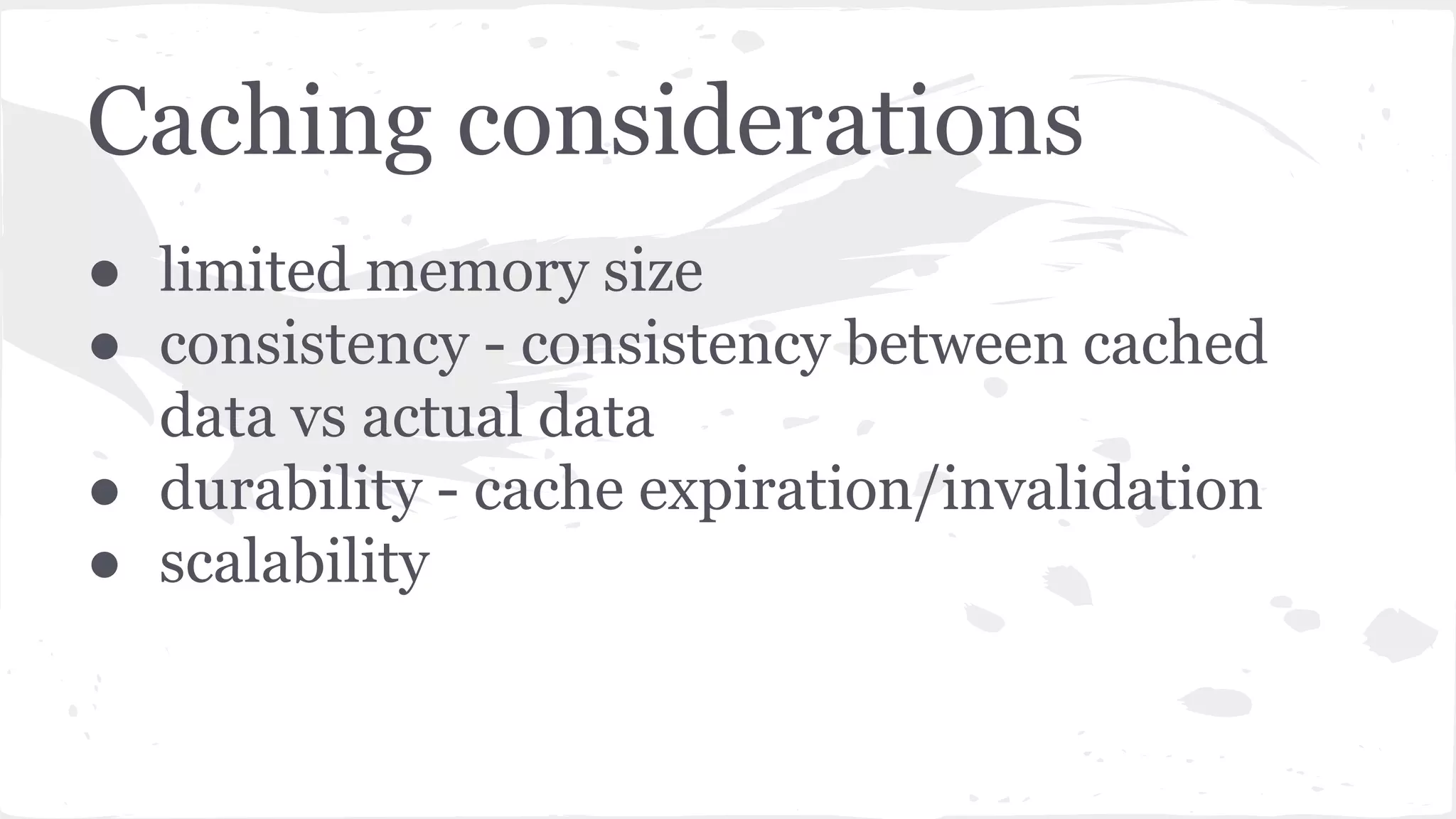
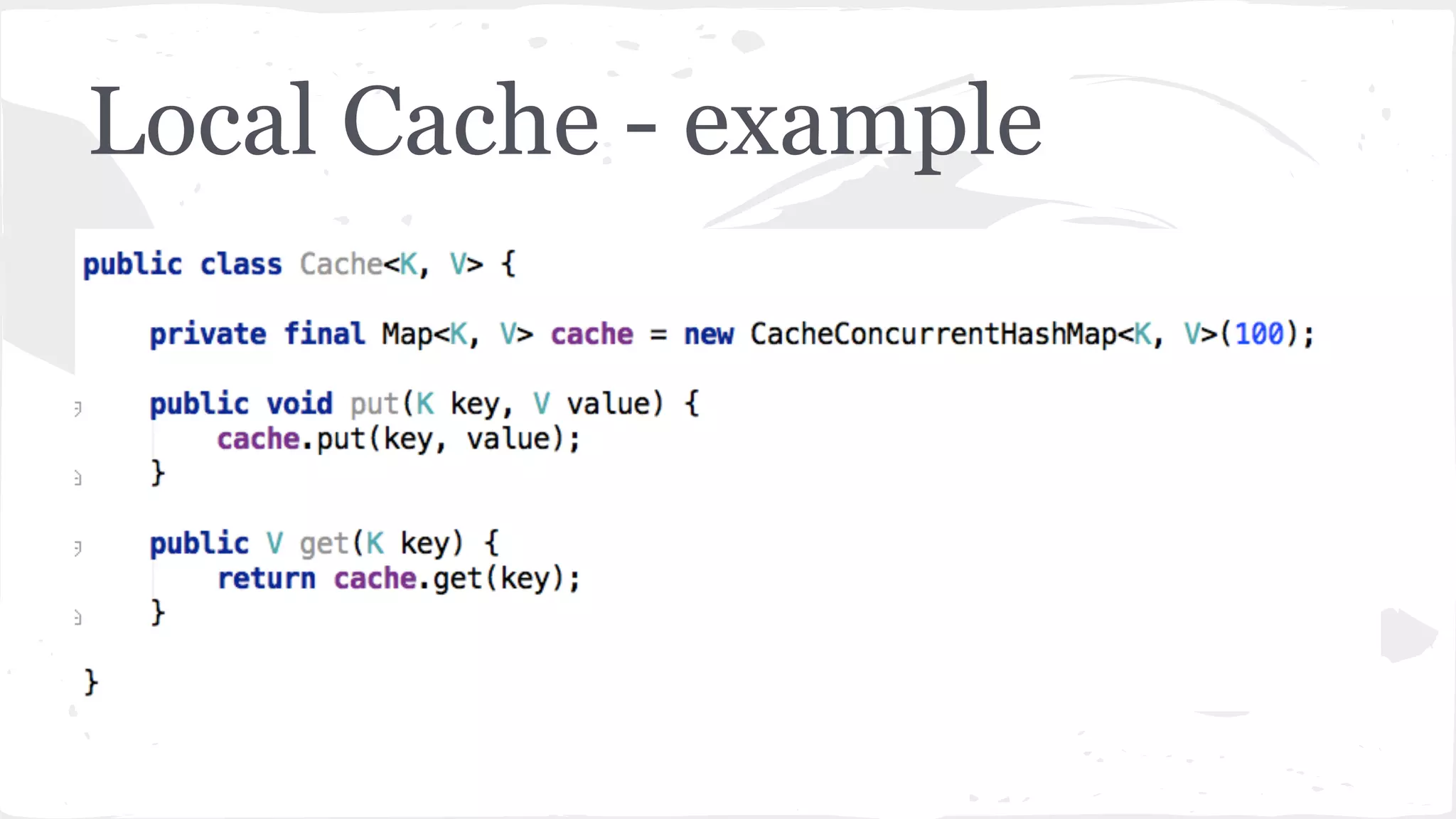
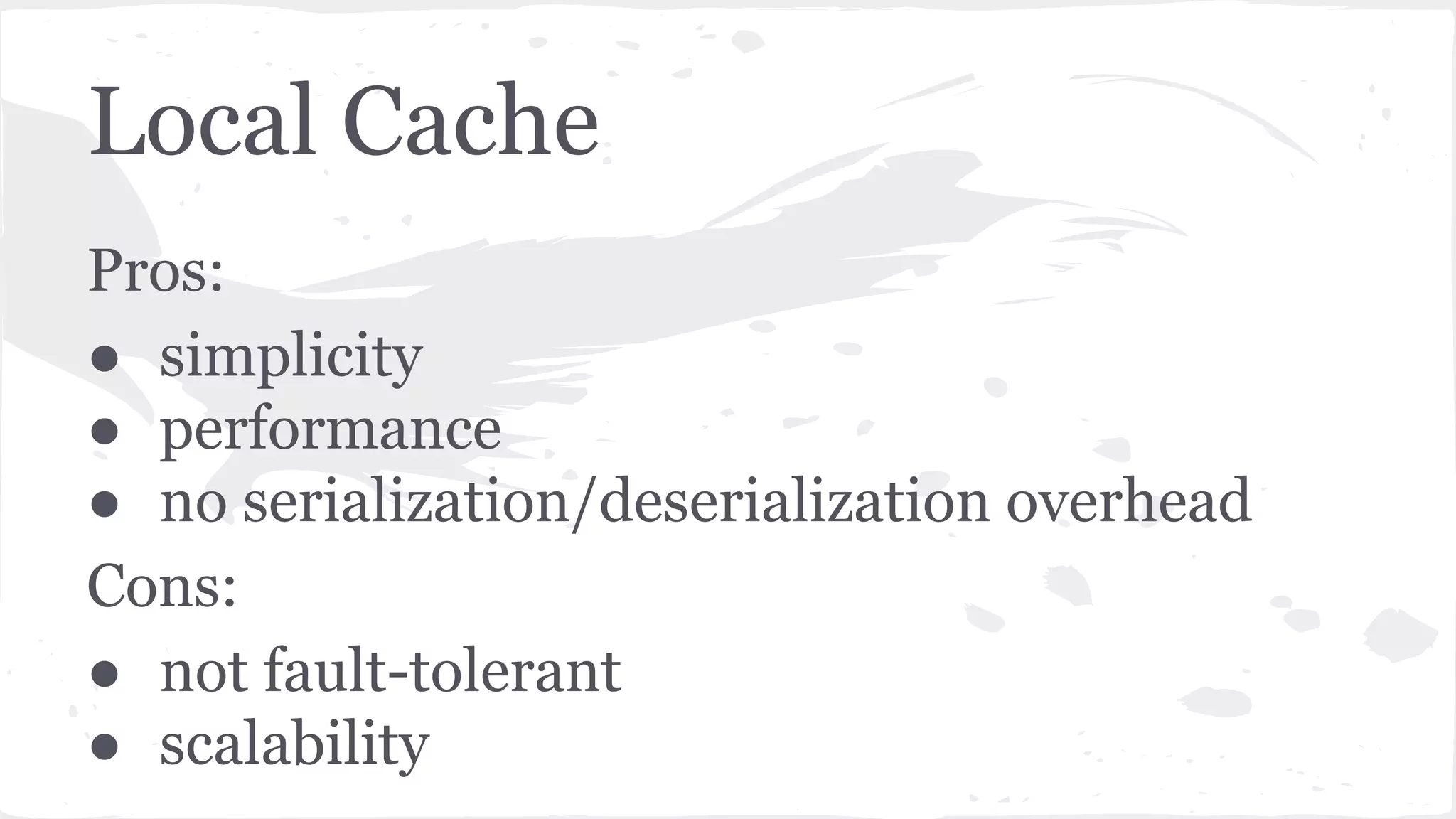
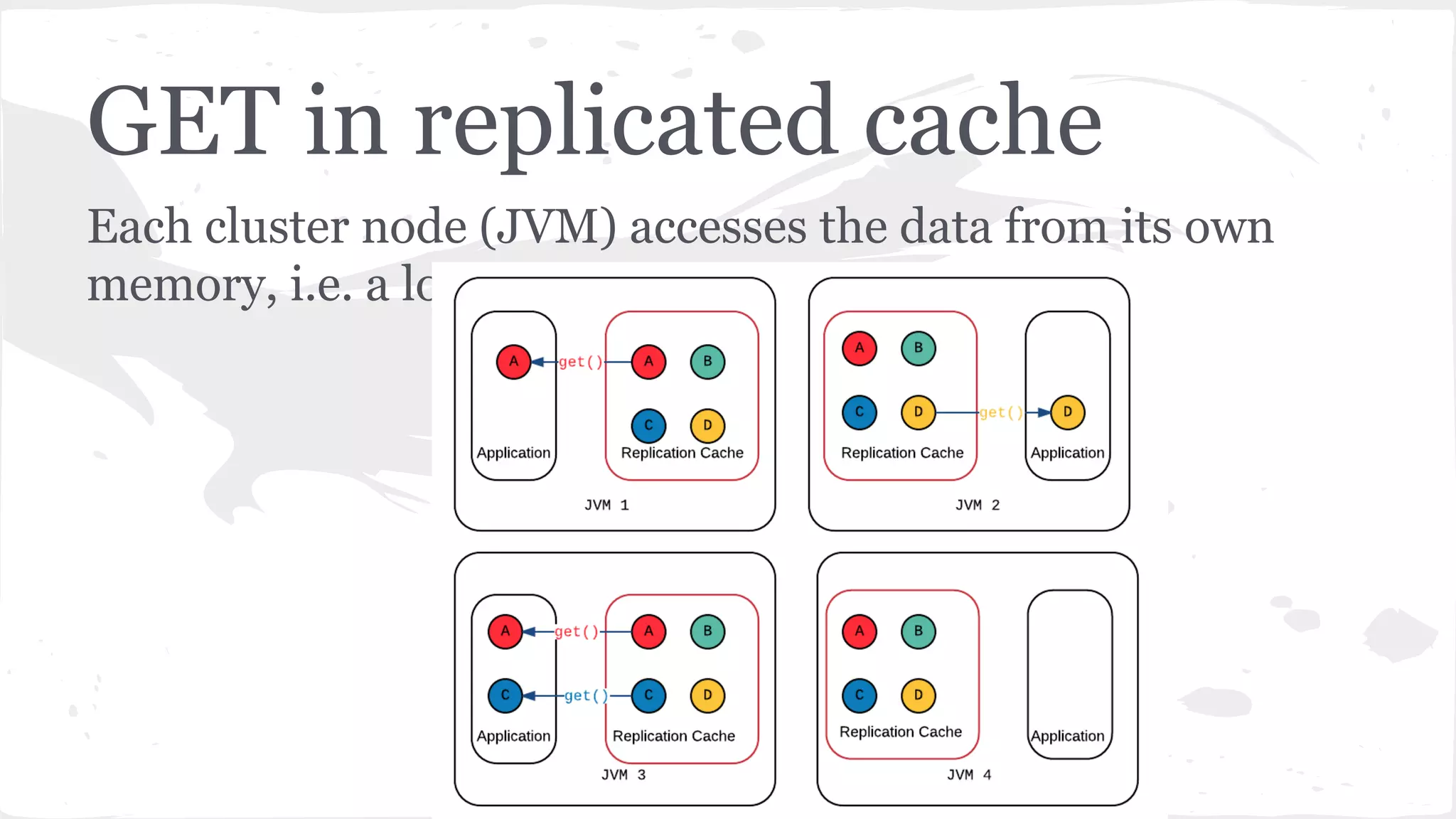
