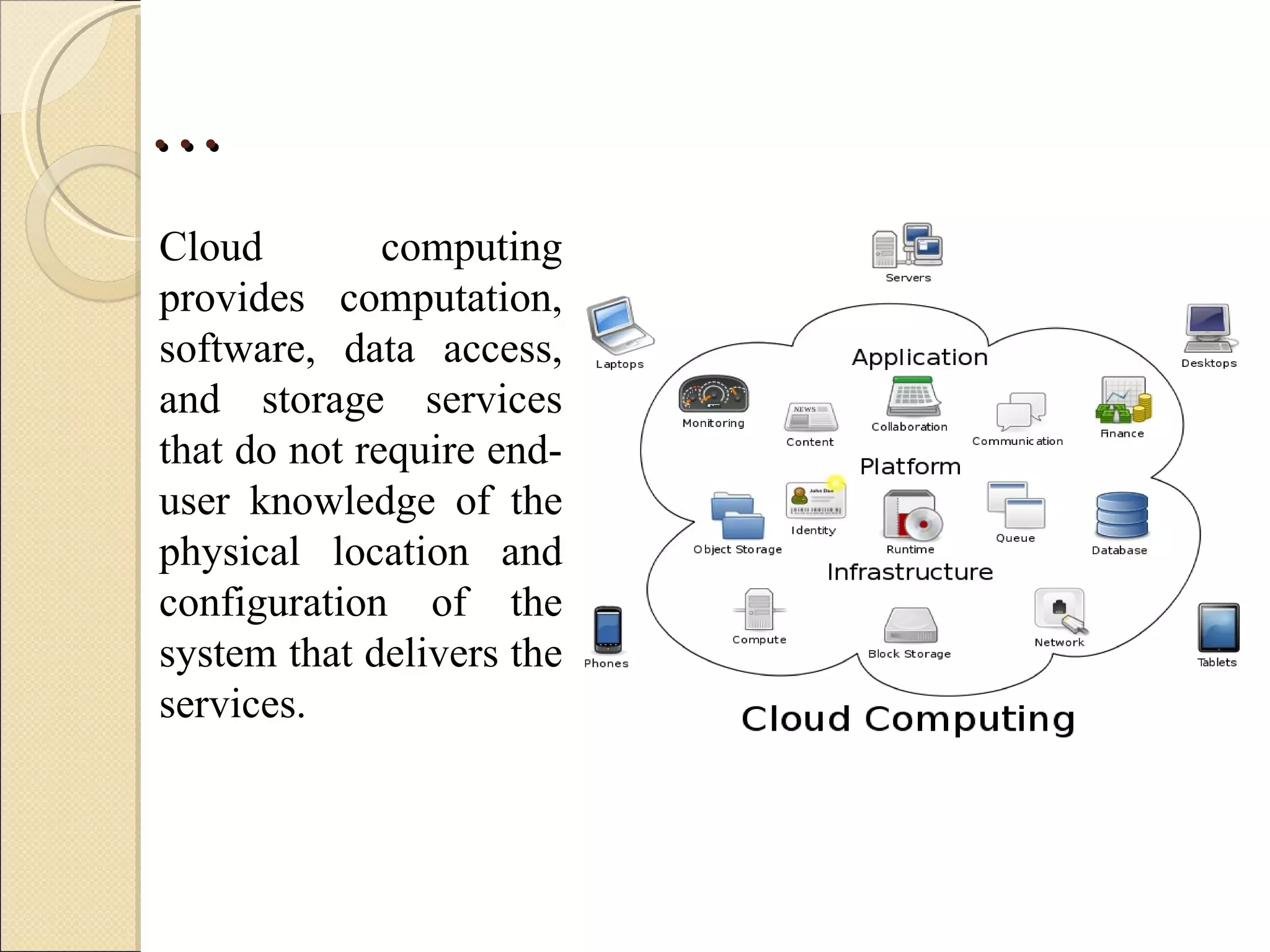
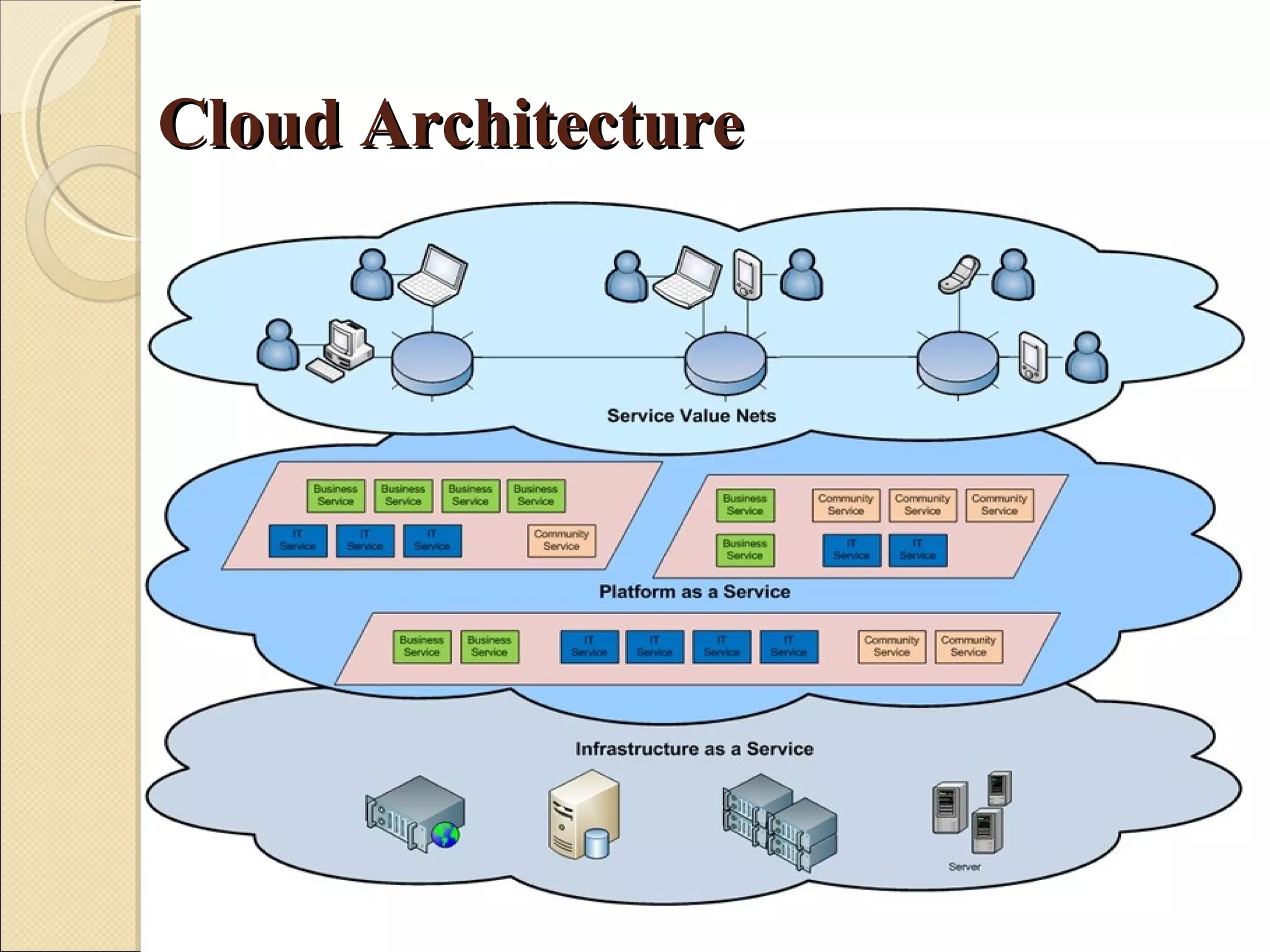
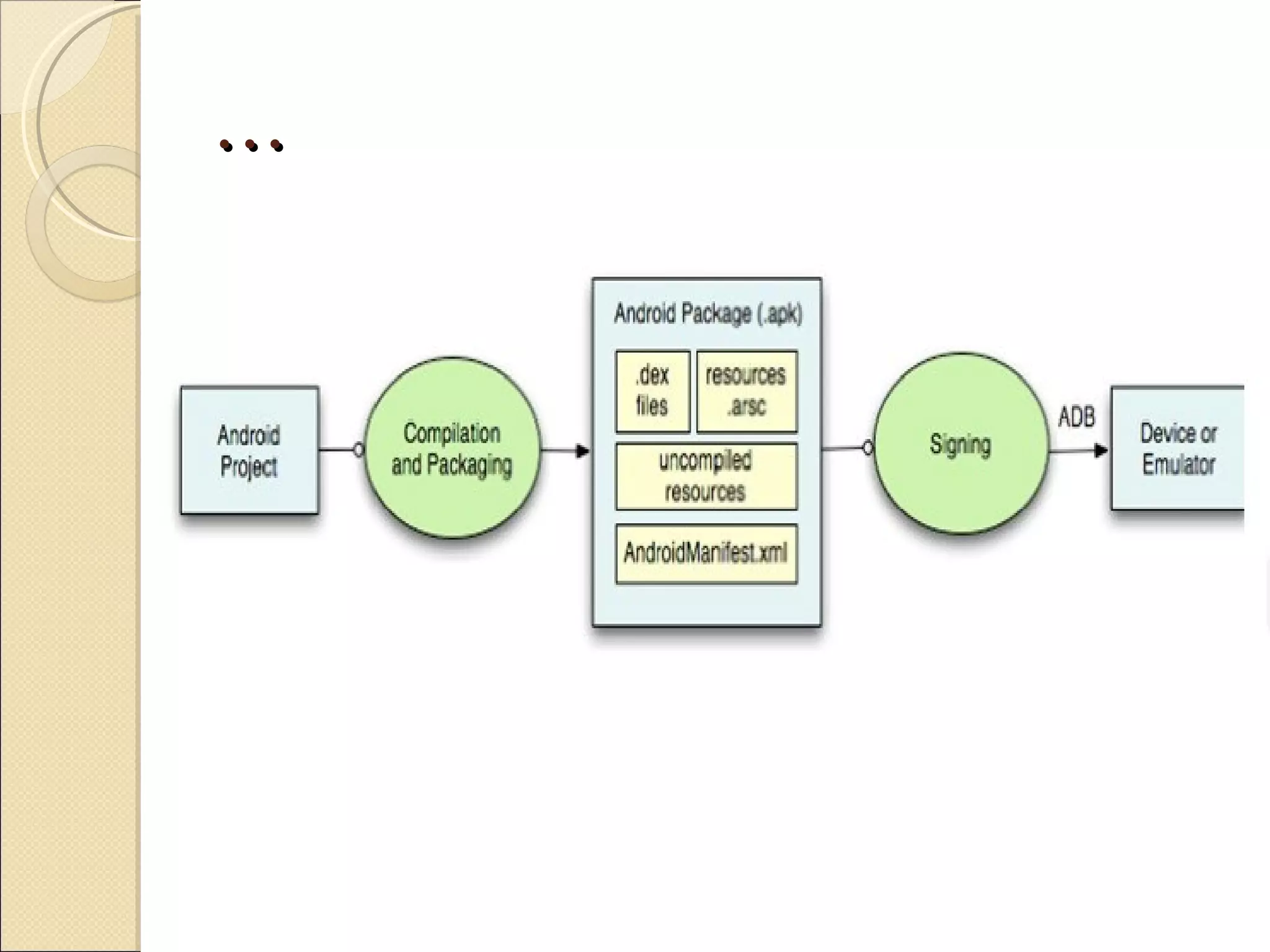
