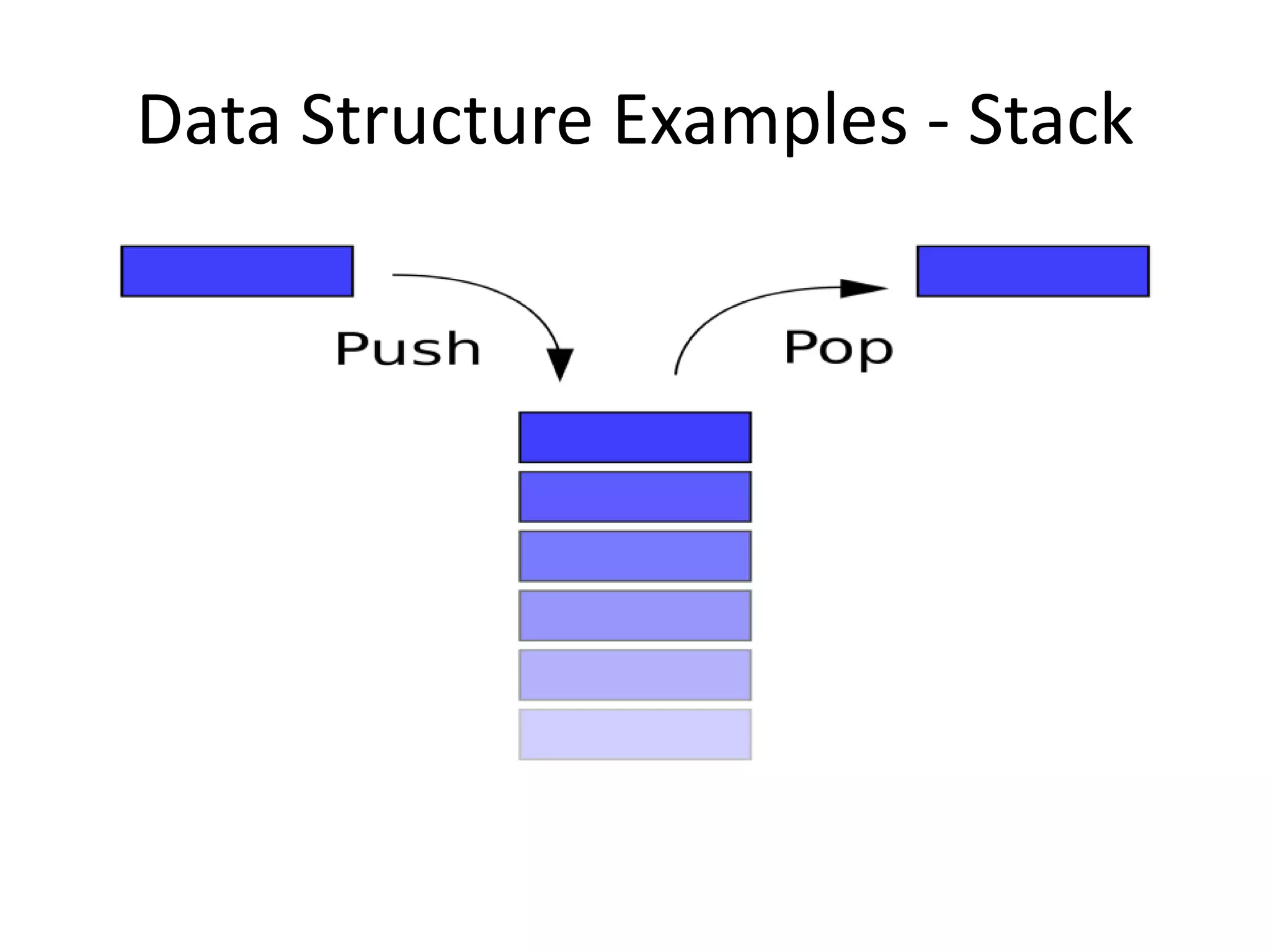
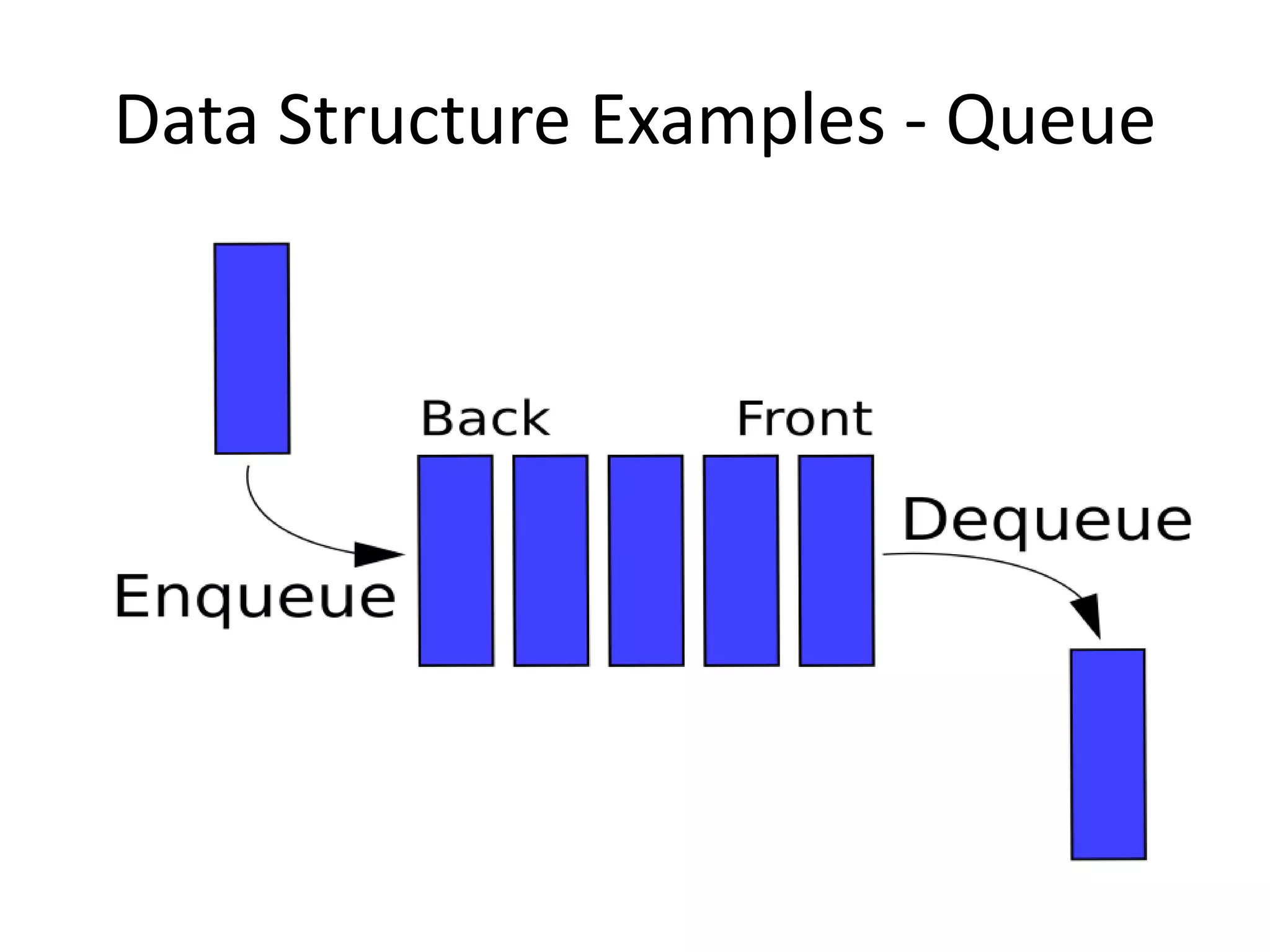
