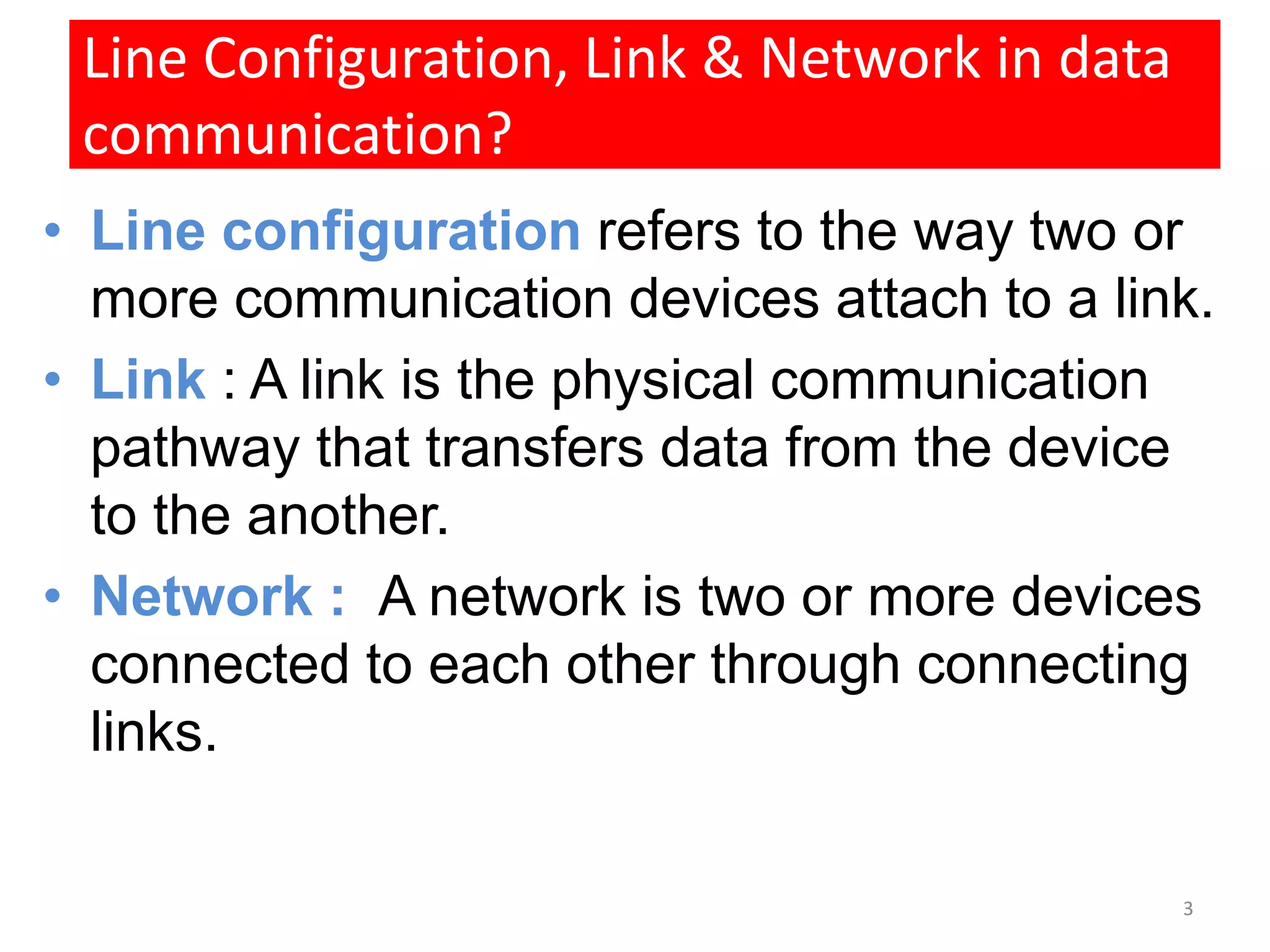
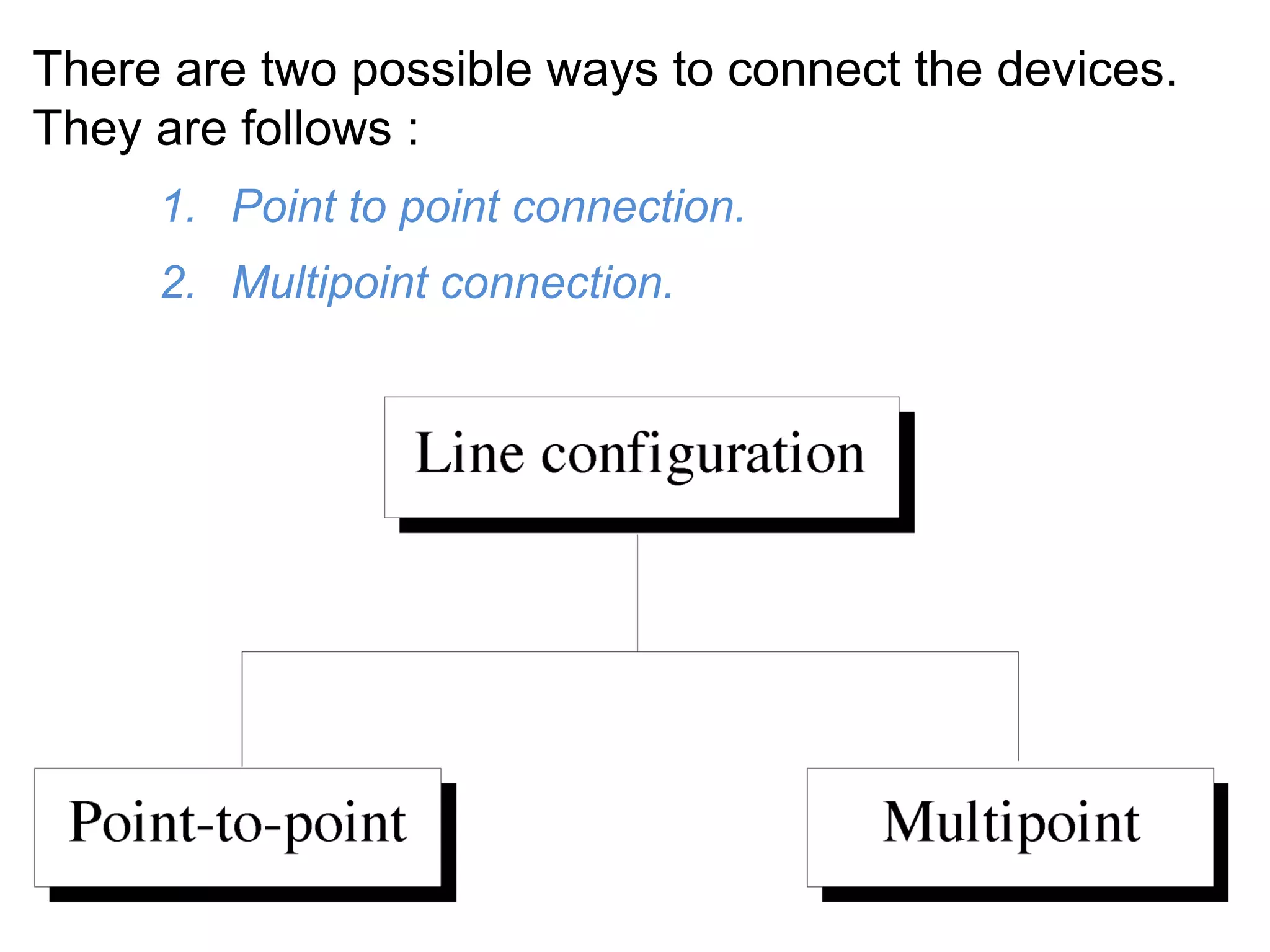
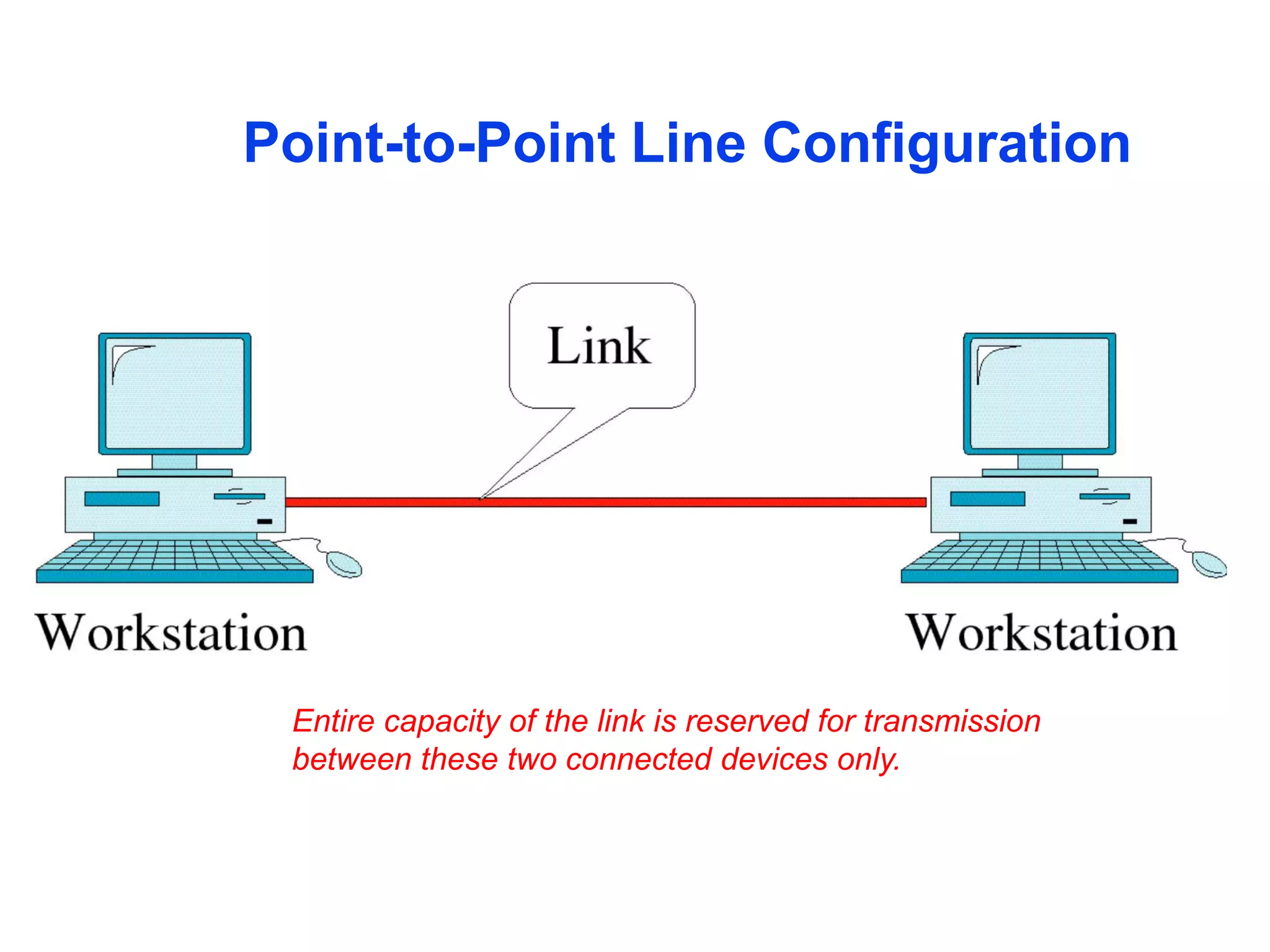
