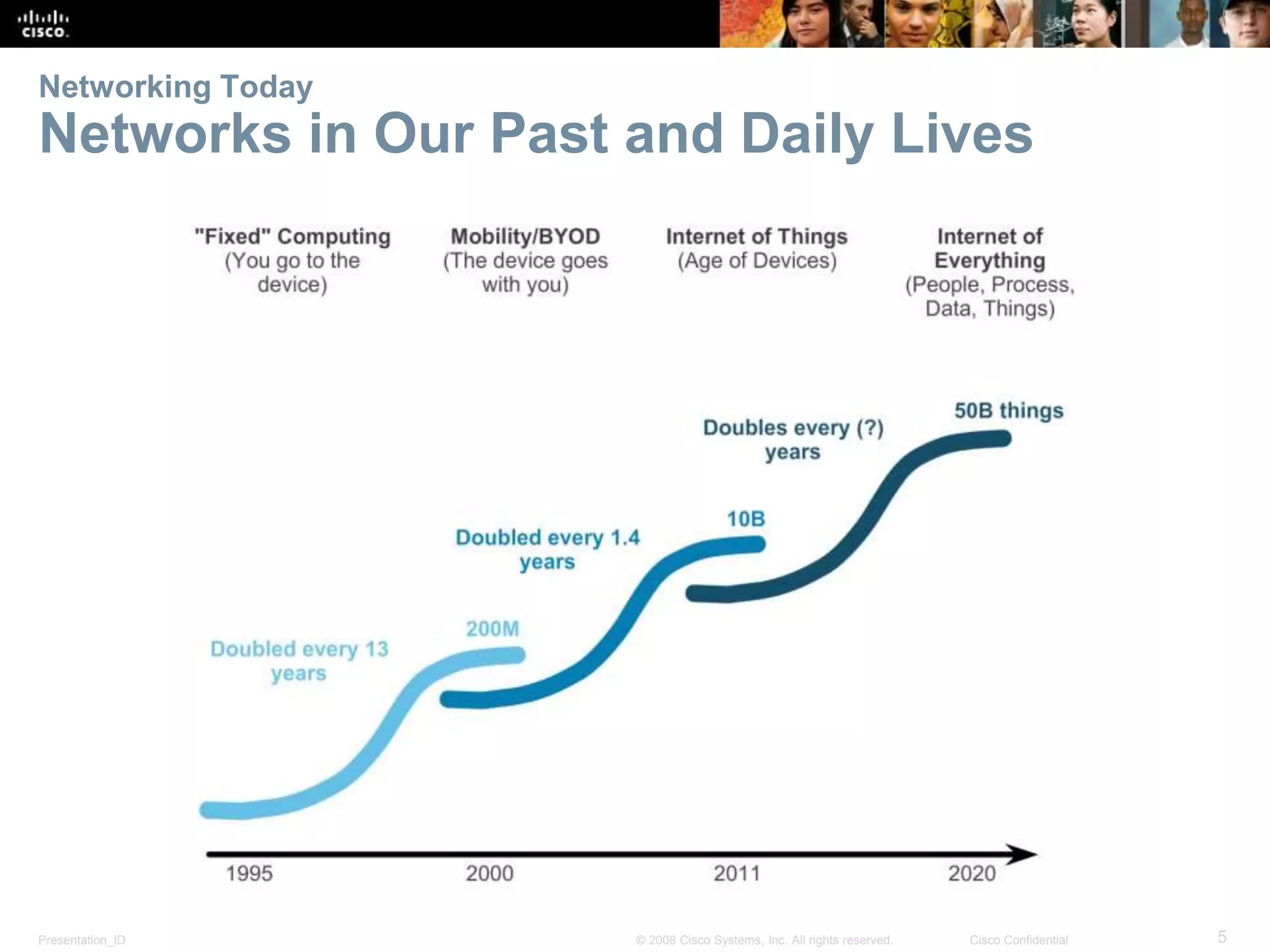
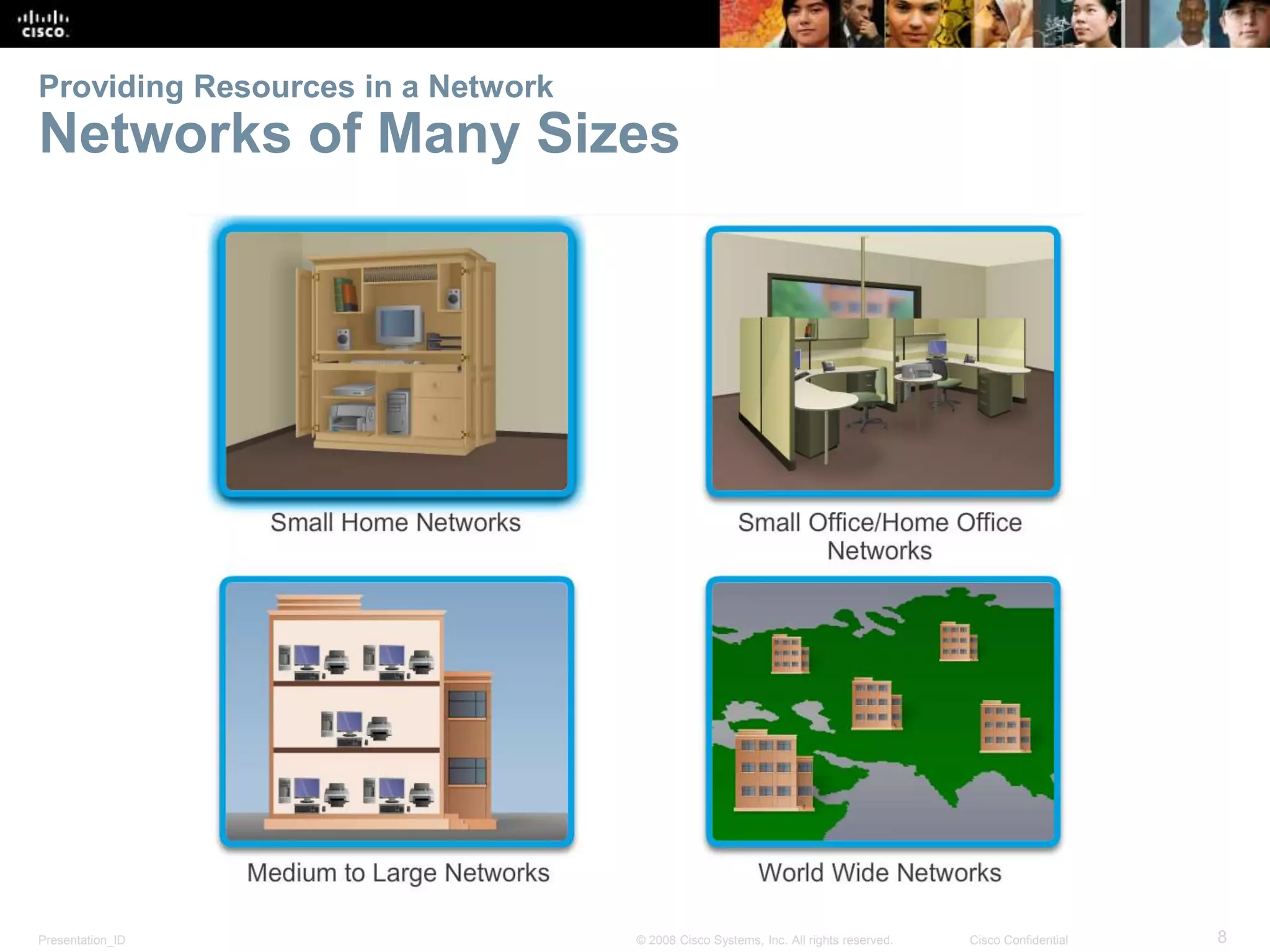
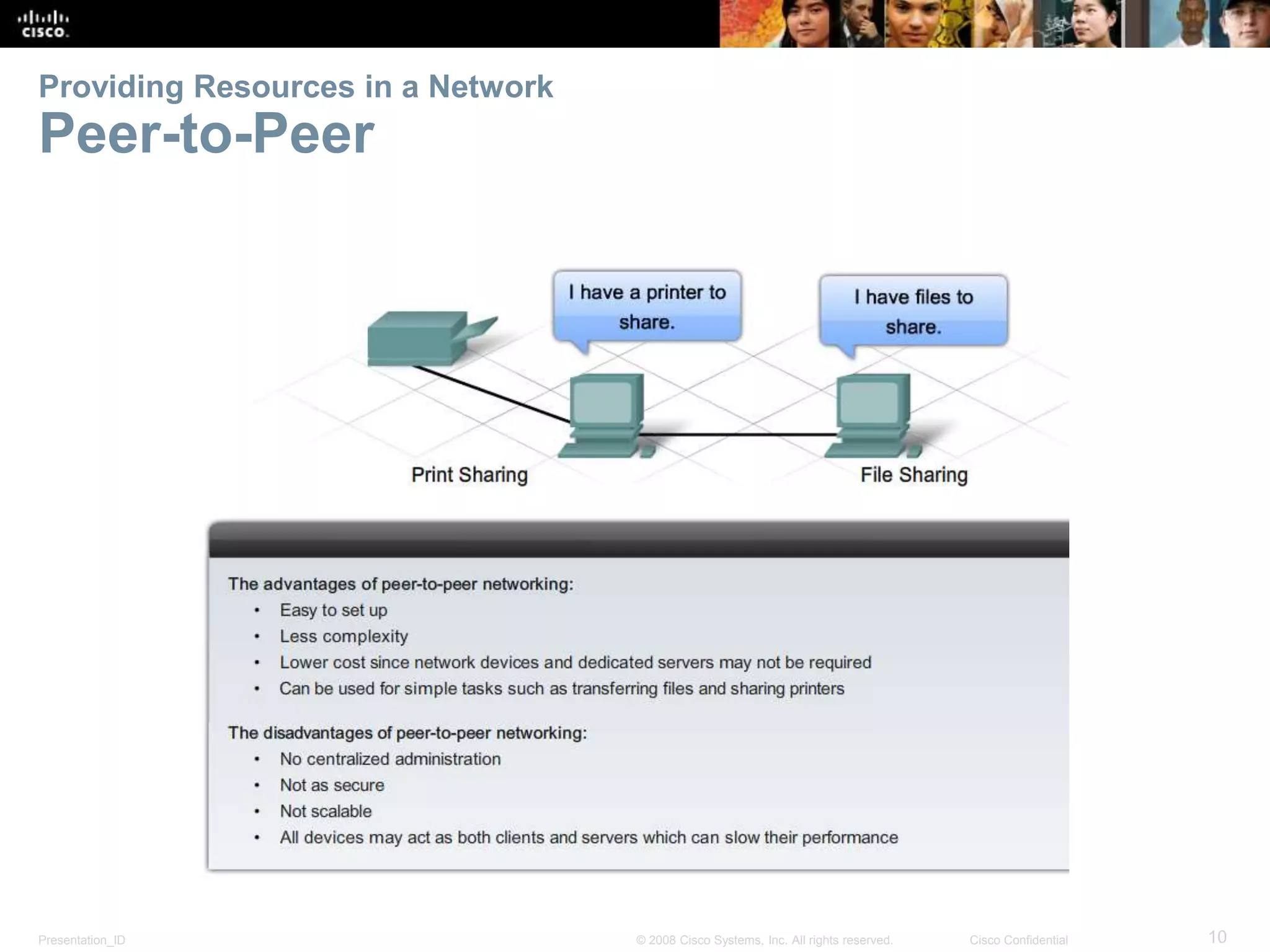