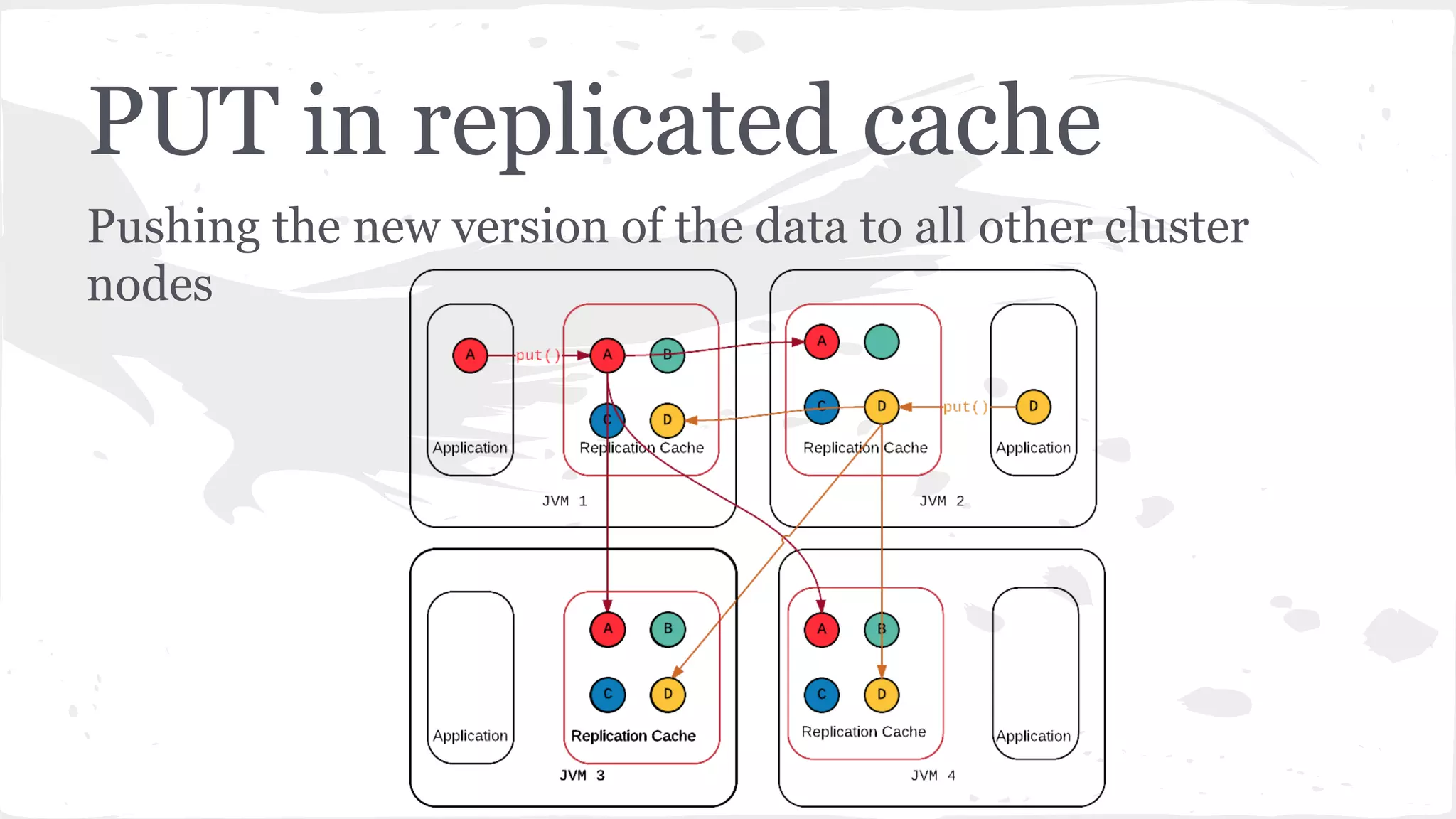
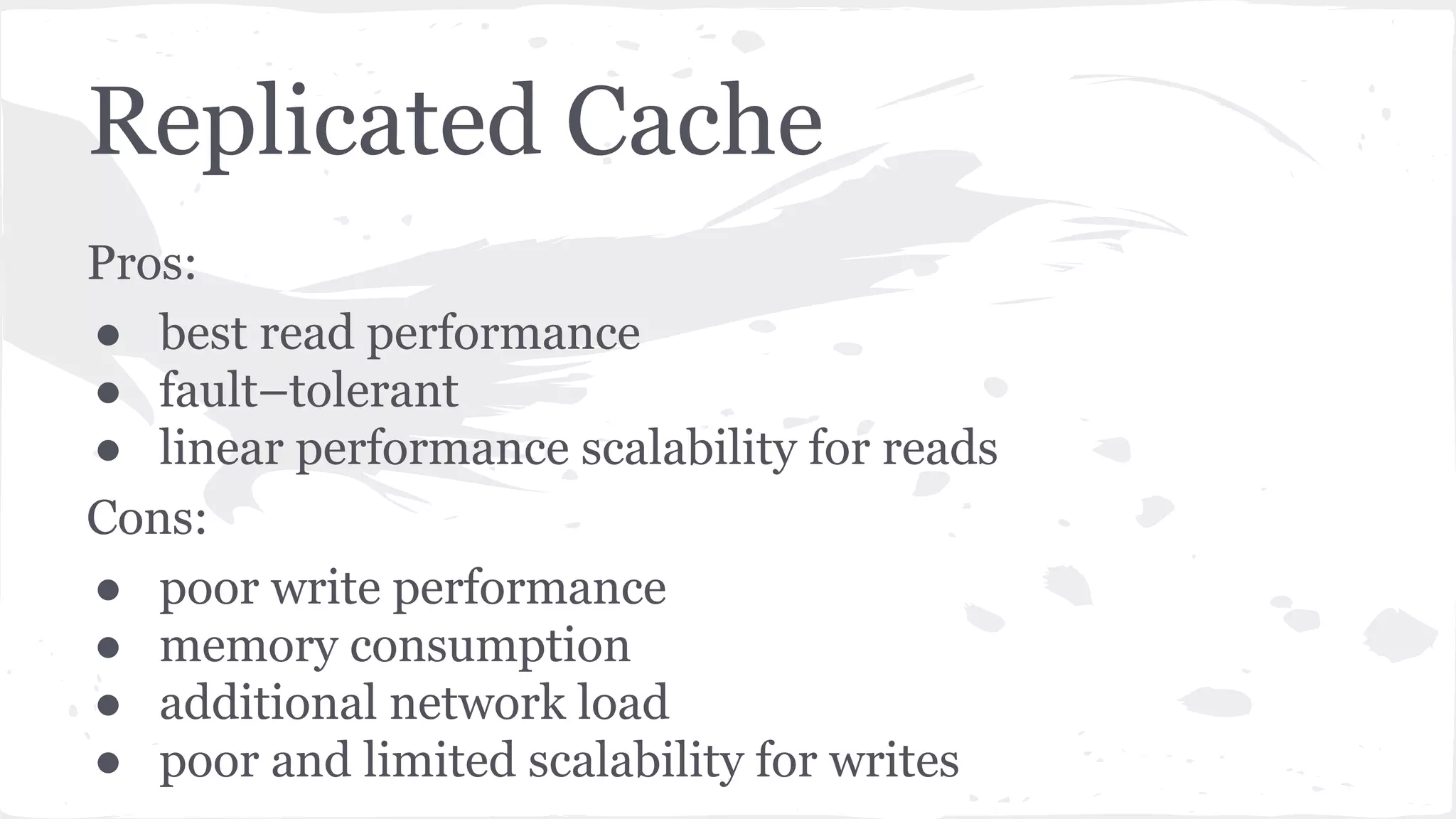
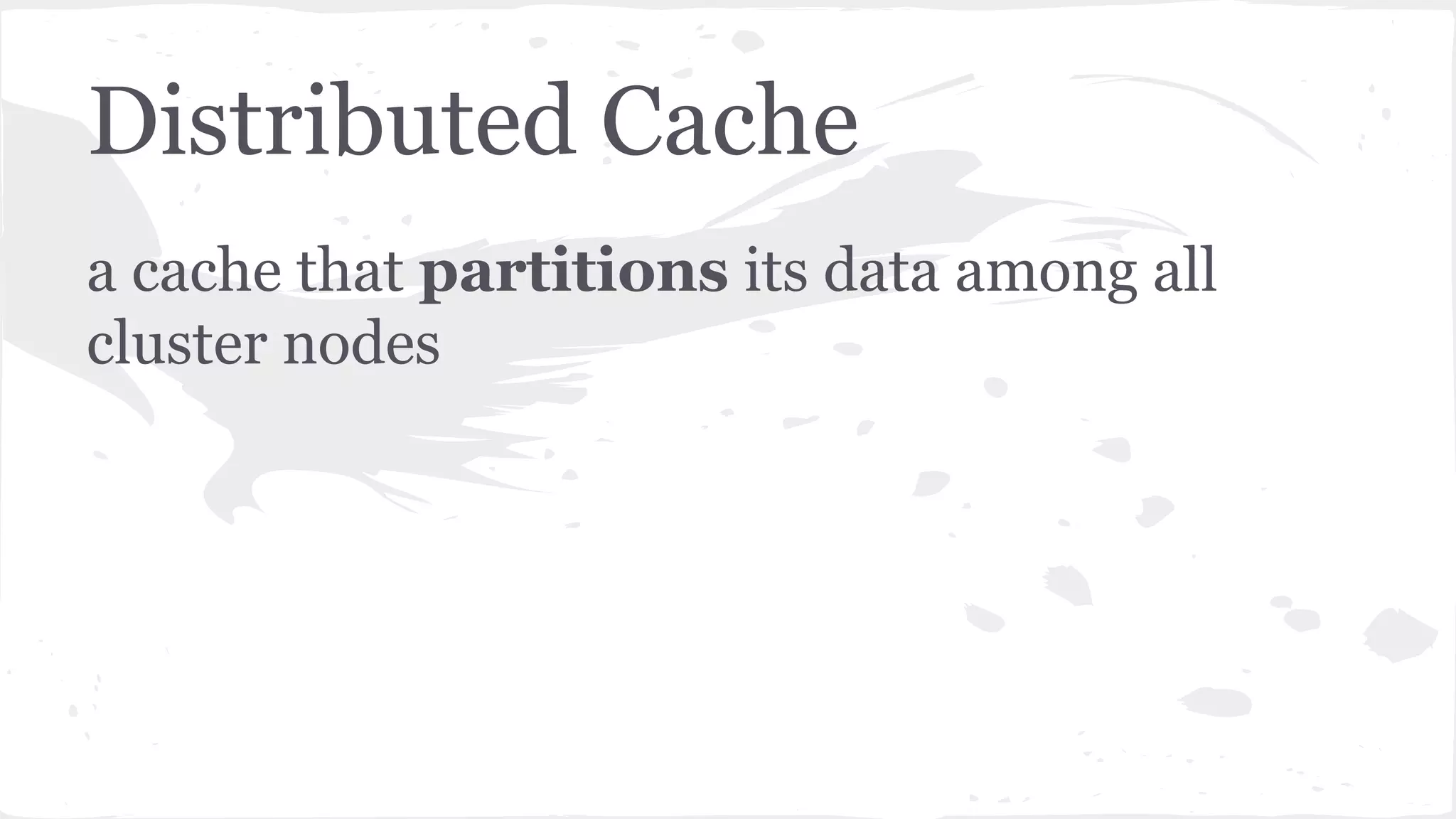