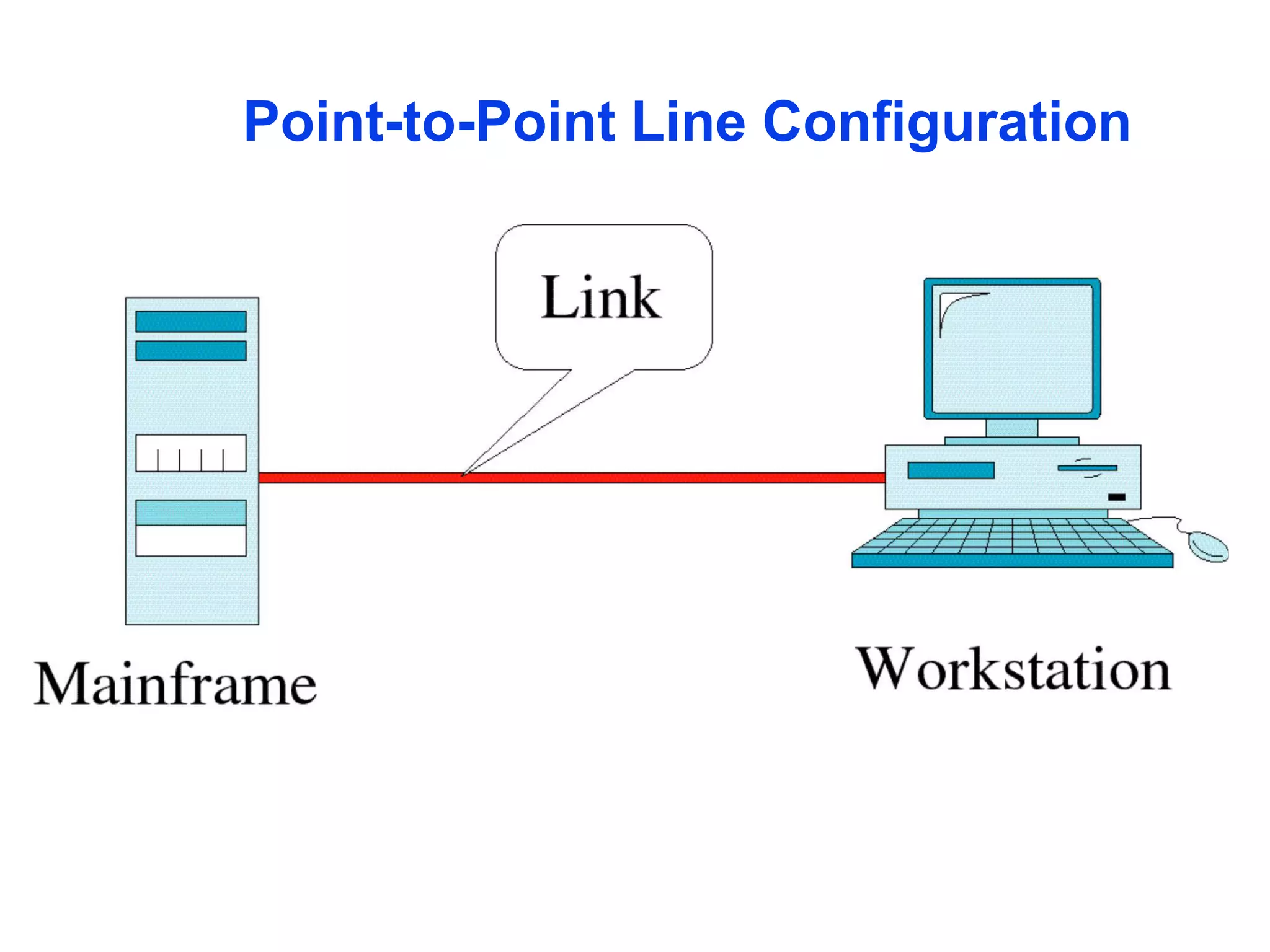
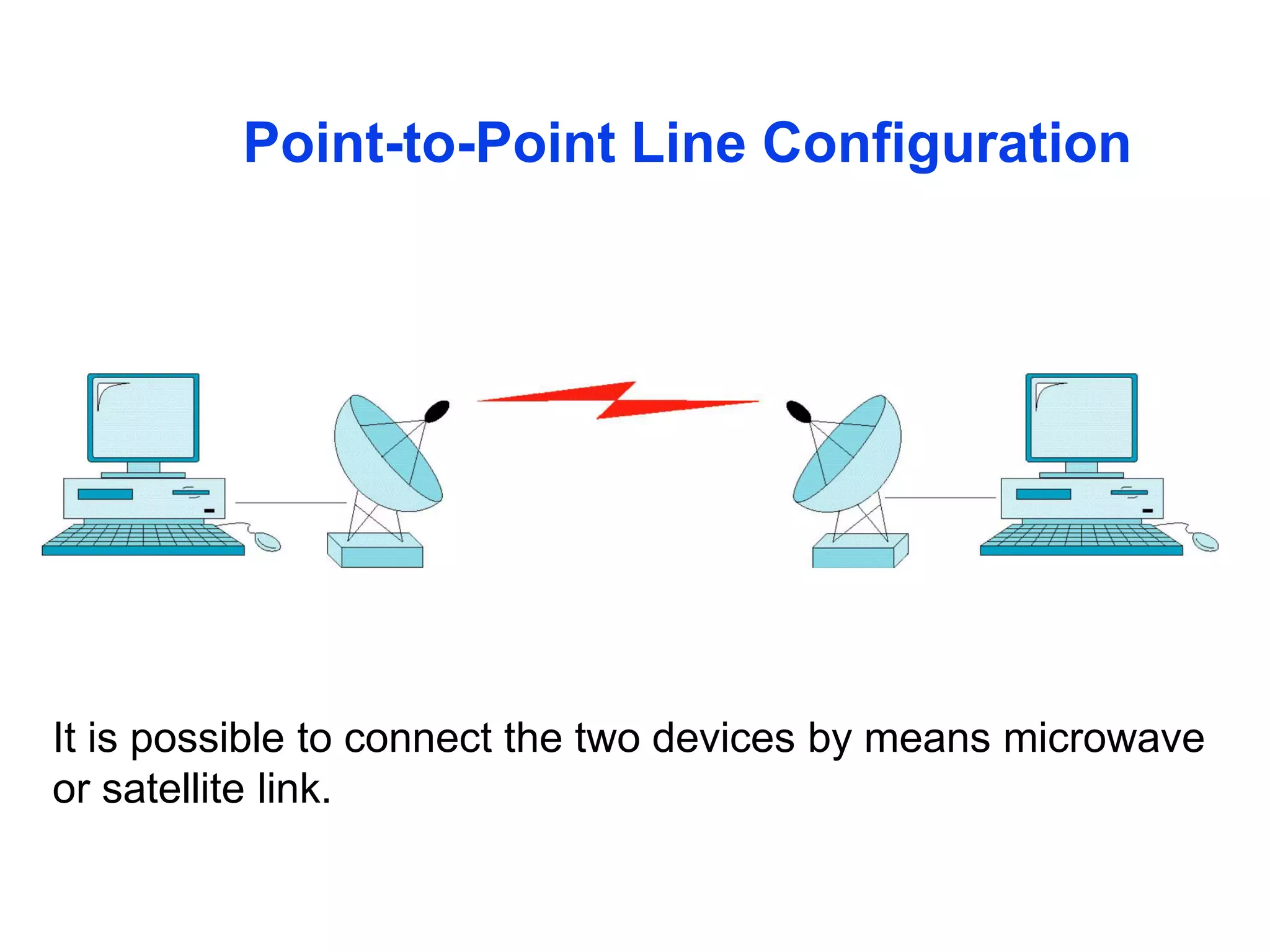
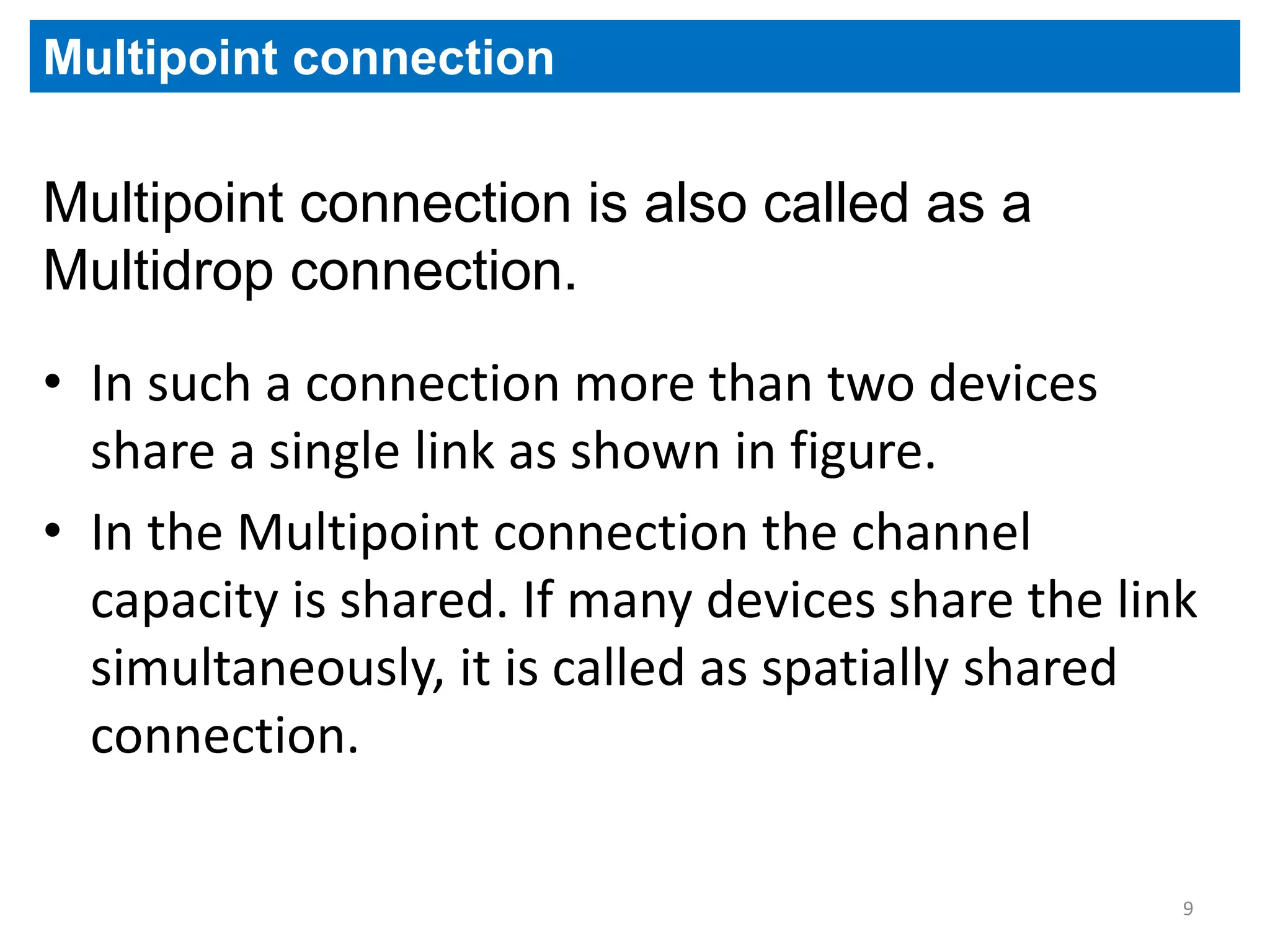
