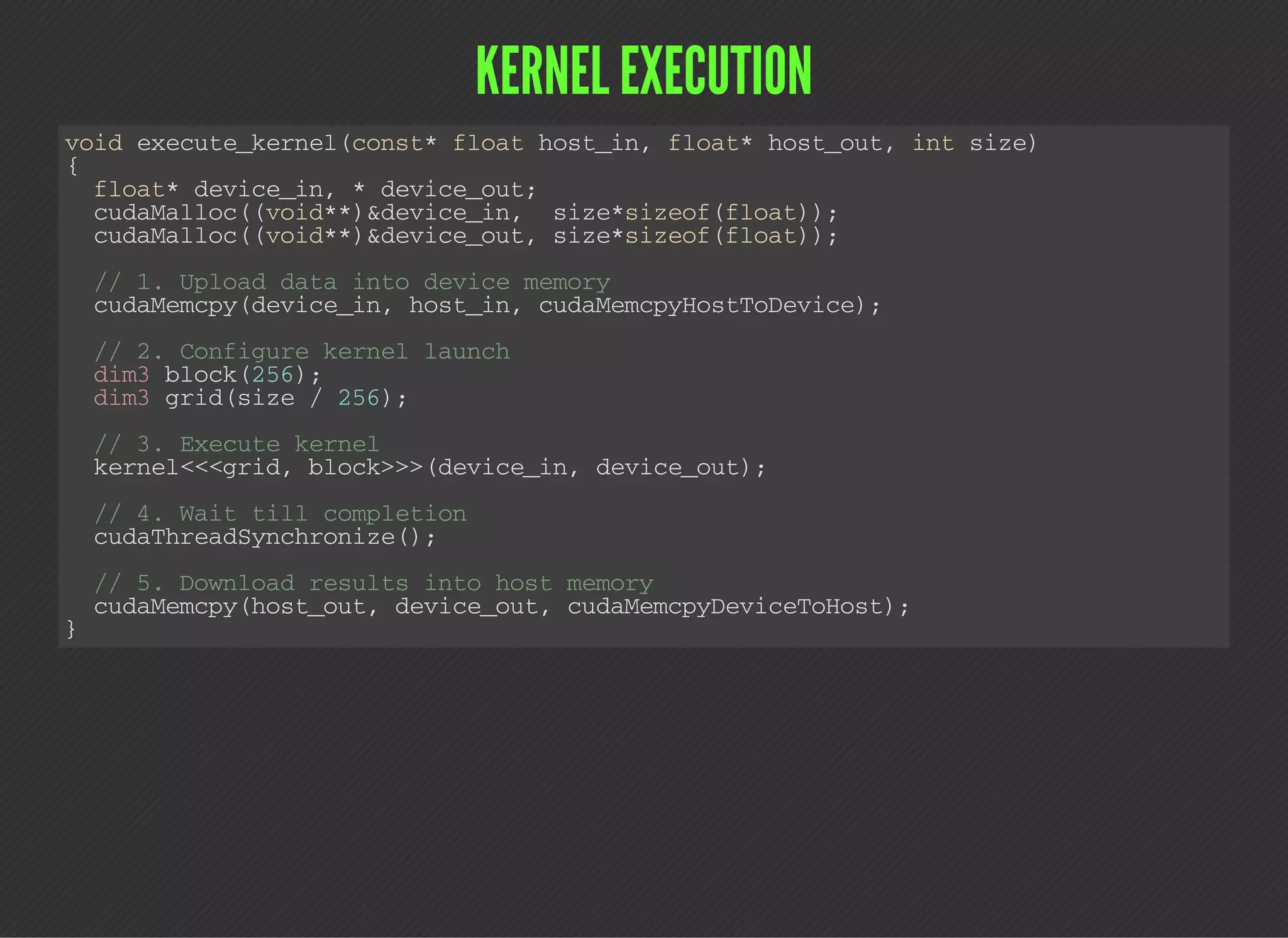
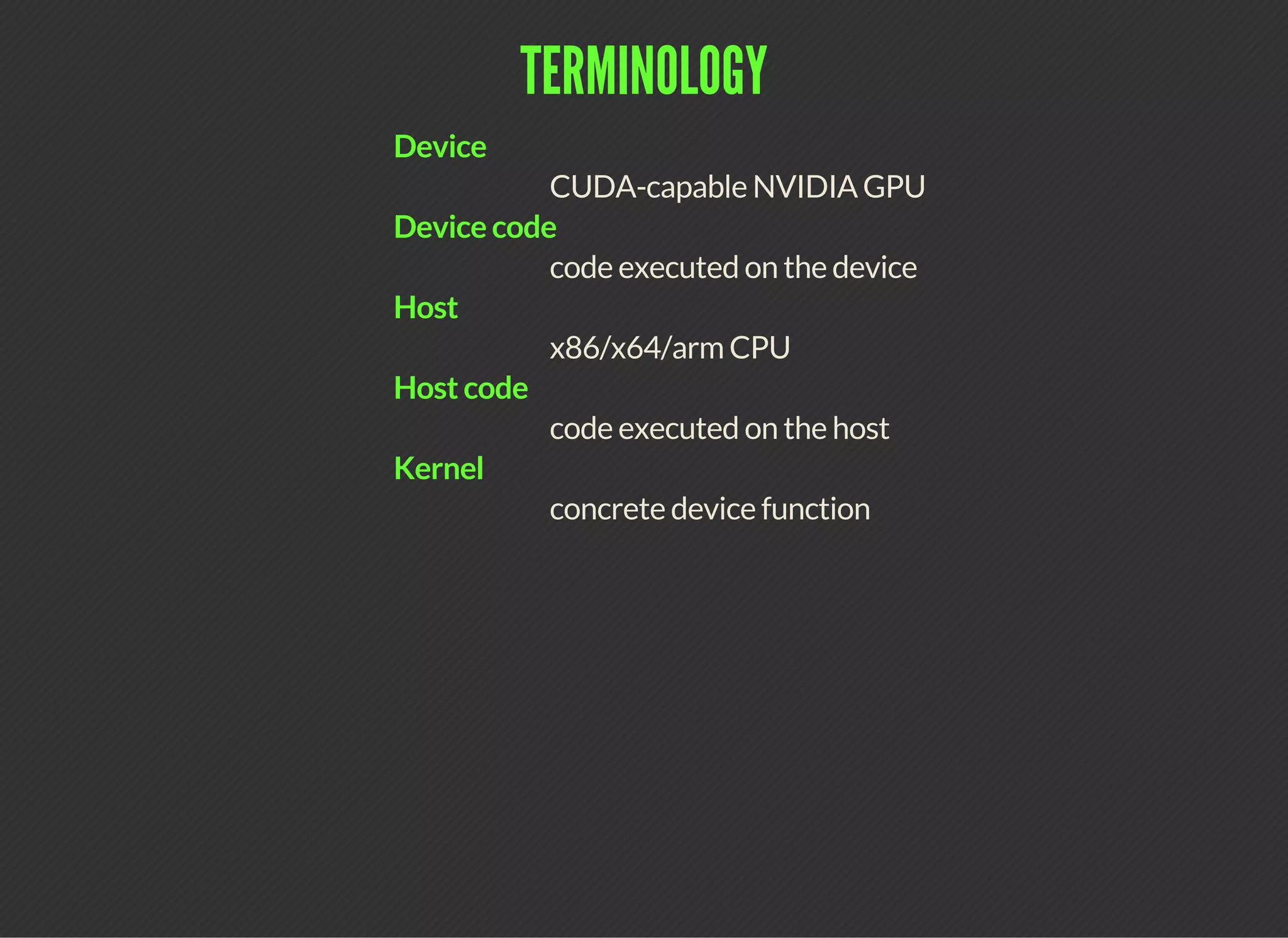
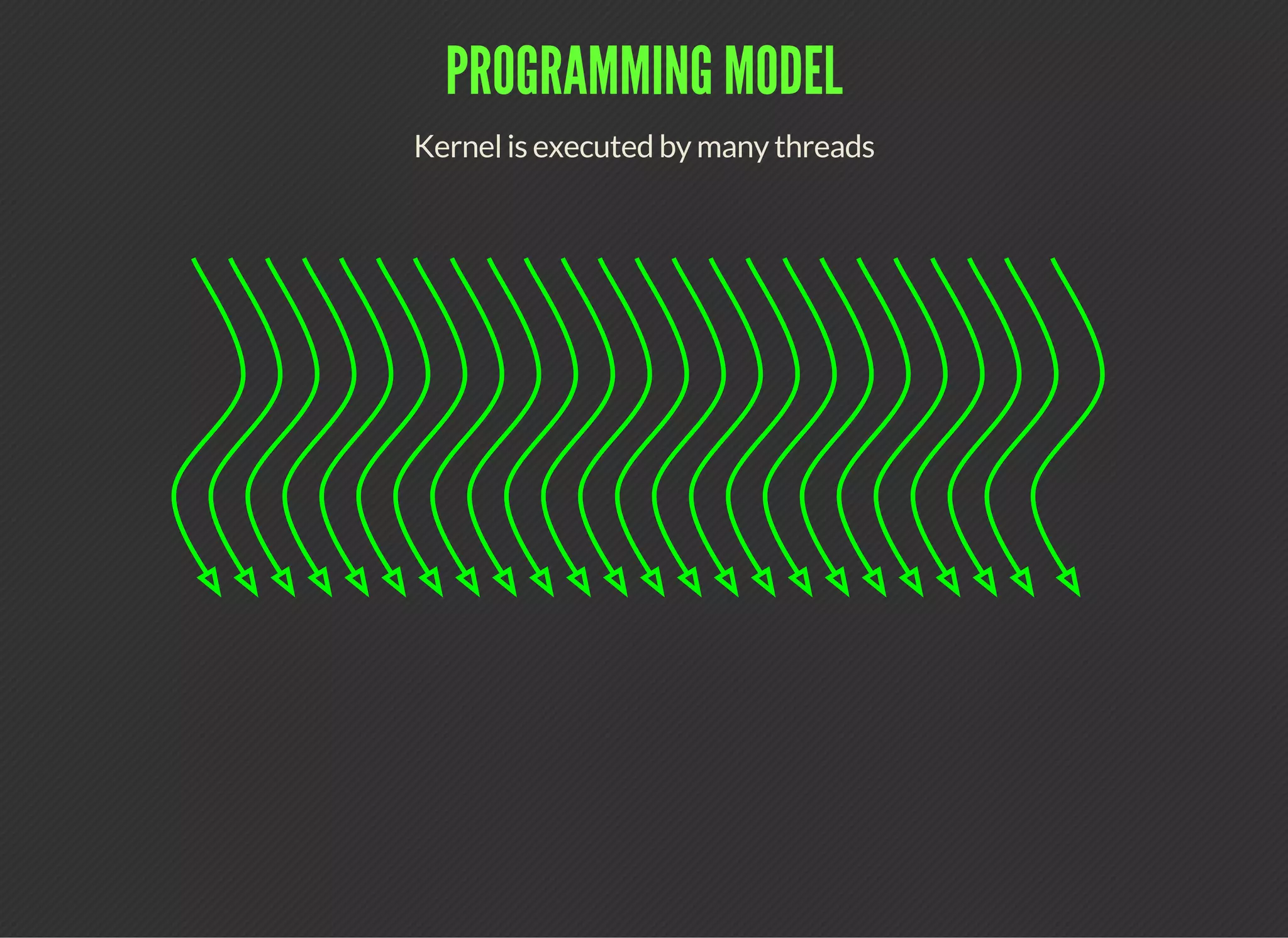
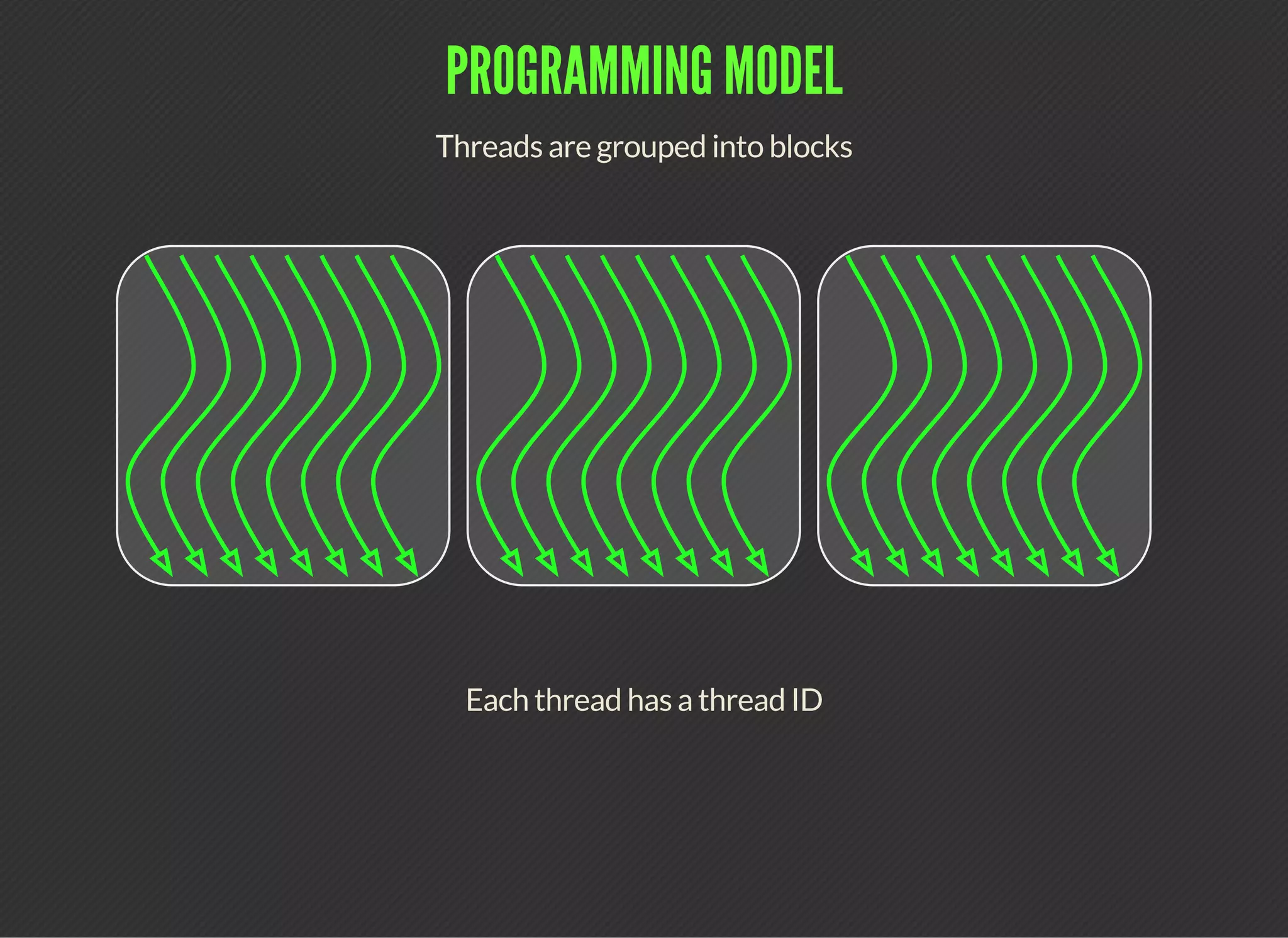
