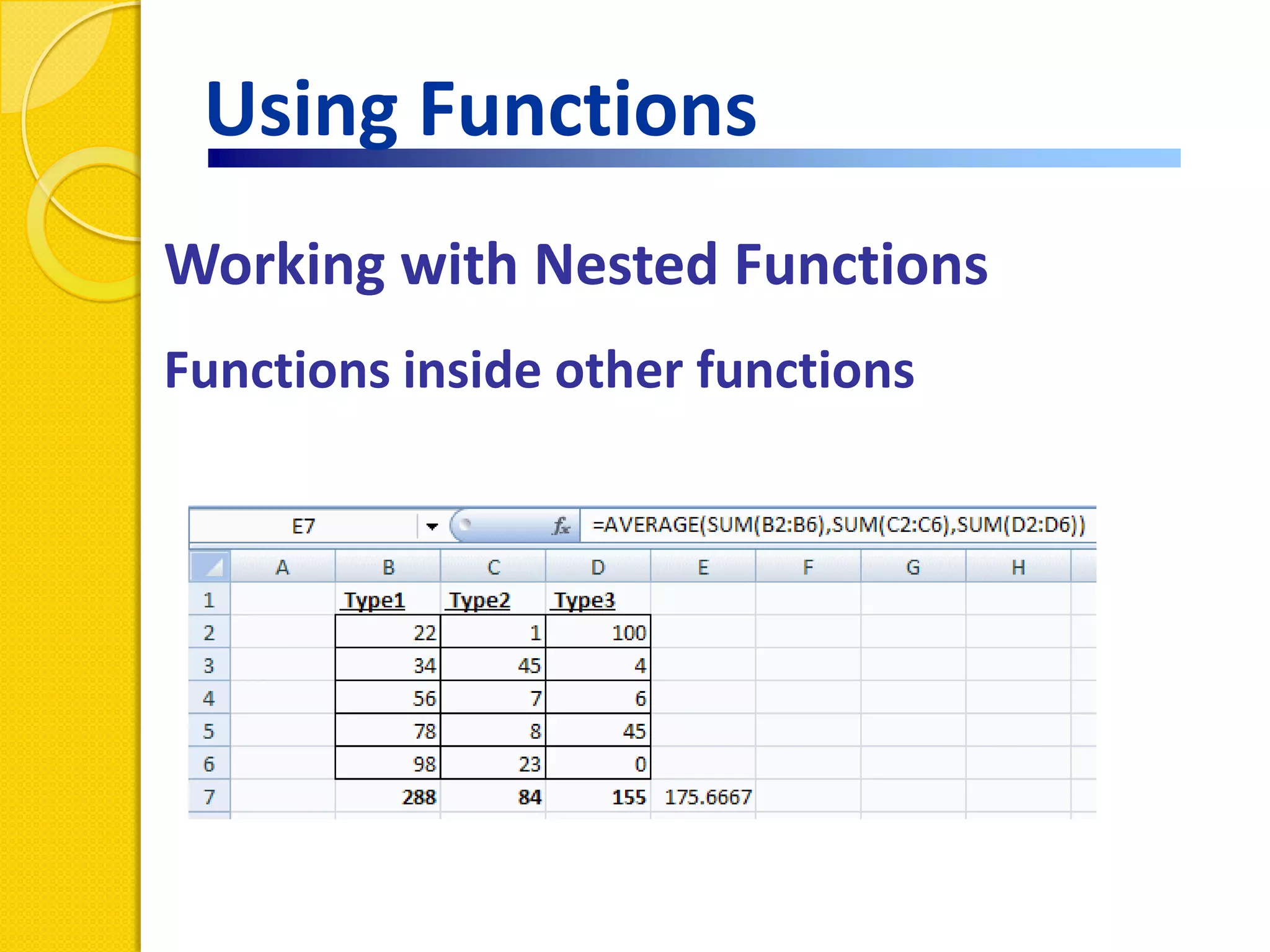
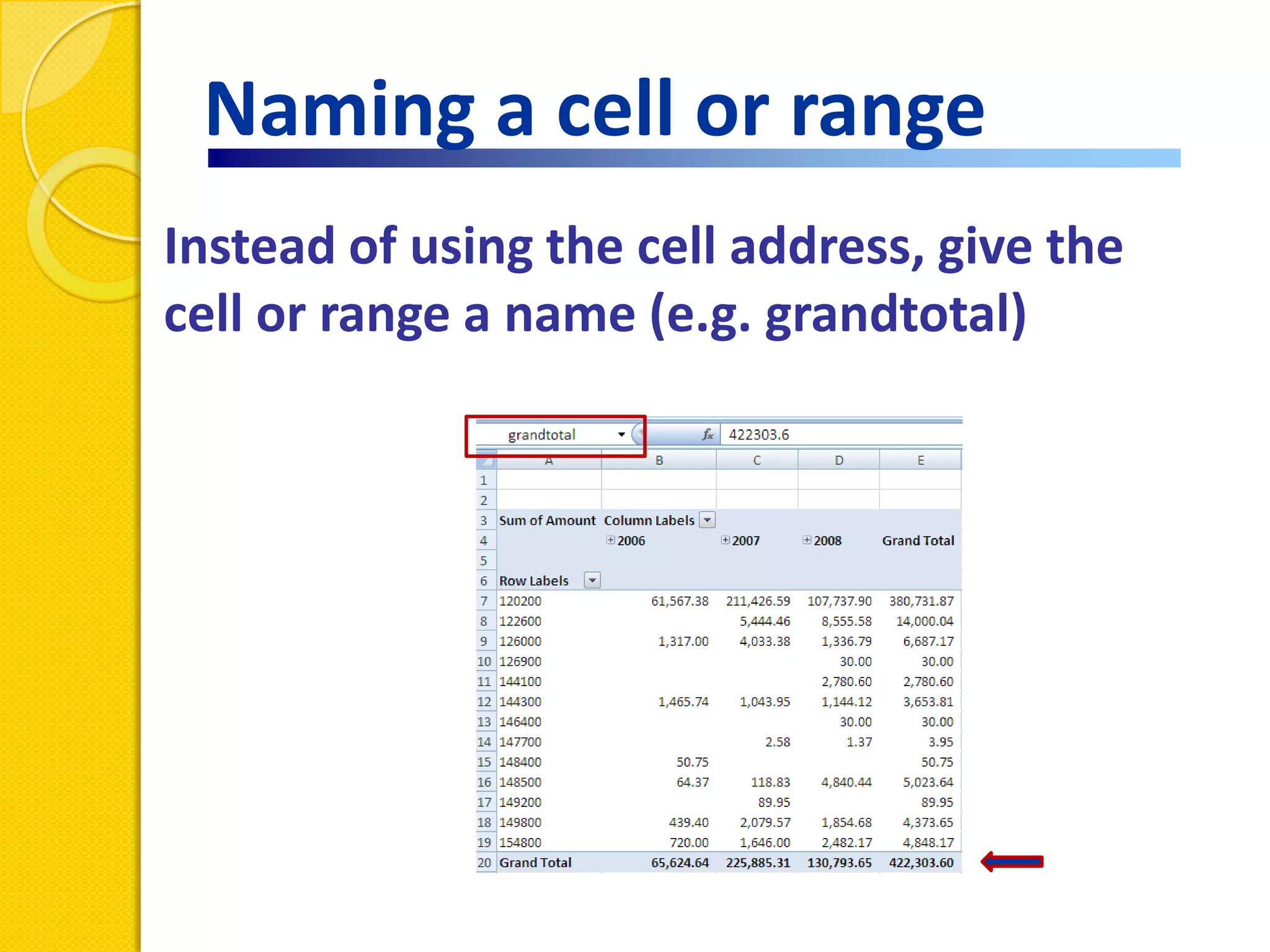
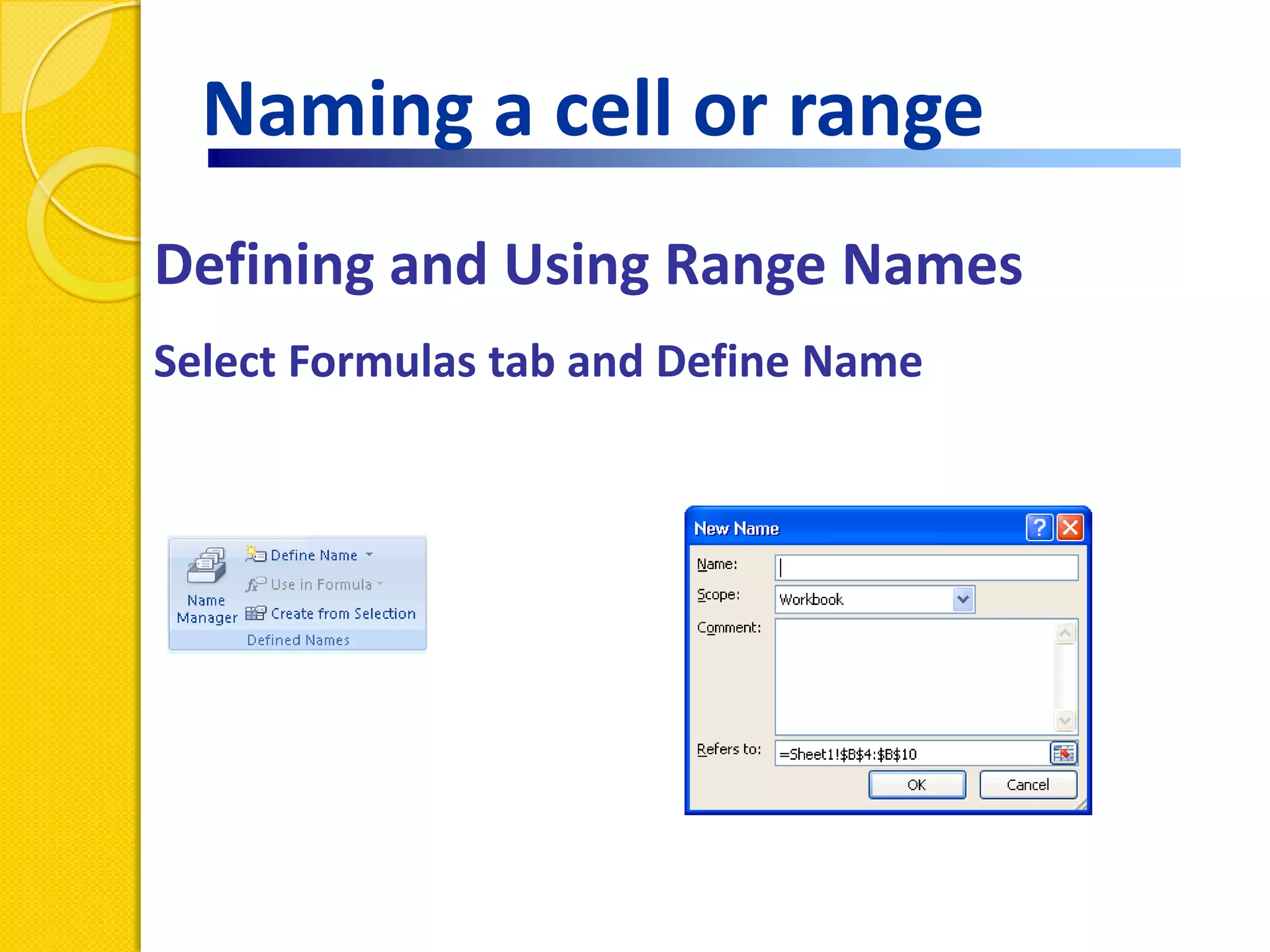
This document provides an overview of using formulas and functions in Excel 2007, including mathematical operators, cell references, common functions like SUM and IF, finding the right function, fixing errors, naming cells, and other tips. Key topics covered are basic formulas, relative and absolute cell references, using functions, the IF function, displaying formulas, the function library, and identifying common errors. Users will learn the basics of working with formulas and functions in Excel.