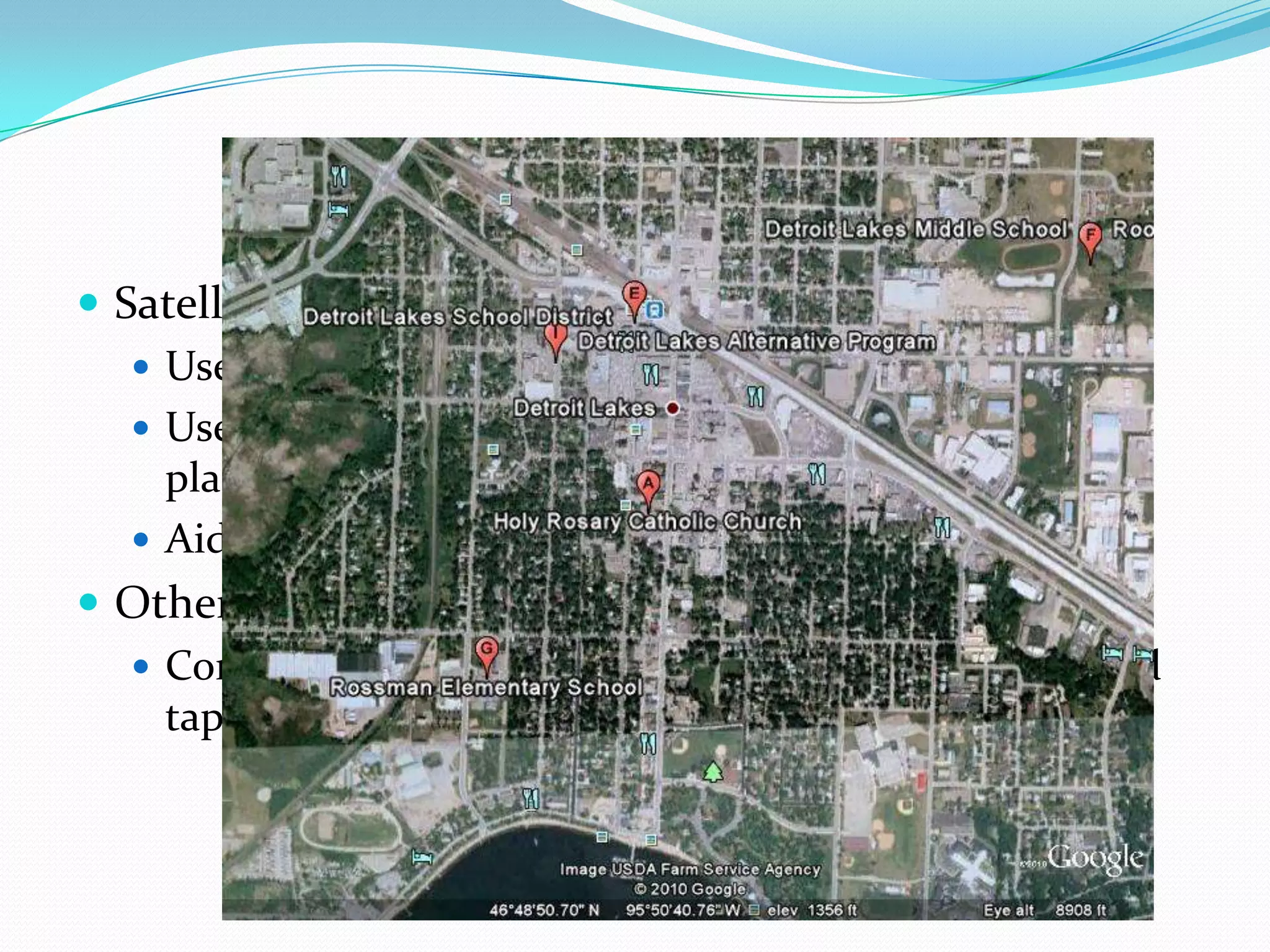
Geographers study the relationships between people and their environments on local, regional, and global scales. They examine how physical processes shape the Earth and how human activities impact landscapes. Geographers use tools like maps, globes, and satellite images to collect and analyze spatial data to better understand where things are located and how places differ. They seek to explain issues like economic changes, cultural shifts, and human-environment interactions.