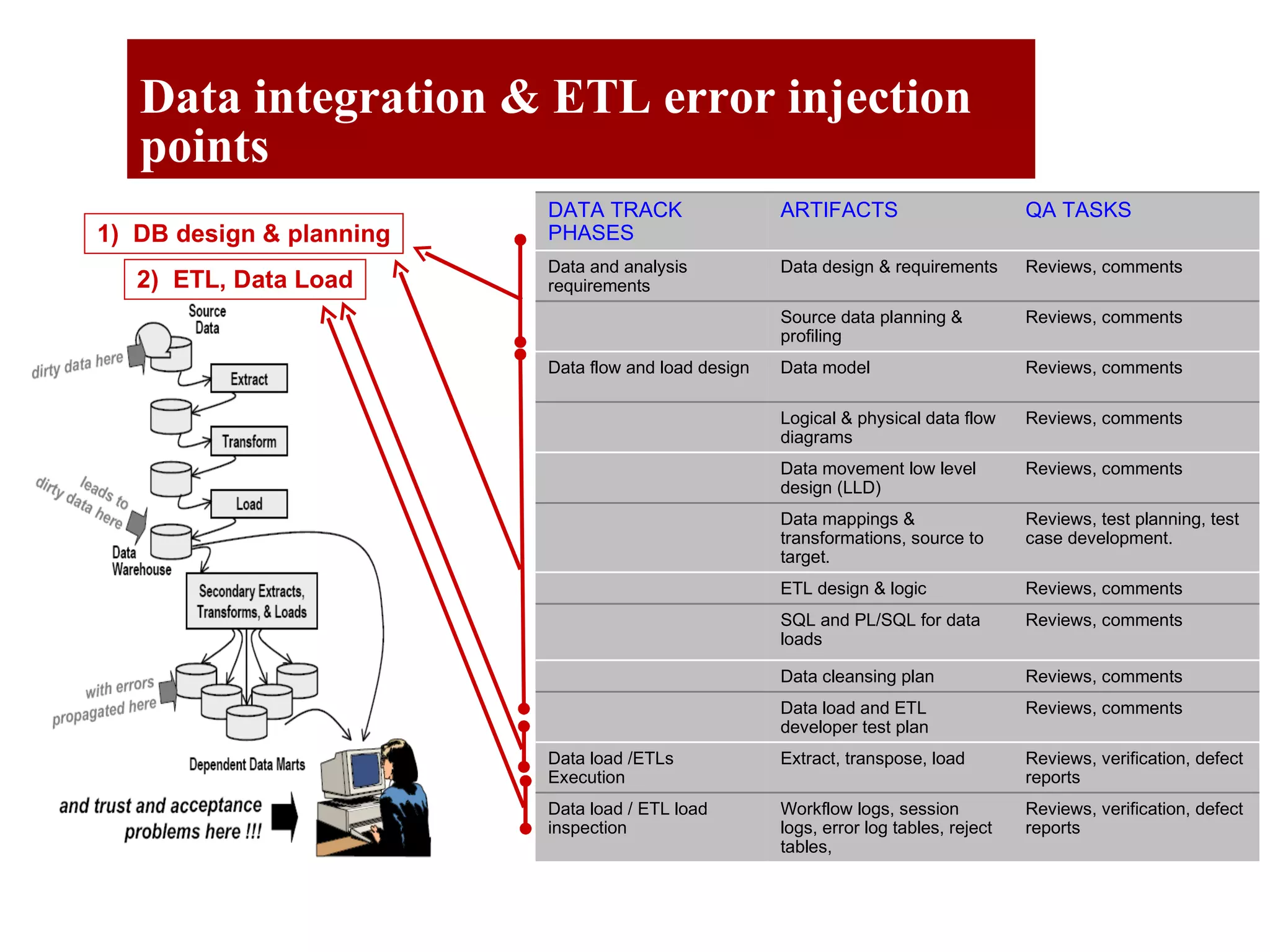
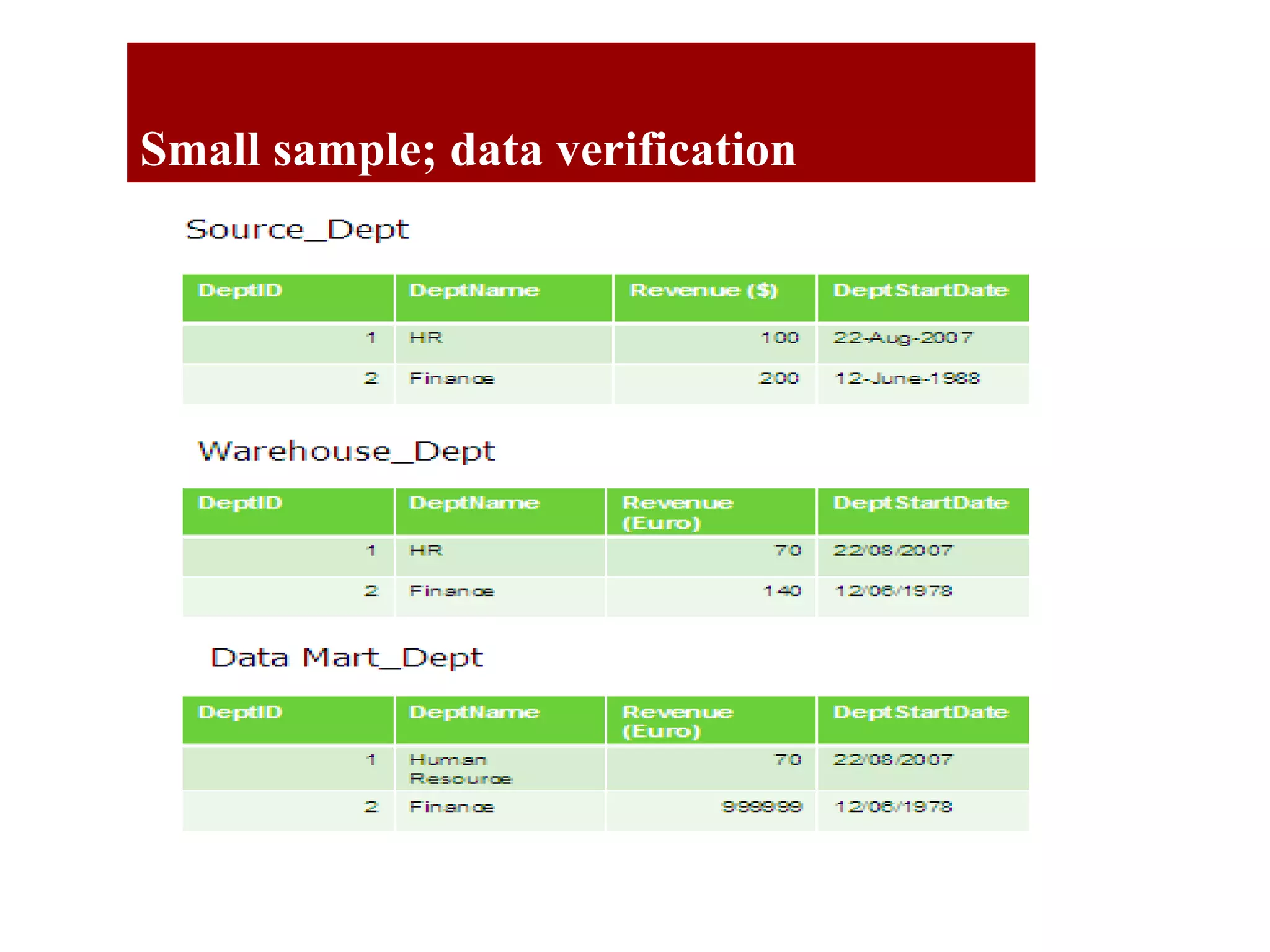
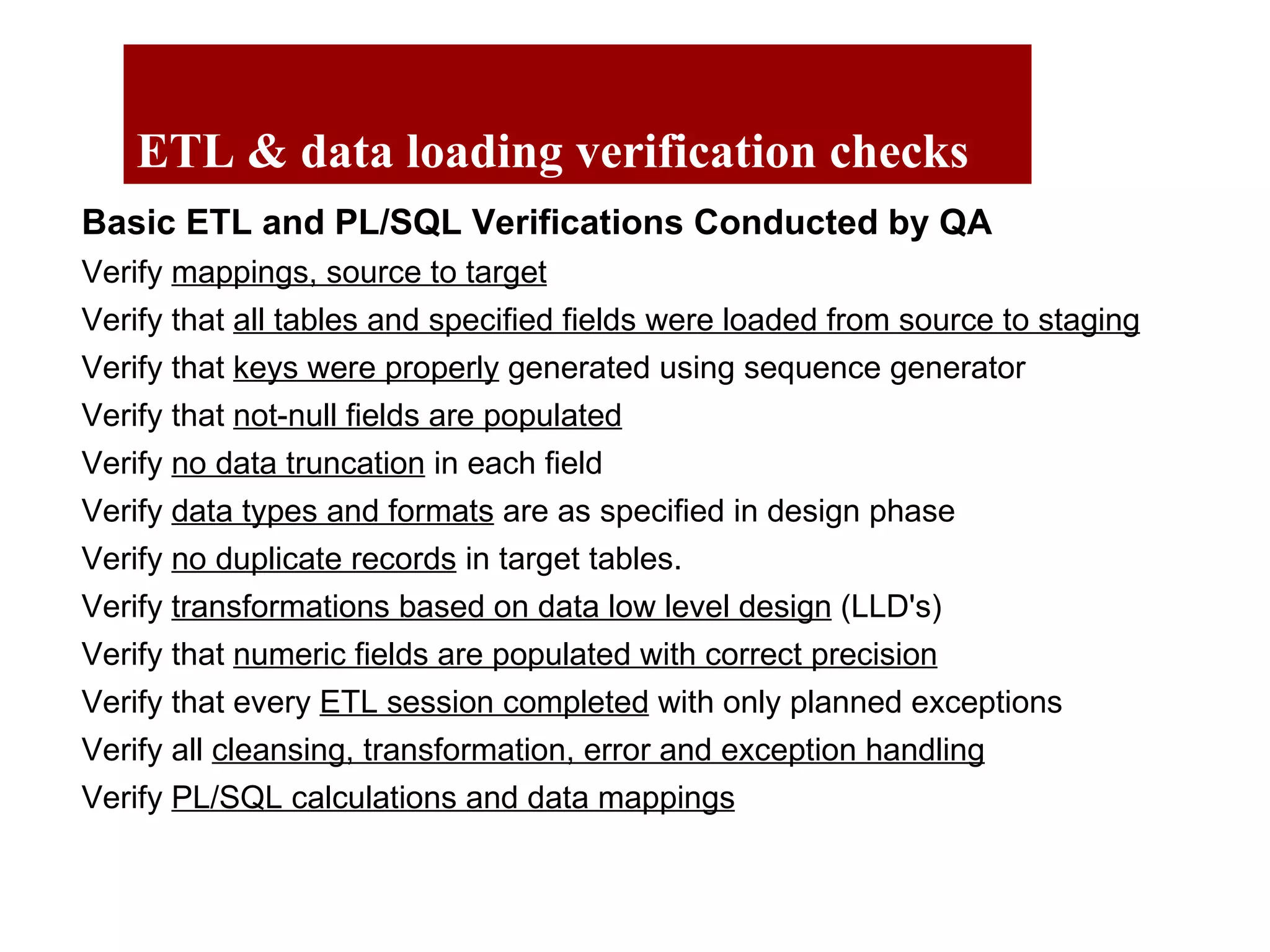
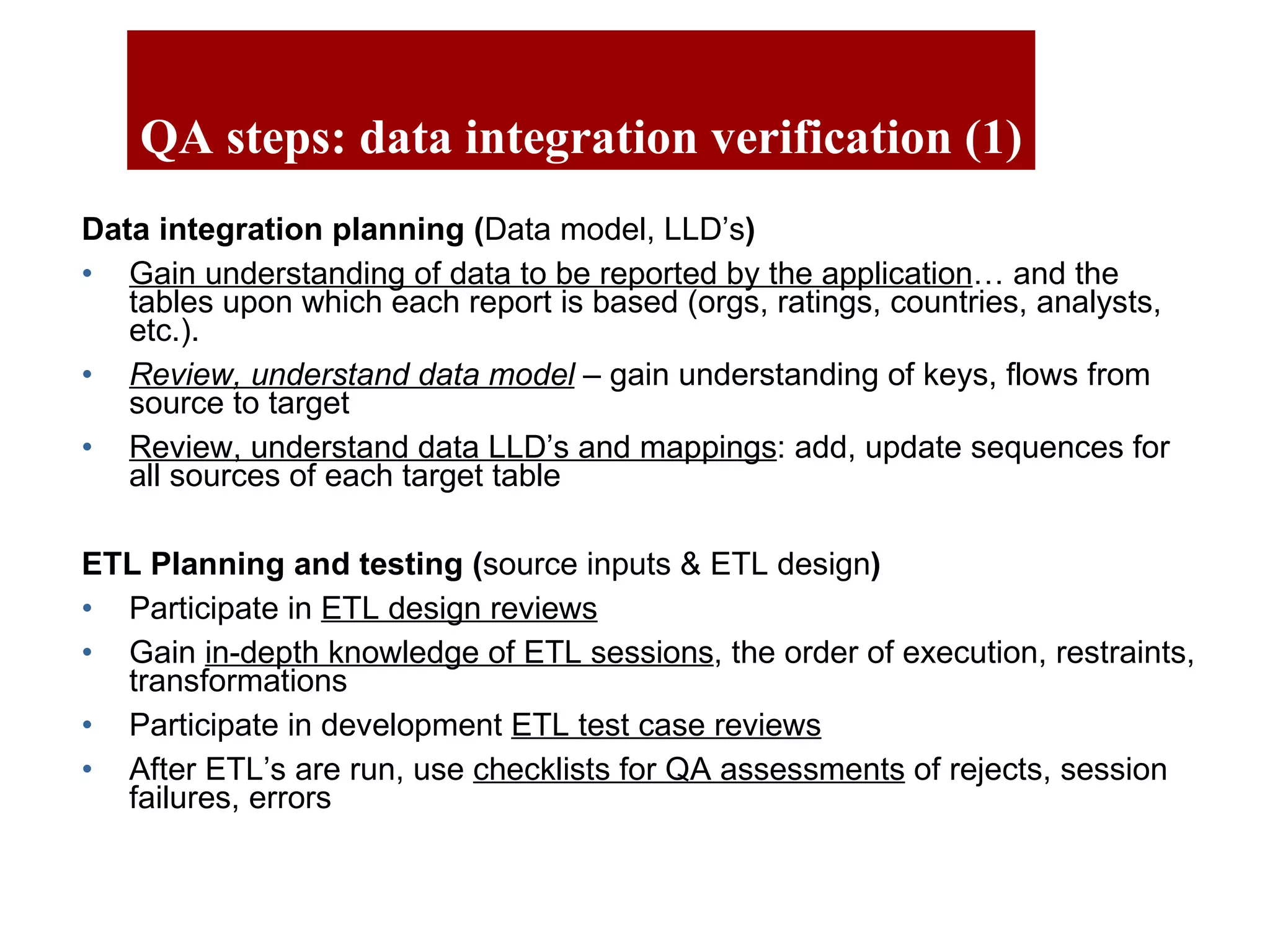
