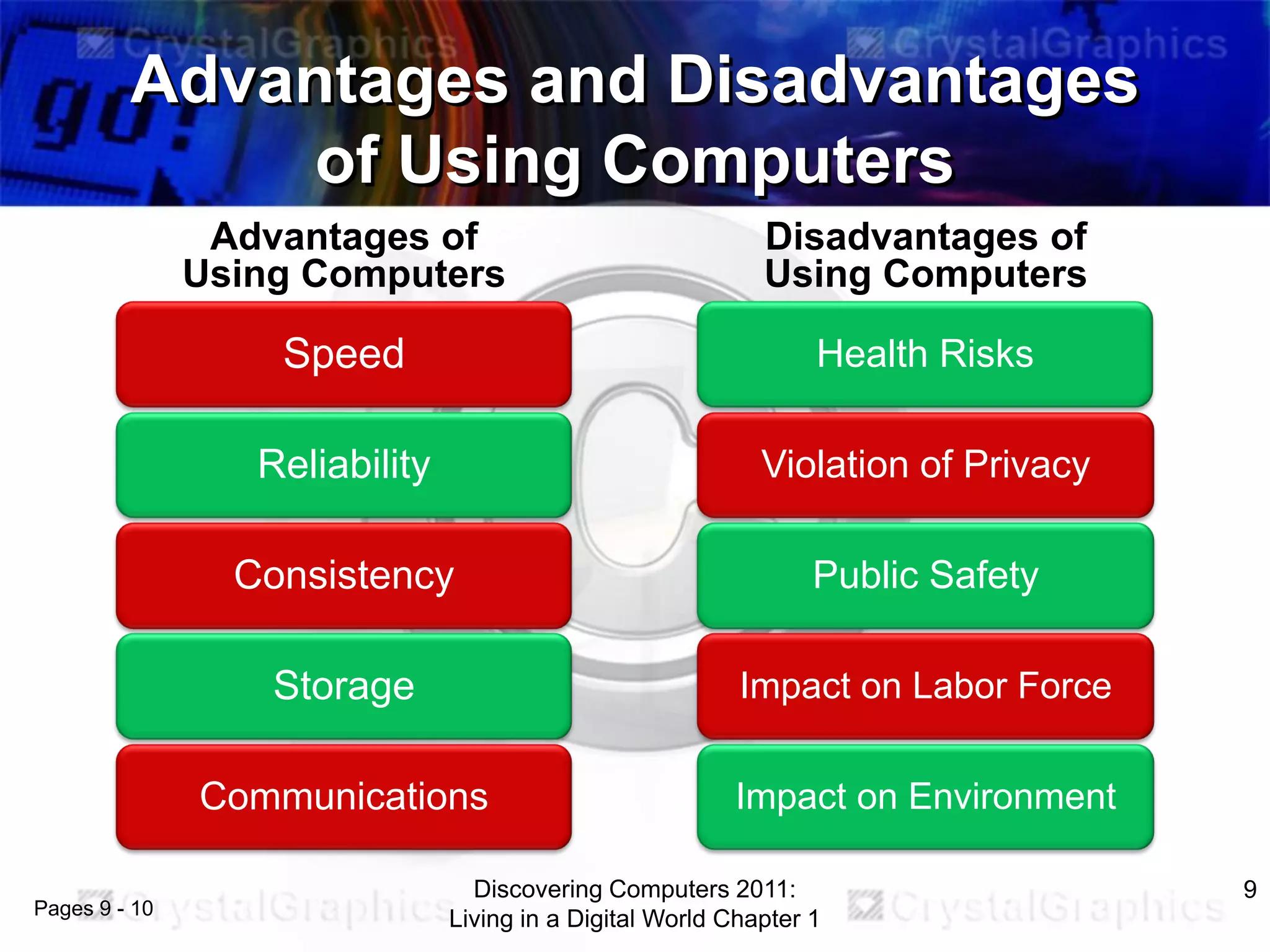
This document provides an overview of the objectives and content covered in the CSC134 course on computer and information