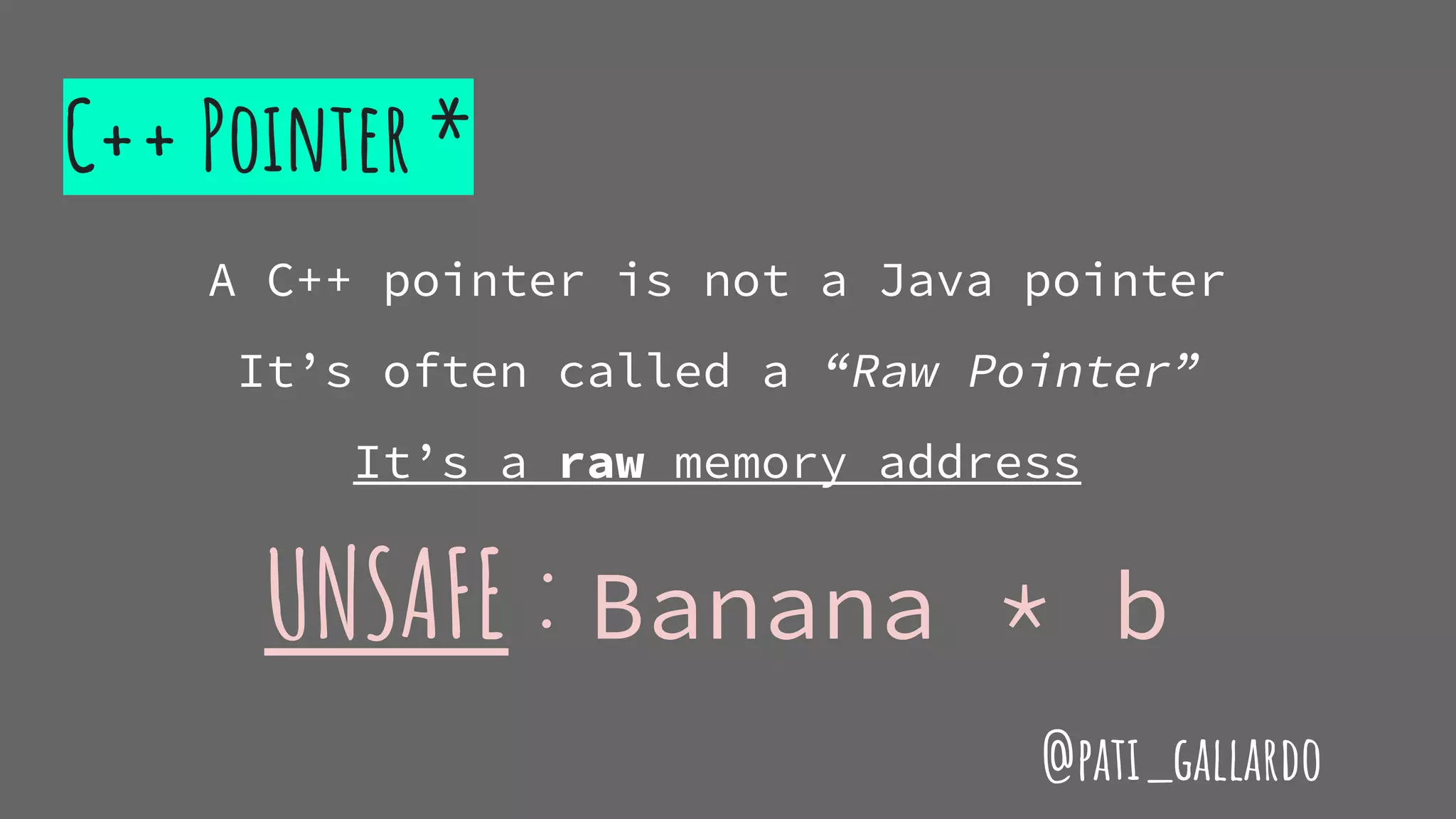
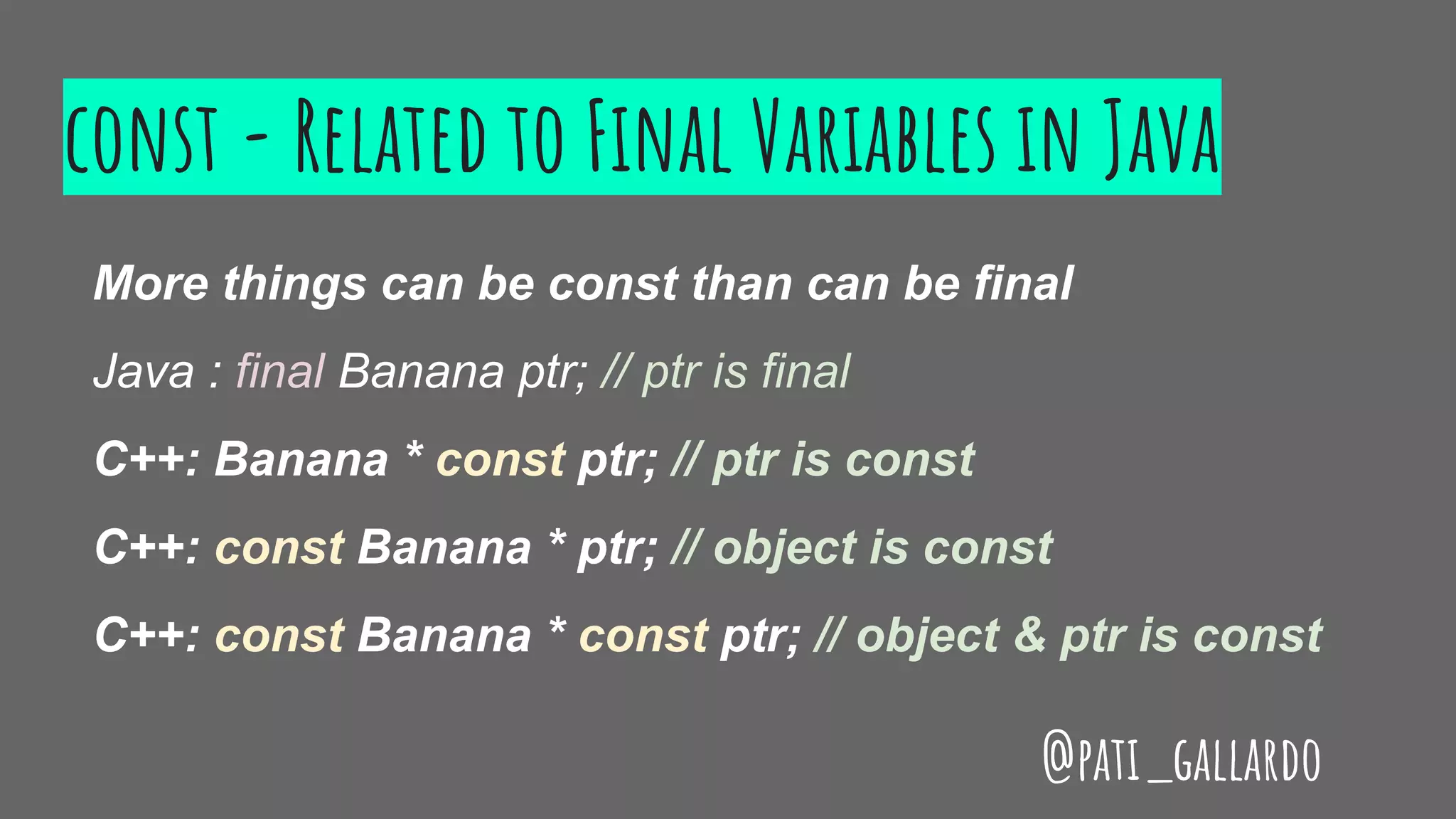
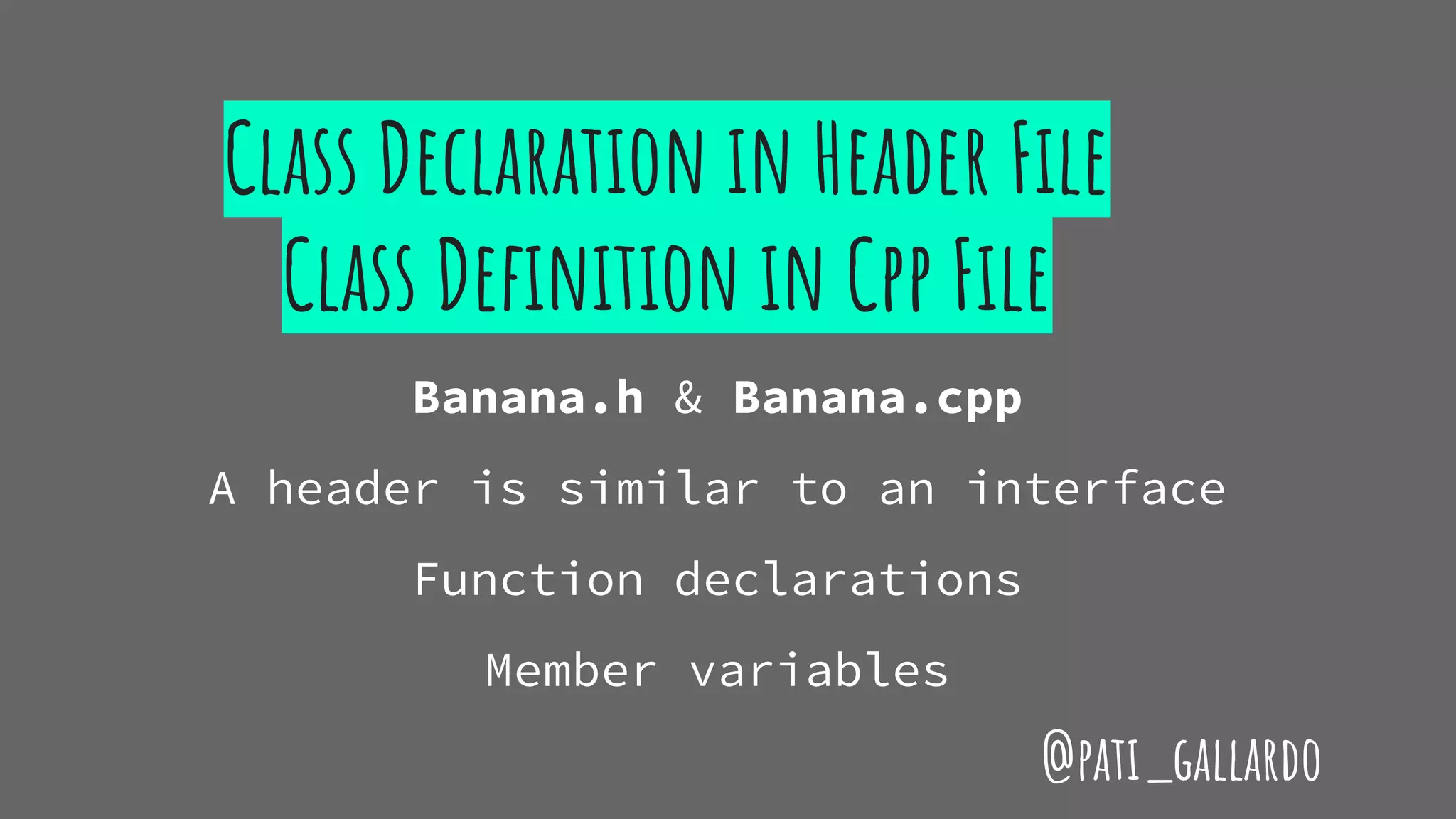
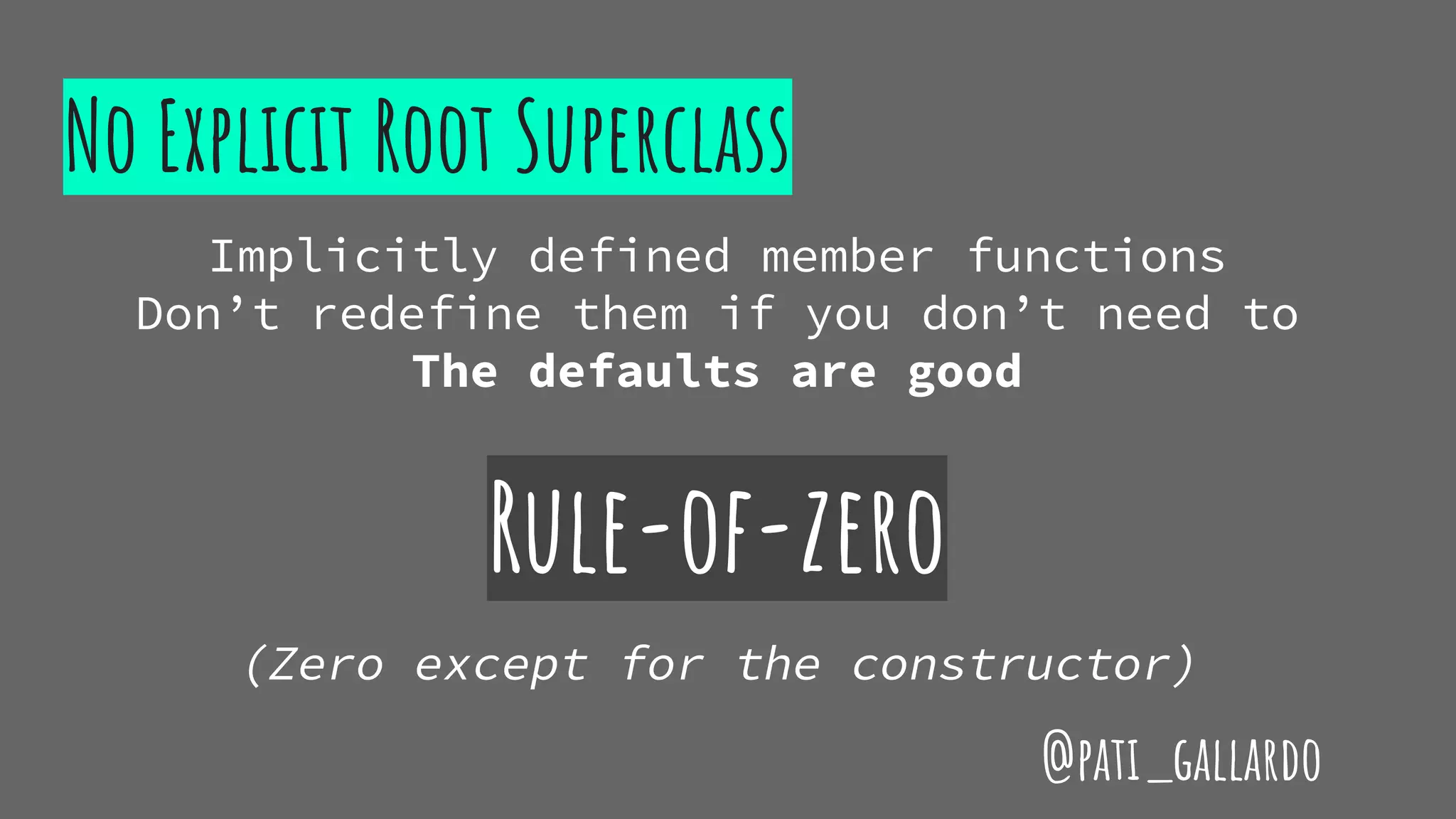
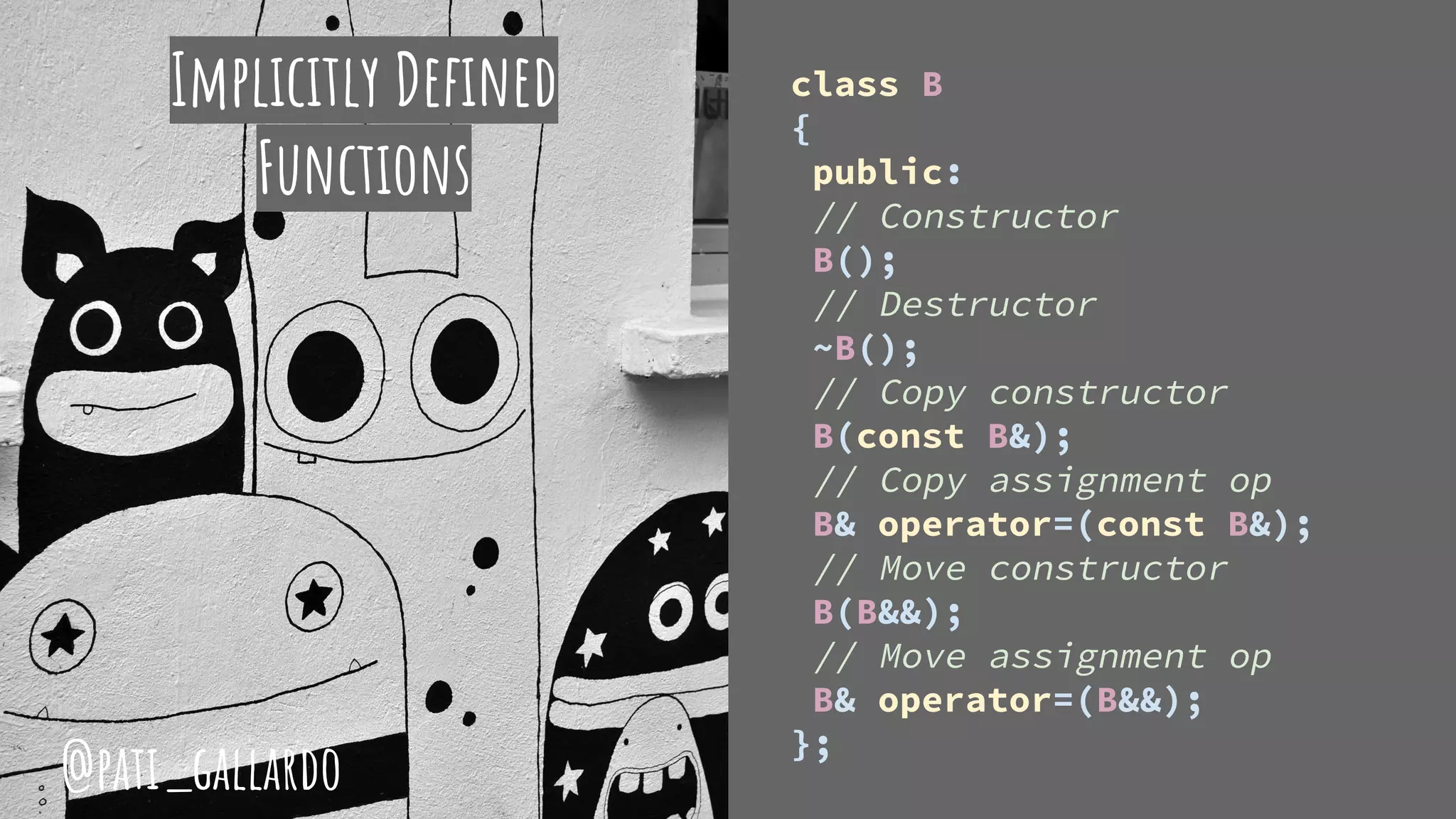