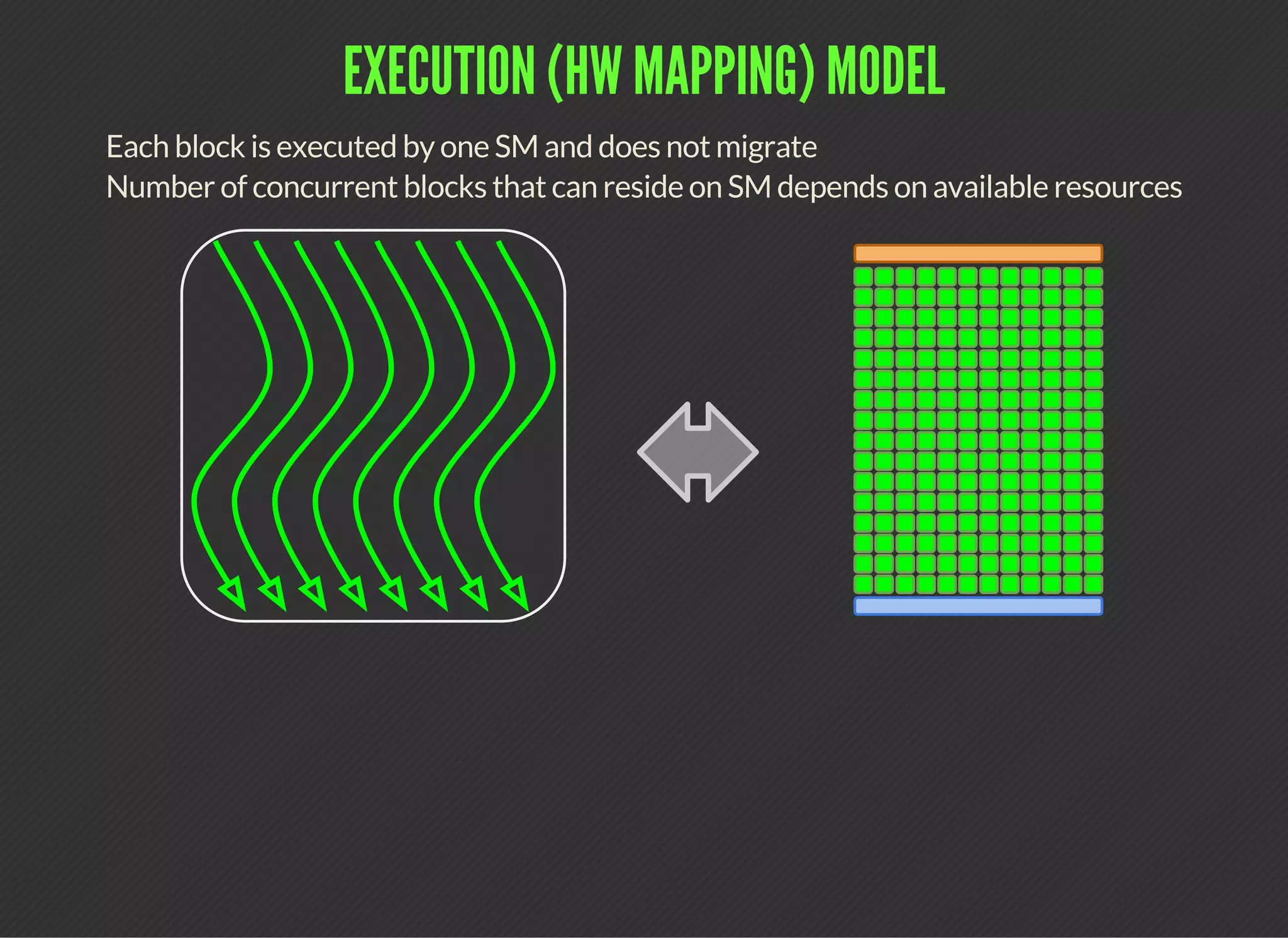
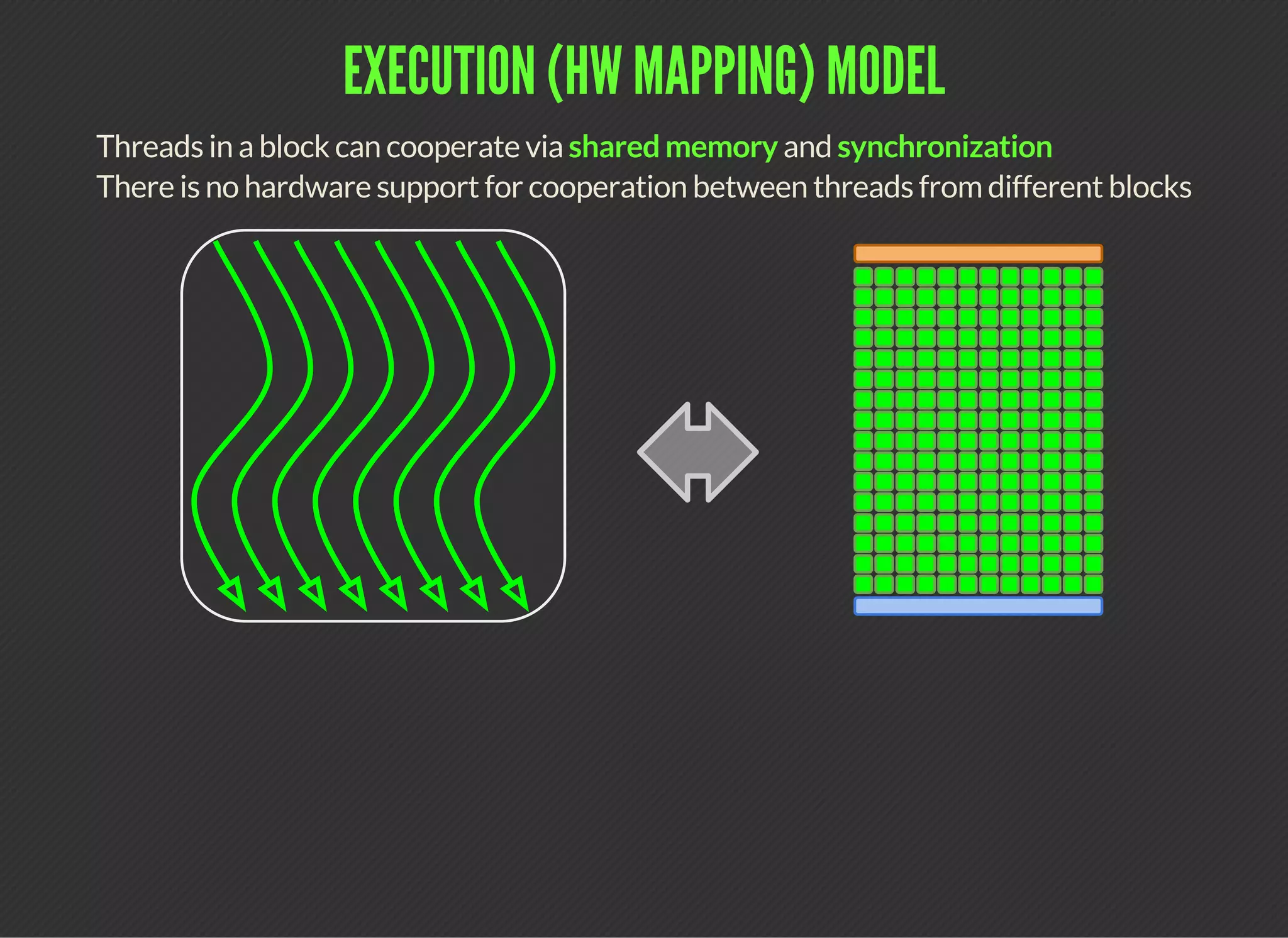
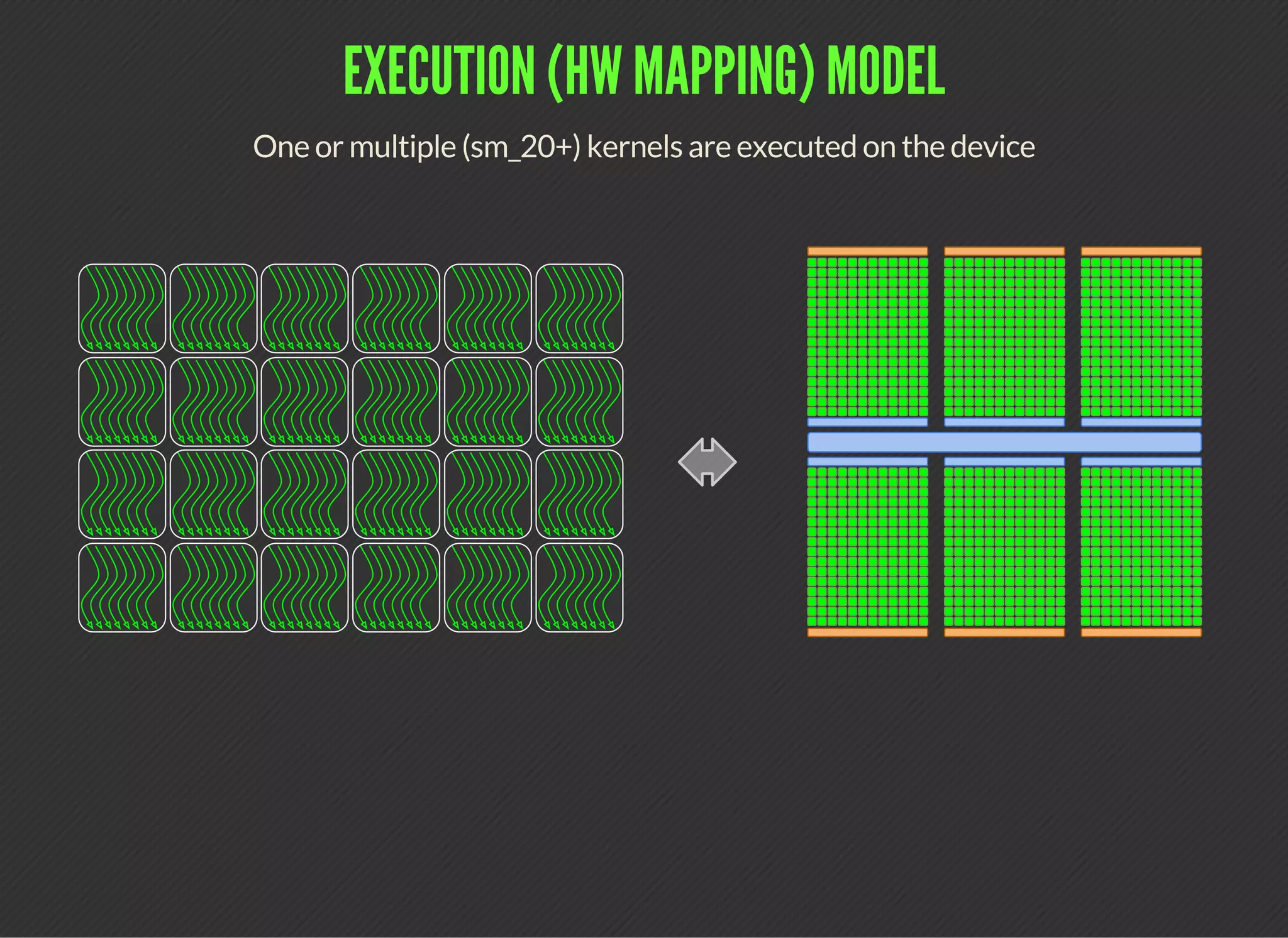
