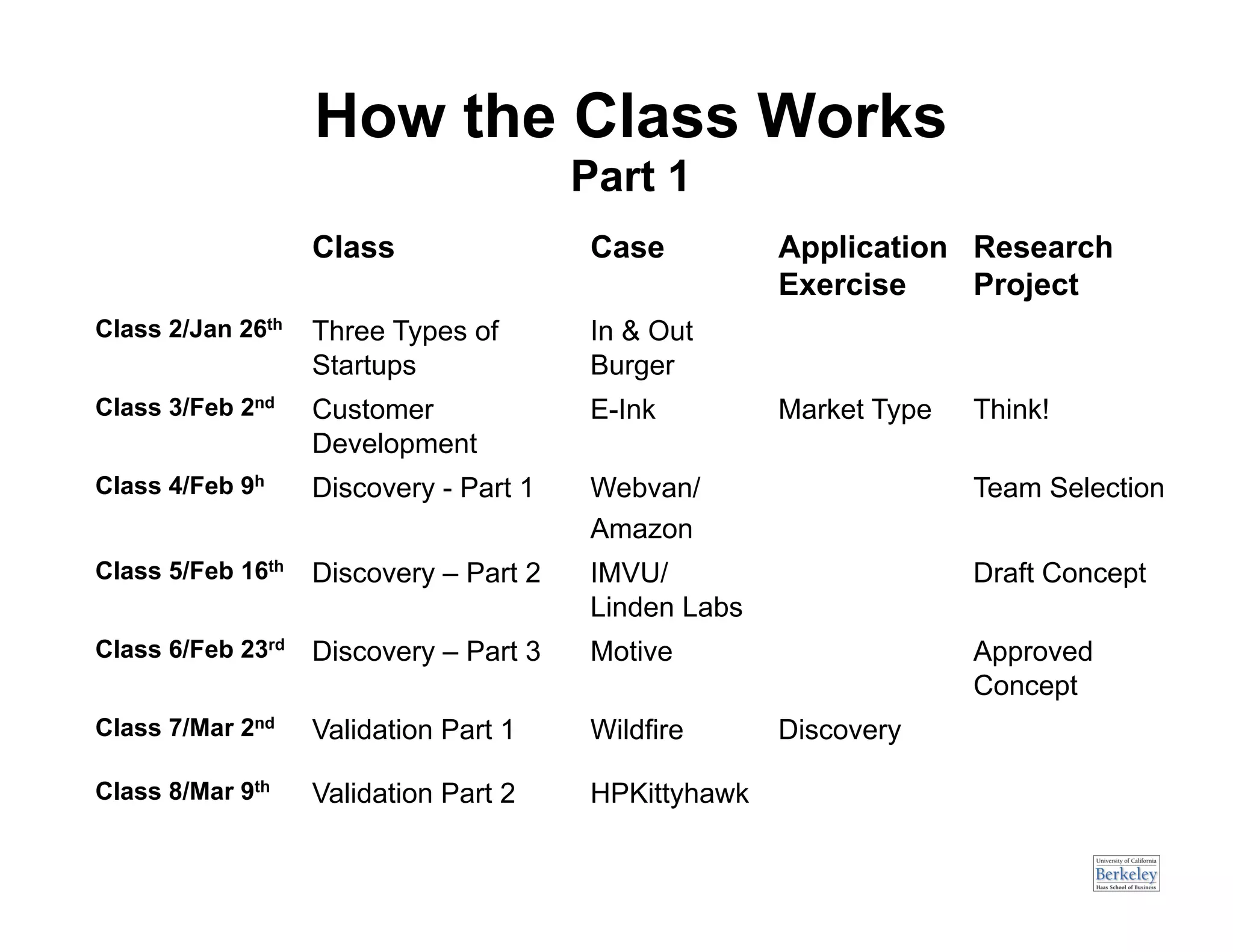
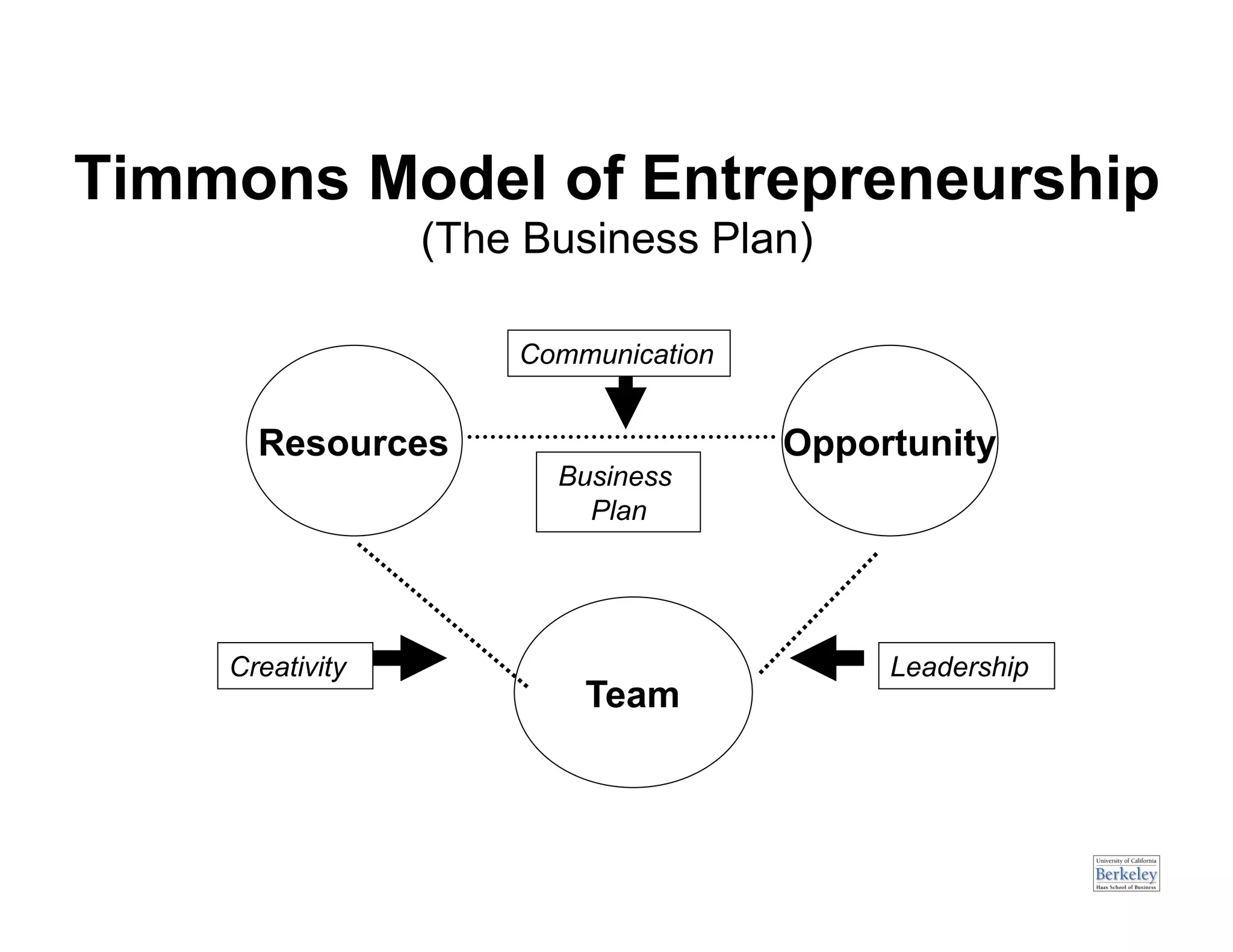
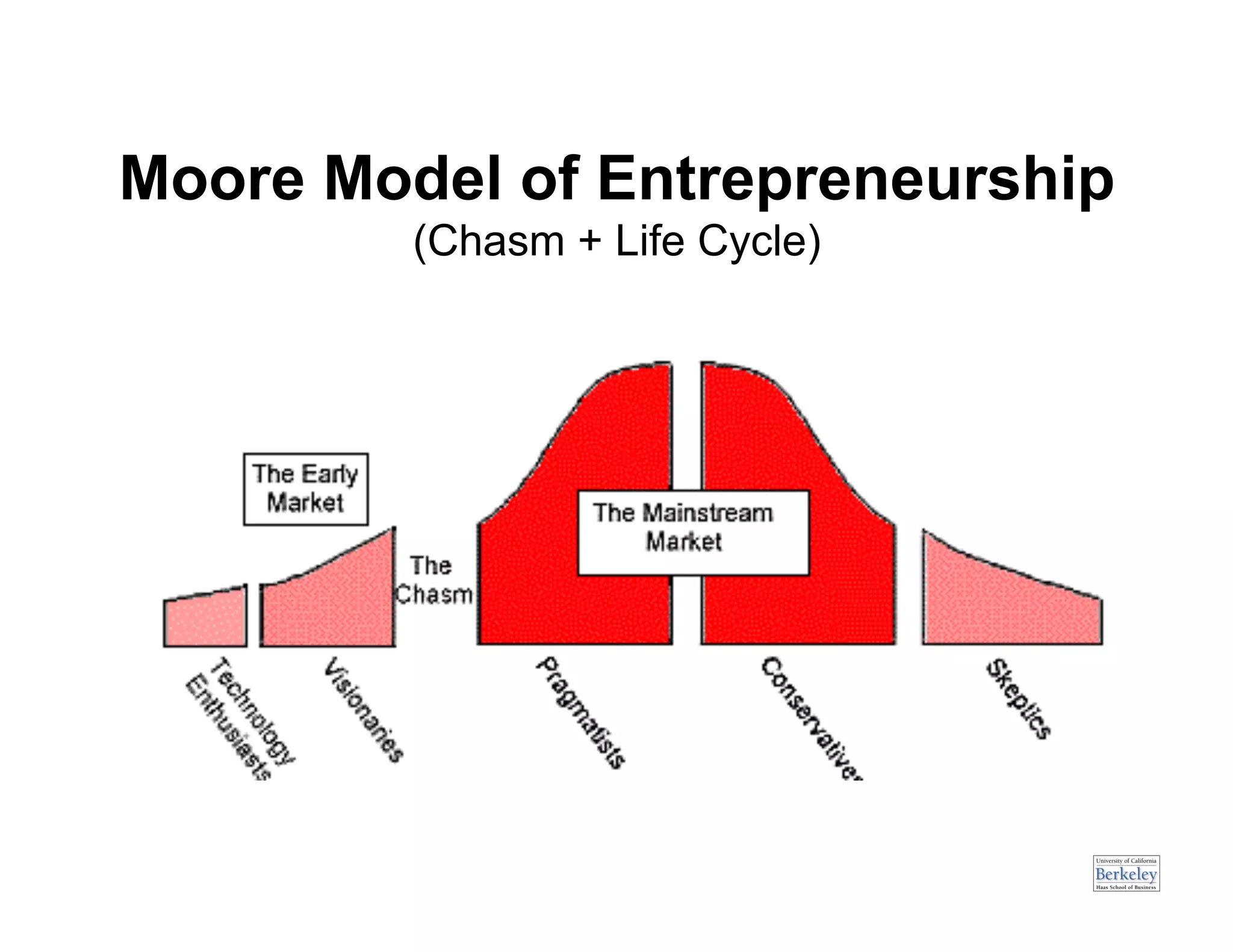