processing. The key topics covered include:
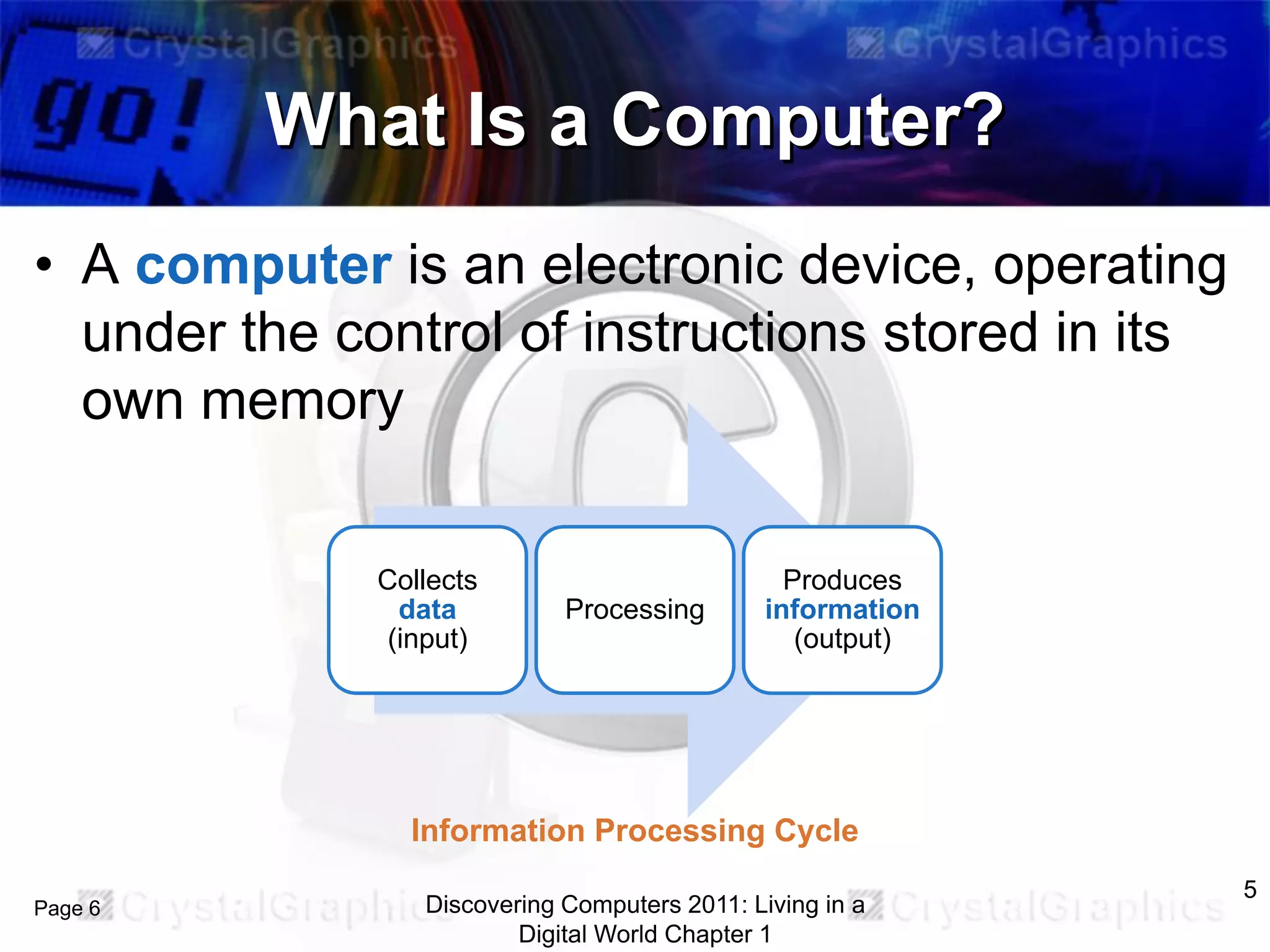
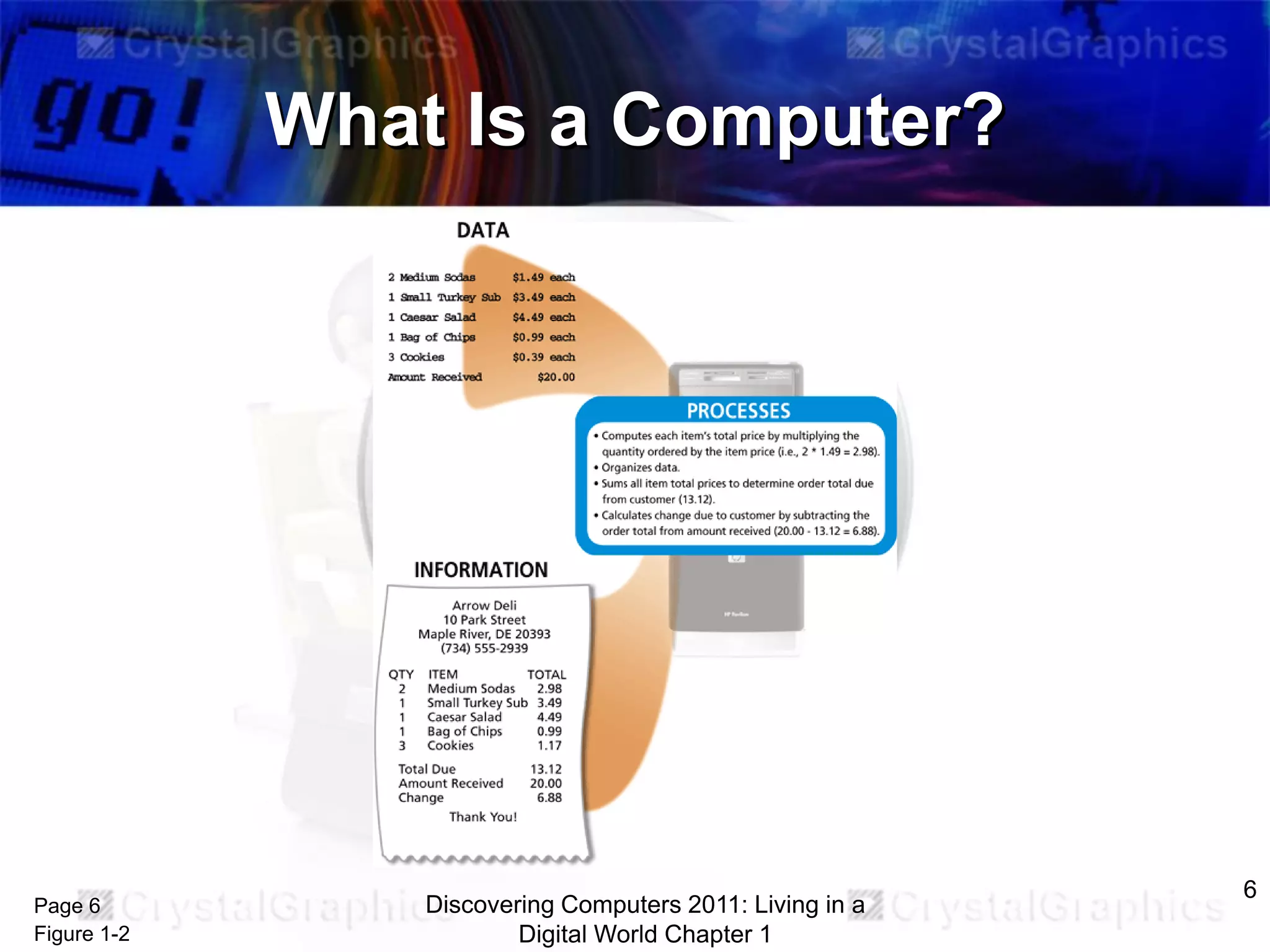
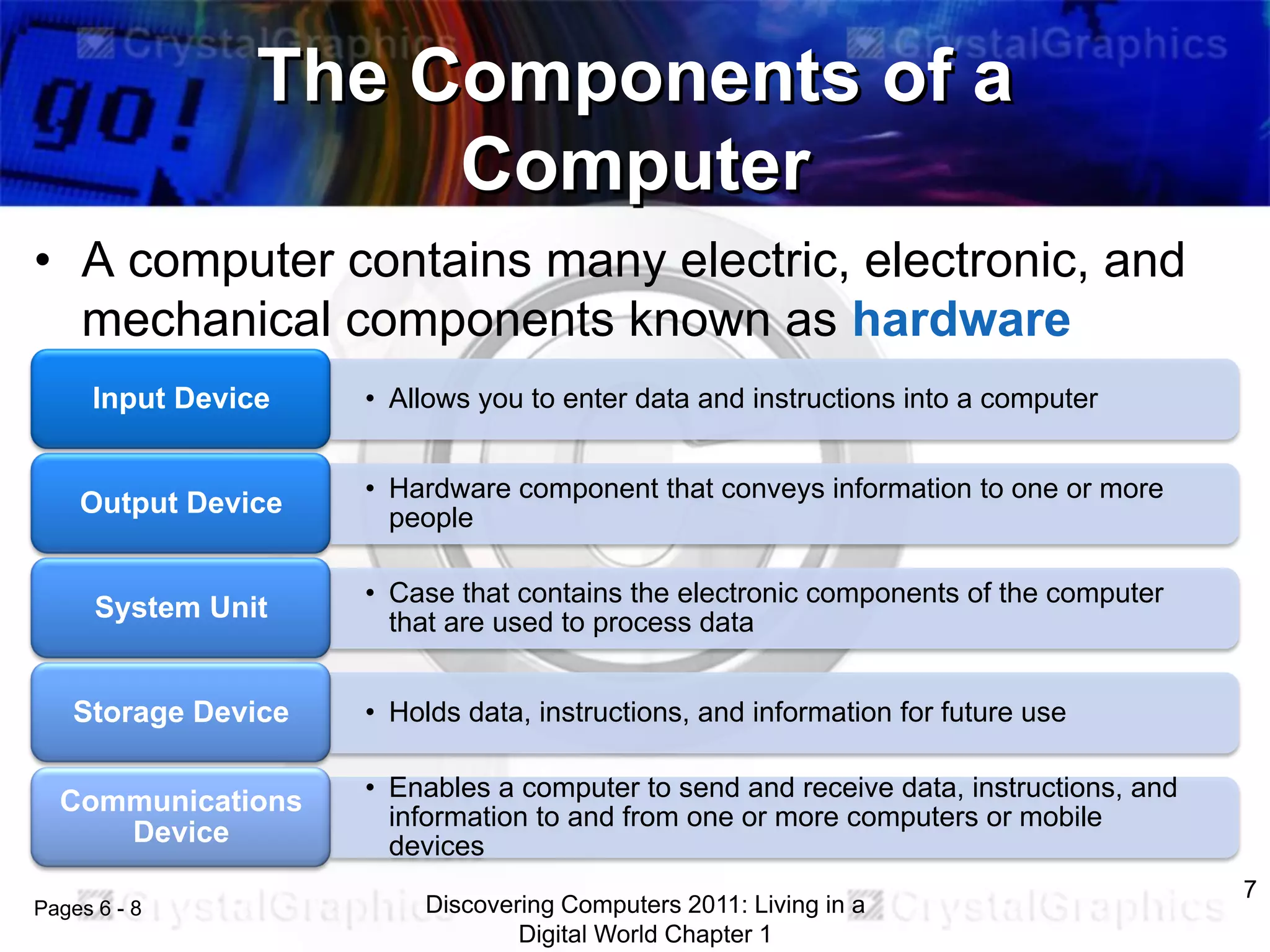