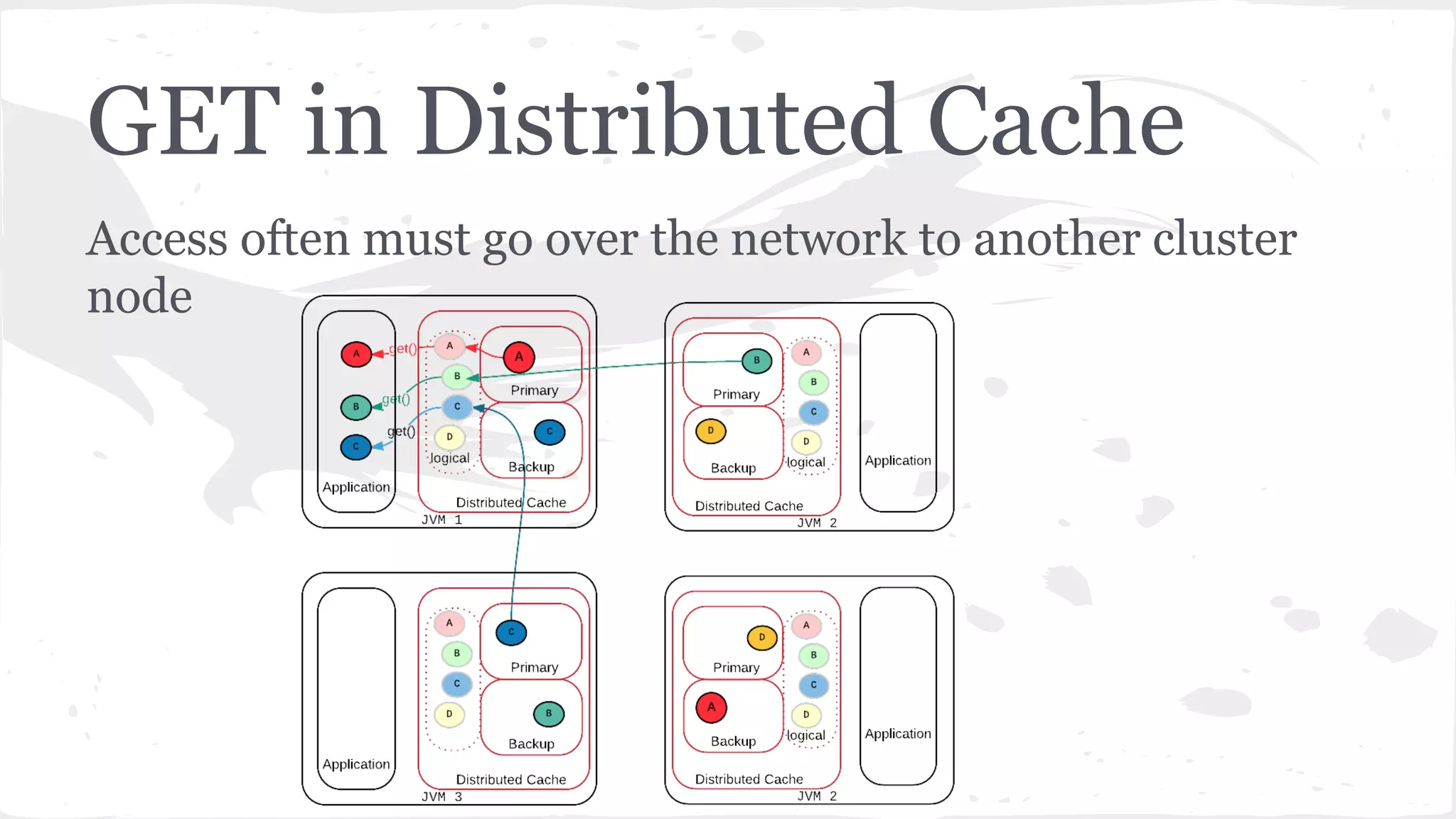
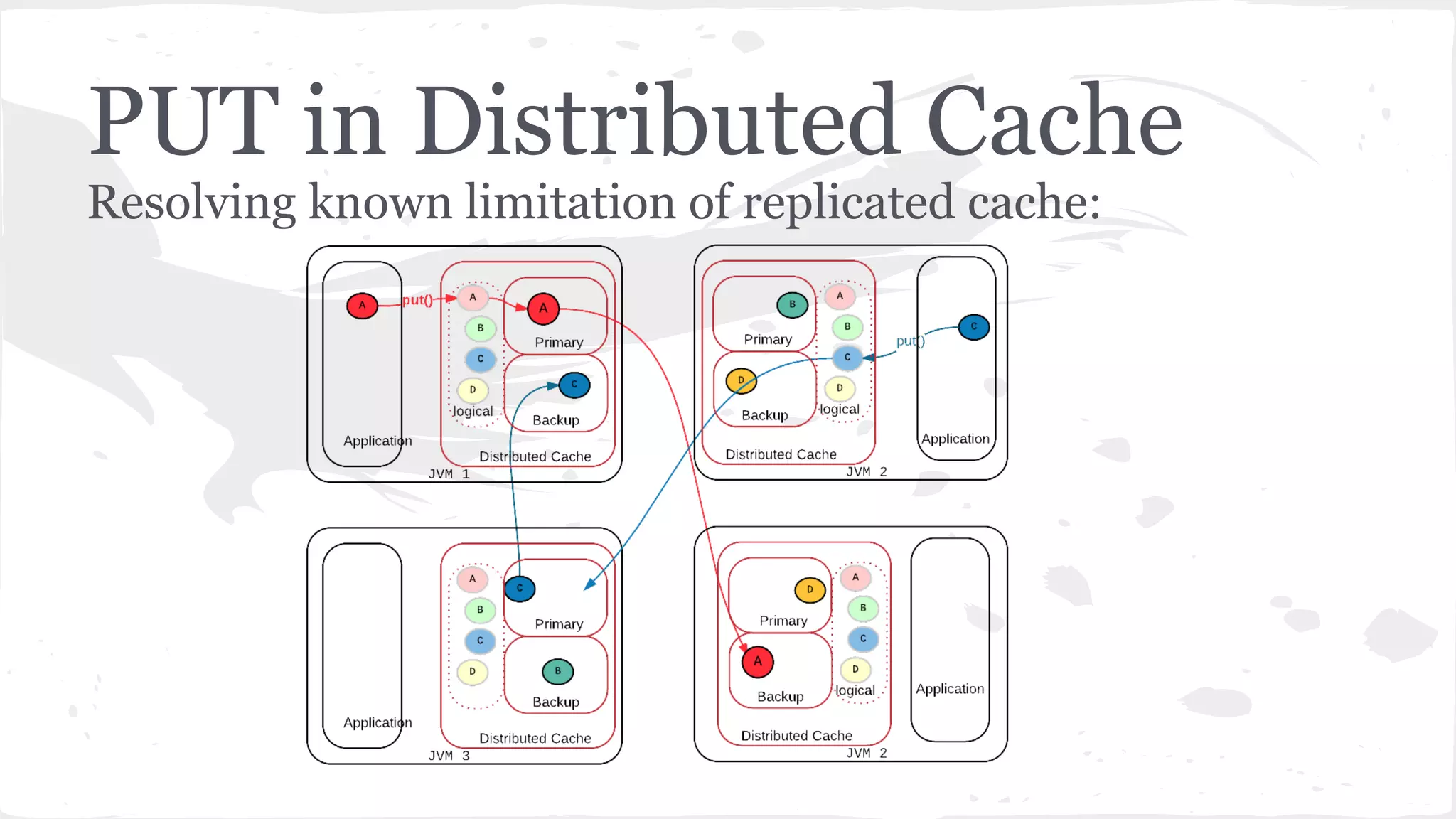
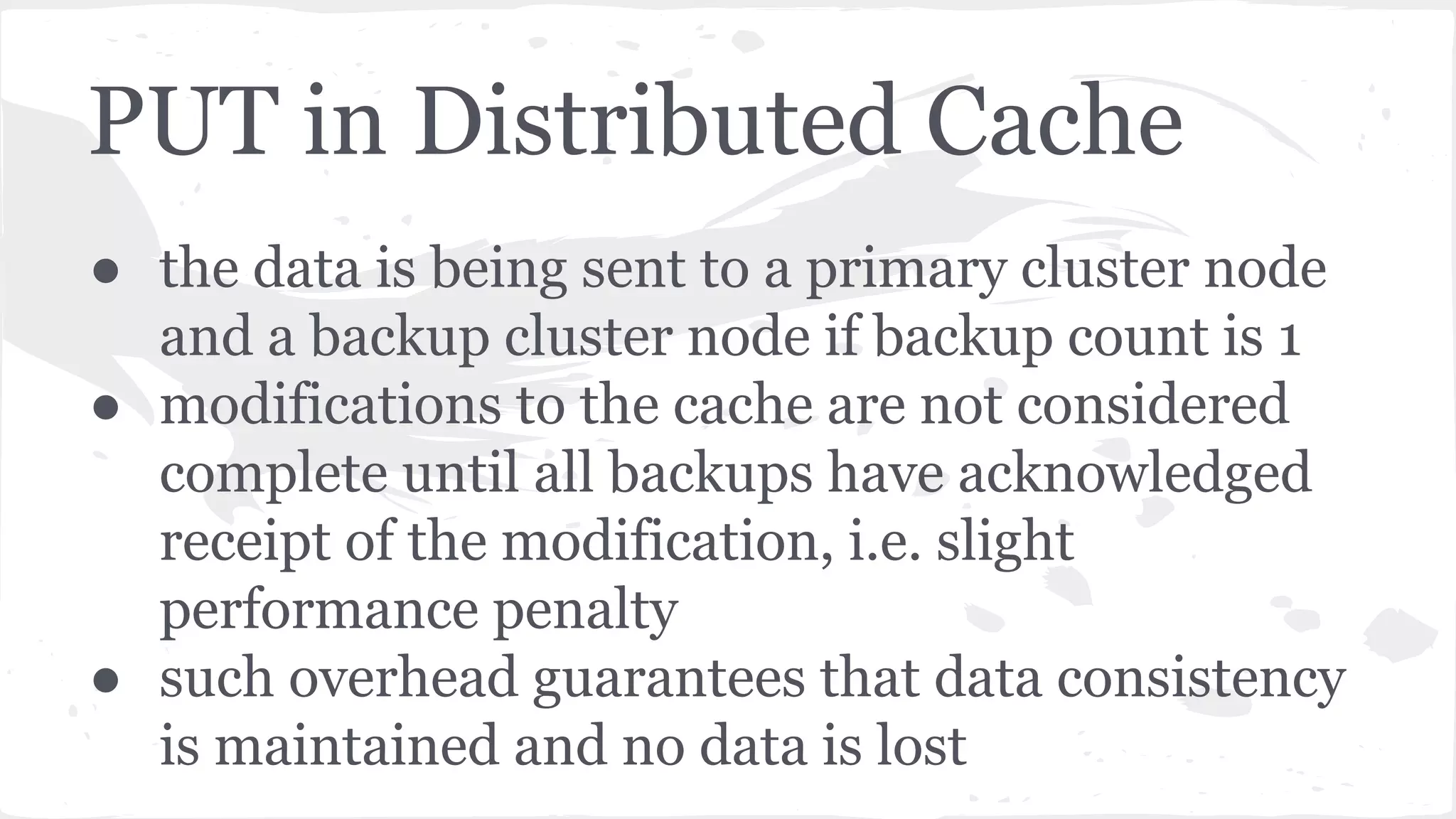
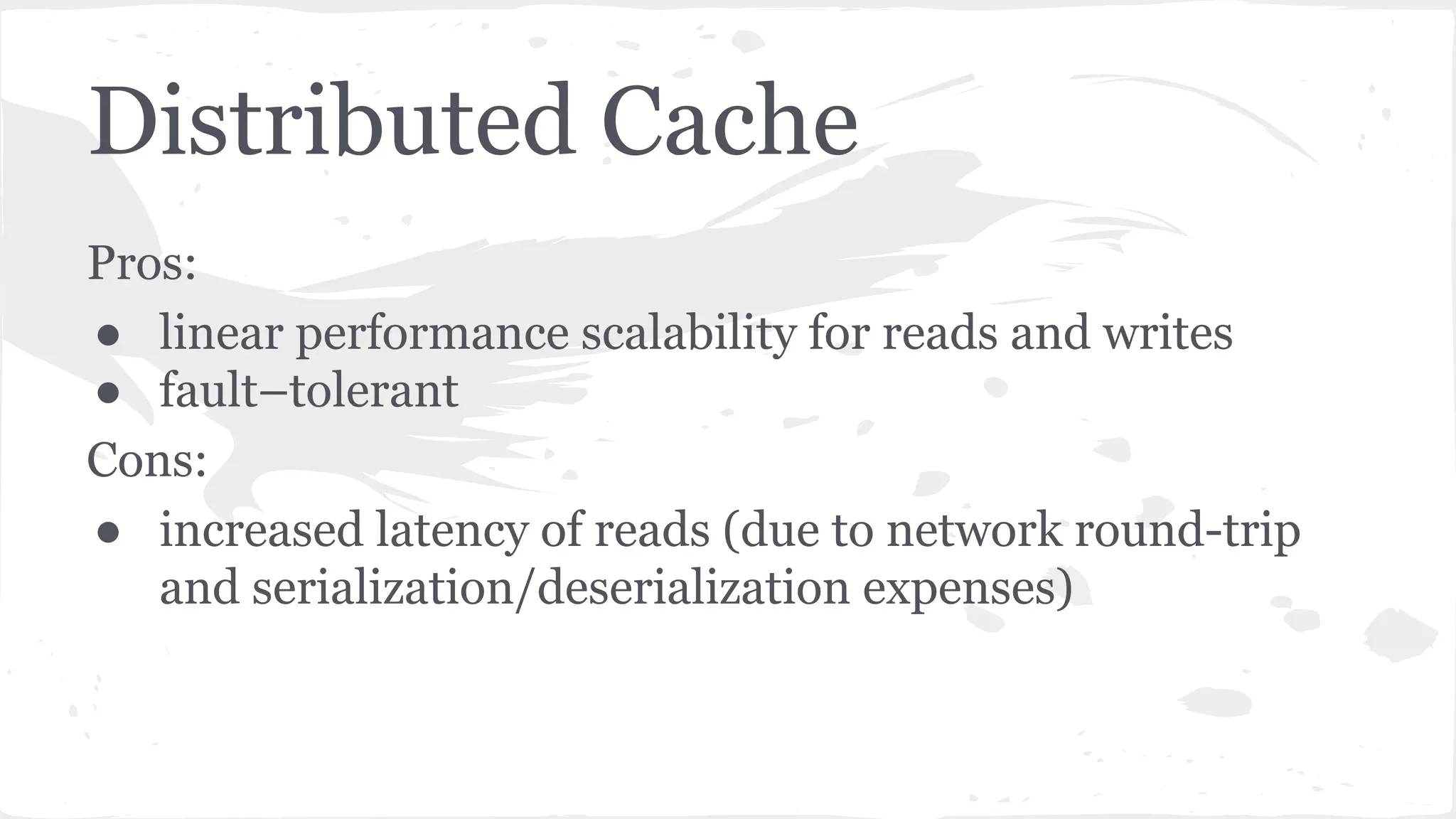
