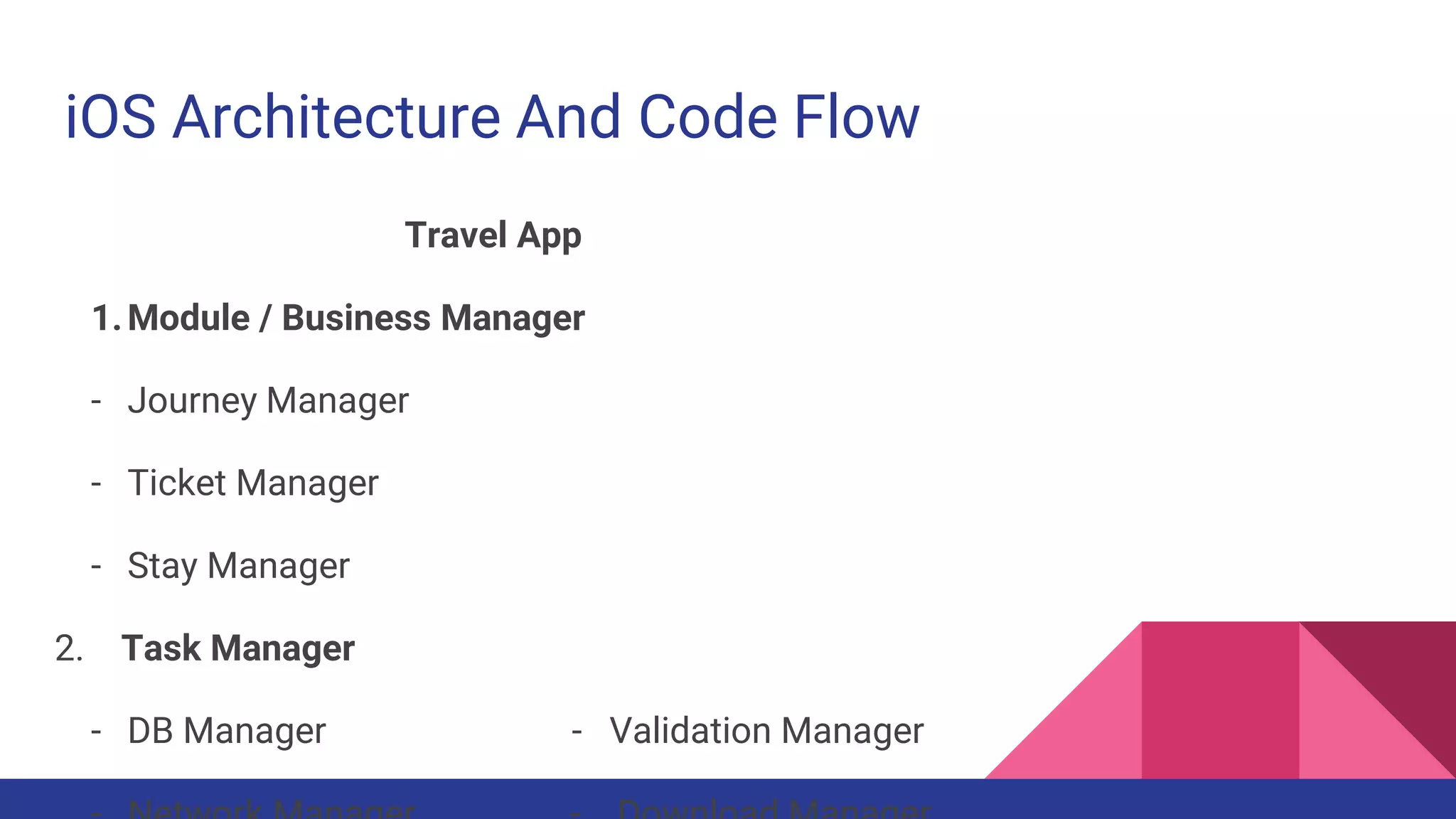
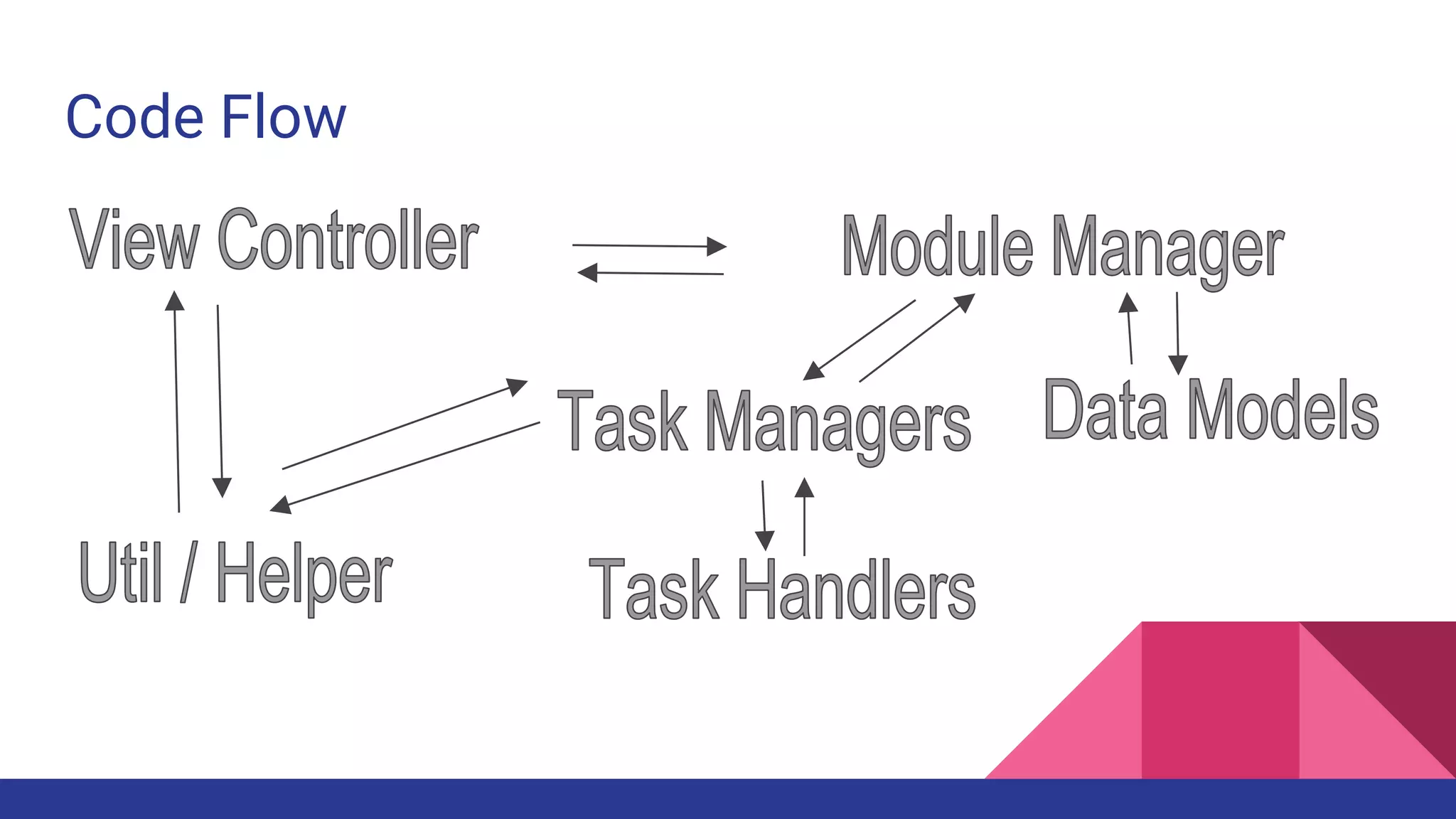
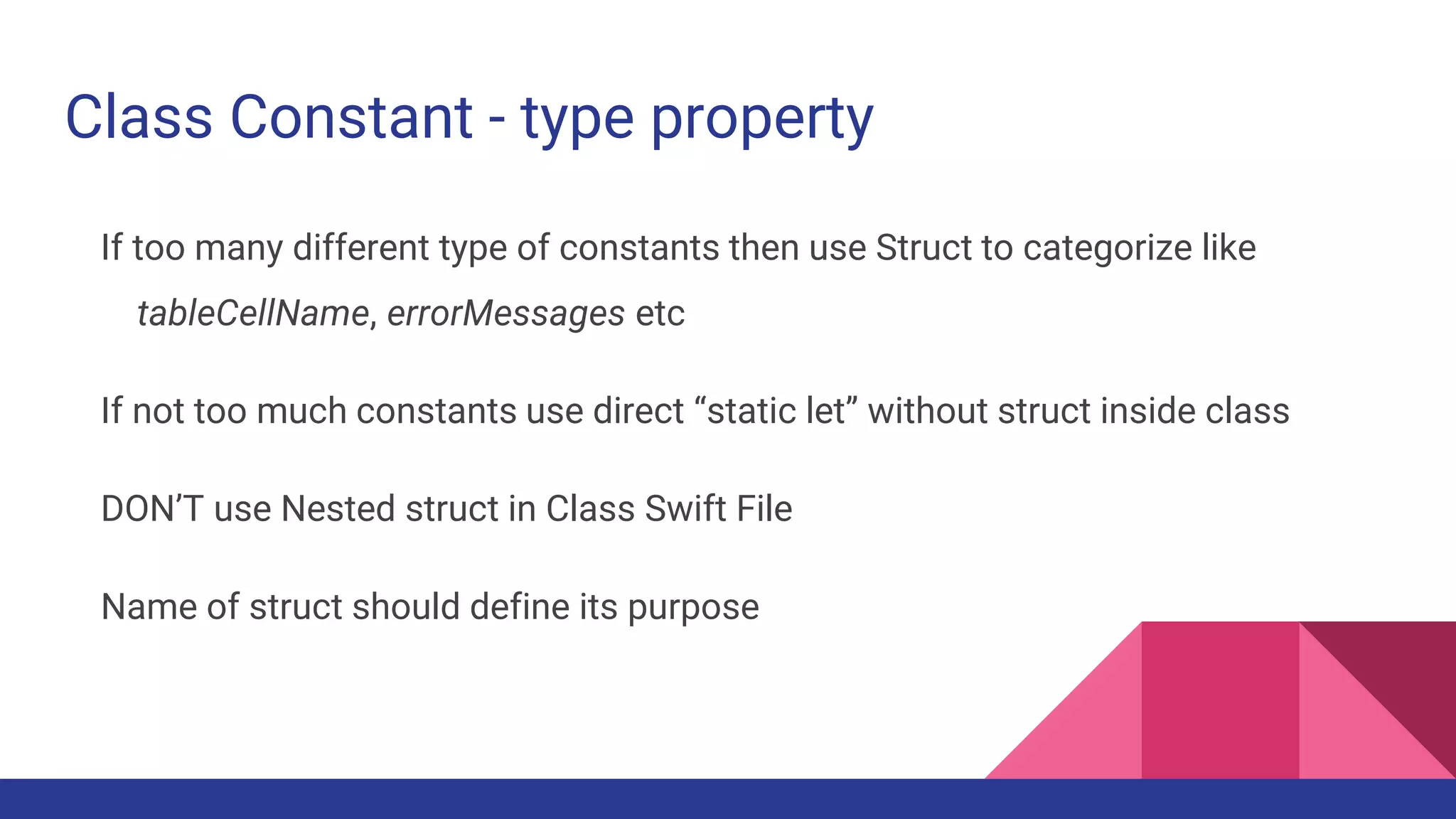
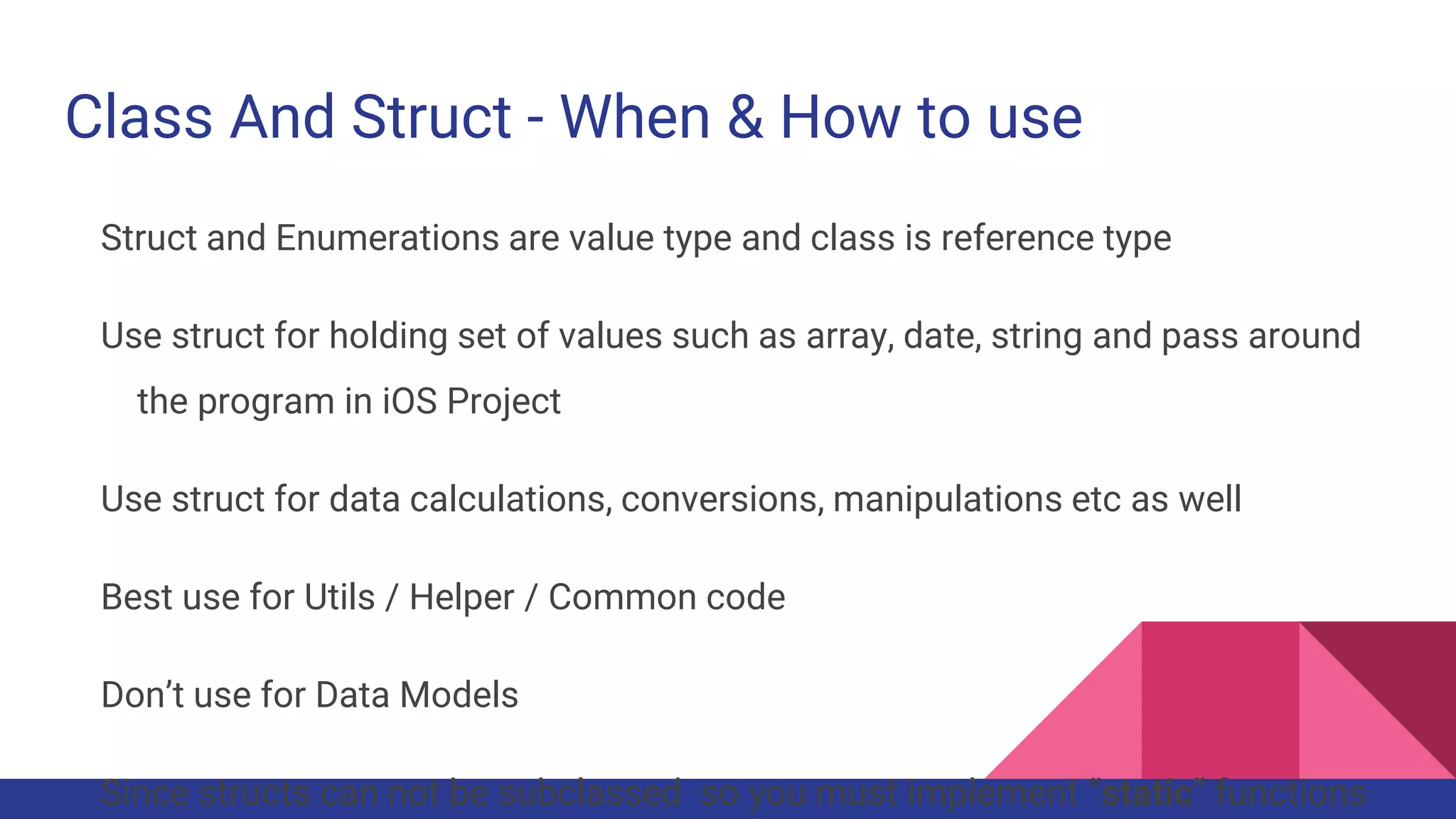
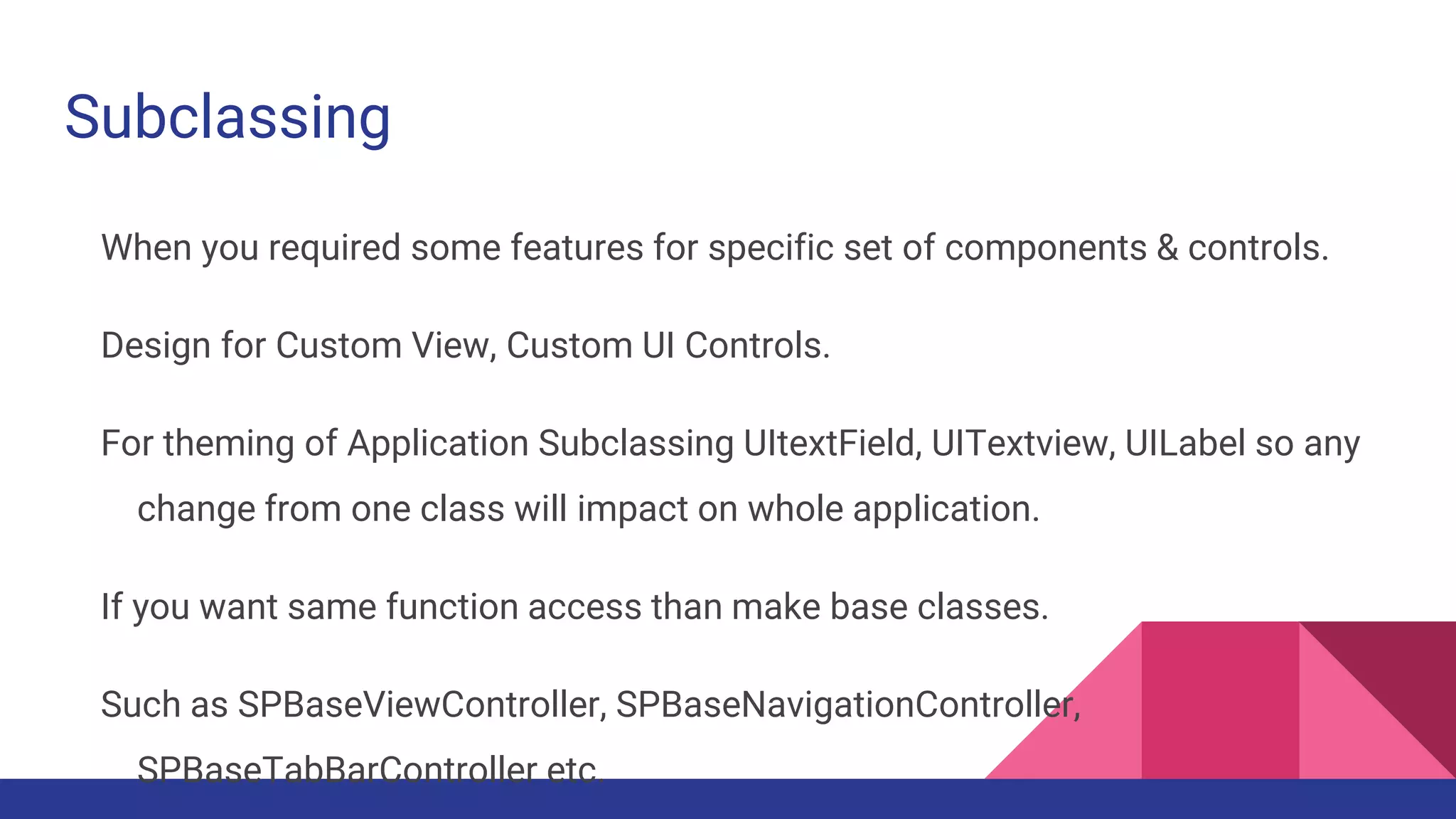
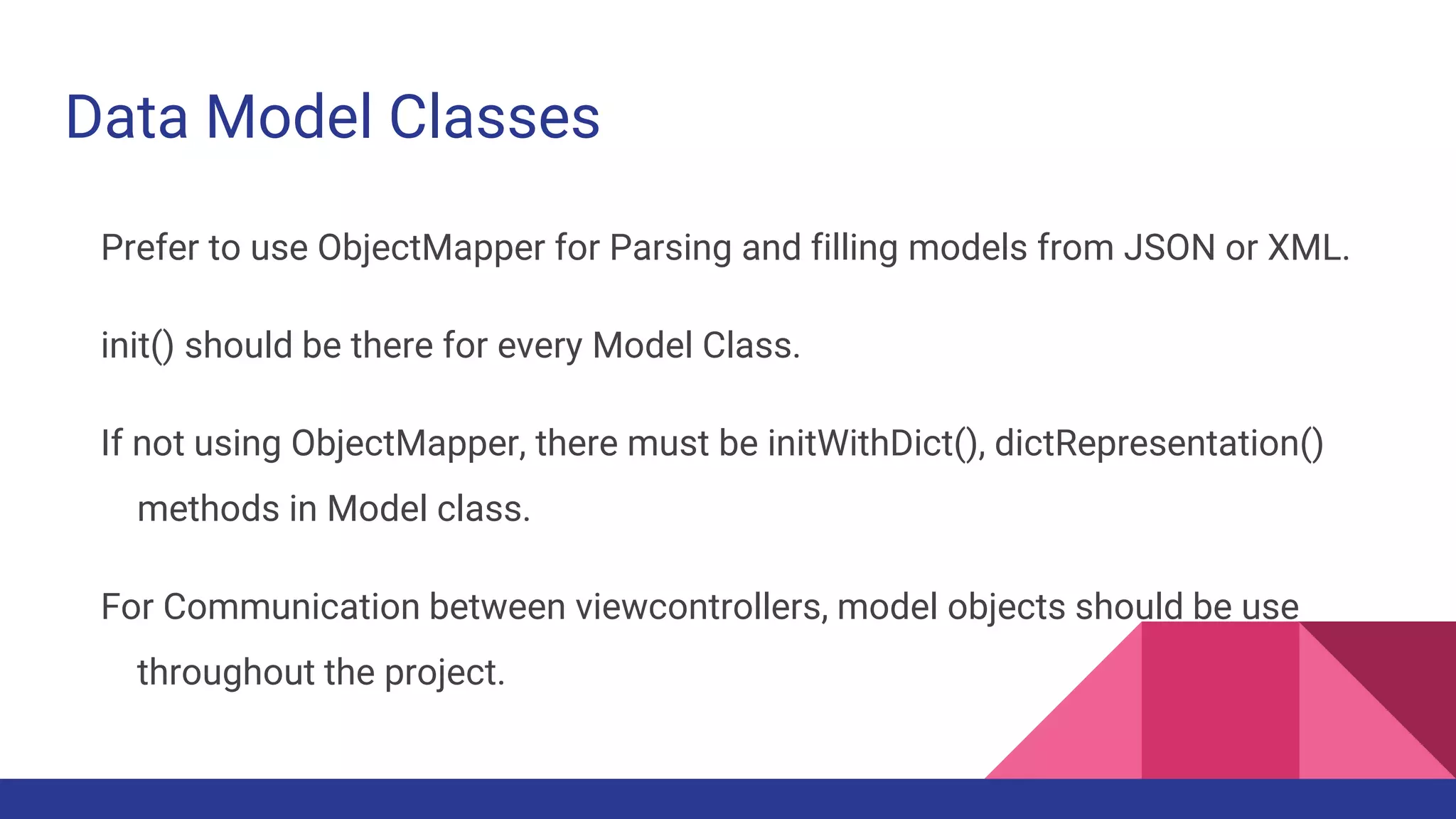