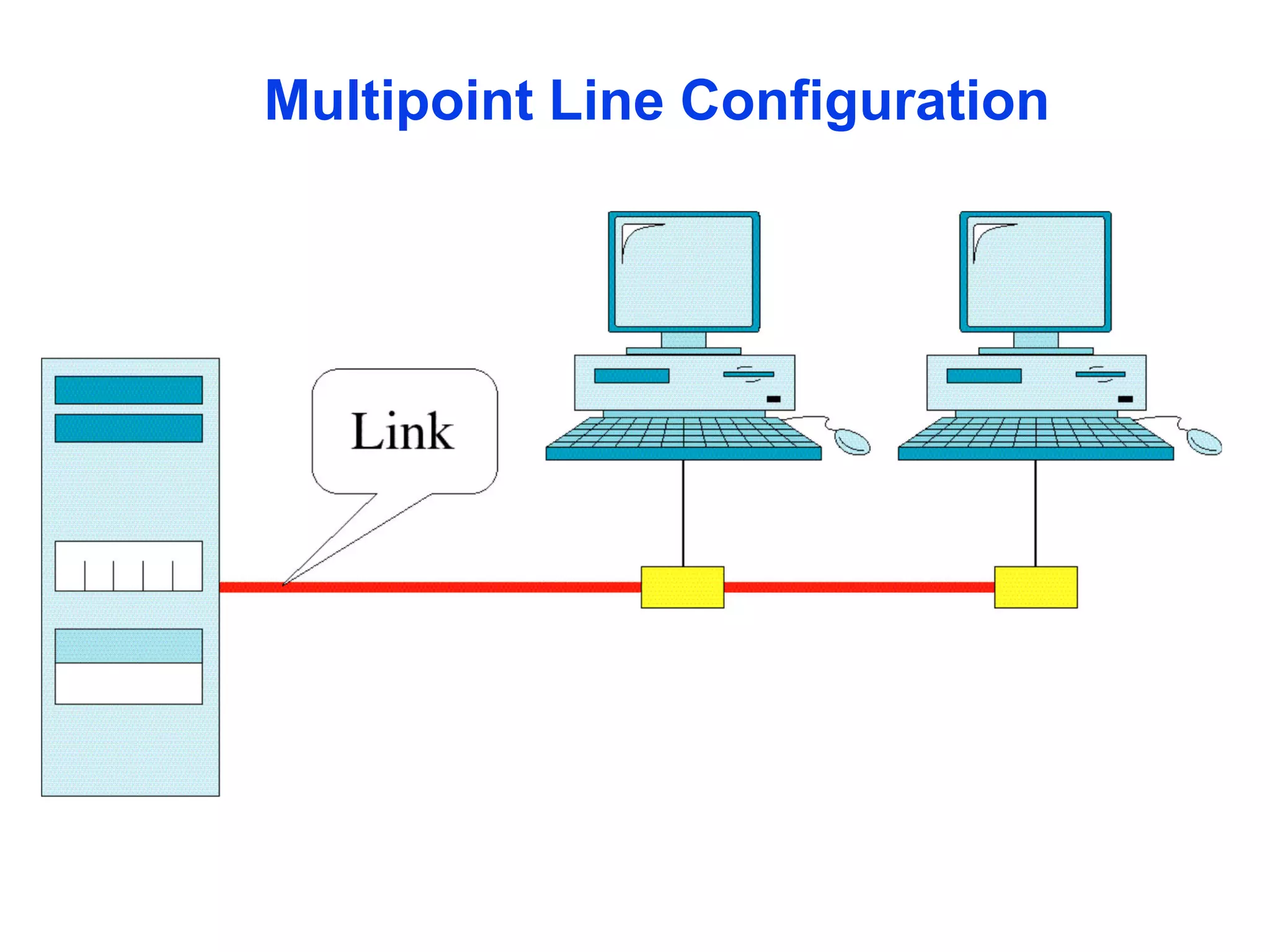
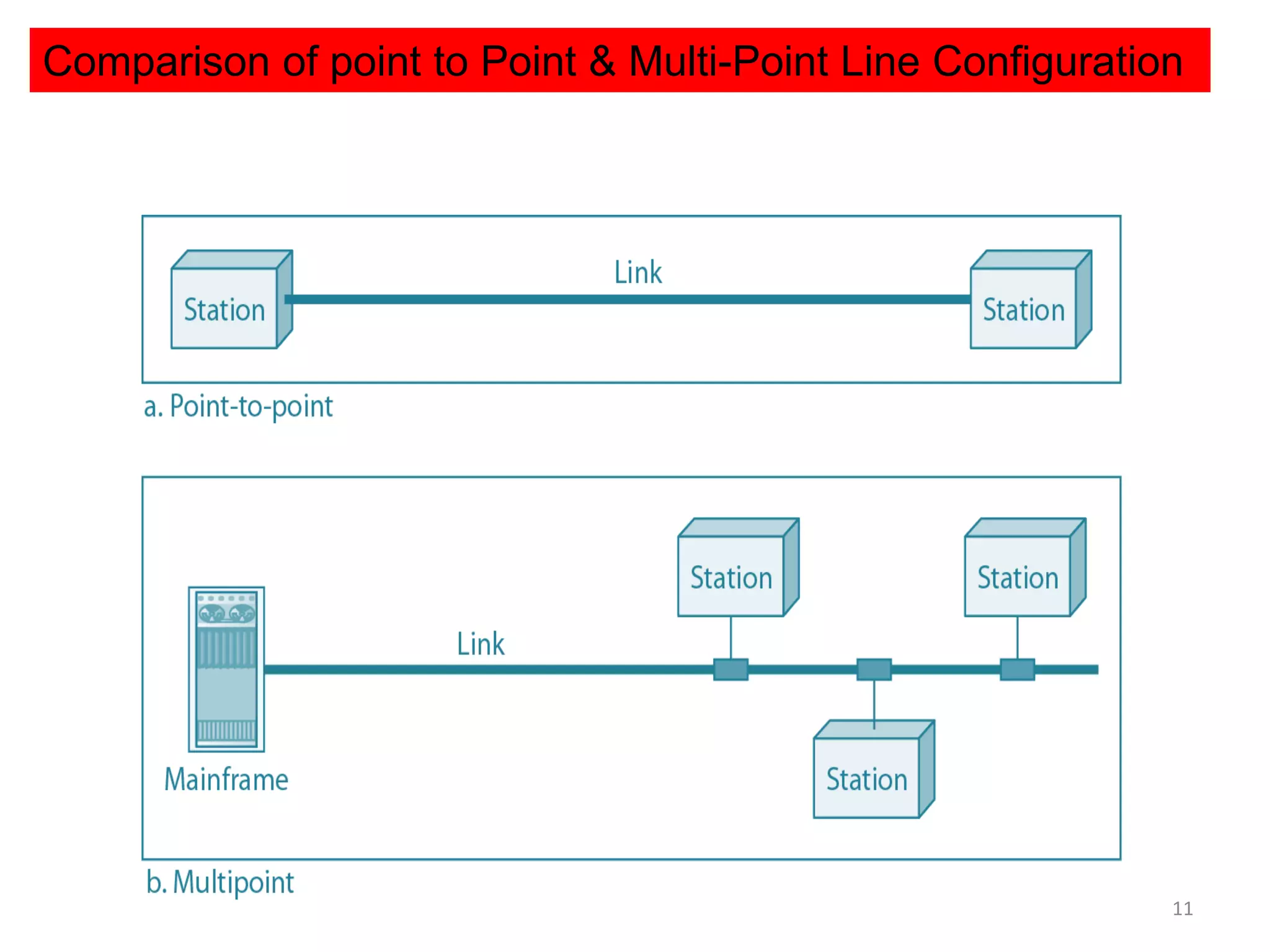
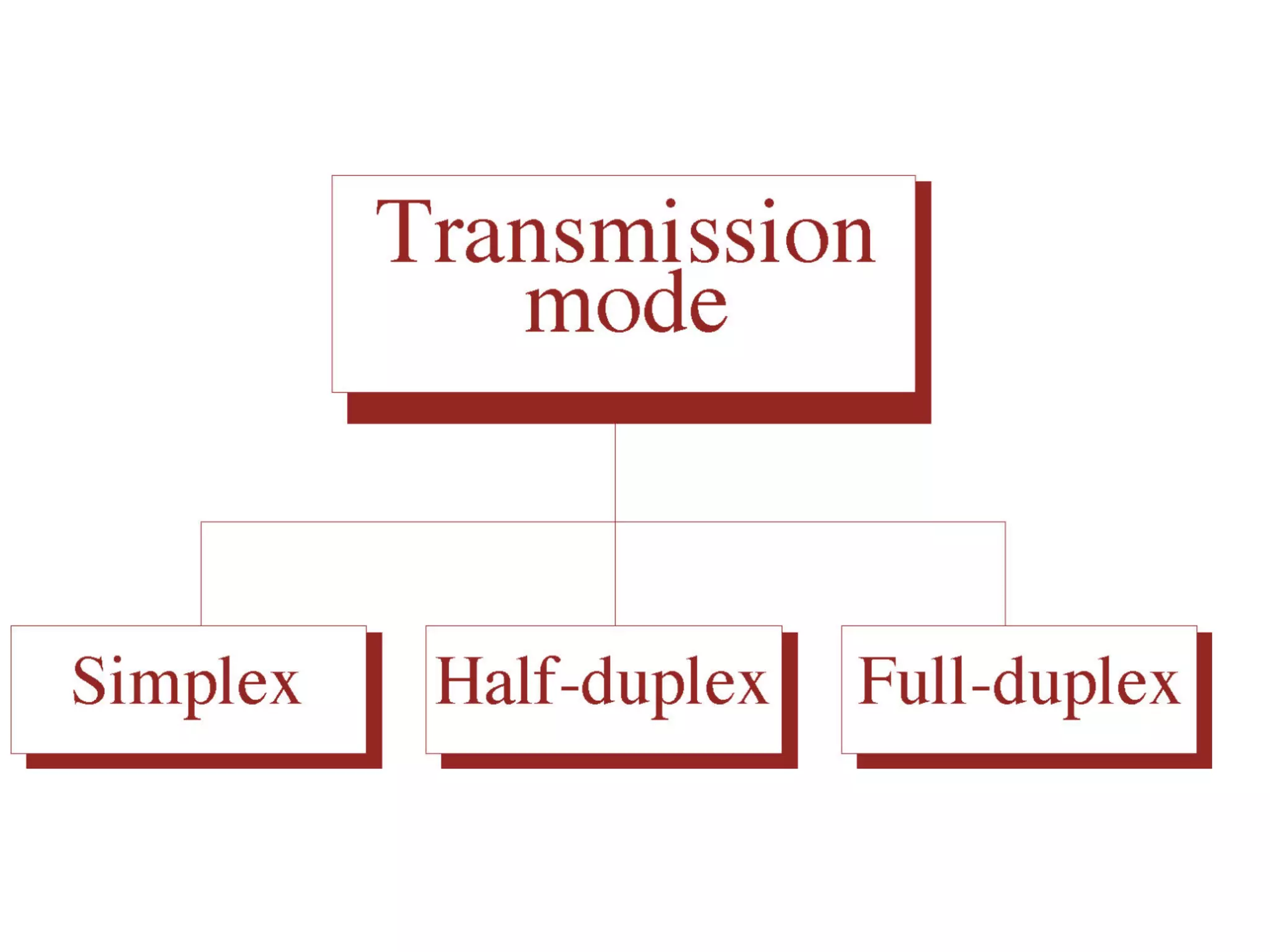
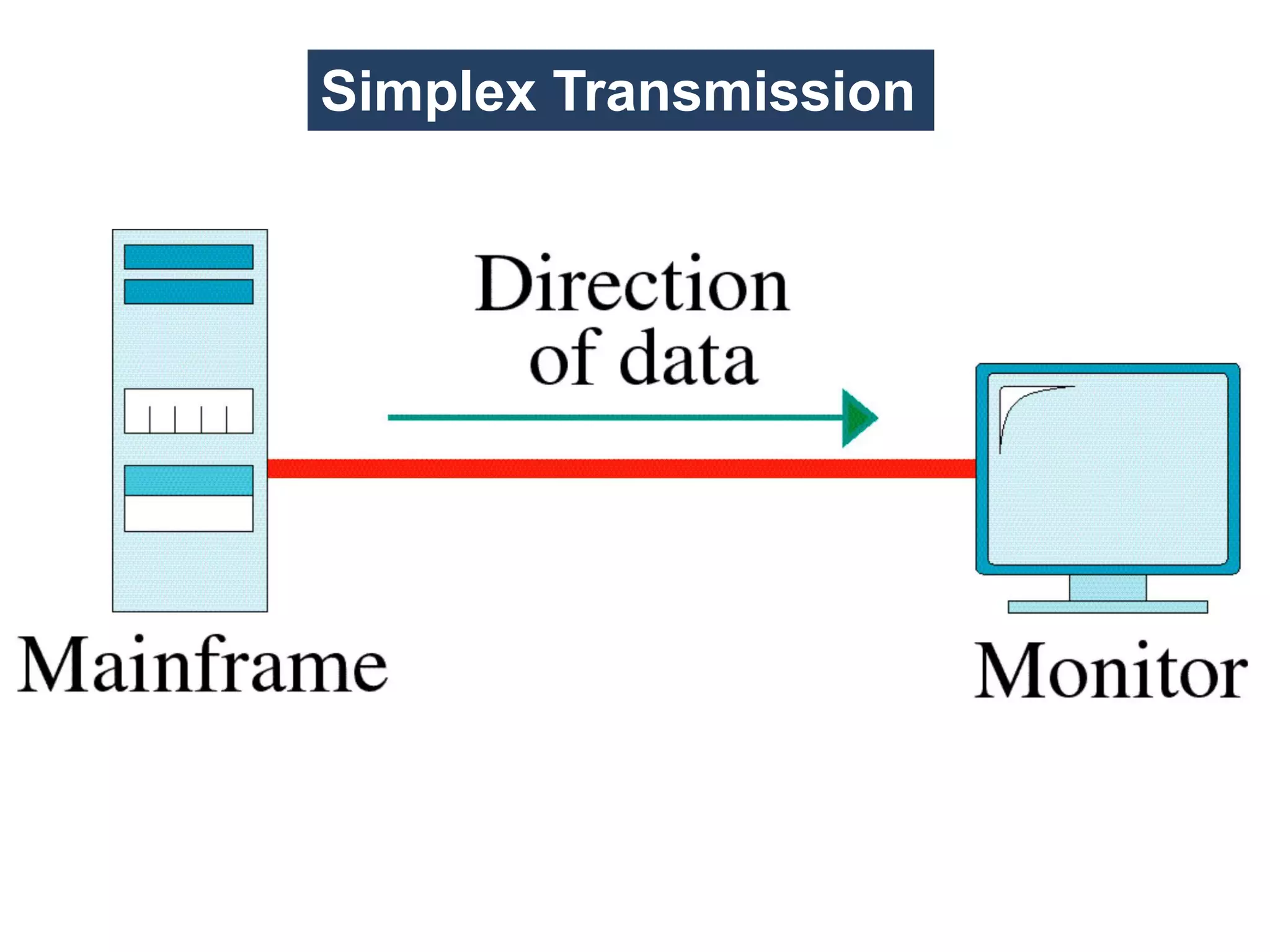
