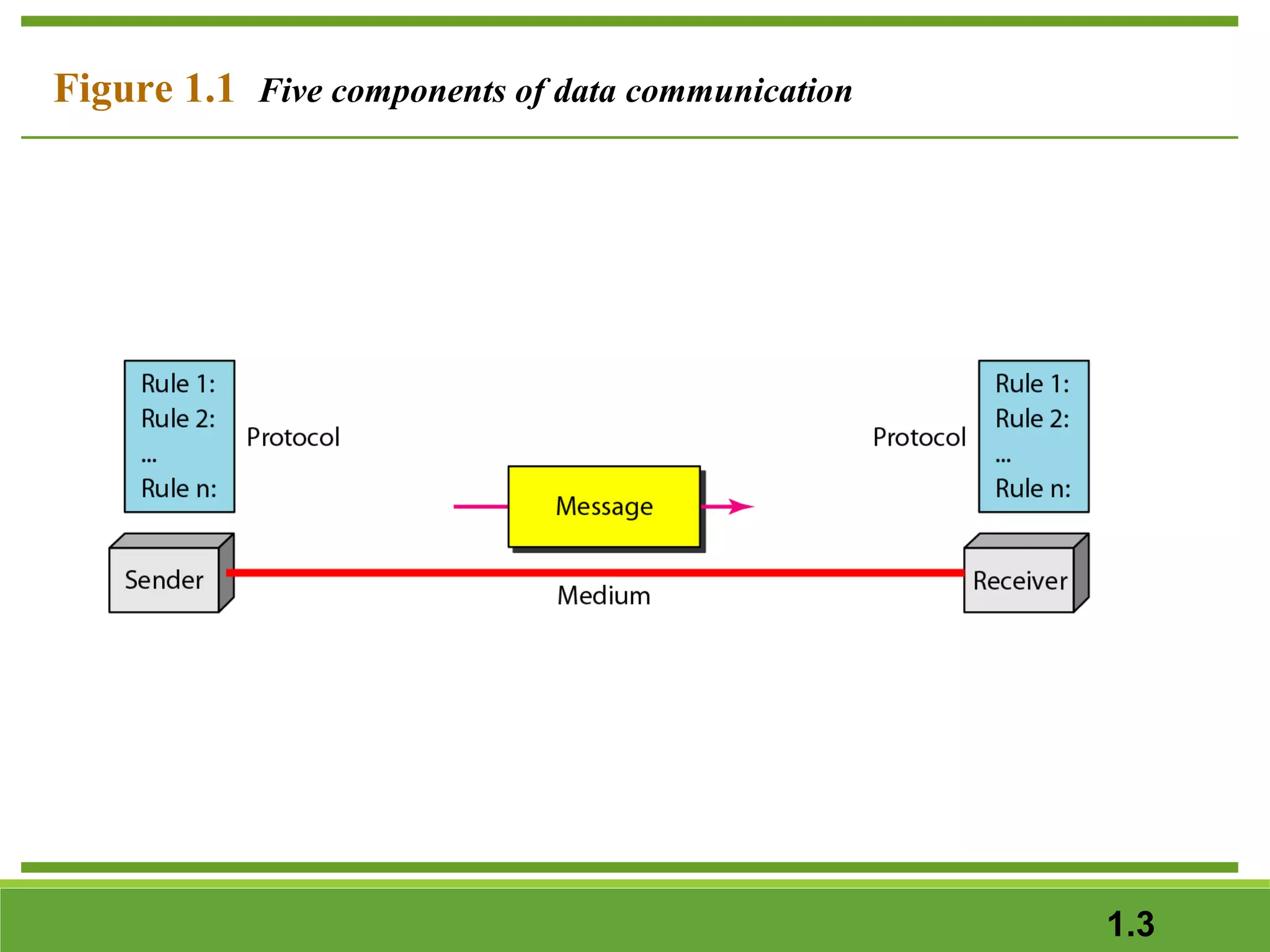
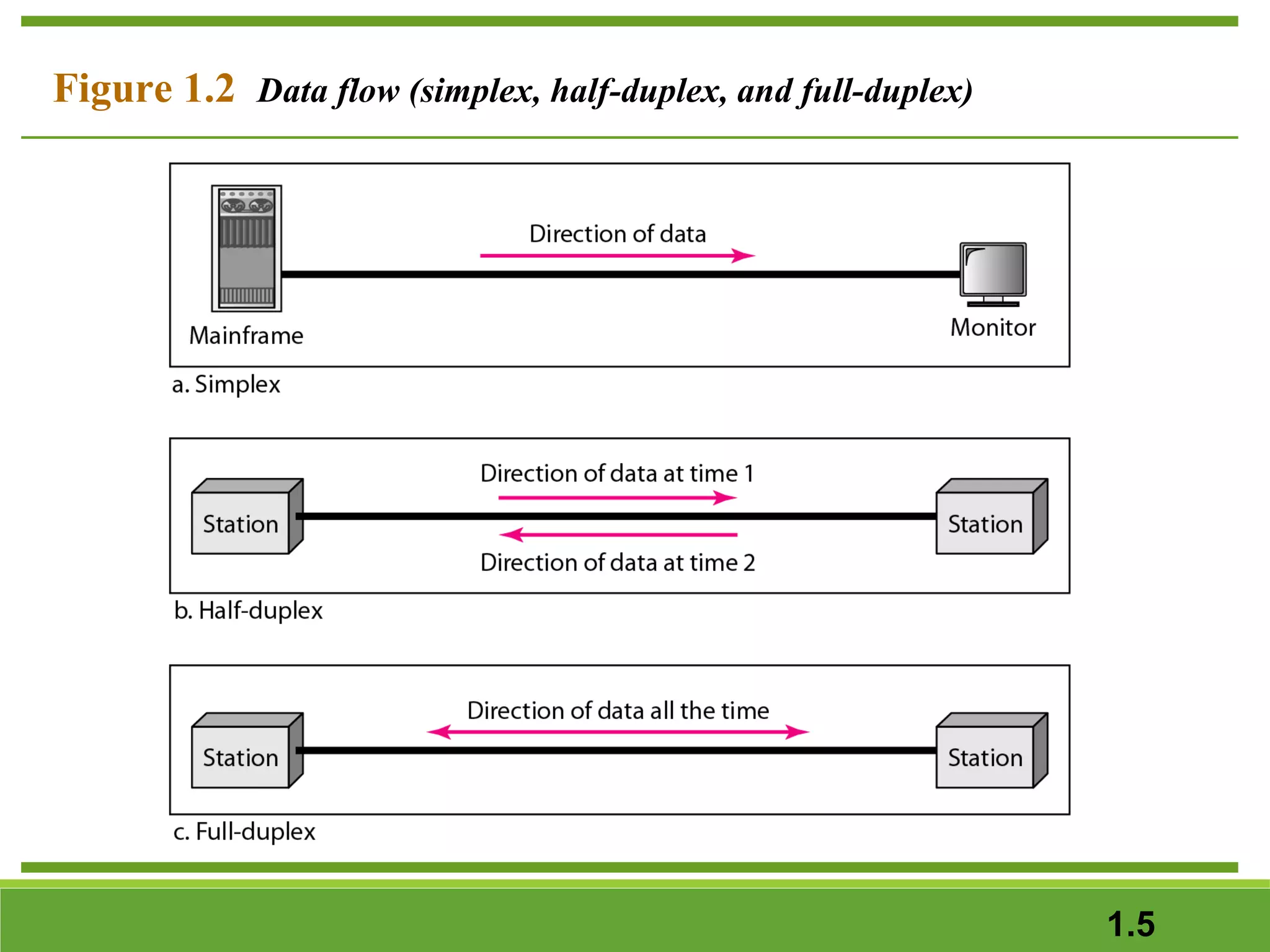
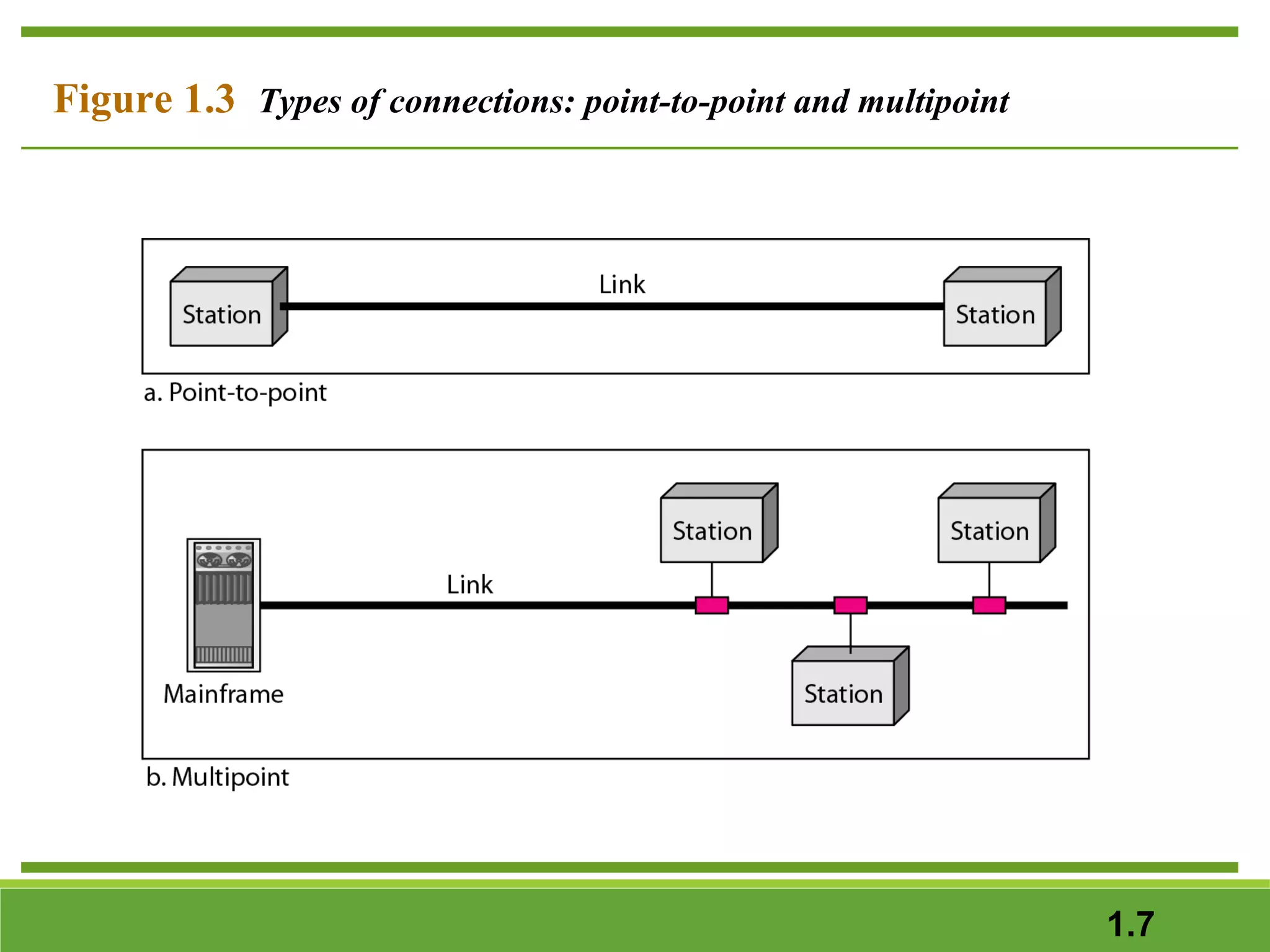