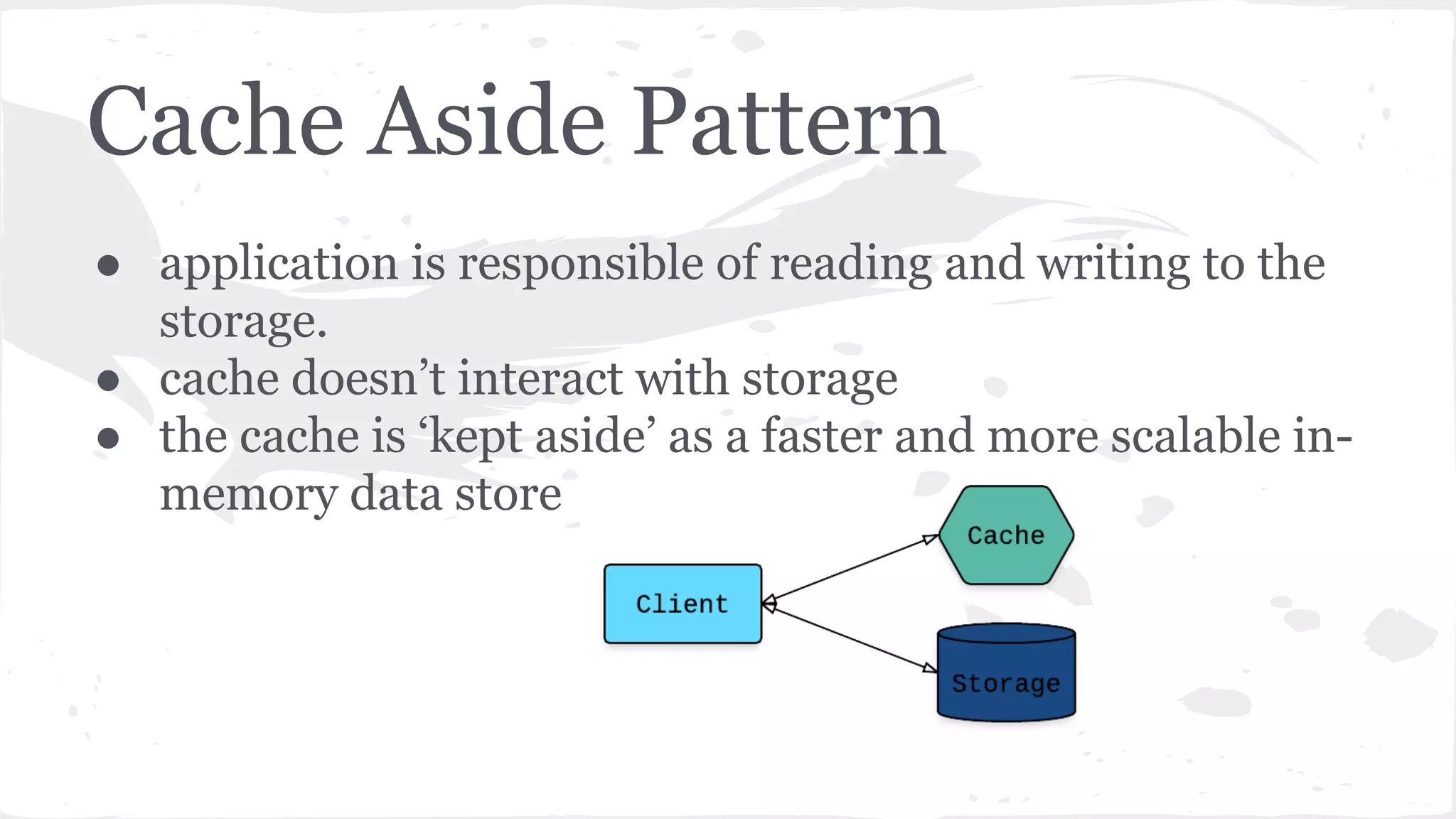
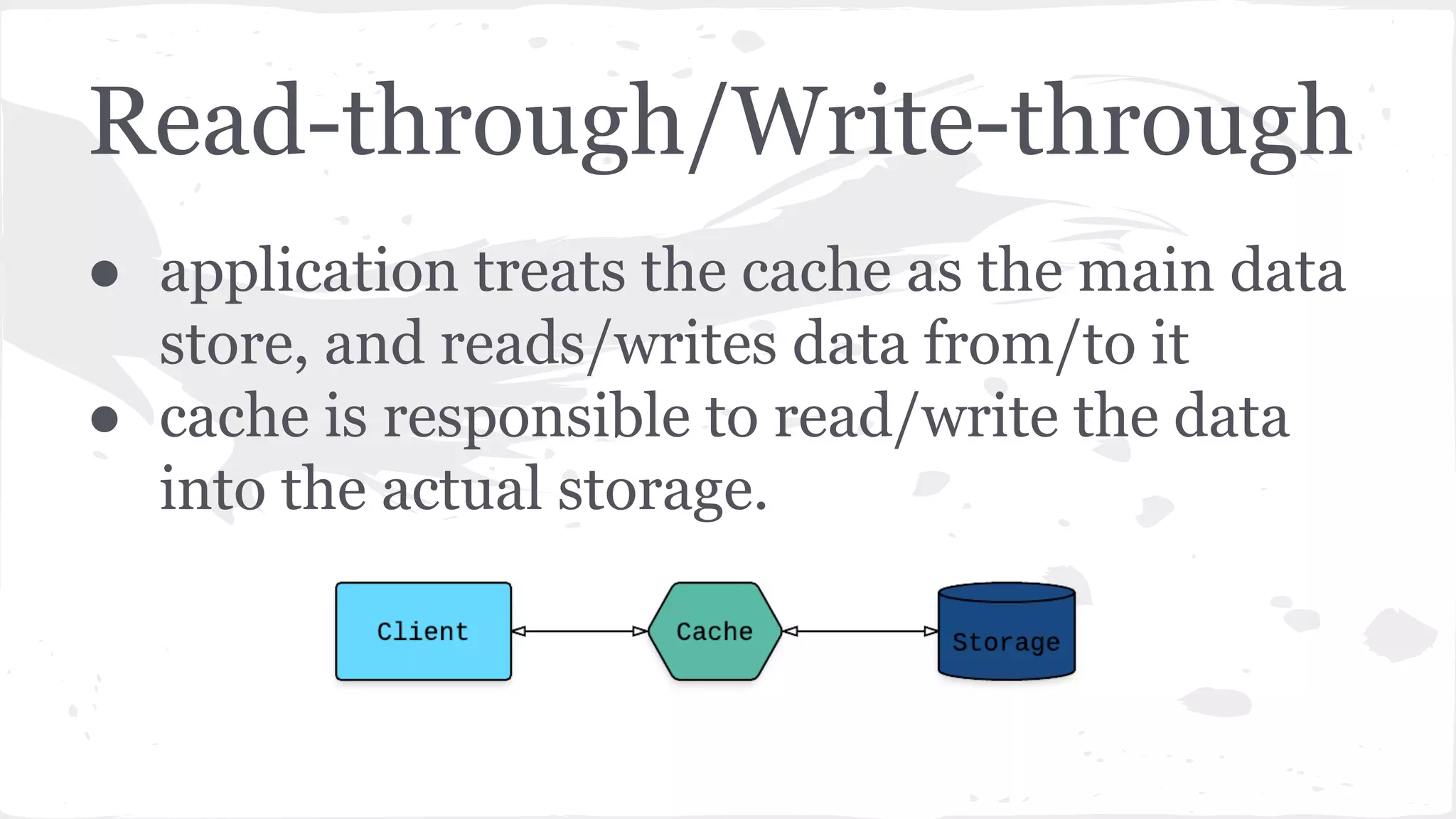
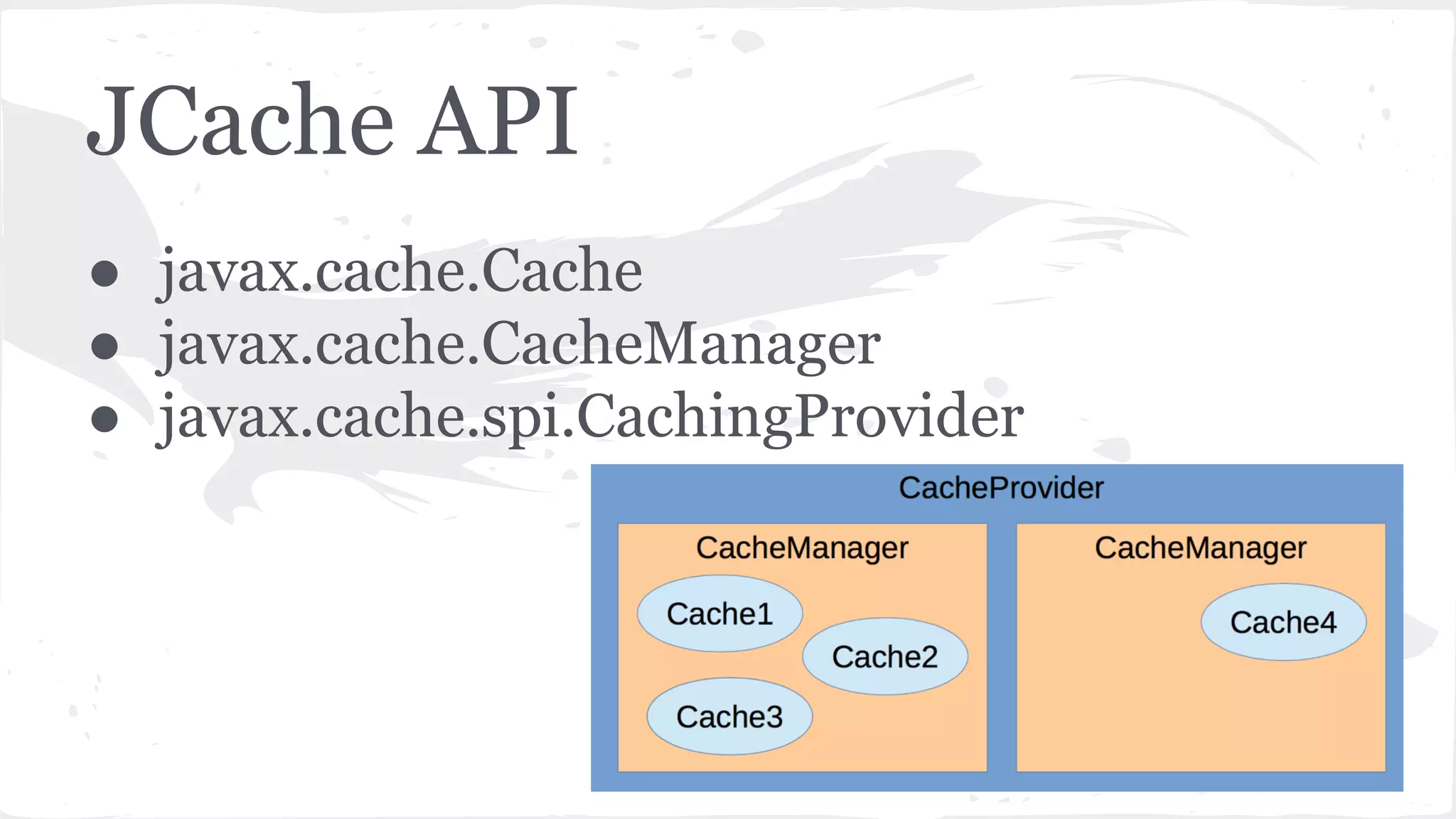
