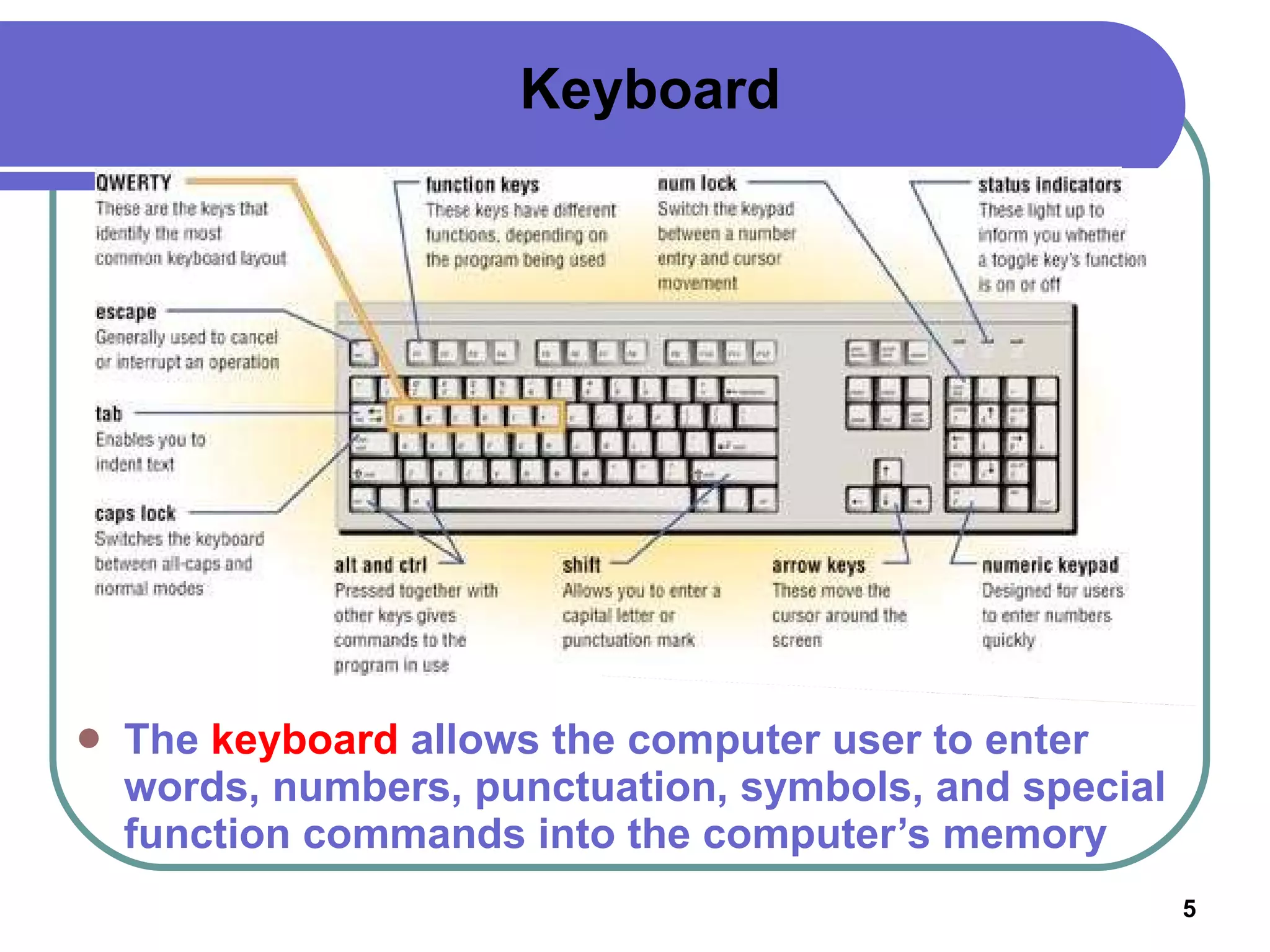
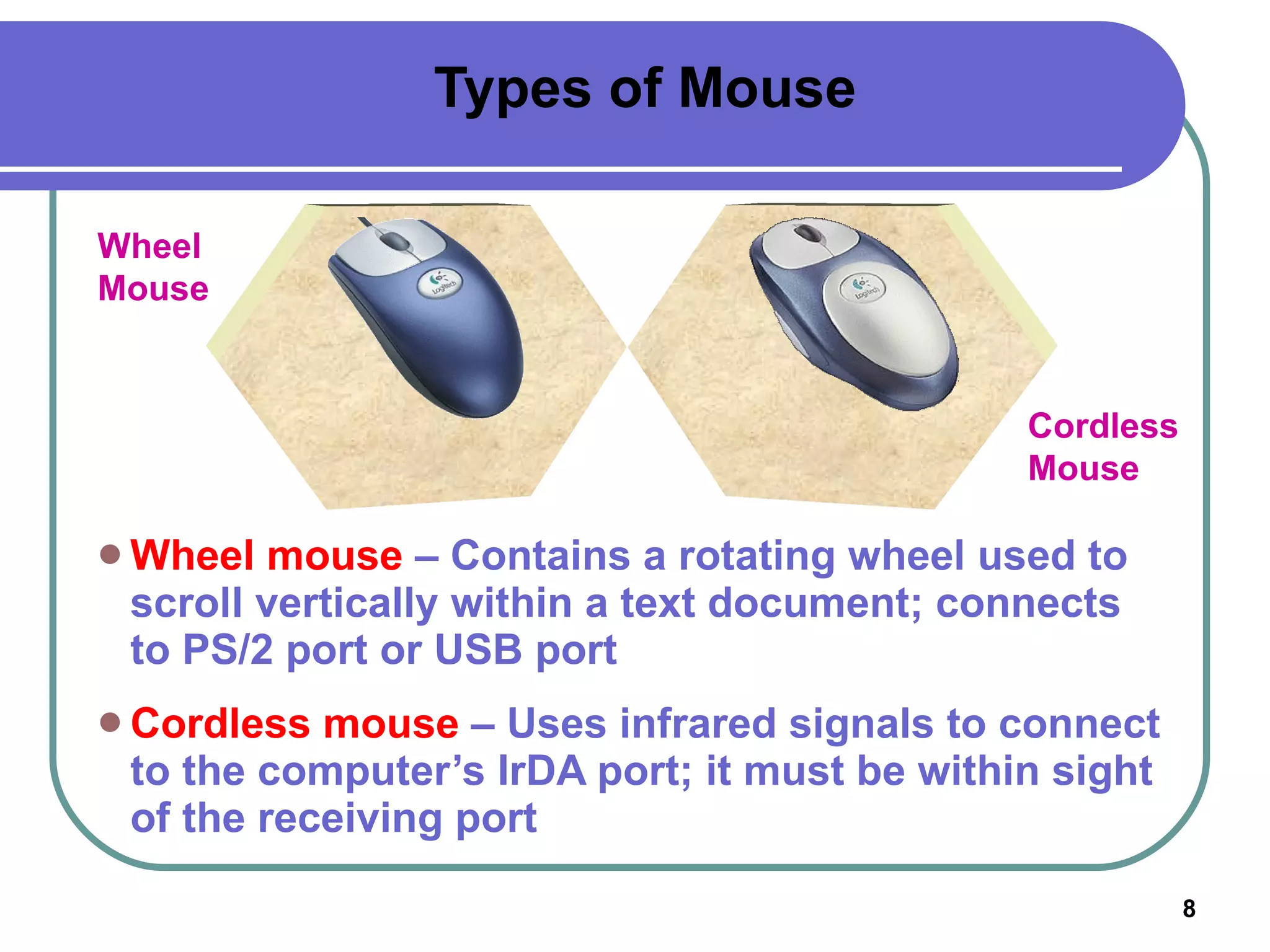
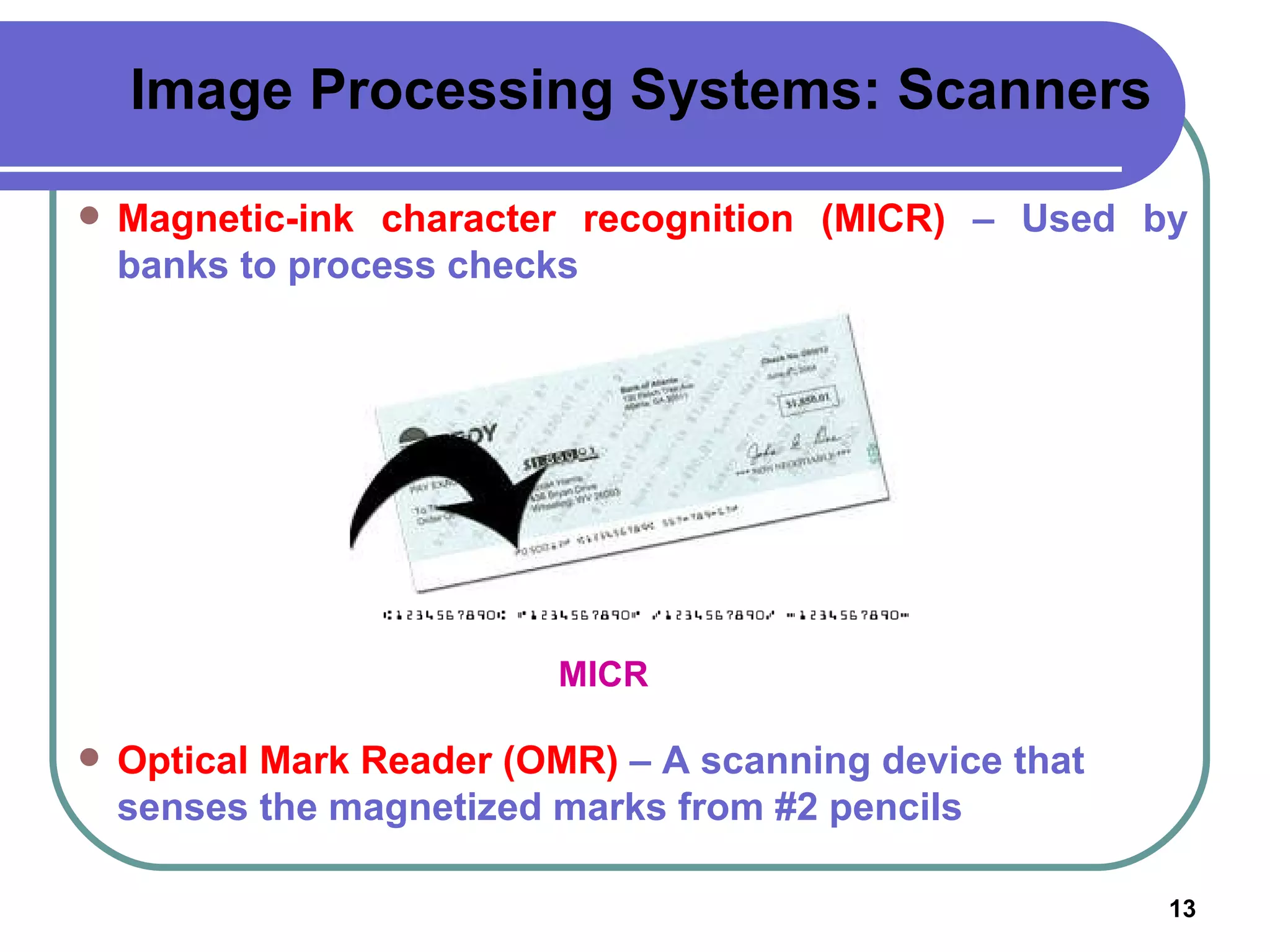
