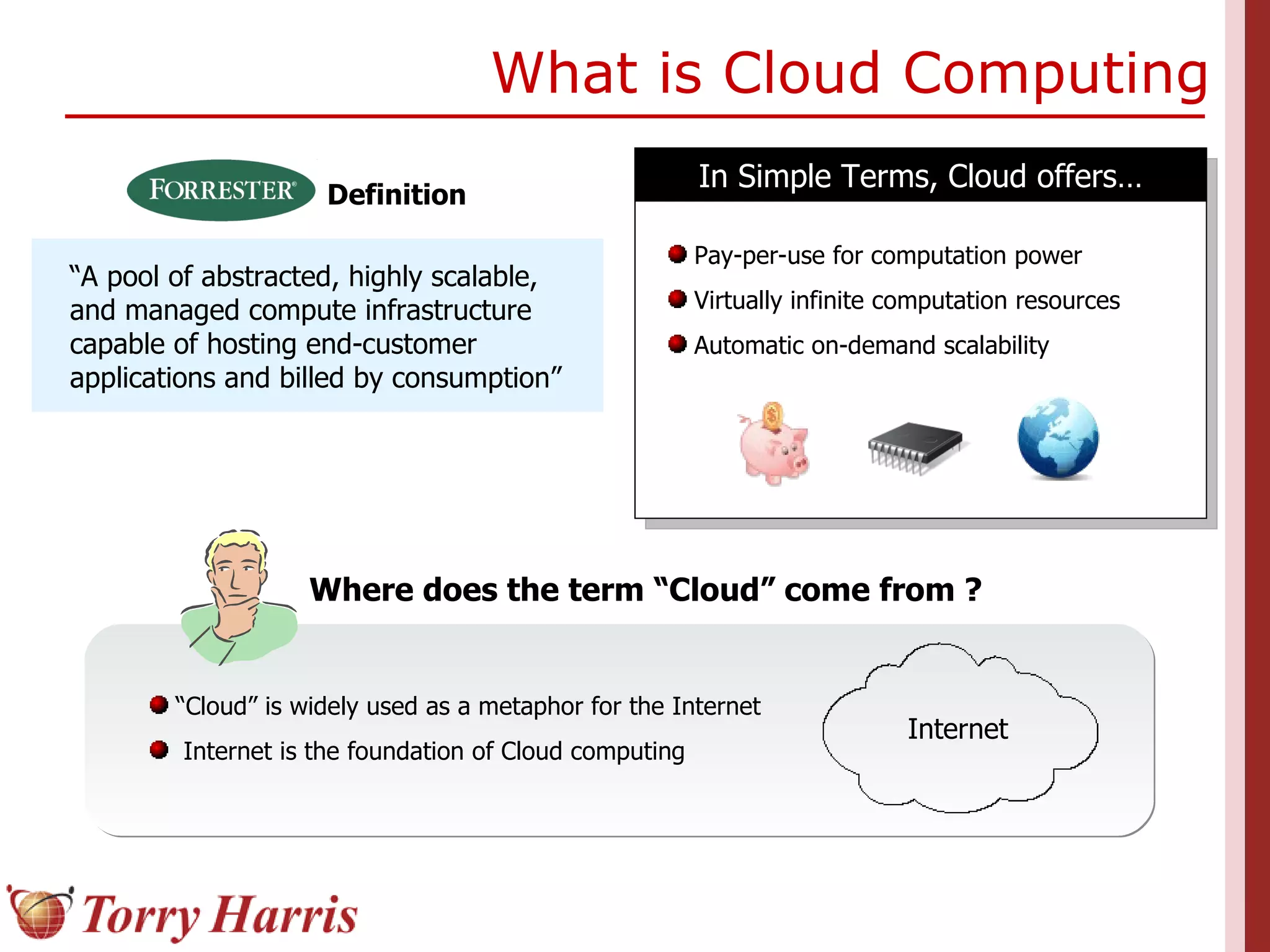
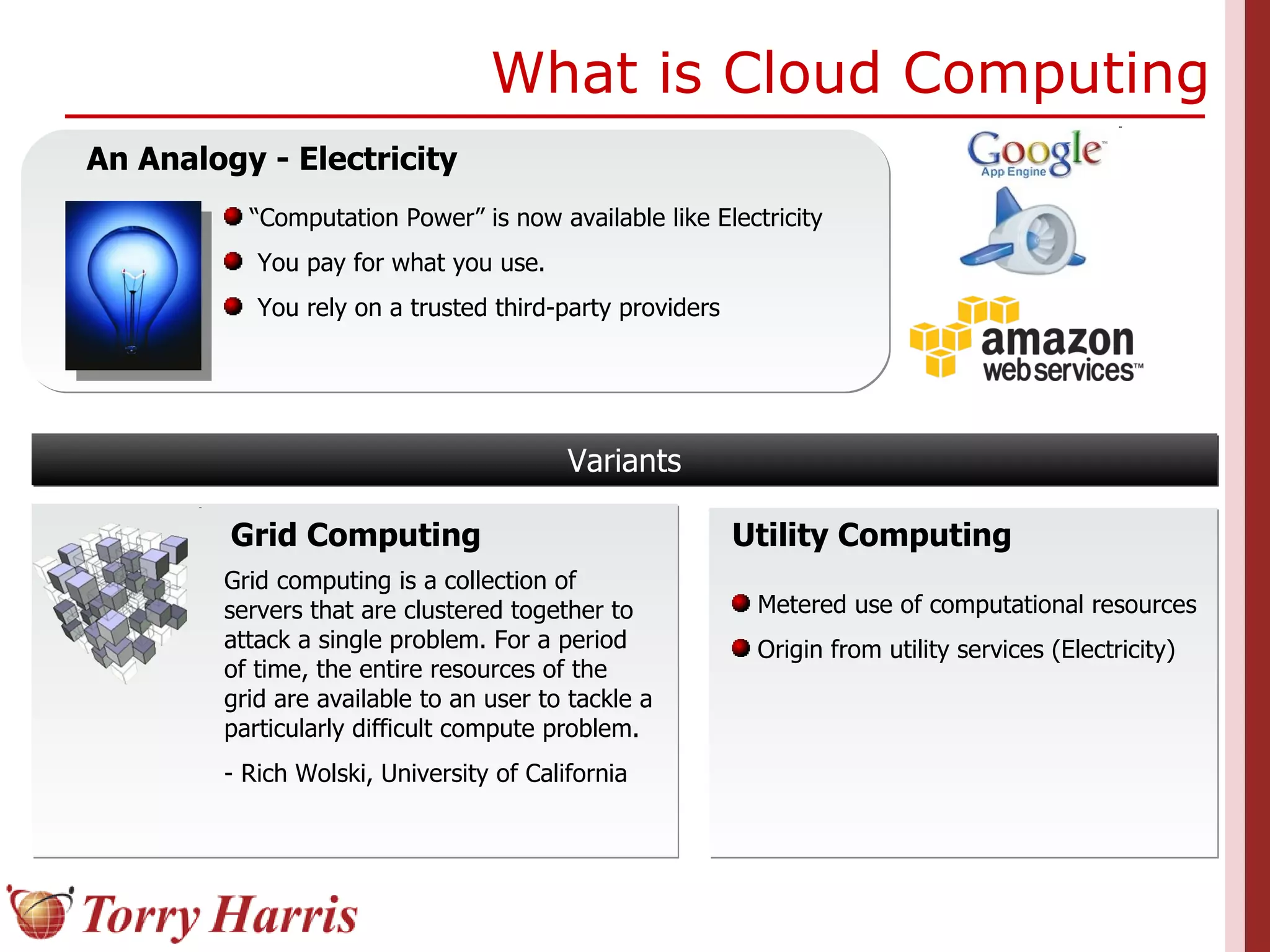
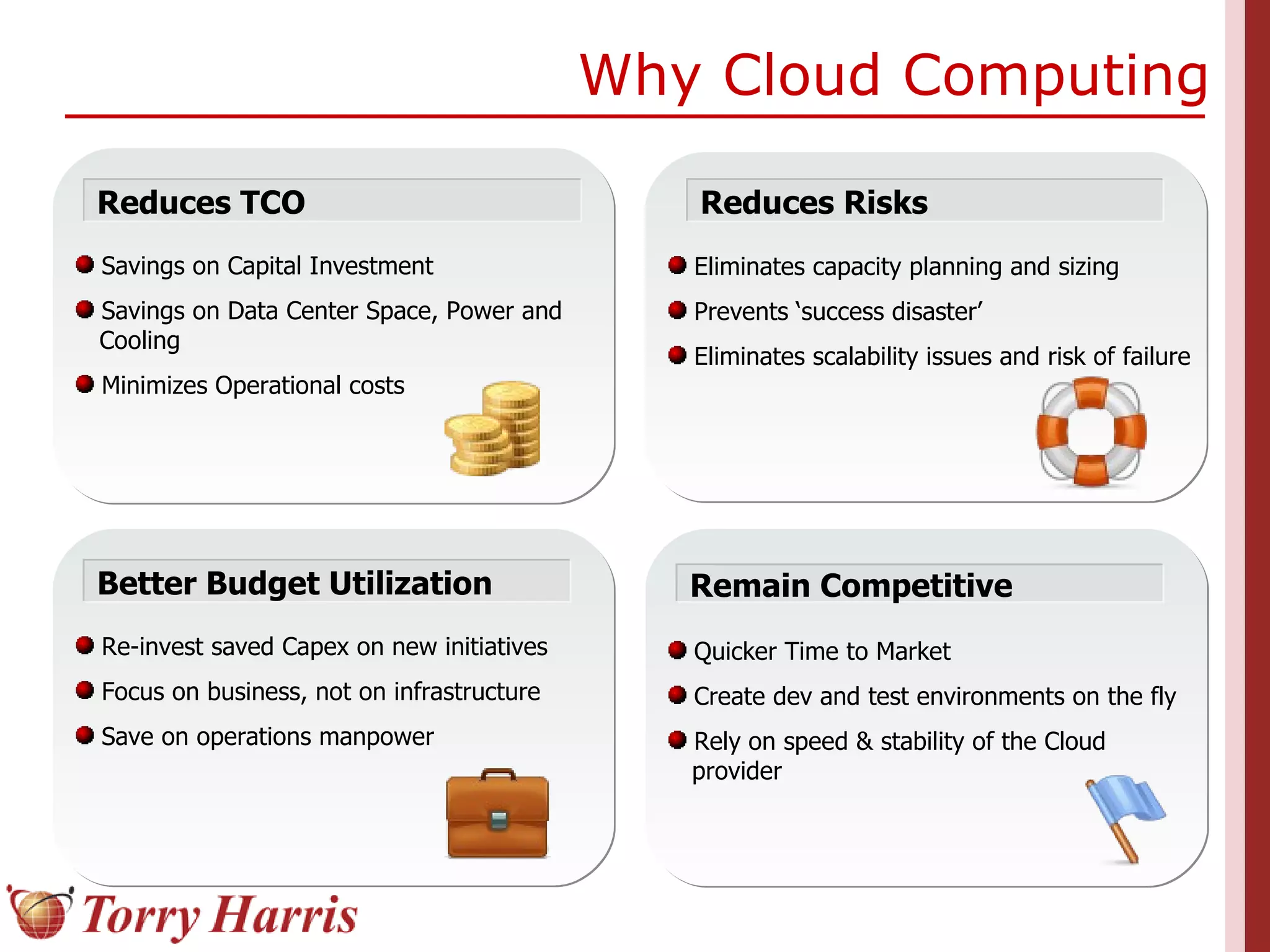