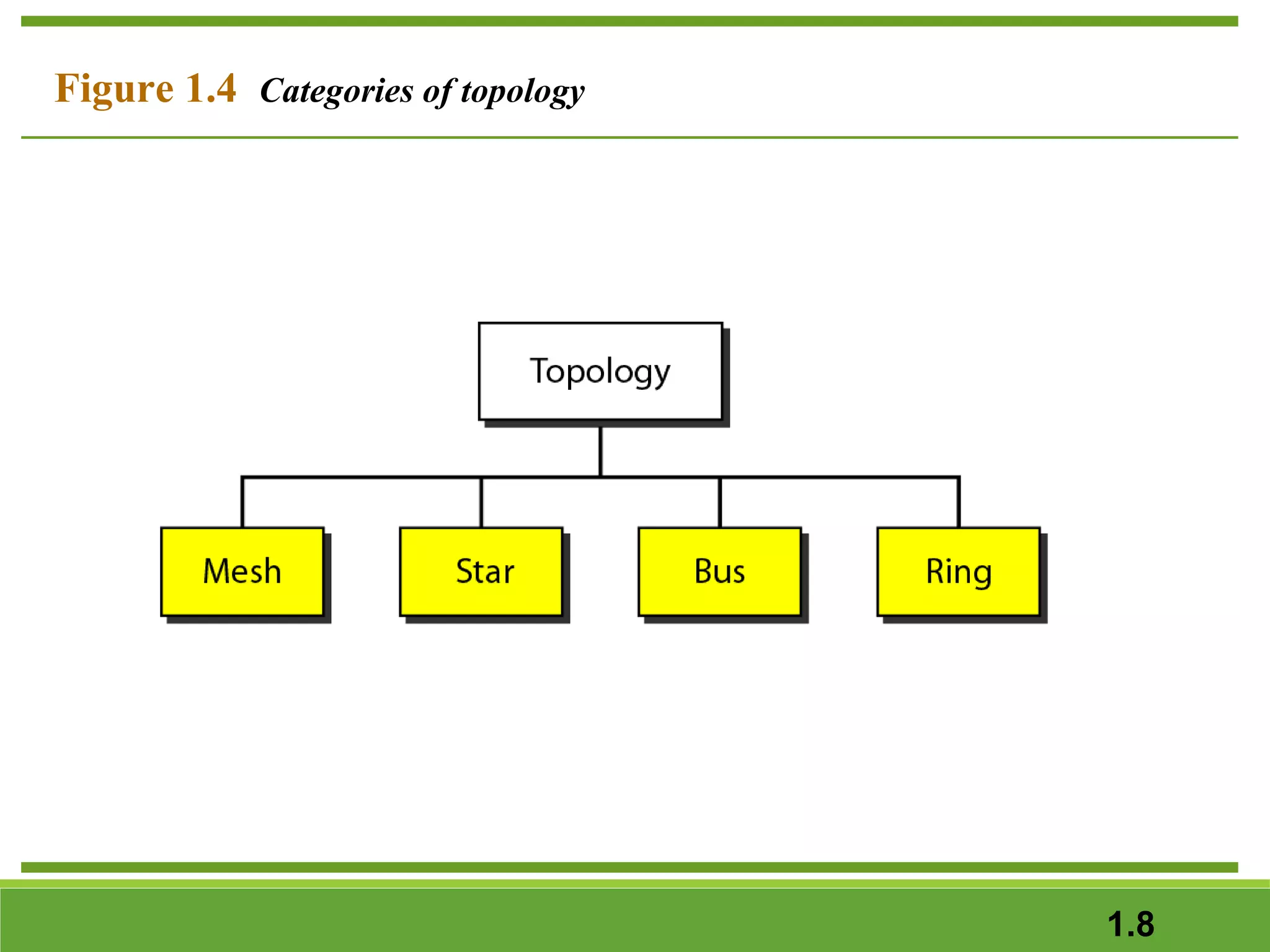
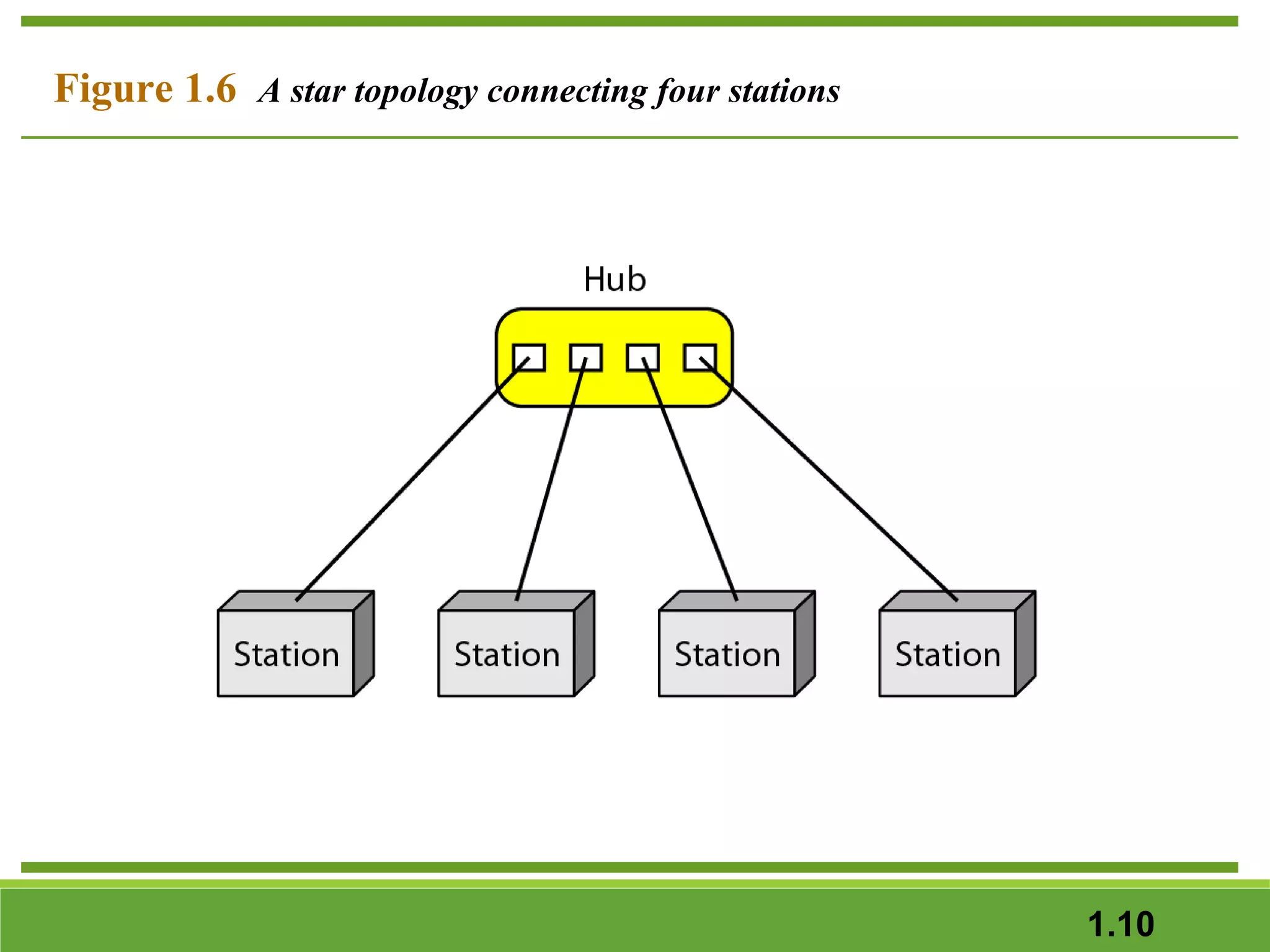
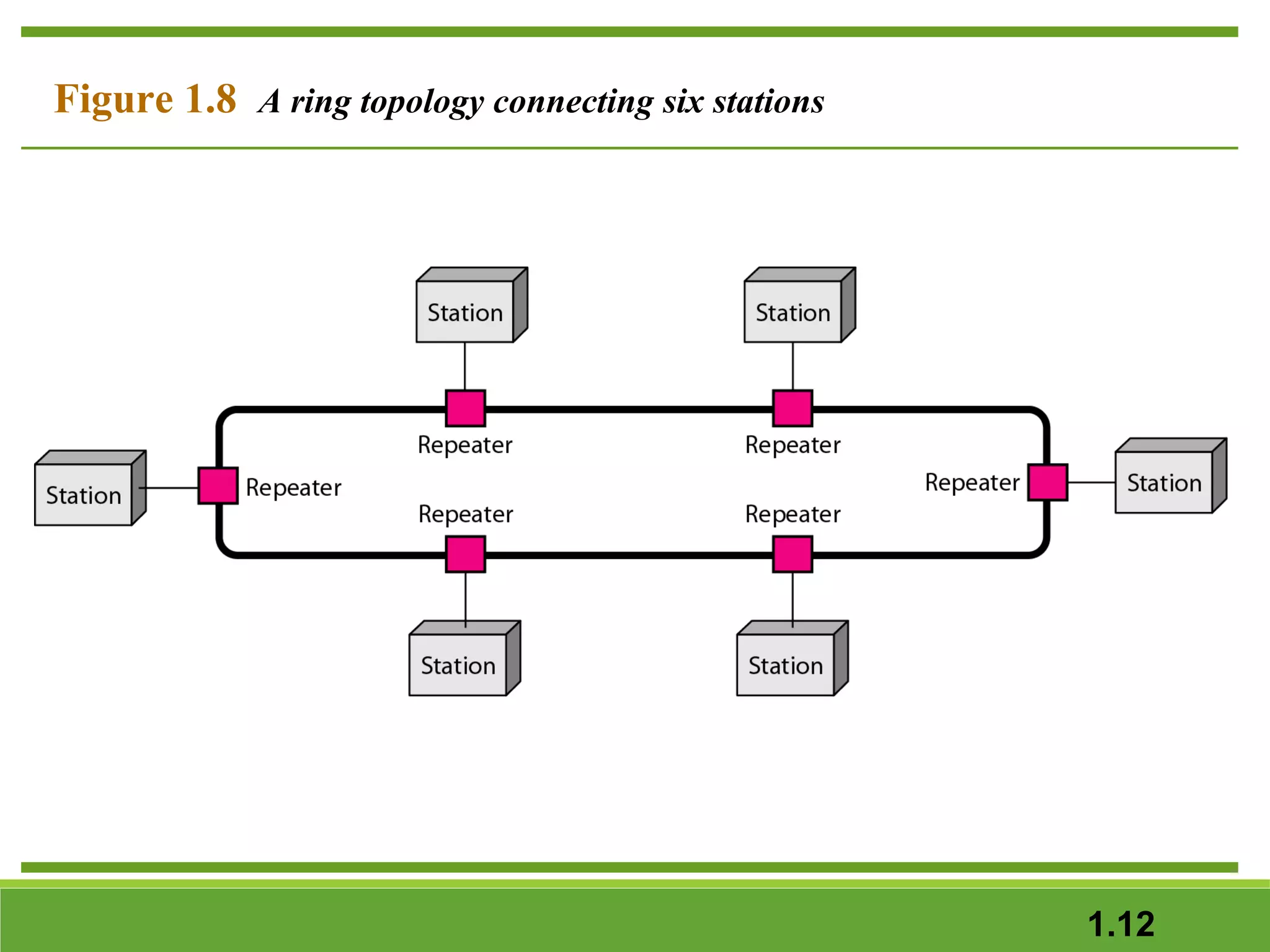
