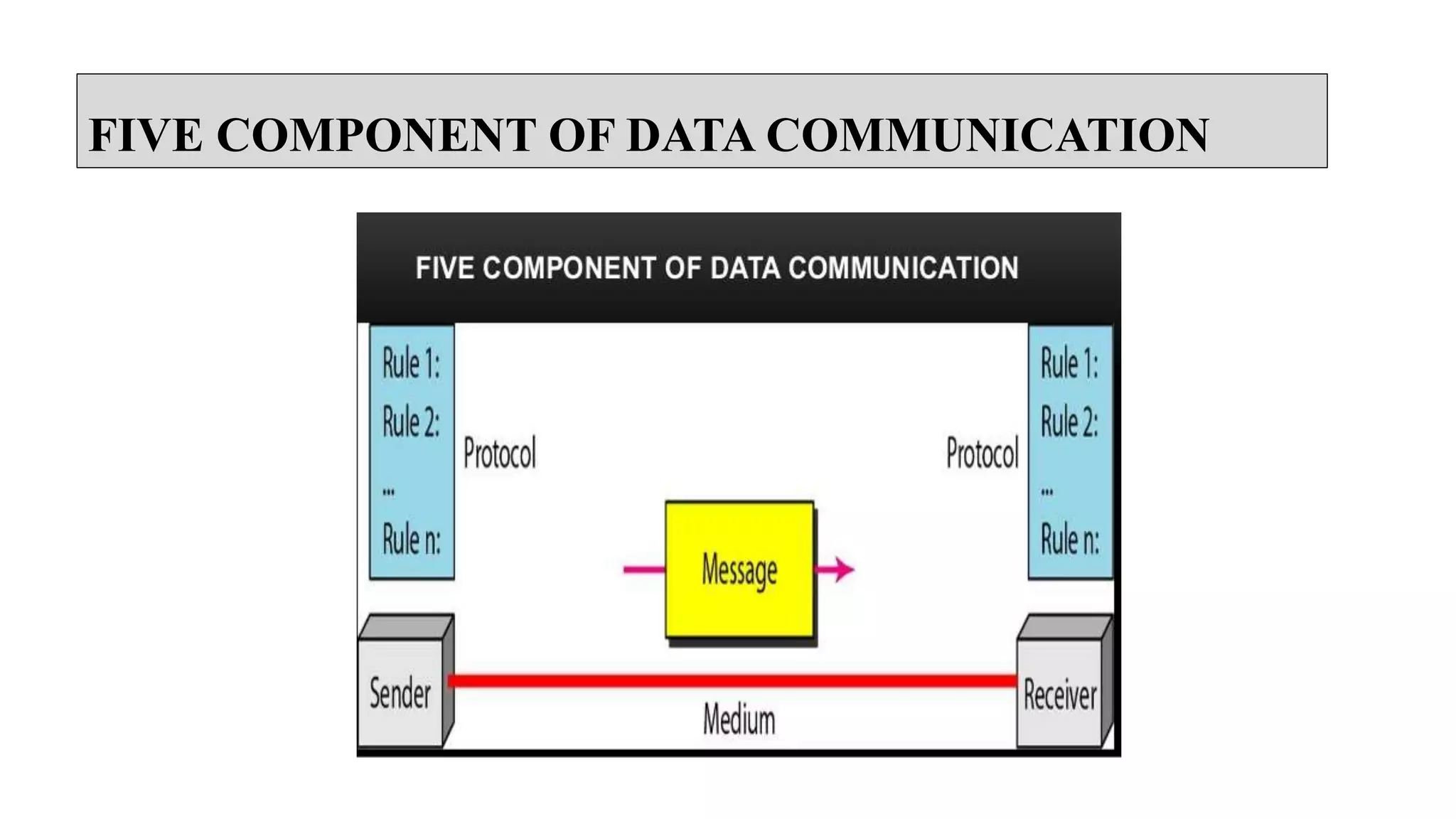
Data communication involves the exchange of data between two devices via transmission media like wires or wireless signals. It can be local, involving devices in the same building, or remote, over longer distances. Effectiveness relies on accurate and timely delivery of data to the correct destination. The core components of any data communication system are the message being communicated, the sender and receiver devices, the transmission medium between them, and protocols governing the communication. Data is converted to signals and transmitted according to the agreed protocols.