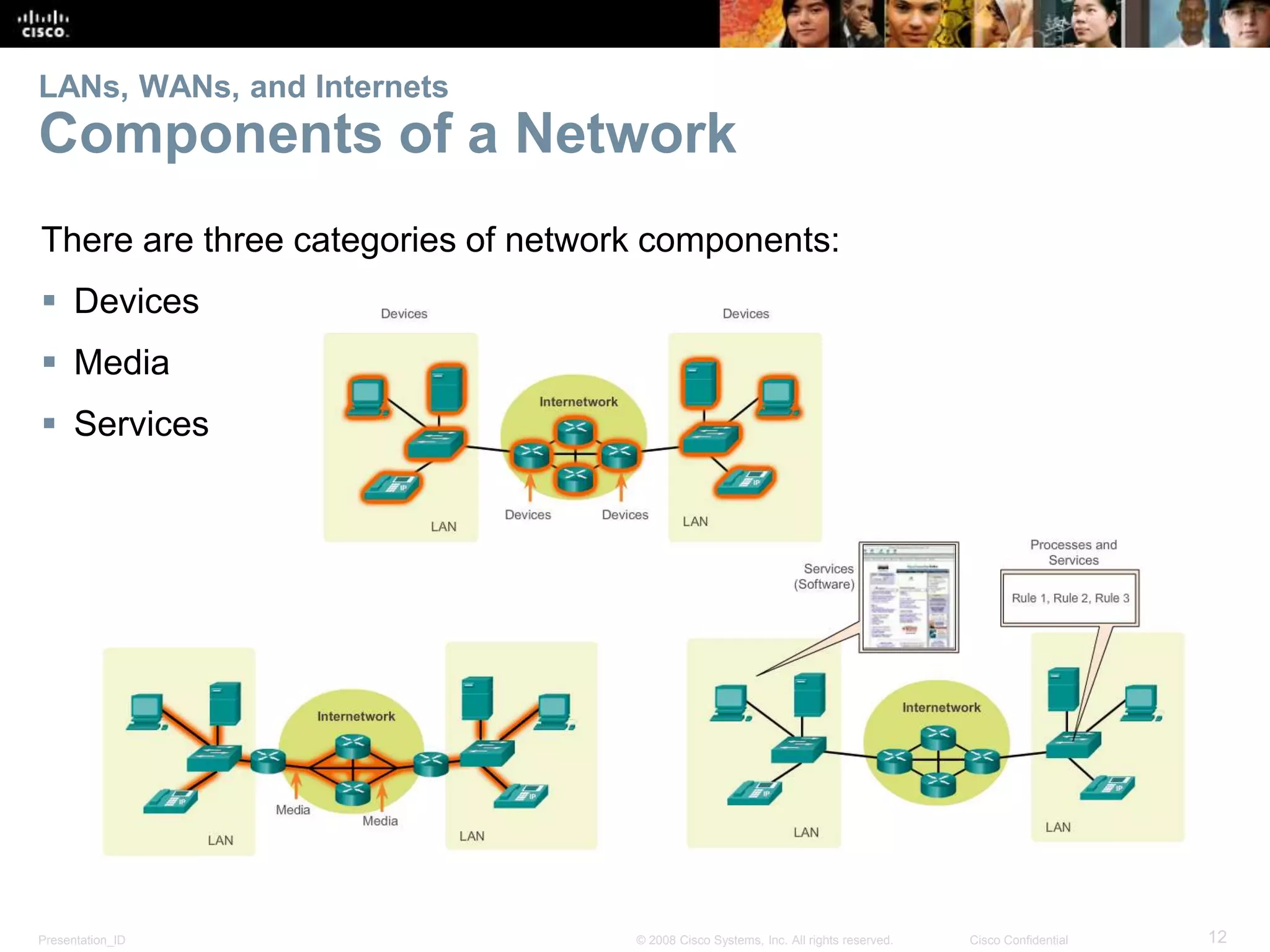
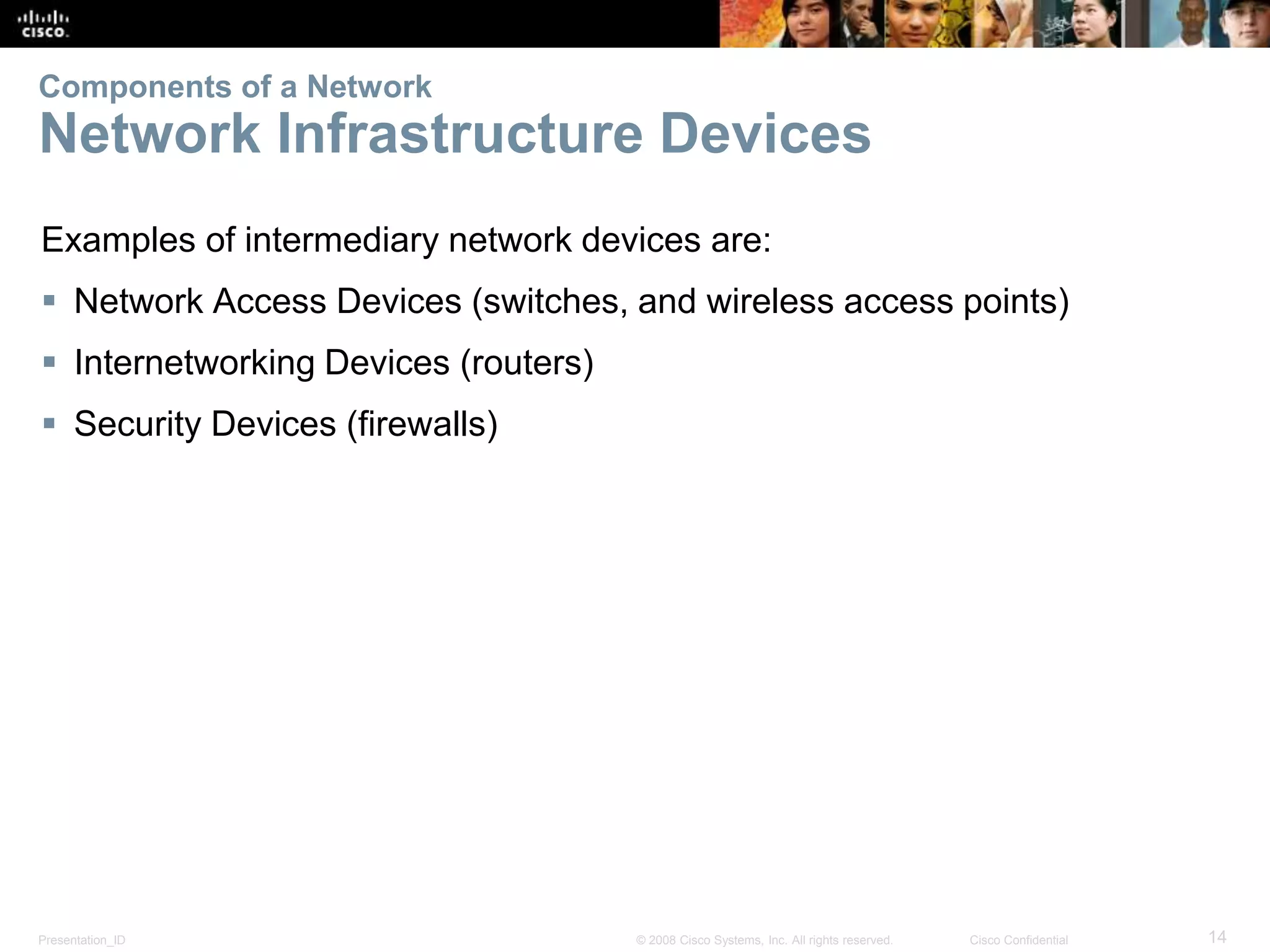
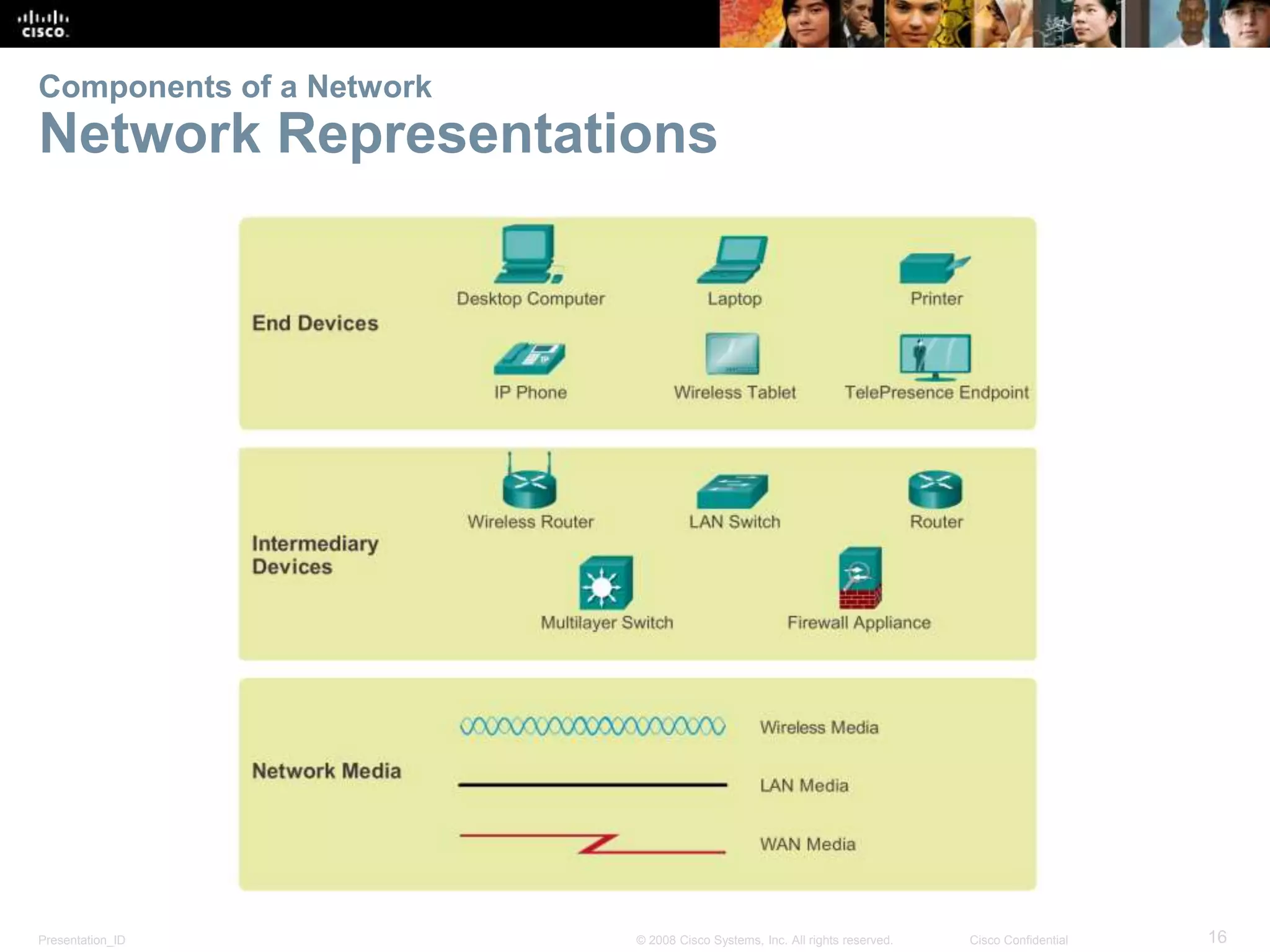