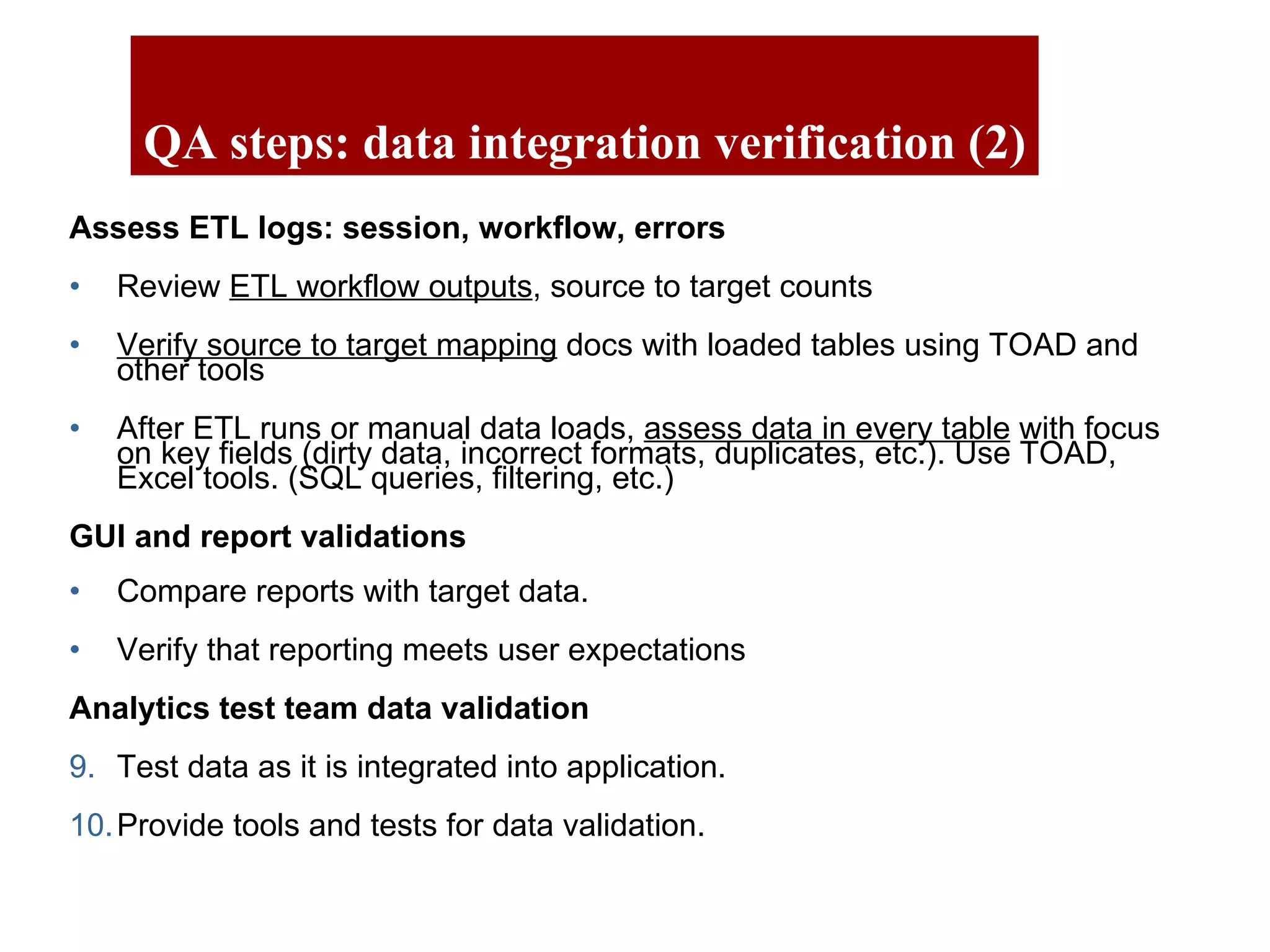
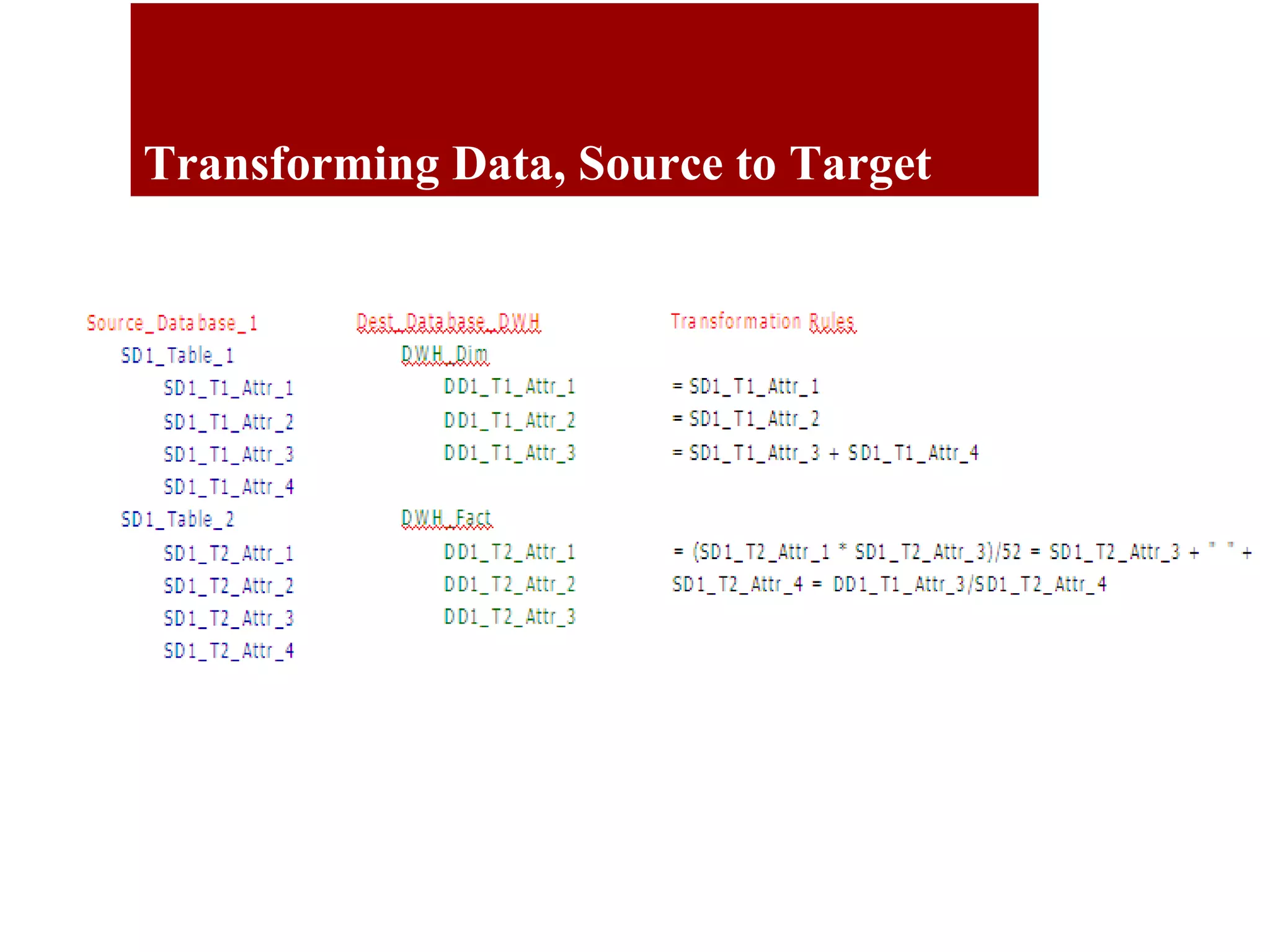
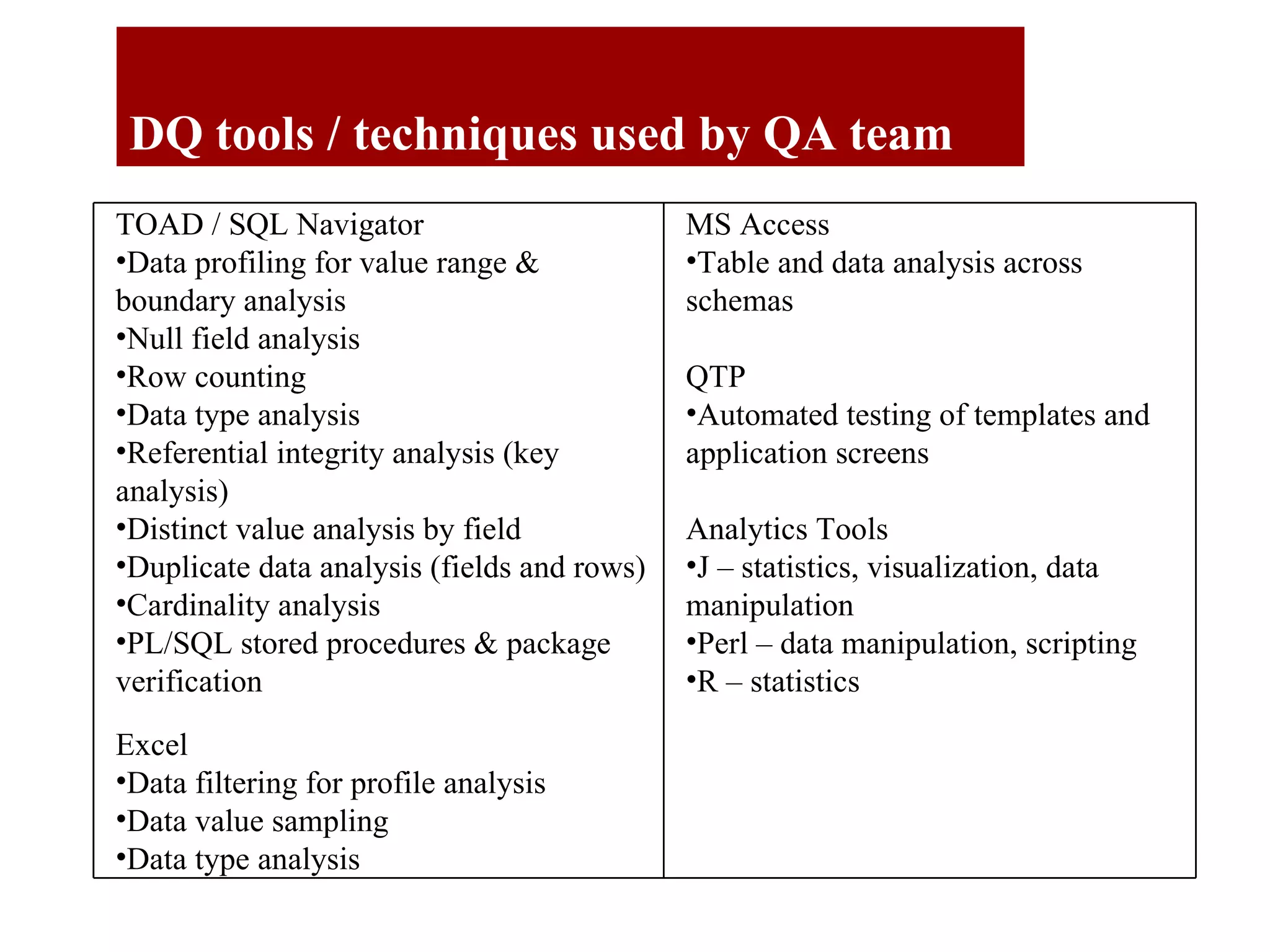
The document outlines the QA objectives and processes for ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and data loading projects, emphasizing the importance of early involvement in data verification to identify and correct defects. It discusses common data defects, QA's role in data verification, and includes recommendations for improving ETL processes, such as maintaining documentation and utilizing data quality tools. Additionally, it presents findings from previous QA projects and highlights the need for improved data integration and verification methods.
![Database and ETL Testing Process Methods, Issues, Recommendations Jan. 19, 2010 W. Yaddow [email_address] For internal use only – Not for external distribution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataverificationinqadepartmentfinal-100406154903-phpapp01/75/Data-Verification-In-QA-Department-Final-1-2048.jpg)