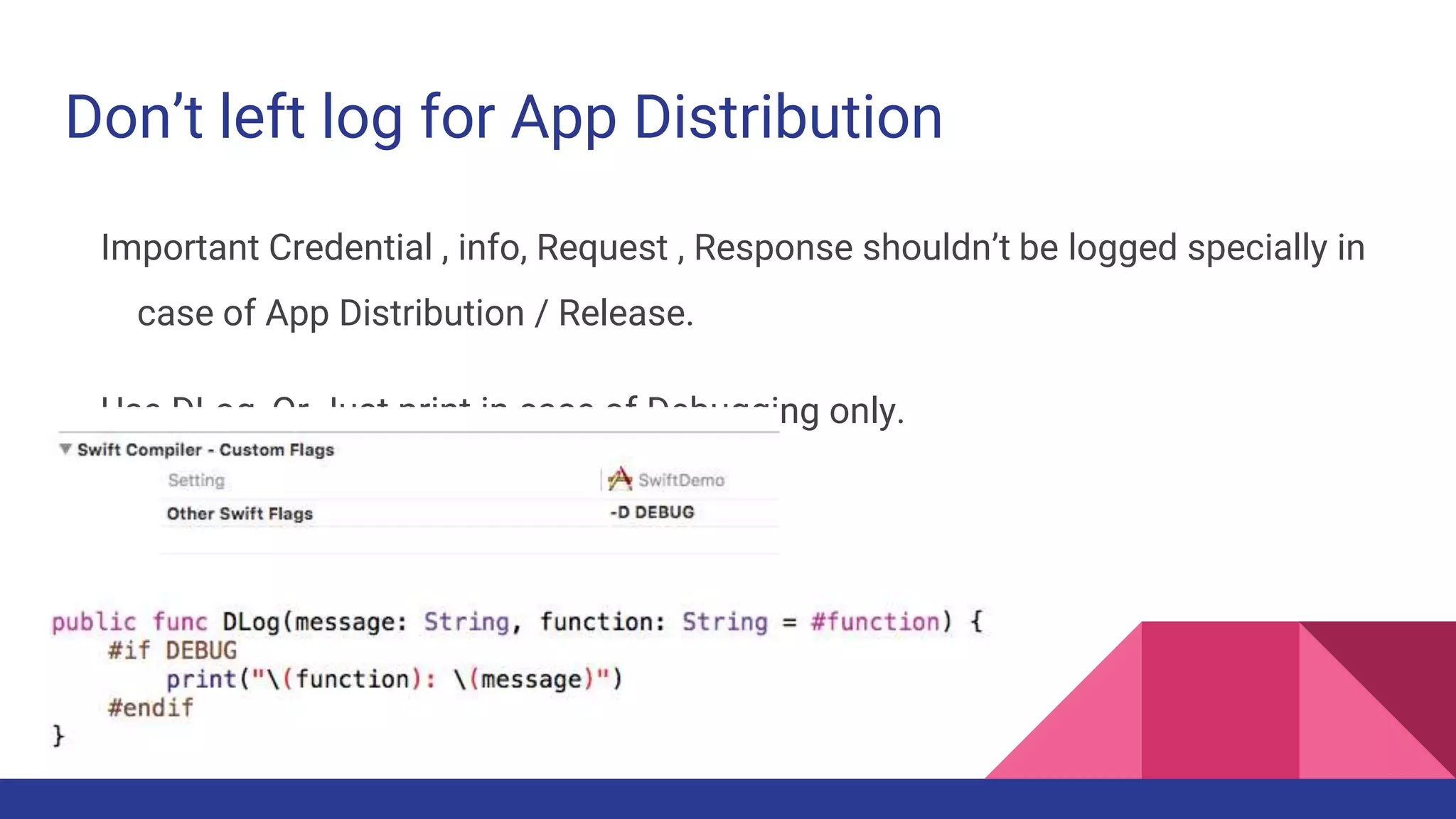
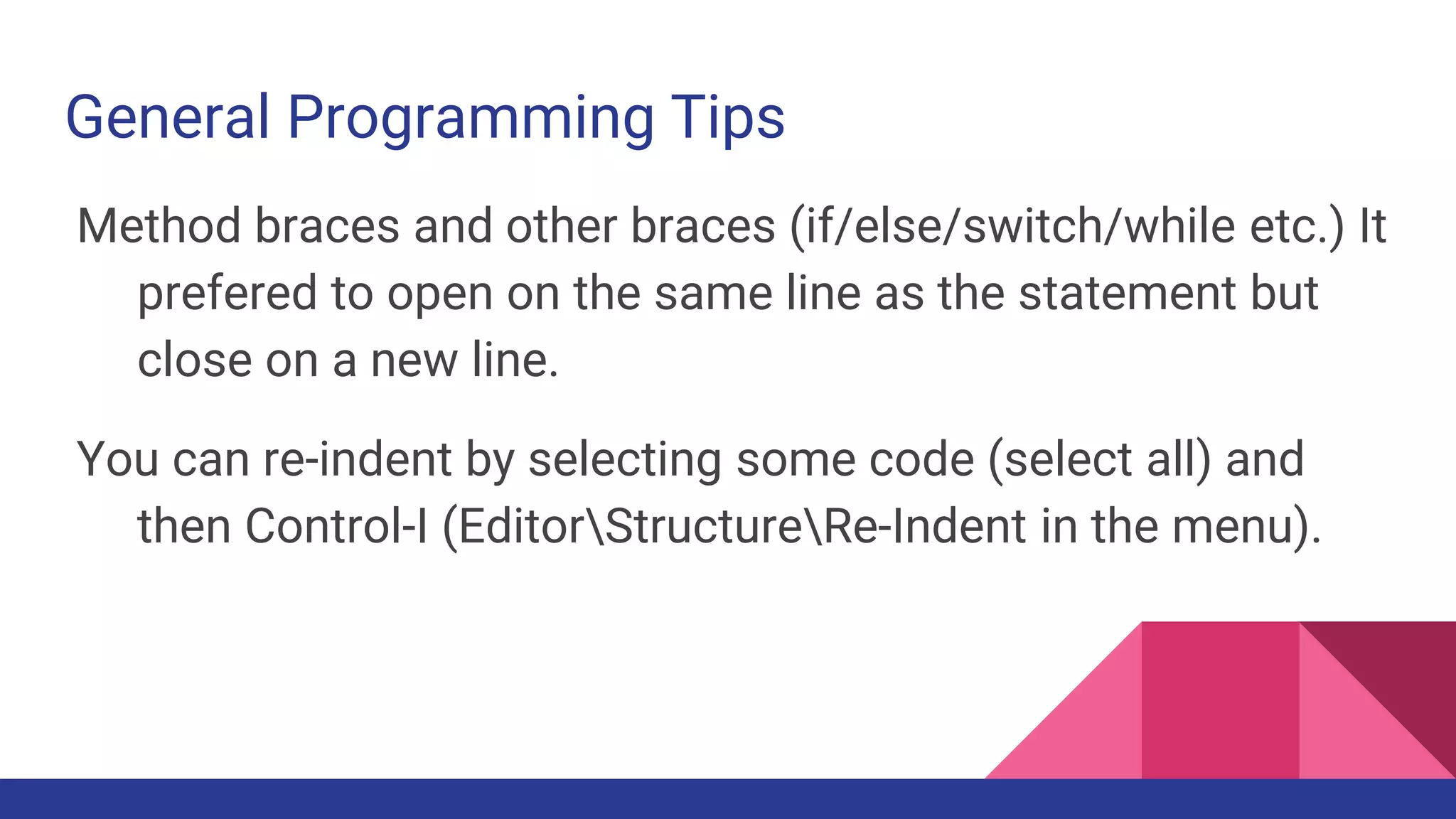
This document provides guidelines for code quality management in iOS projects. It discusses best practices for file and folder naming conventions using capital letter prefixes, code organization using