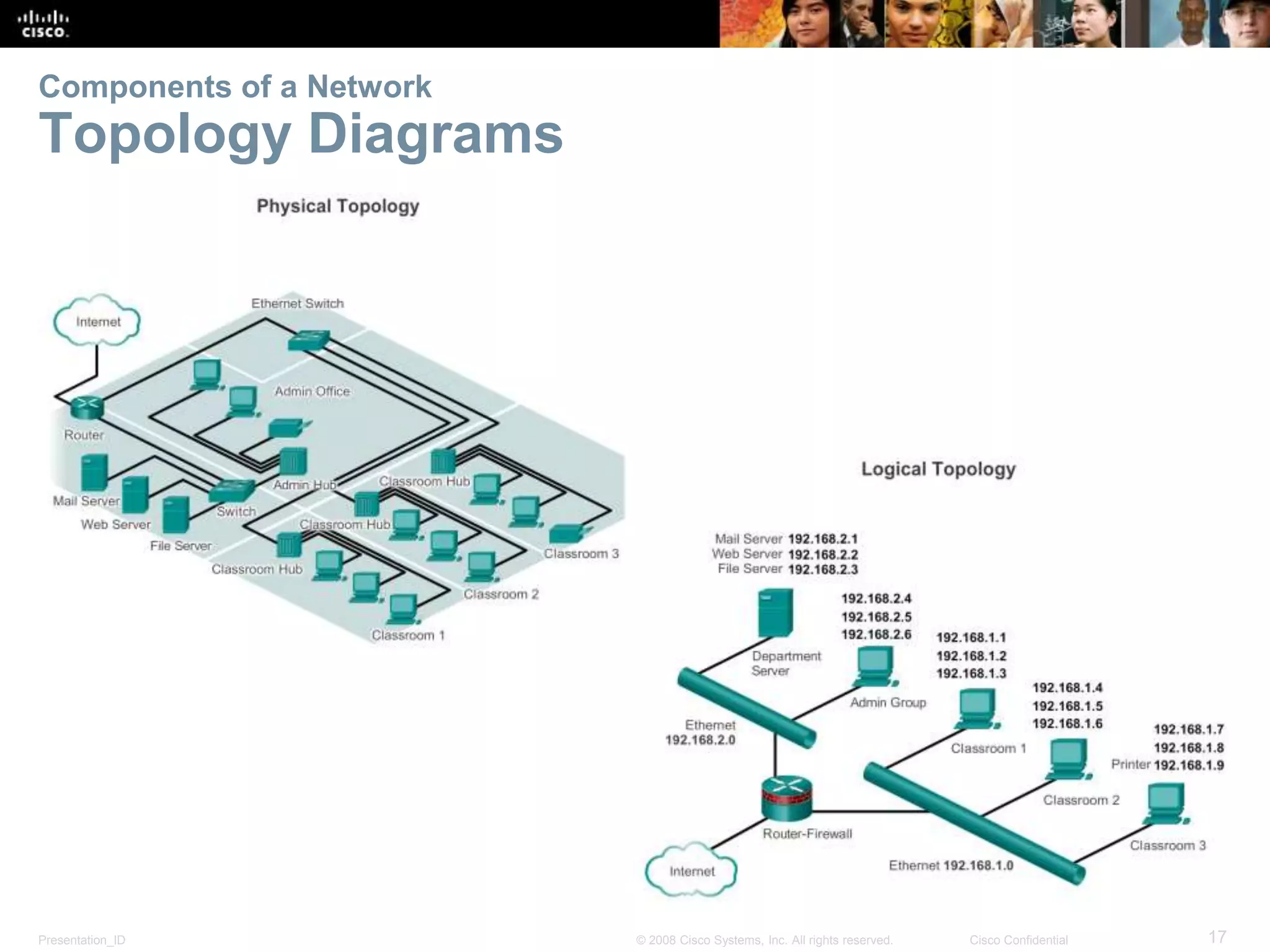
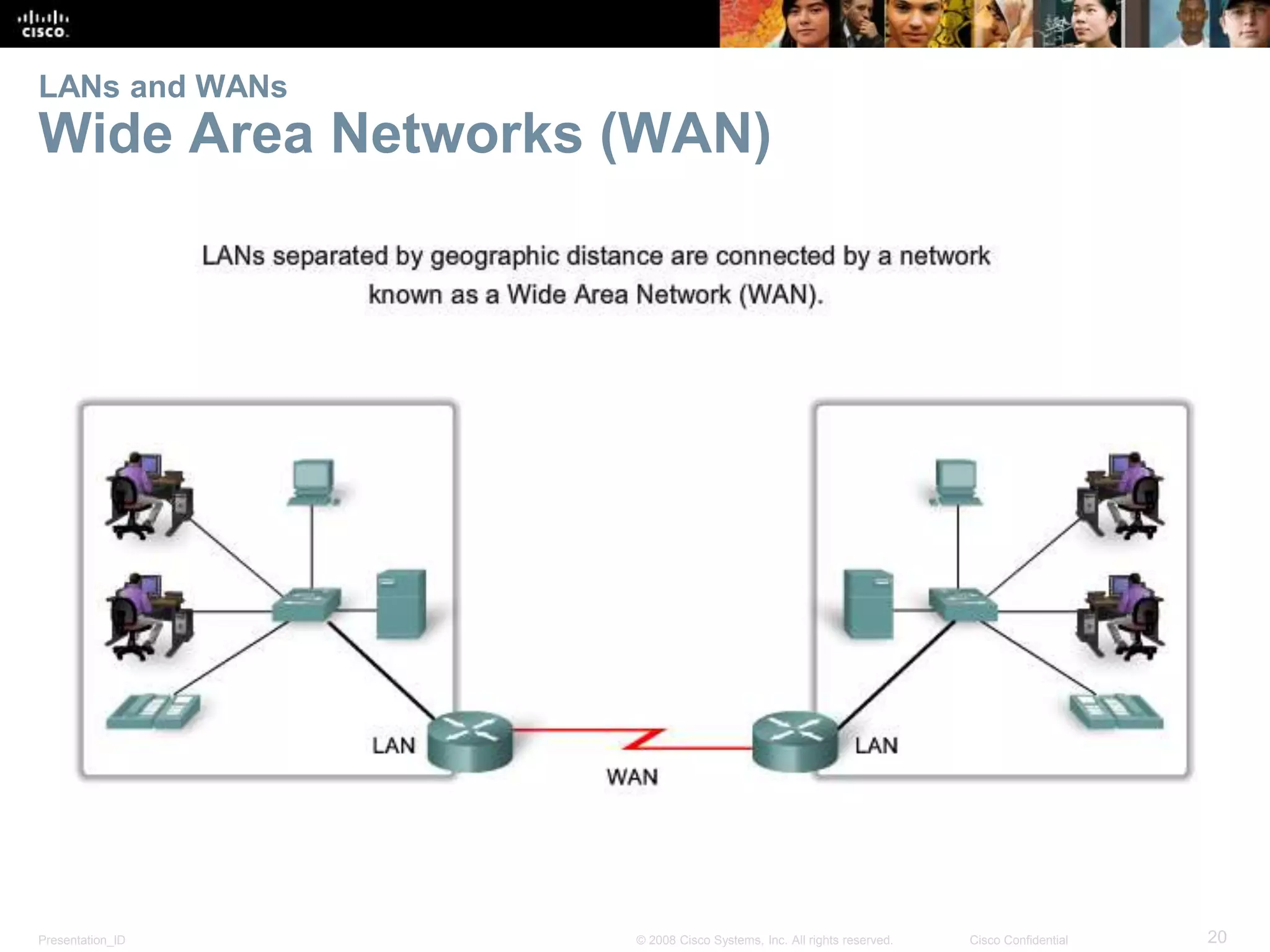
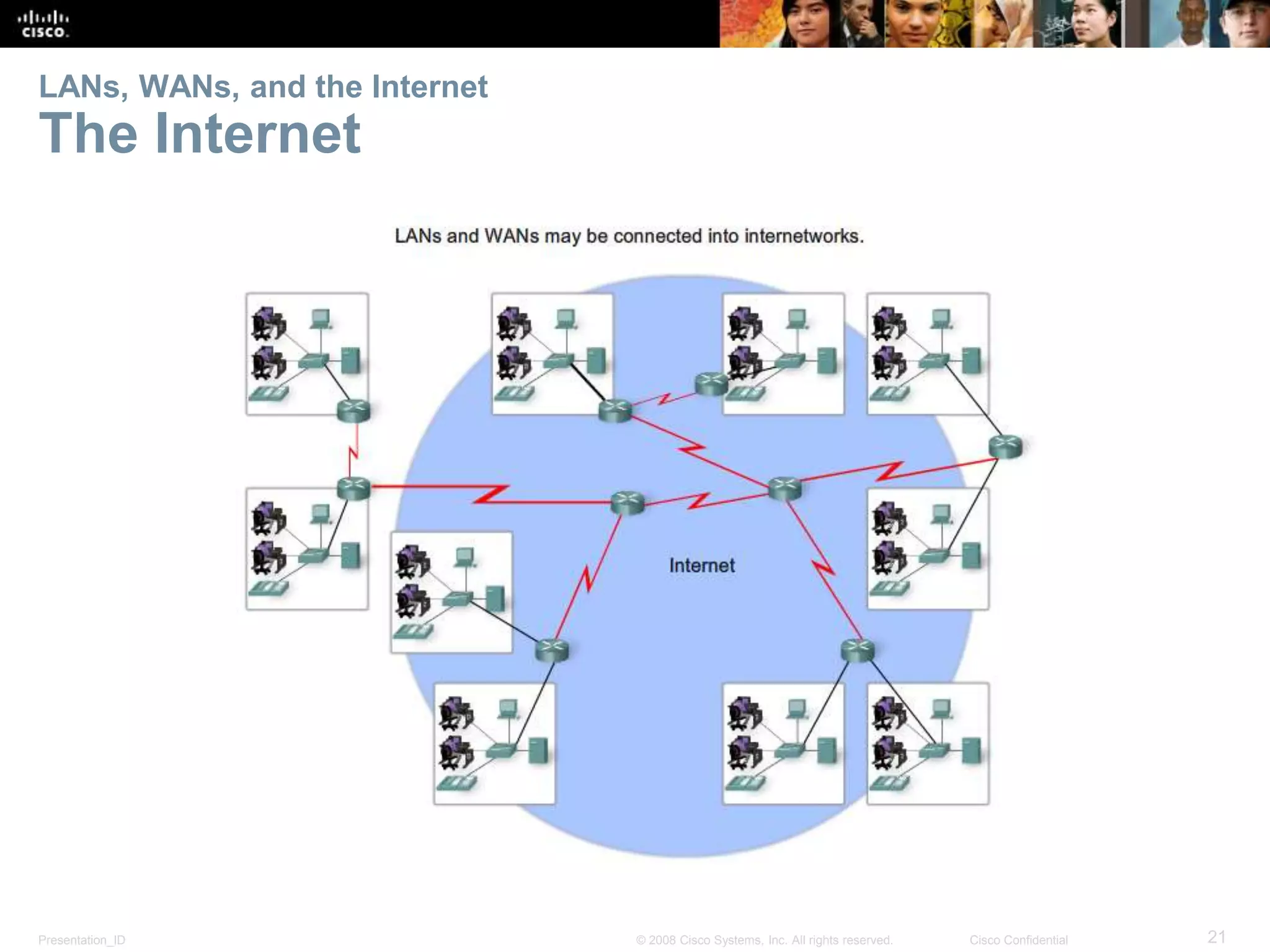
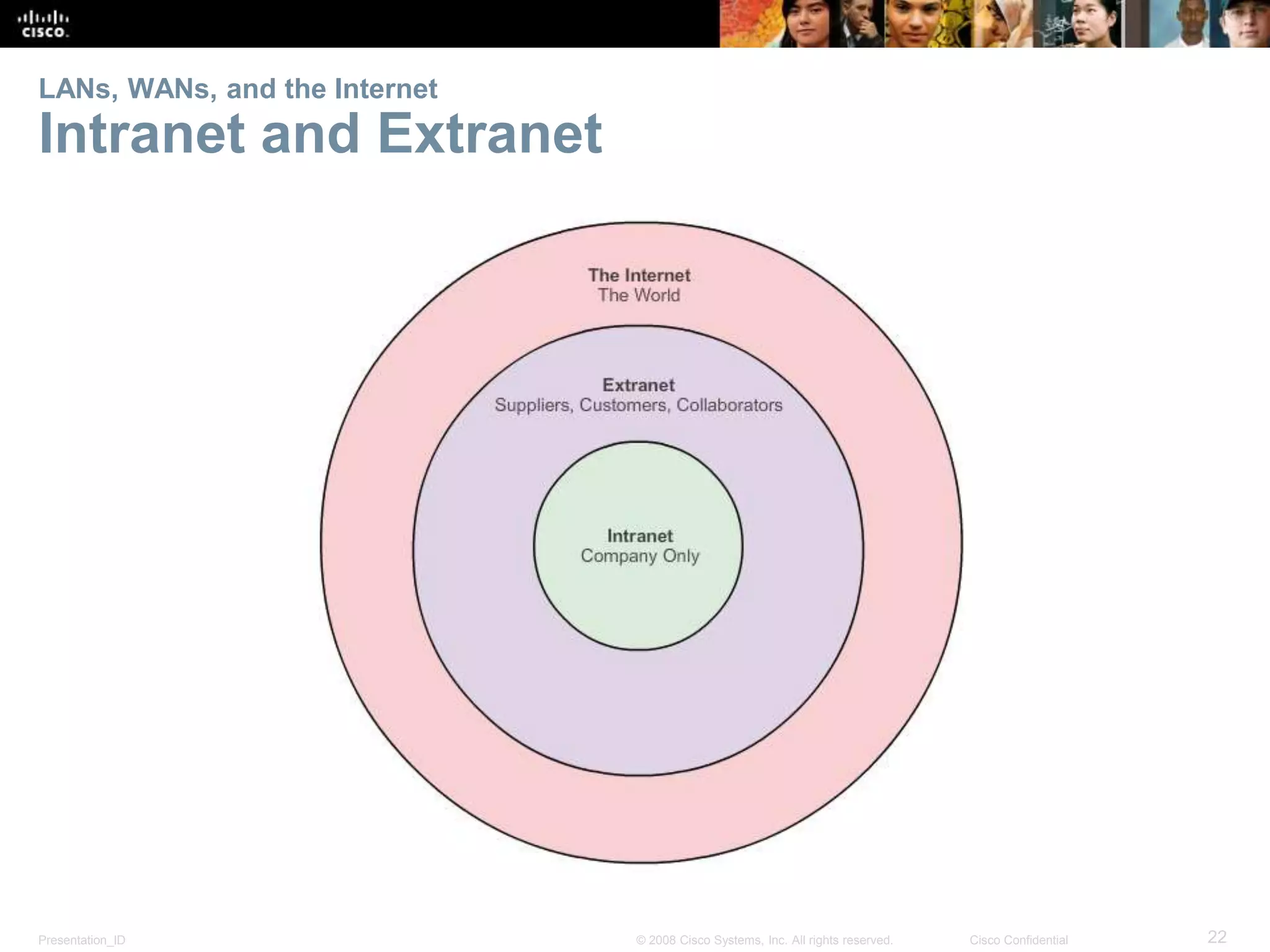