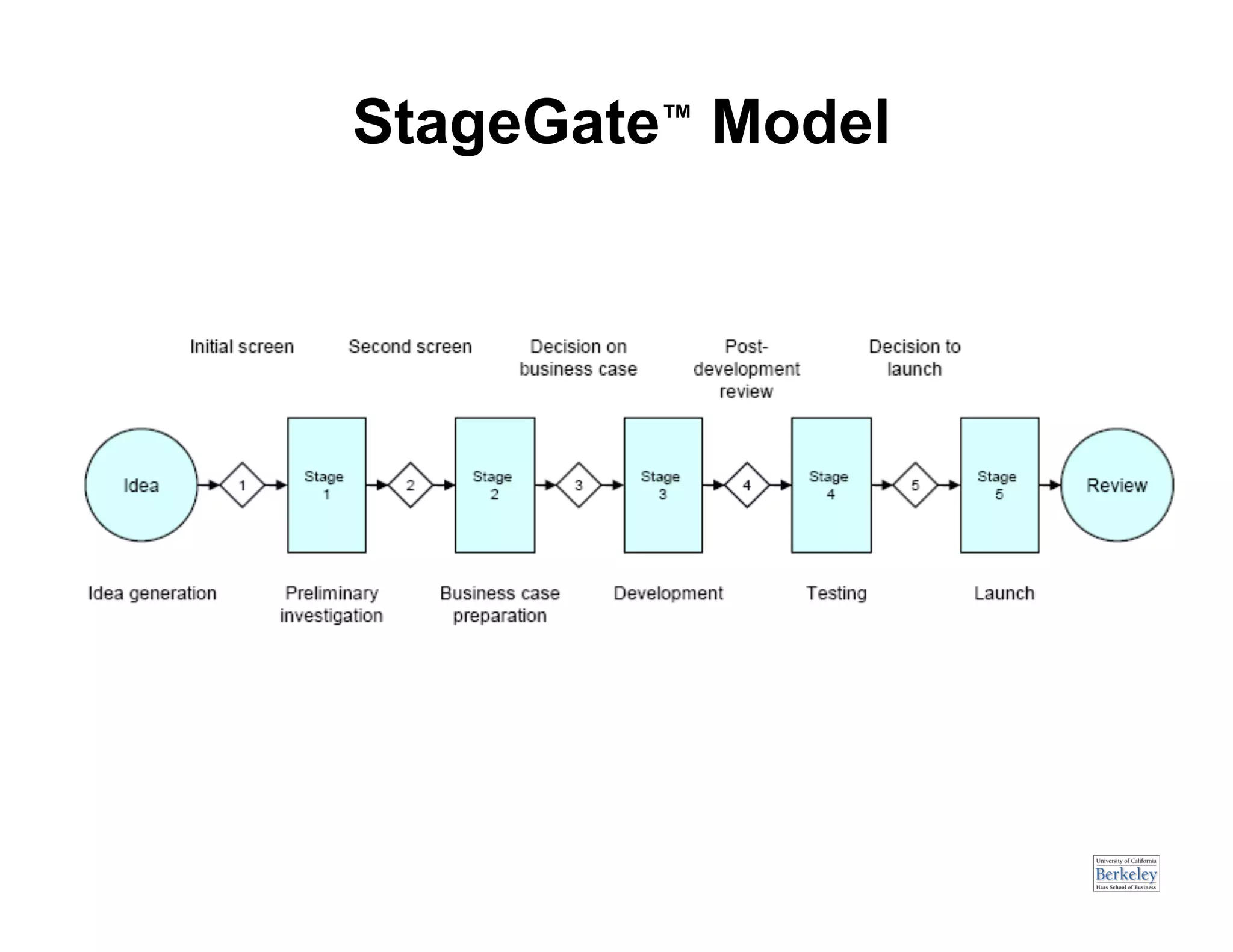
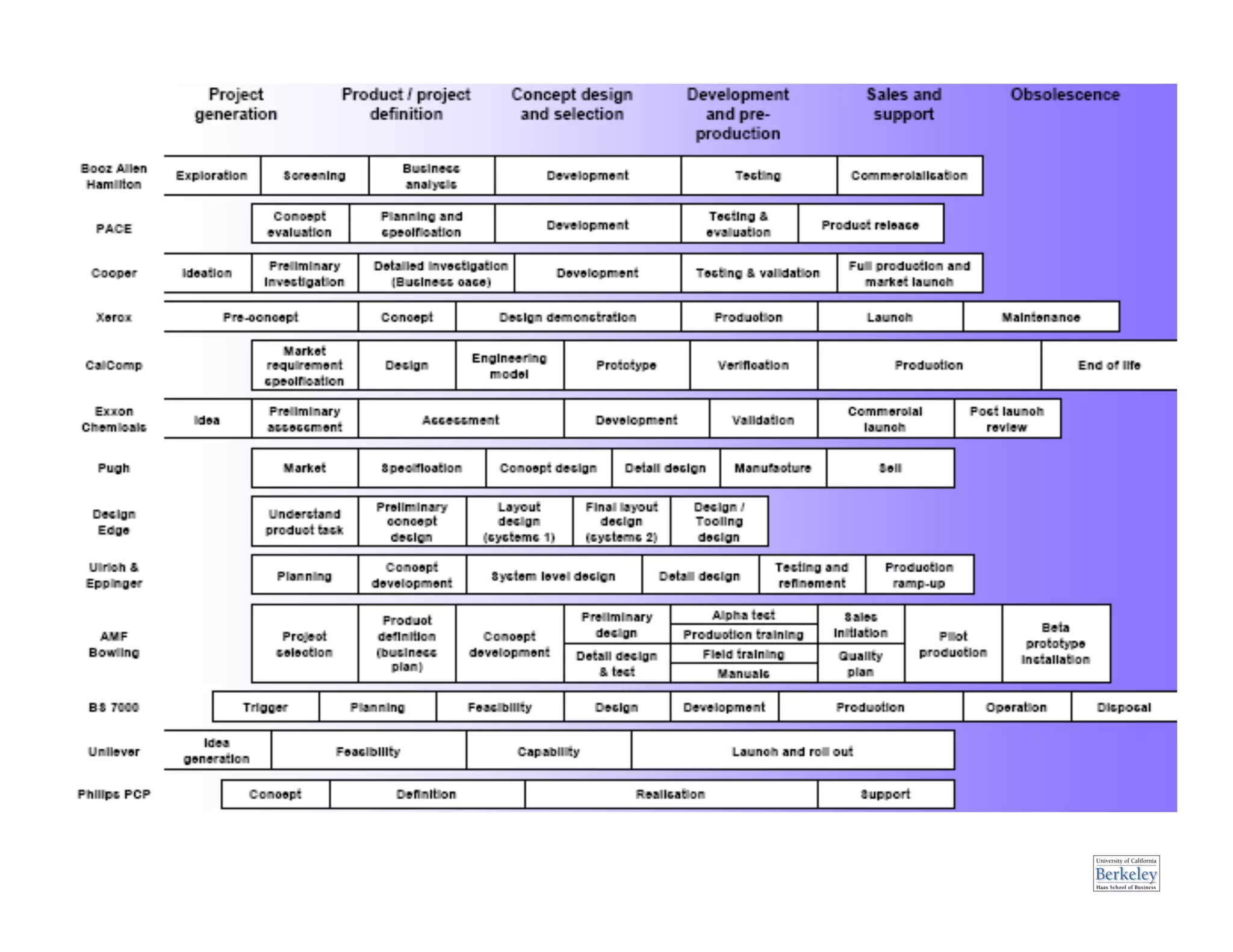
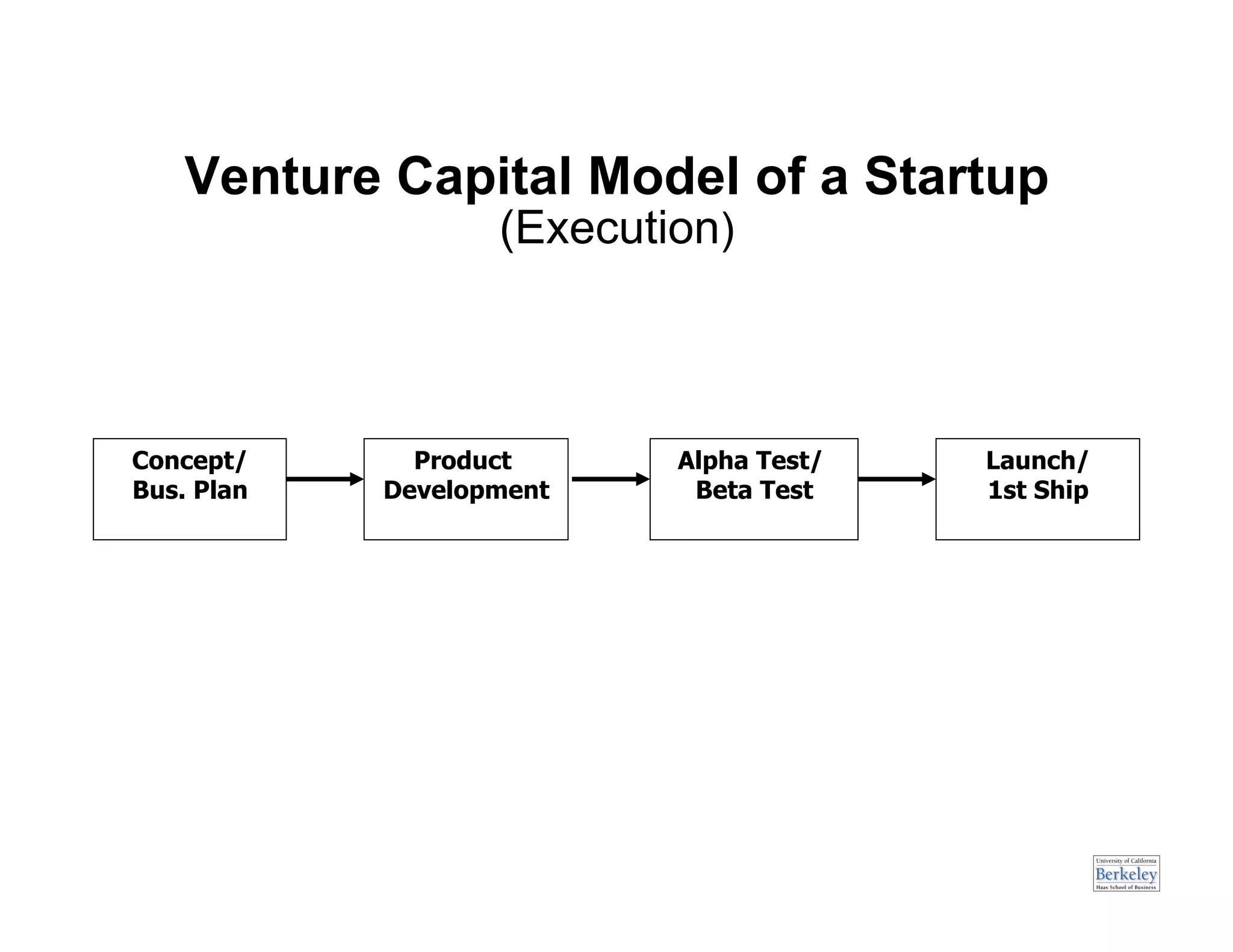
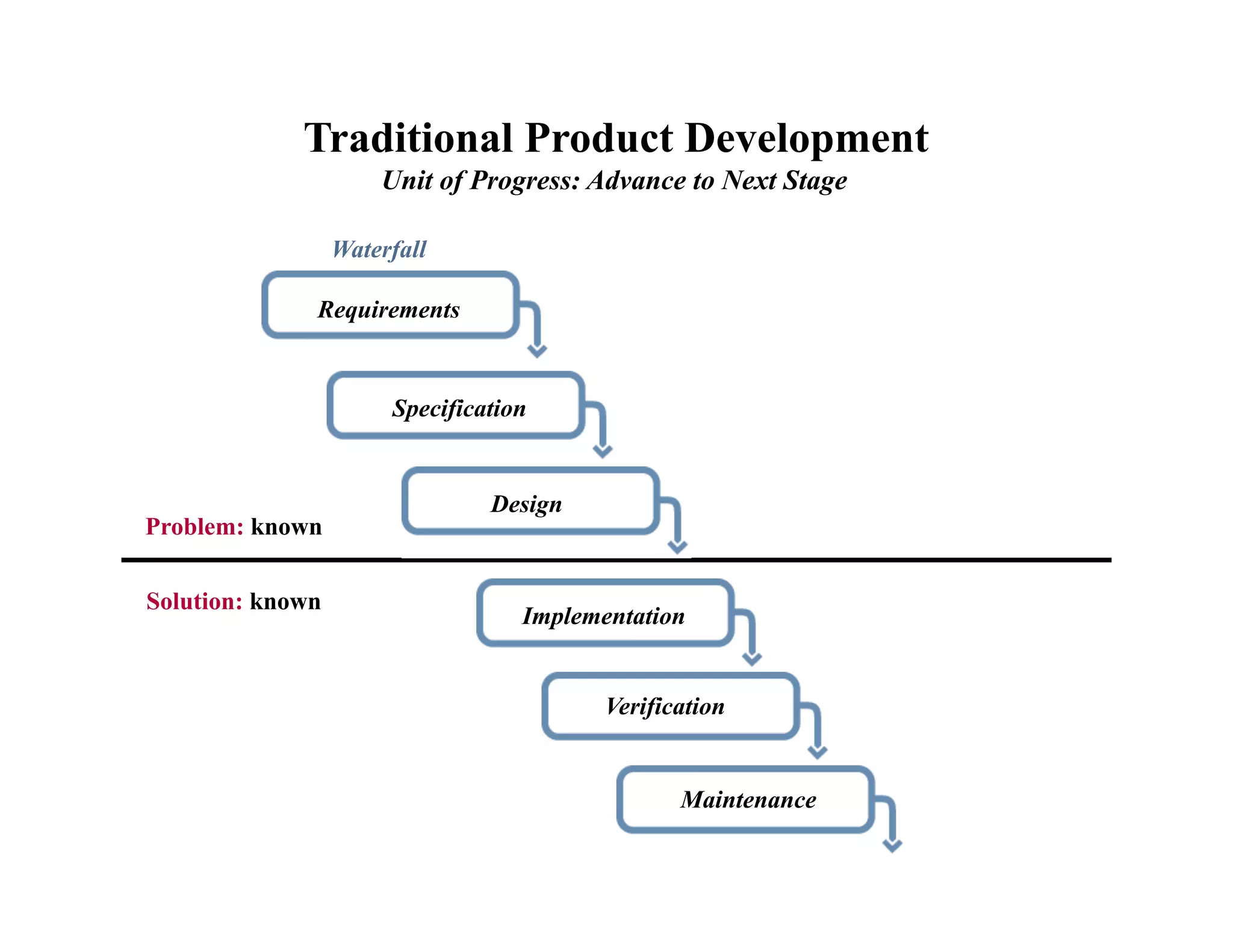
