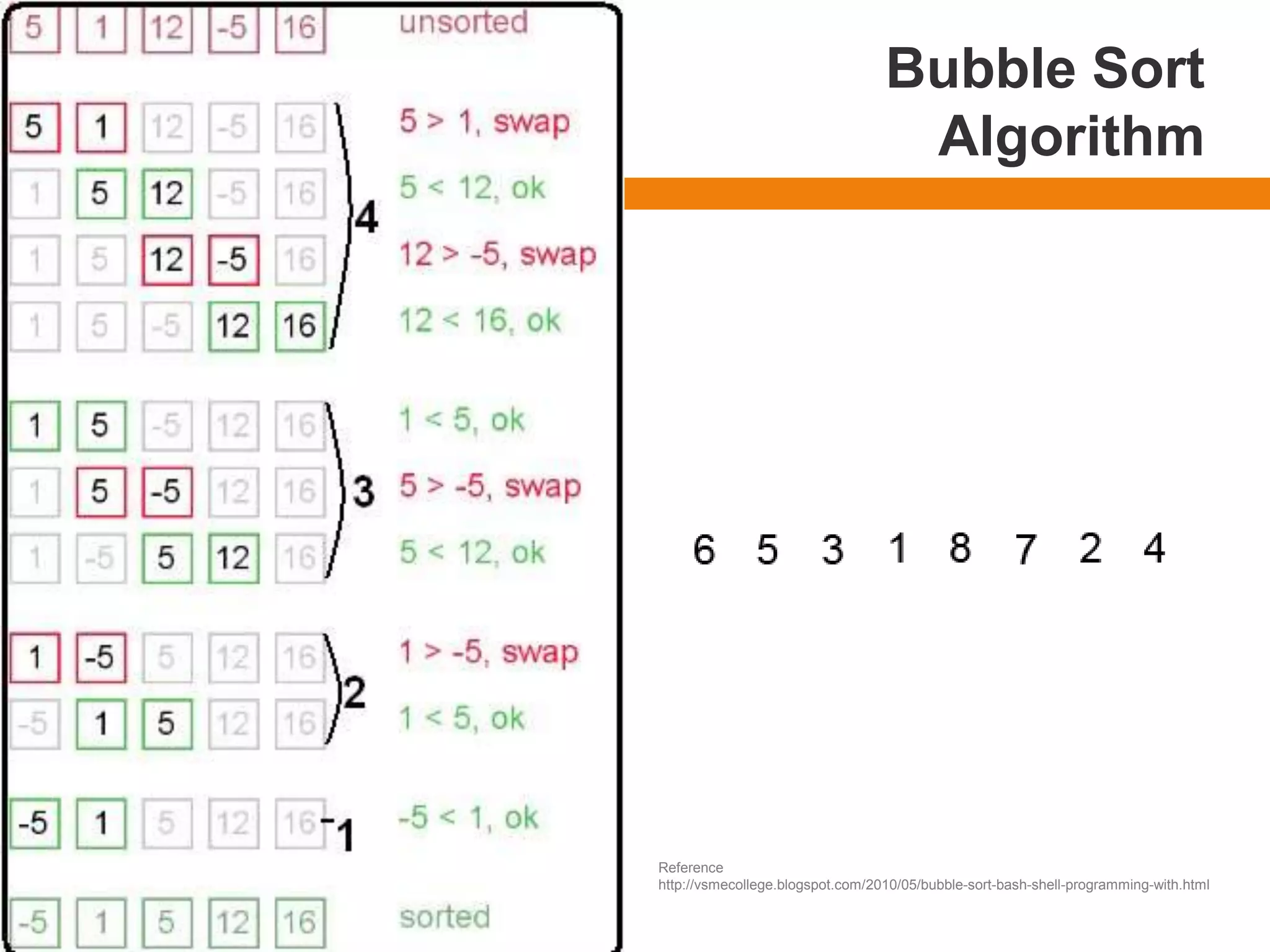
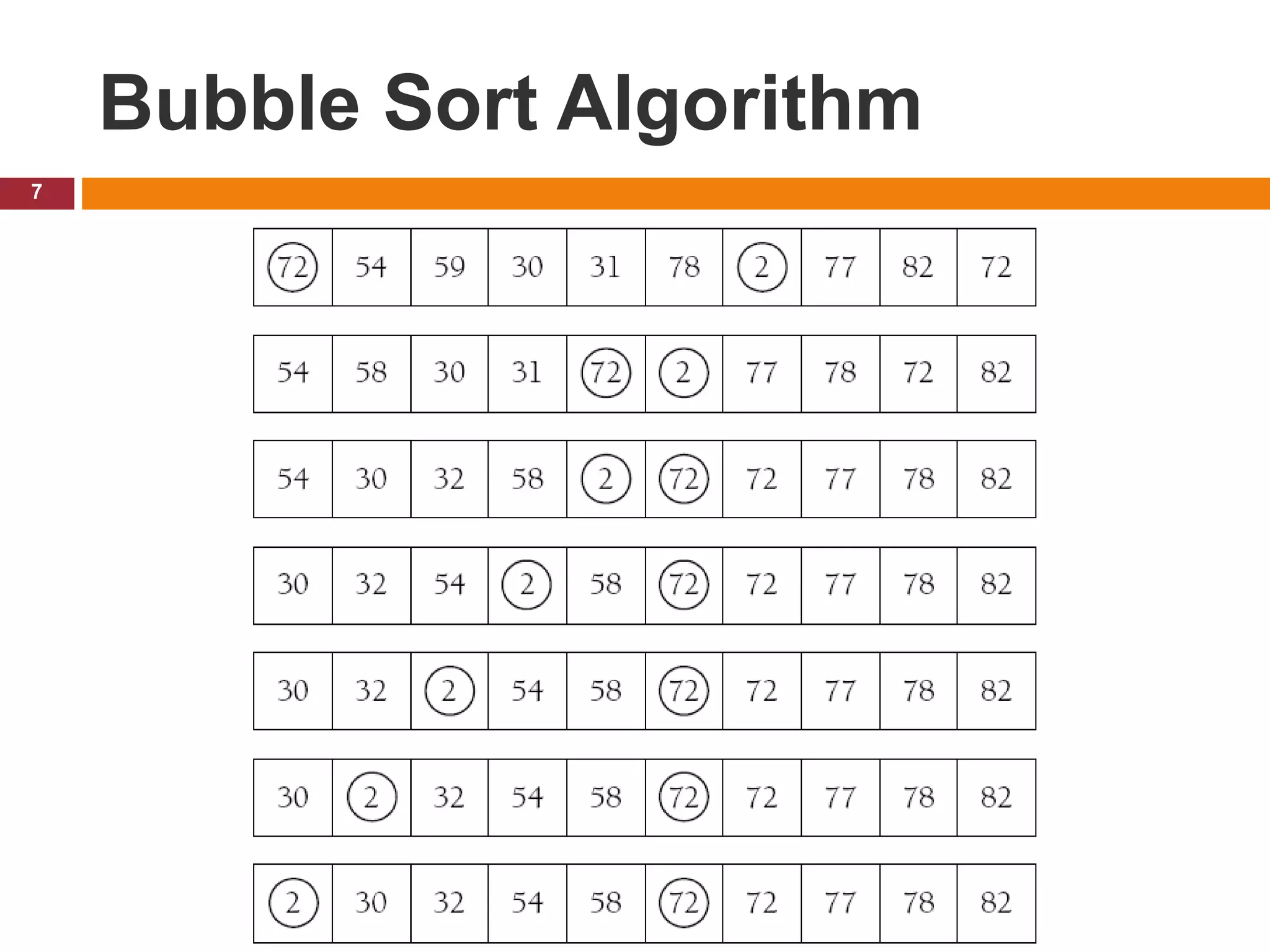
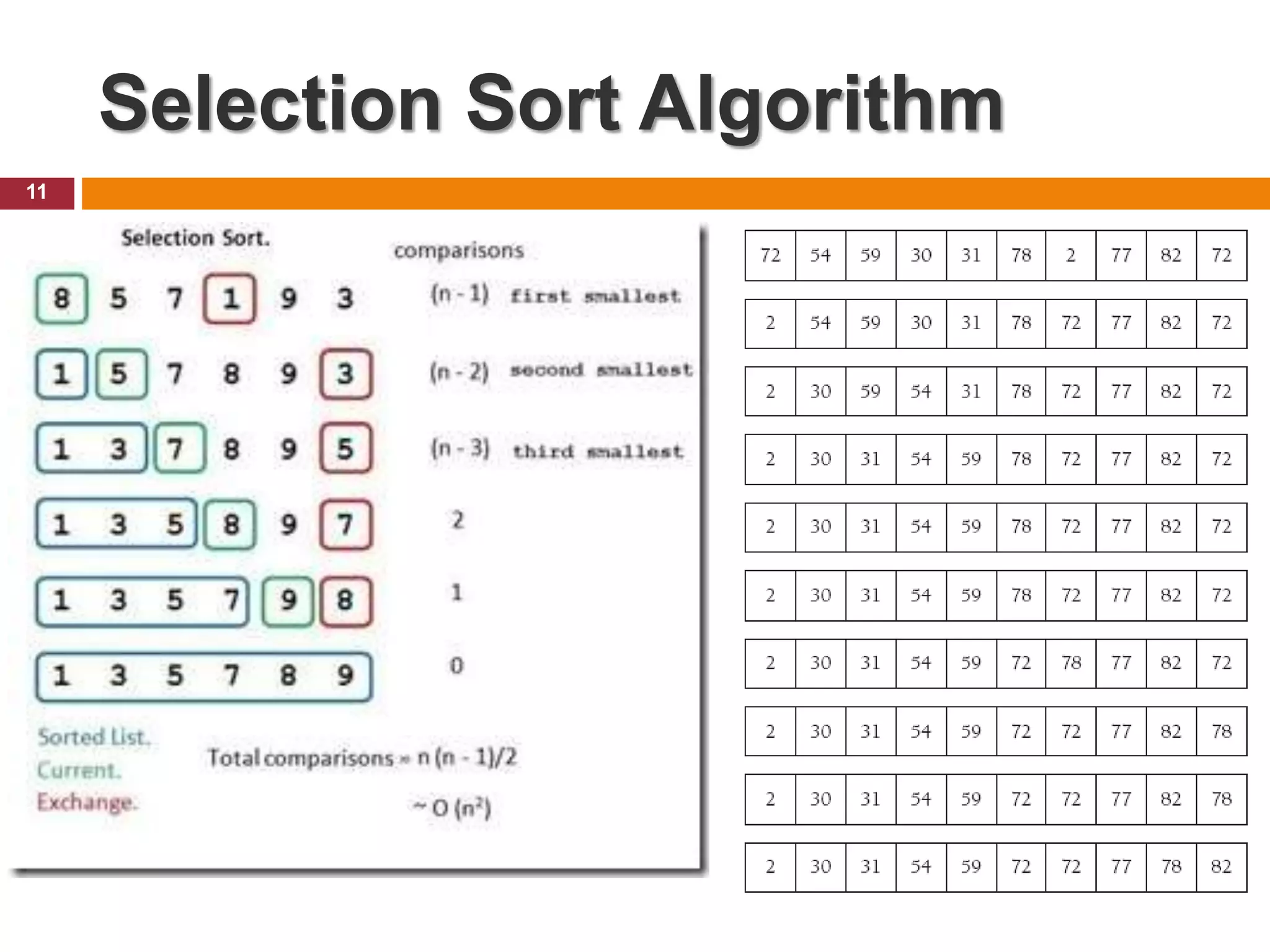
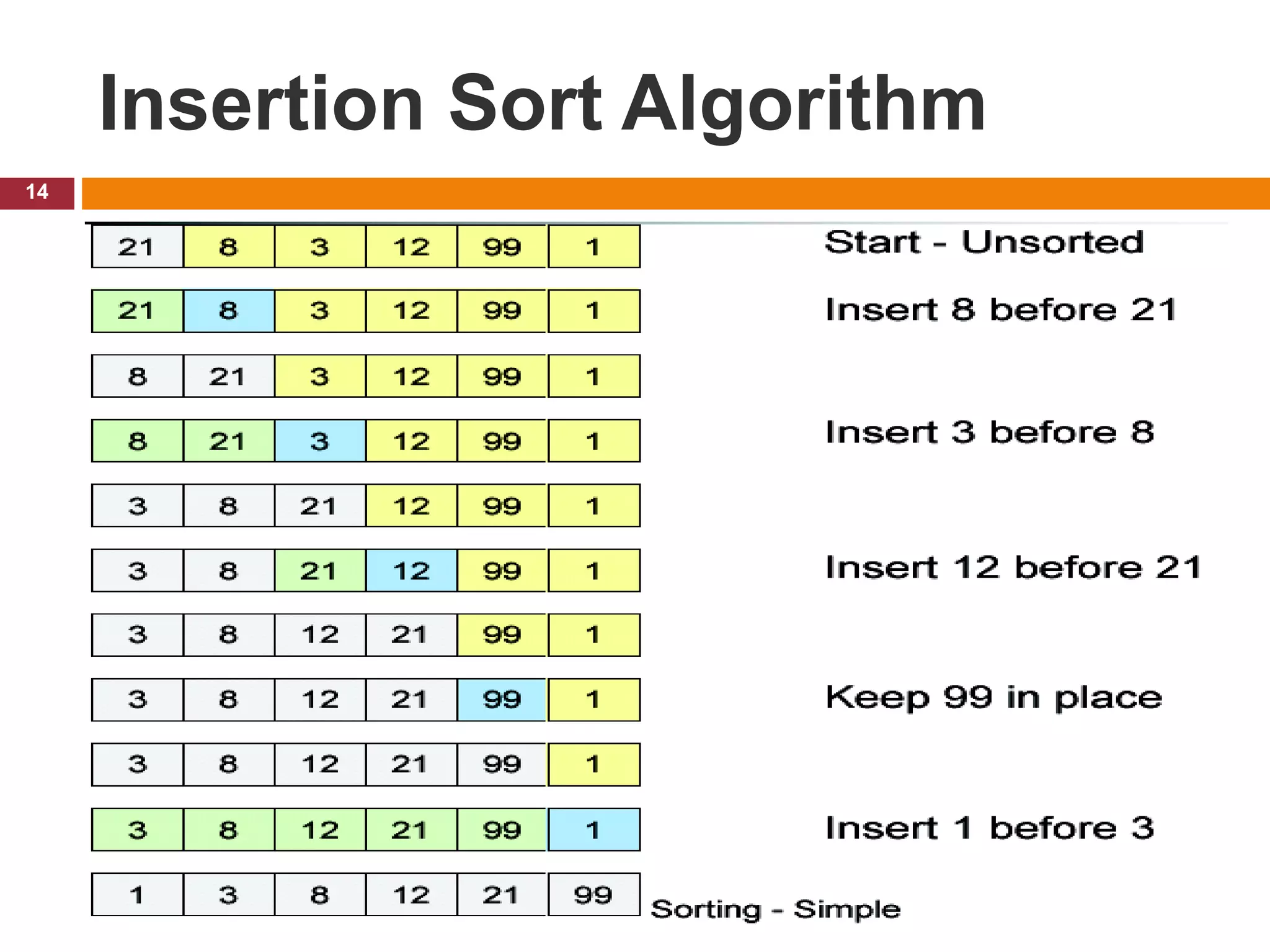
The document provides an outline and introduction for a chapter on basic sorting algorithms, including bubble sort, selection sort, and insertion sort algorithms. It includes pseudocode examples and explanations of each algorithm. It notes that bubble sort is one of the slowest but simplest algorithms, involving values "floating" to their correct positions. Selection sort finds the smallest element and places it in the first position, then repeats to find the next smallest. Insertion sort works by moving larger elements to the right to make room for smaller elements inserted from the left.