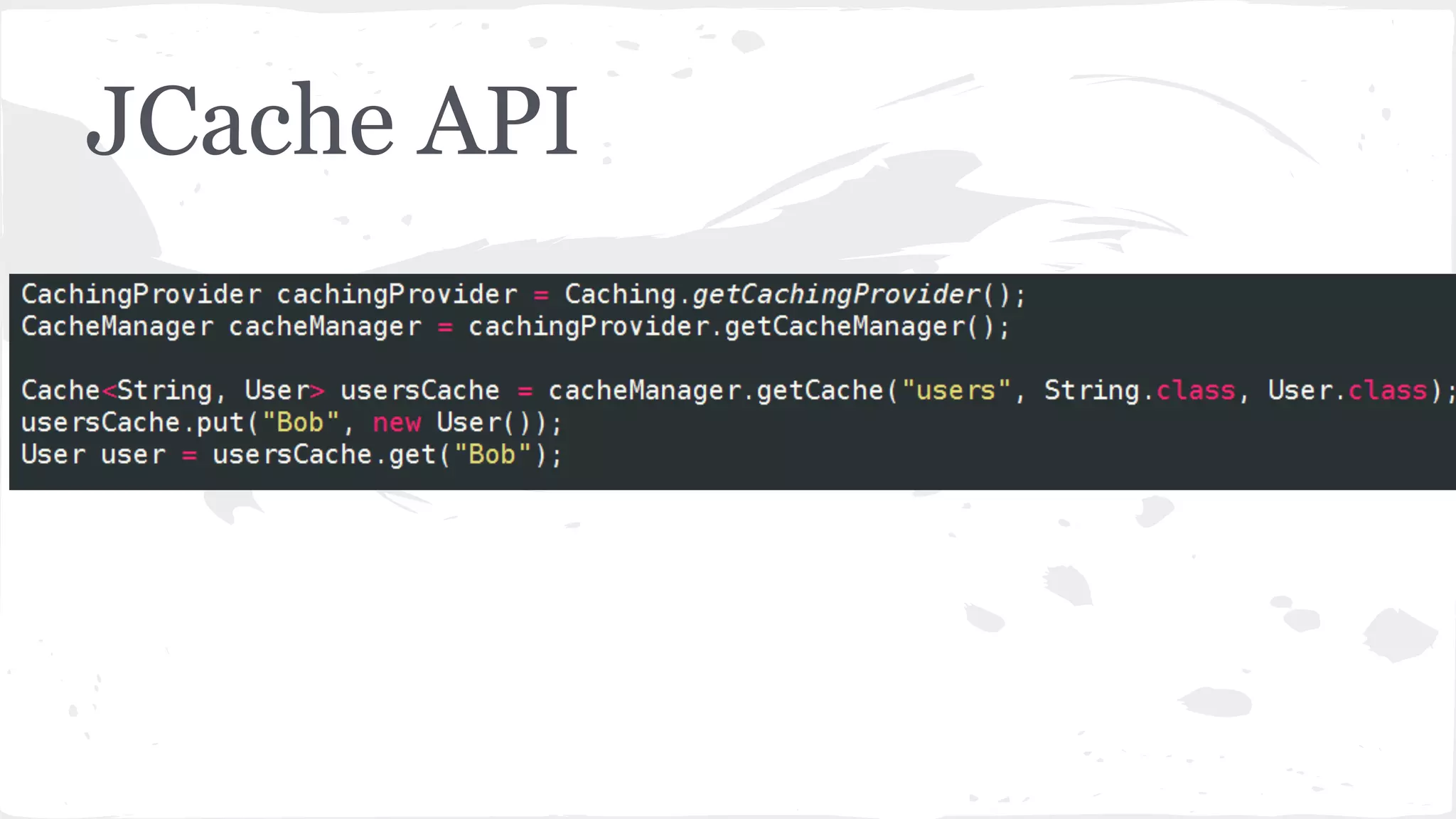
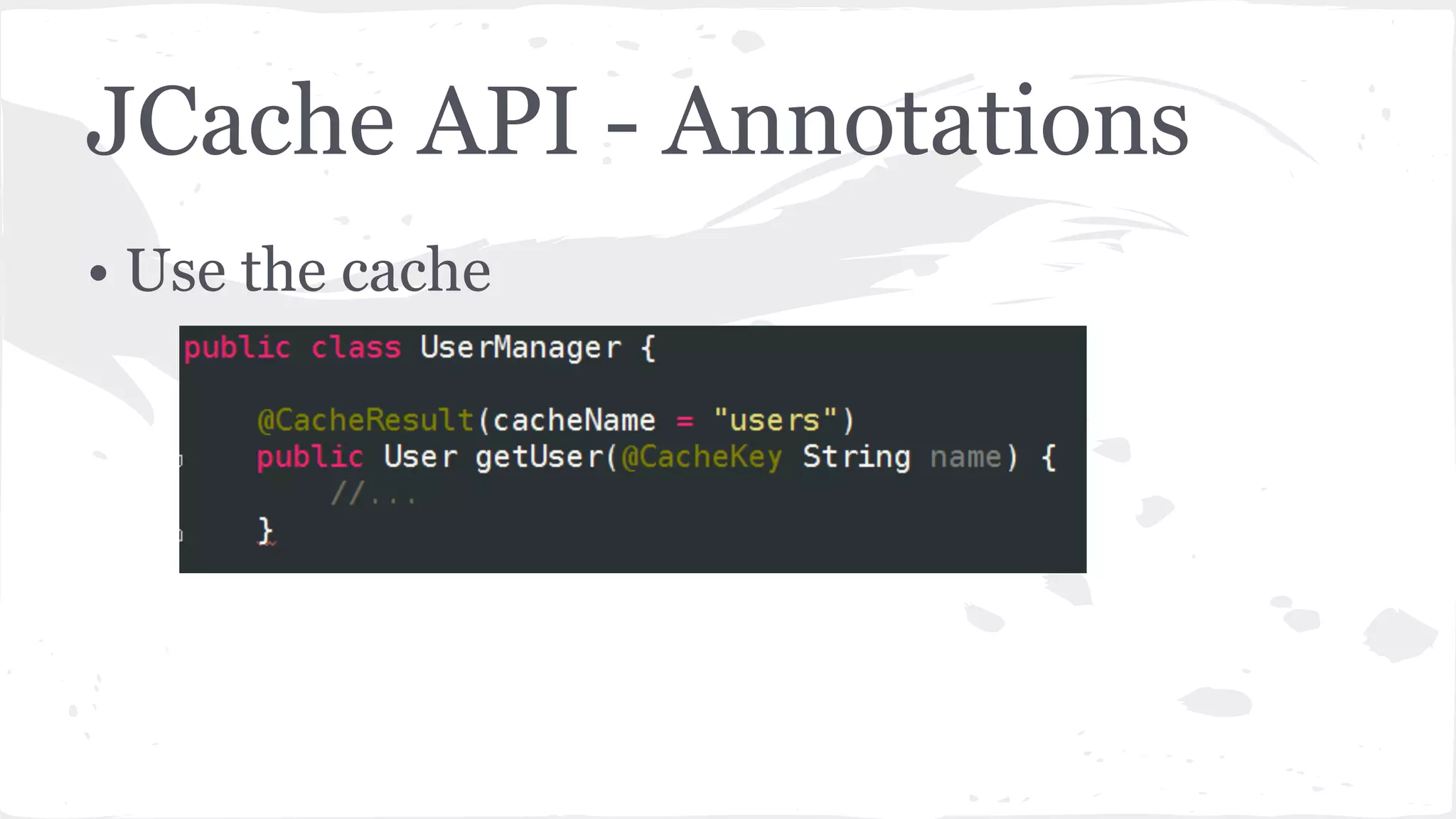
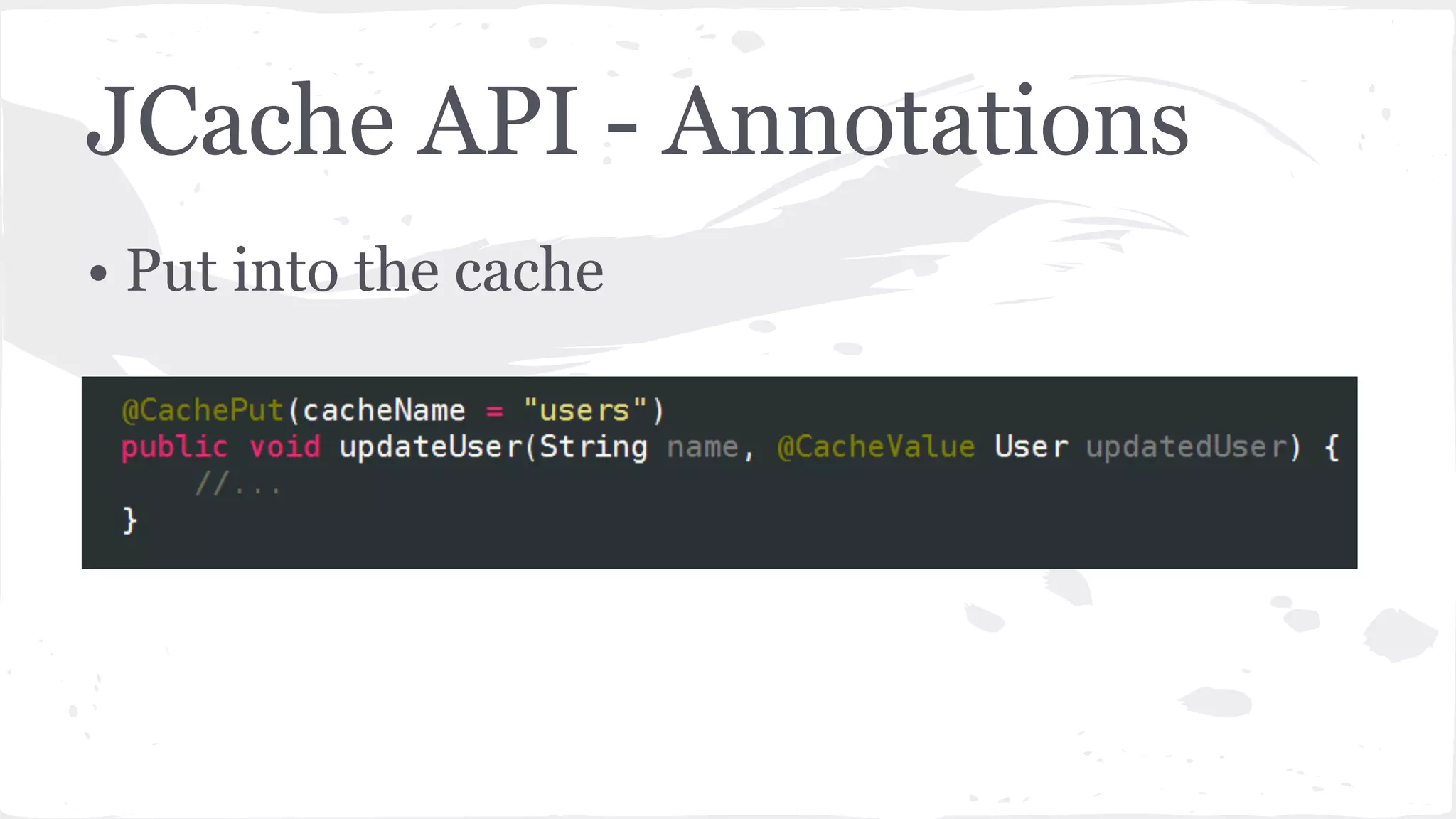
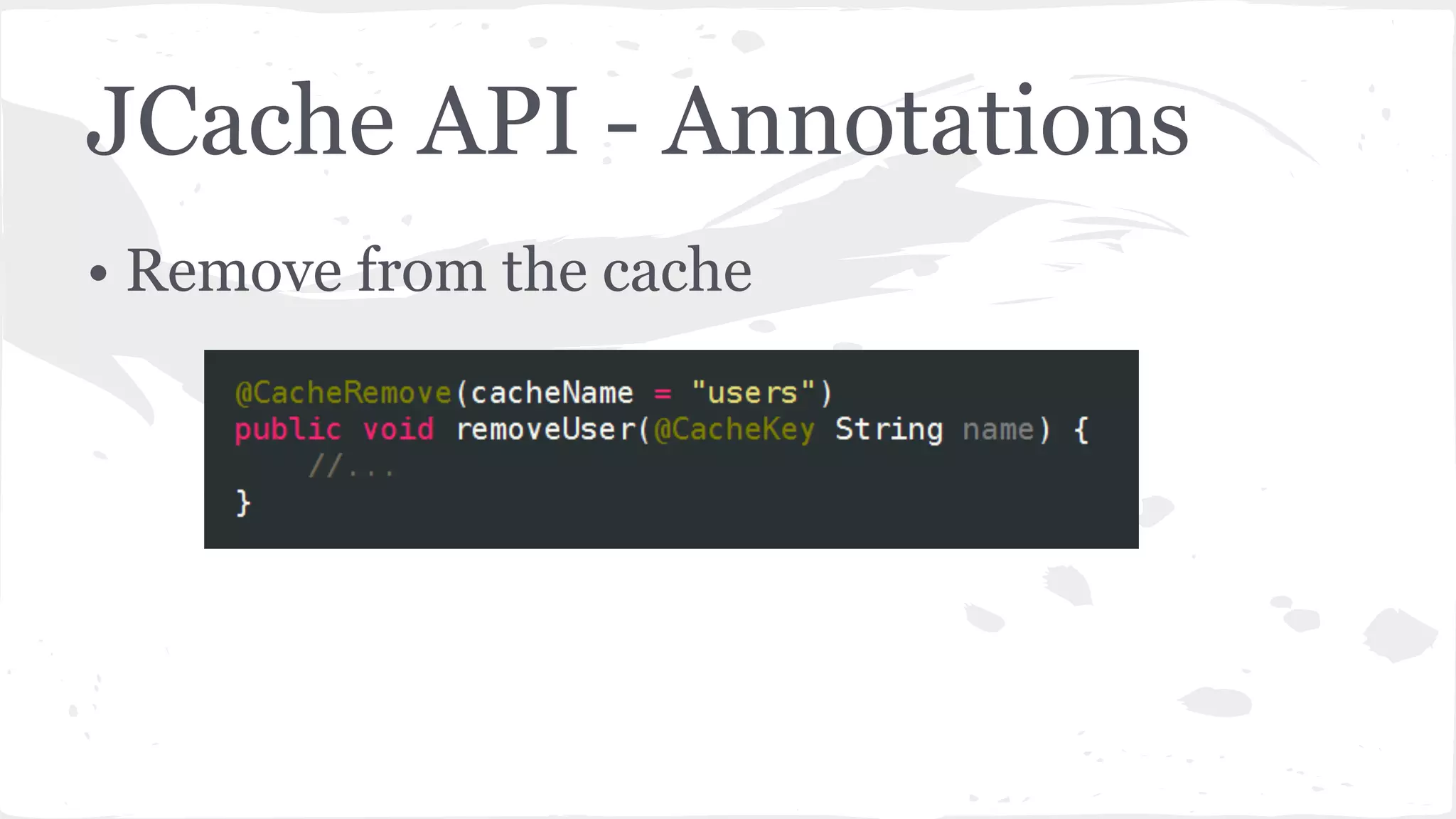
The document discusses distributed caching with Java, explaining its necessity for improving application performance by addressing data retrieval bottlenecks. It compares various cache types including local, replicated, and distributed caches, detailing their pros, cons, and access patterns. Additionally, it introduces the Java JCache specification as a standard API for caching mechanisms and provides examples of its implementations.