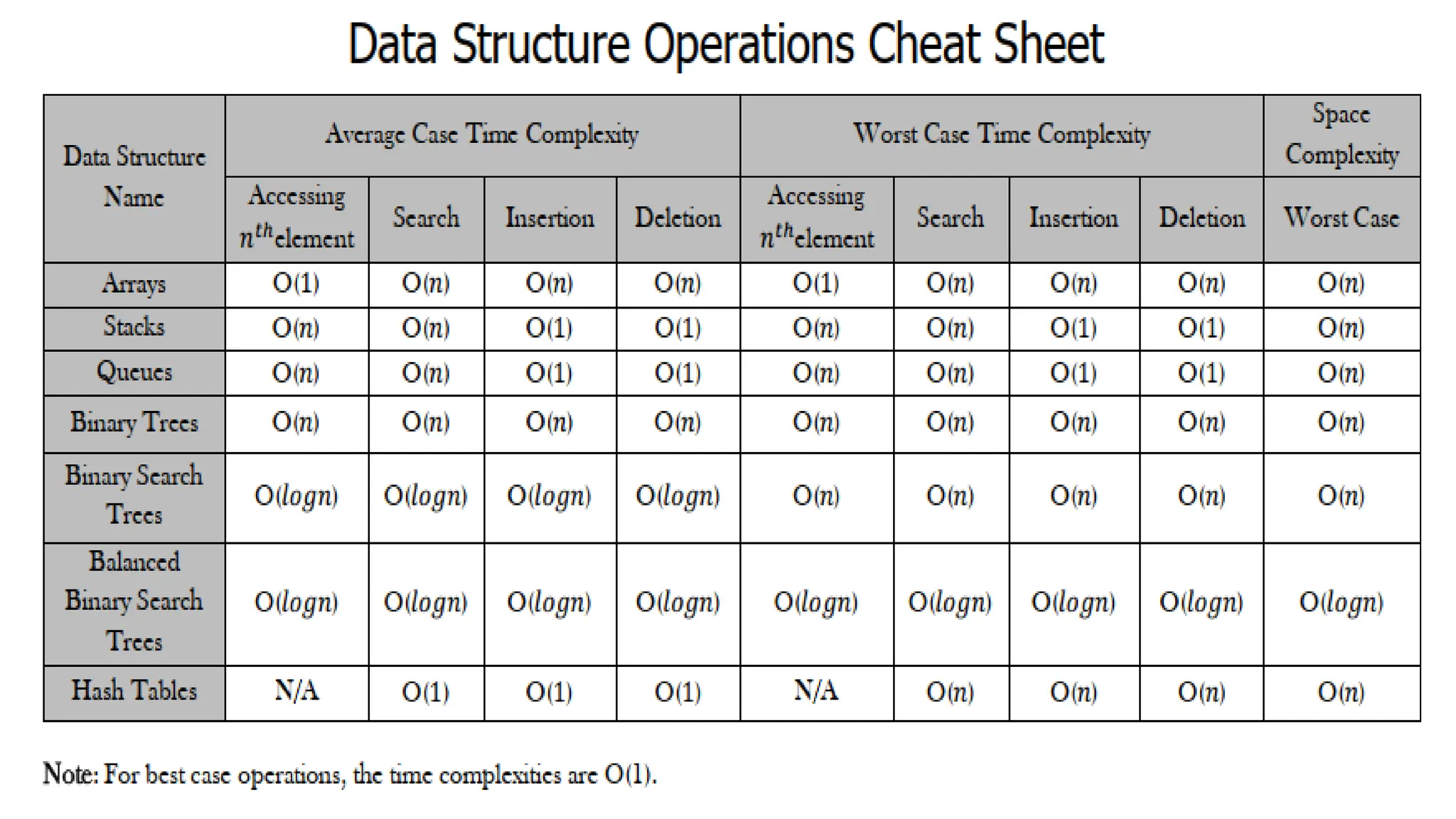
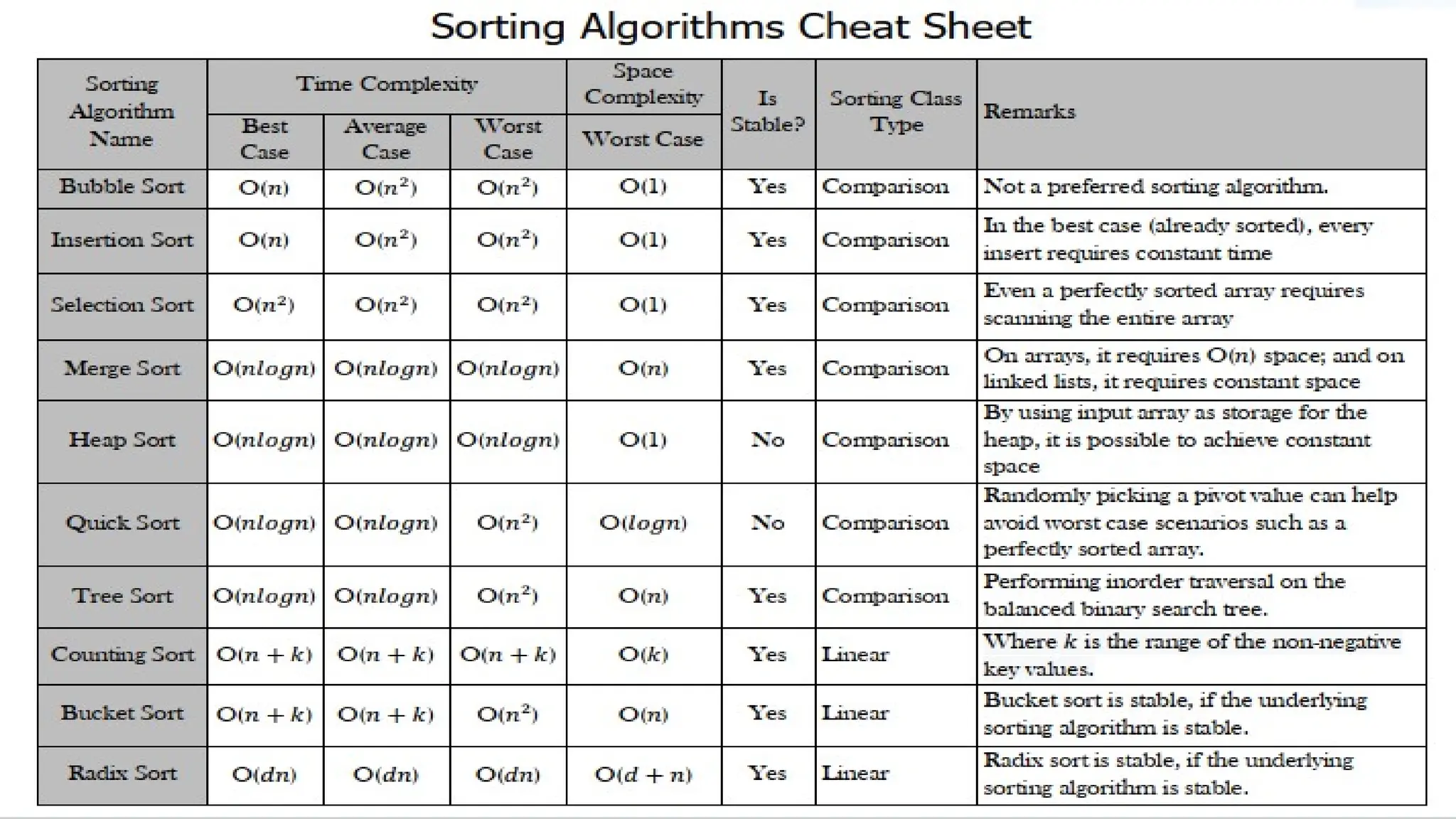