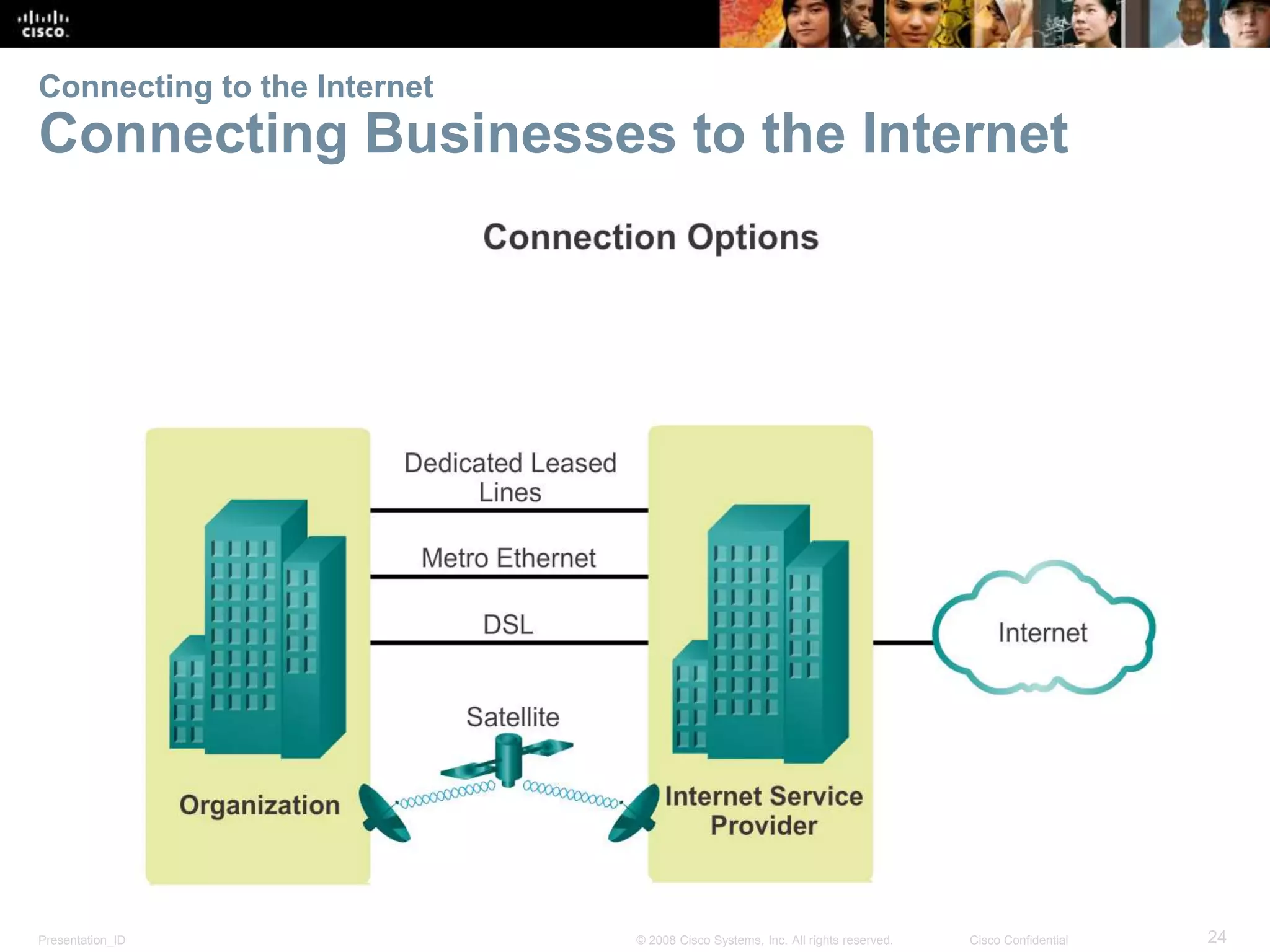
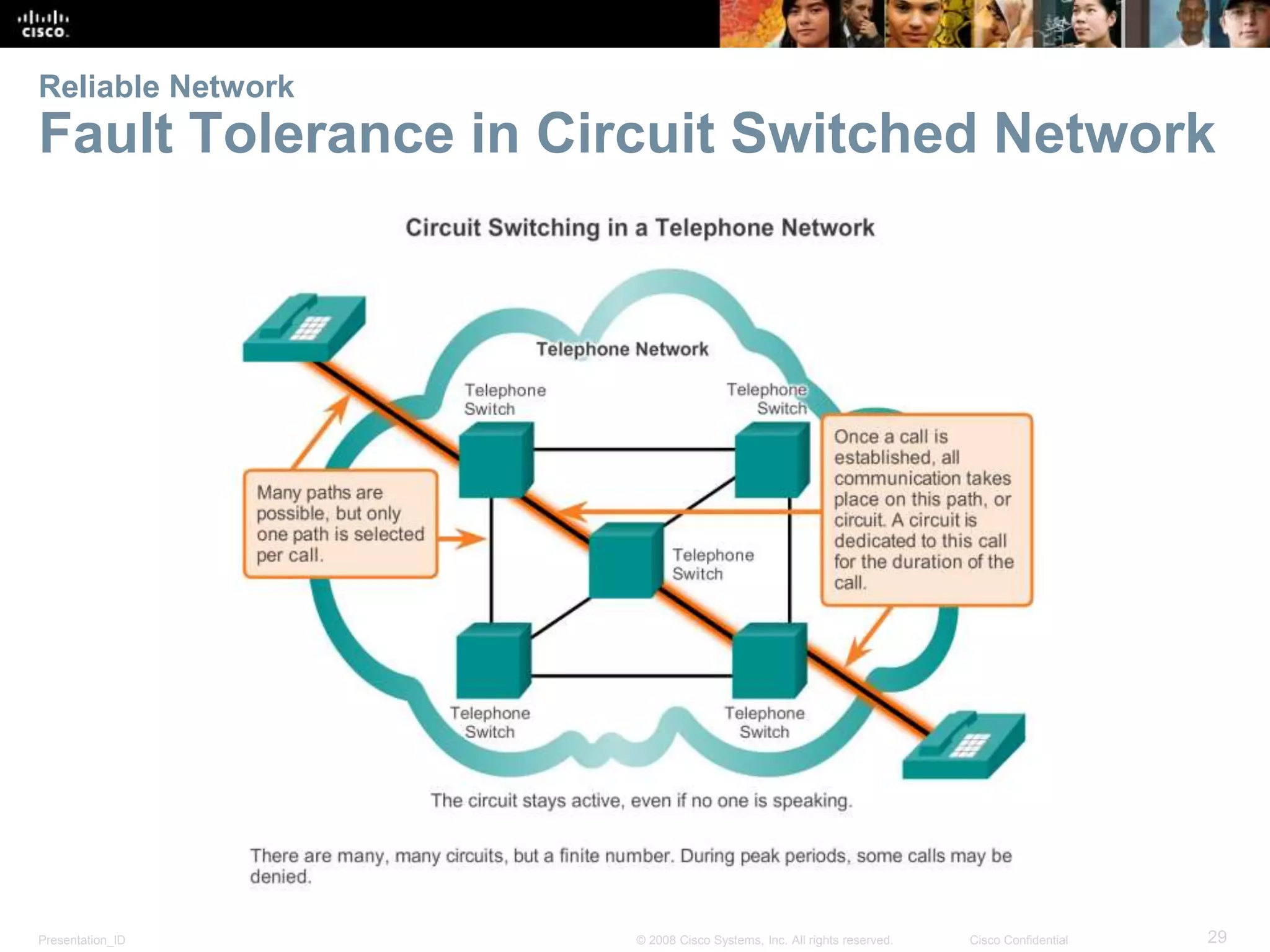
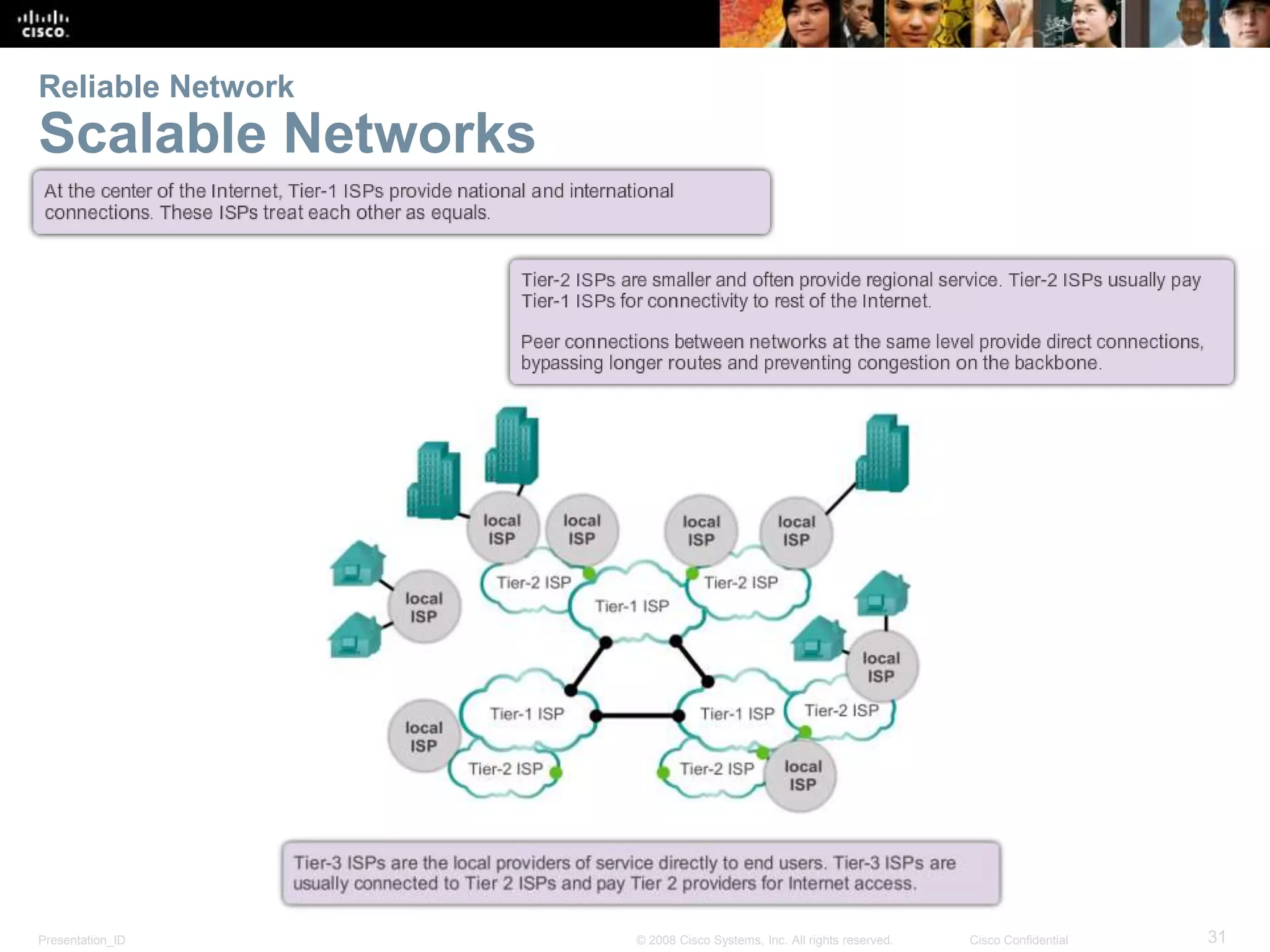
