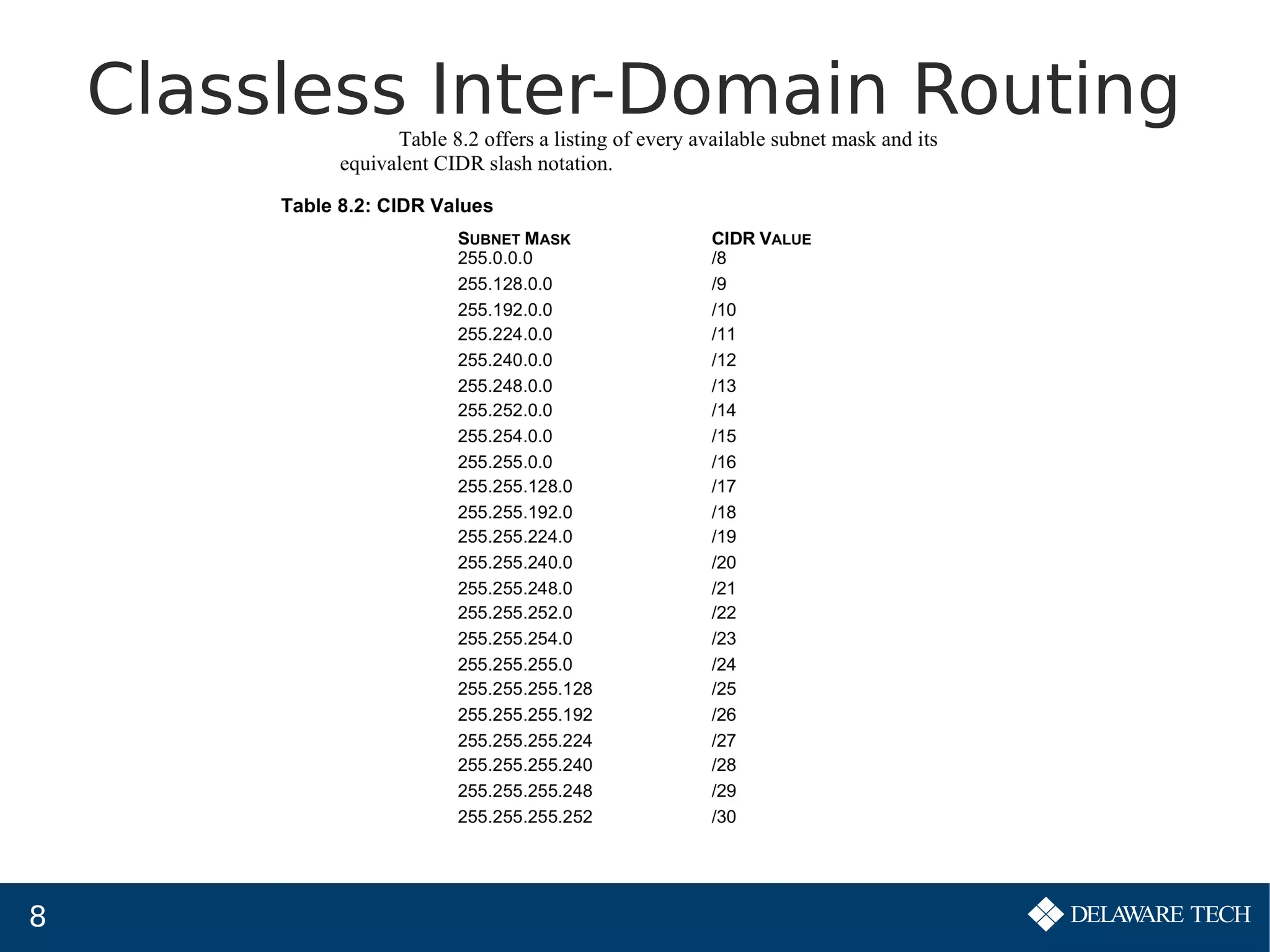
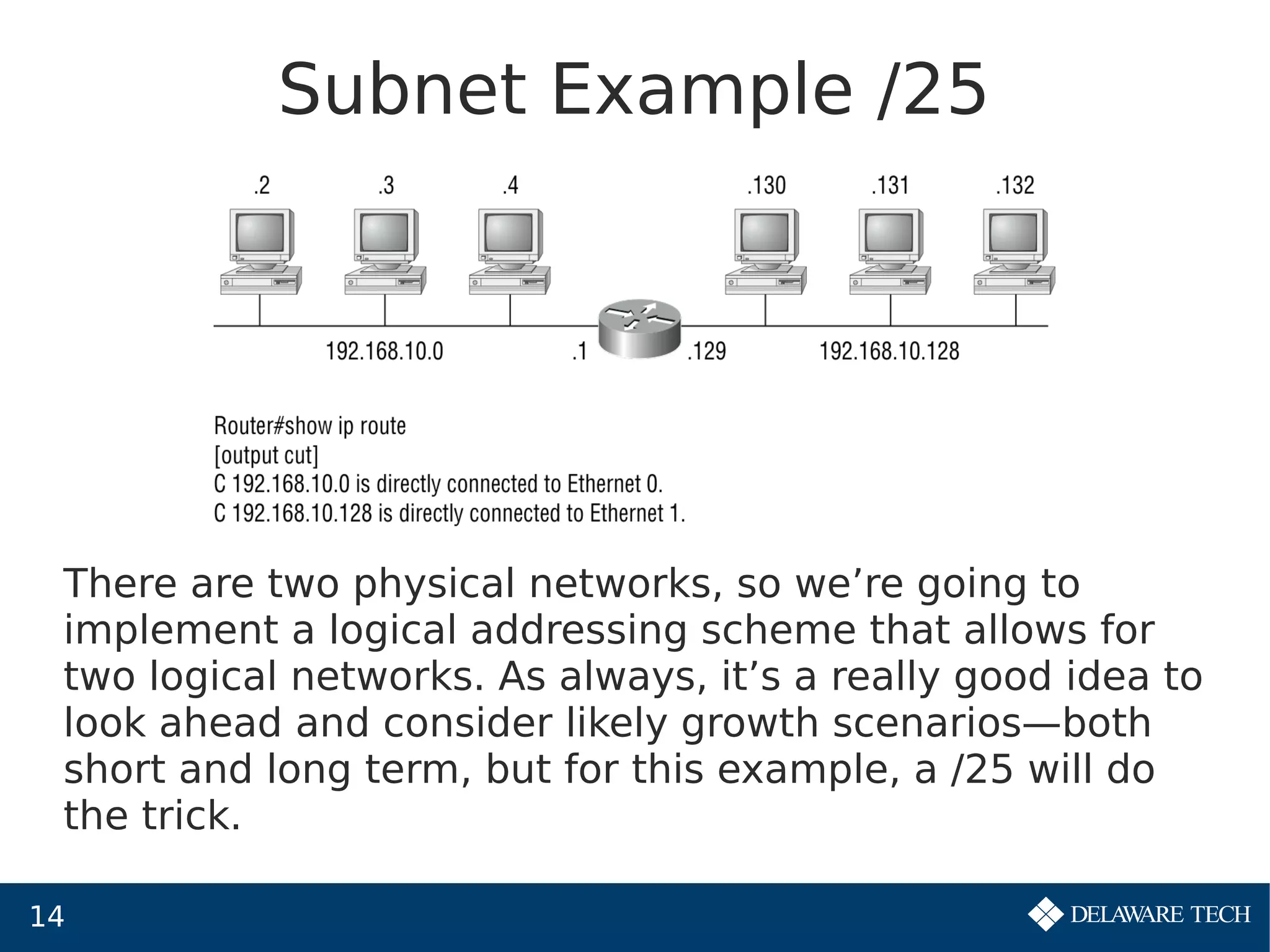
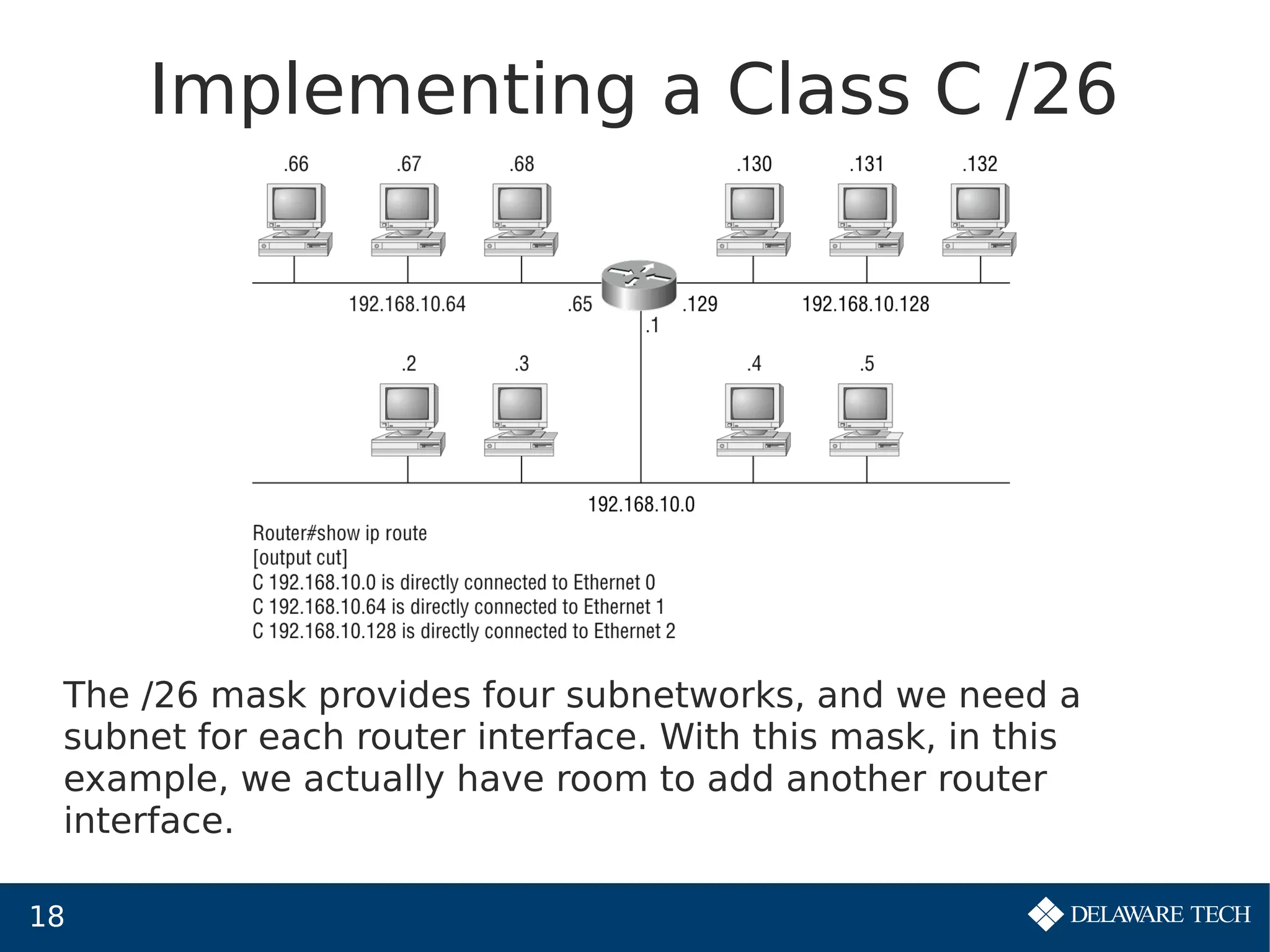