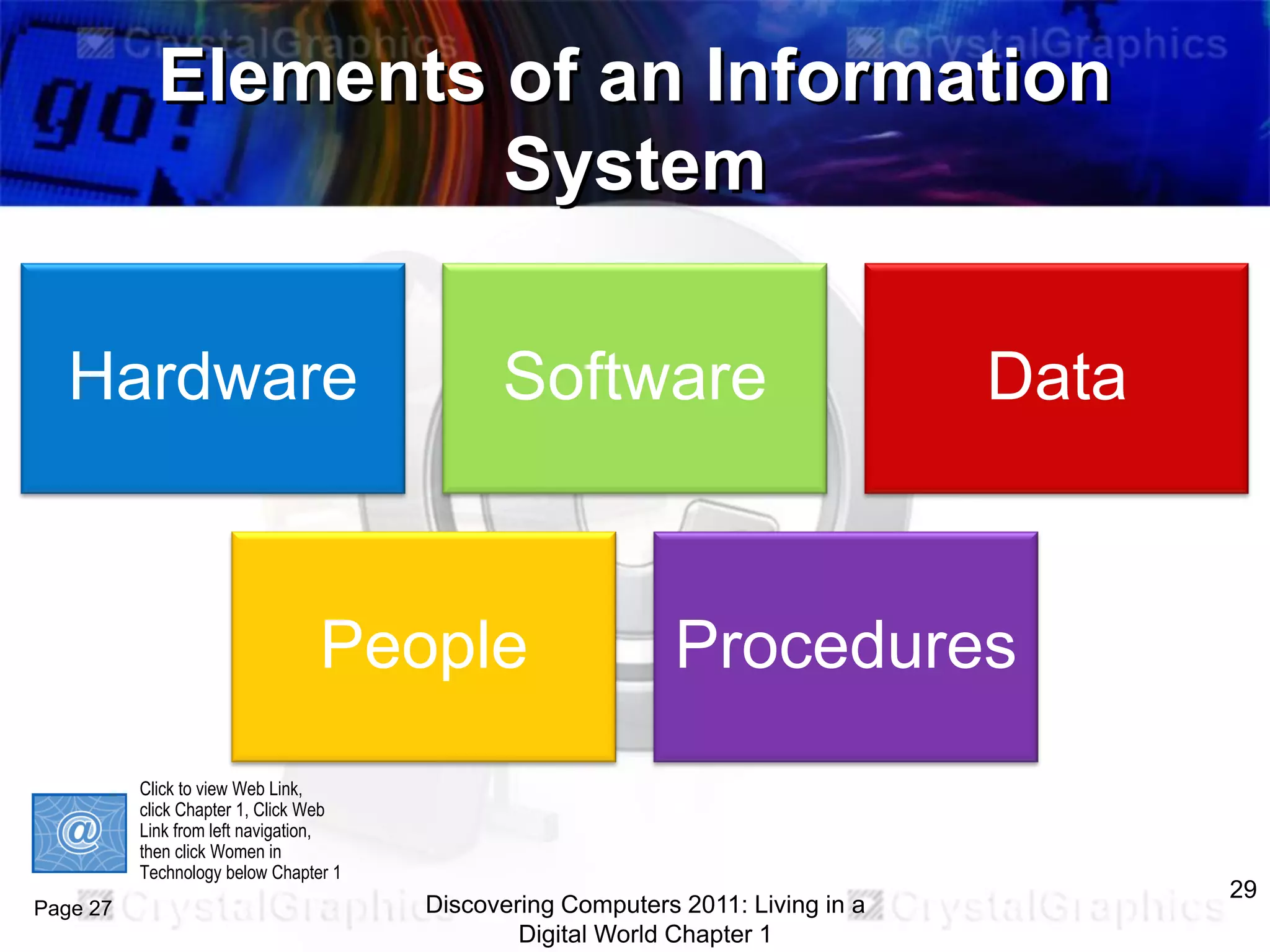
1) An introduction to computers and their components, including the system unit, storage, input/output devices, and how data is processed.