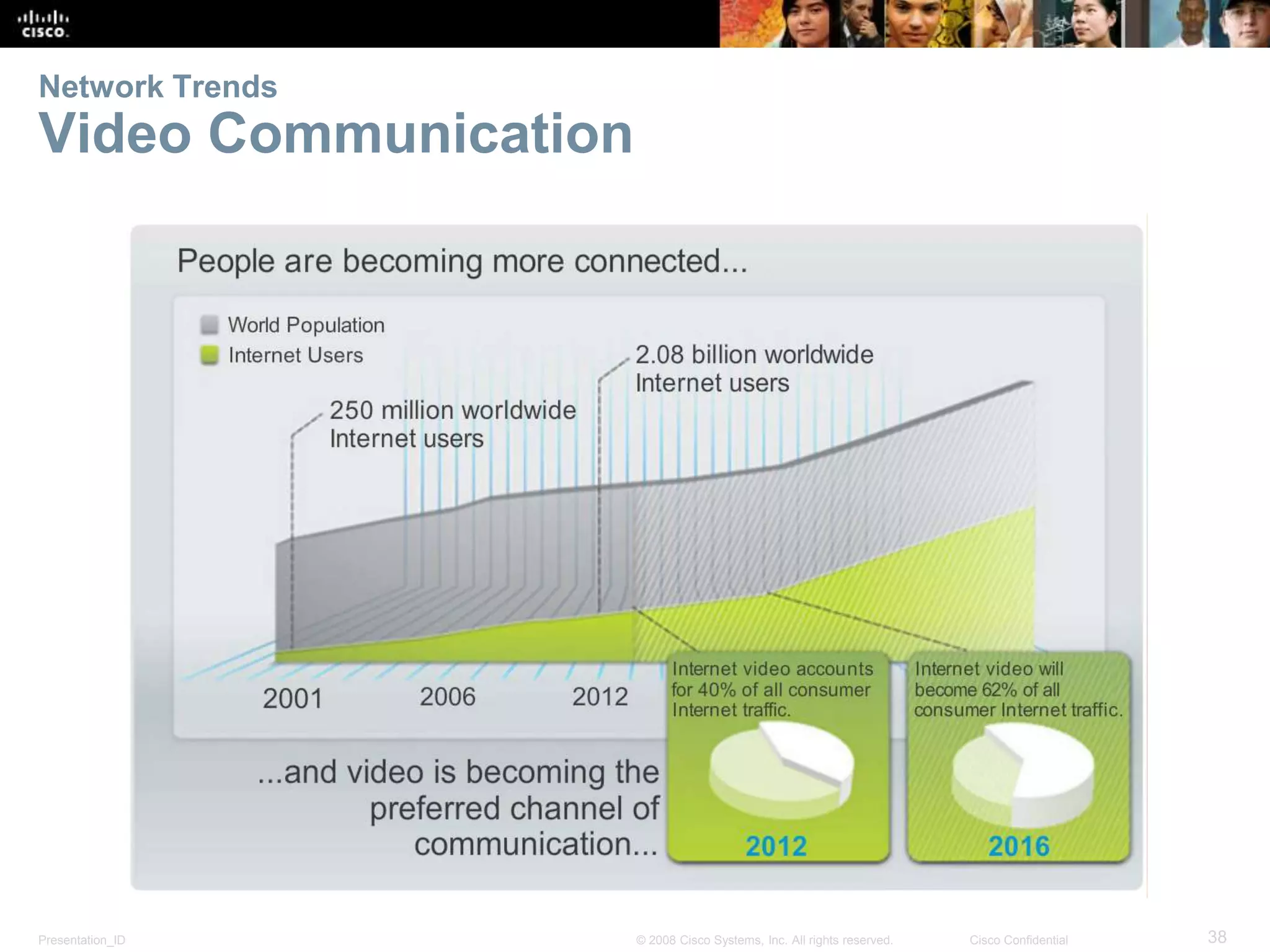
This document summarizes key points from Chapter 1 of a Cisco networking textbook. It introduces networking concepts like LANs, WANs and the Internet. It discusses how networks are used in daily life for communication, work and entertainment. It also outlines trends that will impact networks, such as BYOD, online collaboration, video and cloud computing. The chapter objectives are to explain network topologies, devices and characteristics used in small to medium businesses.