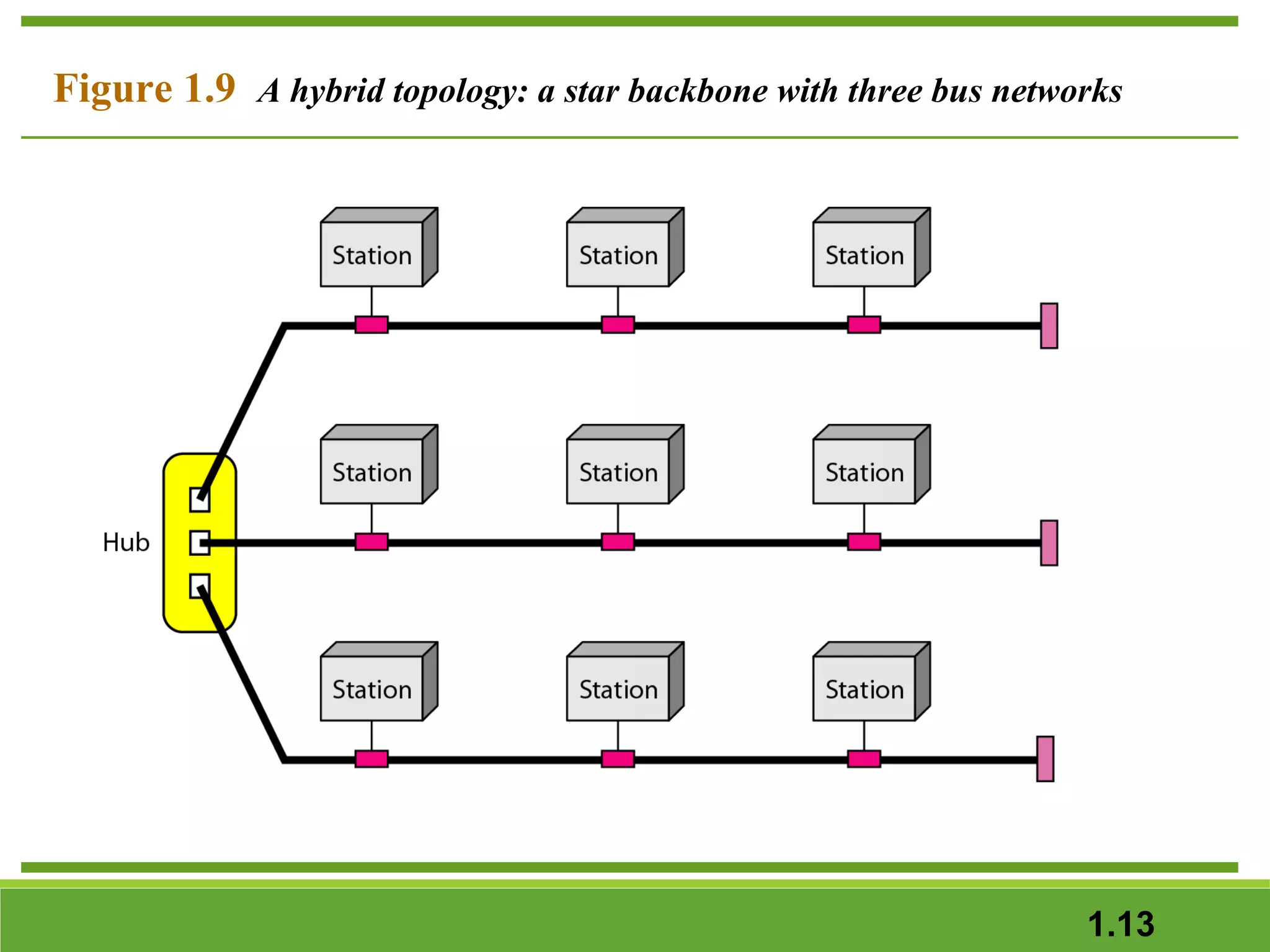
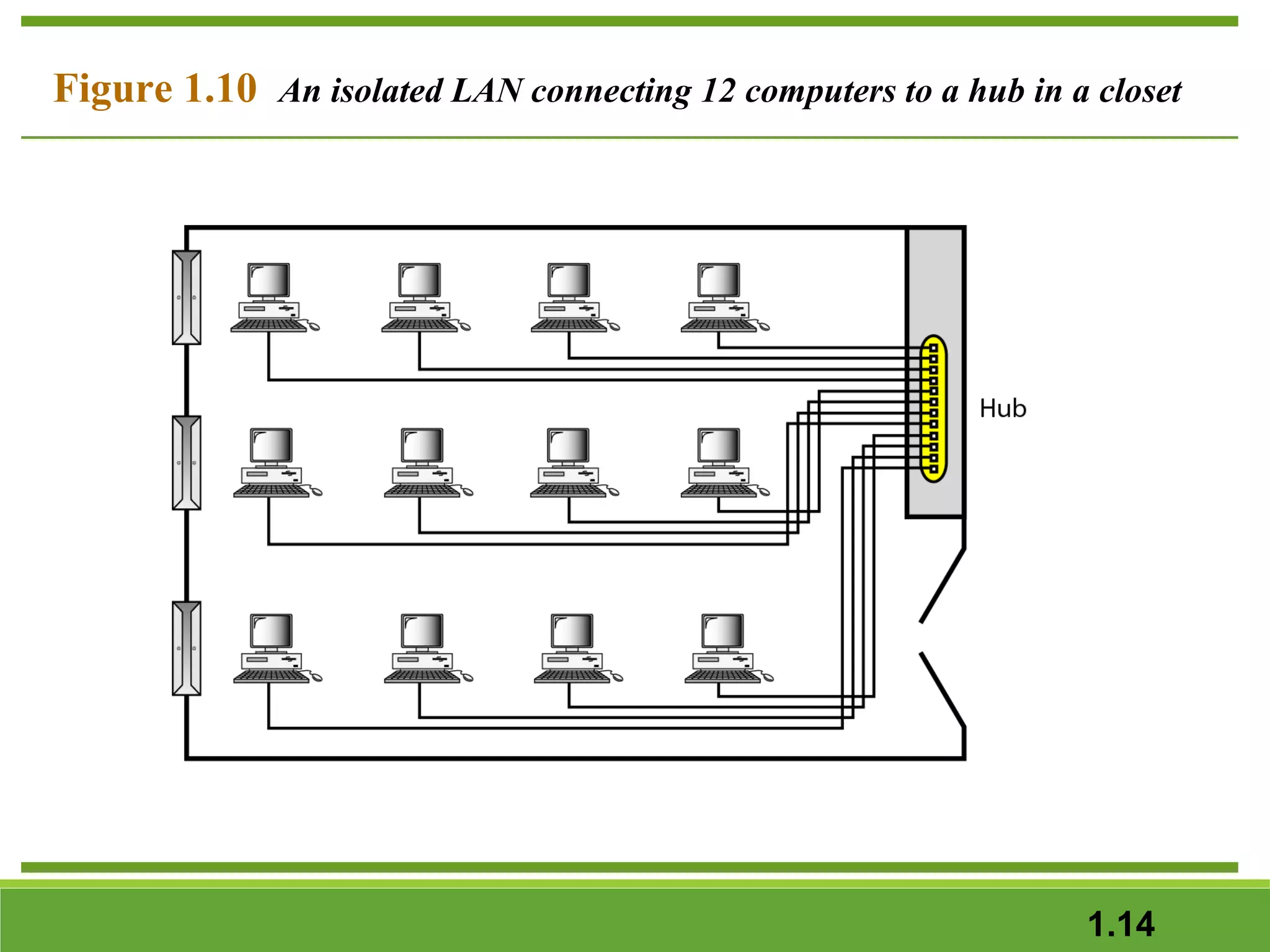
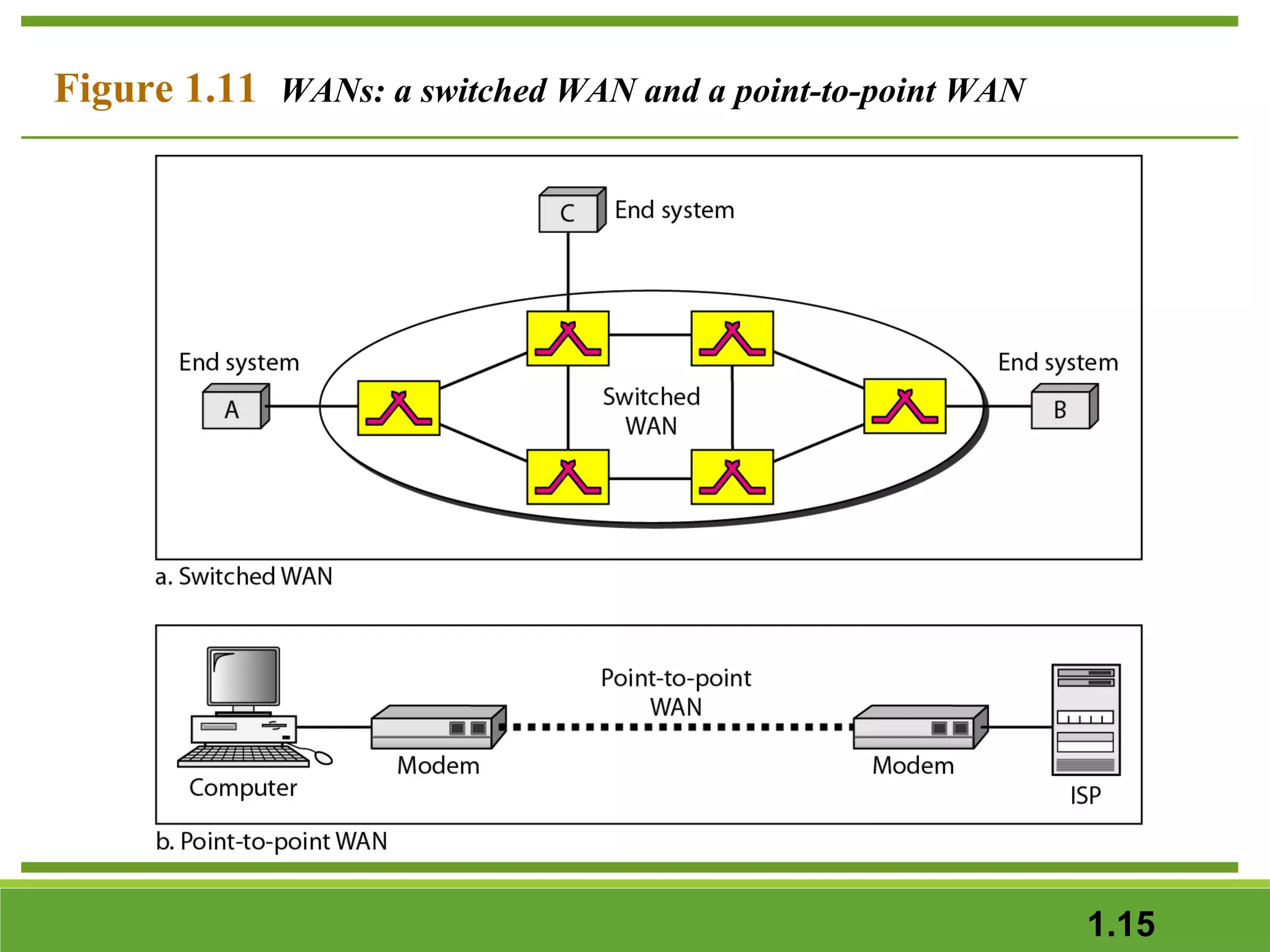
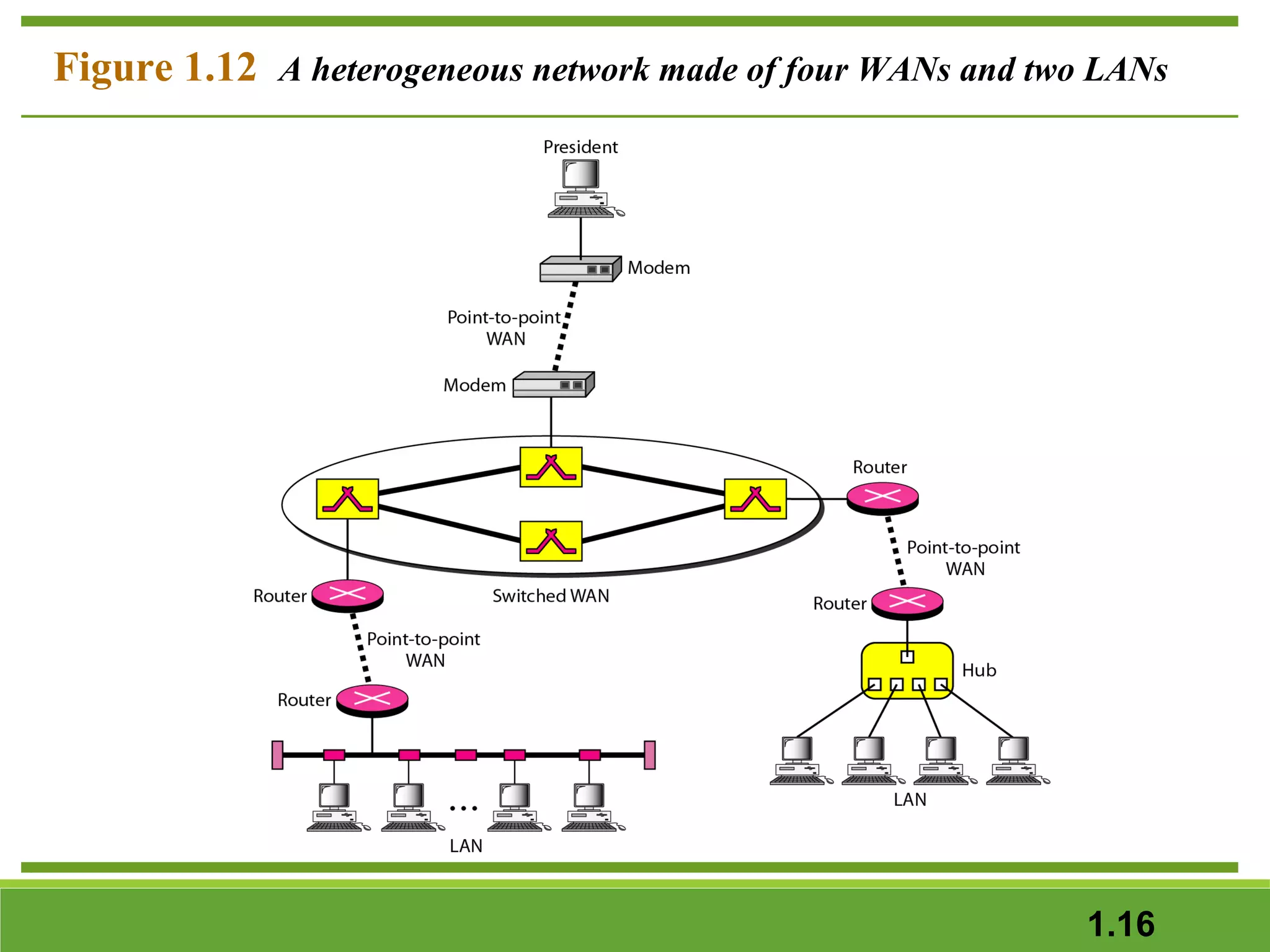