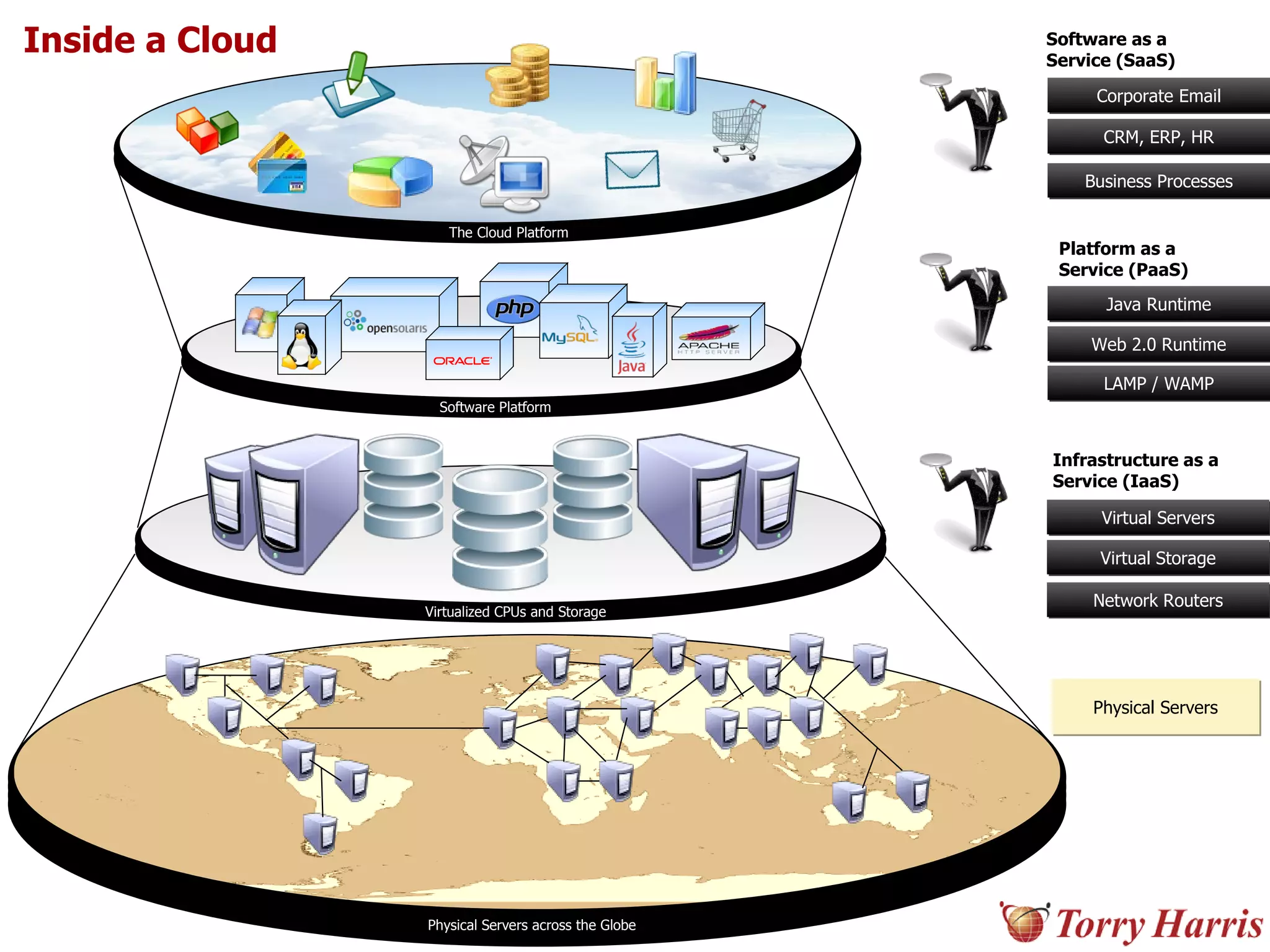
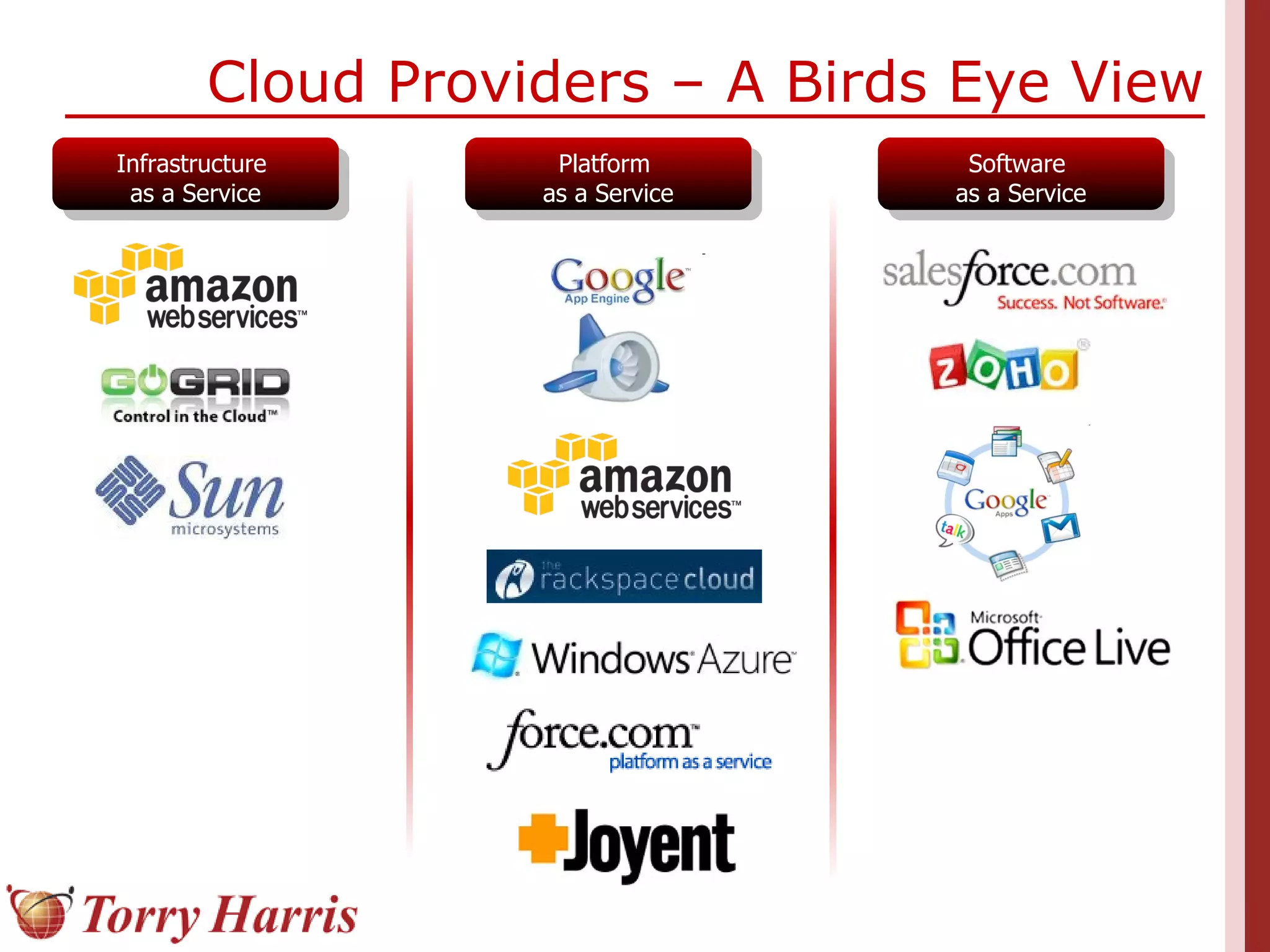
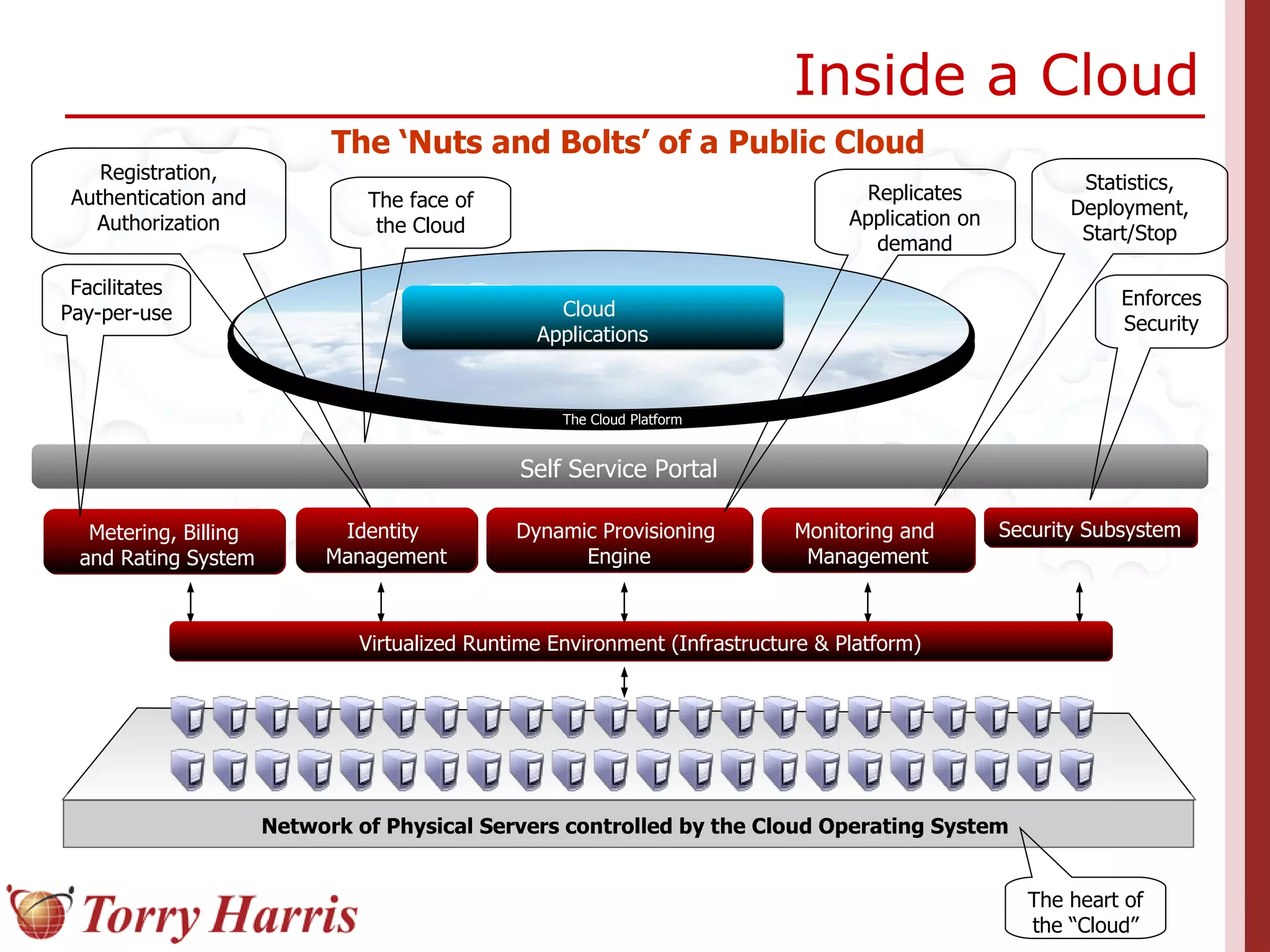
