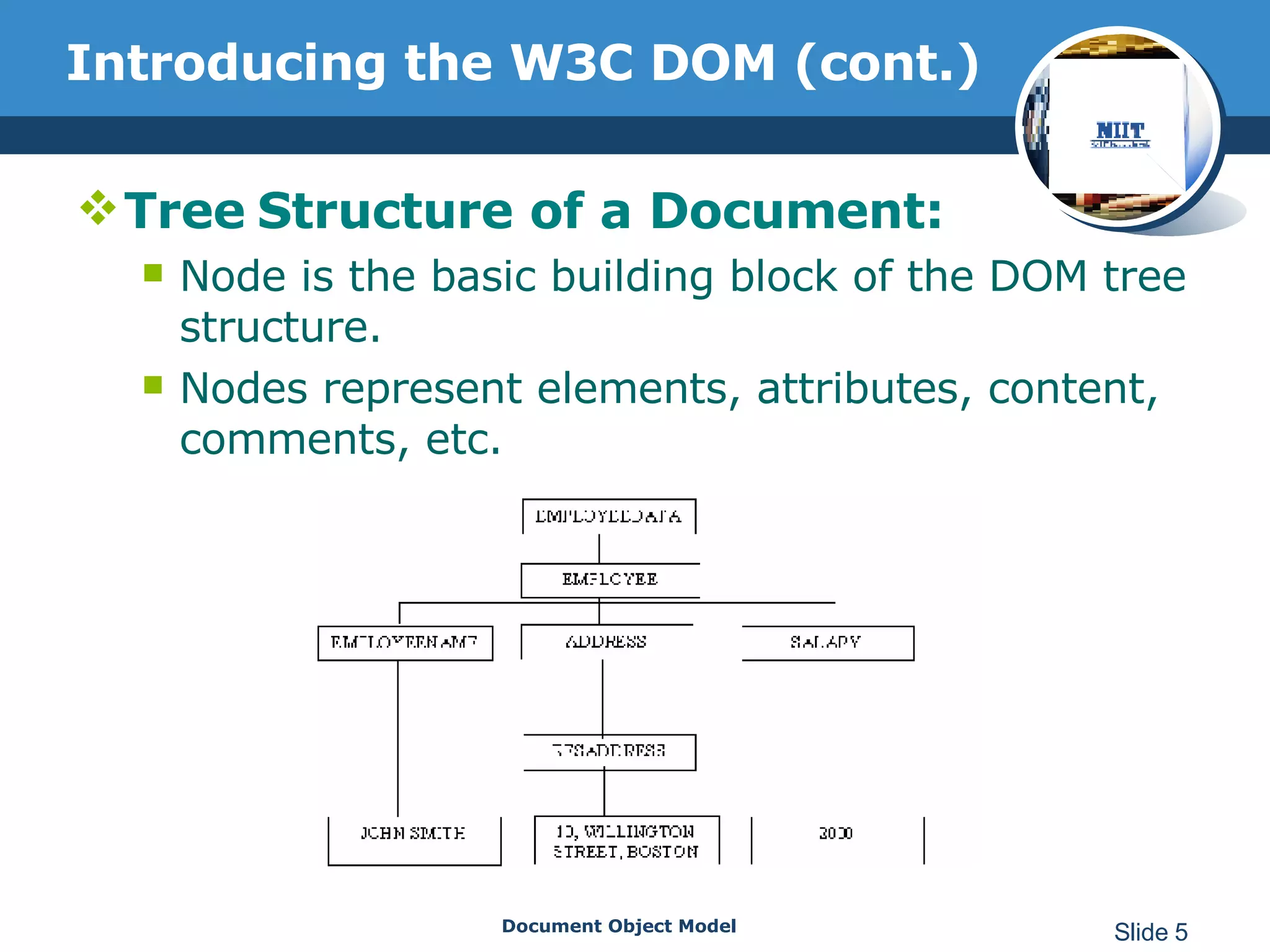
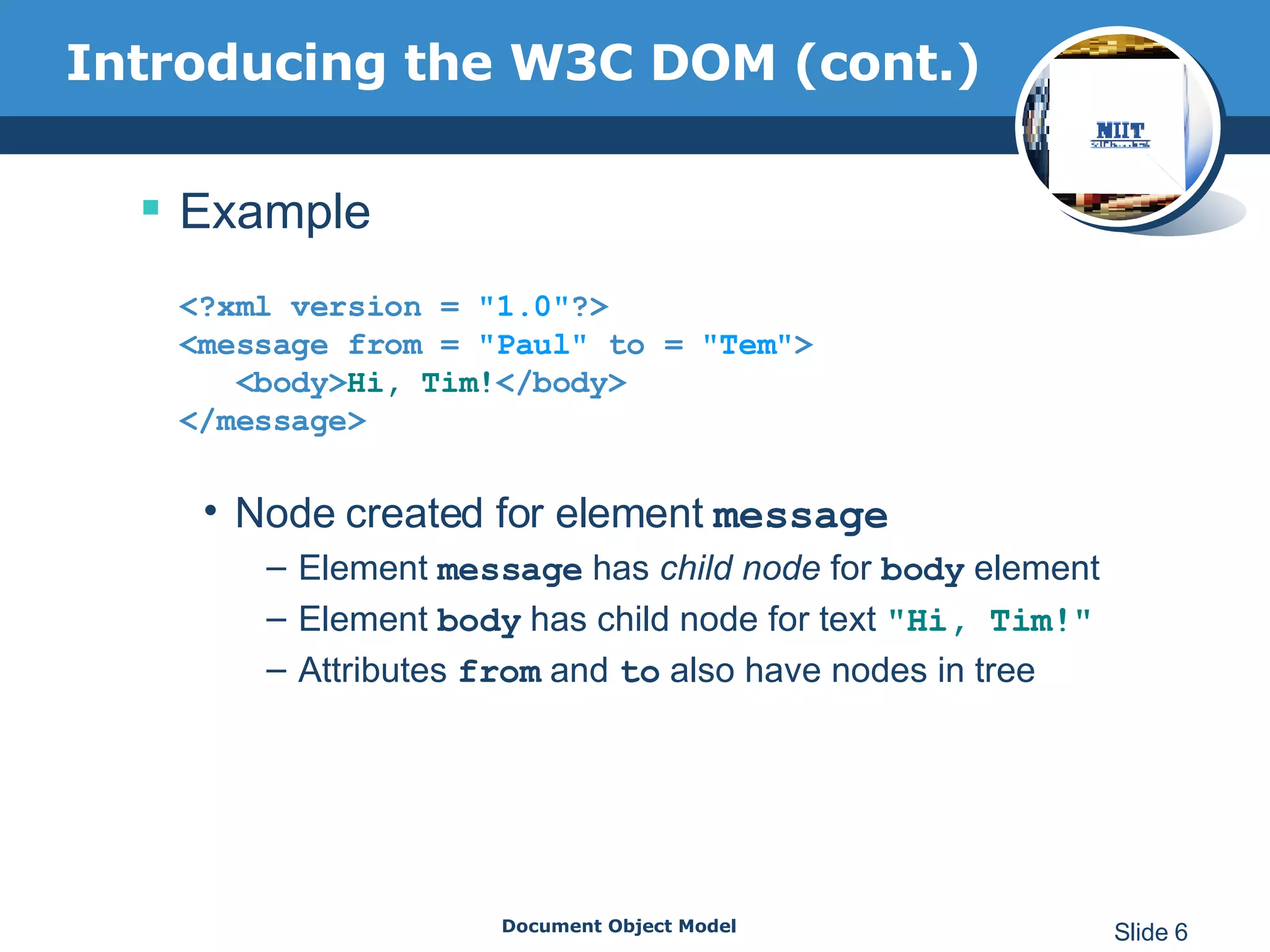
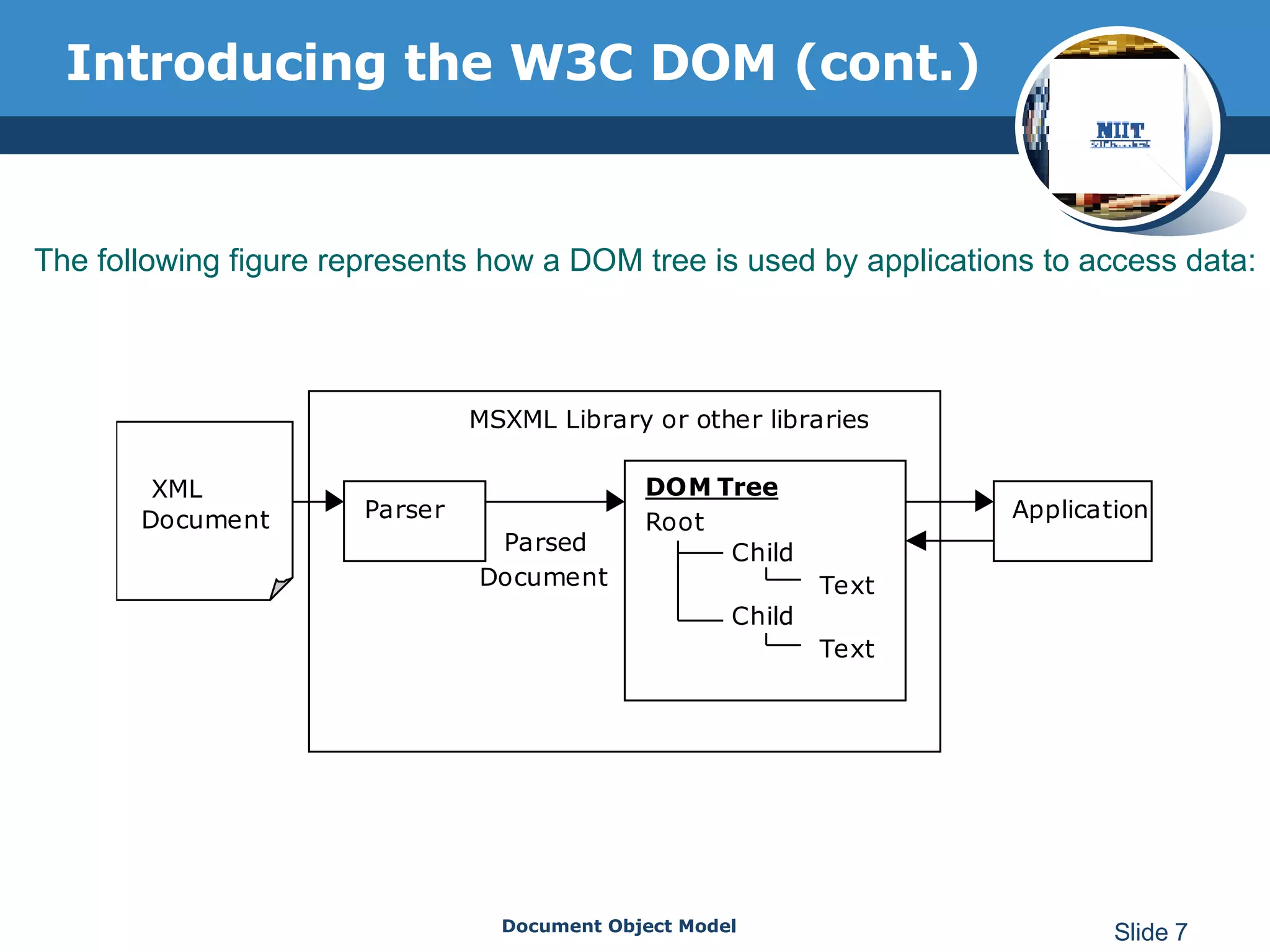
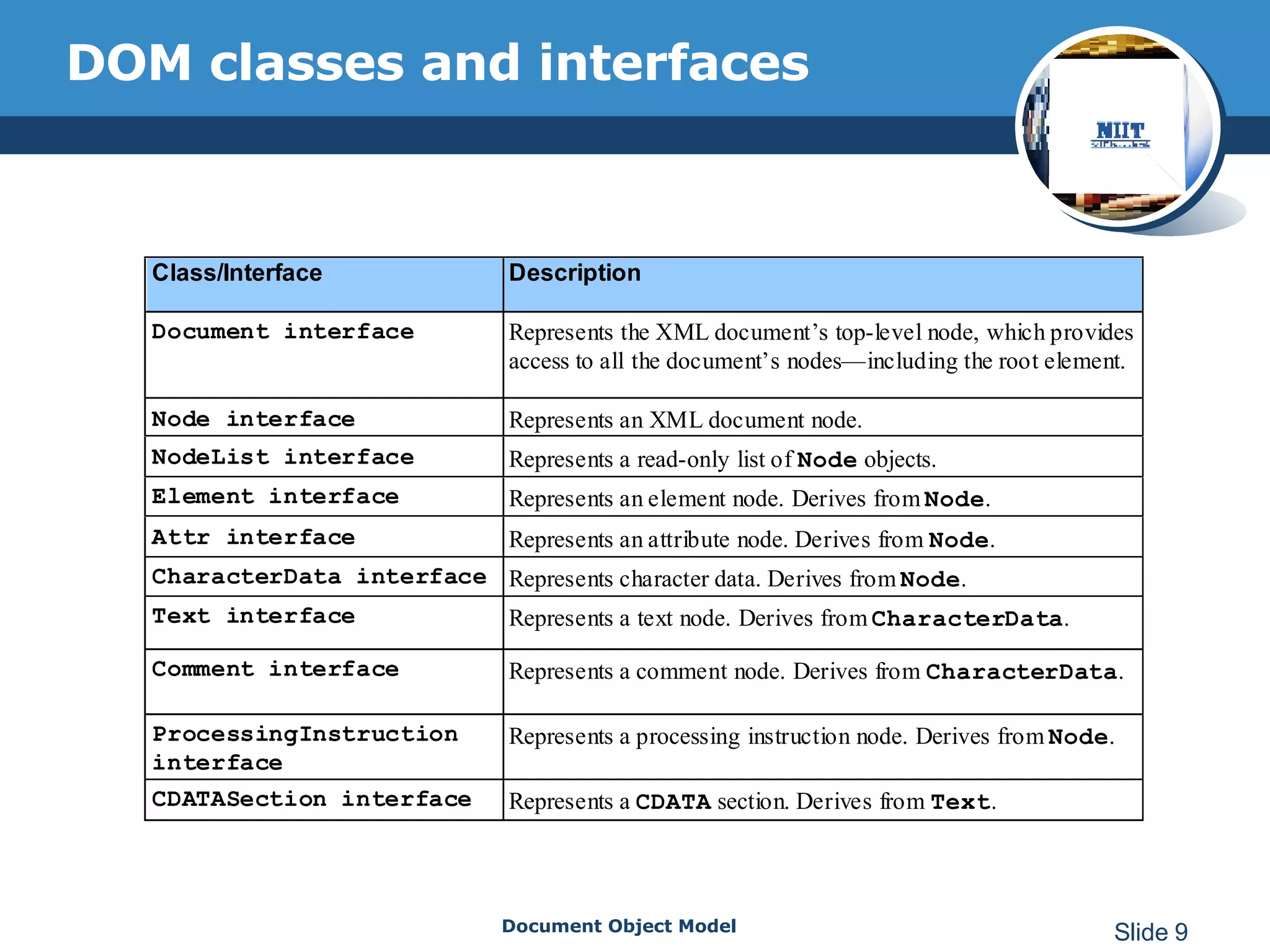