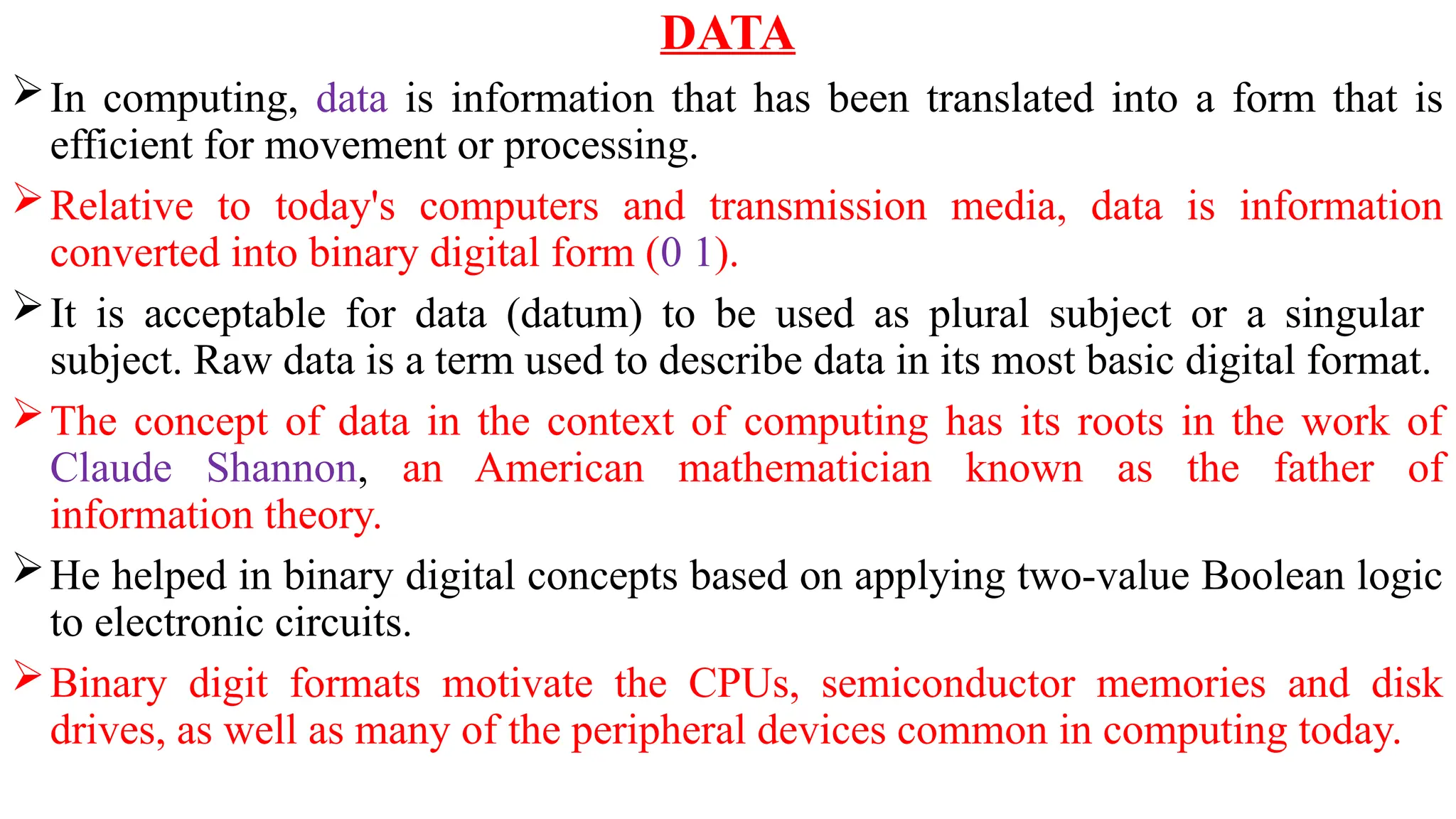
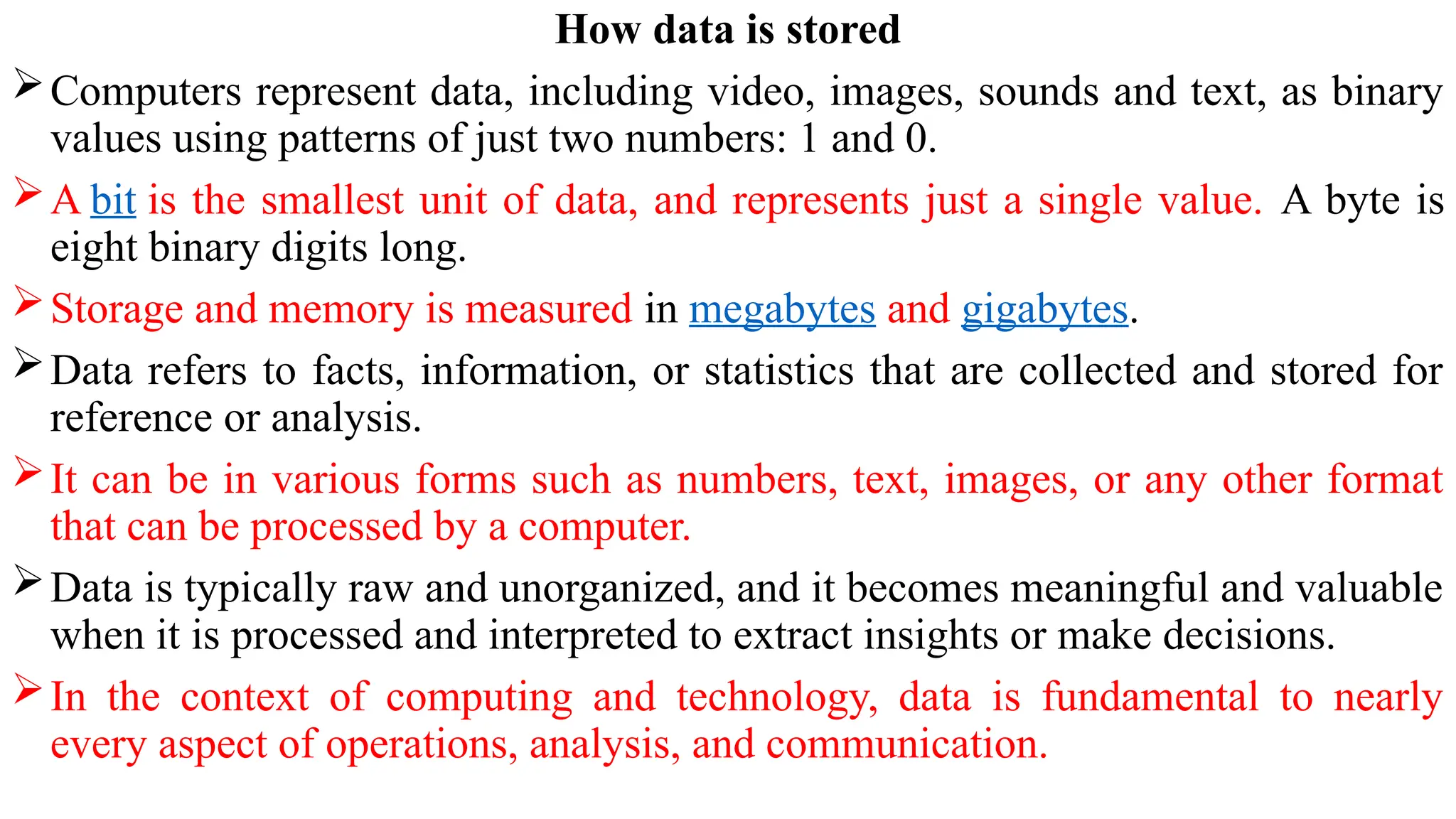
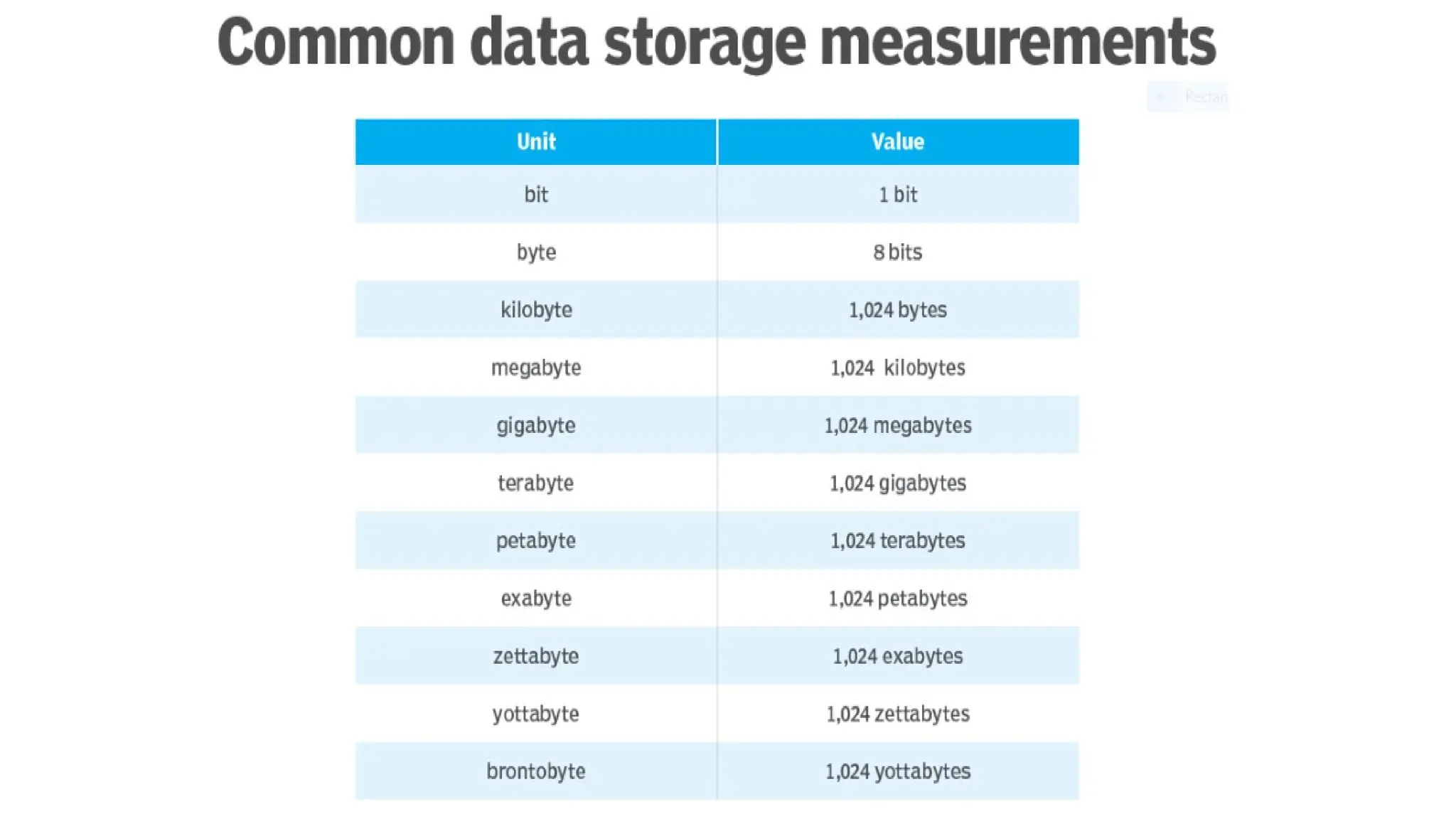