![Bubble Sort Algorithm
8
البيانات تراكيب مساق
إعداد العلمية المادة
/
أ
.
ا َّالفــر رفيق محمود
1. for ( int pass = 1, pass < length, pass++ )
2. for ( int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++ )
3. if ( b[ i ] > b[ i + 1 ] )
4. Swap(b[ i ], b[ i +1] );
The outer loop uses to repeat the process of
comparison.
The inner loop compares the two adjacent positions
indicated by i and i +1, swapping them if necessary.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3basicsortingalgorithmsdatastructurebcs-210125211722/75/Chapter-3-basic-sorting-algorithms-data-structure-8-2048.jpg)
![Bubble Sort Algorithm
9
1. static void Main(string[] args)
2. {
3. int[] id = { 12, 30, 1, 4, 7, 2 };
4. Console.Write(" Elements of Array Before Sorting ");
5. for (int x = 0; x < id.Length; x++)
6. Console.Write(" " + id[x]);
7. Console.WriteLine(" ");
8. for (int i =0; i< id.Length; i++)
9. for (int j =0; j< id.Length-1; j++)
10. if (id[j] > id[j + 1])
11. {
12. int hold = id[j];
13. id[j] = id[j + 1];
14. id[j + 1] = hold; }
15. Console.Write(" Elements of Array After Sorting ");
16. for (int x = 0; x < id.Length; x++)
17. Console.Write(" "+id[x]); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3basicsortingalgorithmsdatastructurebcs-210125211722/75/Chapter-3-basic-sorting-algorithms-data-structure-9-2048.jpg)

![Selection Sort Algorithm
12
1. static void Main(string[] args)
2. {
3. int[] a = { 10, 2, 34, 4, 3, 1, 100 };
4. int hold;
5. for (int i = 0; i < a.Length; i++) {
6. for (int j = i + 1; j < a.Length; j++)
7. if (a[j] < a[i]) {
8. hold = a[j];
9. a[j] = a[i];
10. a[i] = hold; } }
11. for (int k = 0; k < a.Length; k++)
12. Console.WriteLine(a[k]);
13. Console.Read(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3basicsortingalgorithmsdatastructurebcs-210125211722/75/Chapter-3-basic-sorting-algorithms-data-structure-12-2048.jpg)
![Insertion Sort Algorithm
16
البيانات تراكيب مساق
إعداد العلمية المادة
/
أ
.
ا َّالفــر رفيق محمود
1. static void Main(string[] args) {
2. int[] a = { 10, 2, 34, 4, 3, 1, 100 };
3. int inner, temp;
4. for (int outer = 1; outer < a.Length; outer++)
5. {
6. temp = a[outer];
7. inner = outer;
8. while (inner > 0 && a[inner - 1] >= temp)
9. {
10. a[inner] = a[inner - 1];
11. inner = inner -1; }
12. a[inner] = temp; }
13. Console.WriteLine();
14. for (int k = 0; k < a.Length; k++)
15. Console.WriteLine(" " + a[k]);
16. Console.Read(); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3basicsortingalgorithmsdatastructurebcs-210125211722/75/Chapter-3-basic-sorting-algorithms-data-structure-16-2048.jpg)