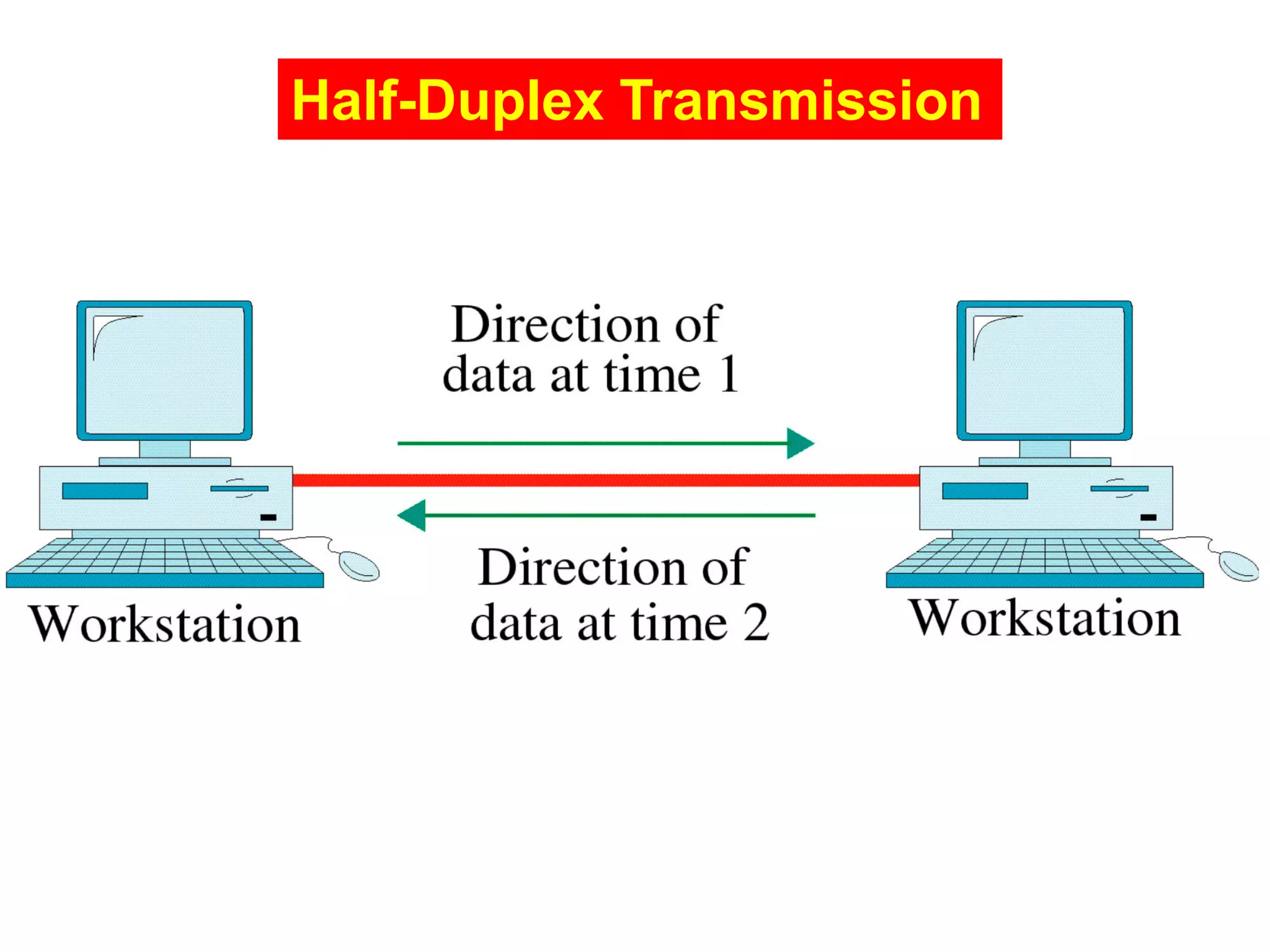
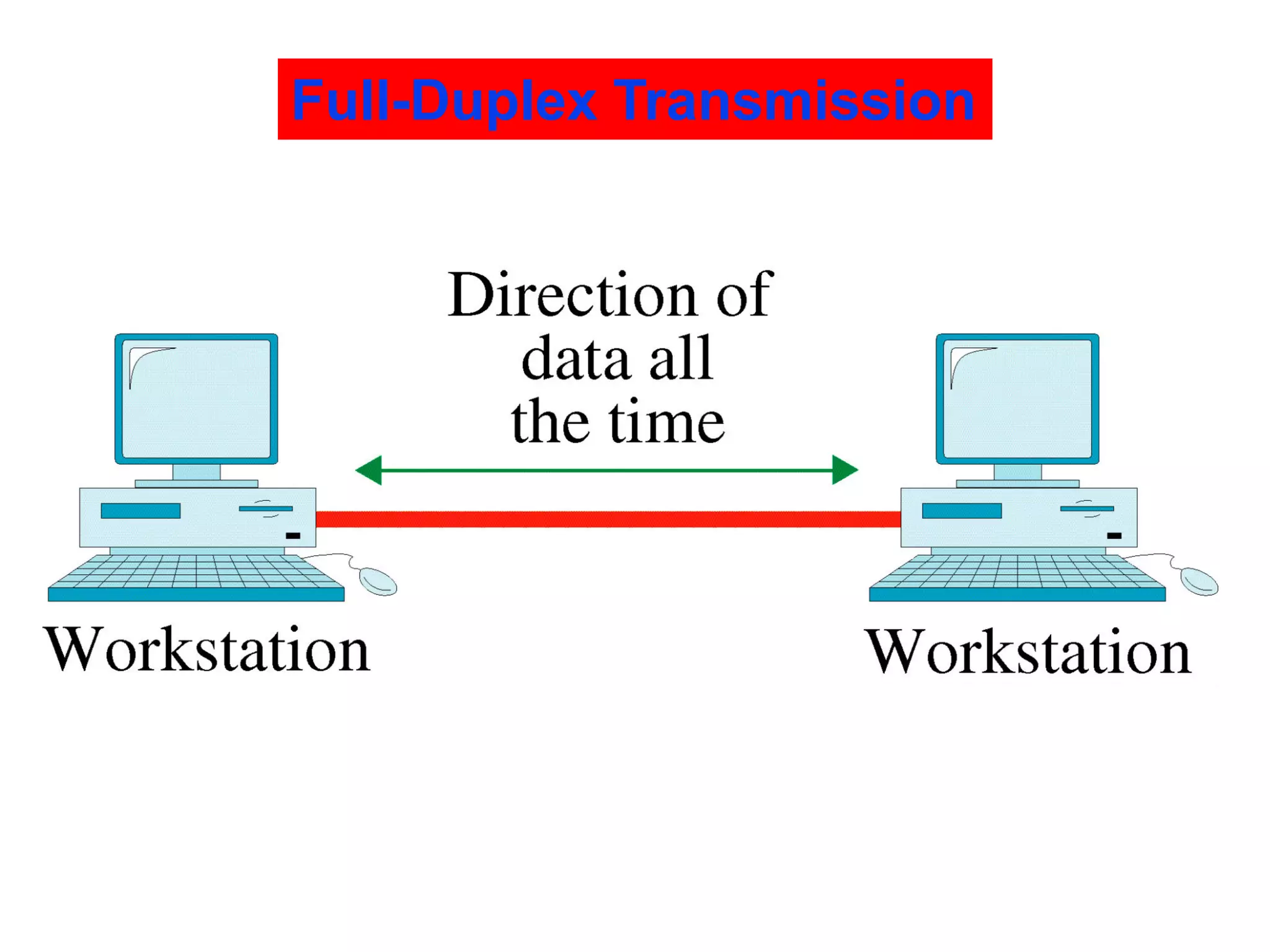
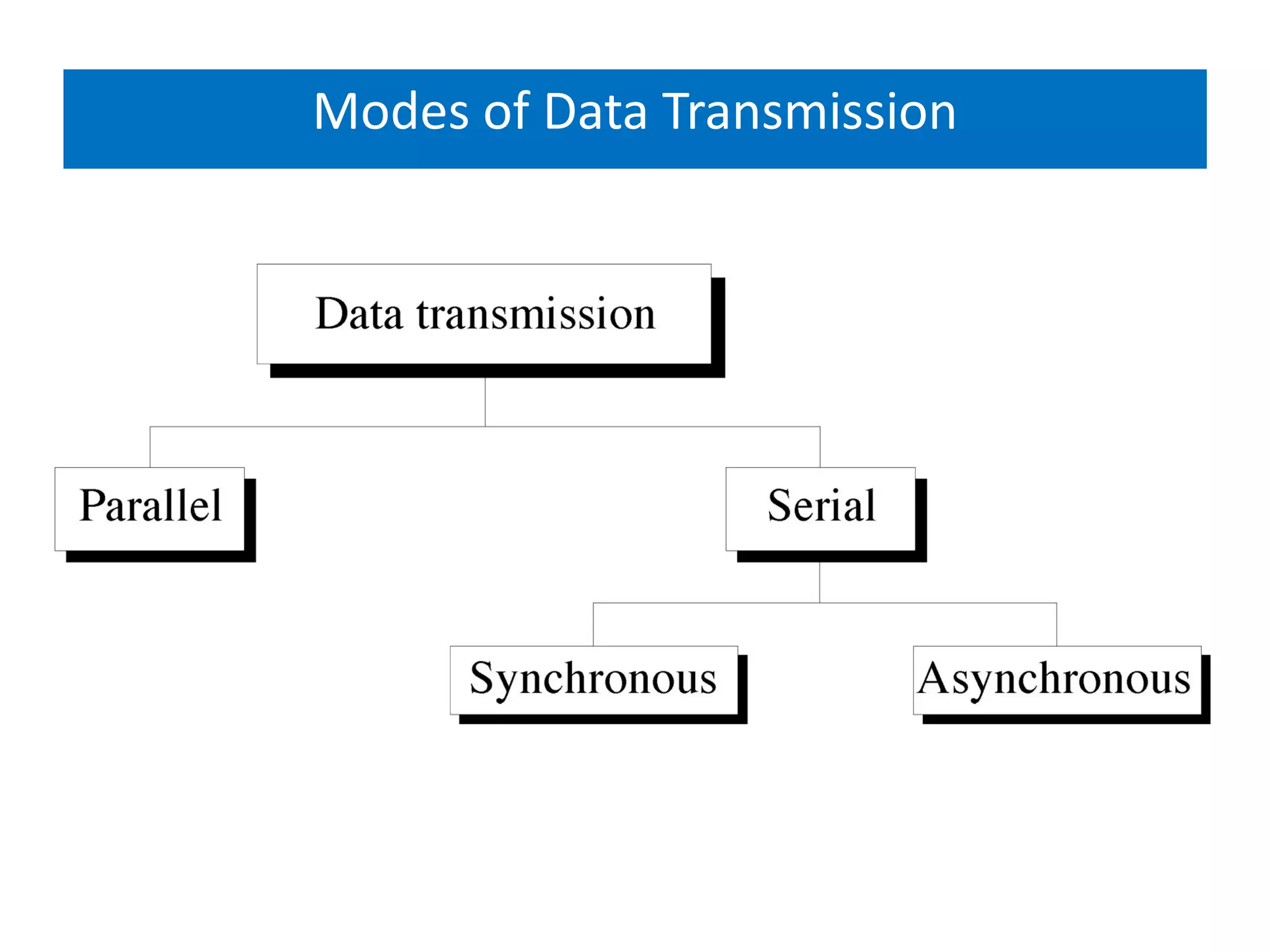