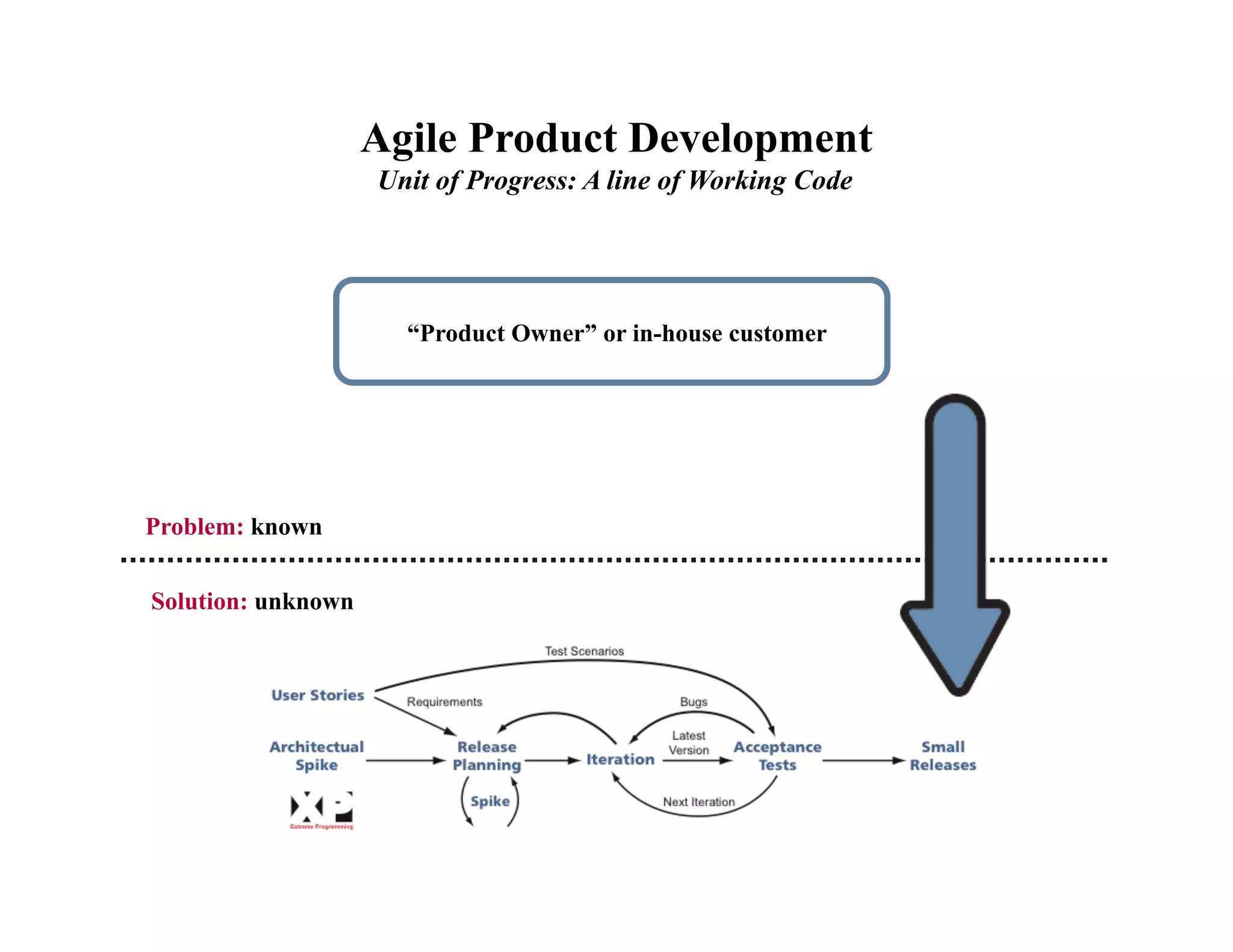
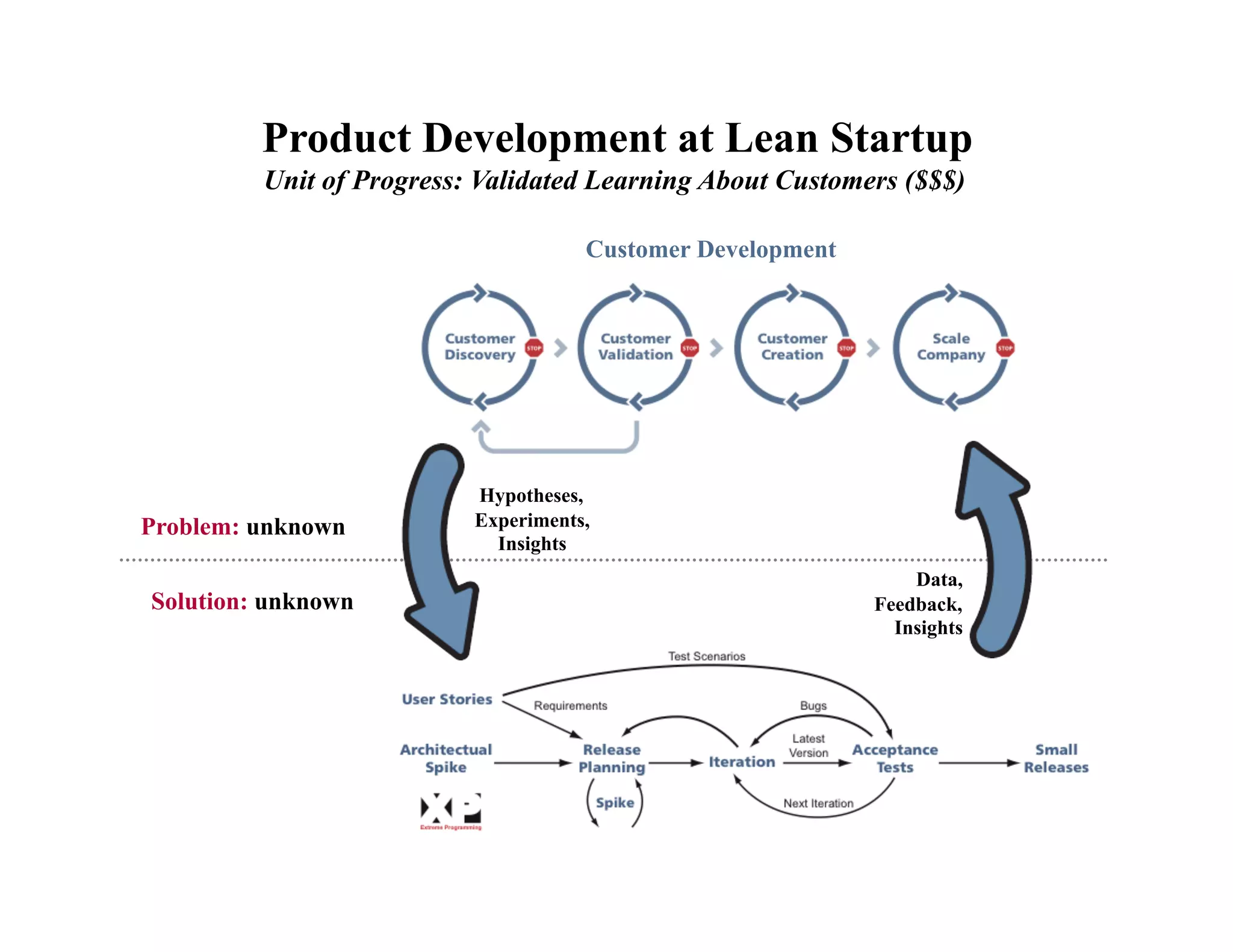
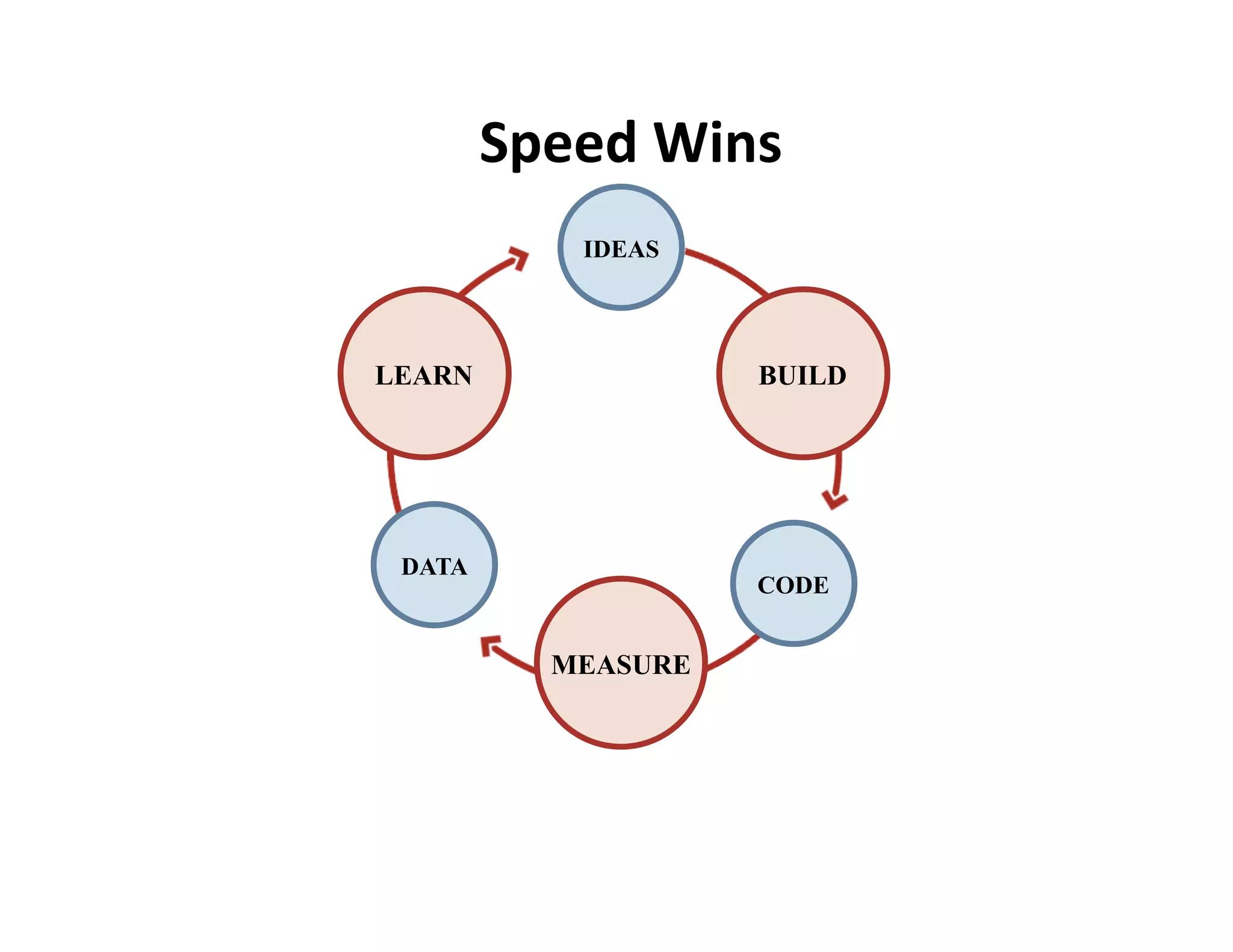
