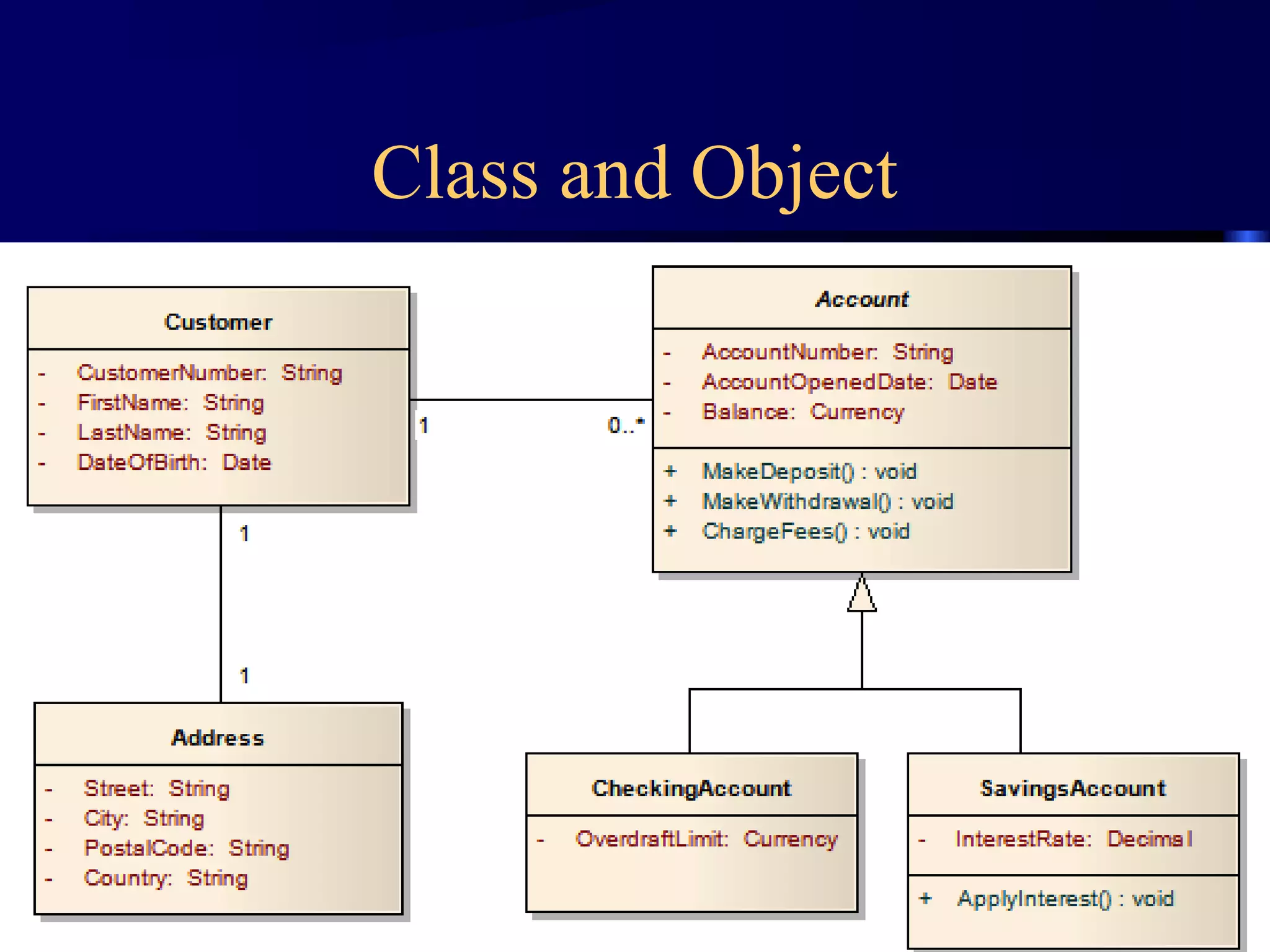
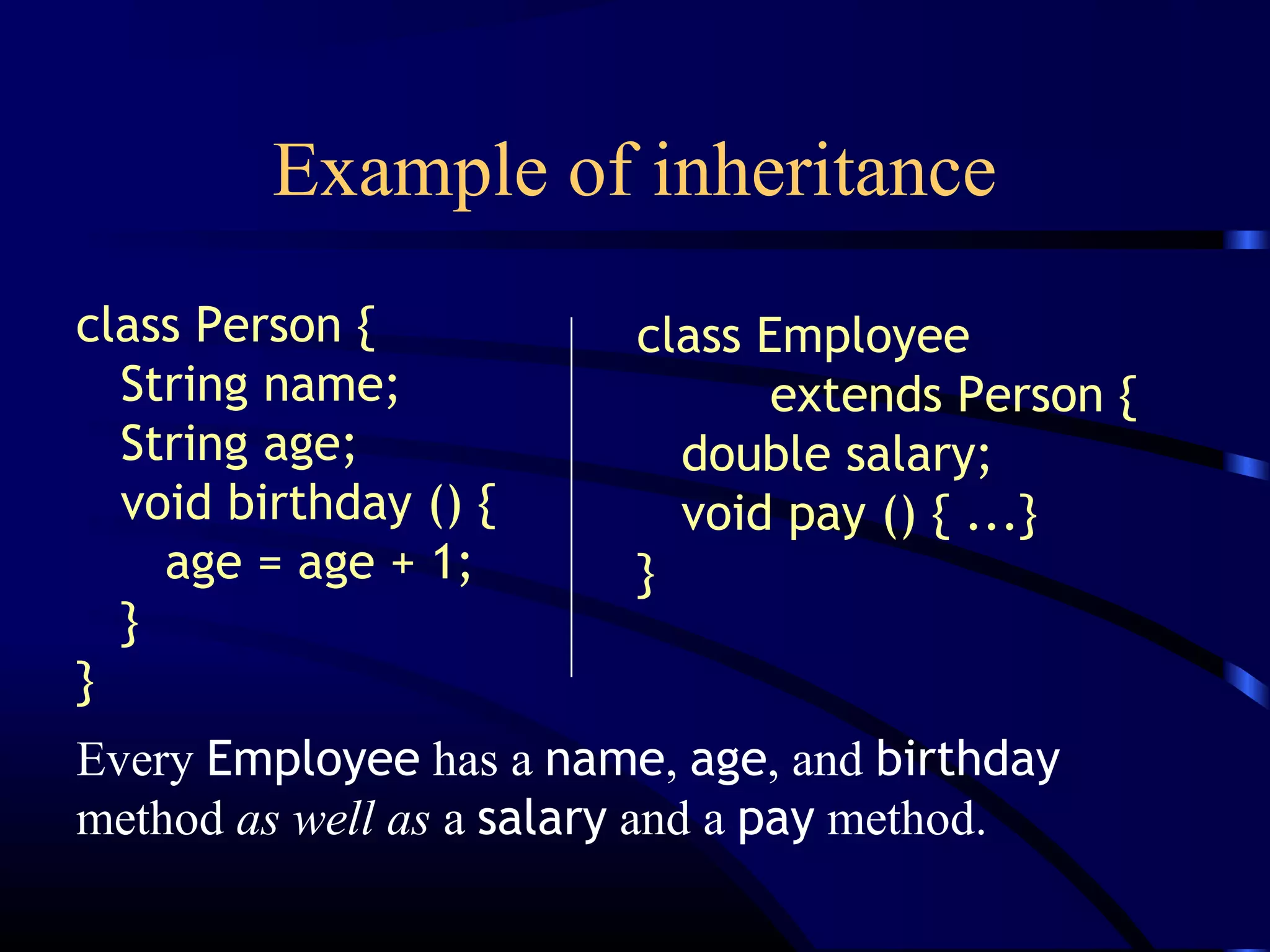
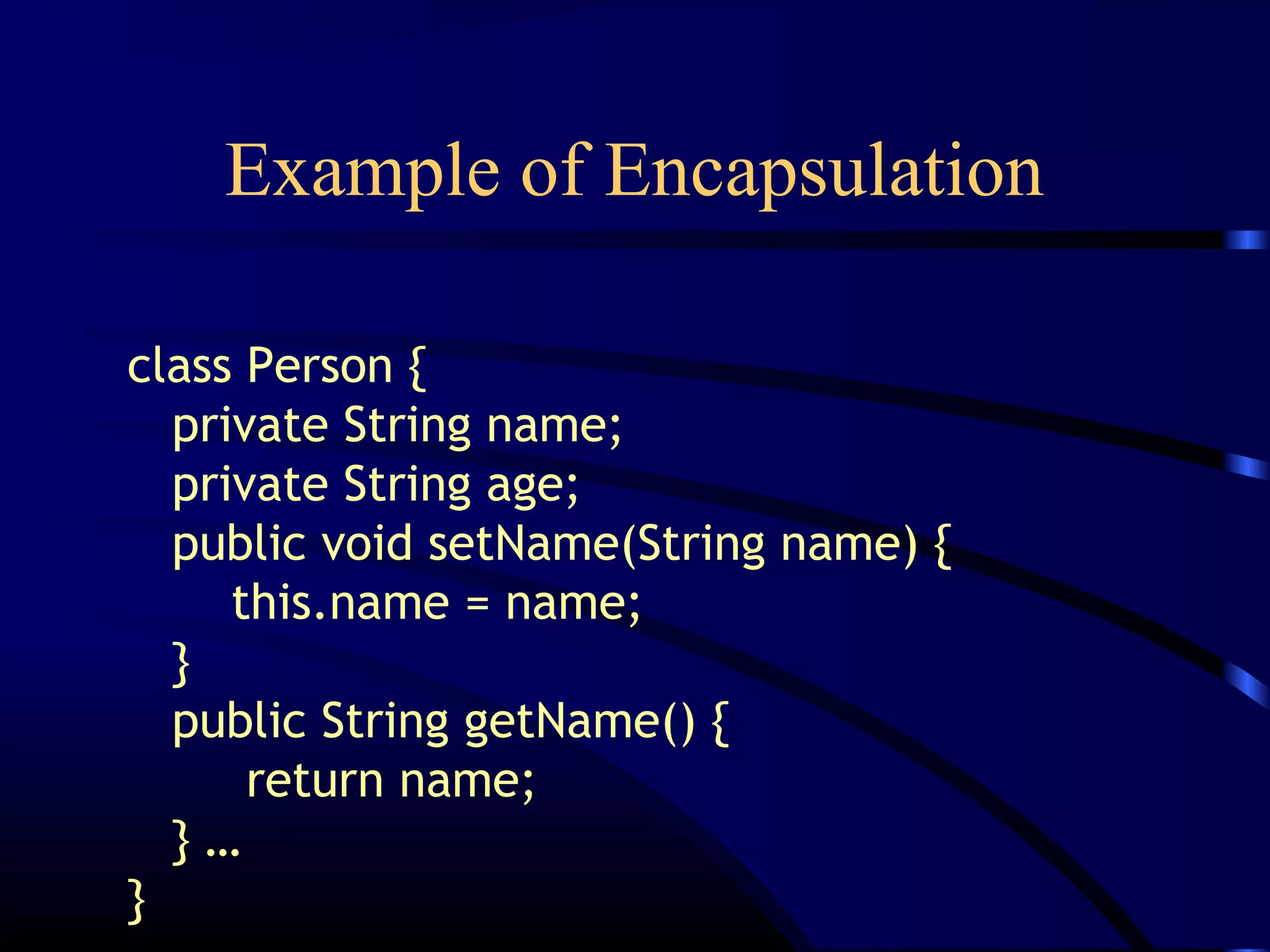
The document discusses basic object-oriented concepts such as classes, objects, inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism, and interfaces with examples in Java. It explains terminology like fields, methods, and constructors, and provides code snippets demonstrating these concepts. Key ideas include how objects are created, methods of class inheritance, and the use of interfaces to define behaviors.










![Example of Polymorphism
public class VirtualDemo {
public static void main(String [] args) {
SalaryEmployee s = new SalaryEmployee("Mohd Mohtashim", "Ambehta,
UP", 3, 3600.00);
Employee e = new Salary("John Adams", "Boston, MA", 2, 2400.00);
System.out.println("Call mailCheck using Salary reference --");
s.mailCheck();
System.out.println("n Call mailCheck using Employee reference--");
e.mailCheck(); }
}
Call mailCheck using Salary reference – 3600
Call mailCheck using Employee reference – Boston, MA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/object-concepts-150531182151-lva1-app6891/75/Basic-Object-Oriented-Concepts-14-2048.jpg)
![Example of Interface
interface Animal {
public void eat();
public void travel();
}
public class MammalInt implements Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Mammal eats");
}
public void travel(){
System.out.println("Mammal travels");
}
public int noOfLegs(){
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
MammalInt m = new MammalInt();
m.eat();
m.travel();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/object-concepts-150531182151-lva1-app6891/75/Basic-Object-Oriented-Concepts-15-2048.jpg)



