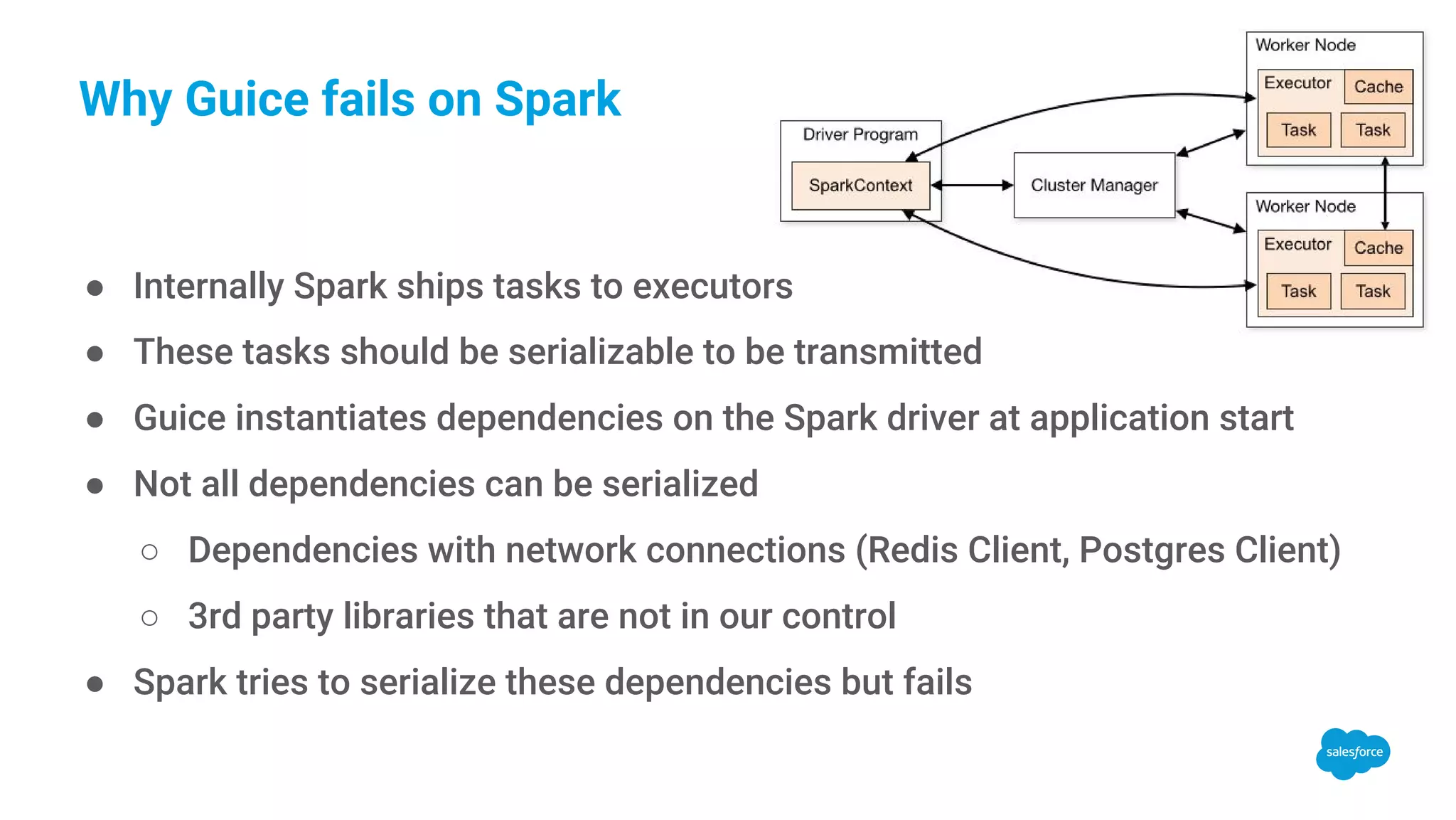
The document discusses dependency injection in Apache Spark applications, specifically within the Signals team at Salesforce. It covers the use of the Guice framework for managing dependencies, highlights potential pitfalls related to serialization of non-serializable dependencies, and introduces a custom library called Injector Provider that facilitates creating serializable injectors. The document concludes that while modular Spark jobs are challenging, using an Injector Provider enables effective dependency injection in Spark environments.



![Simple Spark application
val spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("Example").master("local").getOrCreate()
import spark.implicits._
// Create DataFrame representing the stream of input lines
val lines = spark.readStream
.format("socket")
.option("host", "localhost")
.option("port", 9999)
.load()
// Split the lines into words
val words = lines.as[String].flatMap(_.split(" "))
// Generate running word count
val wordCounts = words.groupBy("value").count()
// Start running the query that saves word counts to redis
val query = wordCounts.writeStream
.foreach(new BasicRedisWriter)
.outputMode("update")
.start()
query.awaitTermination()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectioninapachesparkapplications-170524003017/75/Dependency-Injection-in-Apache-Spark-Applications-6-2048.jpg)



![Using Guice to inject dependencies
// Inject RedisClient
class GuiceRedisWriter @Inject()(redisClient: RedisClient) extends ForeachWriter[Row] {
...
}
// Inject the abstract ForeachWriter[Row]. Guice module will set the proper implementation
class GuiceExample @Inject()(writer: ForeachWriter[Row]) {
def countWords(spark: SparkSession, lines: DataFrame): StreamingQuery = { ... }
}
// Guice Module that provides implementations for dependencies
class GuiceExampleModule extends AbstractModule with ScalaModule {
@Provides @Singleton
def provideRedisClient(): RedisClient = new RedisClient("localhost", 6379)
@Provides @Singleton
def provideForeachWriter(redis: RedisClient): ForeachWriter[Row] = new GuiceRedisWriter(redis)
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Create the injector and get instance of class
val injector = Guice.createInjector(new GuiceExampleModule)
val wordCounter = injector.getInstance(classOf[GuiceExample])
// Create Spark Session and Stream. Then call countWords of GuiceExample instance
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectioninapachesparkapplications-170524003017/75/Dependency-Injection-in-Apache-Spark-Applications-11-2048.jpg)






![Using Injector Provider
class InjectorProviderExampleModule extends AbstractModule {
@Provides @Singleton
def provideForeachWriter(stub: ProvidedInjectorStub, redisClient: RedisClient): ForeachWriter[Row] = {
new InjectorProviderRedisWriter(stub, redisClient)
}
}
class InjectorProviderRedisWriter @Inject()(stub: ProvidedInjectorStub, _redisClient: RedisClient) extends
ForeachWriter[Row] {
// Make the RedisClient transient and Injectable so it does not get serialized by the JVM
@Inject @transient
private val redisClient = _redisClient
// Deserialize this object and then use stub to inject all members
private def readObject(in: ObjectInputStream): Unit = {
in.defaultReadObject()
stub.injectMembers(this)
}
...
}
// Extend abstract class which internally injects all @Inject annotated objects
class InjectorProviderExample @Inject() (writer: ForeachWriter[Row]) extends ProvidedInjector { /* Same */ }
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Create the injector and get instance
val injector = InjectorProvider.builder().addBootstrapModuleTypes(classOf[InjectorProviderModule]).build()
val wordCounter = injector.getInstance(classOf[InjectorProviderExample])
// Create Spark Session and Stream. Then call countWords of GuiceExample instance
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dependencyinjectioninapachesparkapplications-170524003017/75/Dependency-Injection-in-Apache-Spark-Applications-20-2048.jpg)