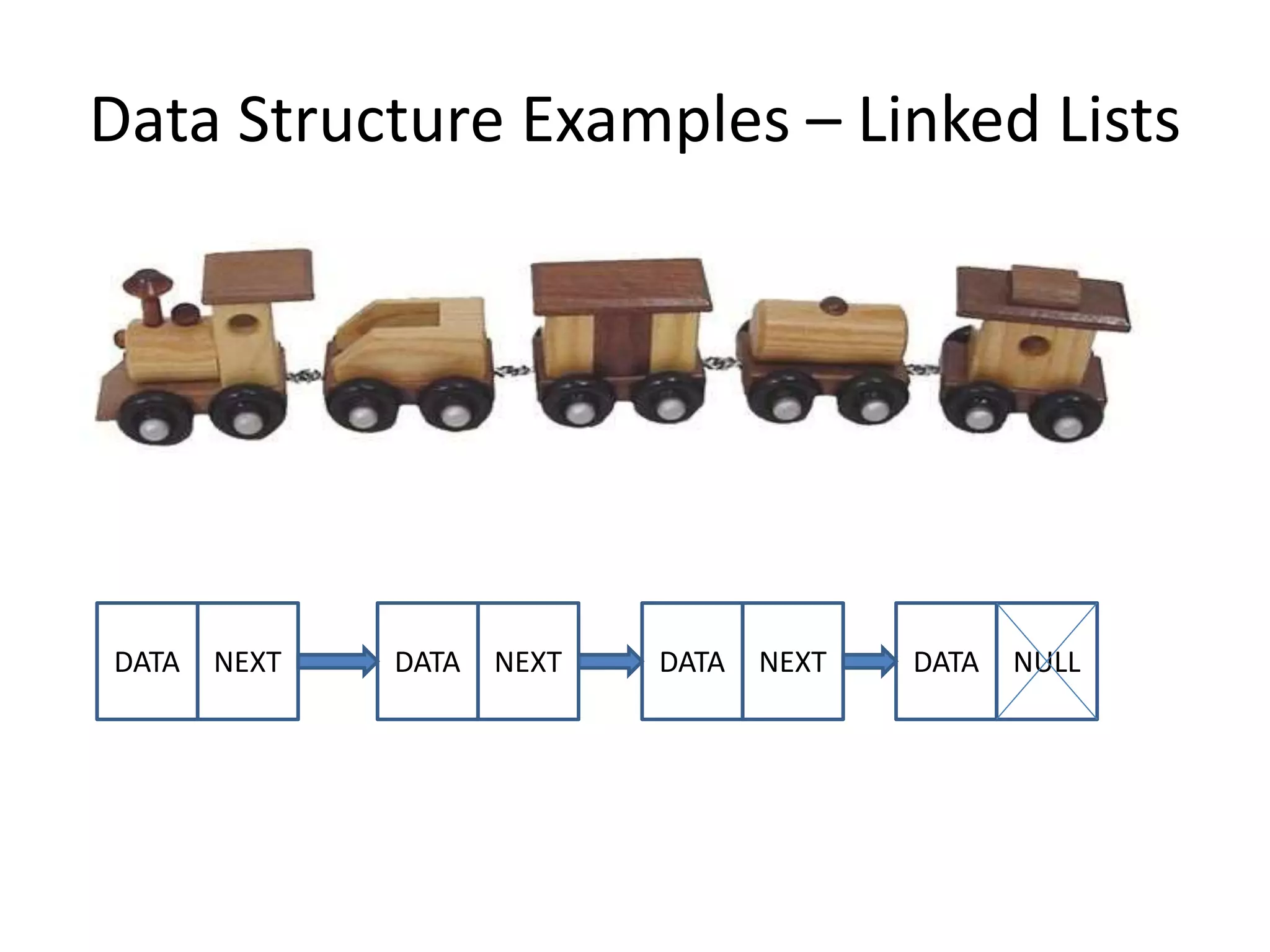
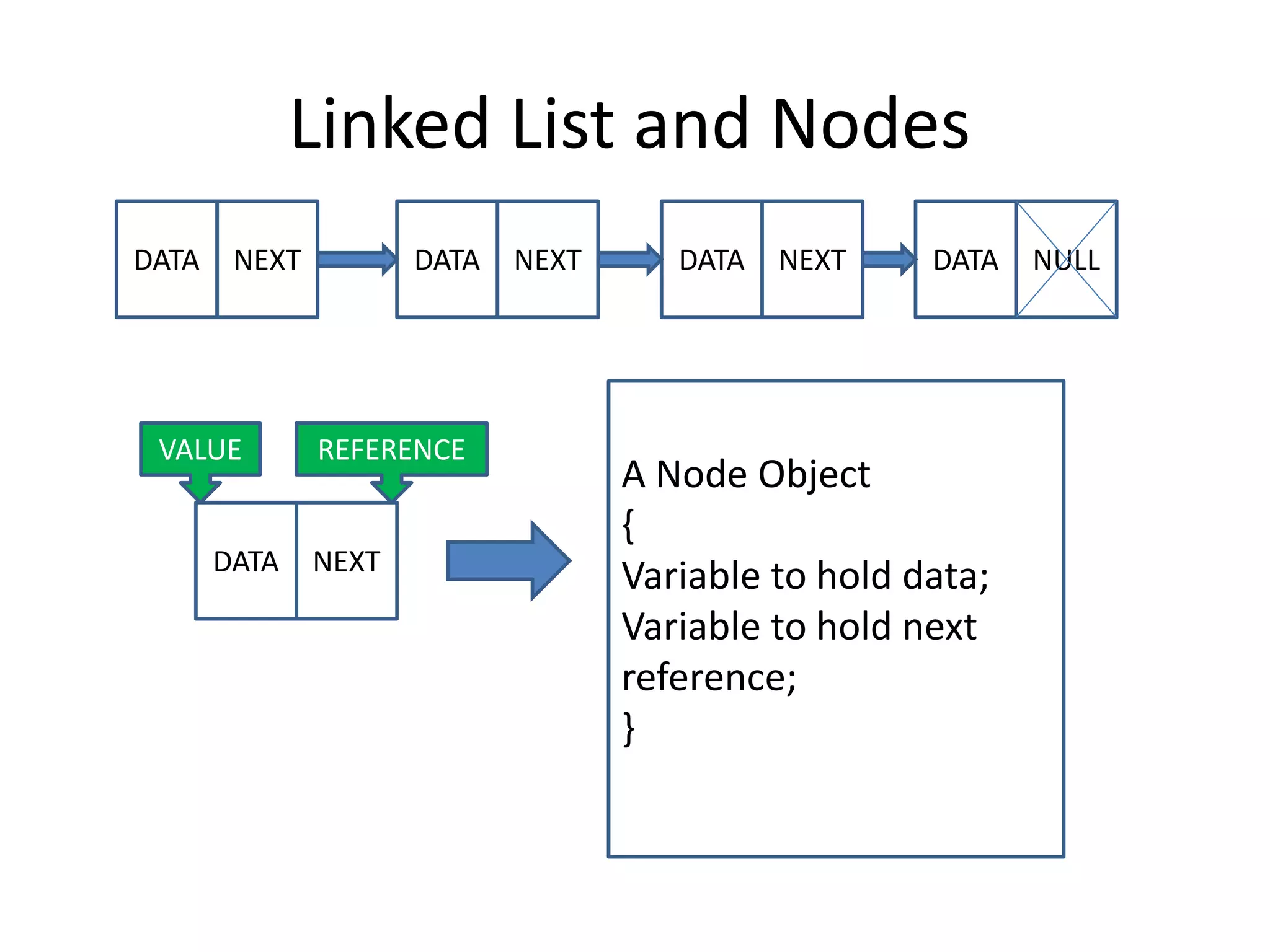
