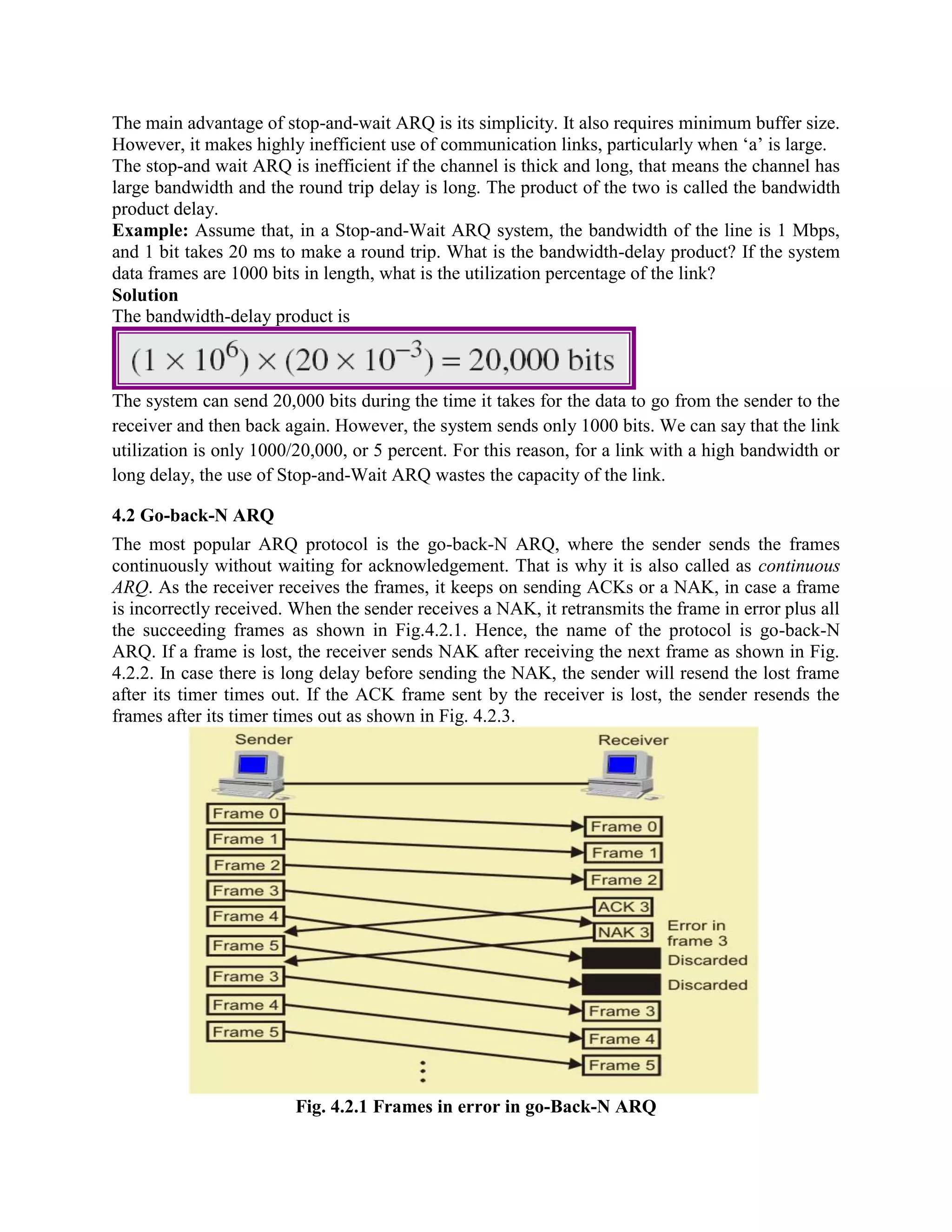
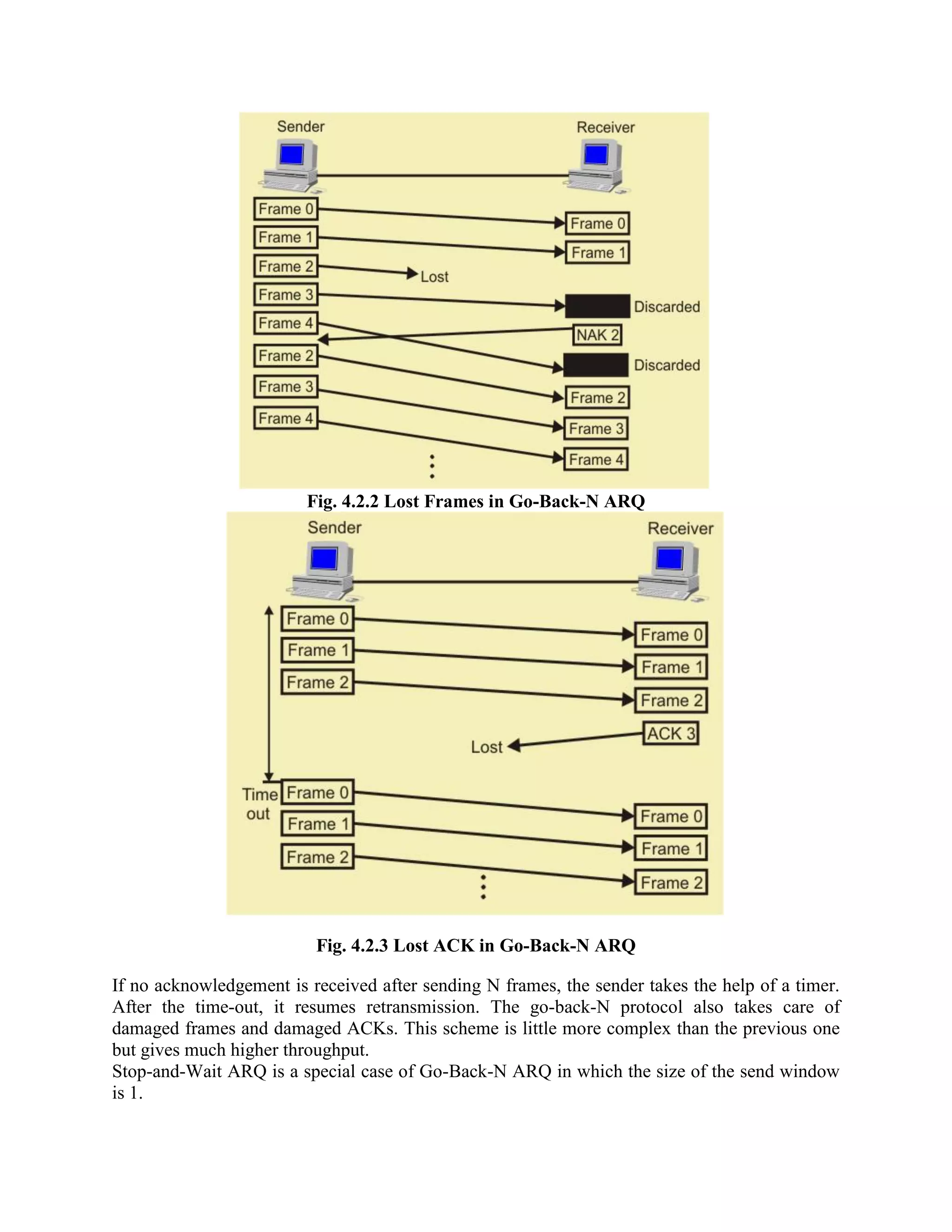
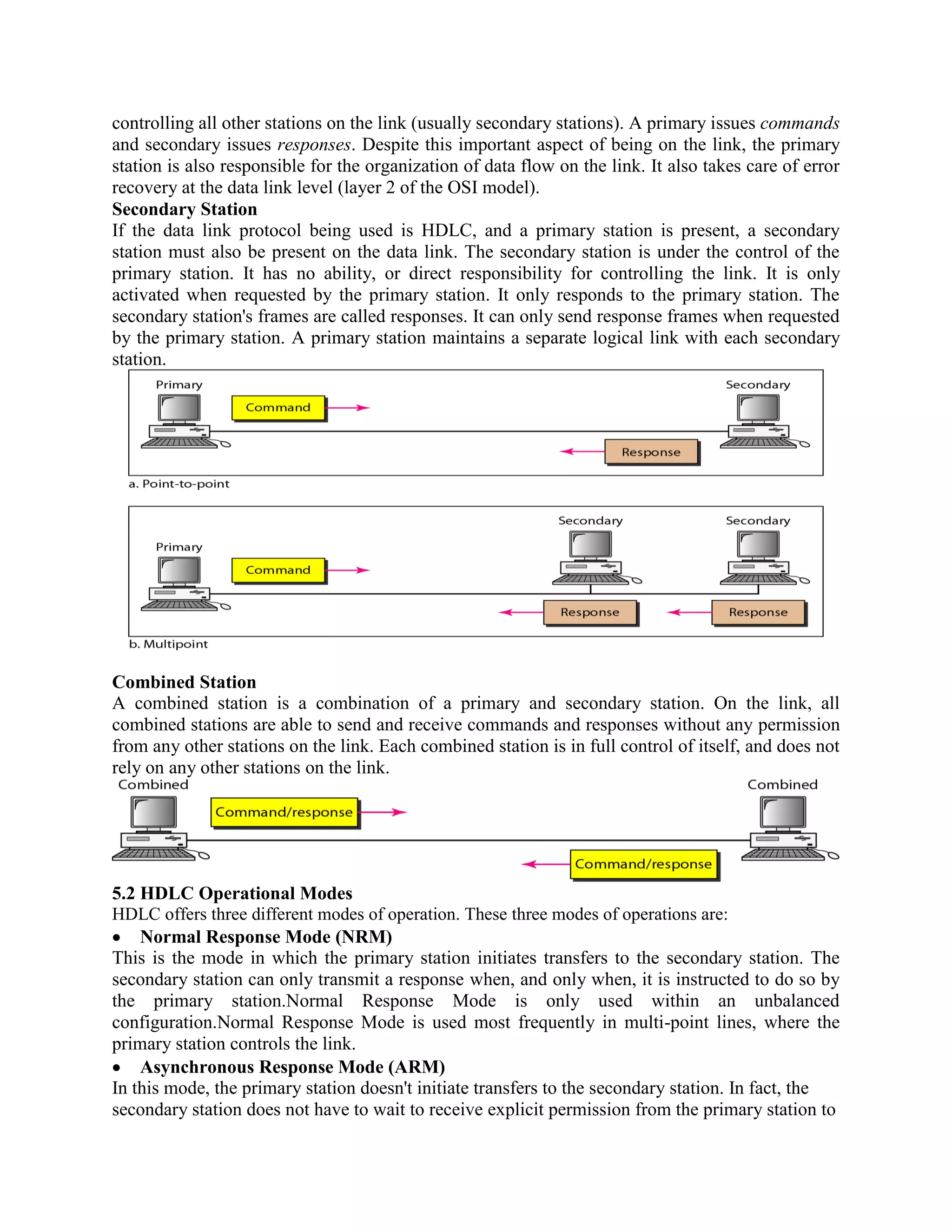
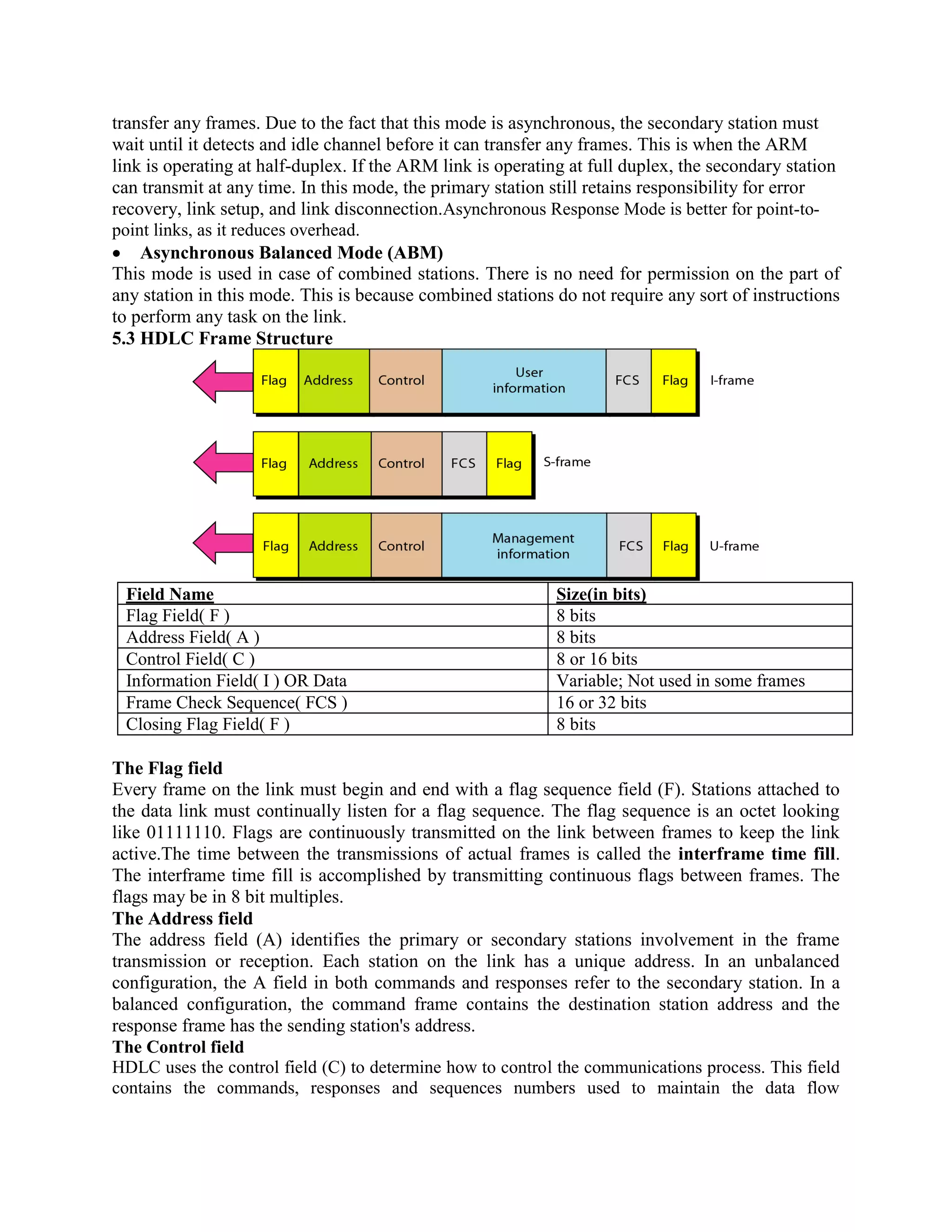
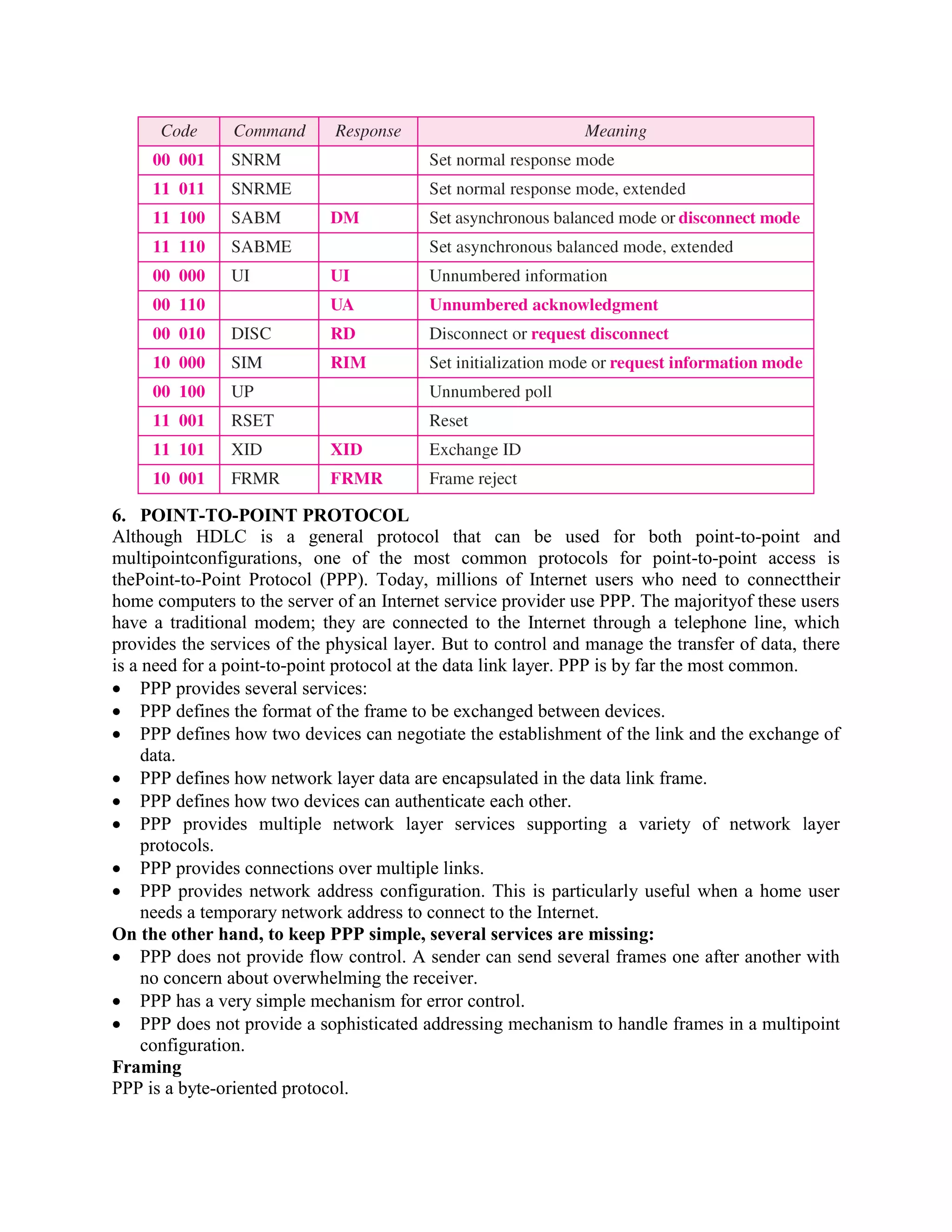
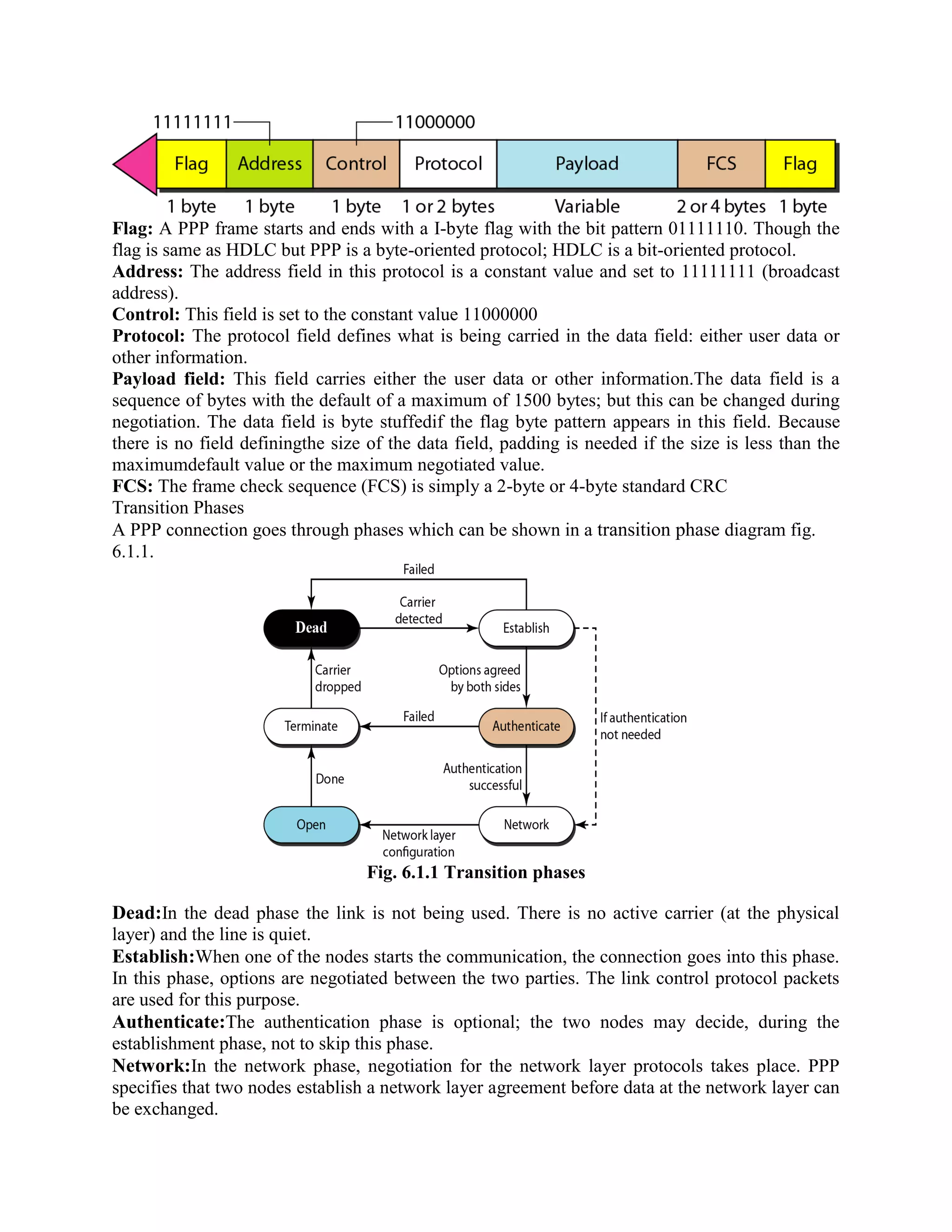
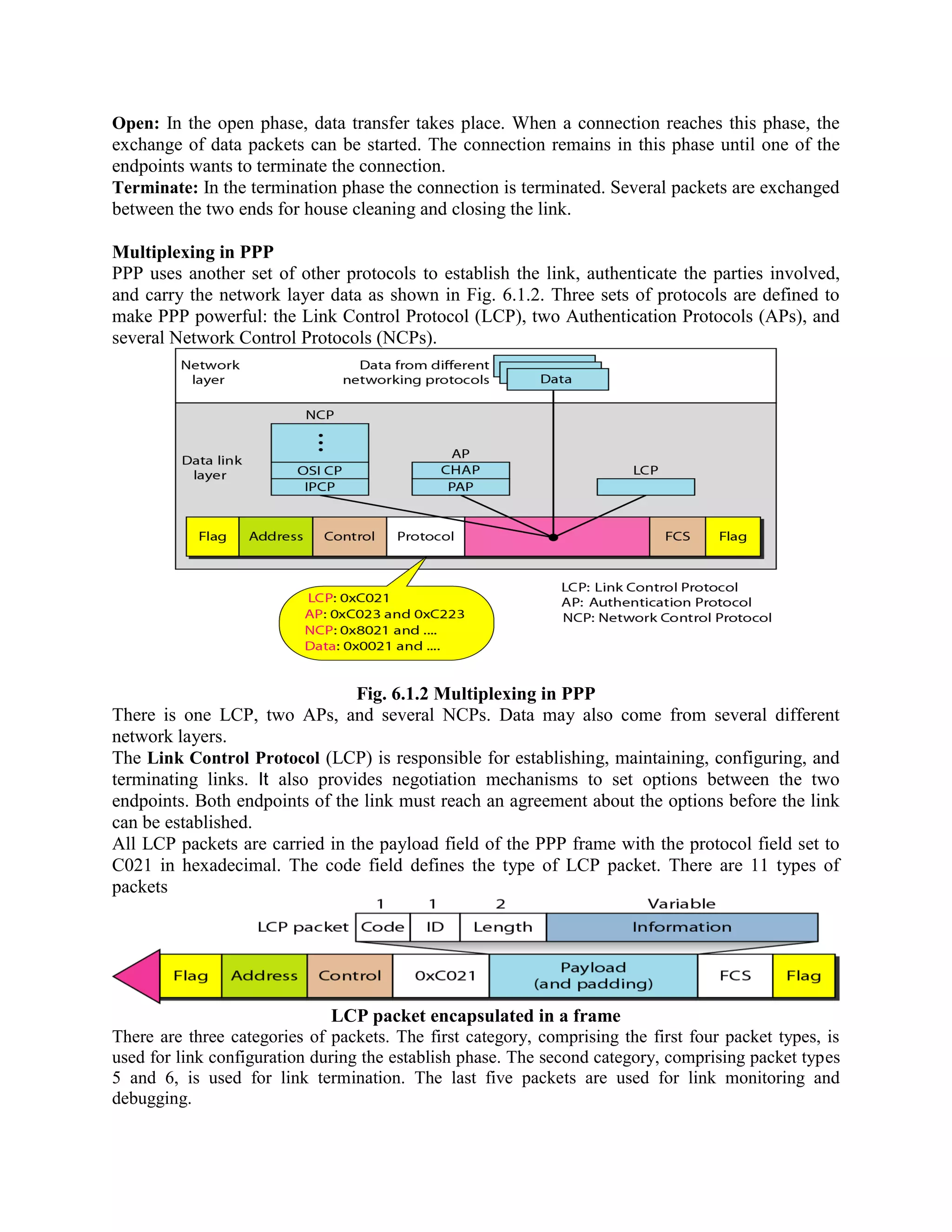
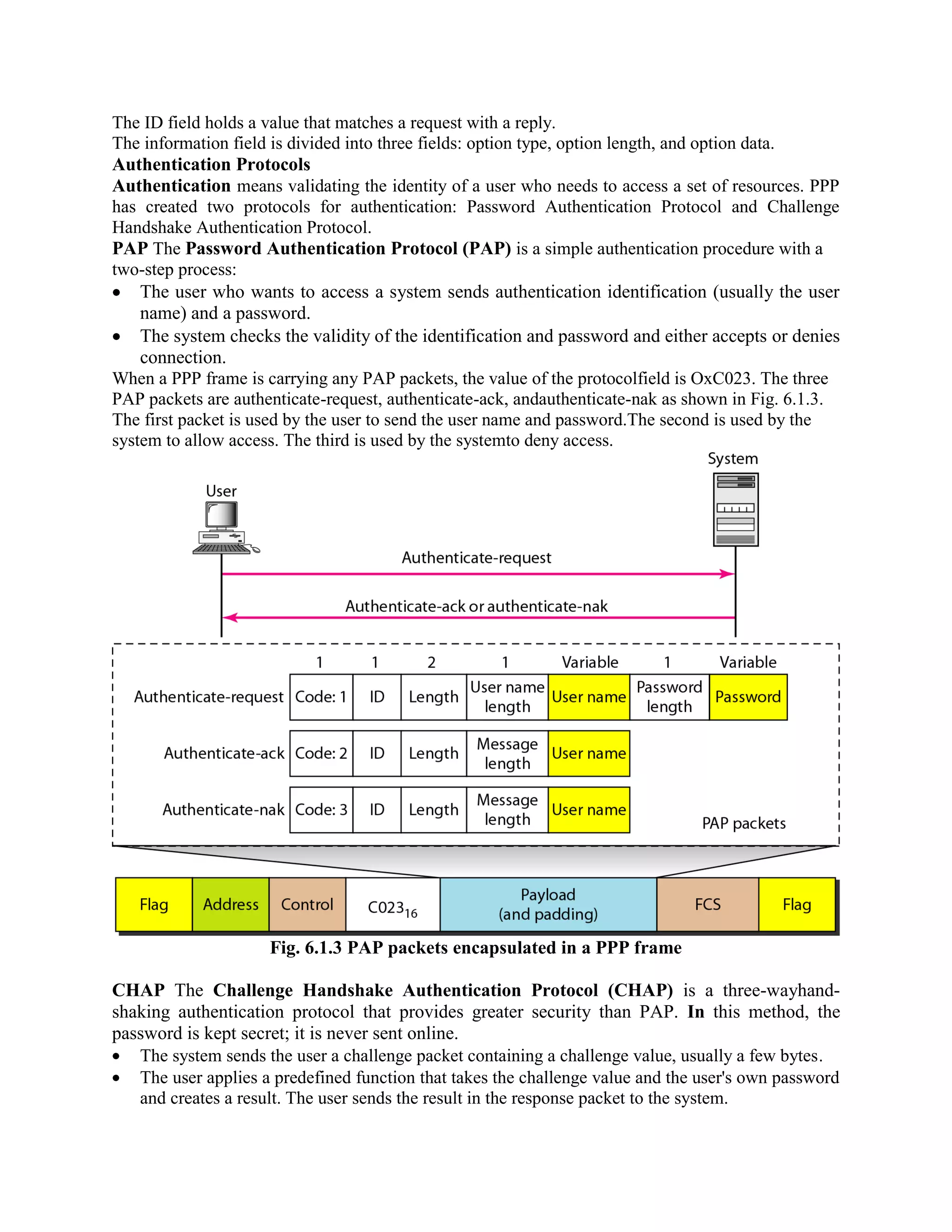
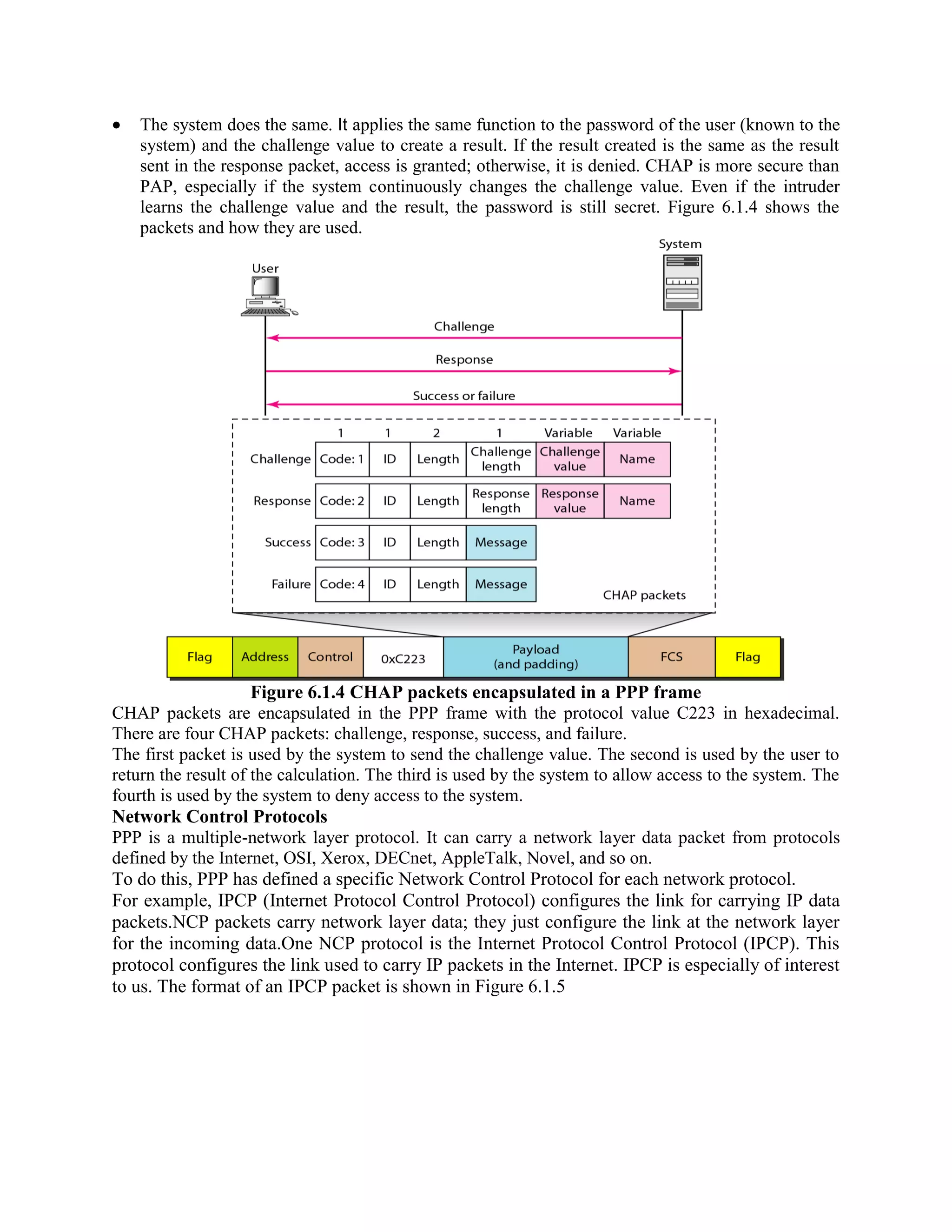
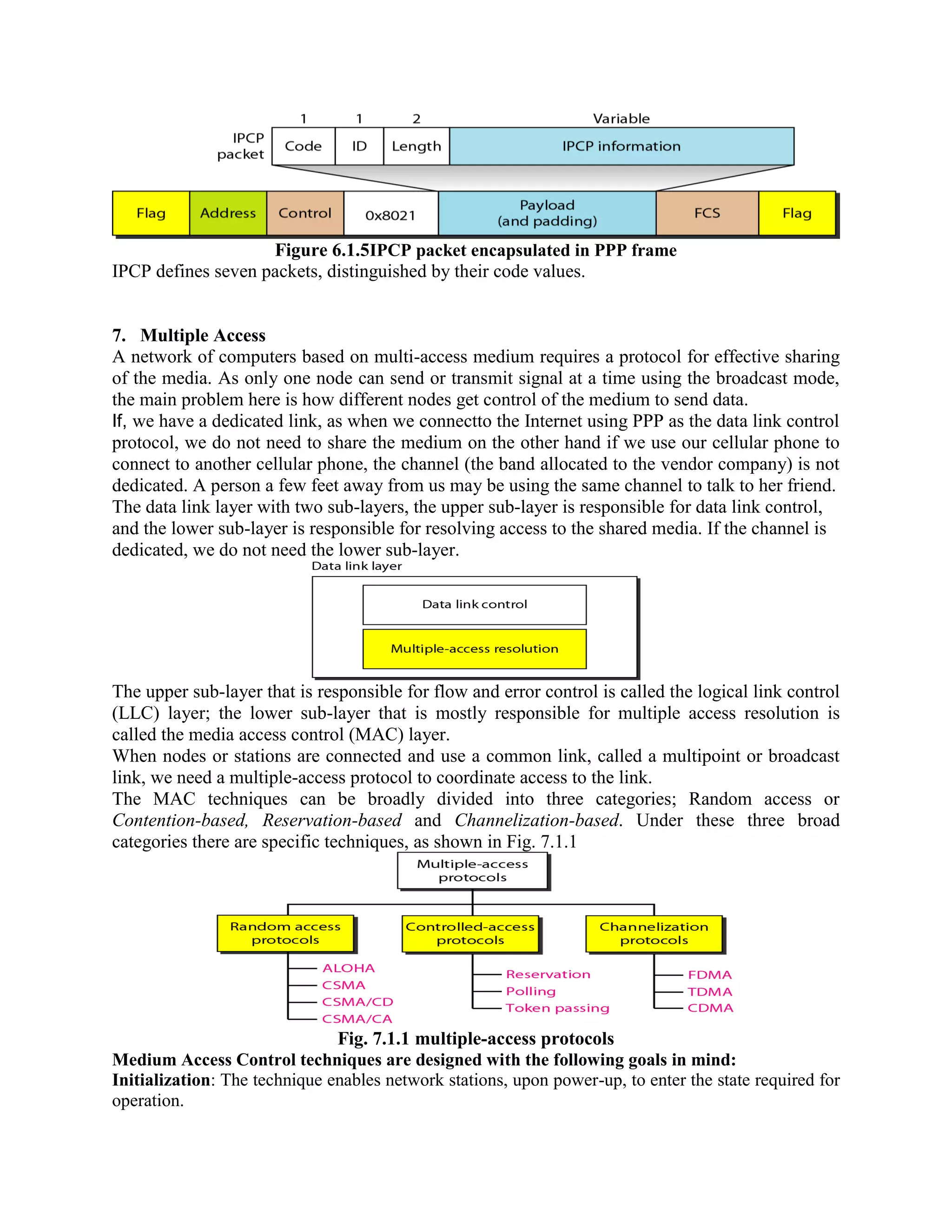
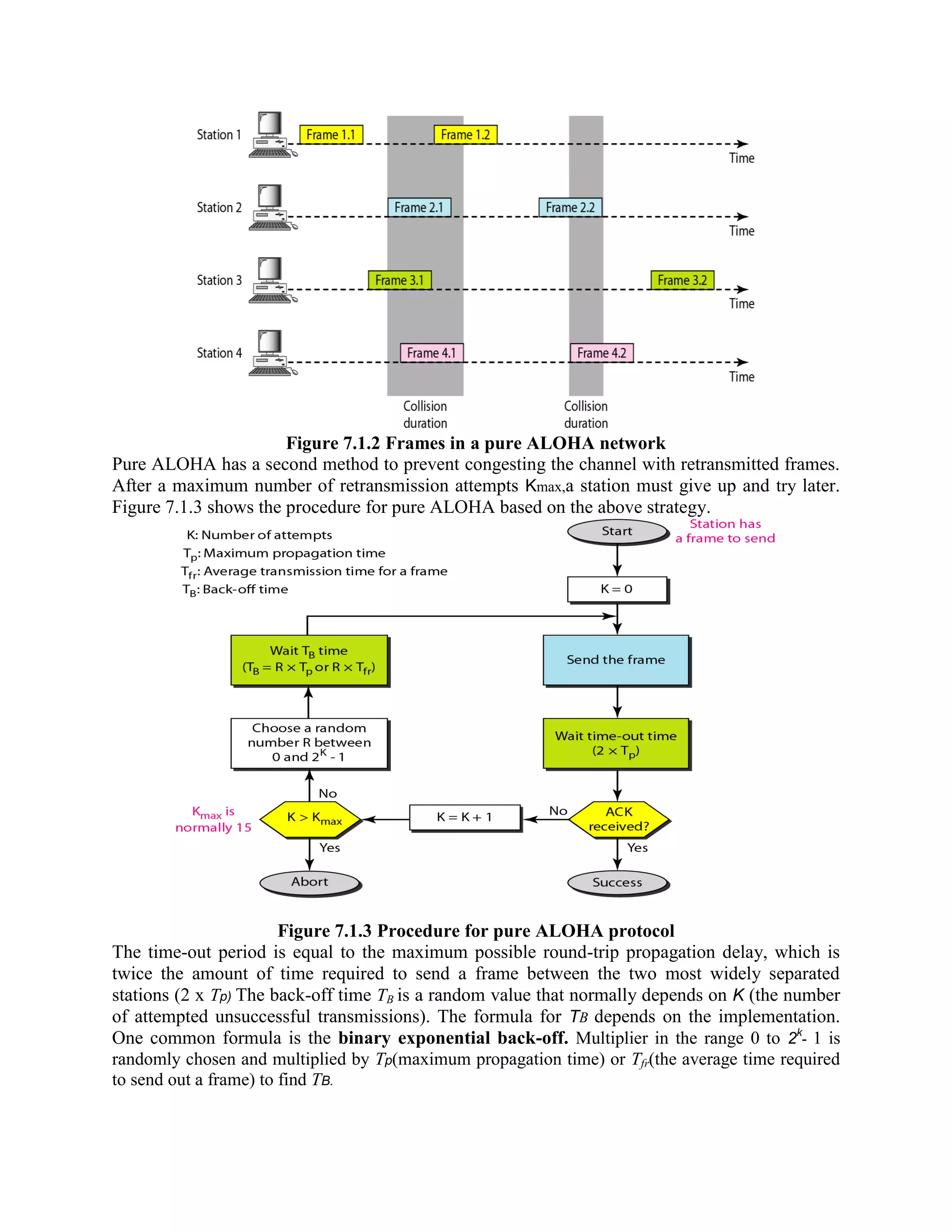
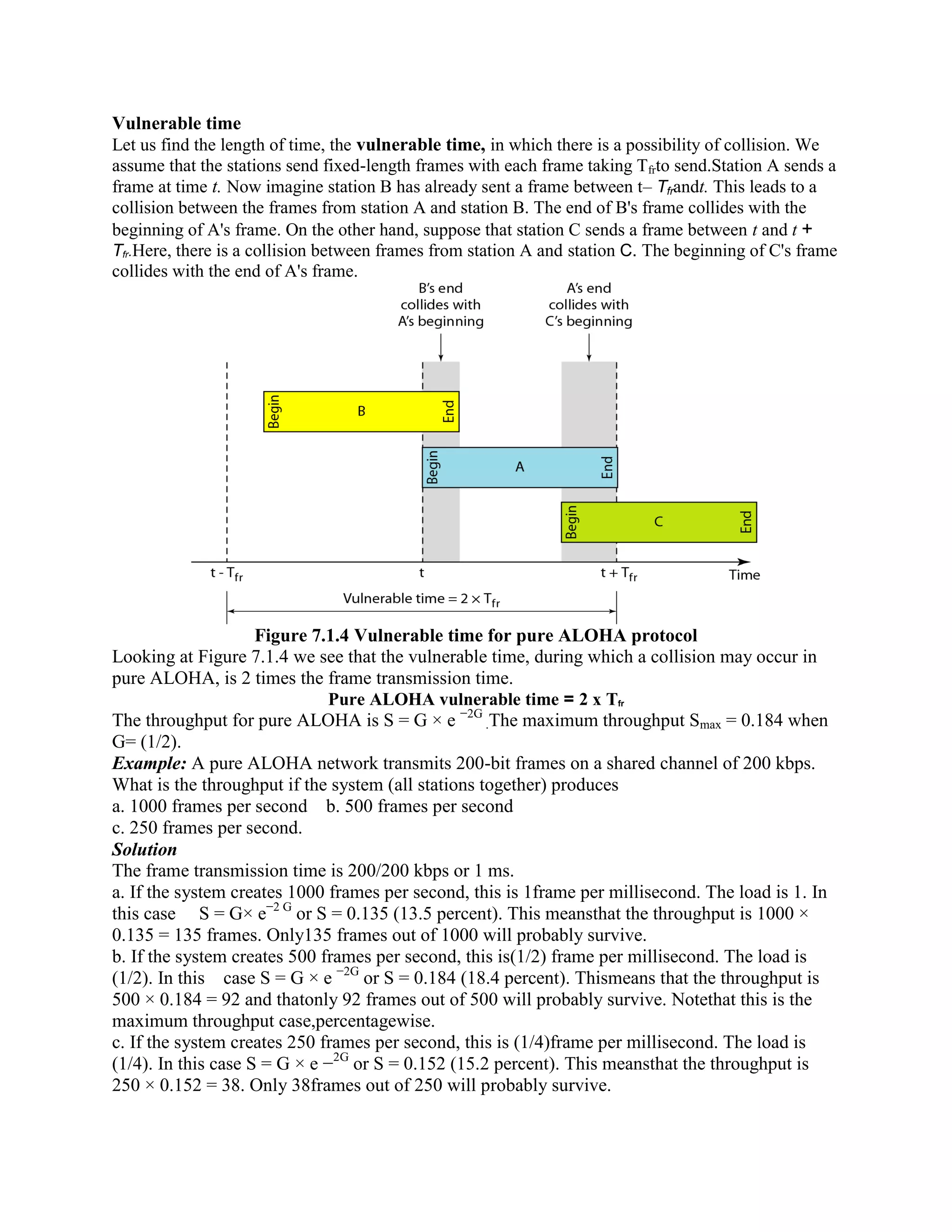