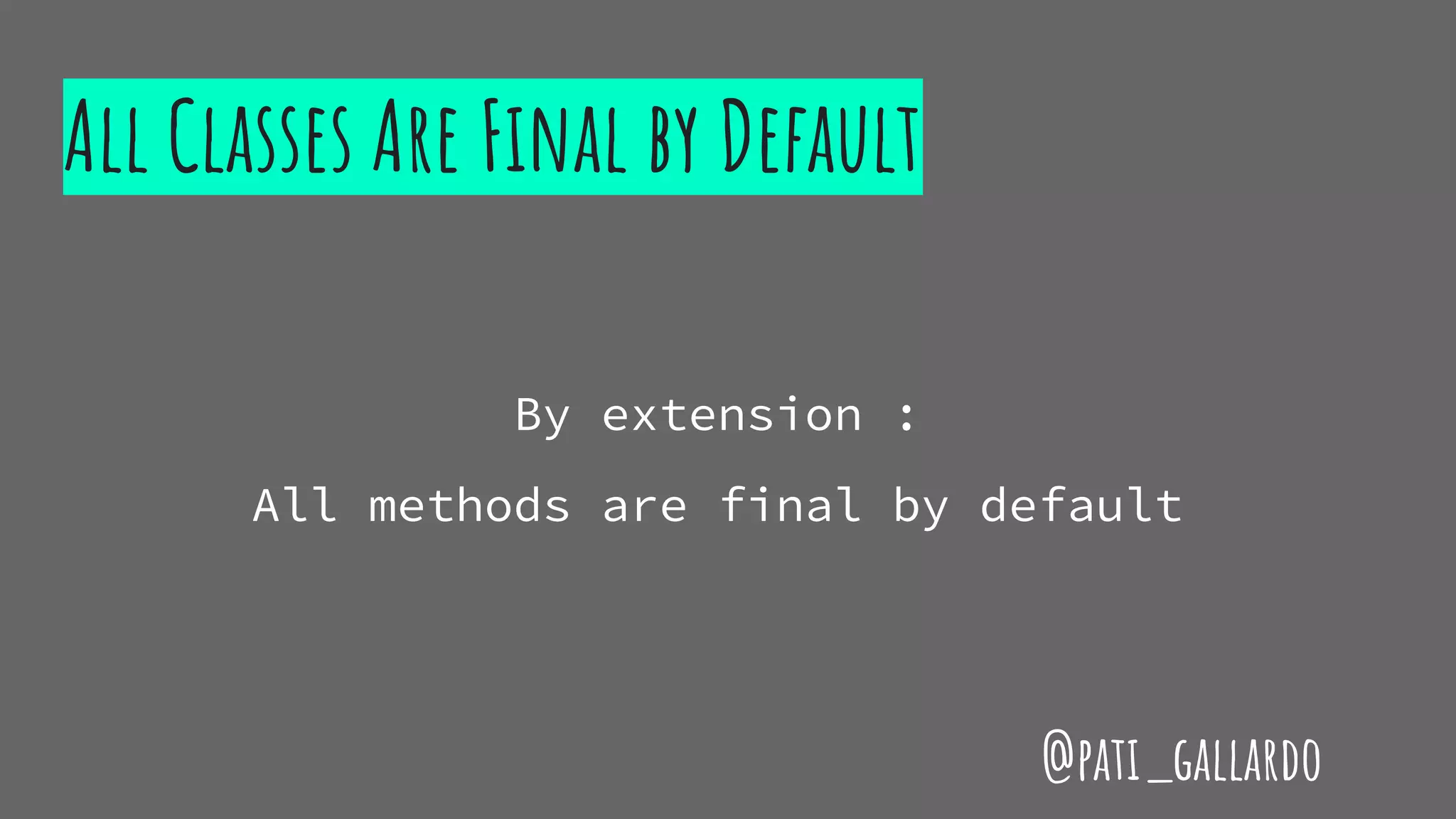
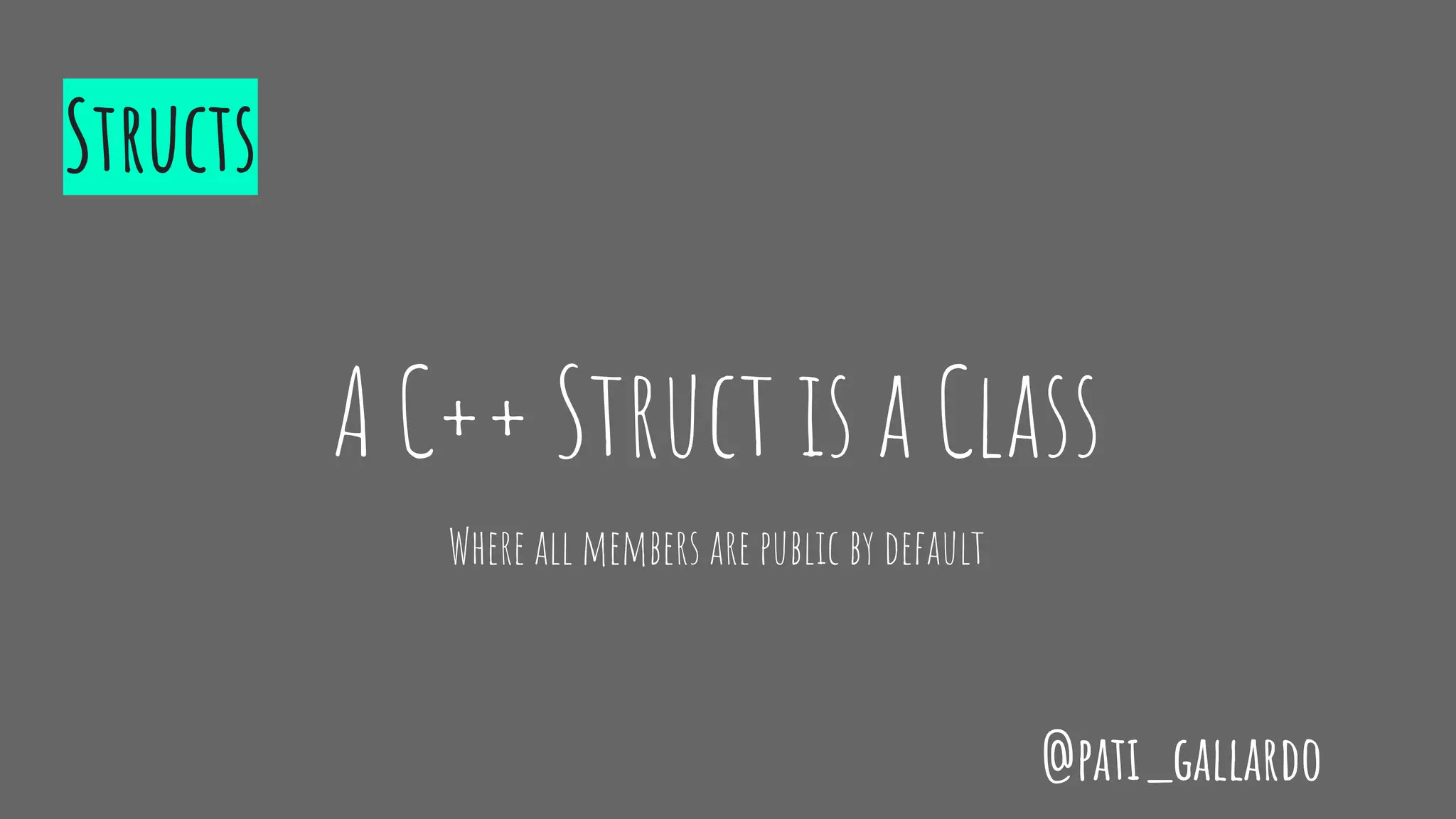
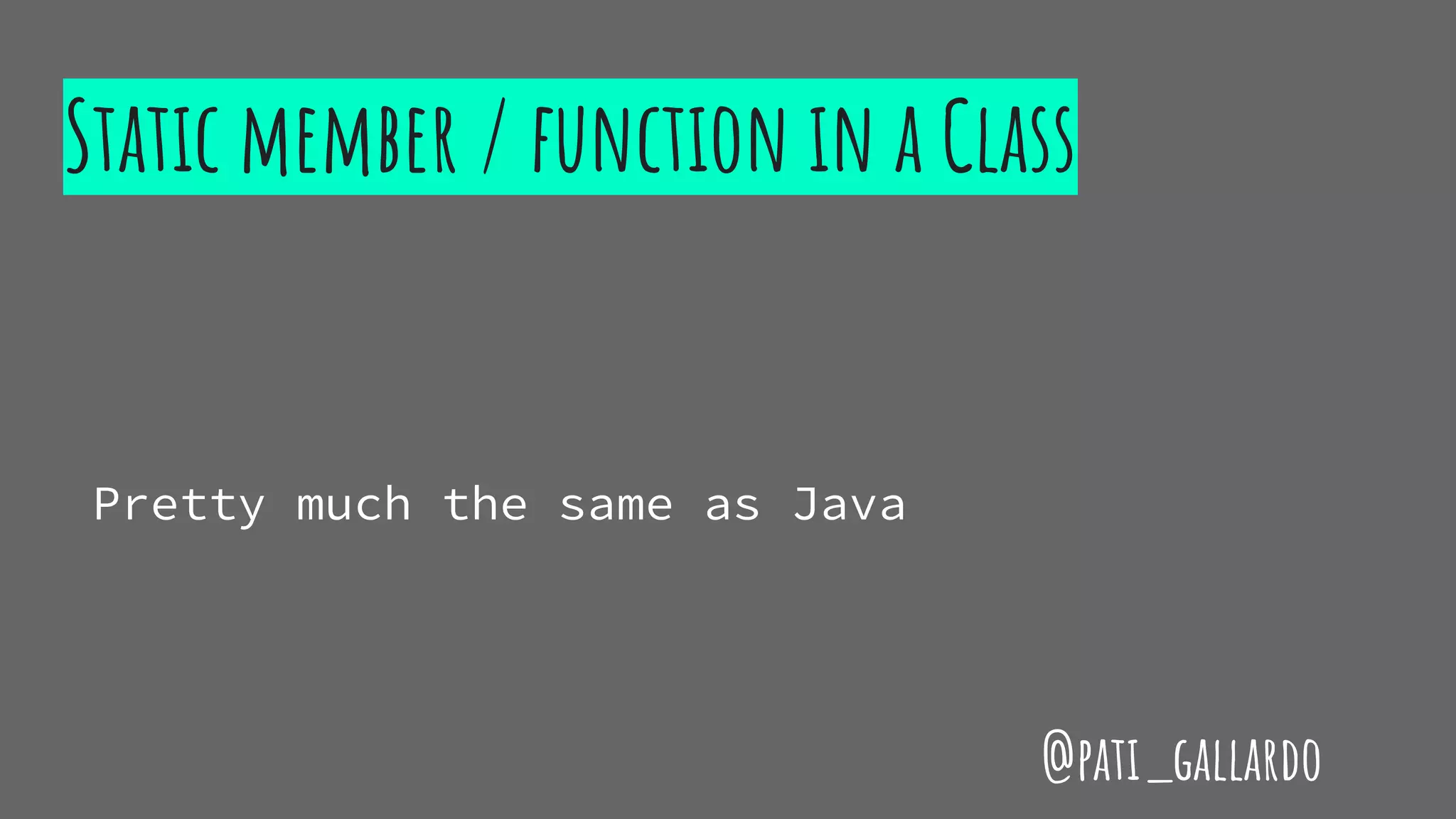
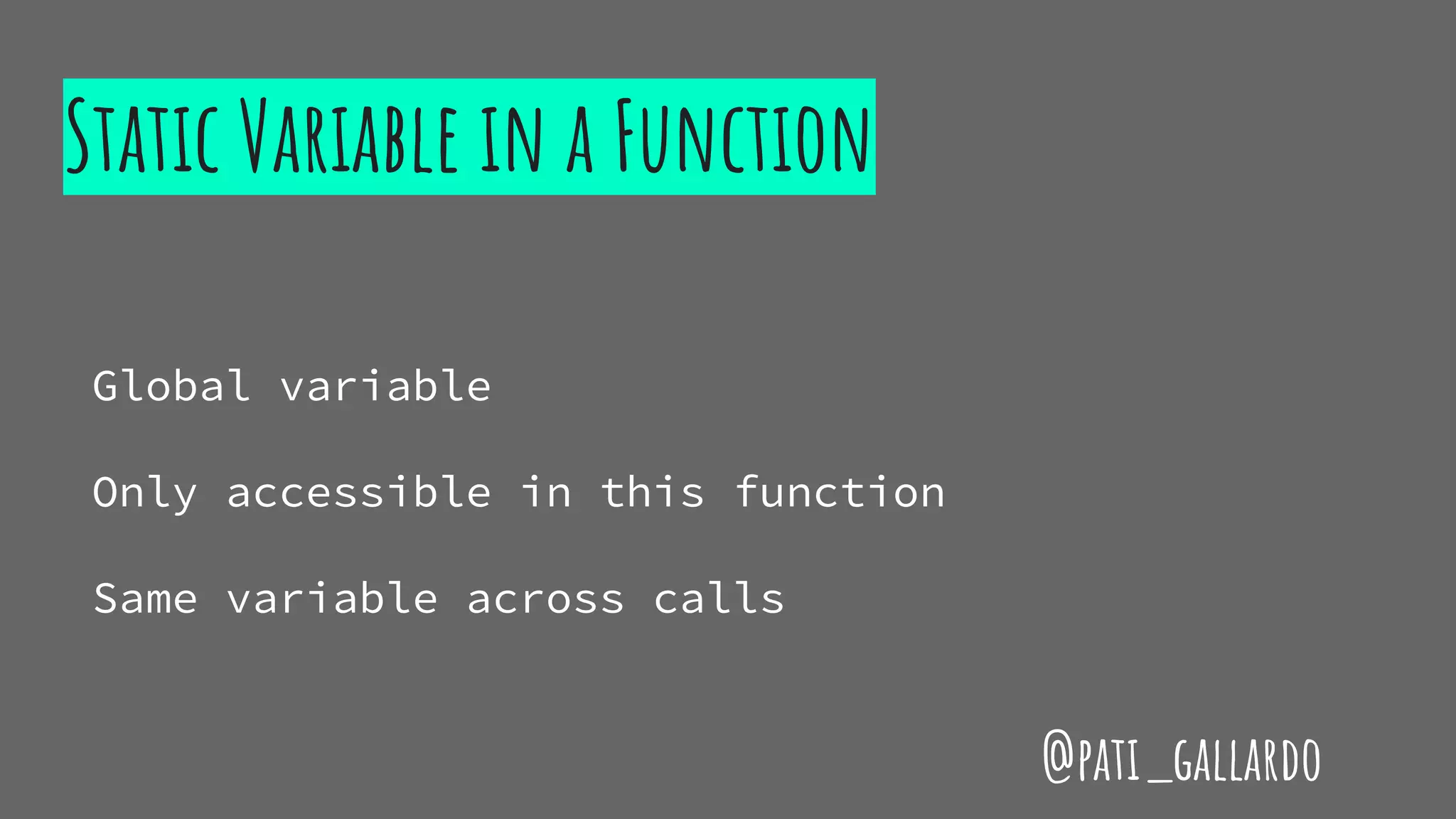
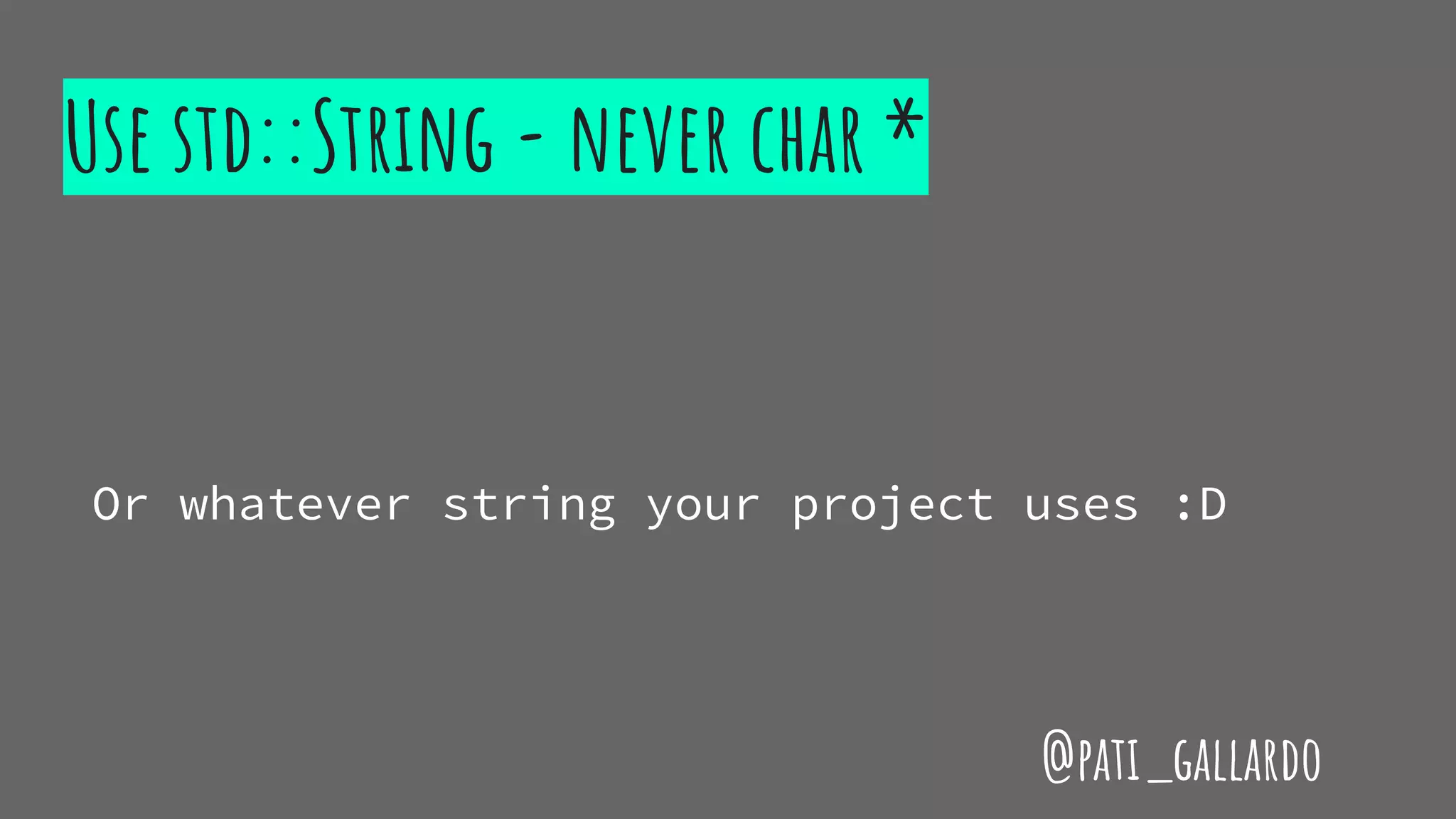
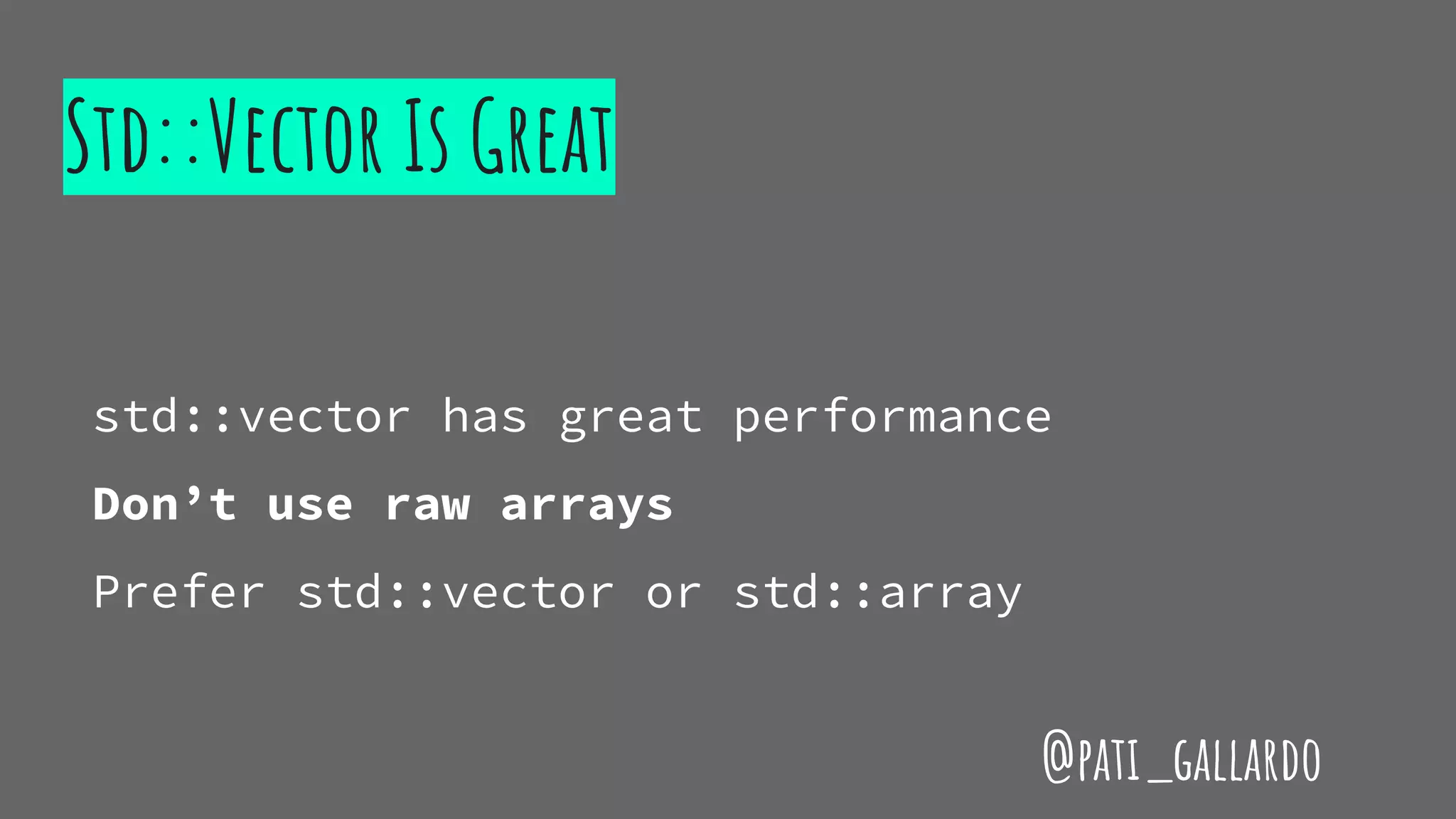
