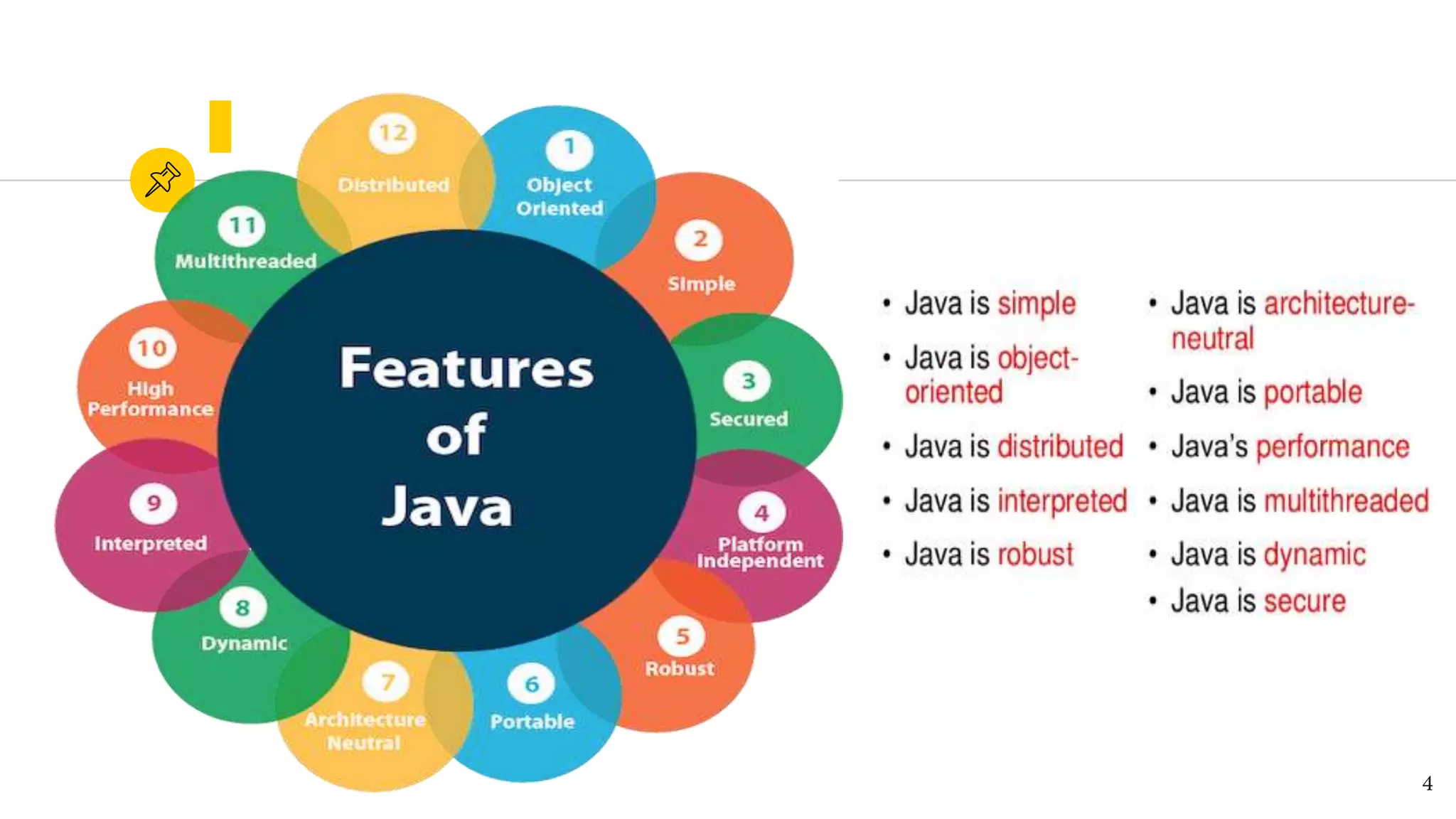
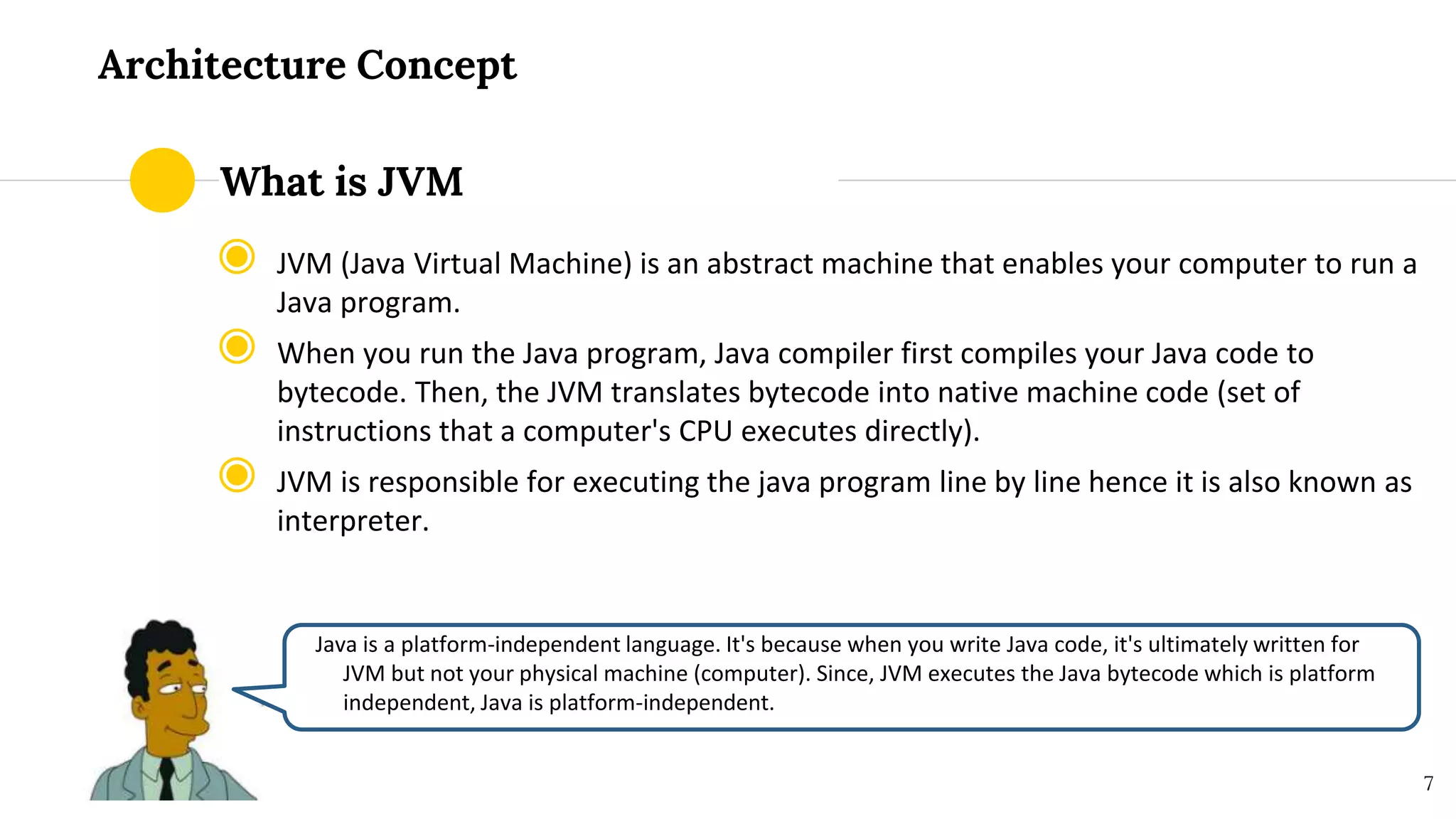
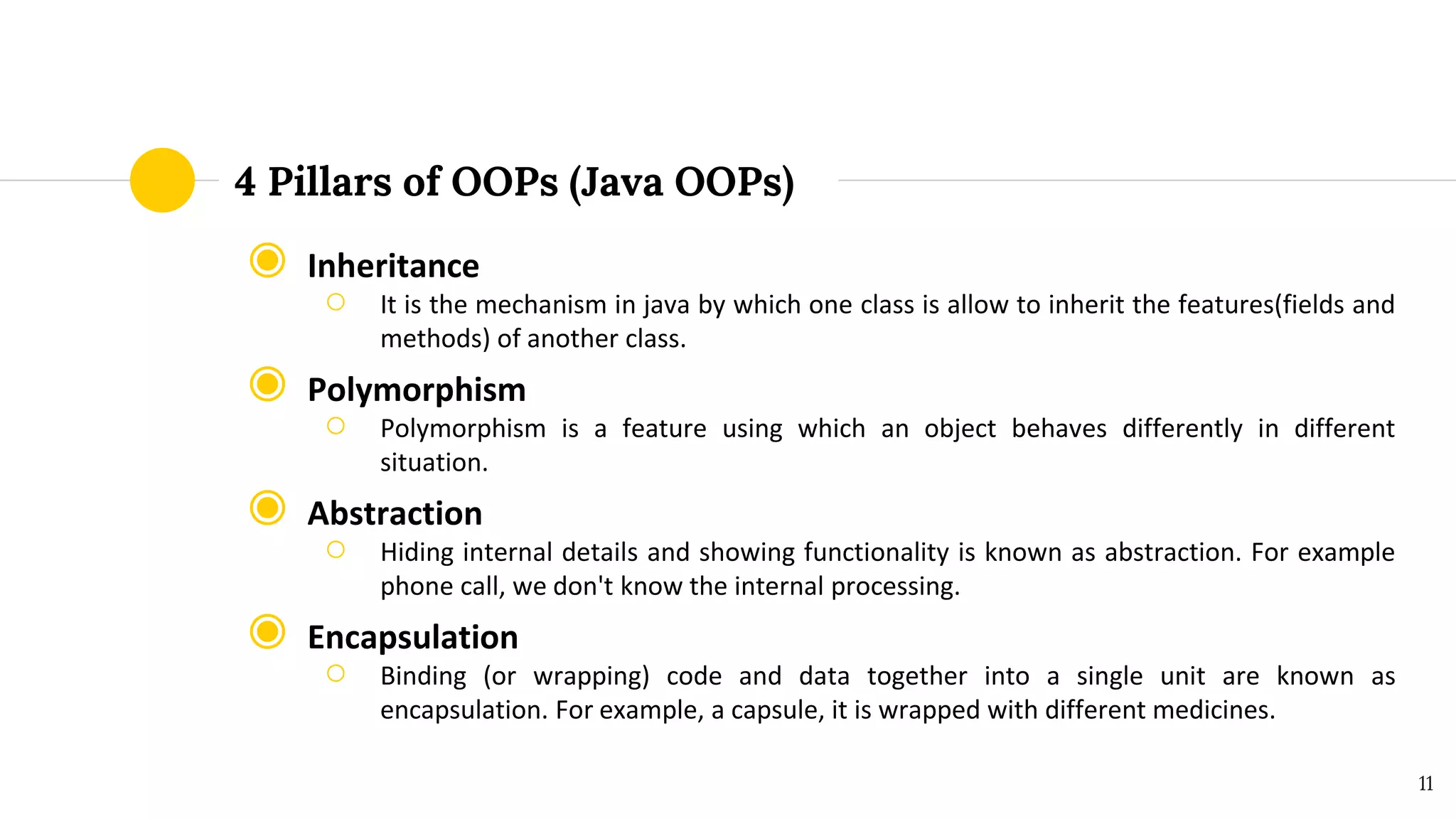
This document provides an overview of core Java for beginners in automation testing, covering topics such as installation, features, architecture, and object-oriented programming concepts. It highlights the importance of Java as a versatile programming language and details components like JRE and JDK. The document further explains the principles of OOP including inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation, along with definitions of classes and objects.