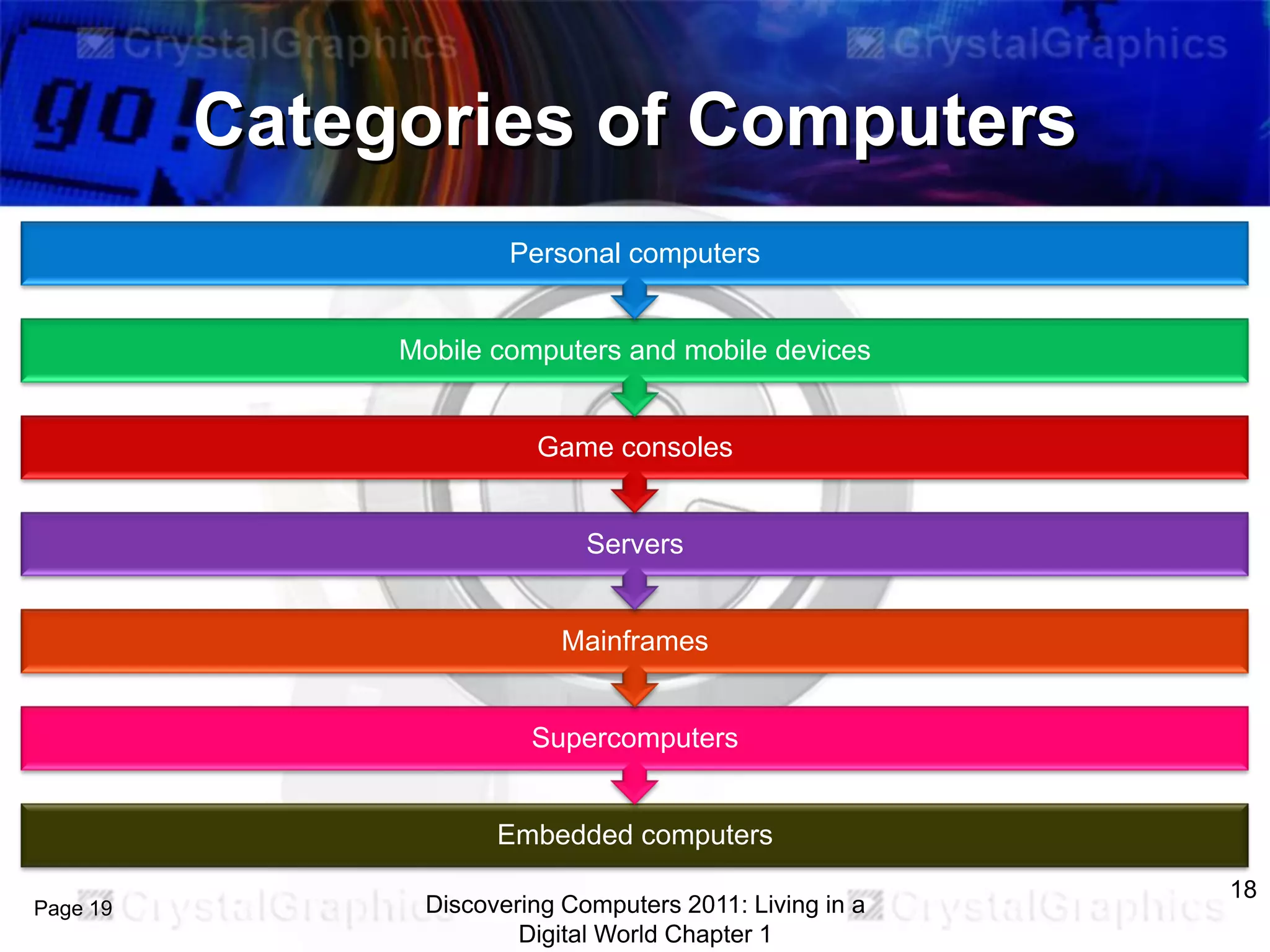
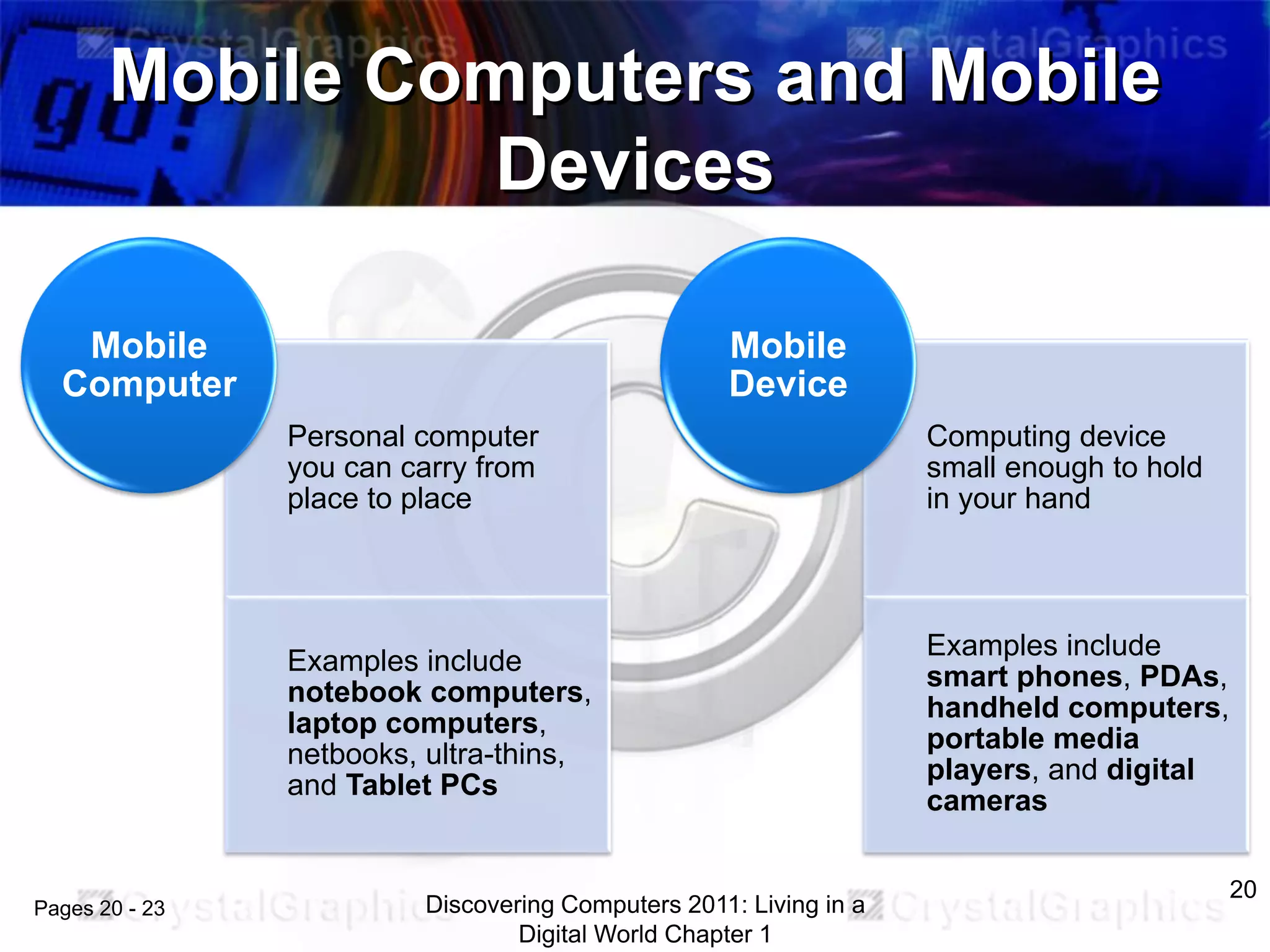
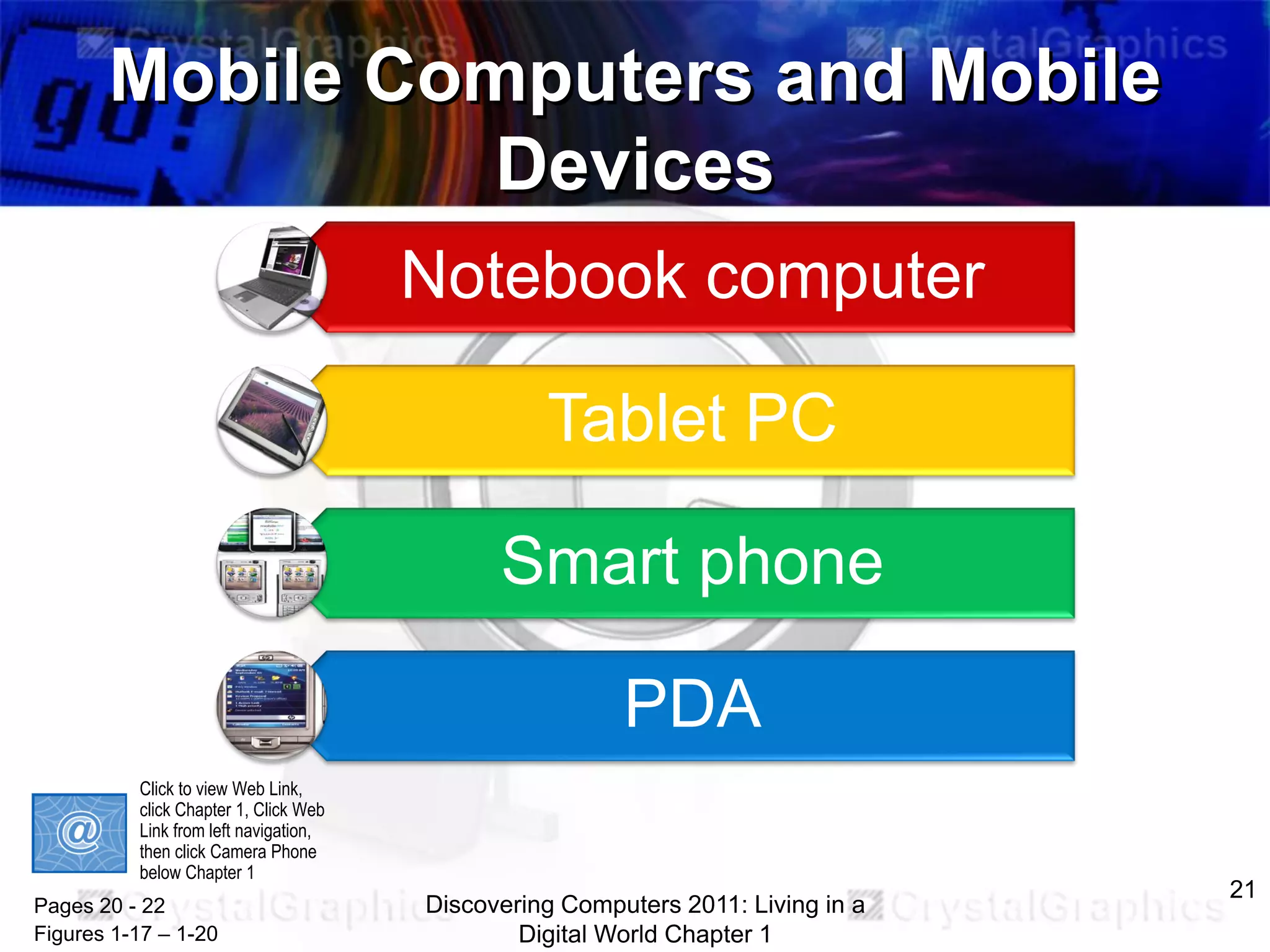