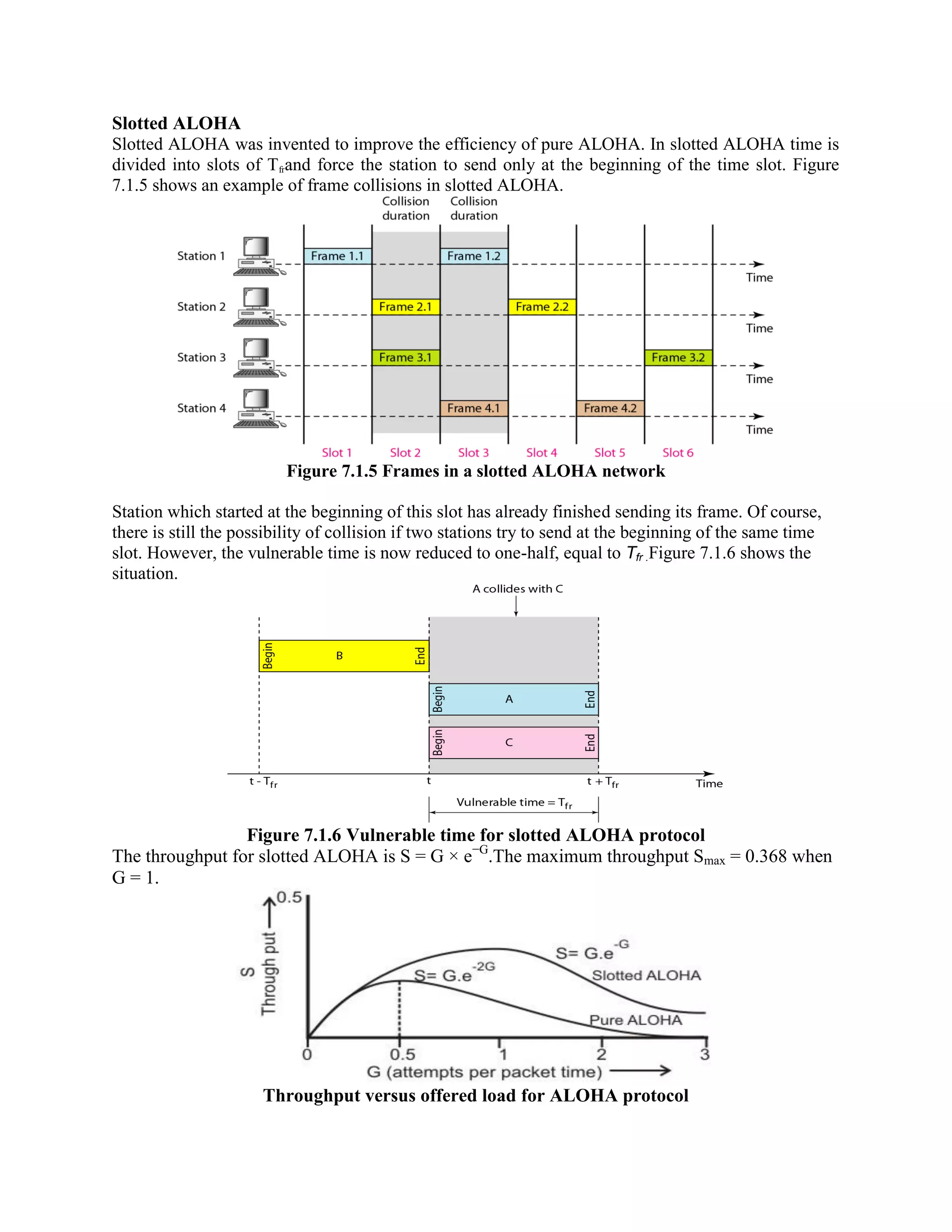
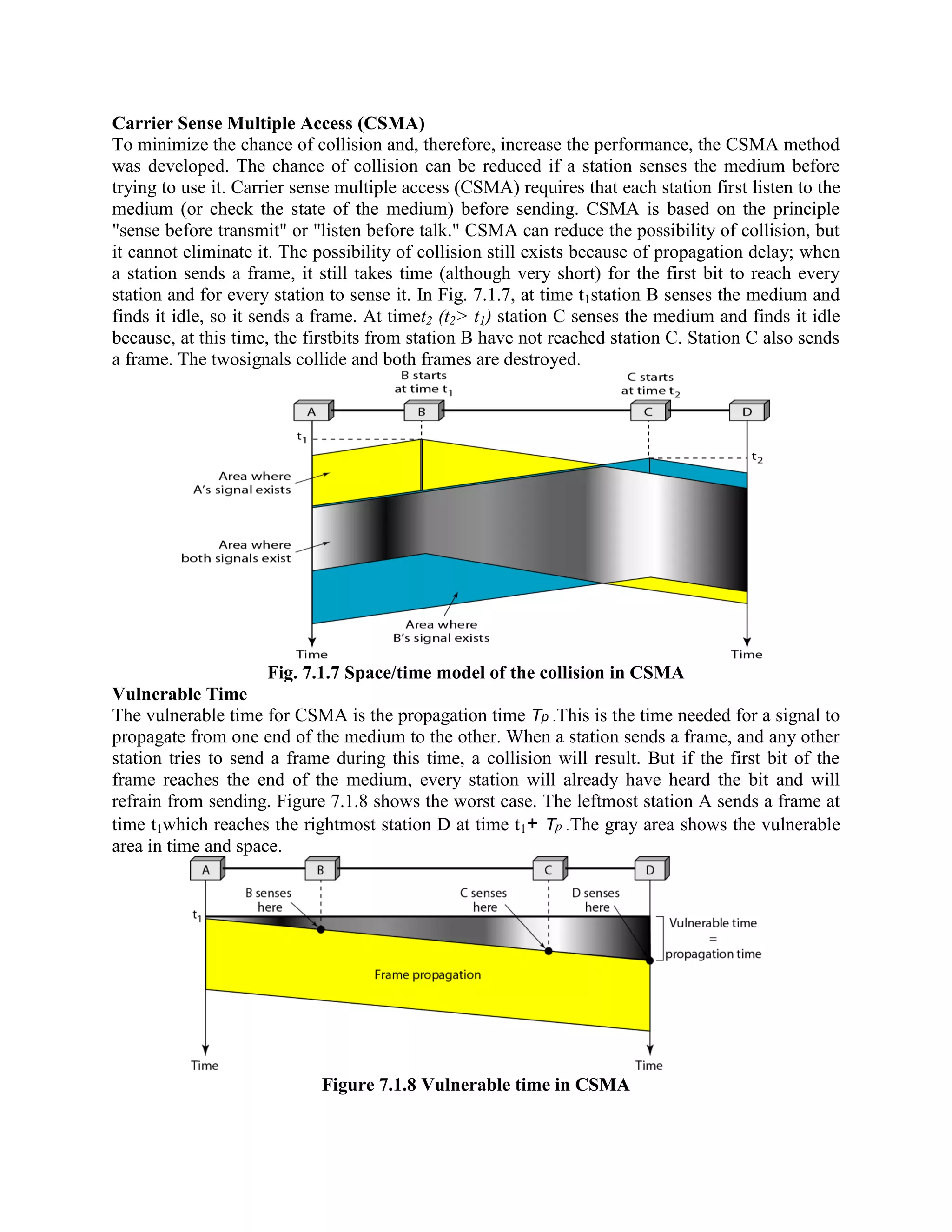
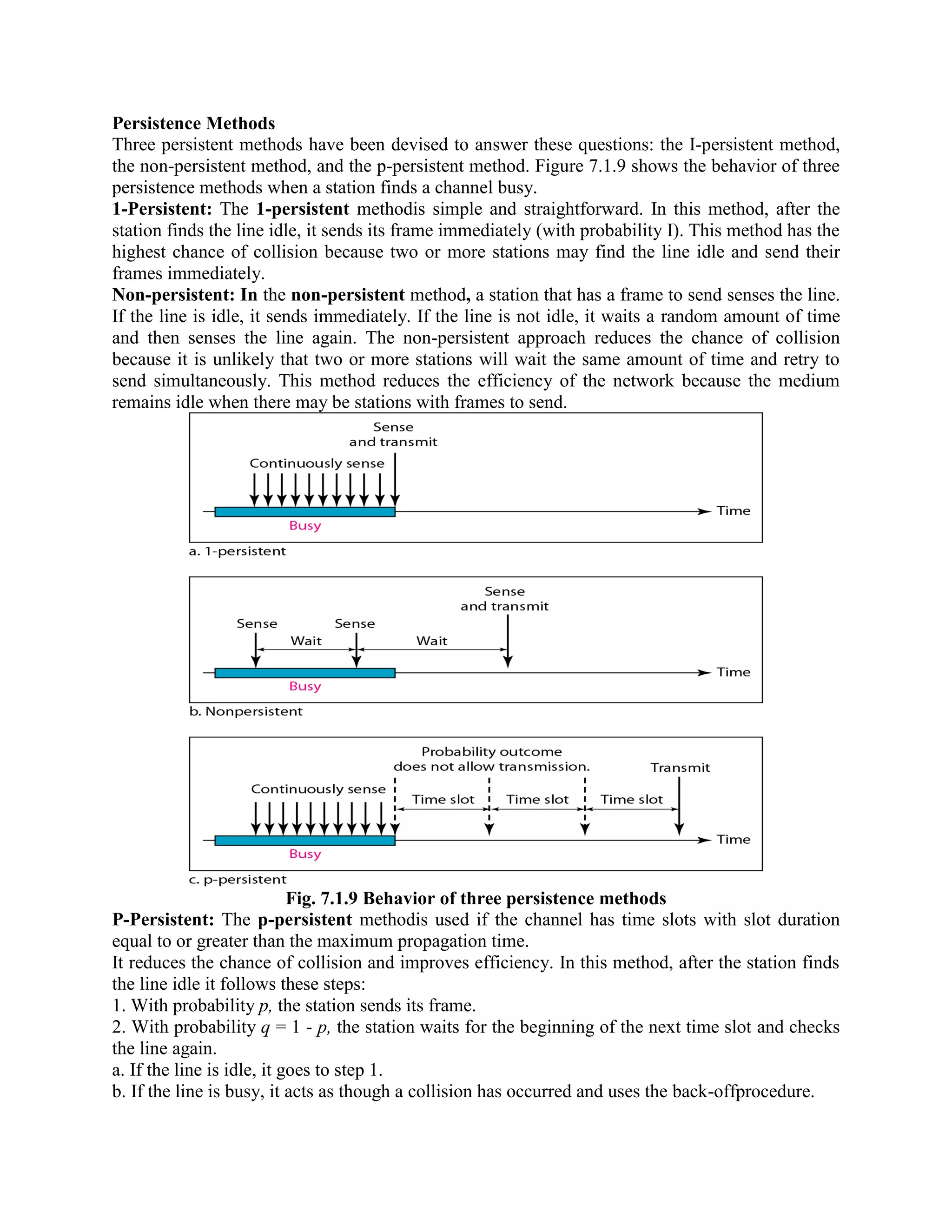
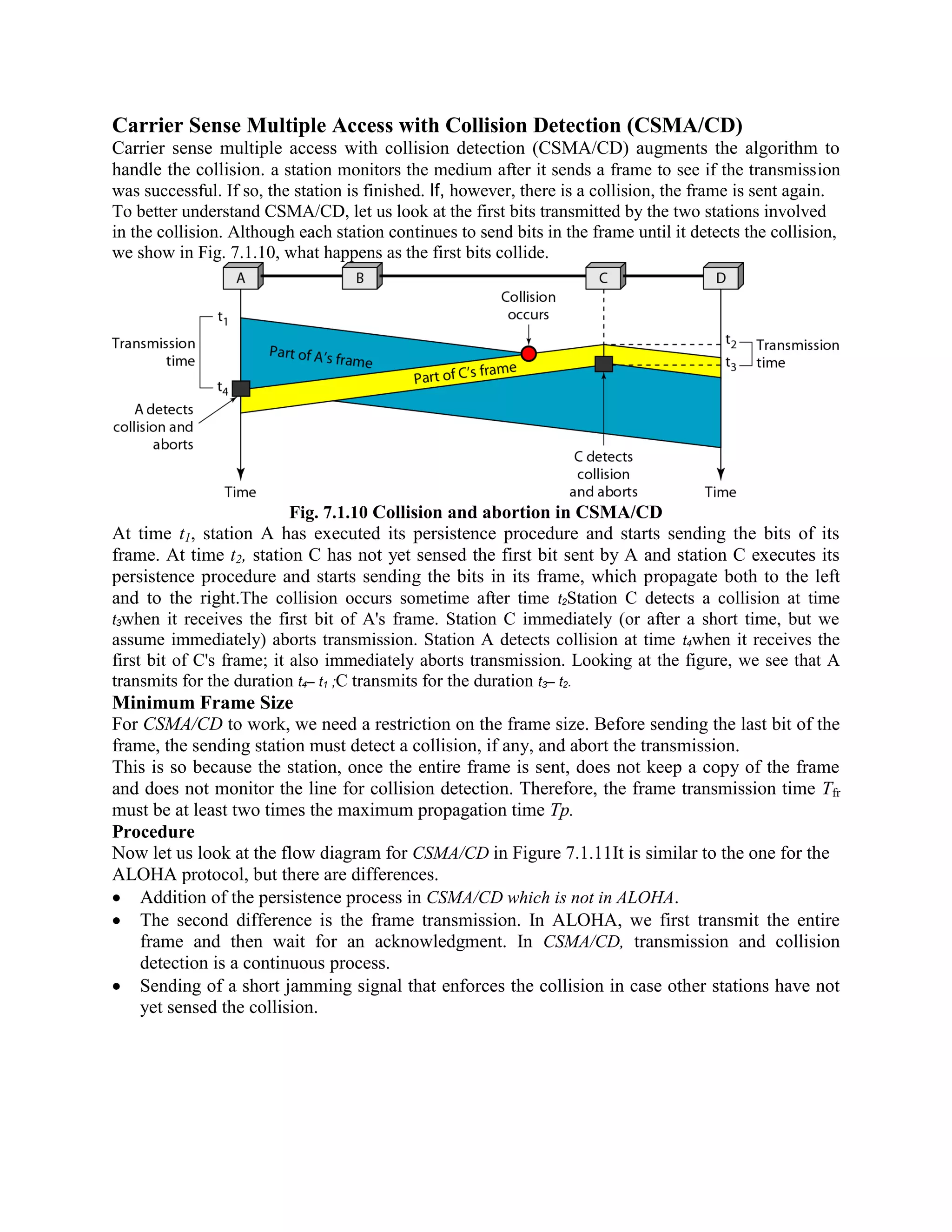
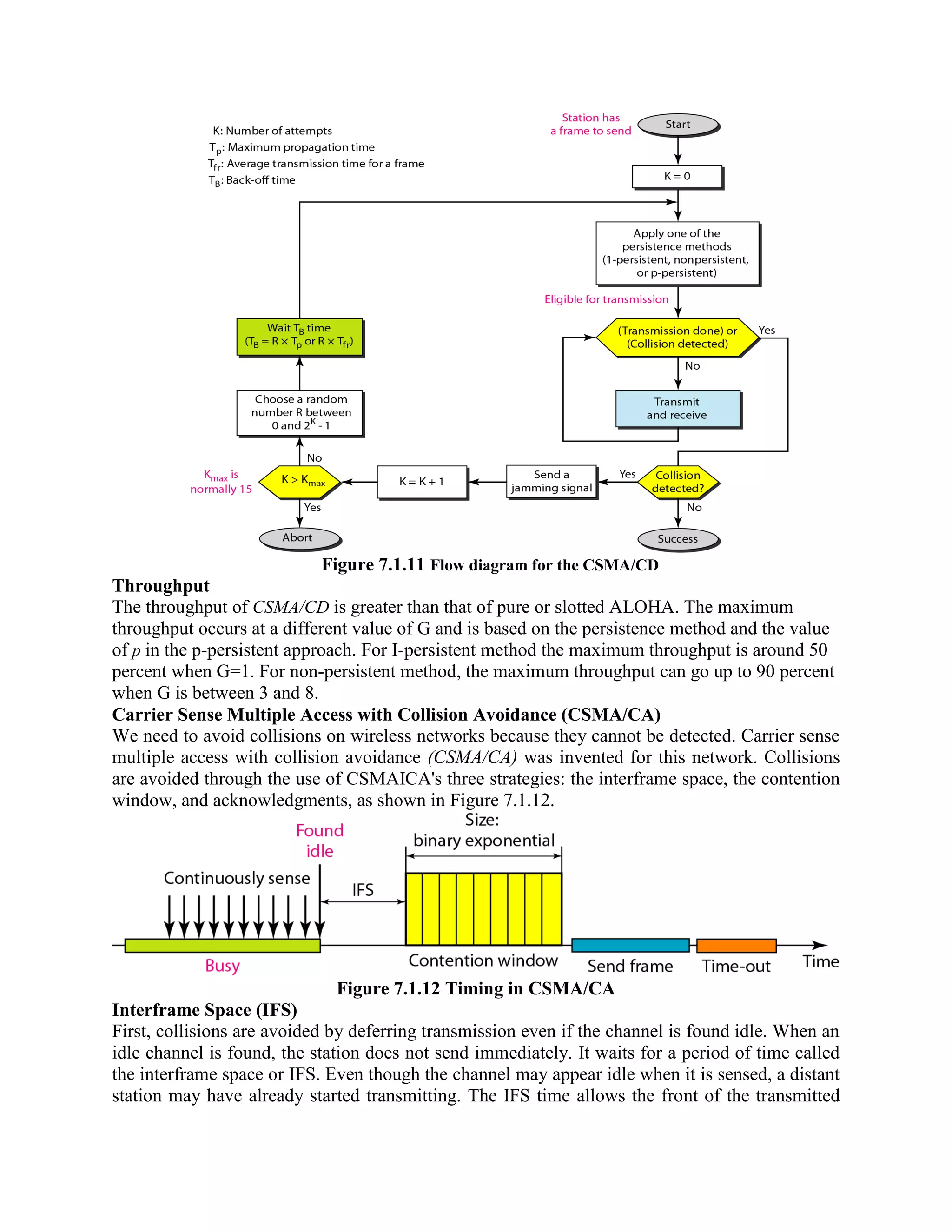
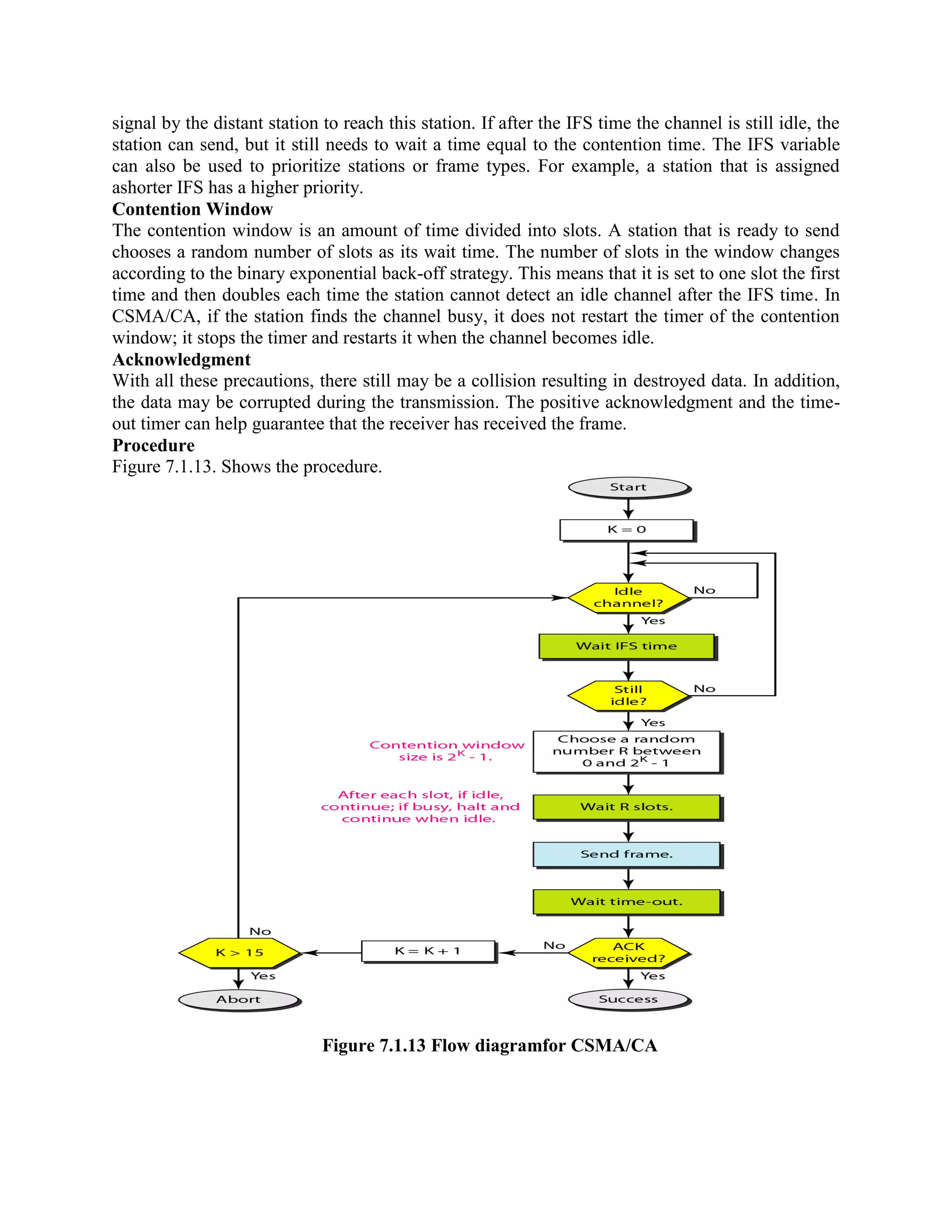
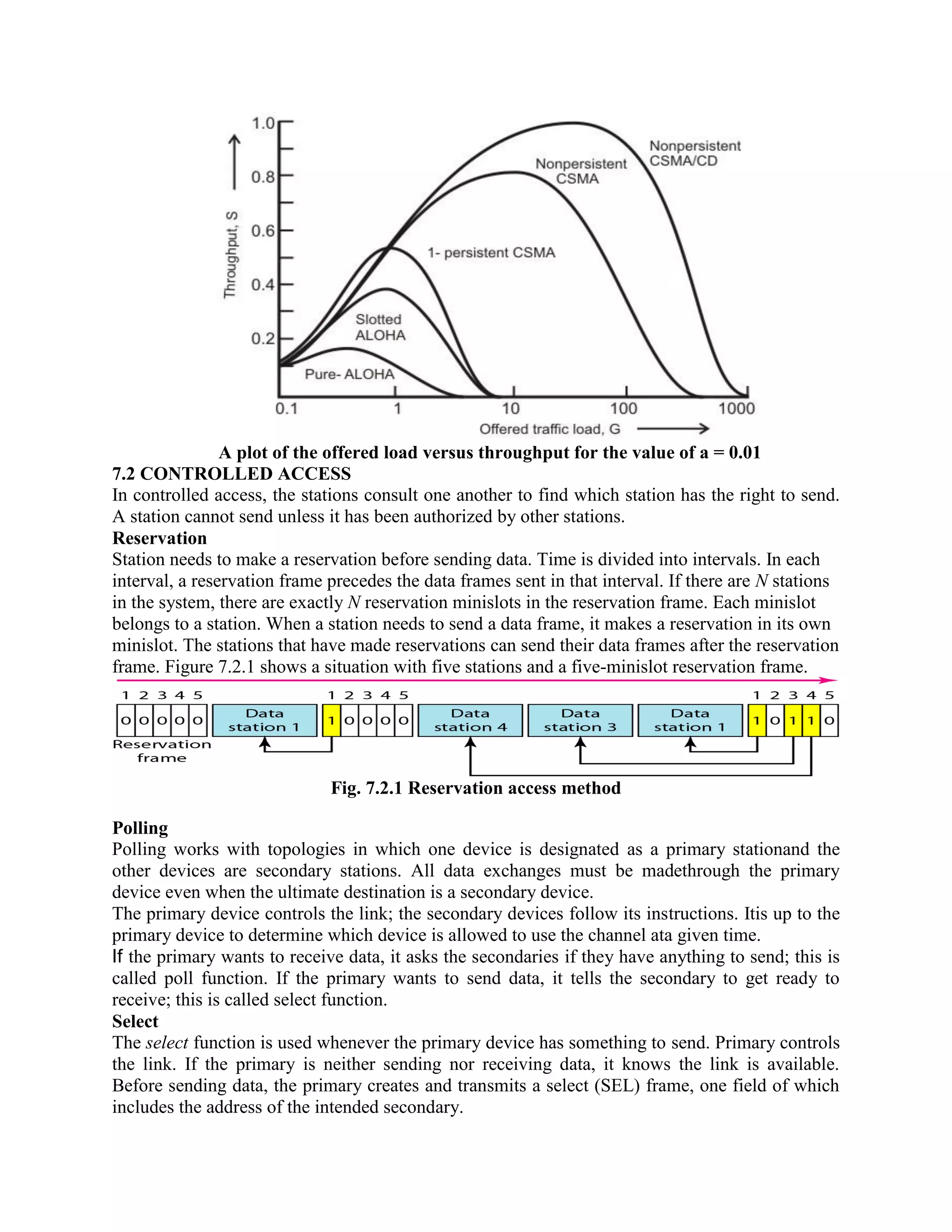
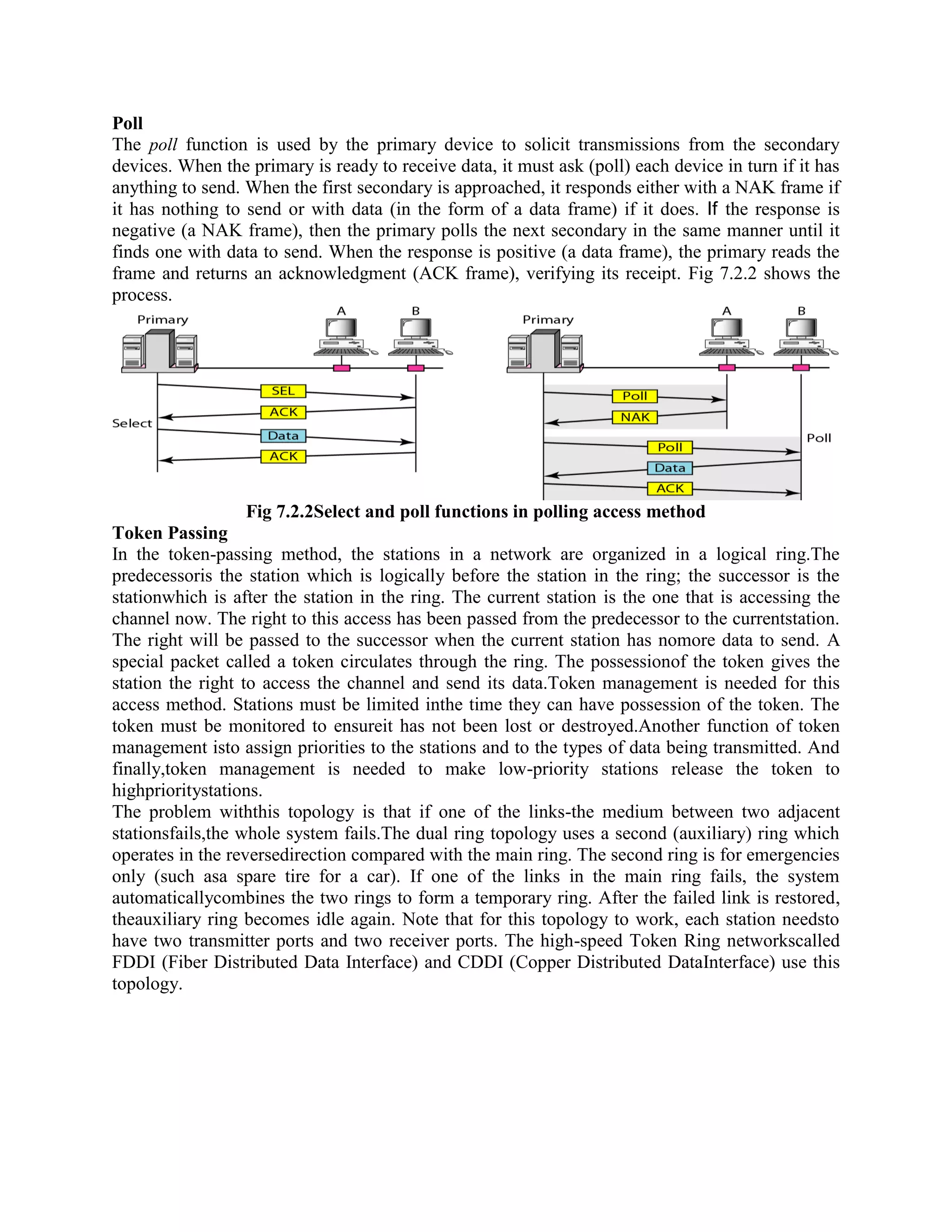
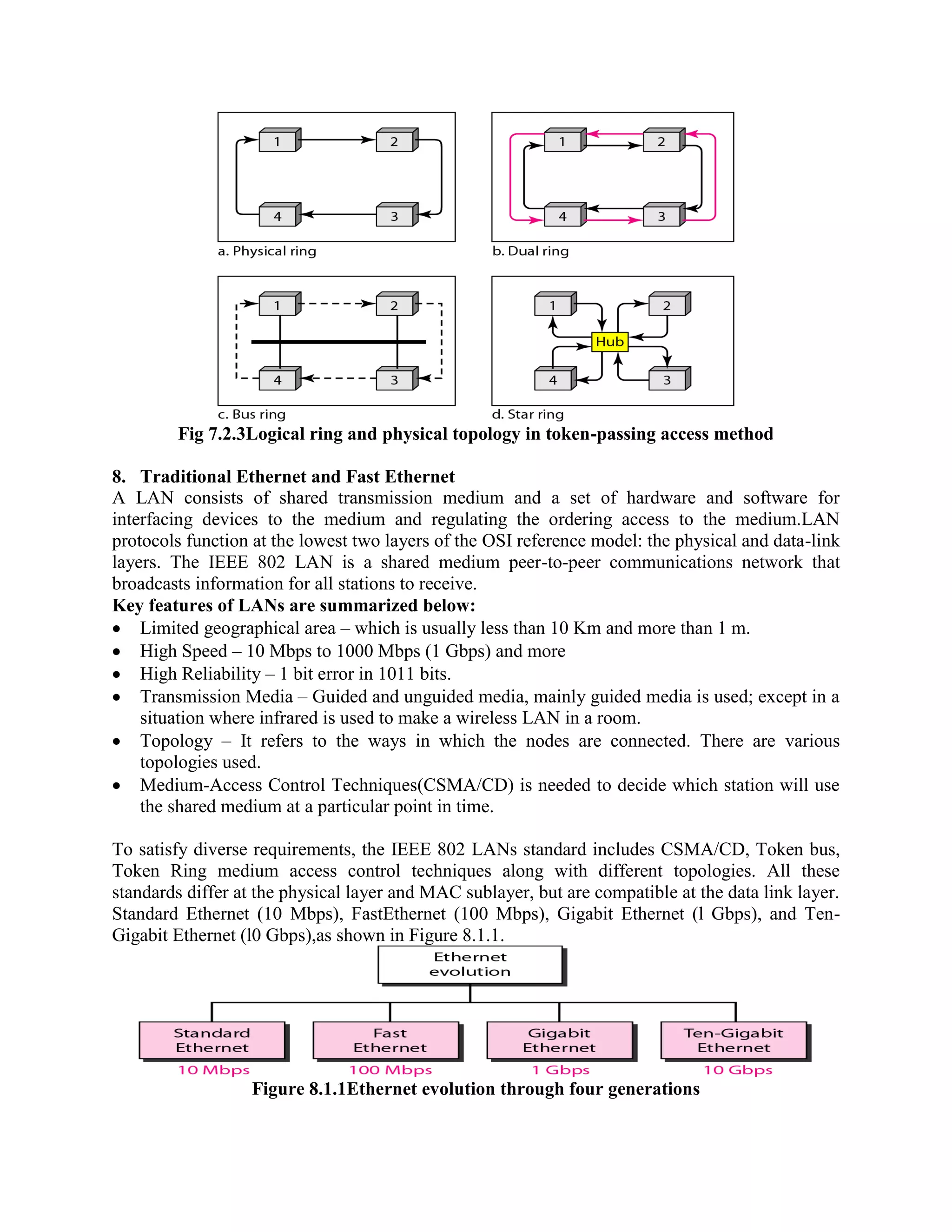
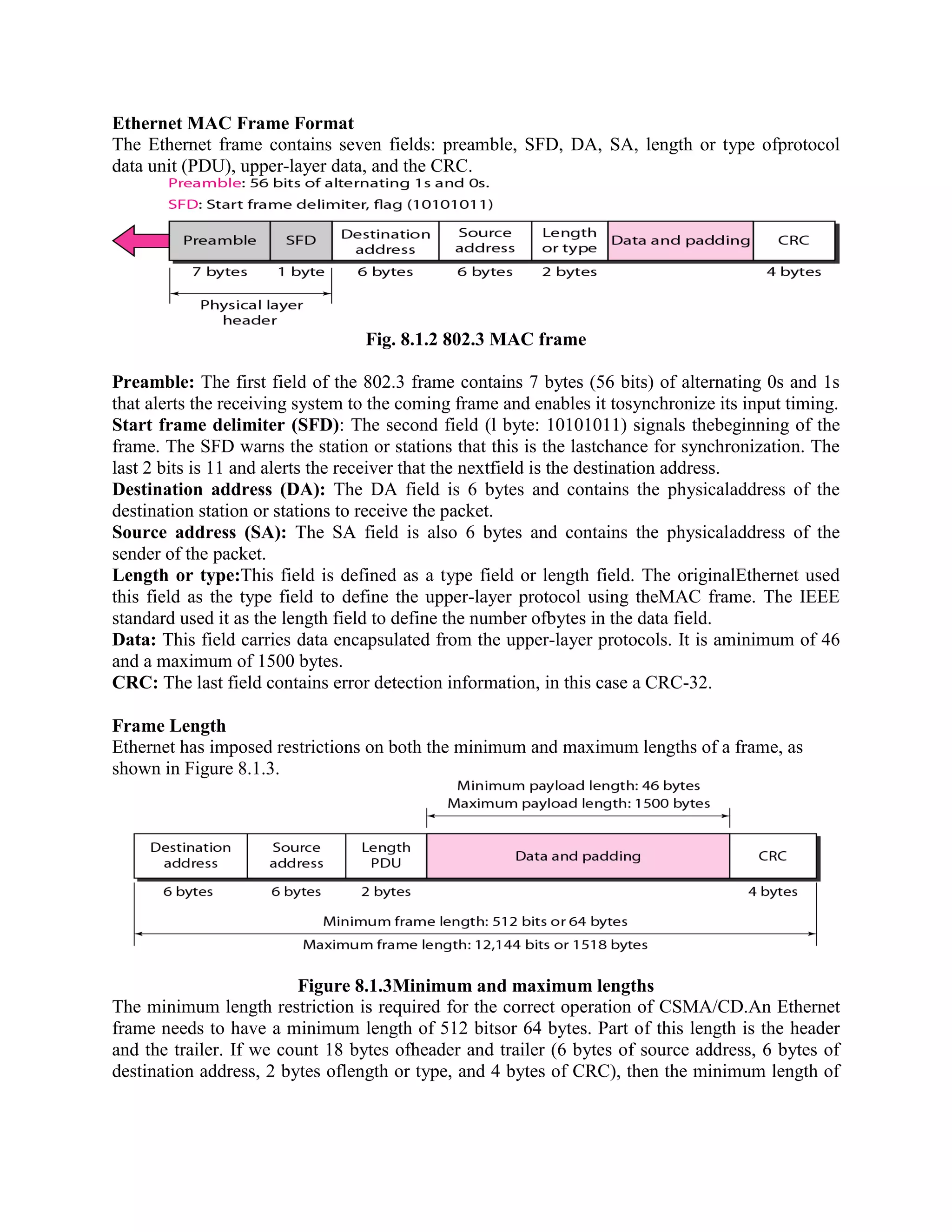
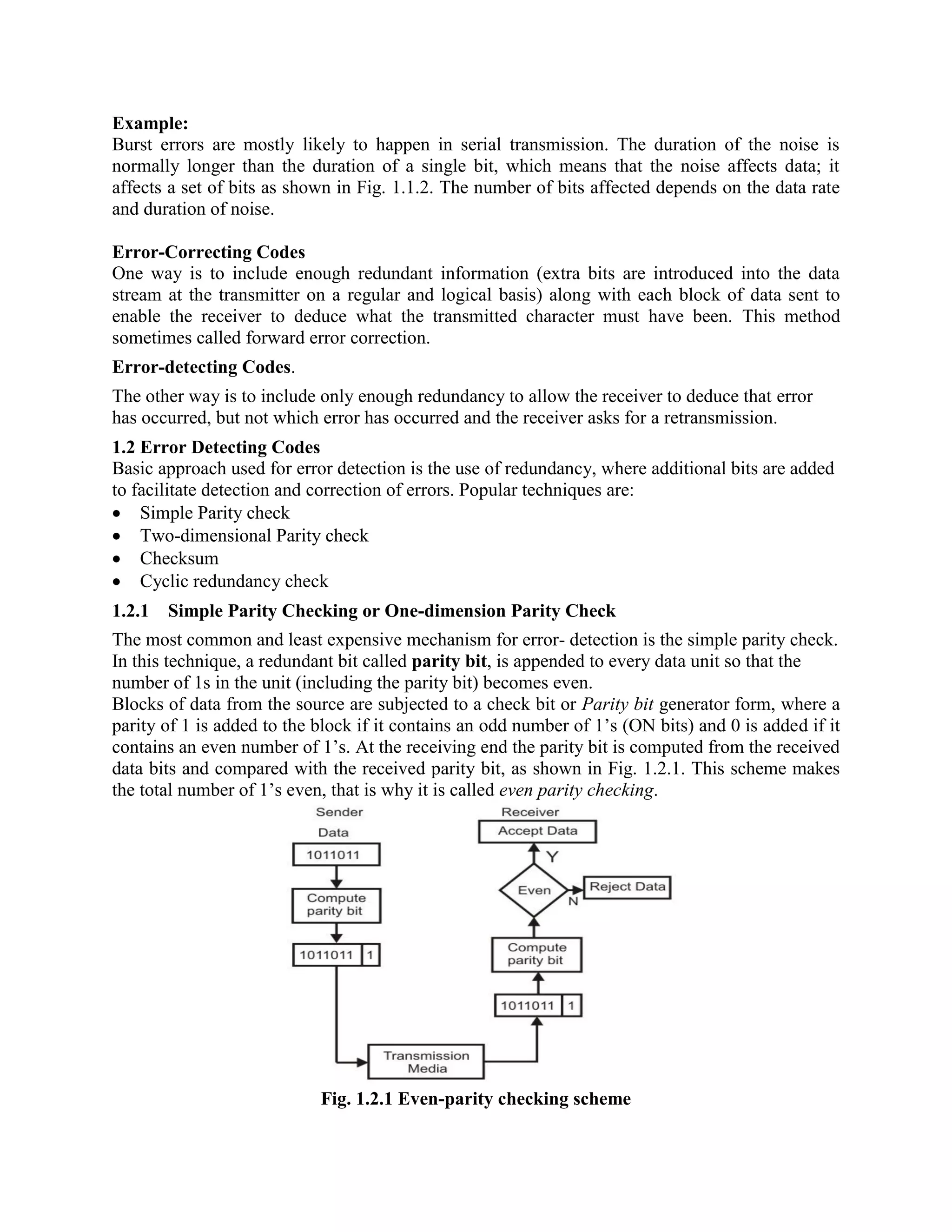
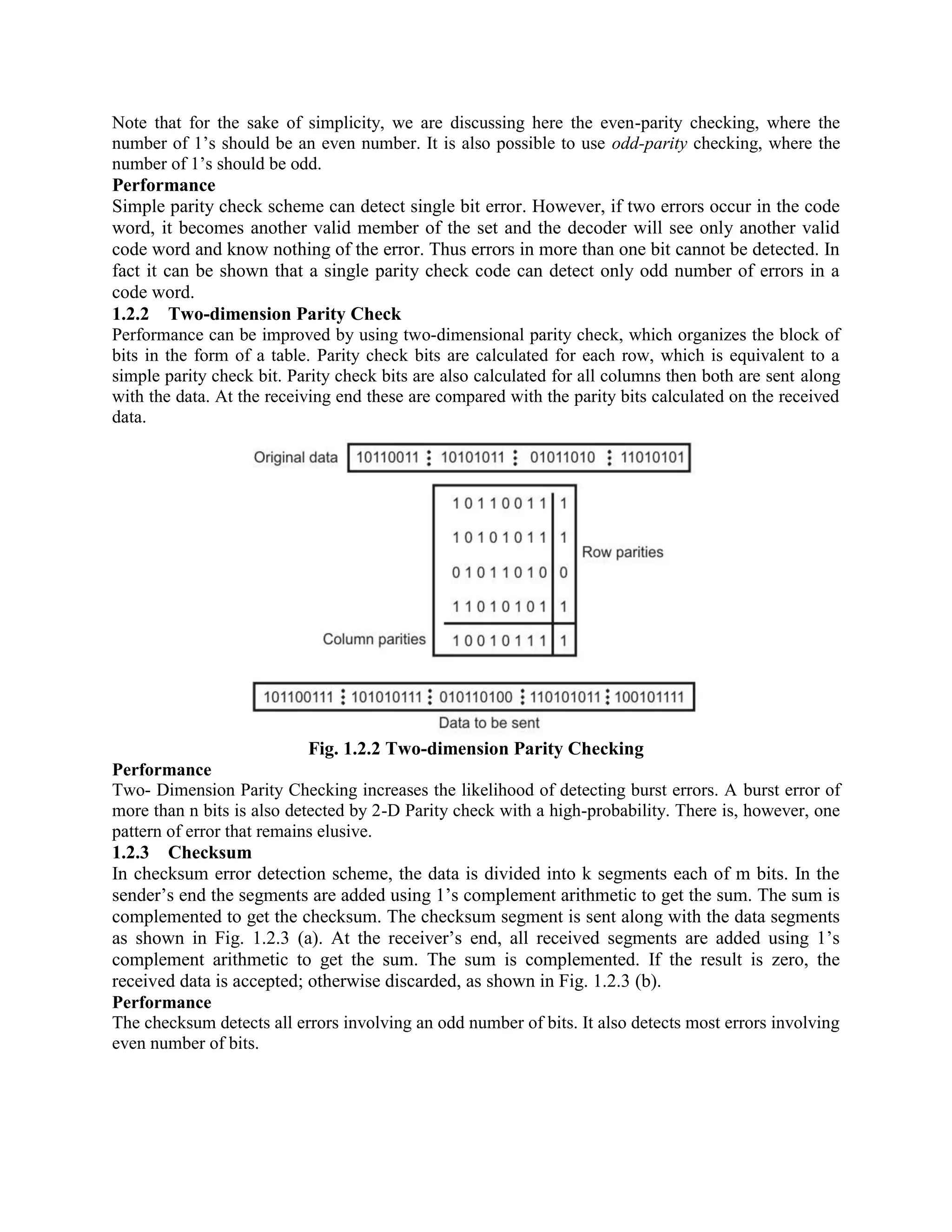
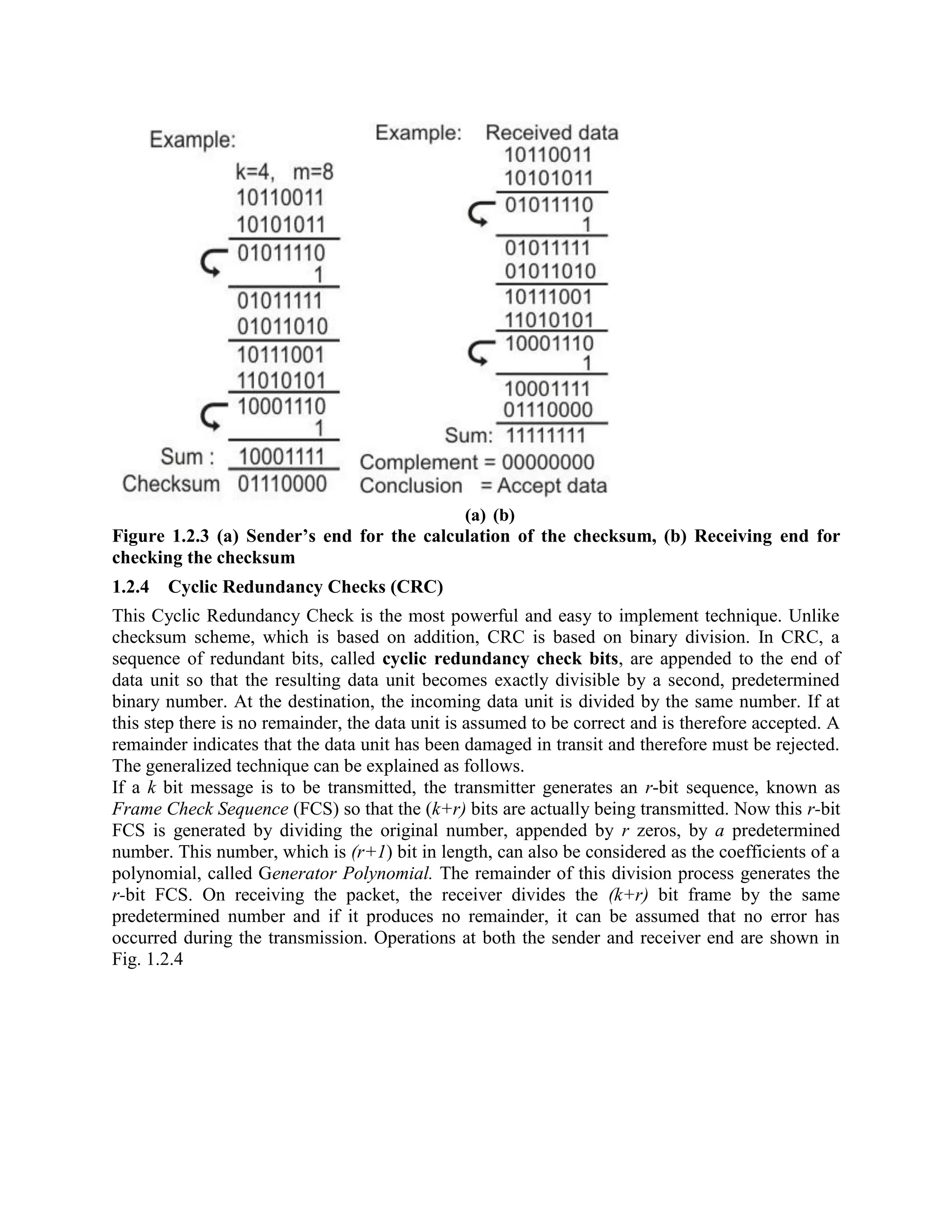