commenting styles, handling global constants in a dedicated file, using classes and structs appropriately, following patterns like singleton, factory, and implementing memory warning handling. The document also provides tips on image assets, data models, error handling, typealias, subclassing, extensions and more.


















![Whitespace within methods should separate functionality,
but having too many sections in a method often means
you should refactor into several methods.
Colons always have no space on the left and one space on
the right. Exceptions are the ternary operator ? : and
empty dictionary [ : ].
class TestDatabase: Database {
var data: [String: CGFloat] = ["A": 1.2, "B": 3.2]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codequalitymanagementios-161010104637/75/Code-Quality-Management-iOS-29-2048.jpg)
![For Empty arrays and Dictionary, use type
annotations
Preferred:
var names: [String] = []
var lookup: [String: Int] = [:]
Not Preferred:
var names = [String]()
var lookup = [String: Int]()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codequalitymanagementios-161010104637/75/Code-Quality-Management-iOS-30-2048.jpg)
![Prefer shortcut versions of type Declarations
rather than full generics syntax
Preferred:
var deviceModels: [String]
var employees: [Int: String]
var faxNumber: Int?
Not Preferred:
var deviceModels: Array<String>
var employees: Dictionary<Int, String>
var faxNumber: Optional<Int>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/codequalitymanagementios-161010104637/75/Code-Quality-Management-iOS-31-2048.jpg)