The document is a presentation on C++ for Java developers. It introduces C++ concepts like classes, references, pointers, memory management and standard libraries. It emphasizes using modern C++ features like the stack instead of heap for memory, values instead of pointers, and standard libraries. It summarizes that developers should use modern C++ practices like values, references, const, and libraries, but most importantly not use raw pointers like "Banana * b = new Banana();".






























![Structured Bindings
std::tuple<int, int> point();
auto [x, y] = point();
@pati_gallardo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javazone2017-170913091216/75/C-for-Java-Developers-JavaZone-2017-37-2048.jpg)
![Lambda and Captures
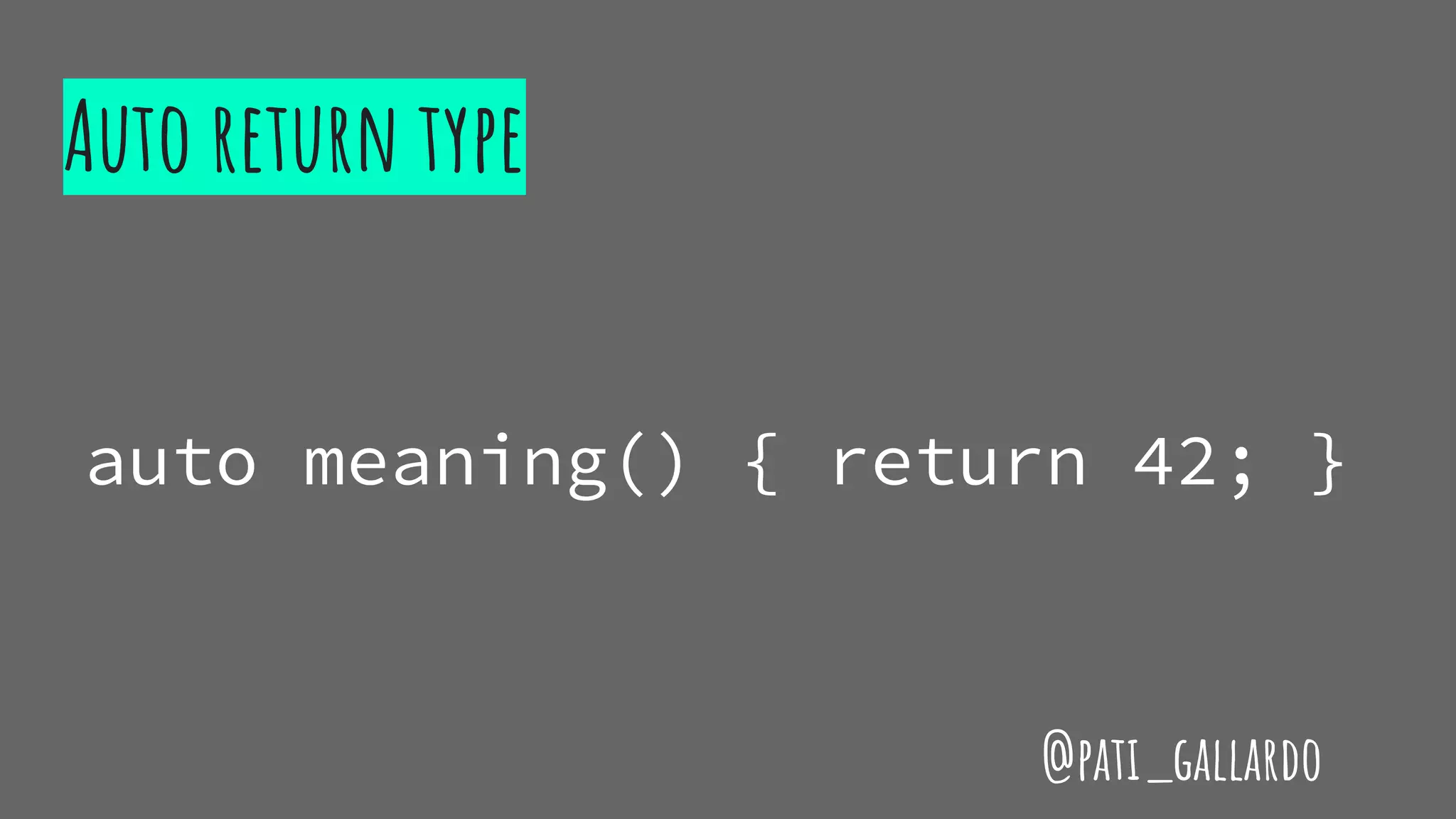
auto meaning = [](){ return 42; }
auto life = 42;
auto meaning = [life]() { return life; }