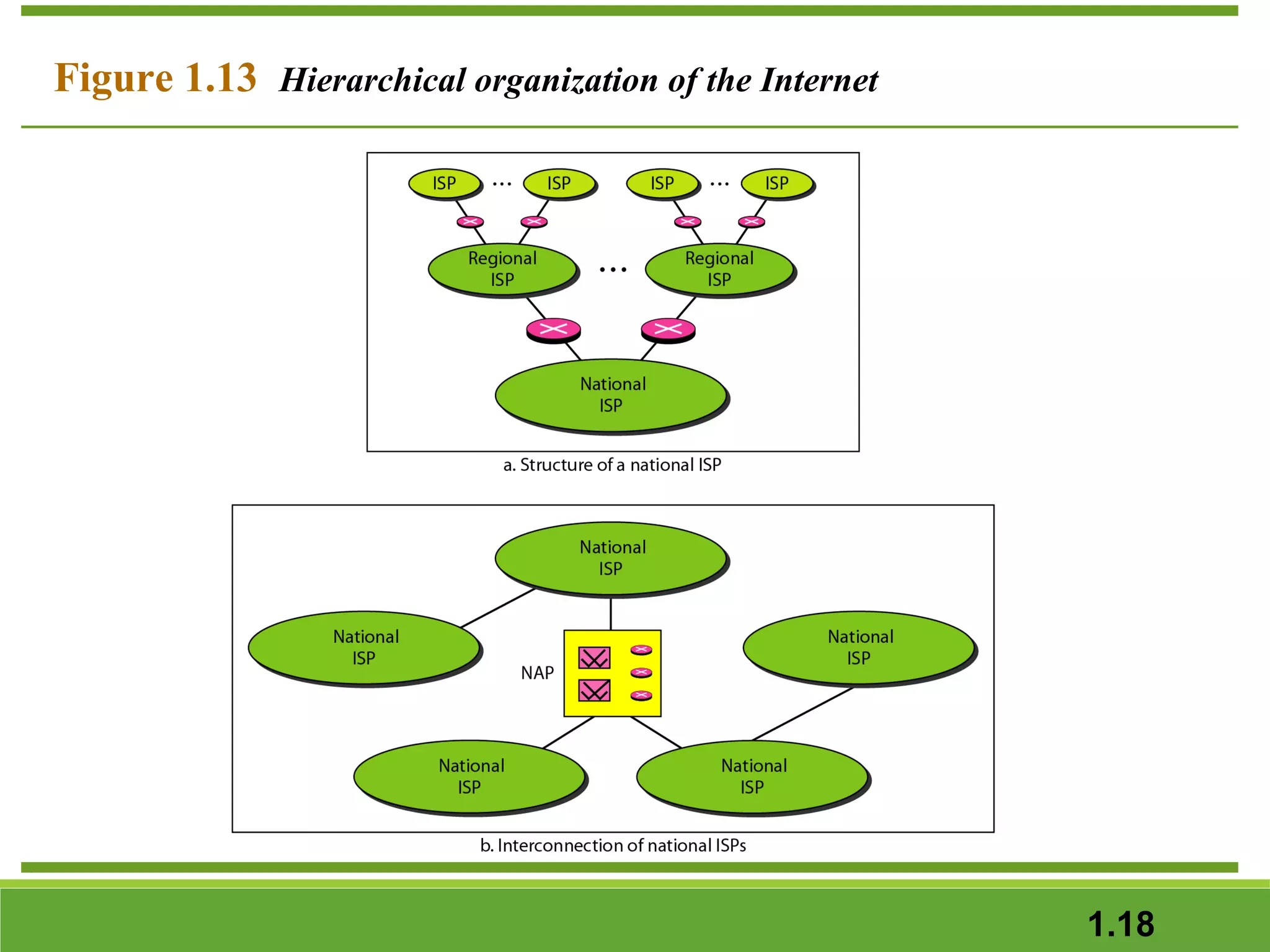
This document provides an overview of data communications and computer networks. It discusses the key components of data communication including transmission medium, data representation, and data flow. It also defines what a computer network is, describing different types of physical structures, topologies, and categories of networks. Specific topics covered include local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and how networks are interconnected through the Internet. The document concludes by defining protocols and standards that govern communication between networked devices.