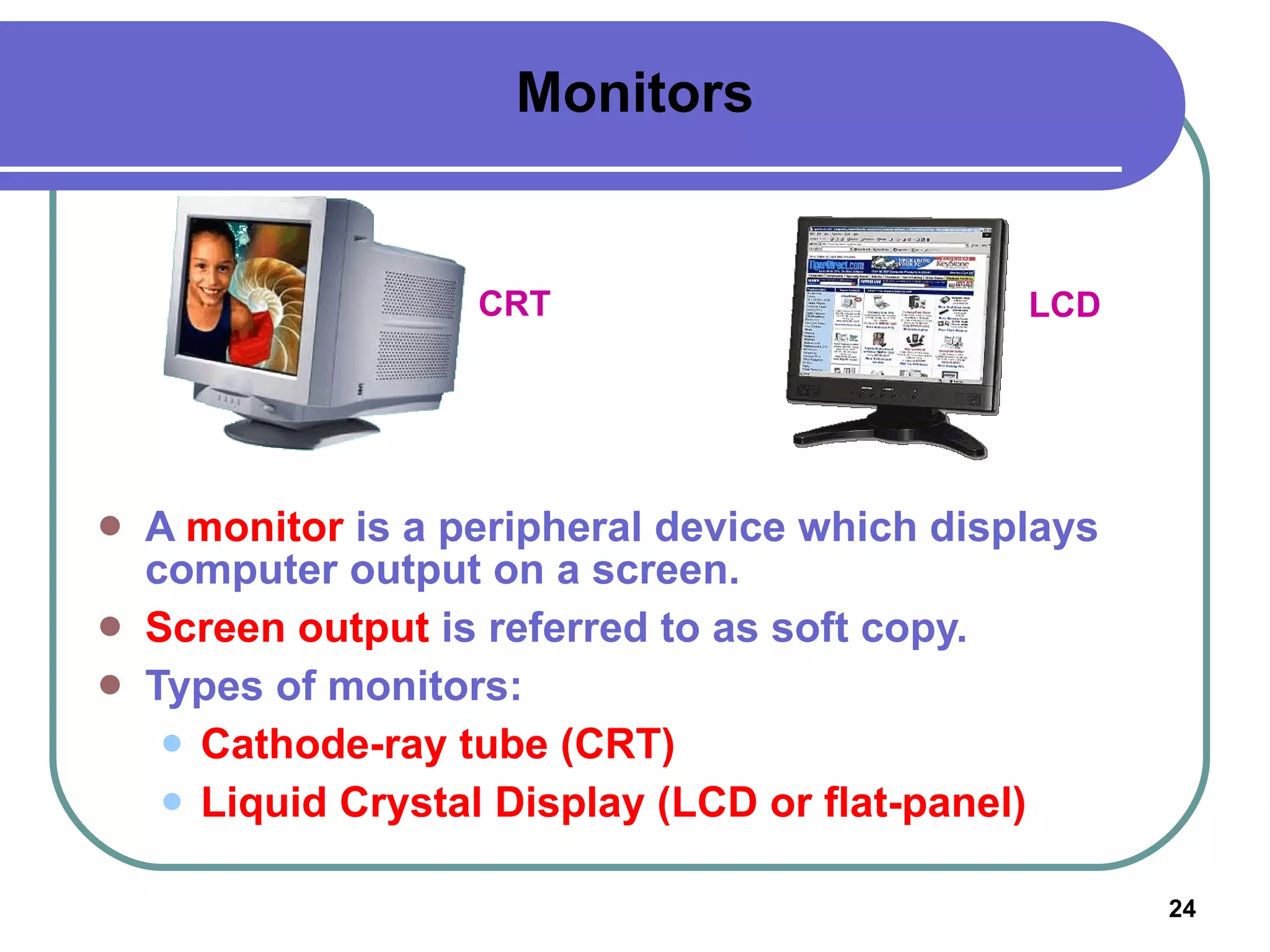
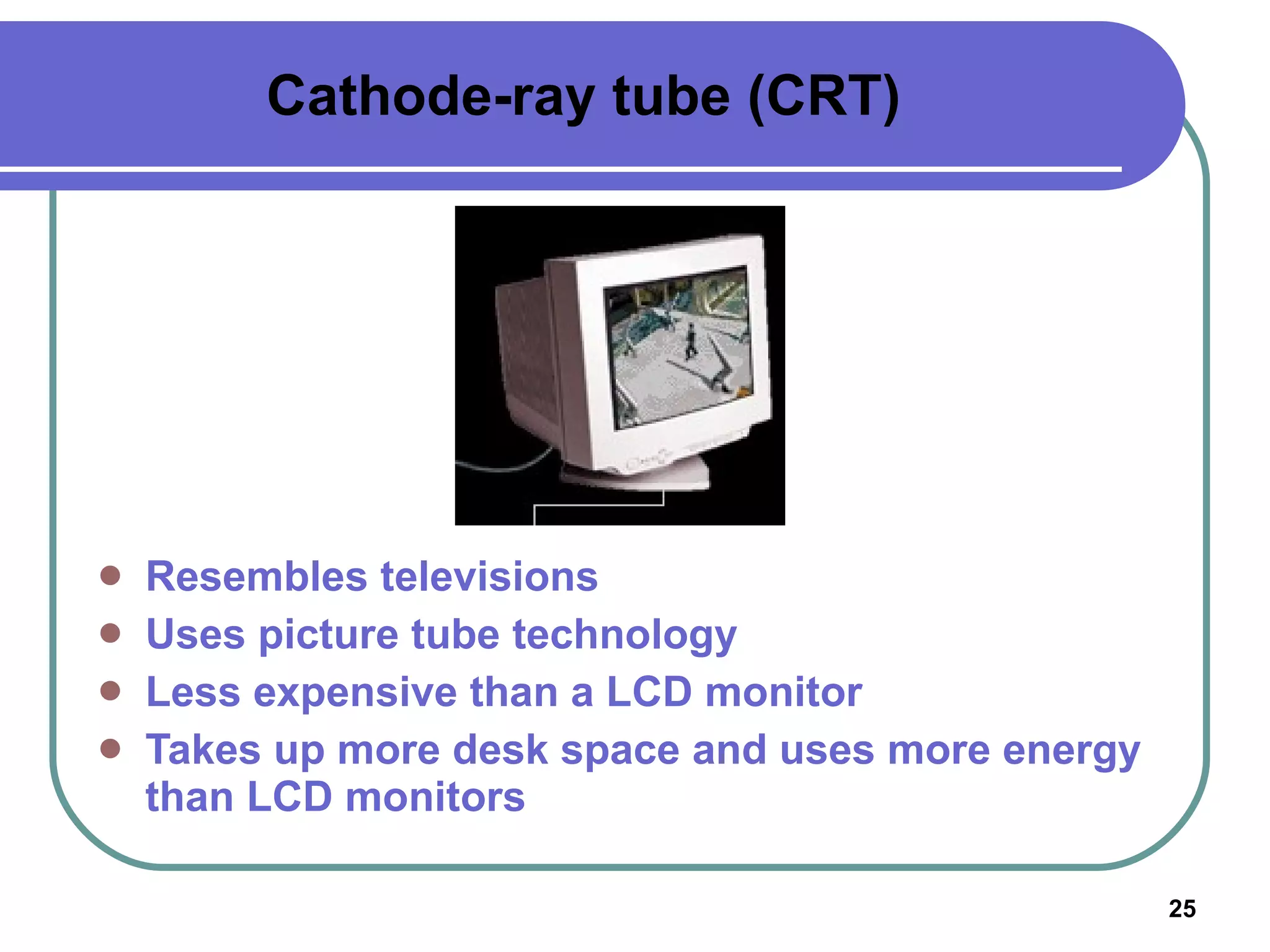
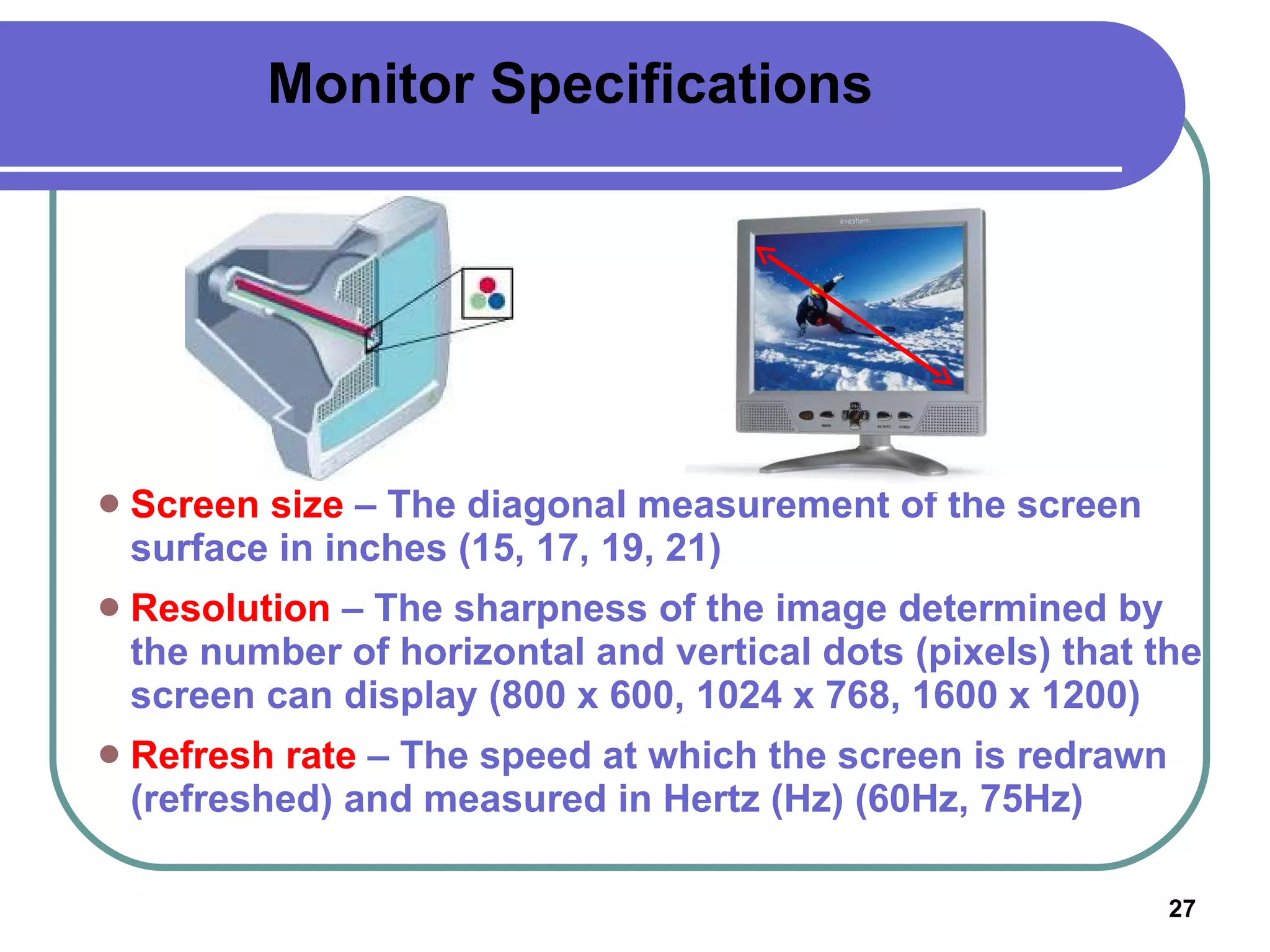