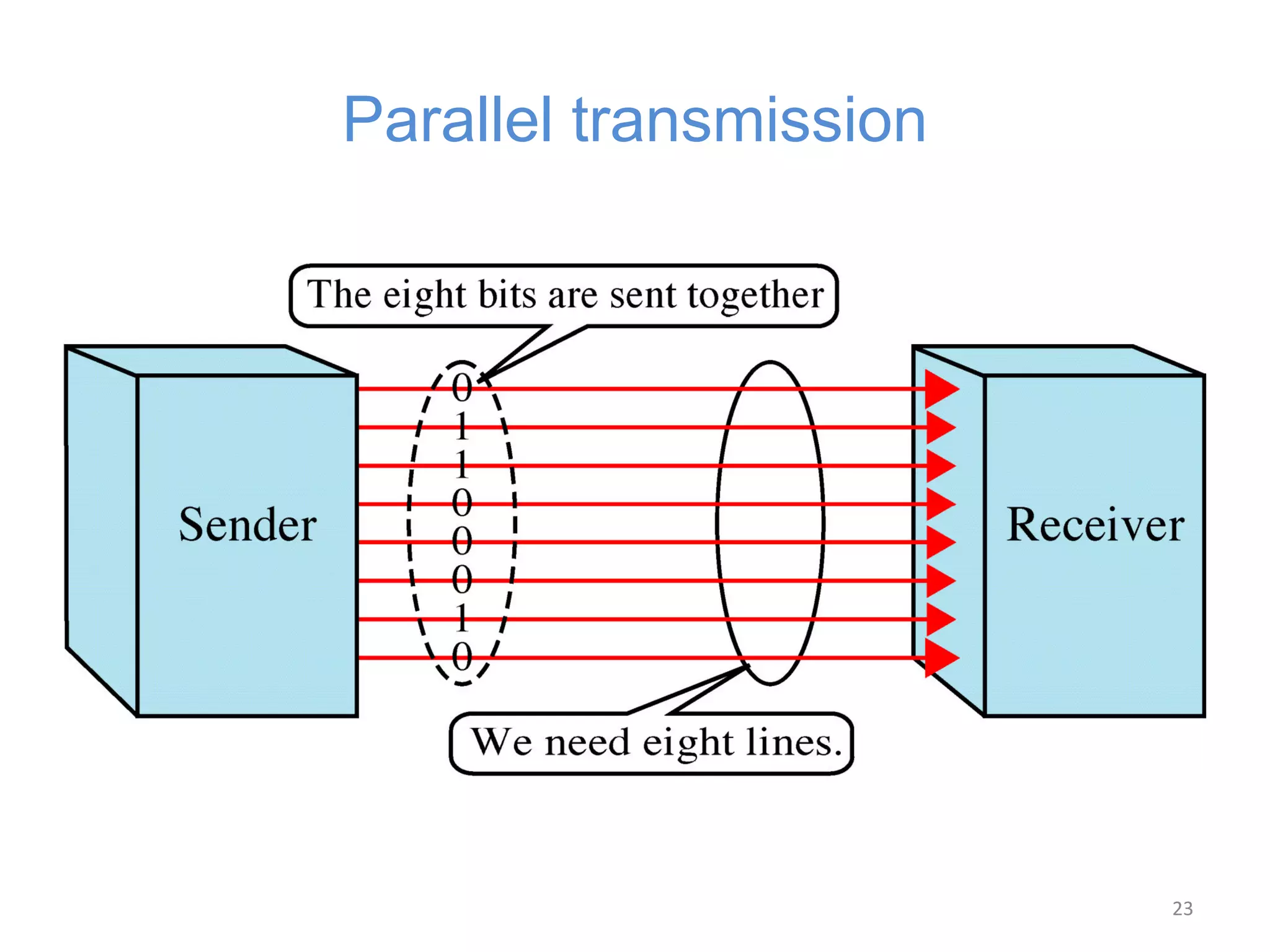
The document covers basic concepts of data communication, specifically channel types, line configurations, and modes of data transmission. It differentiates between point-to-point and multipoint connections, as well as communication systems including simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex. Additionally, it describes parallel and serial transmission methods, highlighting the advantages of parallel transmission in terms of speed and efficiency.