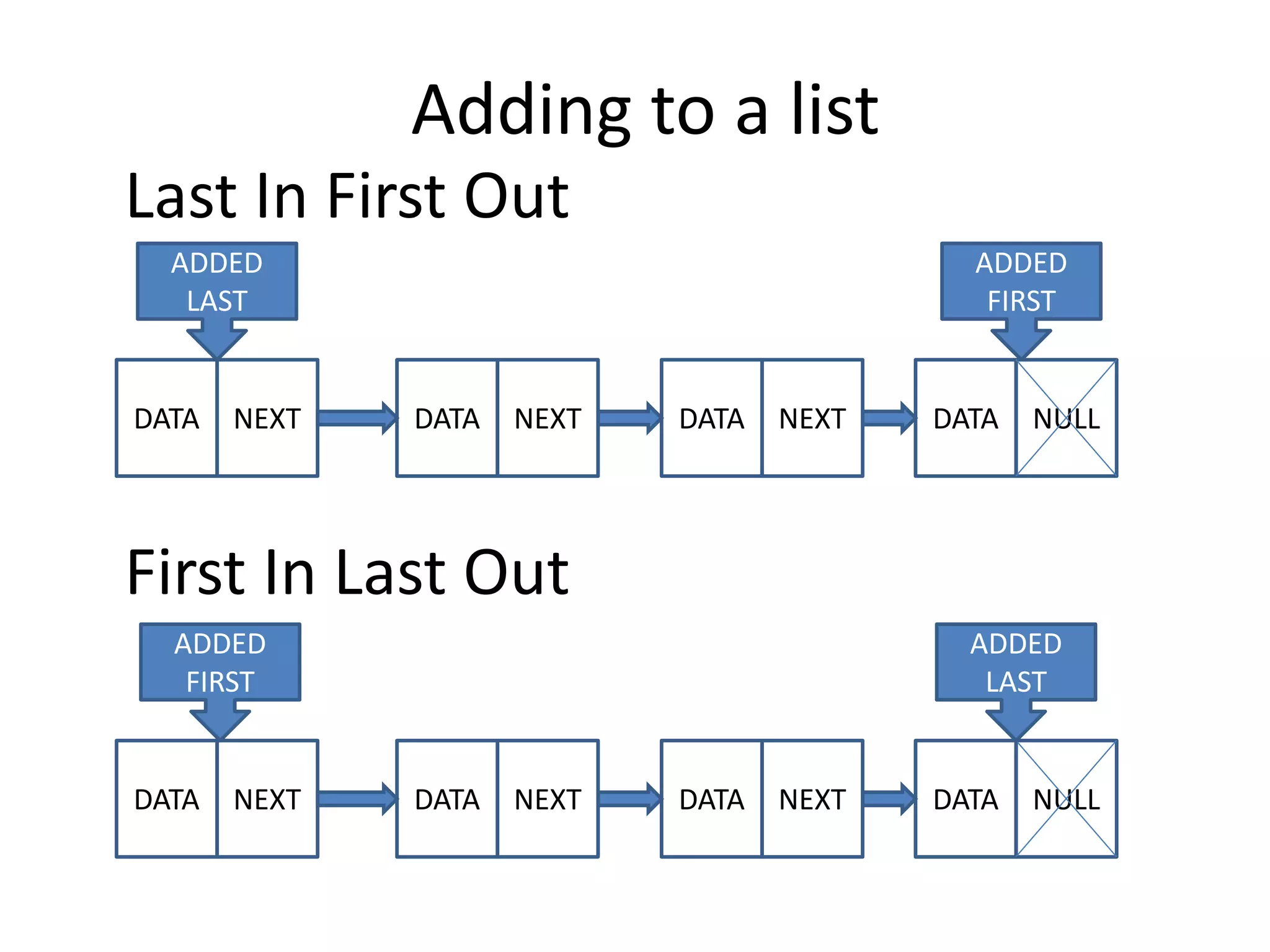
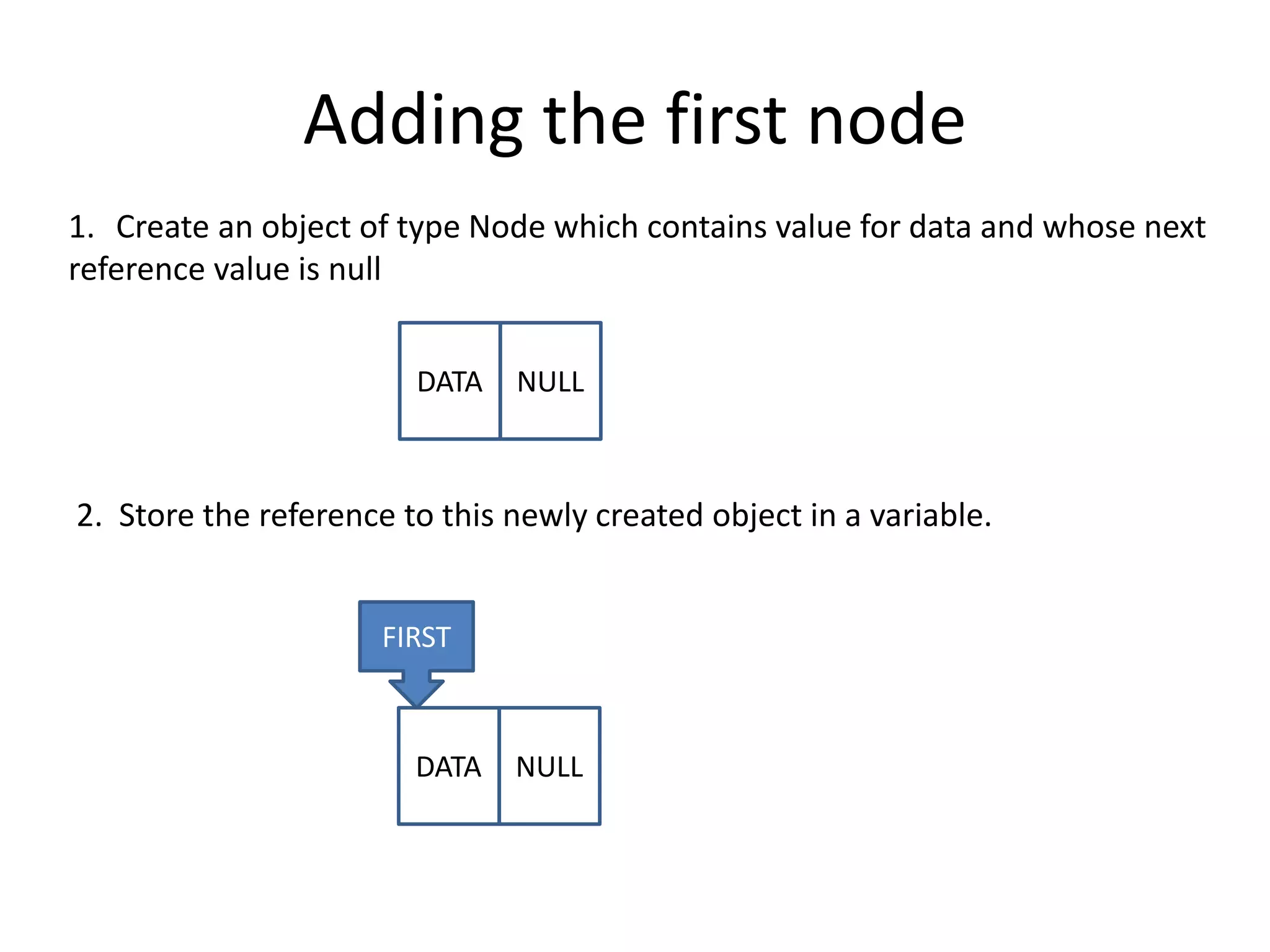