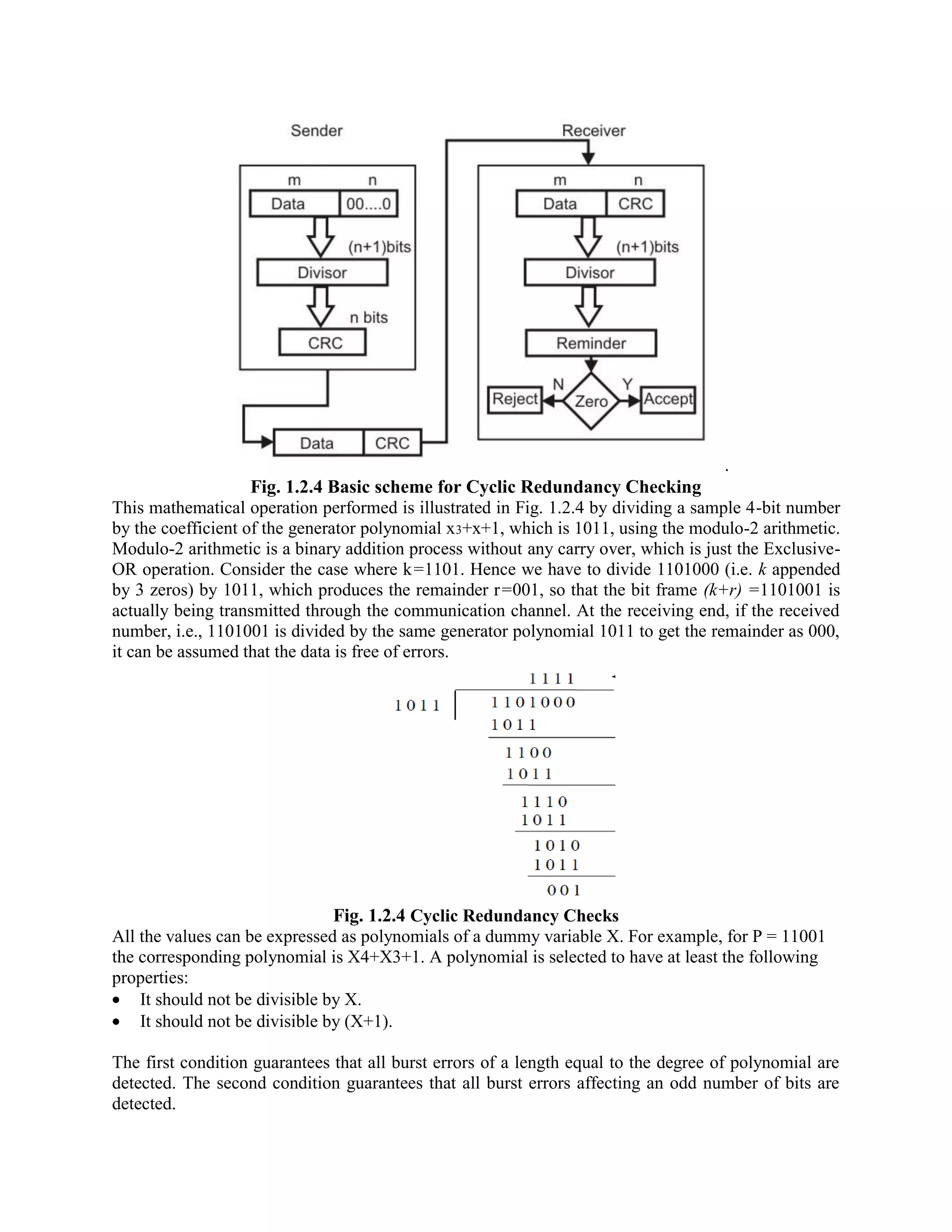
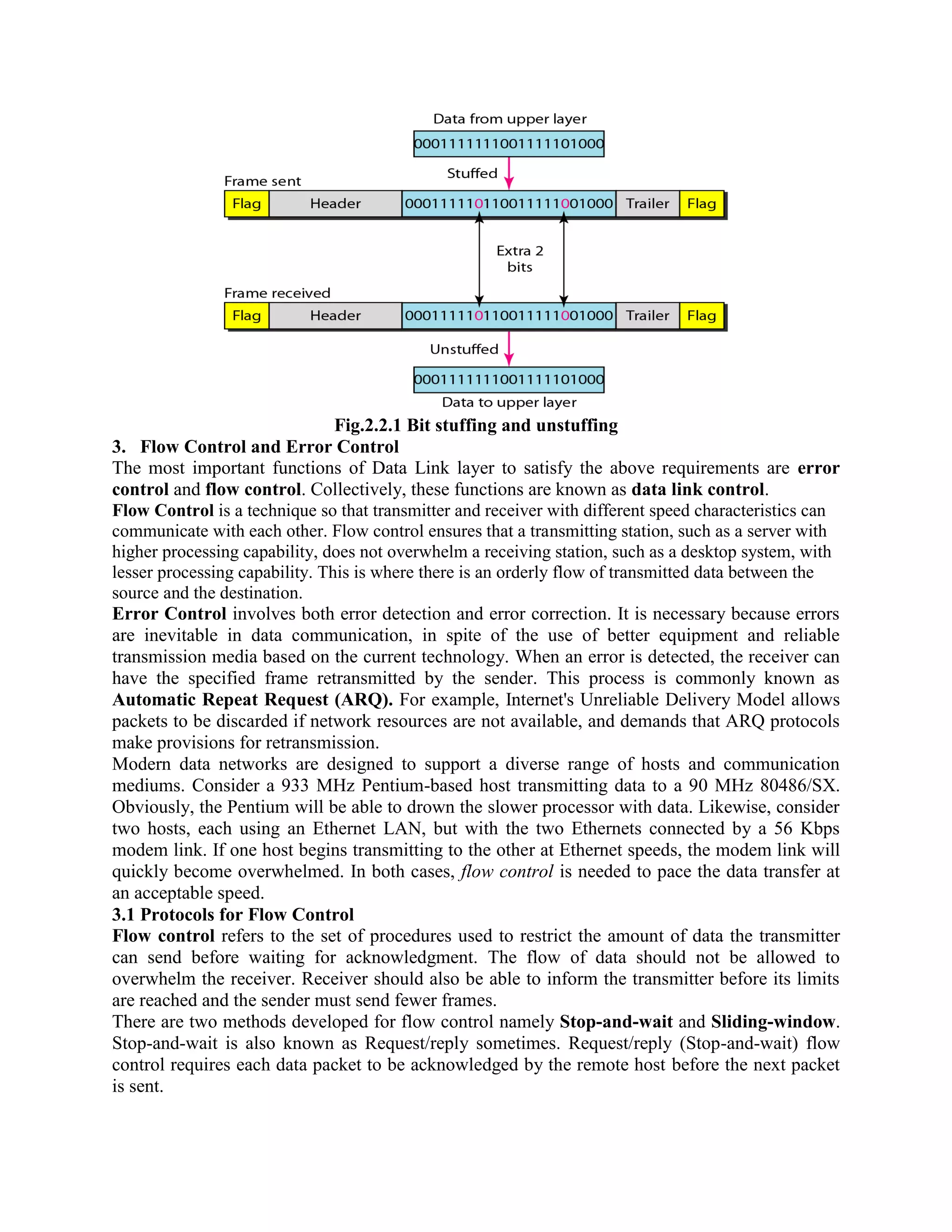
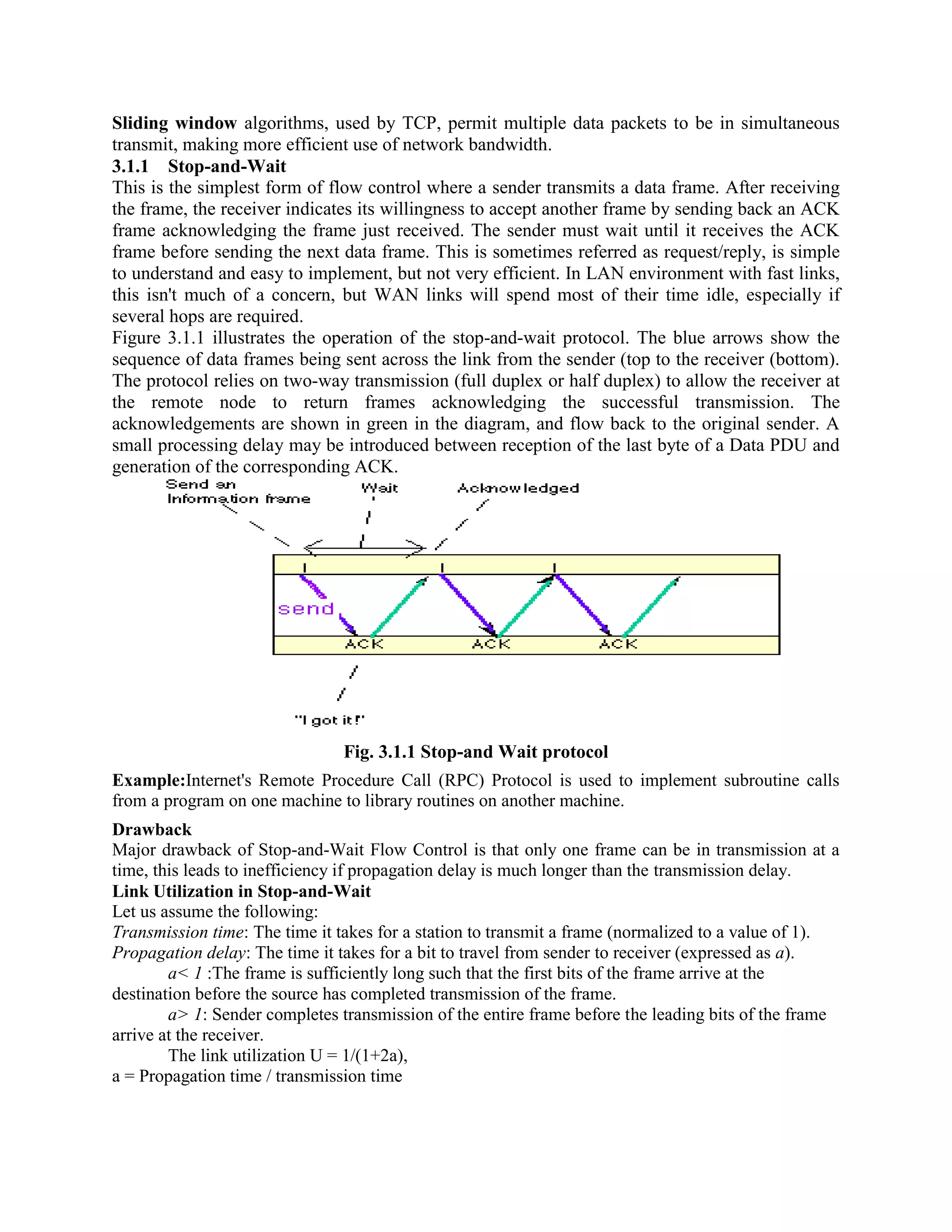
Error coding uses mathematical formulas to encode data bits into longer code words for transmission. This allows errors caused by environmental interference to be detected and sometimes corrected at the destination. There are two main types of error coding: error-detecting codes and error-correcting codes. Error-detecting codes add enough redundancy to allow errors to be