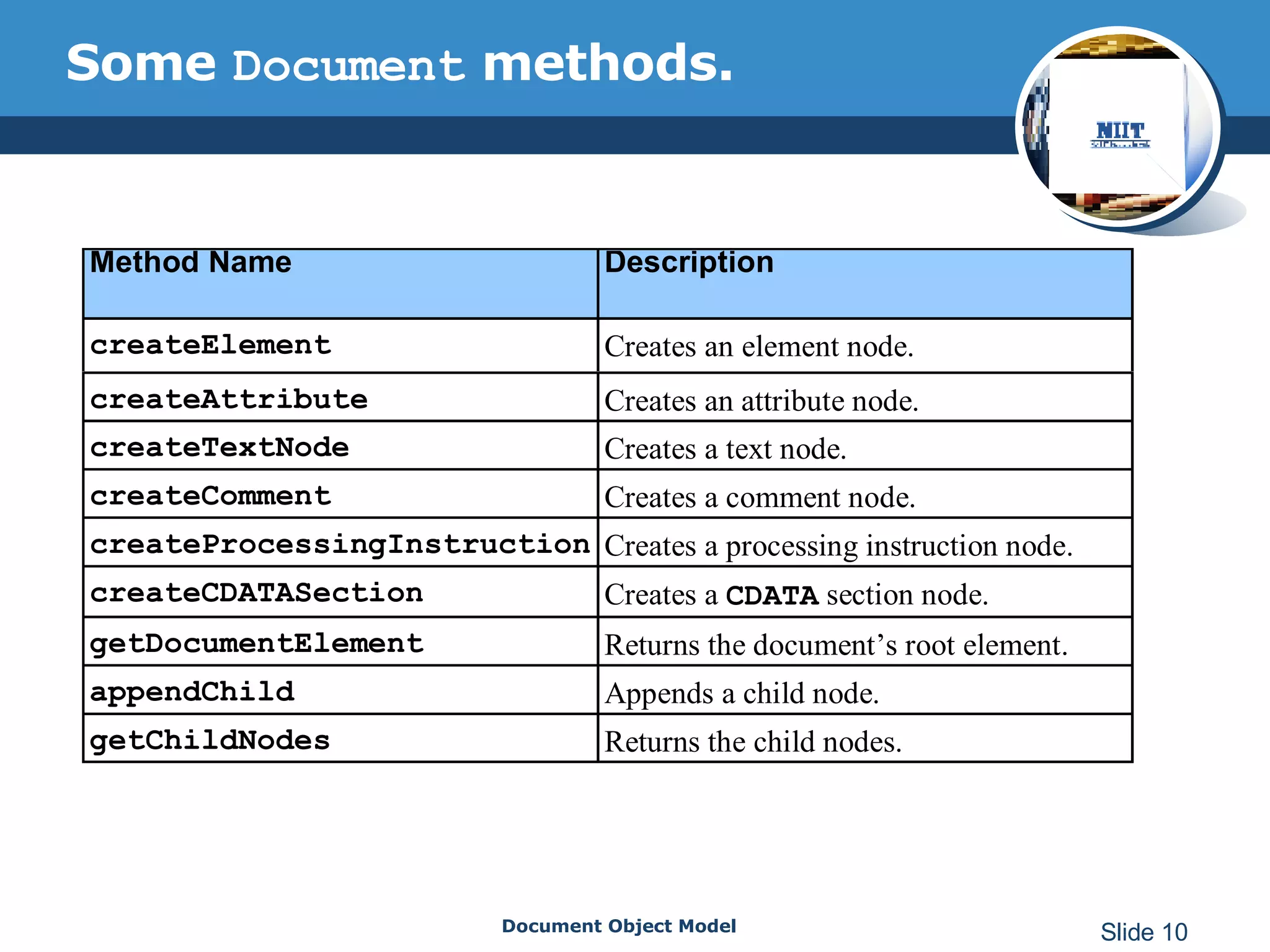
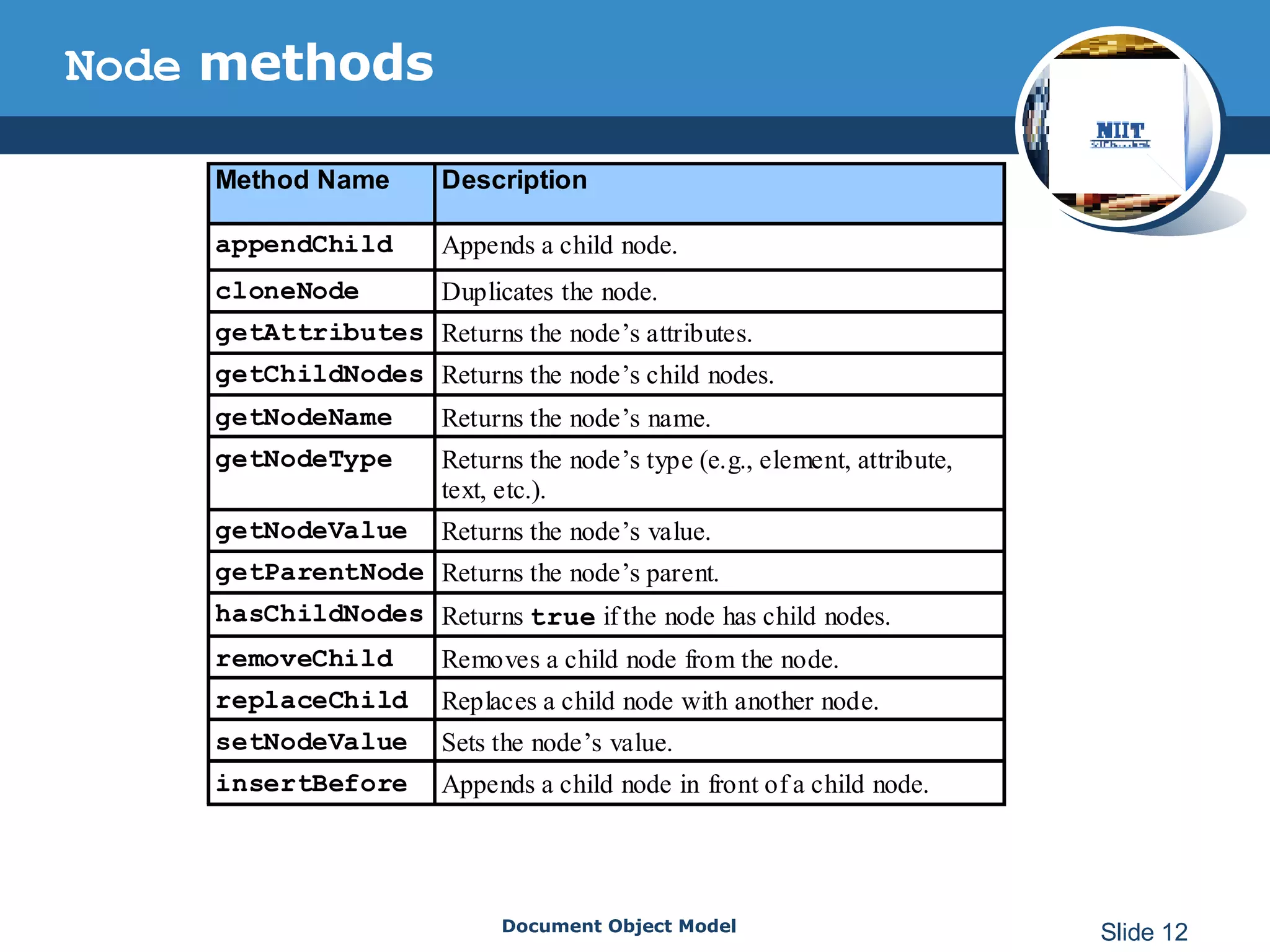
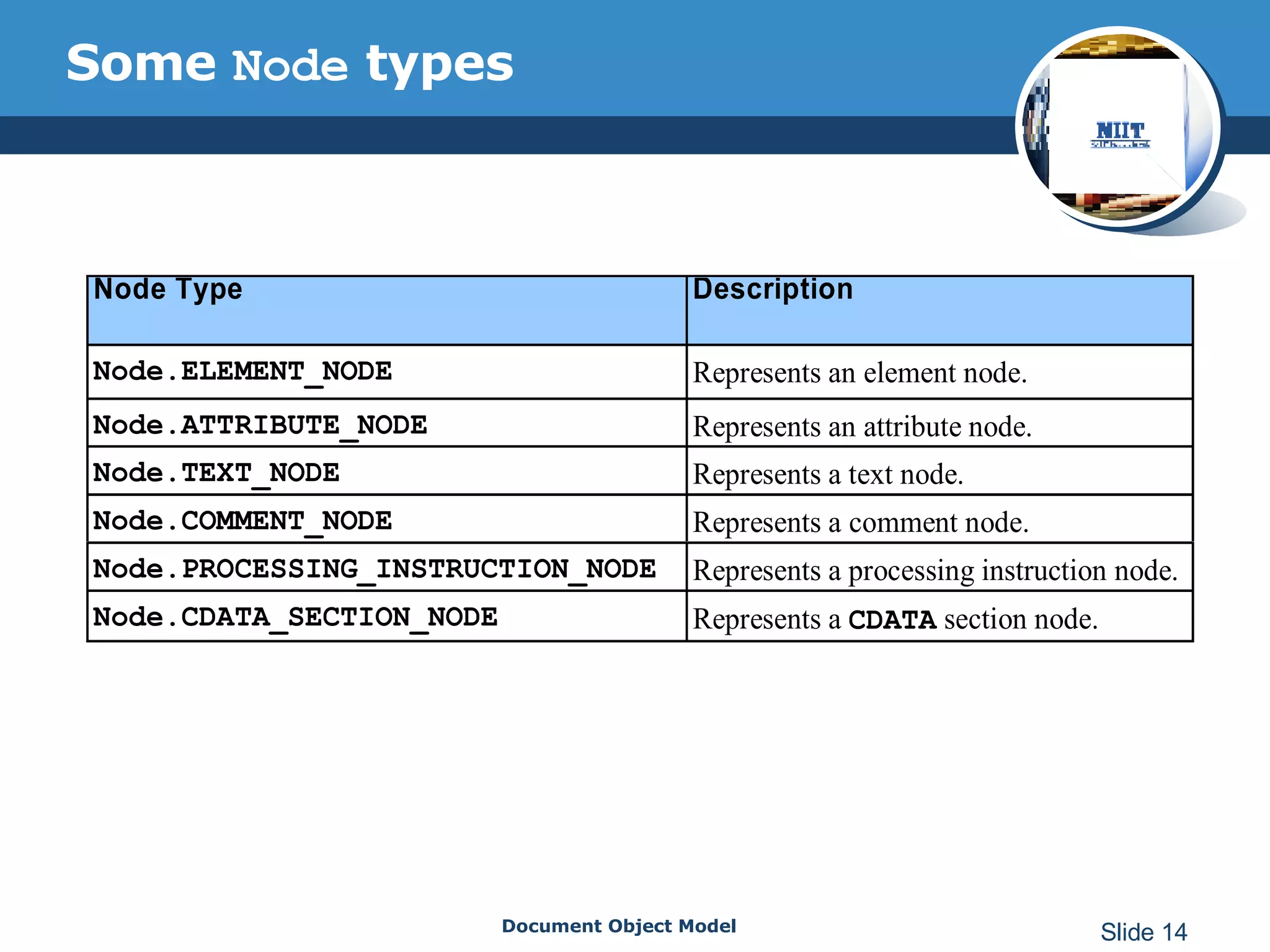
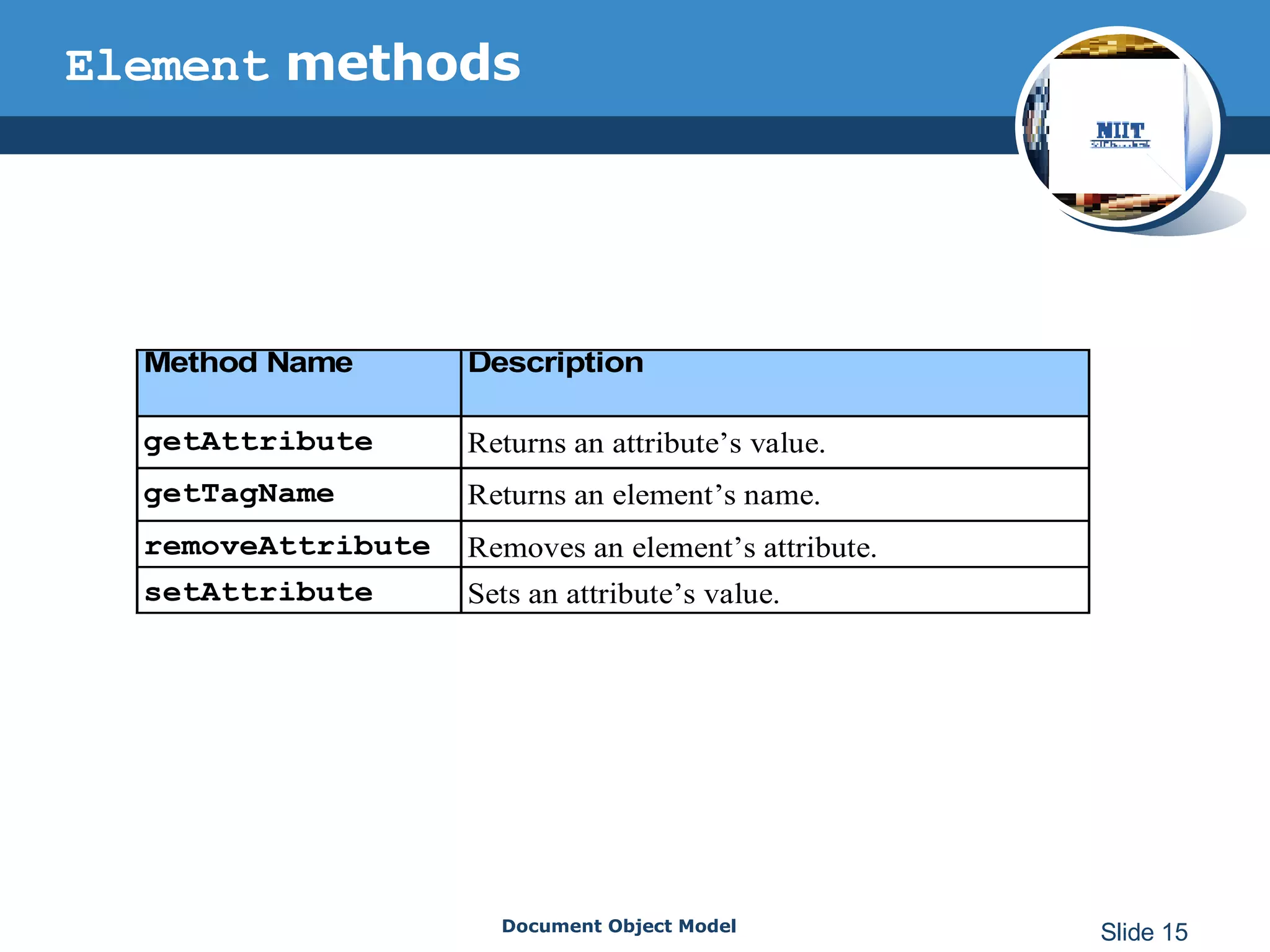