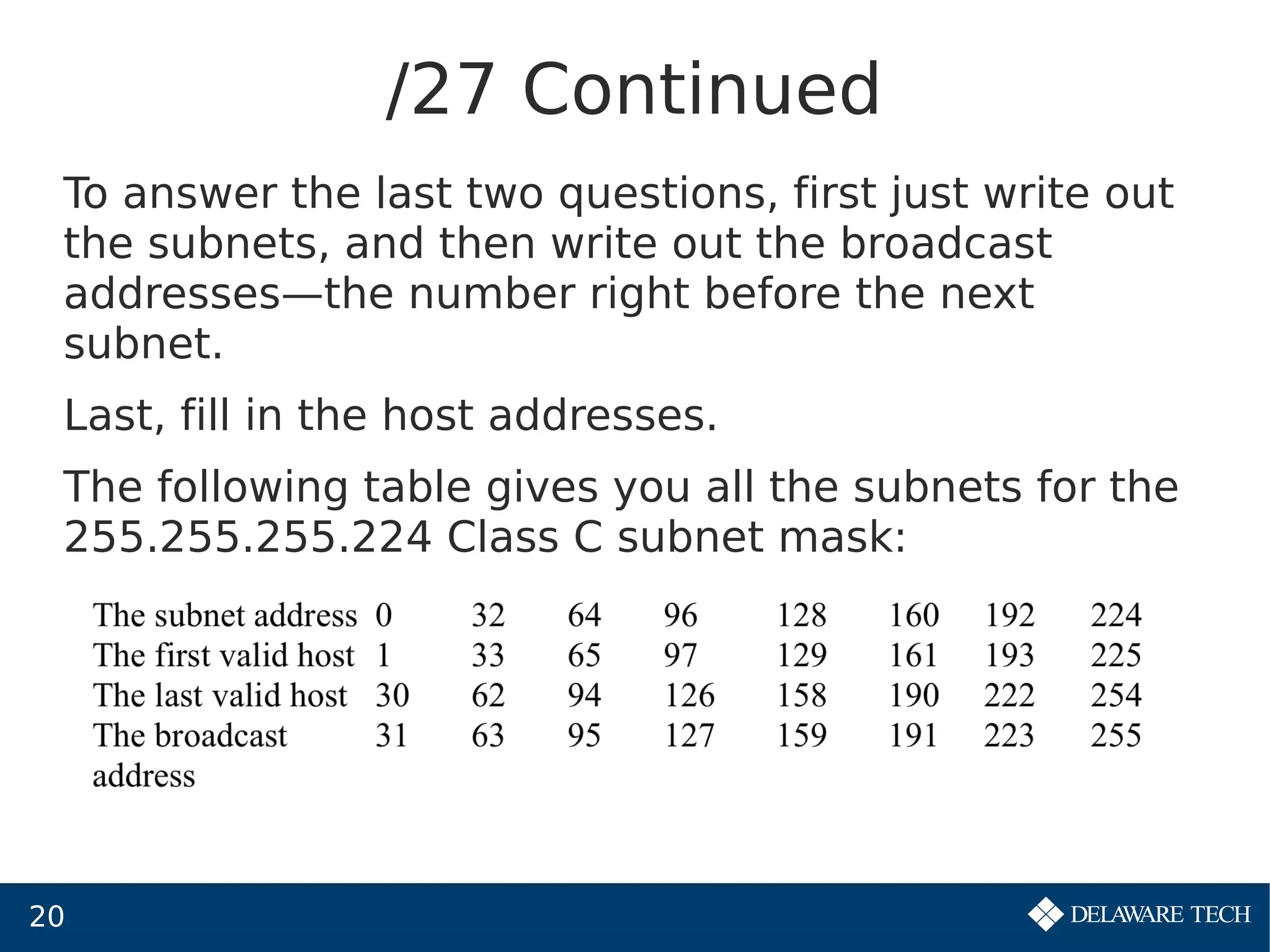
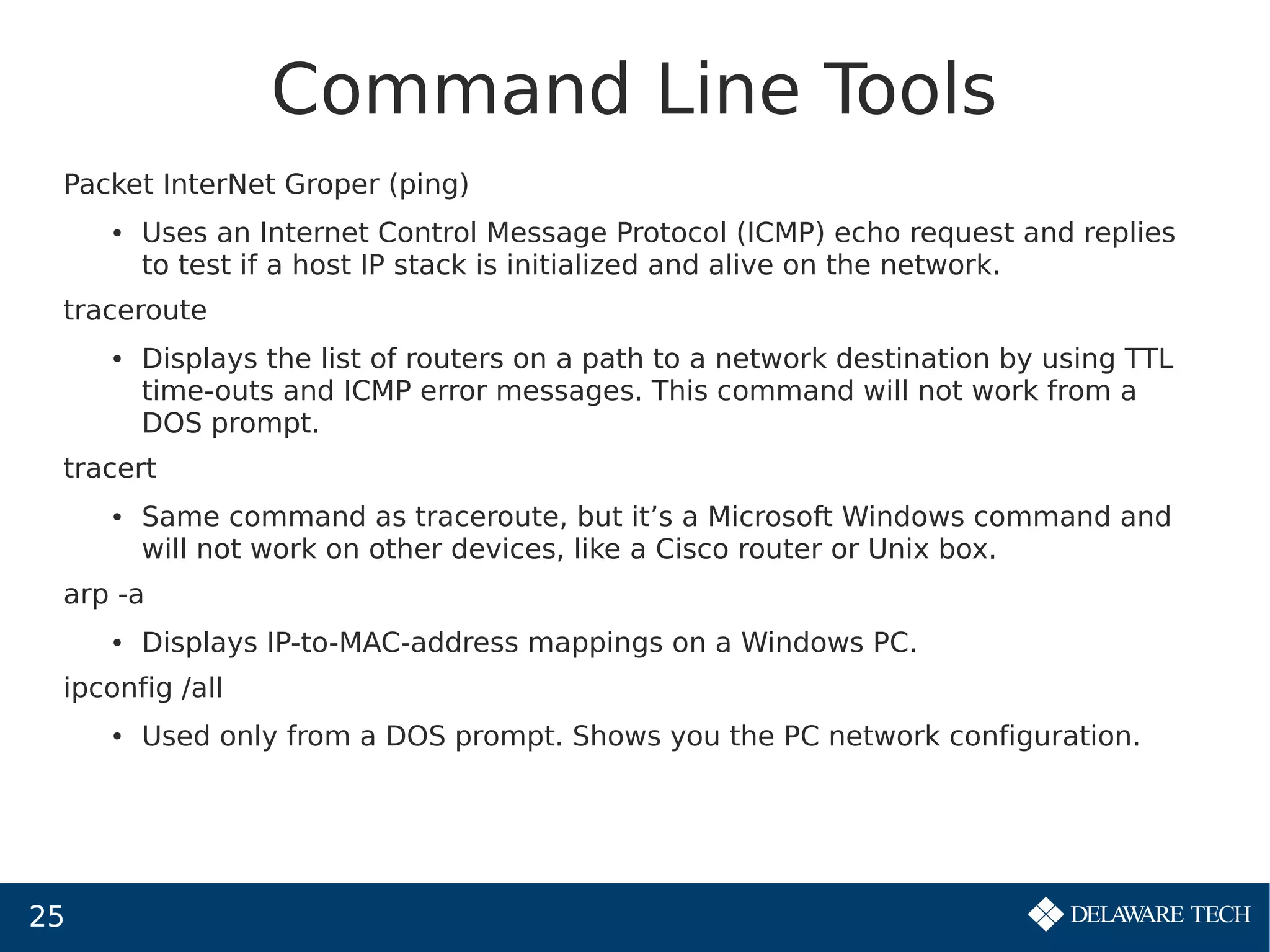
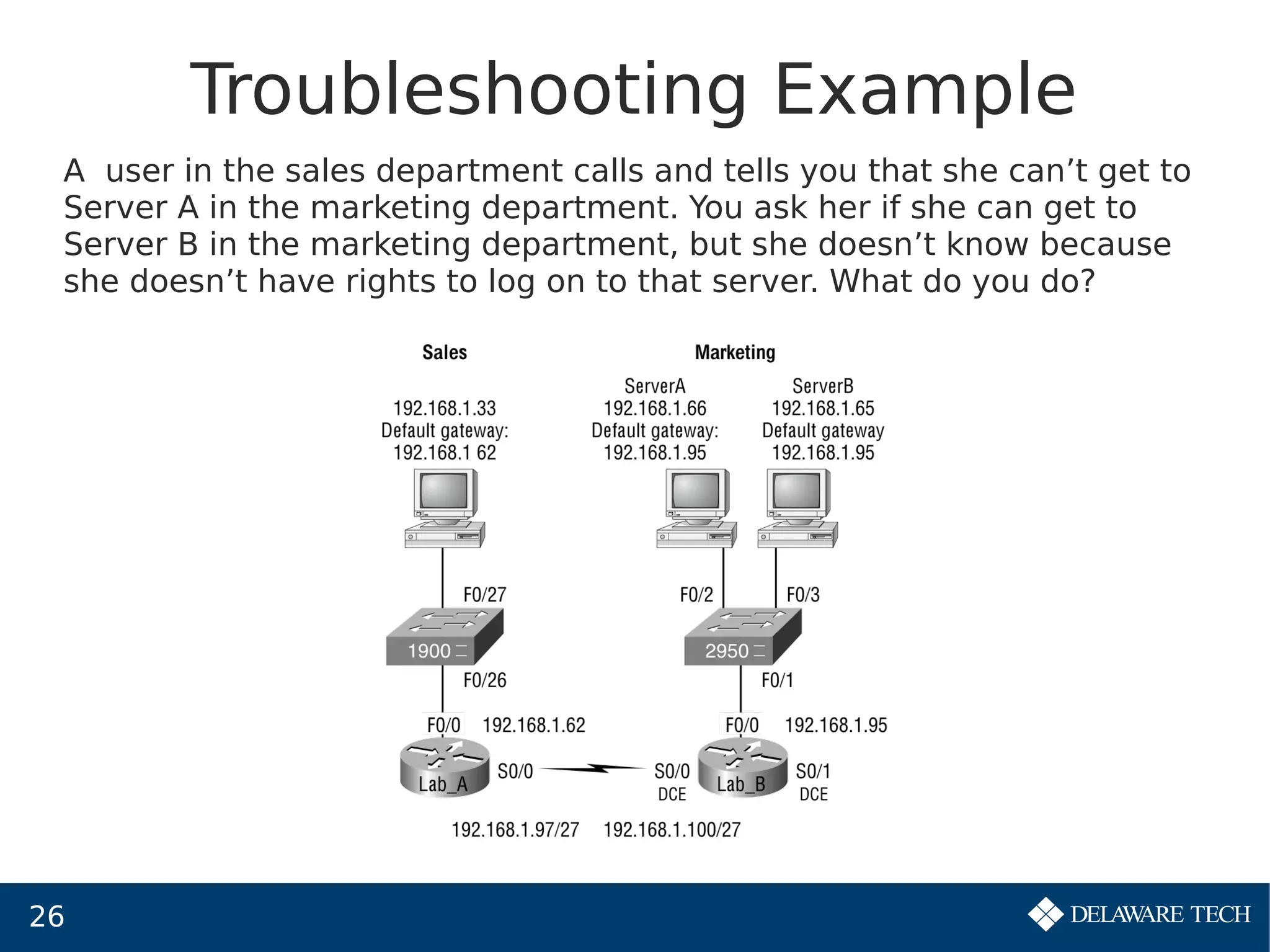
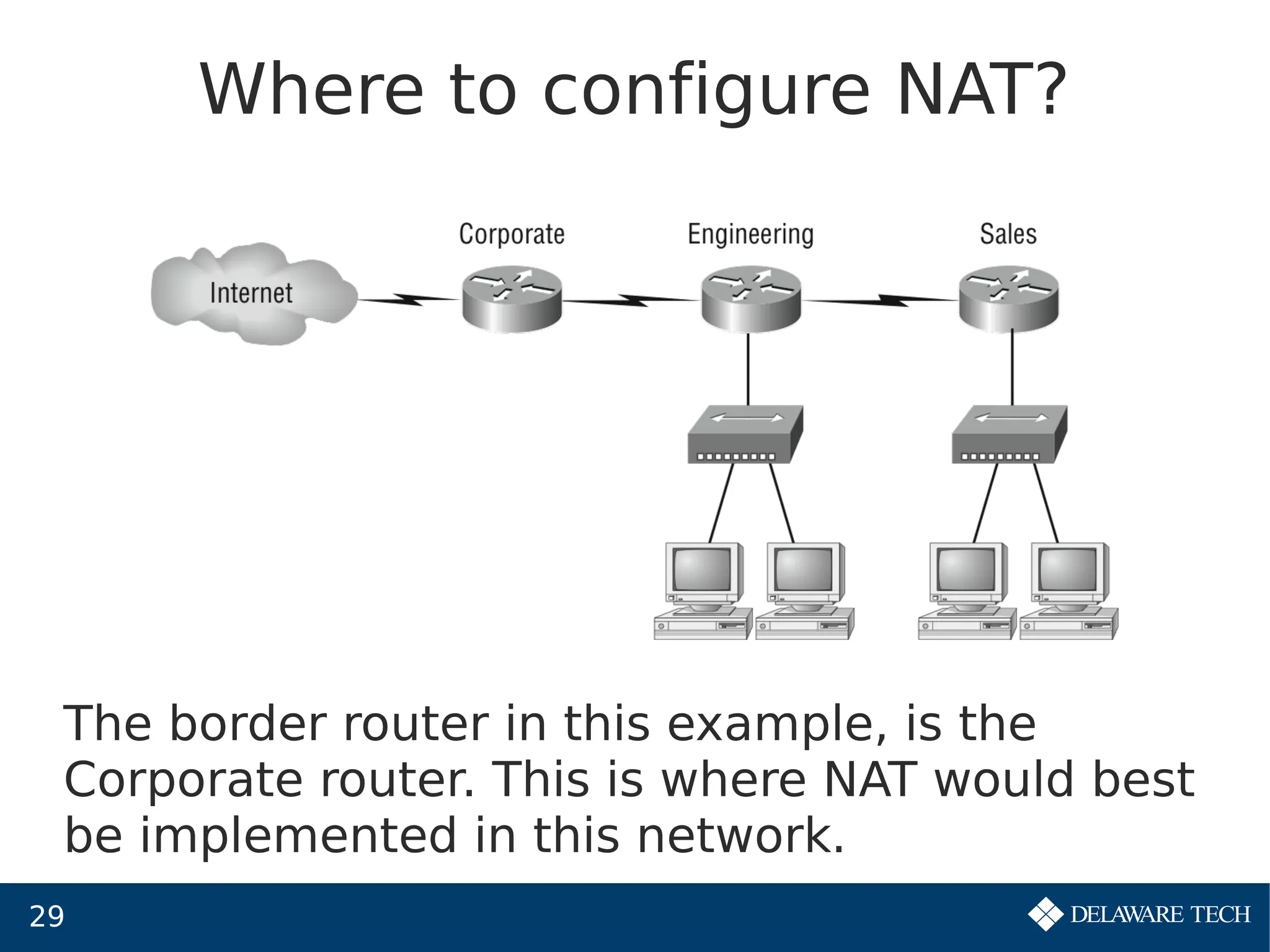