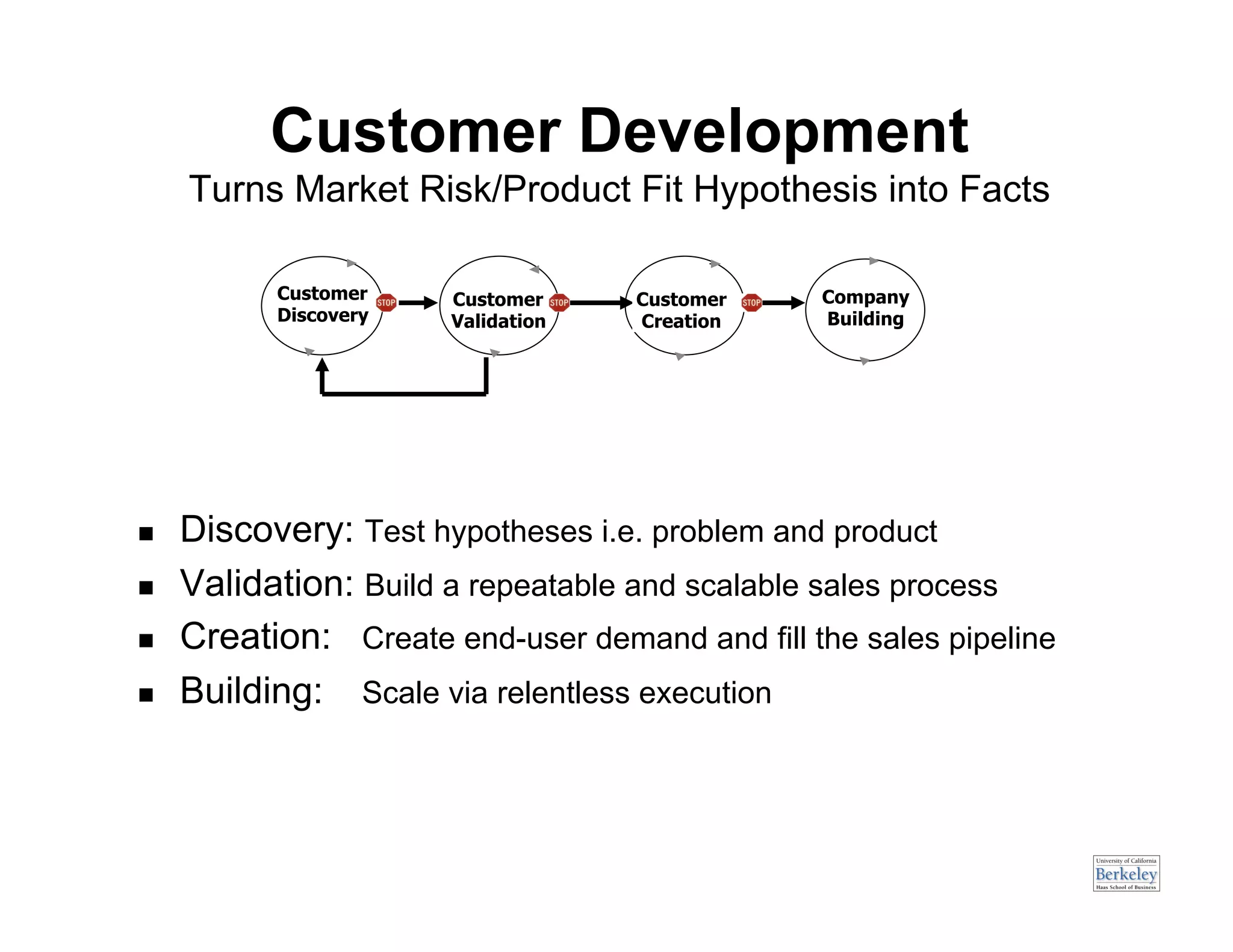
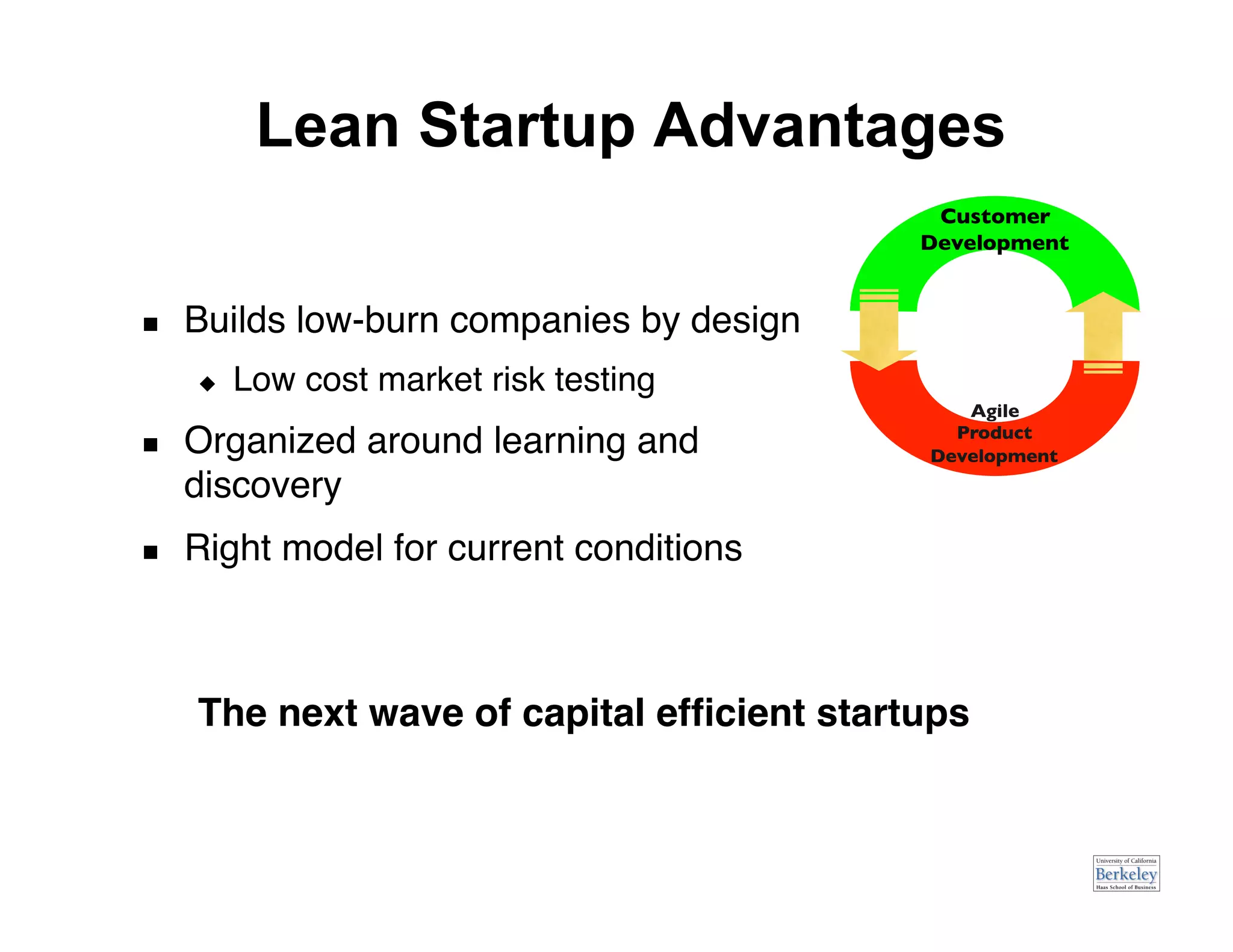
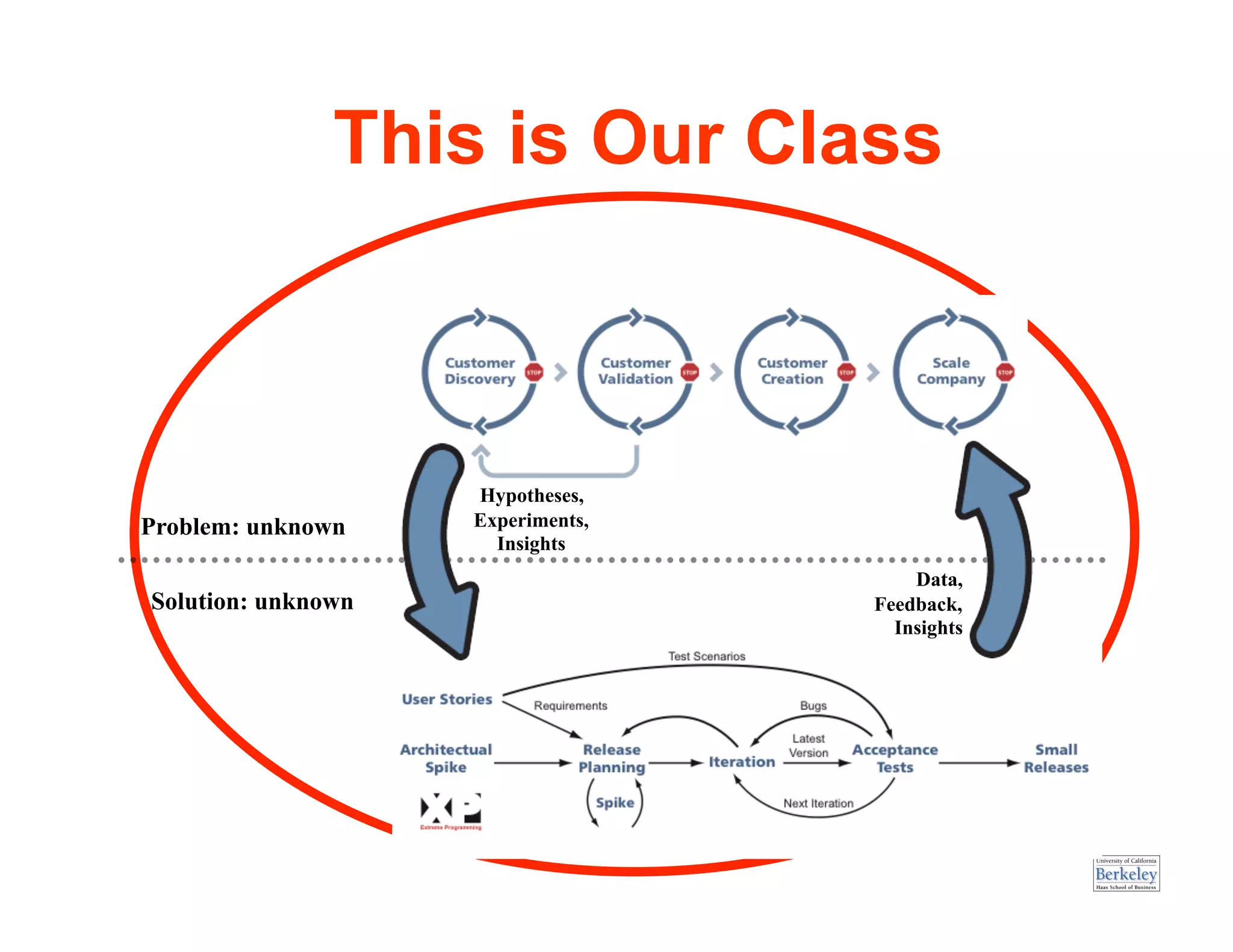
This document provides an introduction to an advanced entrepreneurship course on customer development and the lean startup methodology. It outlines the course objectives, prerequisites, structure, and key concepts that will be covered, including reducing product/market risk, customer development process of discovery, validation, and creation, and building companies with low costs by designing for learning rather than traditional product development processes. The instructors are introduced as Steve Blank and Eric Ries, pioneers of the lean startup approach.