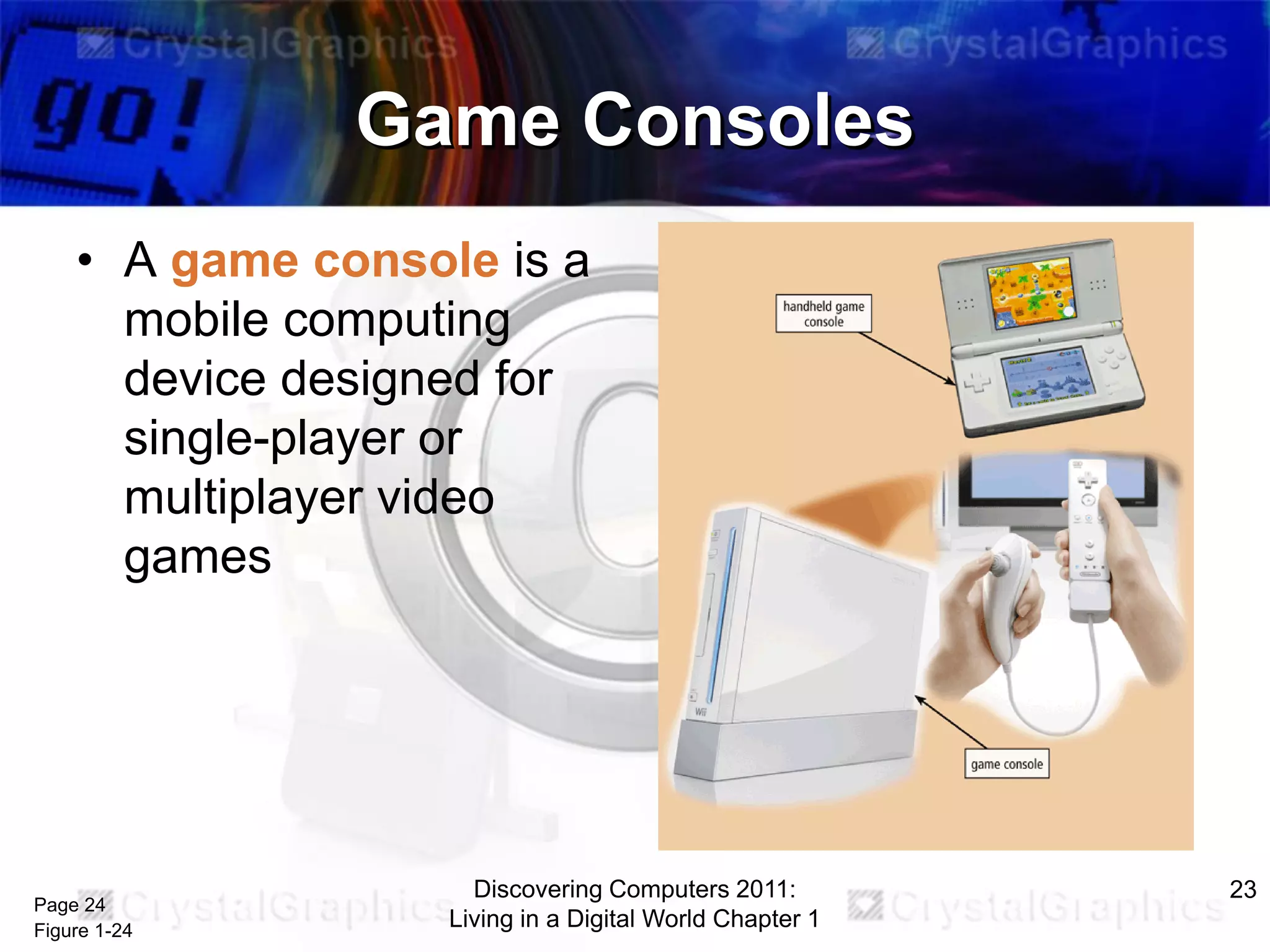
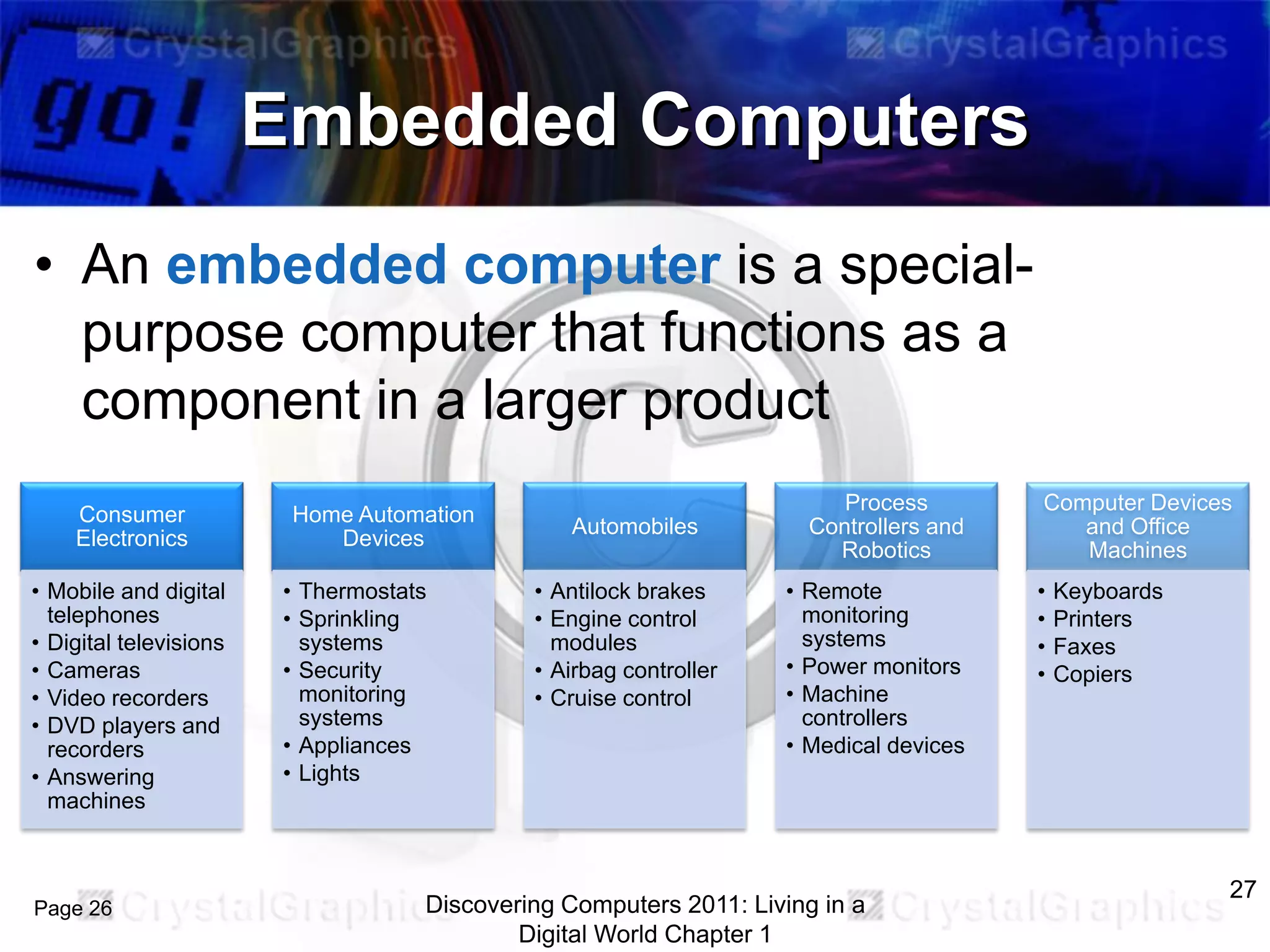