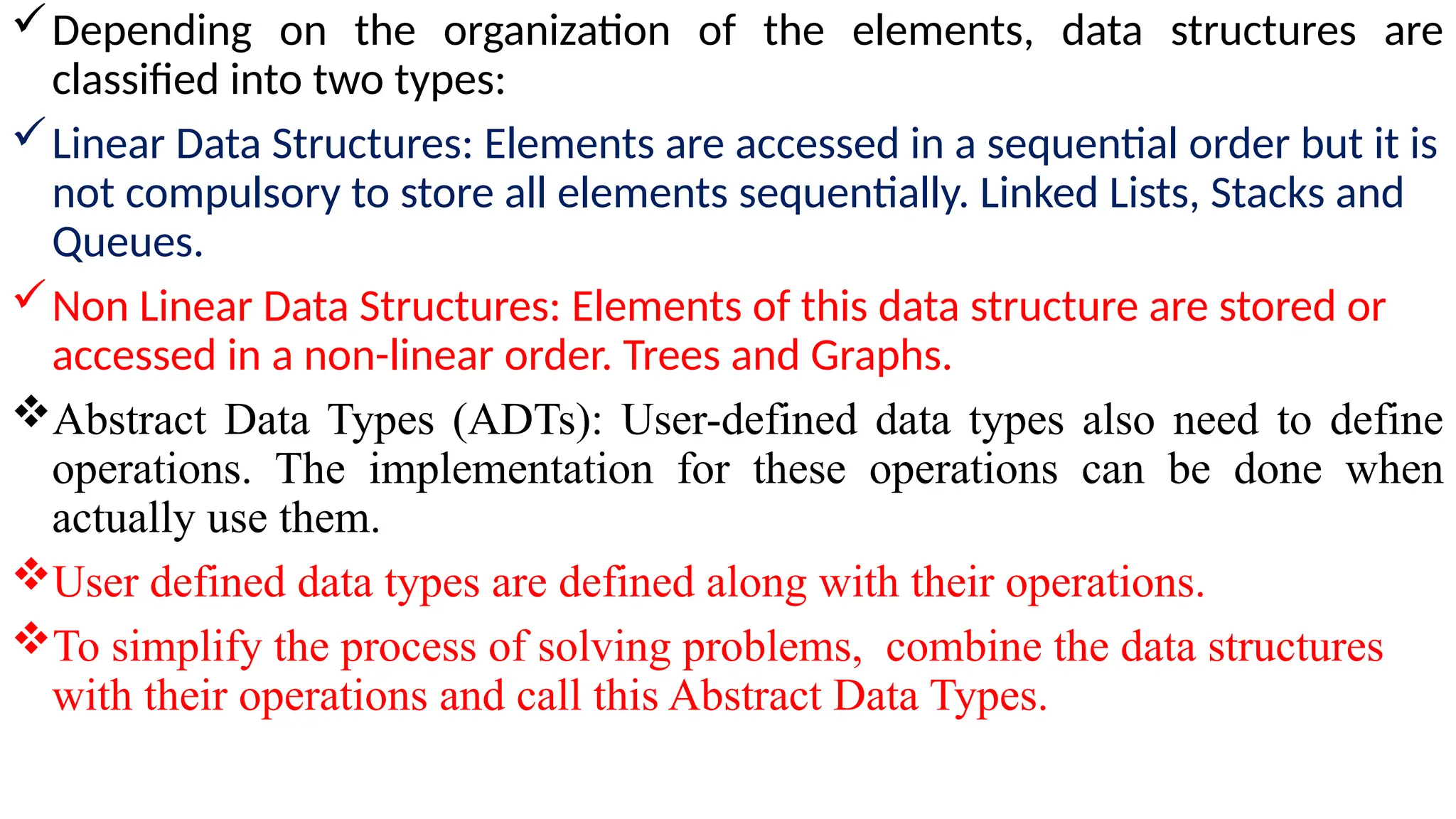
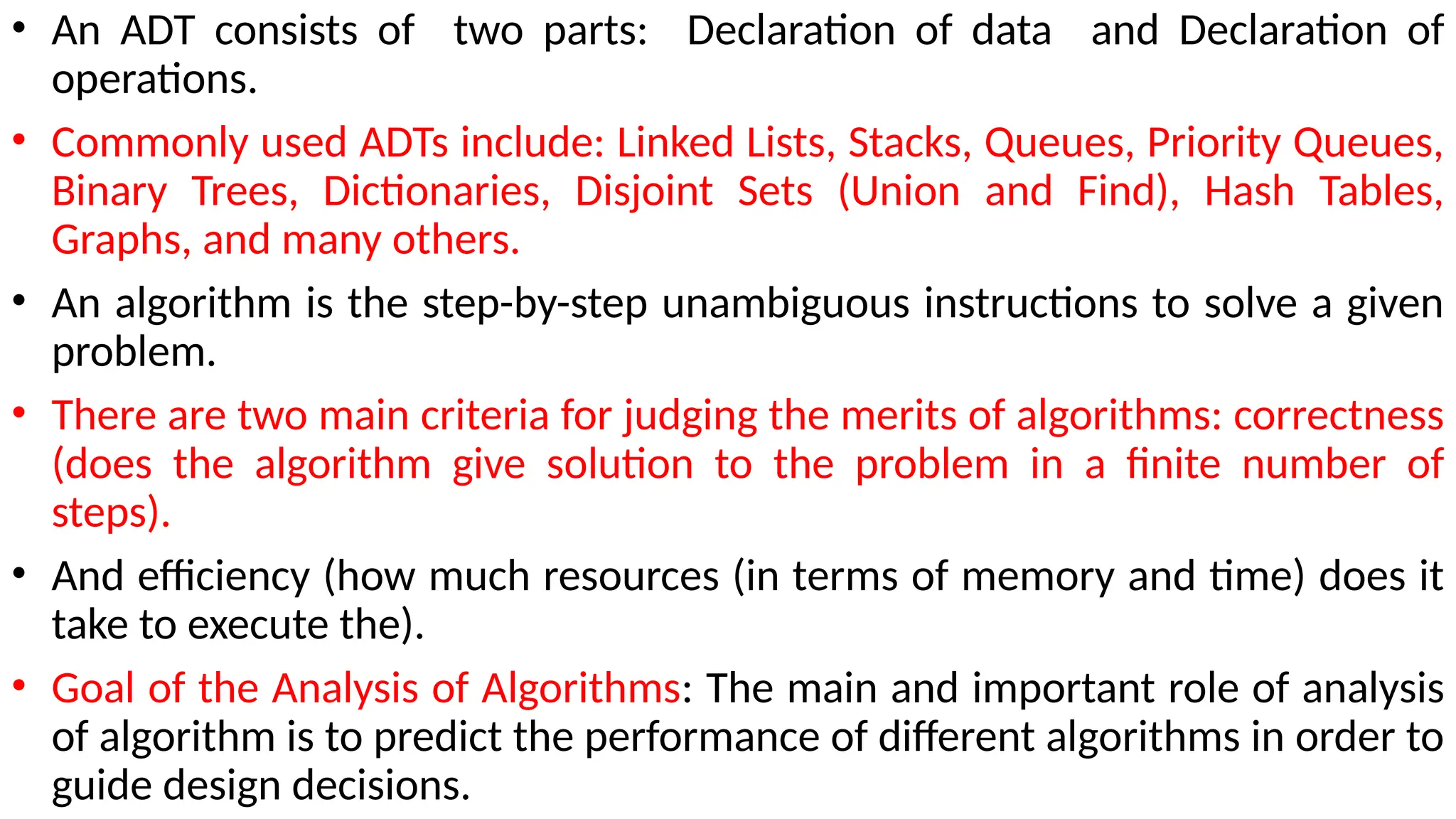
