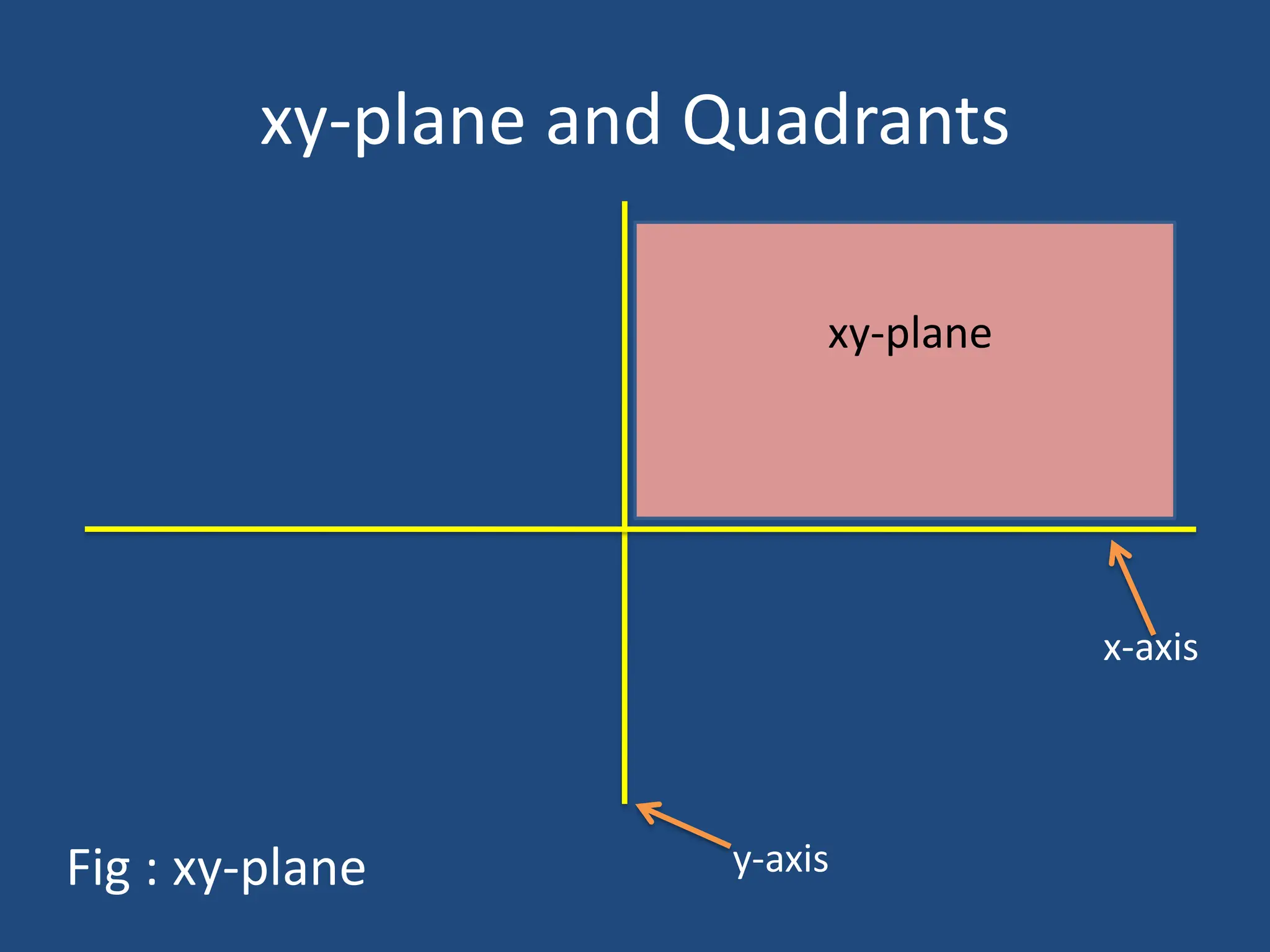
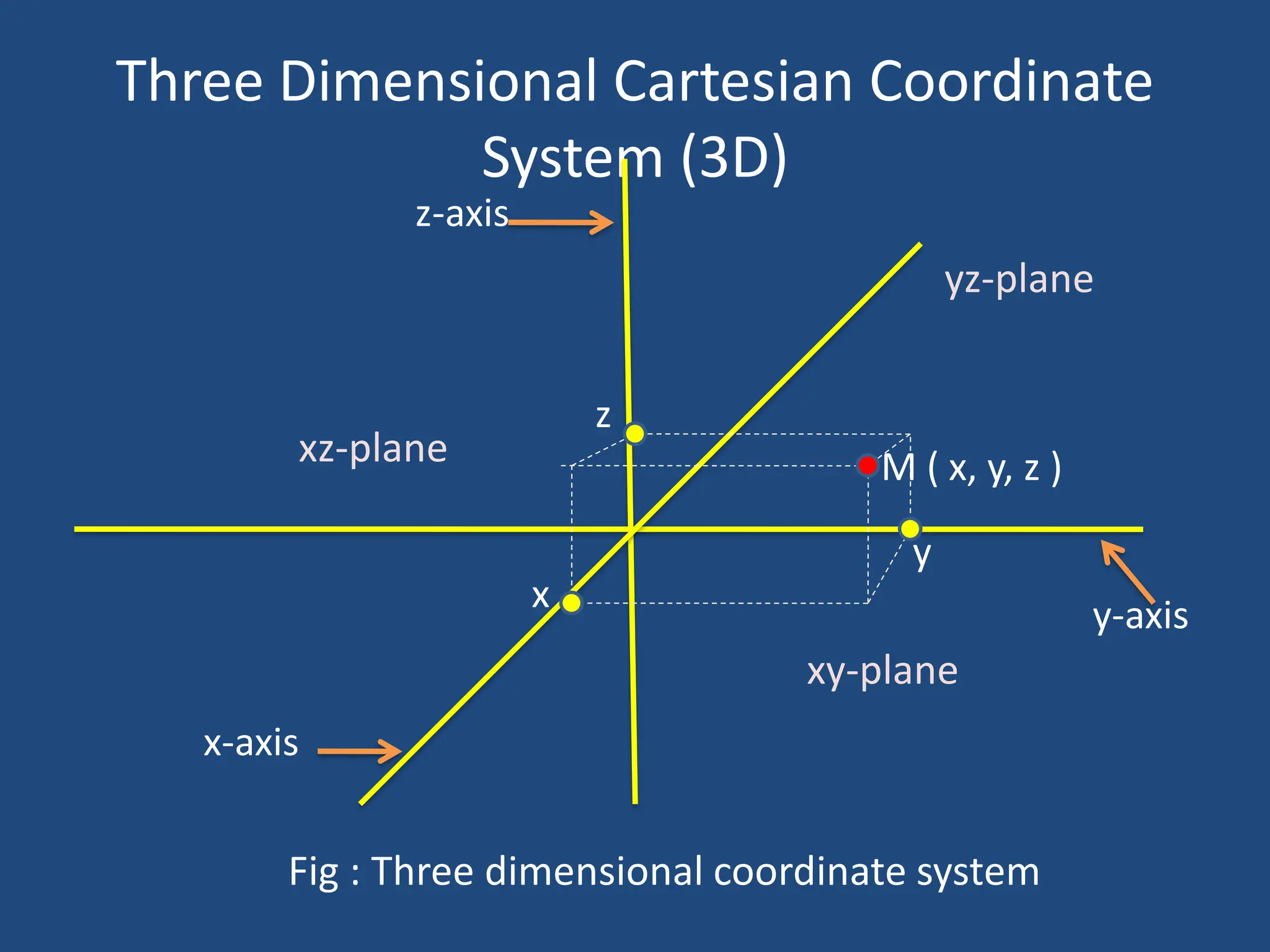
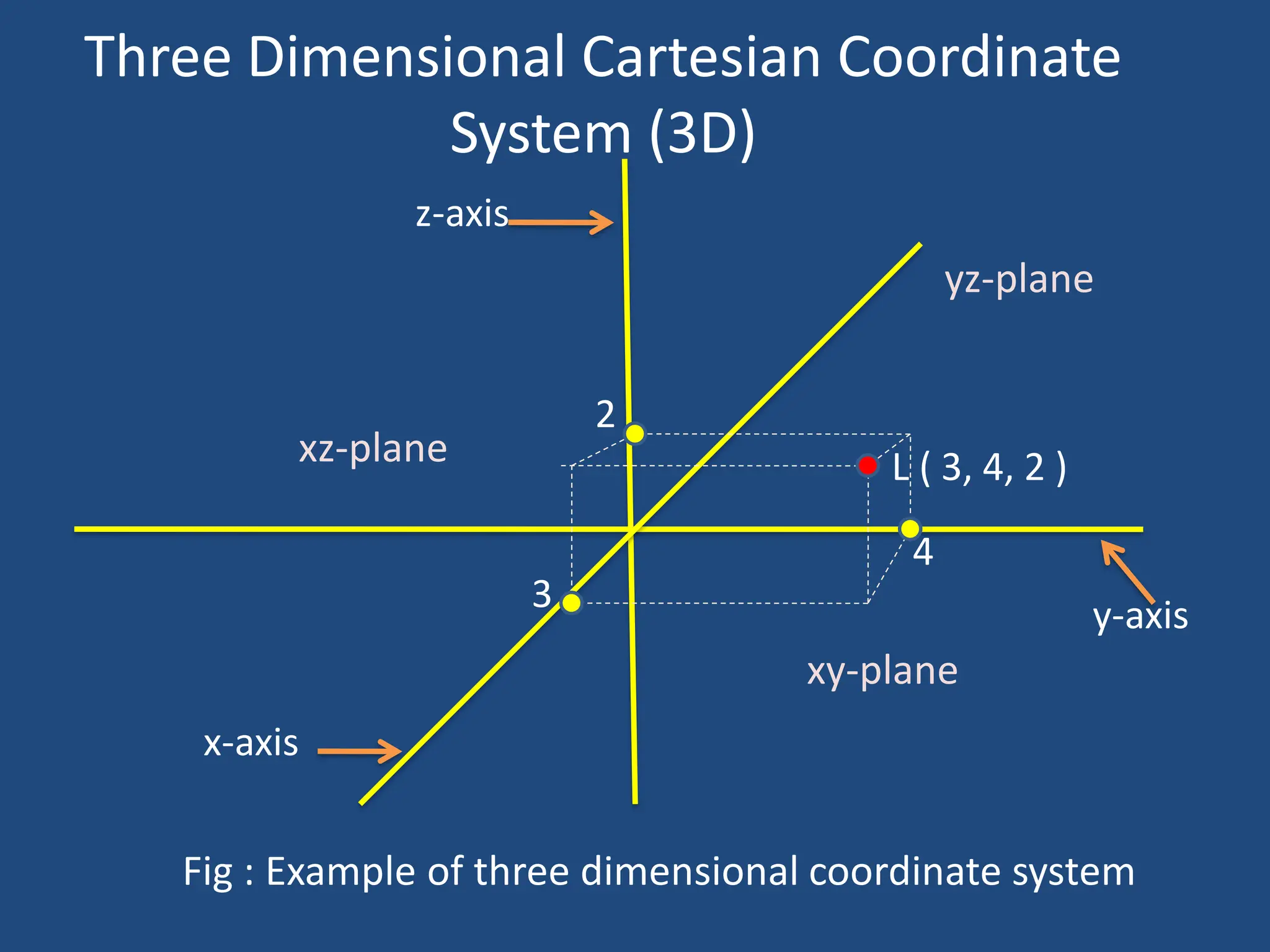
The document explains the Cartesian coordinate system, which is used to determine the position of points in two-dimensional (2D) and three-dimensional (3D) space through perpendicular lines drawn to axes. It outlines the structure of one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and three-dimensional systems, describing how coordinates are identified and how planes and quadrants are utilized for their representation. Additionally, it highlights applications of the Cartesian coordinate system in fields such as computer graphics and design.