auto meaning = [=]() { return life; }
auto meaning = [&]() { life++; return life;}
@pati_gallardo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javazone2017-170913091216/75/C-for-Java-Developers-JavaZone-2017-38-2048.jpg)






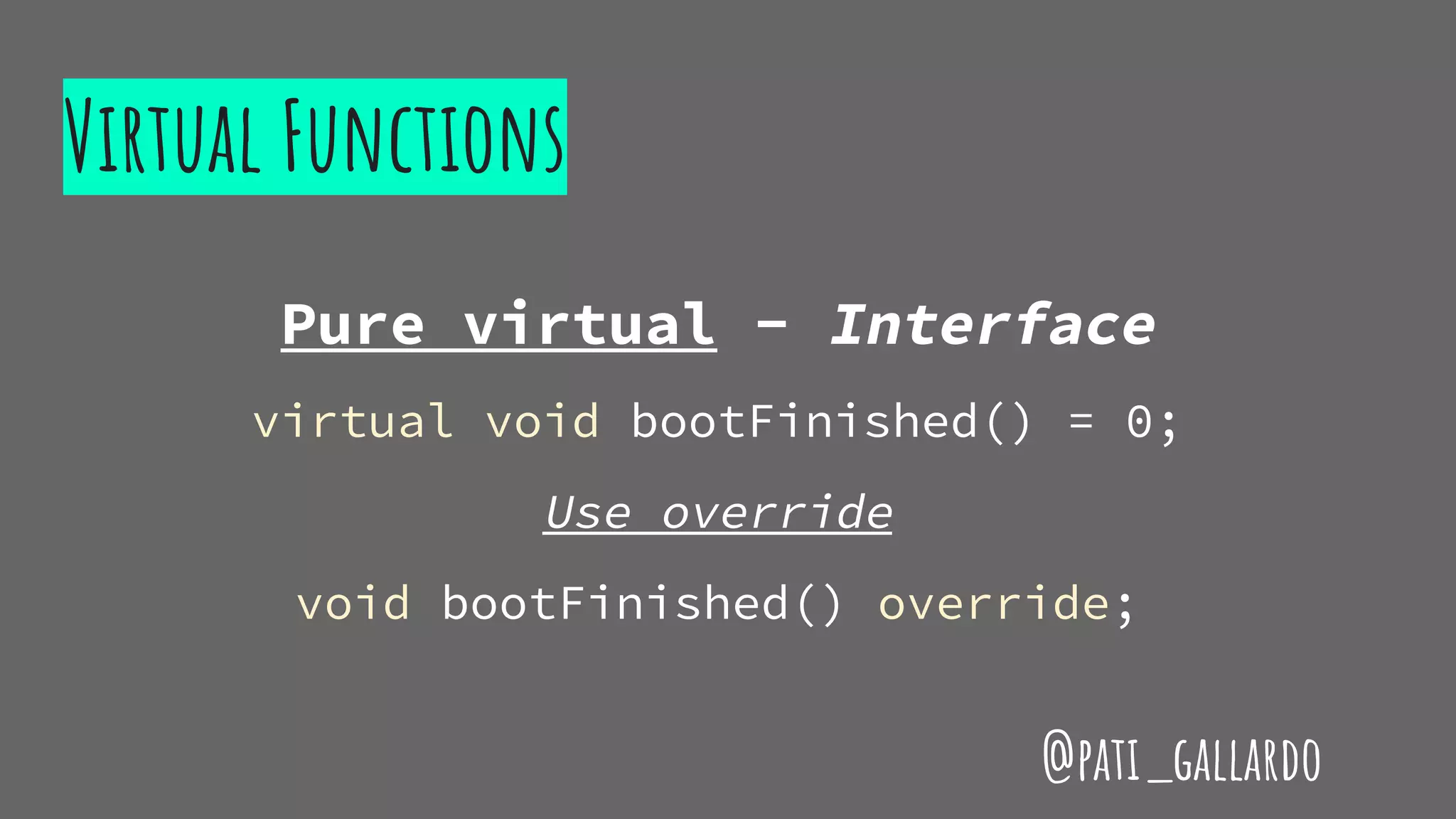





{
return i == 42;
});
@pati_gallardo](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javazone2017-170913091216/75/C-for-Java-Developers-JavaZone-2017-61-2048.jpg)








