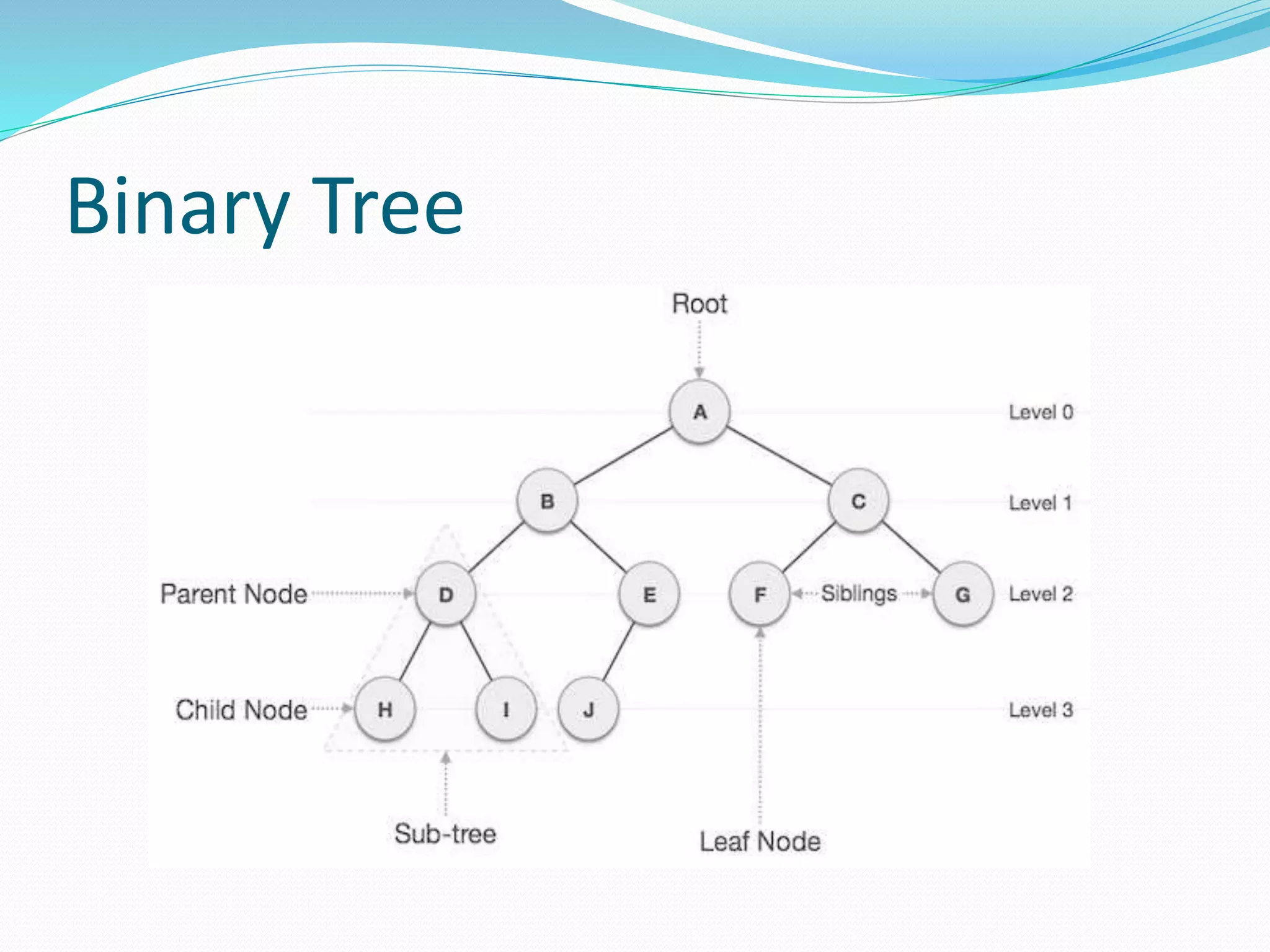
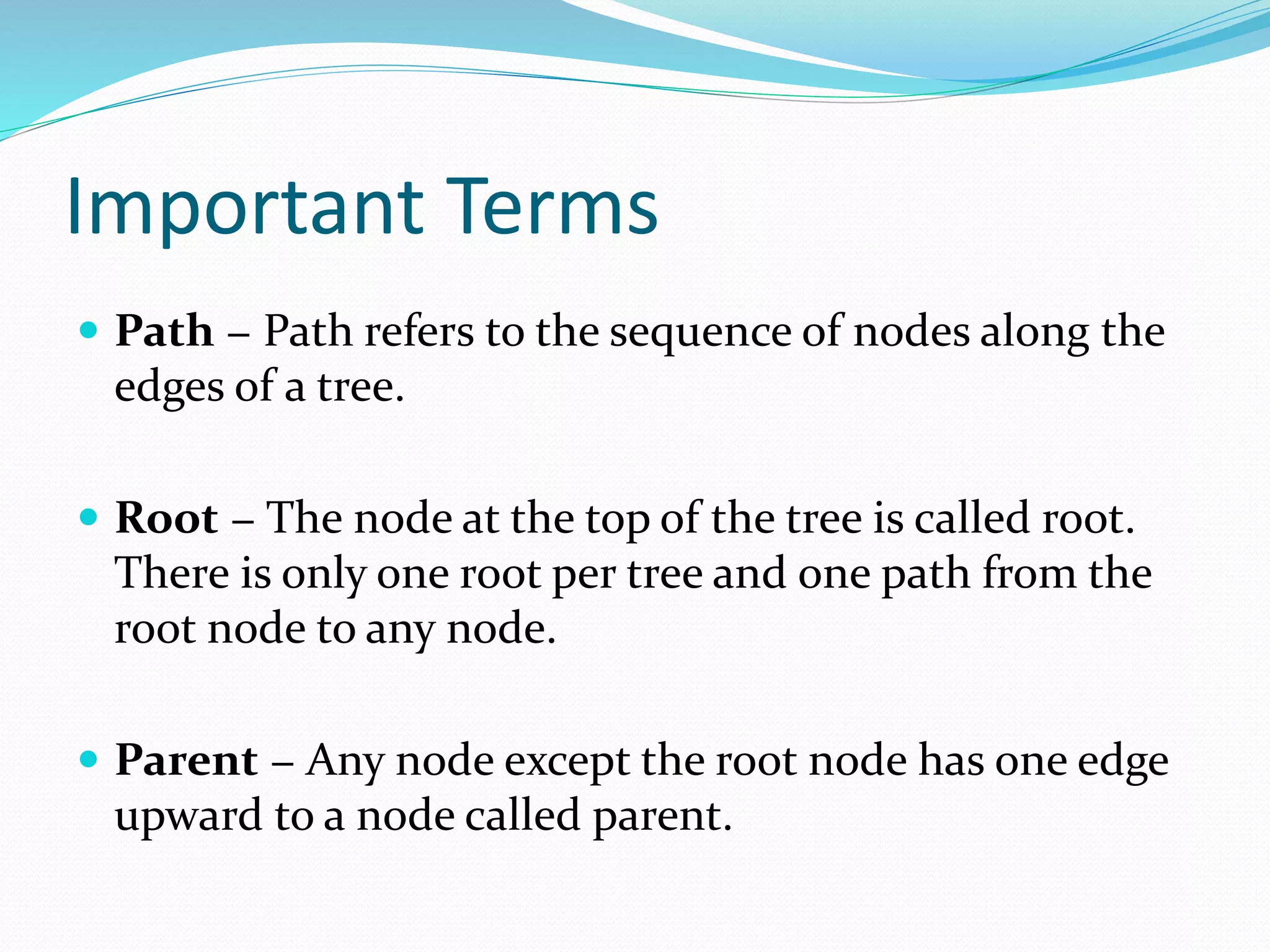
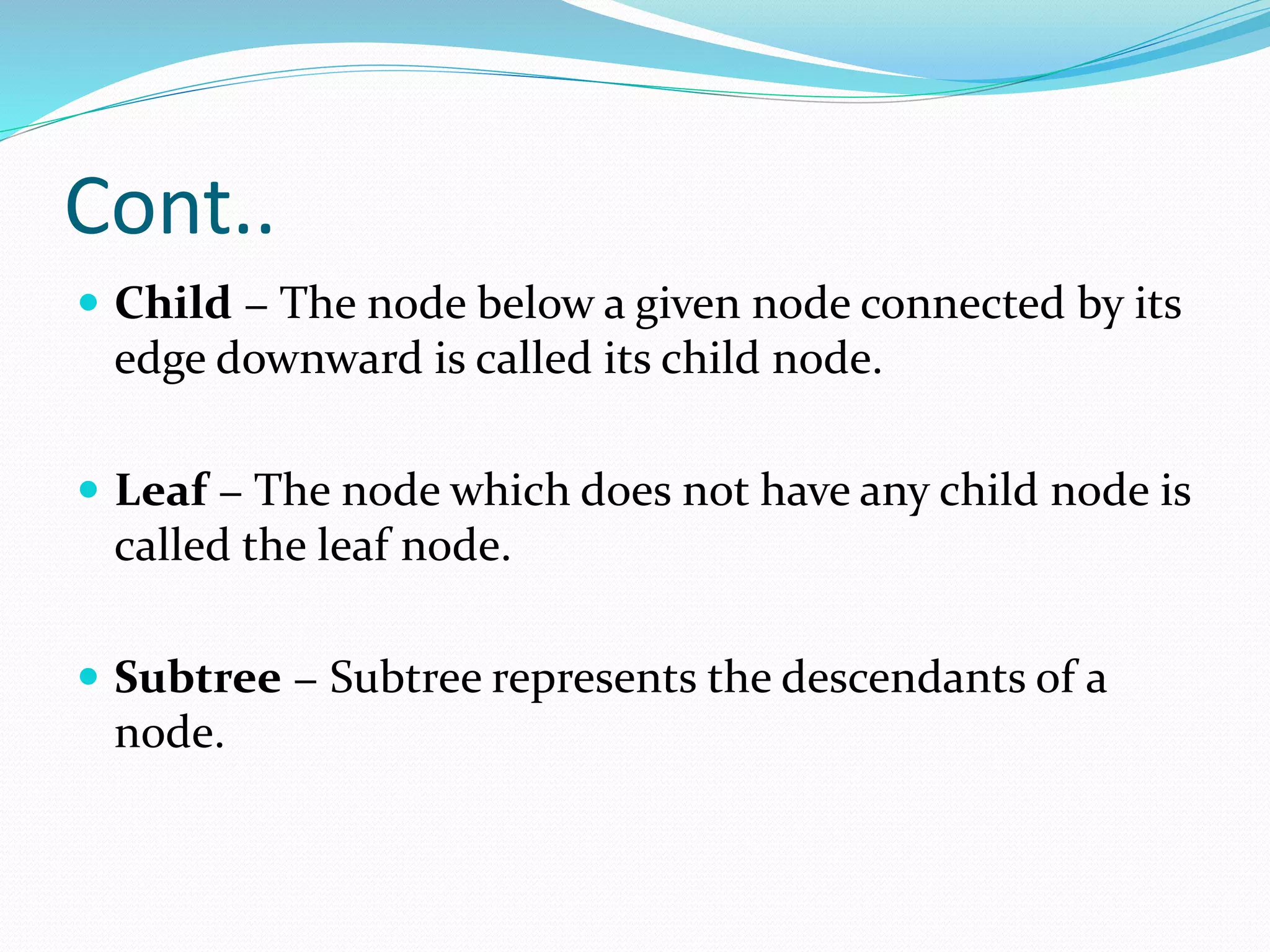
This document defines and describes binary trees, an important data structure. It begins by explaining that a binary tree is a hierarchical structure where each node has at most two children, and contains pointers to its left and right subtrees as well as a data element. It then discusses important binary tree terms like the root node, parent and child nodes, leaf nodes, subtrees, and traversal. Finally, it briefly introduces different types of binary trees based on their structure, such as rooted binary trees and full binary trees. The document is intended to teach students about the basic concepts and components of binary trees.