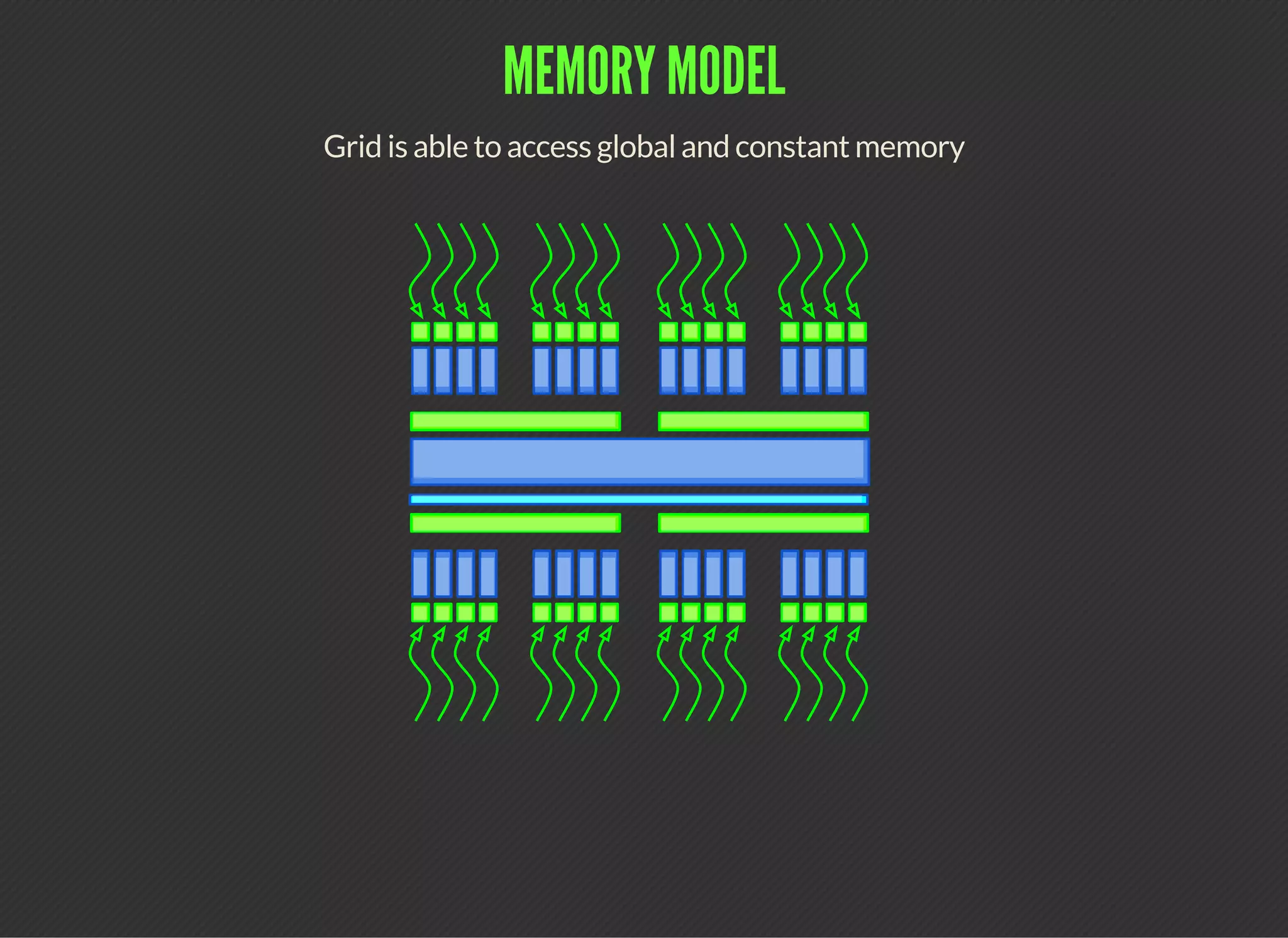
CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a parallel computing platform that allows developers to leverage GPUs for general purpose processing. CUDA defines a programming model where kernels, which represent tasks for threads, are executed across a grid of thread blocks. Each thread has its own registers and local memory, while threads within a block can cooperate via shared memory. Kernels access global memory across the entire grid and are used to offload work from CPUs to GPUs, with the host code managing data transfers and kernel execution.