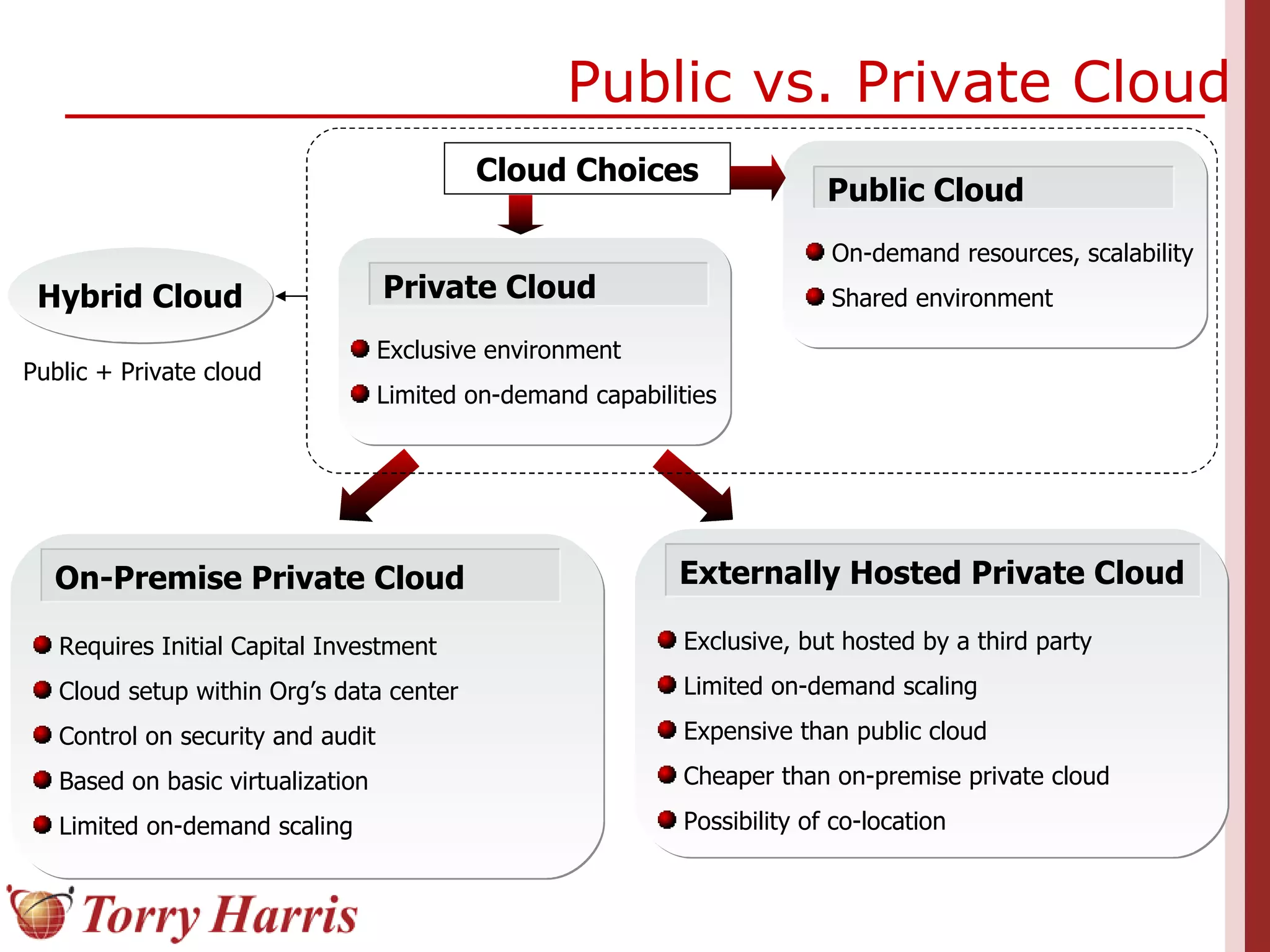
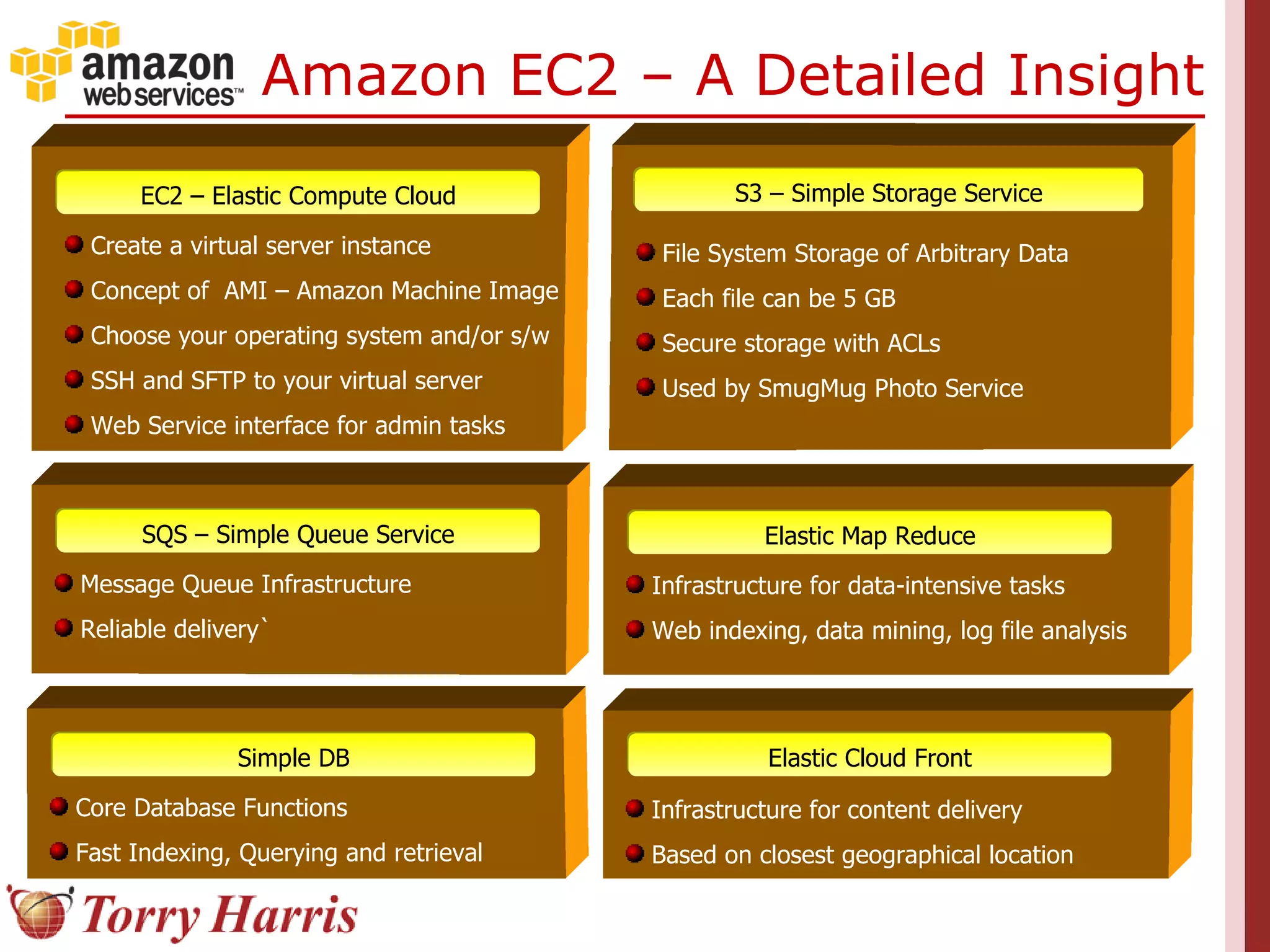
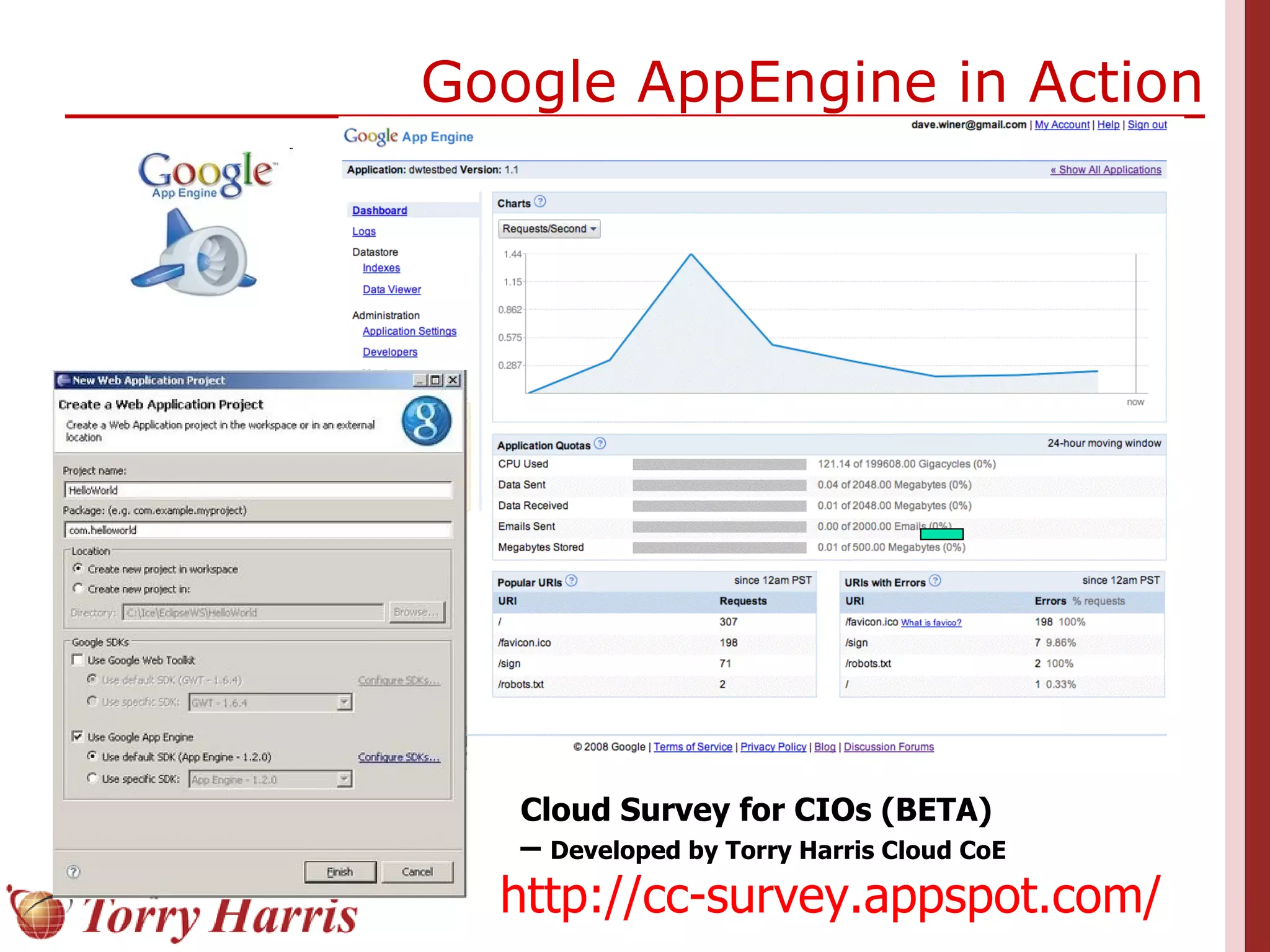