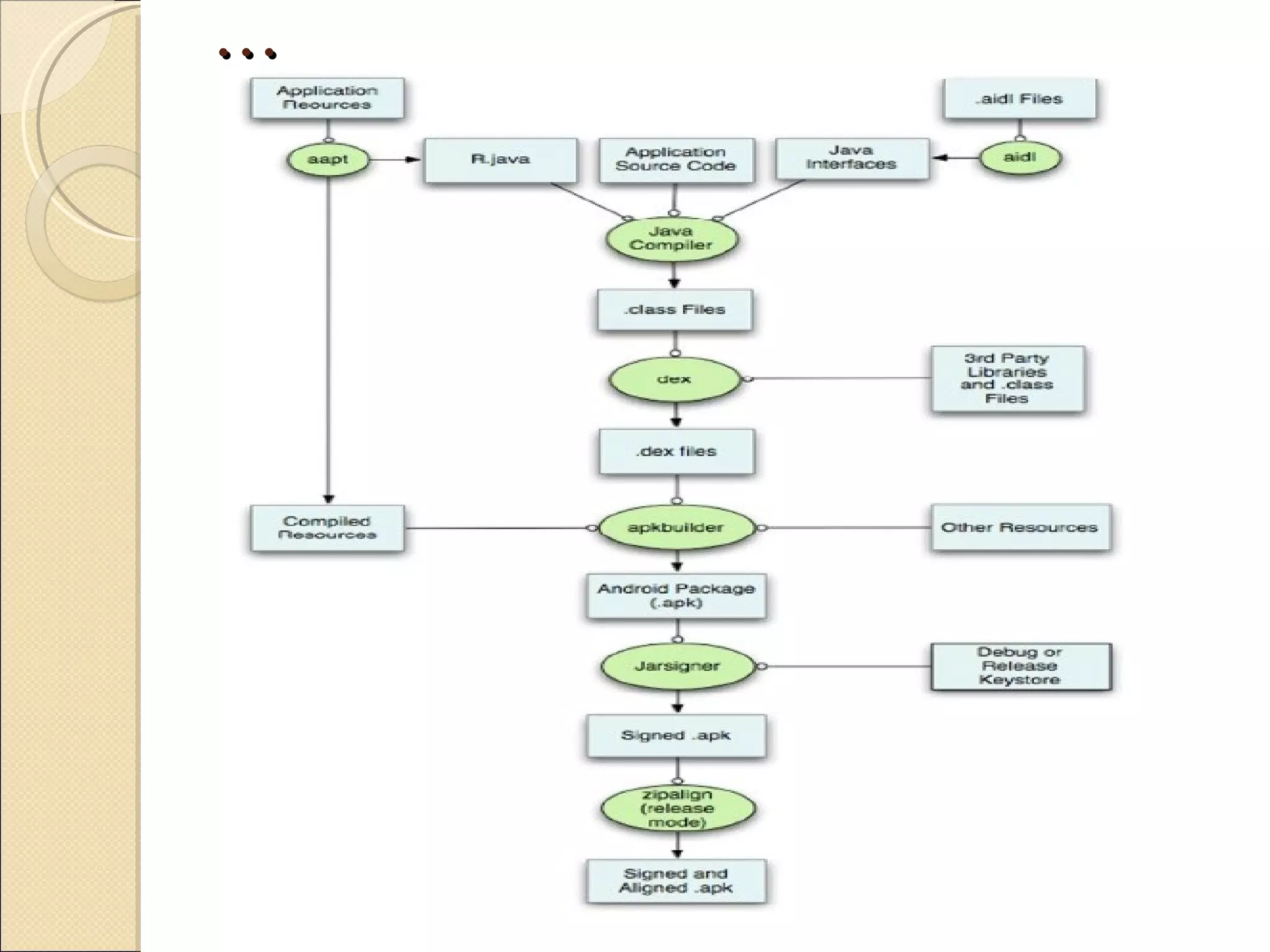
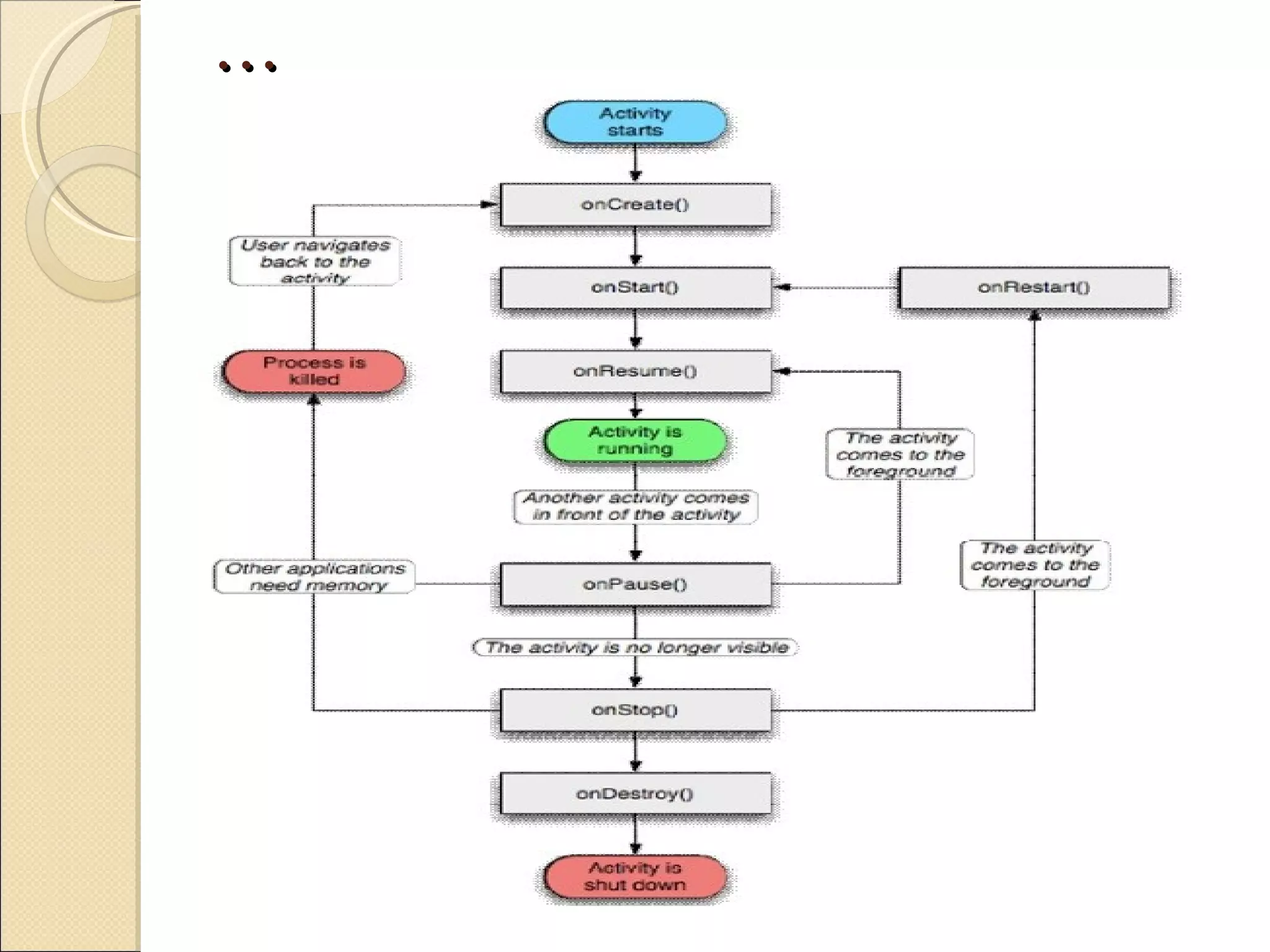
The presentation discusses developing a cloud computing application and Android application for students. The project aims to allow students to develop and execute Java programs on tablets and mobile devices using cloud computing resources. It describes cloud computing concepts, Android architecture, and progress made in linking the Android SDK with Eclipse for application development.