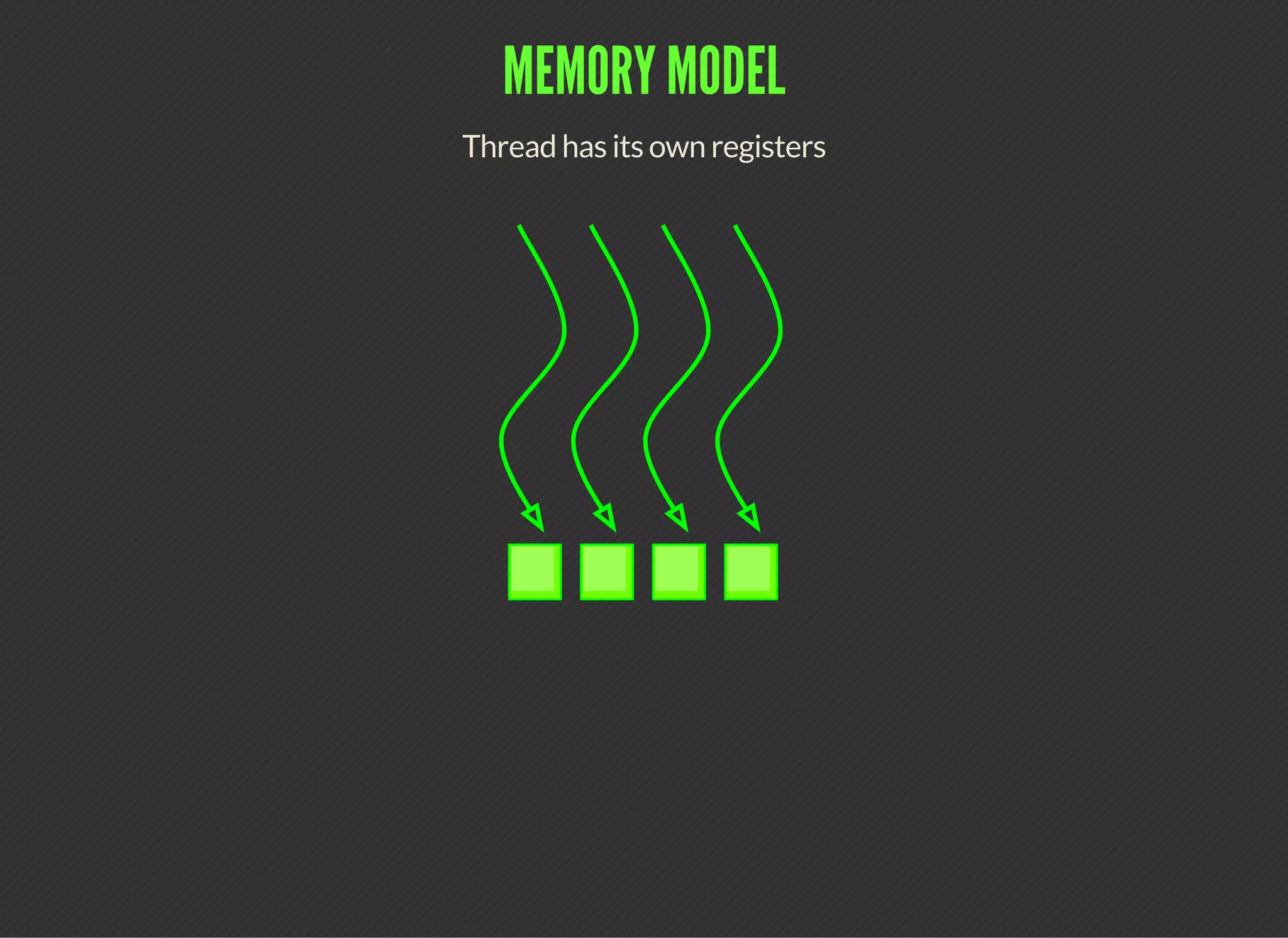
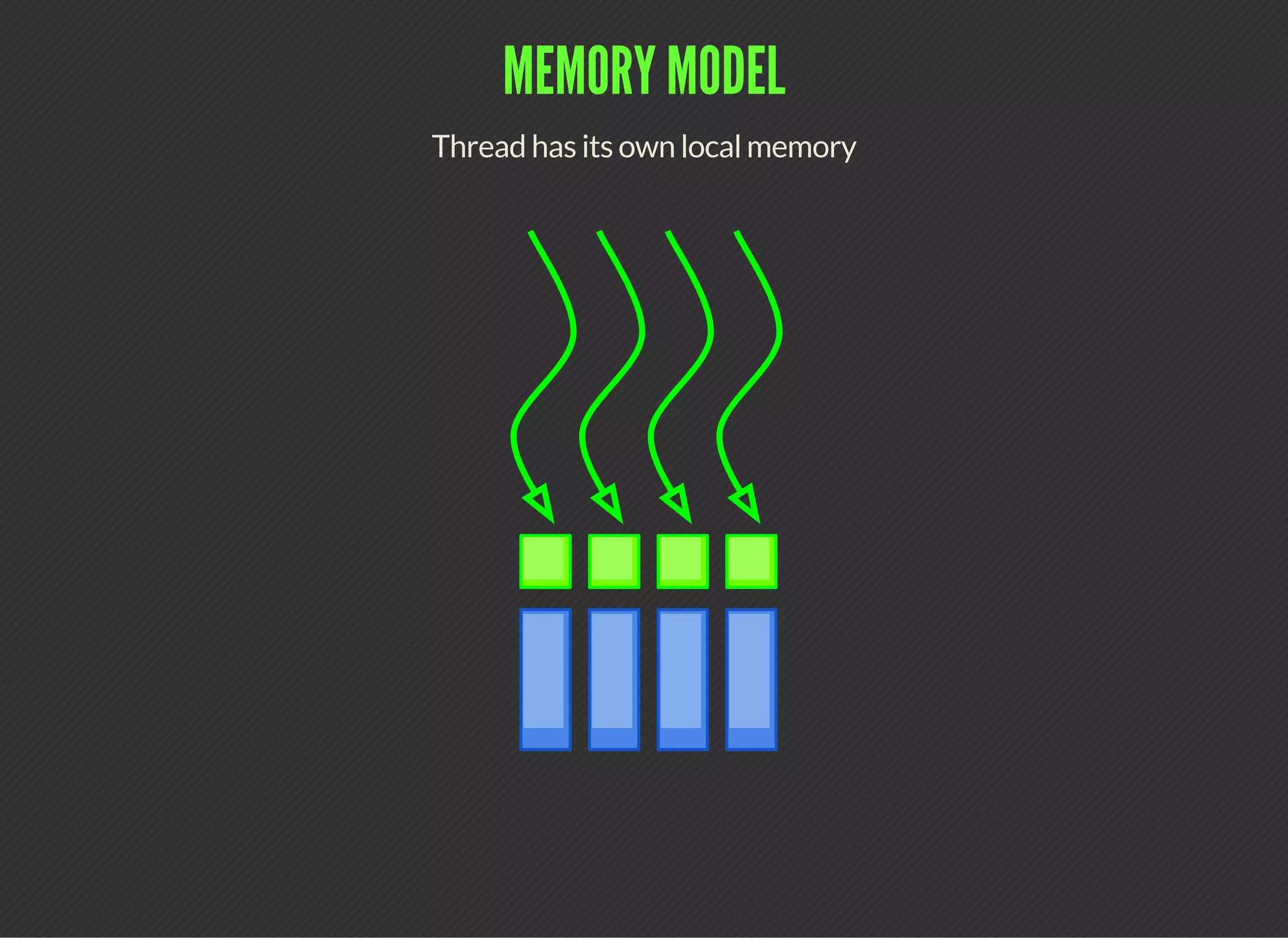
![MEMORY MODEL
Block has shared memory
Pointer to shared memory is valid while block is resident
_ _ s h a r e d _ _ f l o a t b u f f e r [ C T A _ S I Z E ] ;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/code-gpu-with-cuda-1-150915011233-lva1-app6892/75/Code-gpu-with-cuda-CUDA-introduction-15-2048.jpg)
![BASIC CUDA KERNEL
Work for GPU threads represented as kernel
kernel represents a task for single thread (scalar notation)
Every thread in a particular grid executes the same kernel
Threads use their threadIdx and blockIdx to dispatch work
Kernel function is marked with __global__ keyword
Common kernel structure:
1. Retrieving position in grid (widely named tid)
2. Loading data form GPU’s memory
3. Performing compute work
4. Writing back the result into GPU’s memory
_ _ g l o b a l _ _ v o i d k e r n e l ( f l o a t * i n , f l o a t * o u t )
{
i n t t i d = b l o c k I d x . x * b l o c k D i m . x + t h r e a d I d x . x ;
o u t [ t i d ] = i n [ t i d ] ;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/code-gpu-with-cuda-1-150915011233-lva1-app6892/75/Code-gpu-with-cuda-CUDA-introduction-17-2048.jpg)