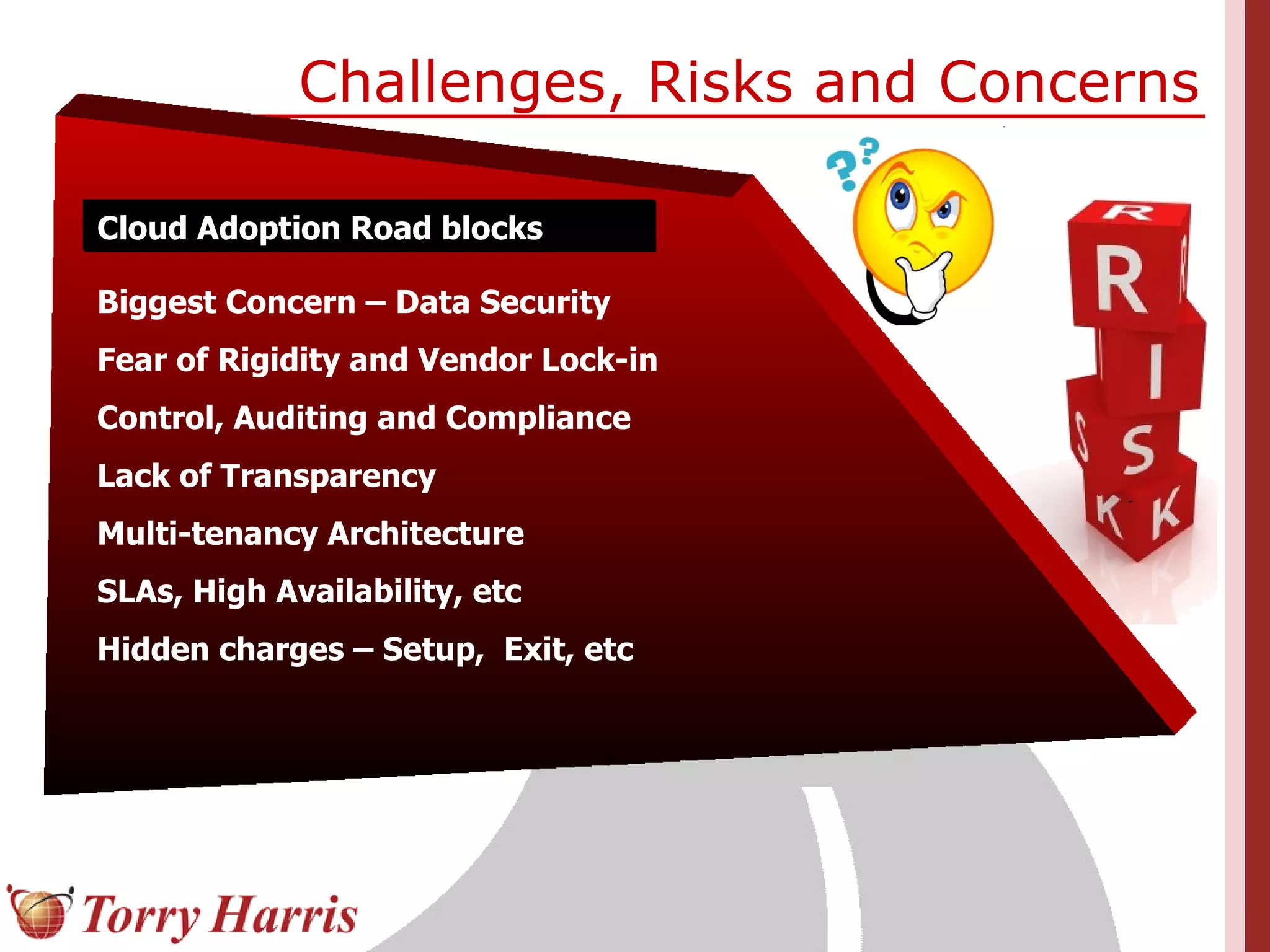
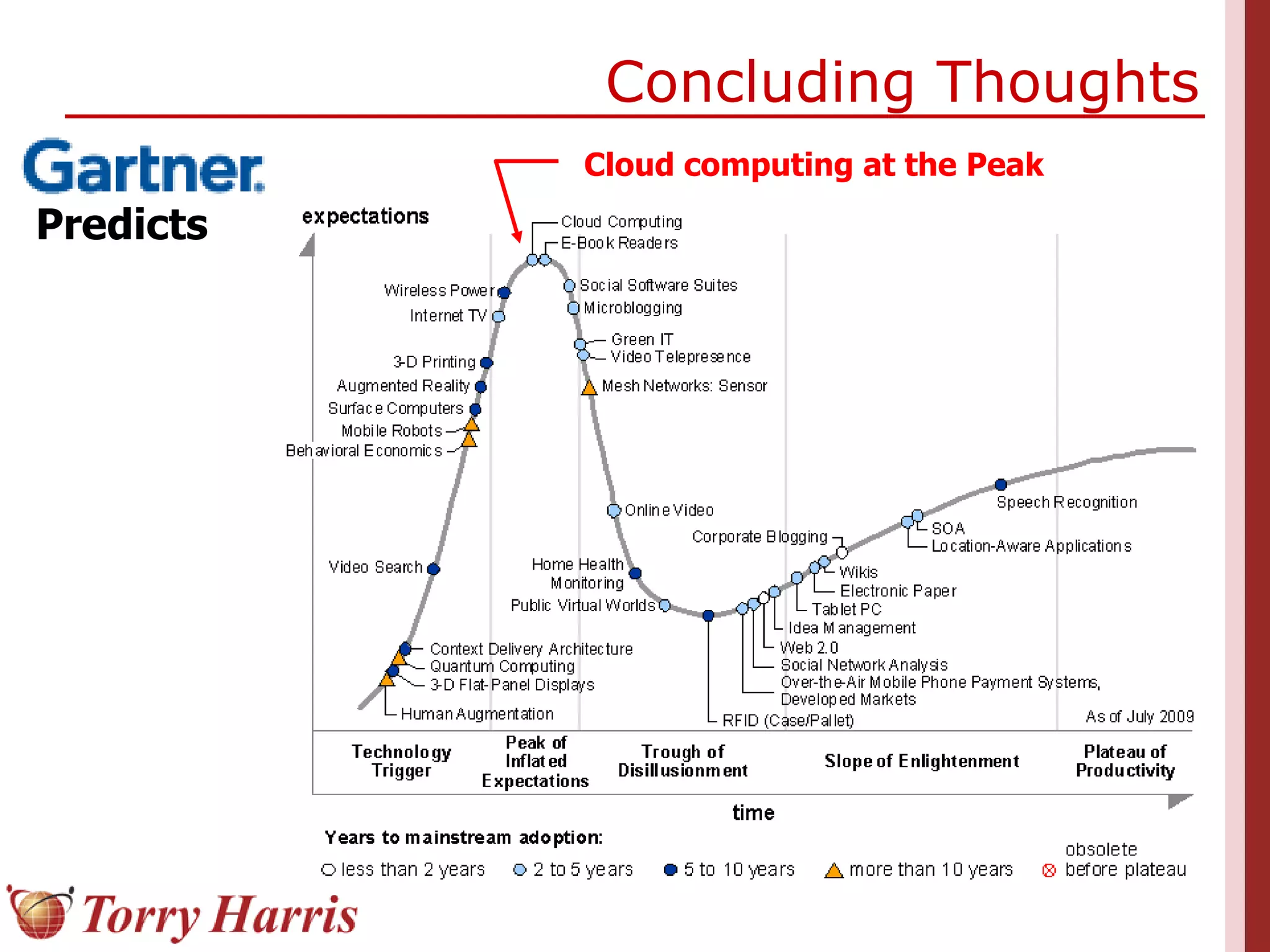
This document provides a comprehensive introduction to cloud computing, explaining its definition, benefits, and service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS). It includes insights on major cloud providers such as Amazon EC2 and Google App Engine, real-world success stories, and addresses challenges like data security and vendor lock-in. Additionally, it outlines the importance of cloud adoption strategies and highlights the offerings from Torry Harris for cloud consulting and implementation.