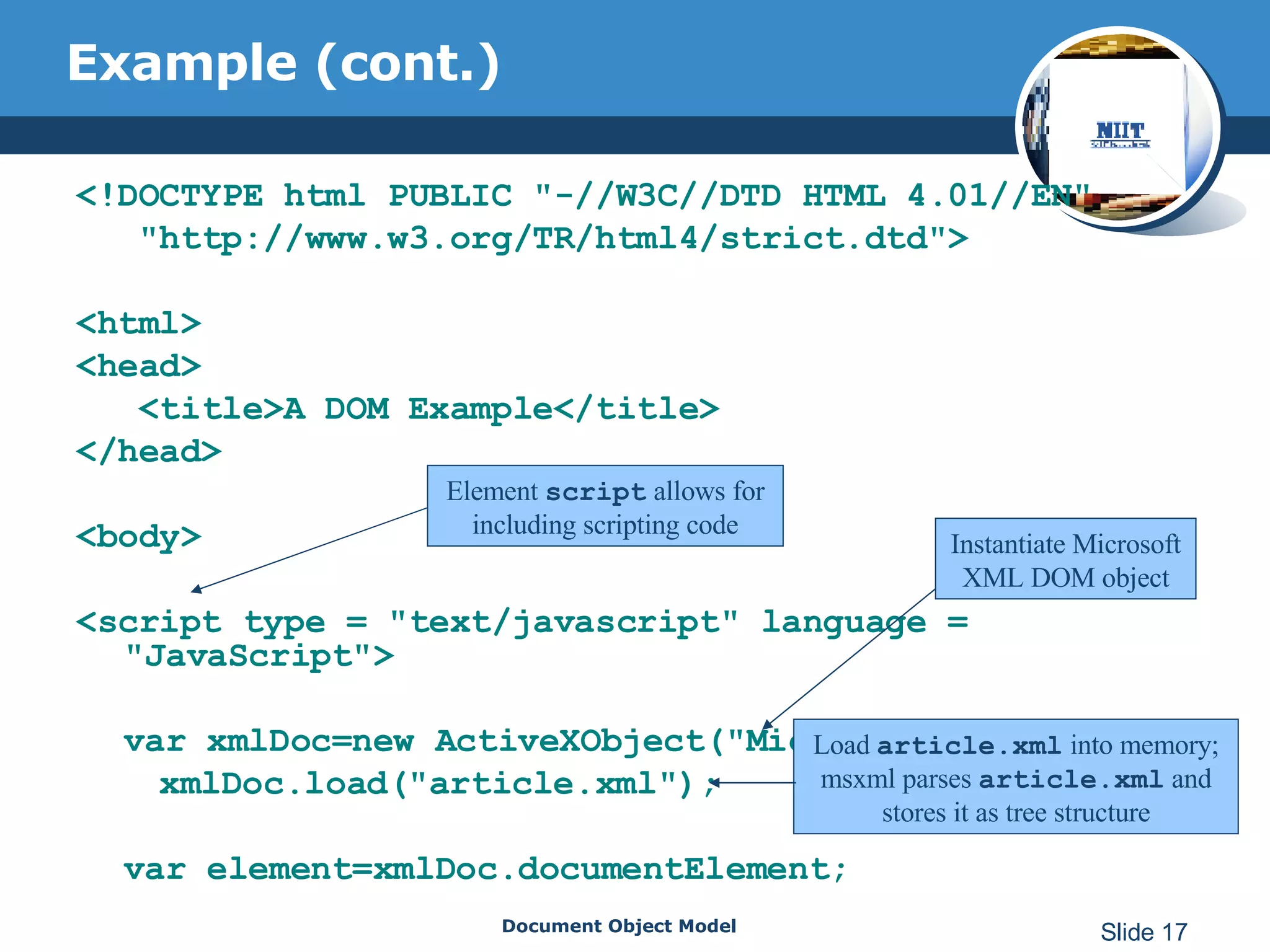
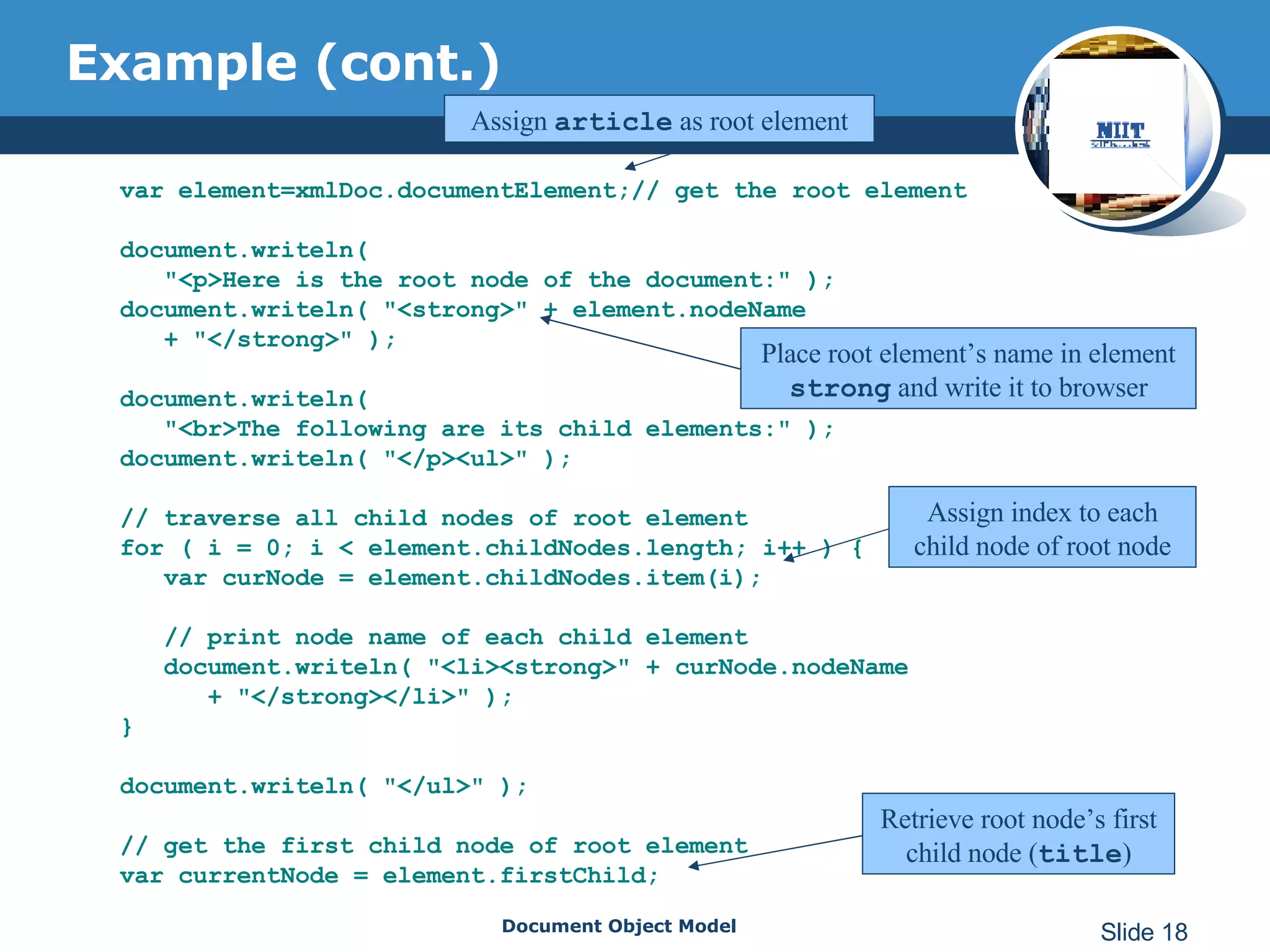
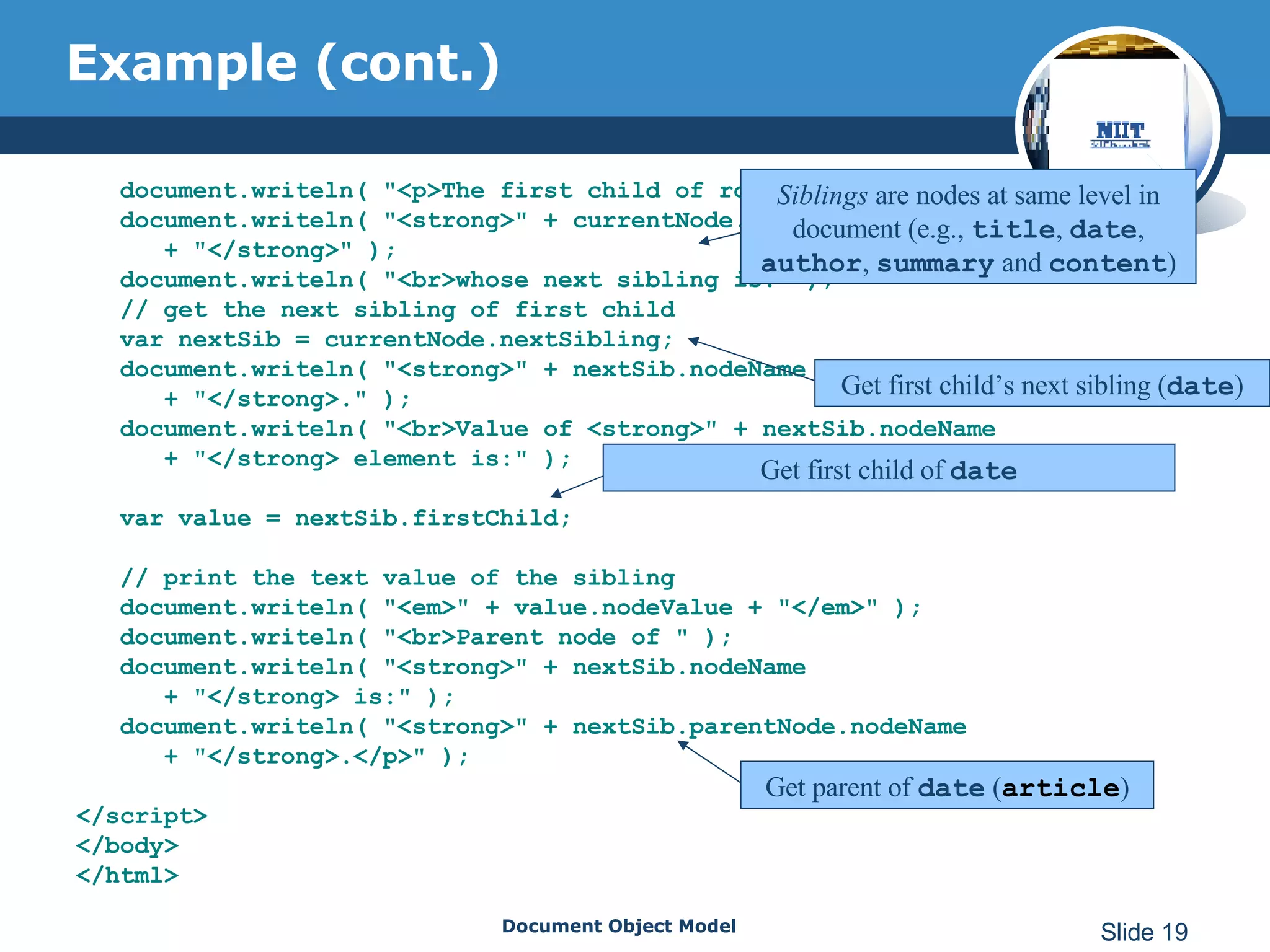
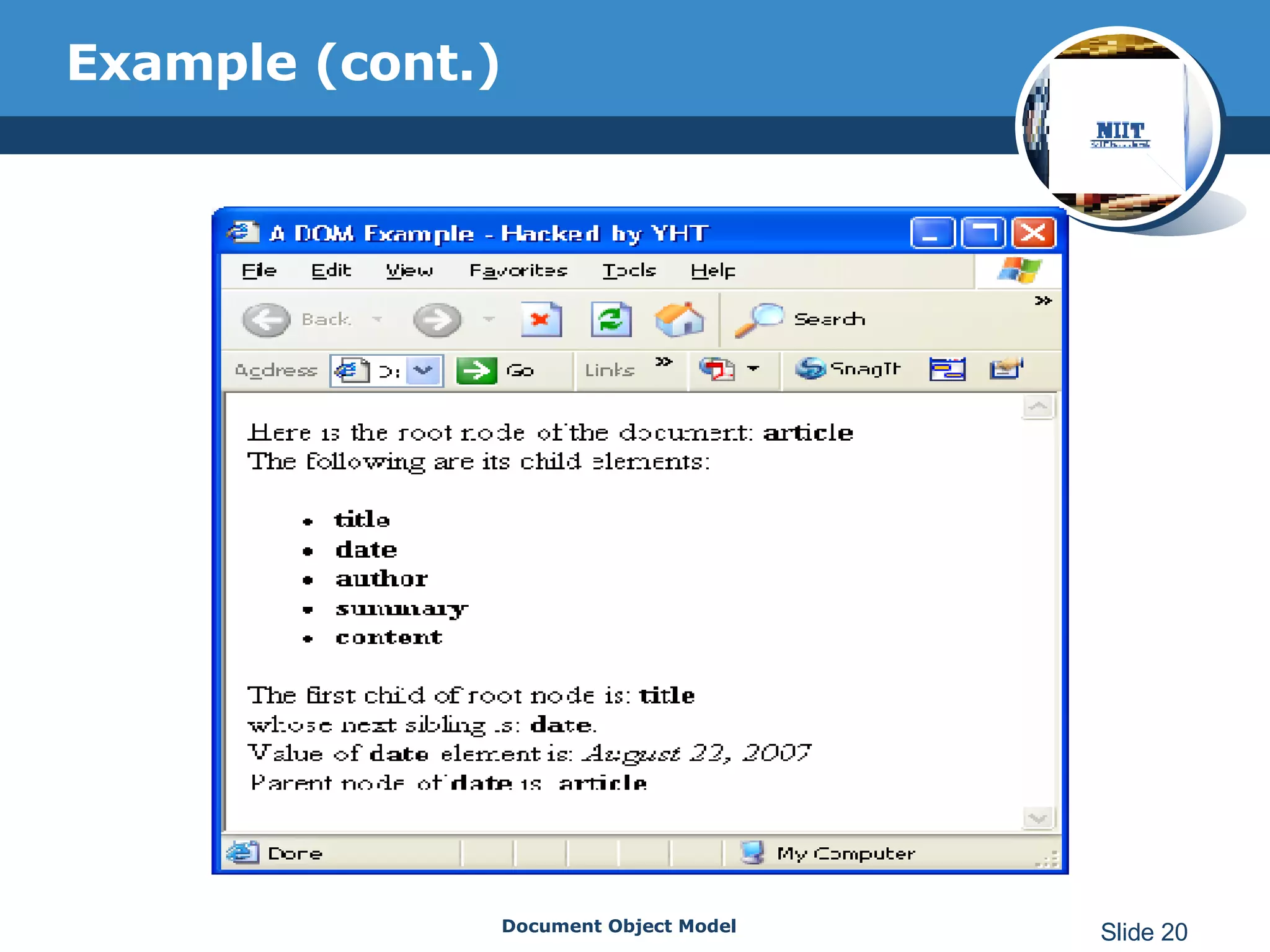
The document introduces the Document Object Model (DOM), which is a W3C standard for representing and interacting with XML and HTML documents as node trees. The DOM represents an XML or HTML document as nodes that can be accessed and manipulated. It defines the logical structure of documents and the way a document is accessed and manipulated. The DOM represents the document as nodes and objects, and uses these programmatically.
![Document Object Model XML http://yht4ever.blogspot.com [email_address] B070066 - NIIT Quang Trung 08/2007](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/document-object-model4061/75/Document-Object-Model-1-2048.jpg)





![Q&A Feel free to post questions at http://yht4ever.blogspot.com or email to: [email_address] or [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/document-object-model4061/75/Document-Object-Model-24-2048.jpg)