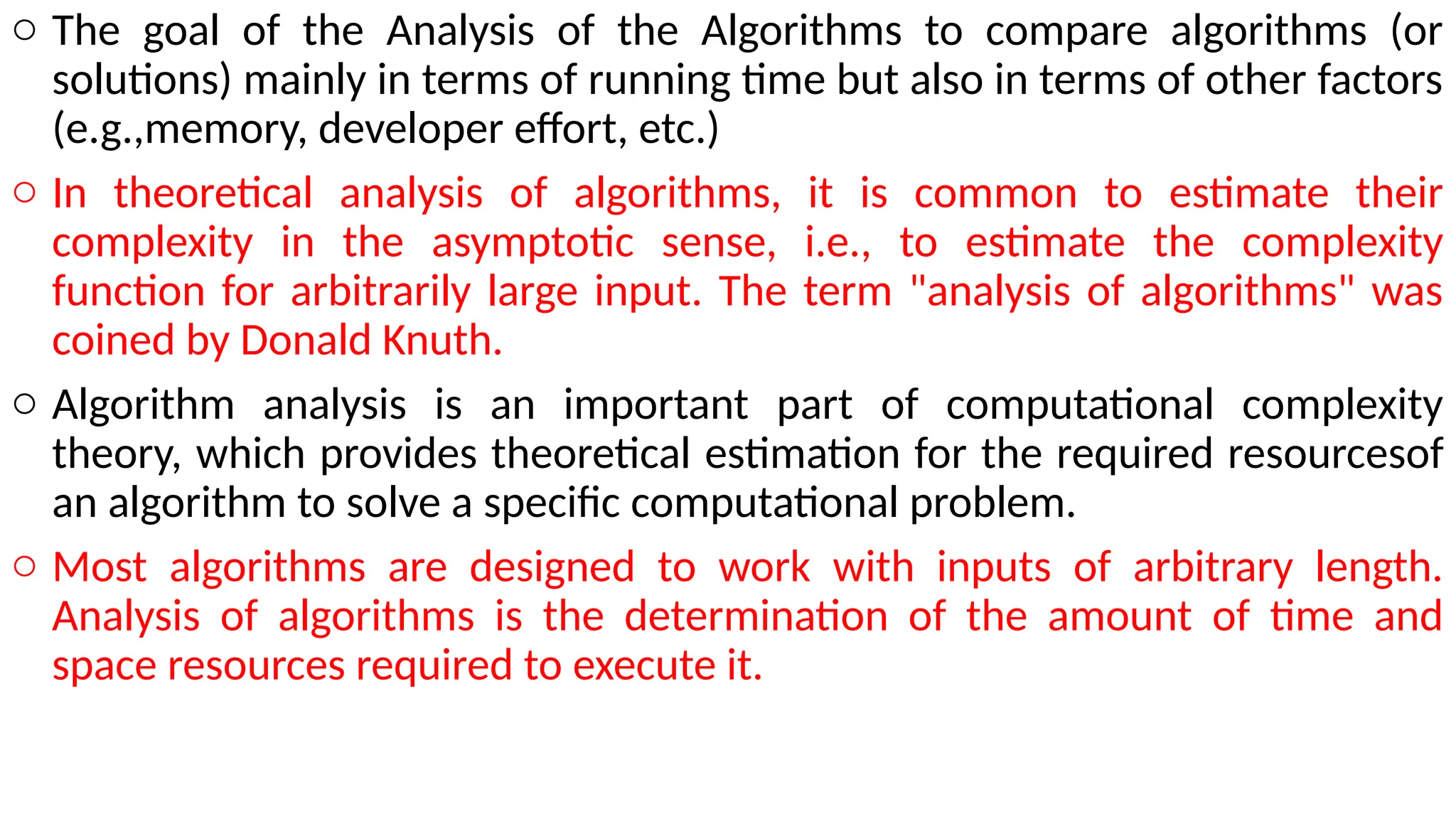
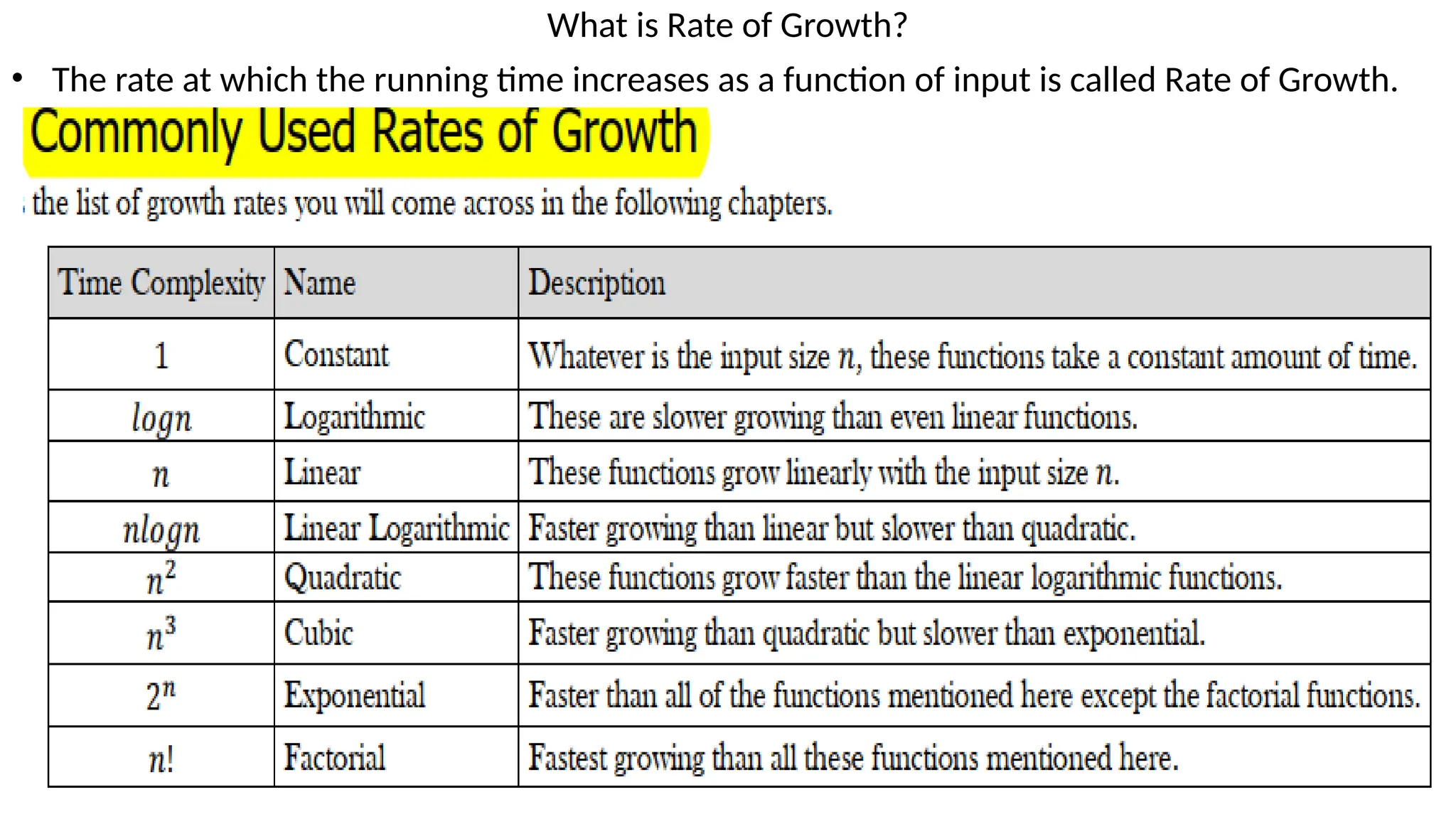
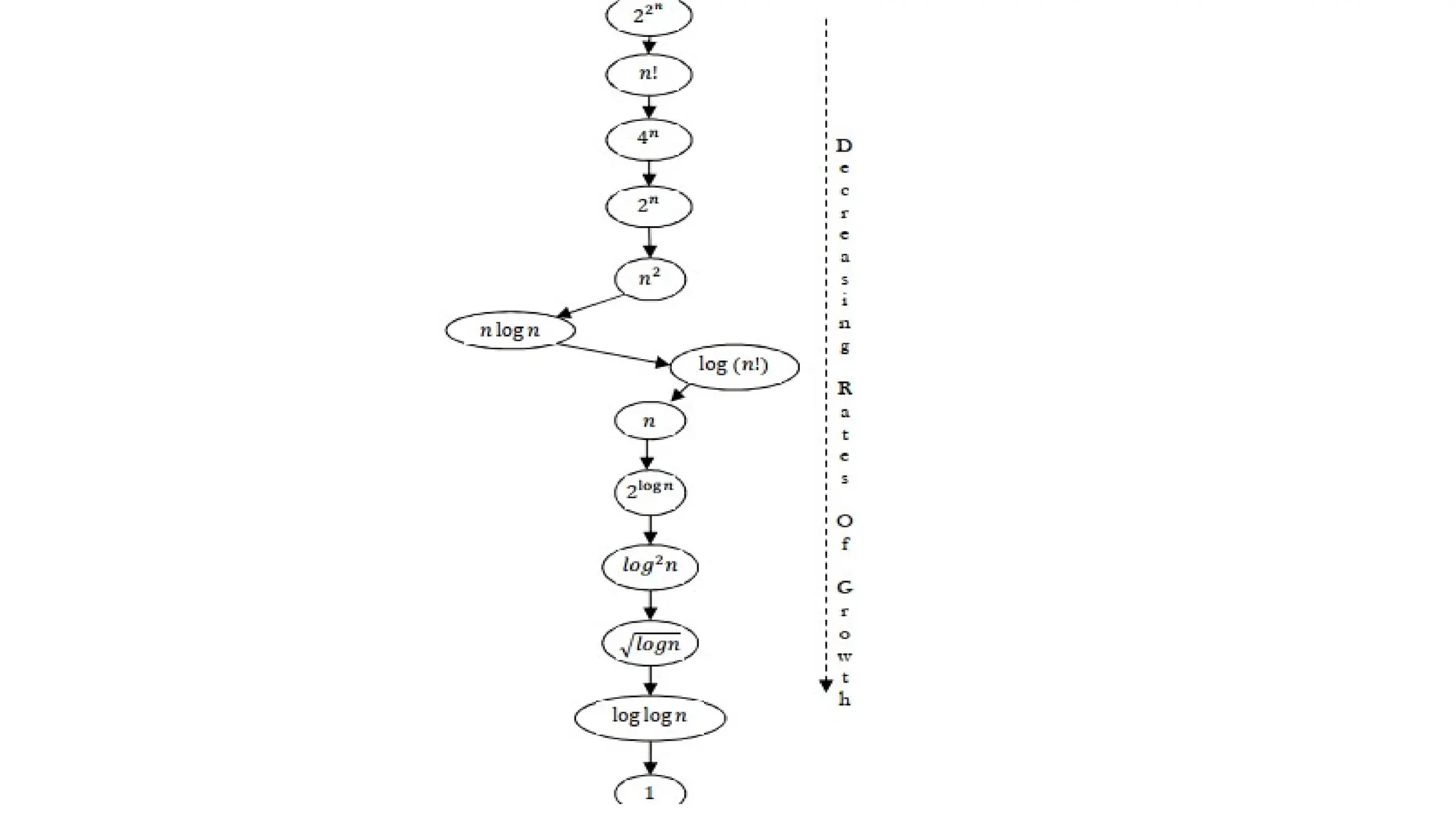
Data in computing refers to information translated into binary form (0 and 1) for efficient processing or movement, with applications rooted in Claude Shannon's information theory. It can manifest in various formats and becomes valuable when processed to extract insights. The document also discusses data types, structures, algorithms, and their analysis in terms of efficiency and correctness.