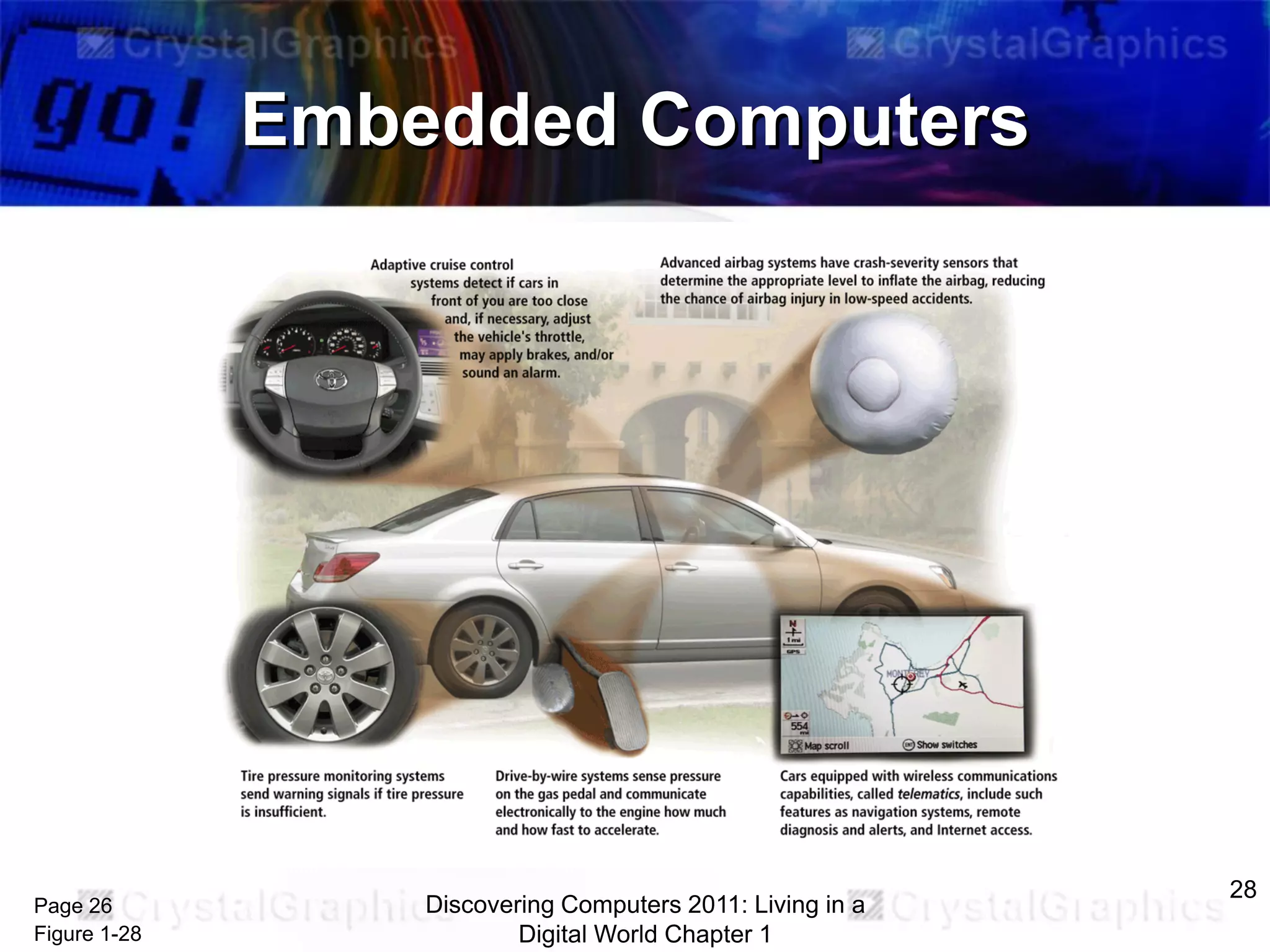
2) Different categories of computers like personal computers, mobile devices, servers, and their uses.
3) Computer software, including system software, application software, and programming.
