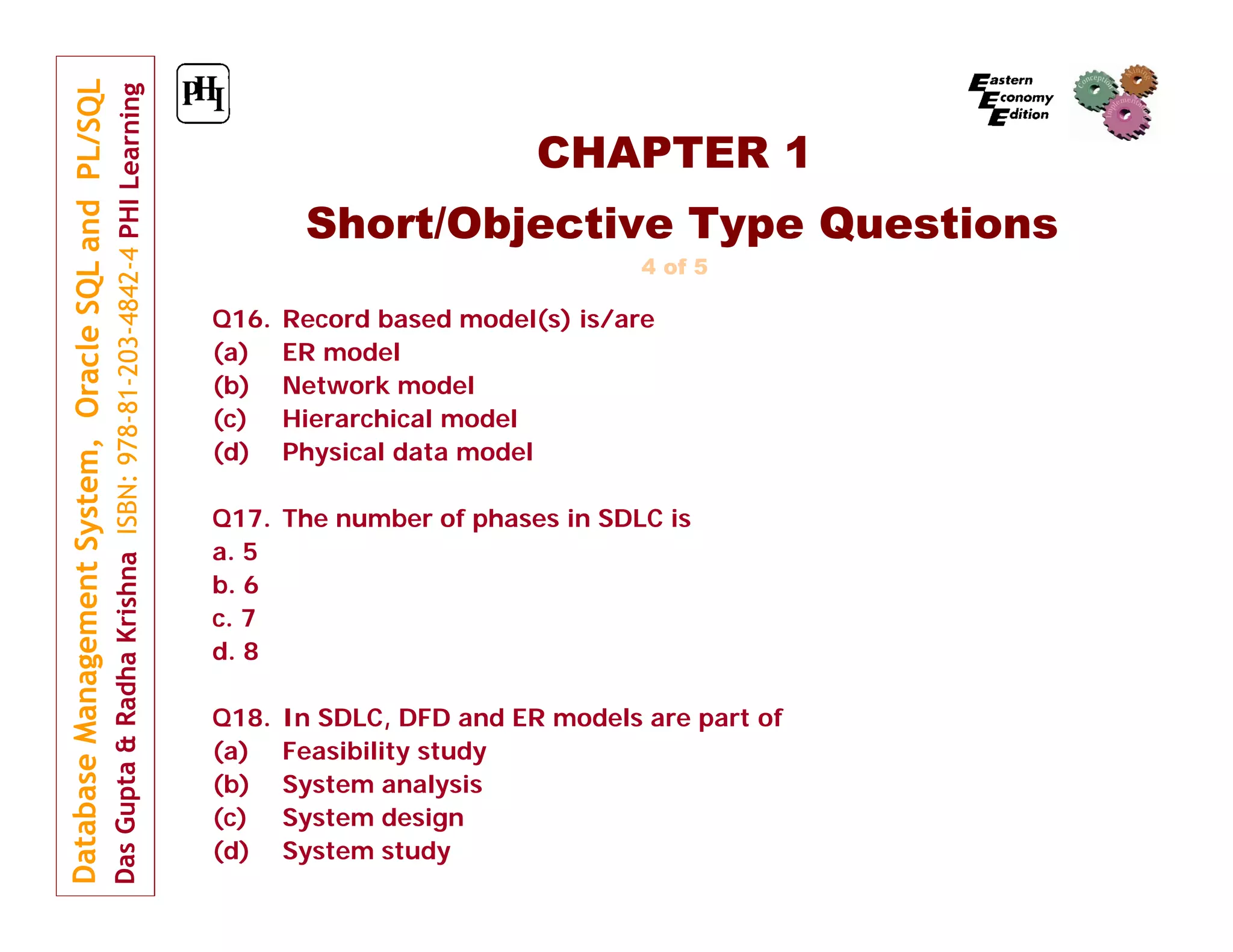
The document summarizes the contents and structure of a book on database management systems using Oracle SQL and PL/SQL. It is divided into three parts that cover fundamental database concepts, Oracle SQL programming, and advanced database topics. Part I focuses on database basics, modeling techniques, SQL queries and functions. It also addresses relational algebra, normalization and database security. The book includes over 300 examples, 400 questions, and 100 exercises to illustrate and reinforce the concepts. Instructors can access additional teaching materials on the publisher's website.
![CHAPTER 1
Database Basics
3 of 3
DBMS ARCHITECTURE
Internal Level
Conceptual Level
External Level
DBMS MODELS
Record-Based Model [ Ex. Network, Hierarchical & Relational]
Object-based Database Model
Physical Data Model
Page reference in the book: 6-7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databasemanagementsystemchapter1-131124025745-phpapp01/75/Database-management-system-chapter1-5-2048.jpg)



![DATABASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
ORACLE SQL AND PL/SQL
PART I : Basic Concepts & Oracle SQL
Periods Proposed - 10
Chapter 1
Database Basics, System Analysis & Design, Data Flow Diagram & ER Model
2 Periods [Theory]
Chapter 2
Relational Algebra and Normal Forms
2 Periods [Theory]
Chapter 3
SQL Basics, Functions, Sub query & Joins
1 Period [Theory]
2 Period [Practical]
Chapter 4
Data Manipulation Language, Objects, Constraints and Security in Oracle
1 Period [Theory]
2 Period [Practical]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/databasemanagementsystemchapter1-131124025745-phpapp01/75/Database-management-system-chapter1-22-2048.jpg)