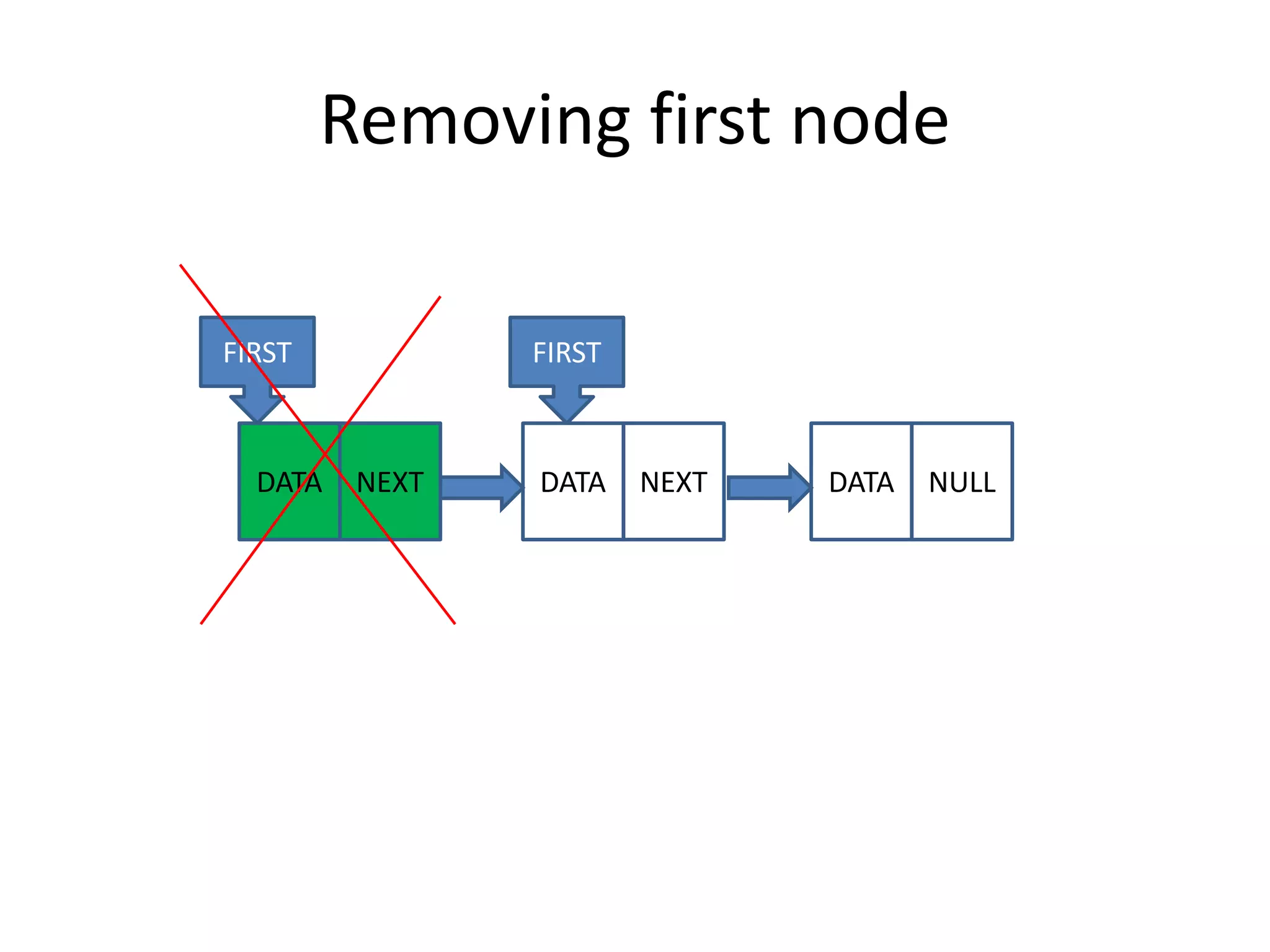
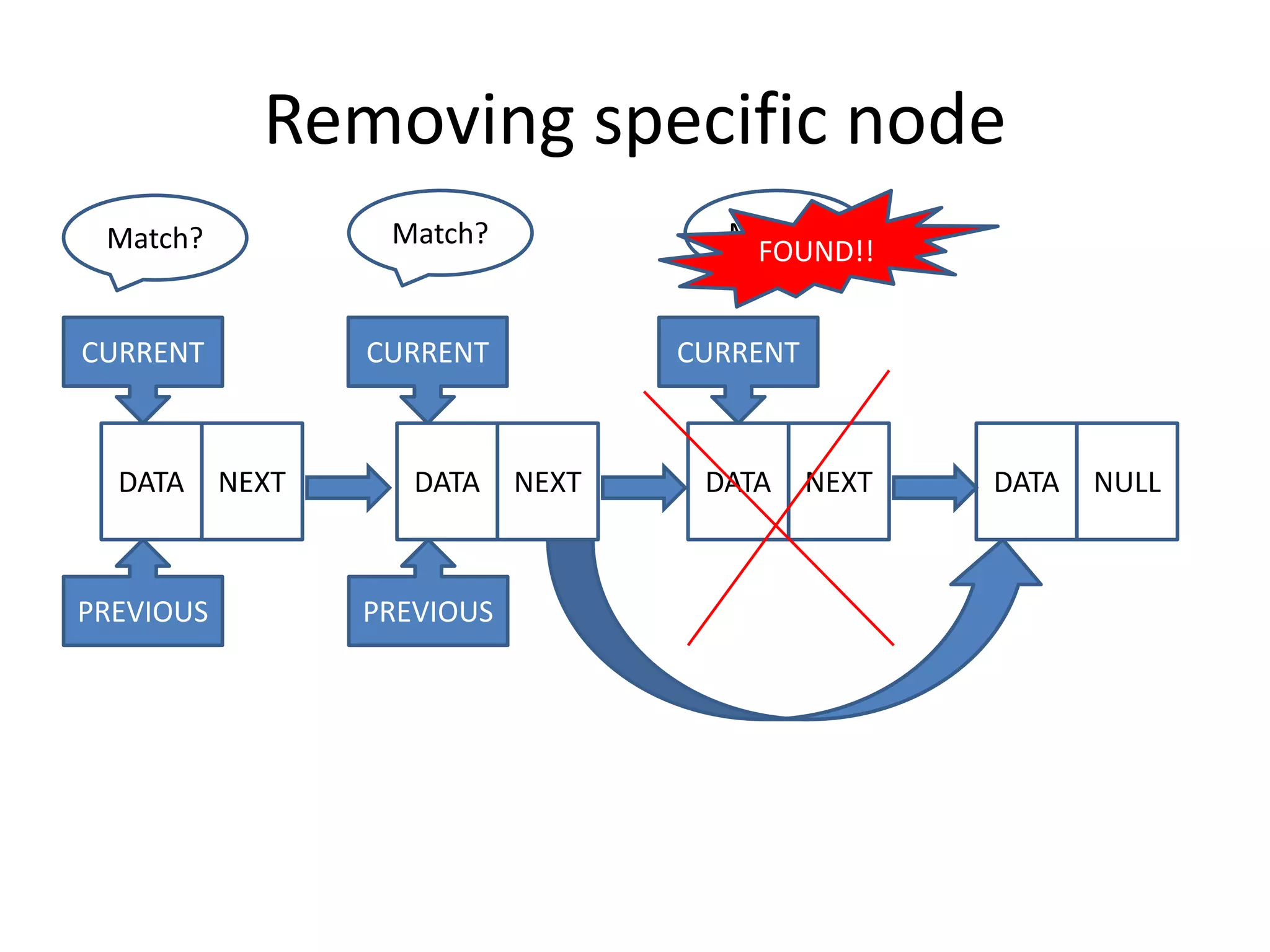
The document discusses data structures, emphasizing their importance in organizing data for efficient program operations. It specifically explains linked lists, including the process of adding and removing nodes within them. Key concepts covered include node creation, linking, and the implications of stack (LIFO) and queue (FIFO) structures.