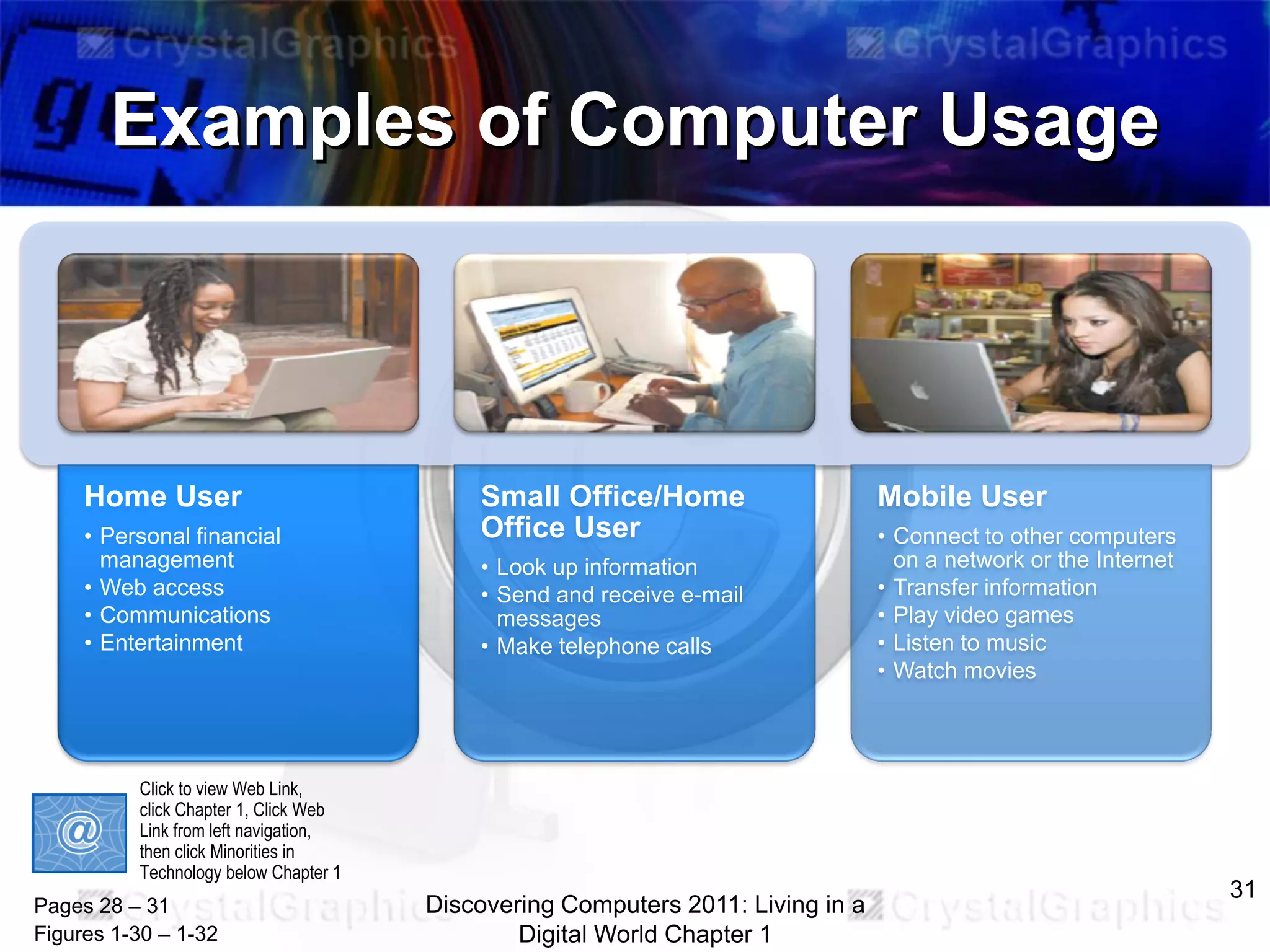
4) How computers are used in various fields like education, healthcare, manufacturing, and by different types of users.
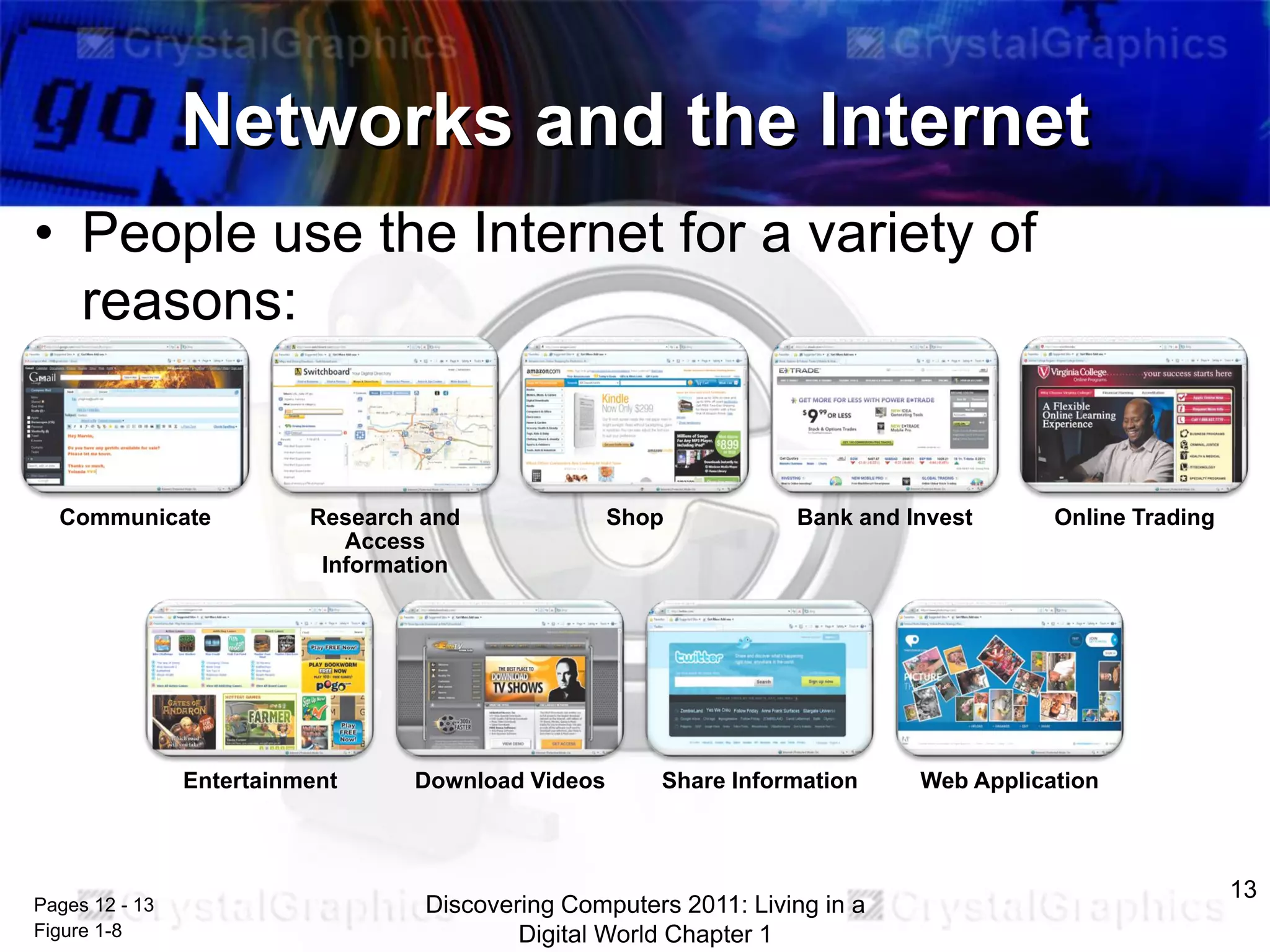
5) Networks and the internet, and how people and organizations utilize these technologies.
6) The impact