detected but not corrected, while error-correcting codes add more redundancy to allow errors to be corrected. Common error-detecting coding techniques include parity checks, checksums, and cyclic redundancy checks (CRCs). These techniques use additional redundant bits appended to the data to facilitate error detection. CRC is particularly powerful as it can detect all single-bit errors and many burst errors.




![number of the next frame expected. This also explicitly announces that it is prepared to receive
the next N frames, beginning with the number specified. This scheme can be used to
acknowledge multiple frames. It could receive frames 2, 3, 4 but withhold ACK until frame 4 has
arrived. By returning an ACK with sequence number 5, it acknowledges frames 2, 3, 4 at one
time. The receiver needs a buffer of size 1.
Fig. 3.1.3 Receiver sliding window
Hence, Sliding Window Flow Control
Allows transmission of multiple frames
Assigns each frame a k-bit sequence number
Range of sequence number is [0…2k
-1], i.e., frames are counted modulo 2k
.
The link utilization in case of Sliding Window Protocol
U = 1, for N > 2a + 1
N/(1+2a), for N < 2a + 1
Where N = the window size, and a = Propagation time / transmission time
Data Link layer can combine framing, flow control and error control to achieve the delivery of
data from one node to another node. The most popular retransmission scheme is known as
Automatic-Repeat-Request (ARQ). Such schemes, where receiver asks transmitter to re-transmit
if it detects an error, are known as reverse error correction techniques.
4. Error Control Techniques
When an error is detected in a message, the receiver sends a request to the transmitter to retransmit
the ill-fated message or packet. The most popular retransmission scheme is known as Automatic-
Repeat-Request (ARQ). Such schemes, where receiver asks transmitter to re-transmit if it detects an
error, are known as reverse error correction techniques. There exist three popular ARQ techniques, as
shown in Fig. 4.1.1.
Fig. 4.1.1 Error control techniques
4.1.1 Stop-and-Wait ARQ
In Stop-and-Wait ARQ, which is simplest among all protocols, the sender (say station A) transmits a
frame and then waits till it receives positive acknowledgement (ACK) or negative acknowledgement
(NACK) from the receiver (say station B). Station B sends an ACK if the frame is received correctly,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/errordetectionandcorrection-130721215120-phpapp01/75/Error-detection-and-correction-11-2048.jpg)