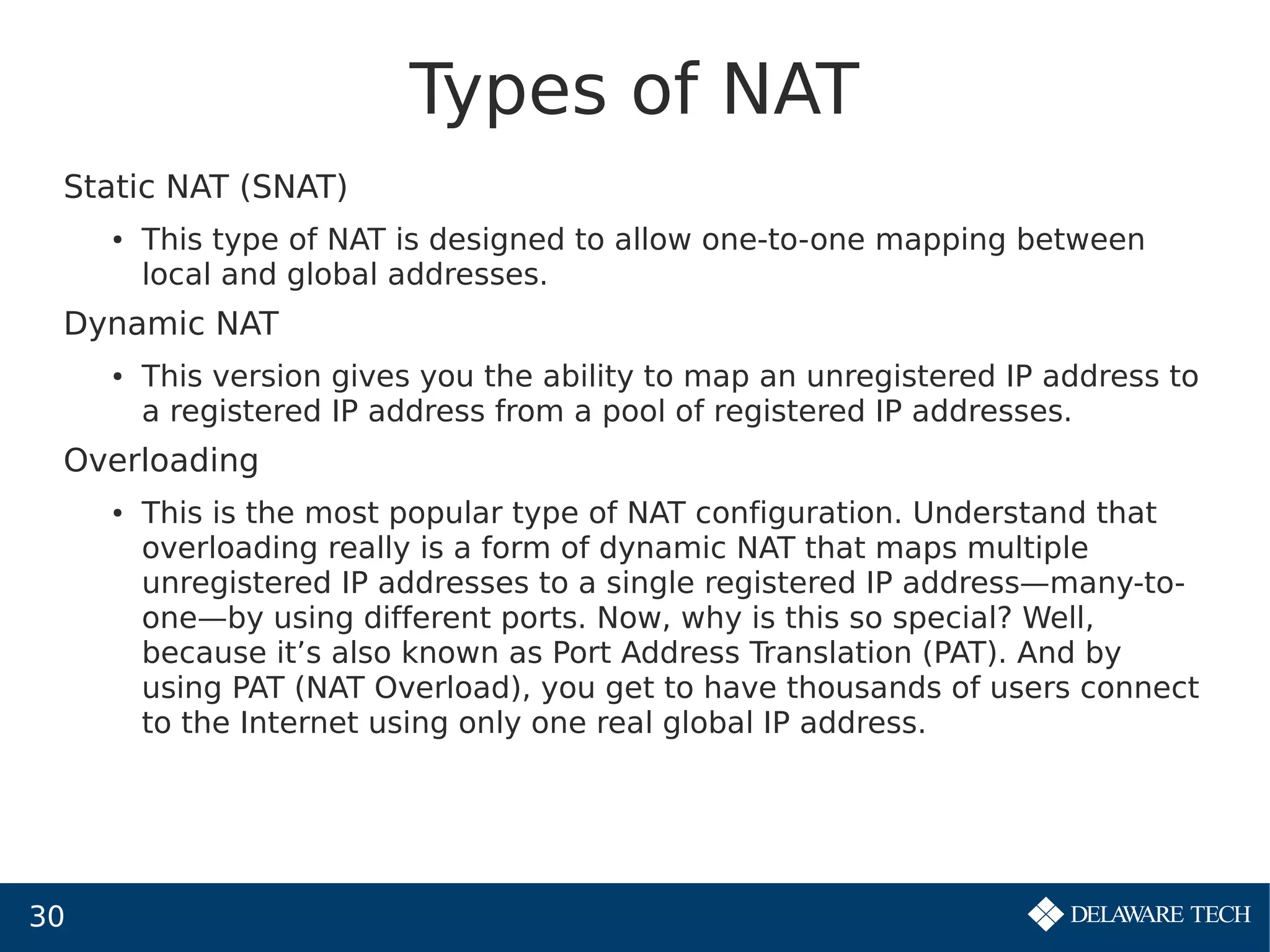
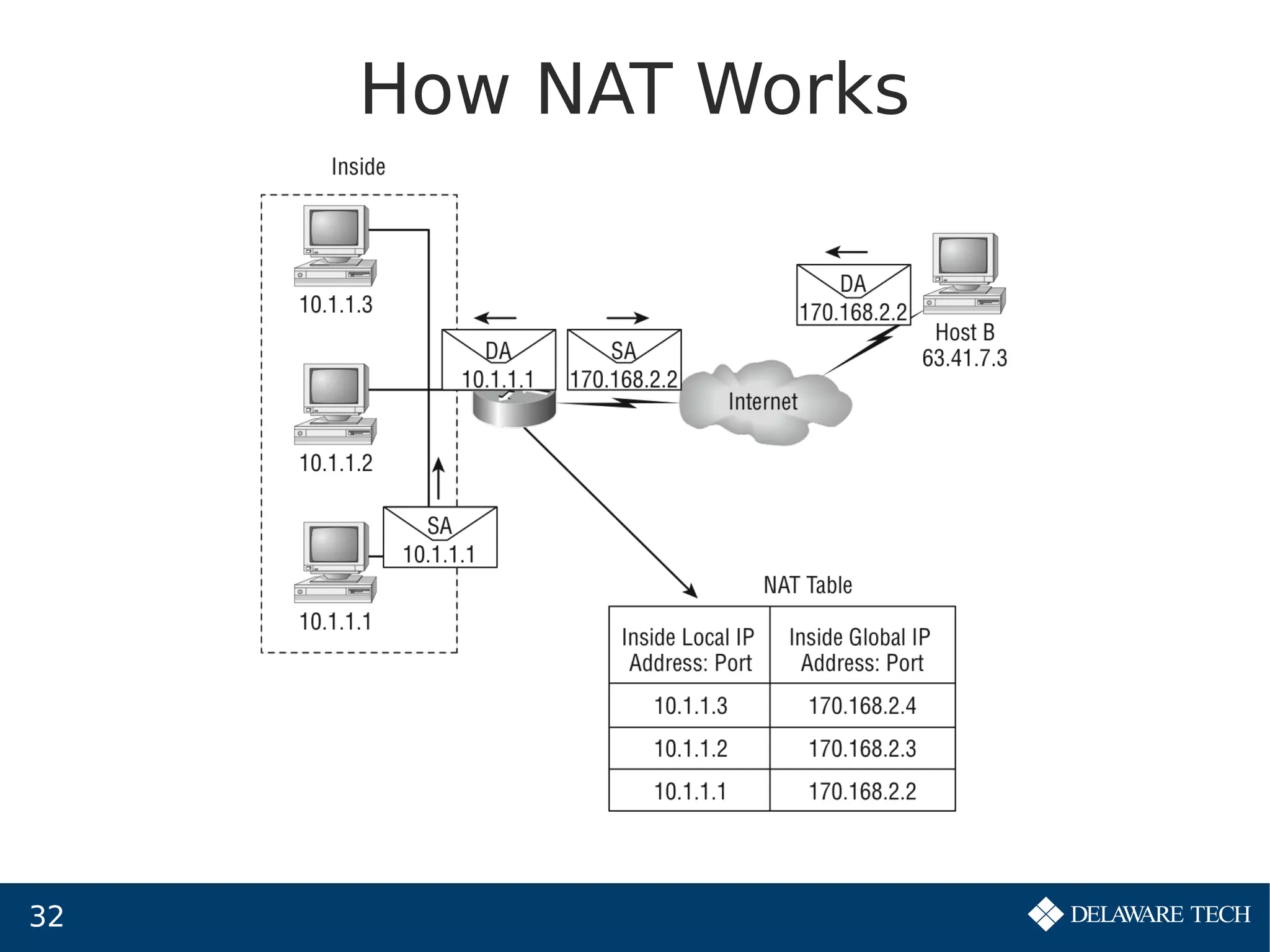
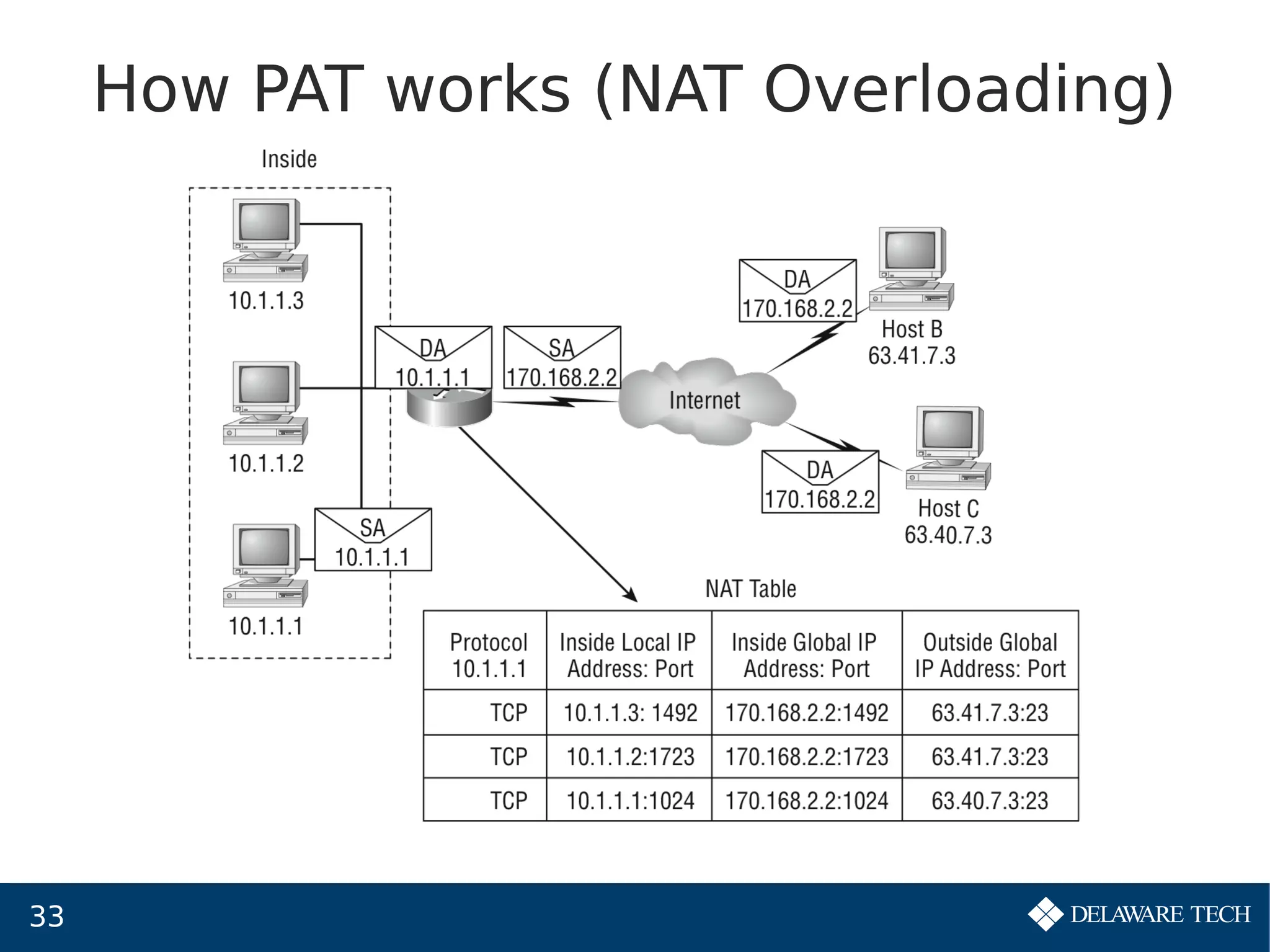
This document provides an overview of IP subnetting, troubleshooting, and network address translation (NAT). It begins by explaining the benefits of subnetting networks, such as reduced traffic and optimized performance. It then discusses how to create subnets by taking bits from the host portion of IP addresses. Several examples are provided of how to subnet Class C networks using different subnet masks. The document also covers troubleshooting IP addressing issues and using command line tools like ping. Finally, it describes network address translation, including different types like static and dynamic NAT, and how NAT works to allow private IP addresses to access the public internet.