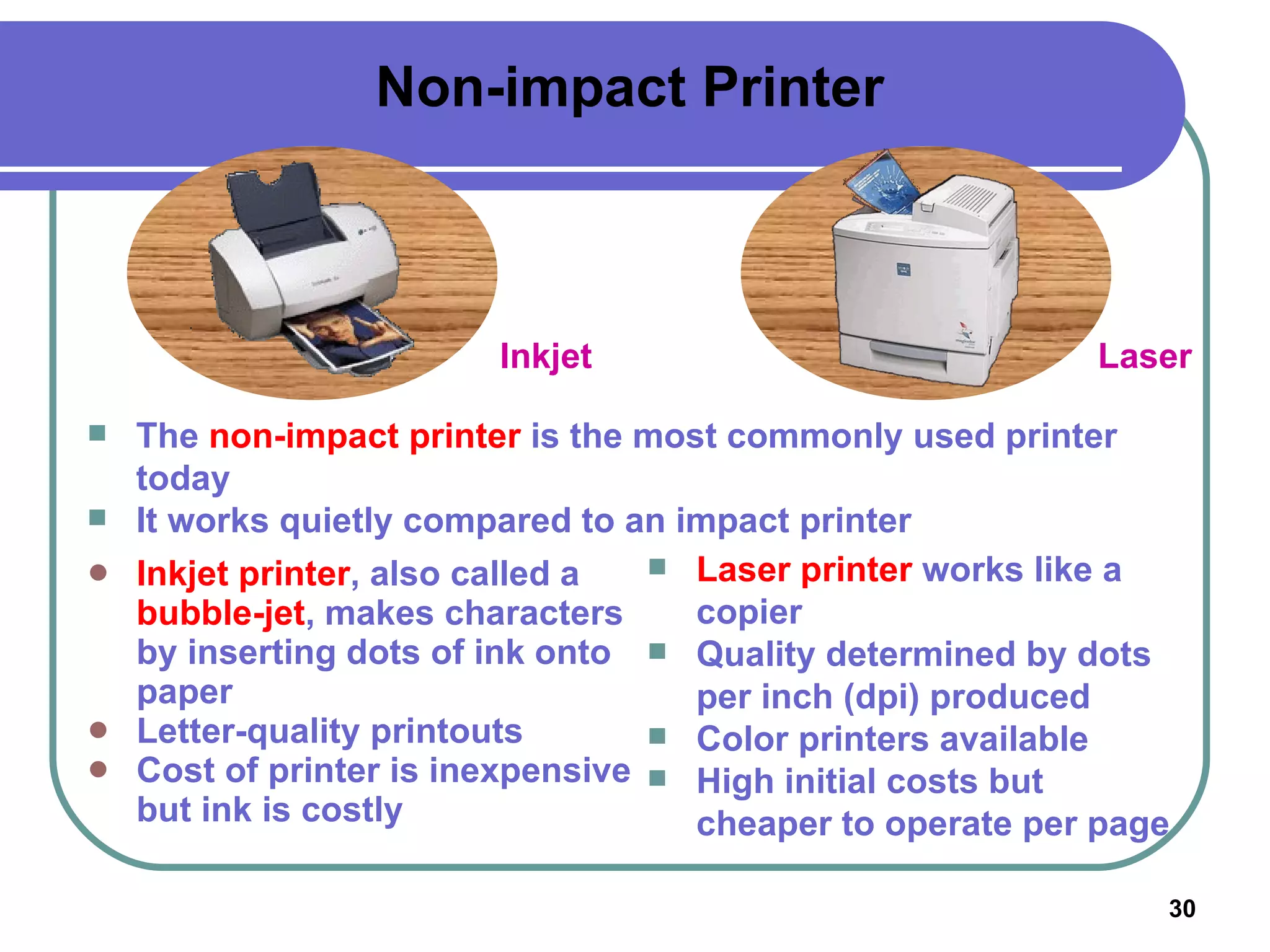
Input devices such as keyboards, mice, and scanners allow users to enter data into a computer. Common input devices include keyboards for text entry, mice for navigation, and scanners for digitizing images and documents. Output devices like monitors, printers, and speakers allow users to see, hear, and physically output the computer's processed data. Monitors are either CRT or LCD and are described by their screen size, resolution, and refresh rate. Printers include inkjet, laser, and multifunction printers and produce physical copies of digital documents.