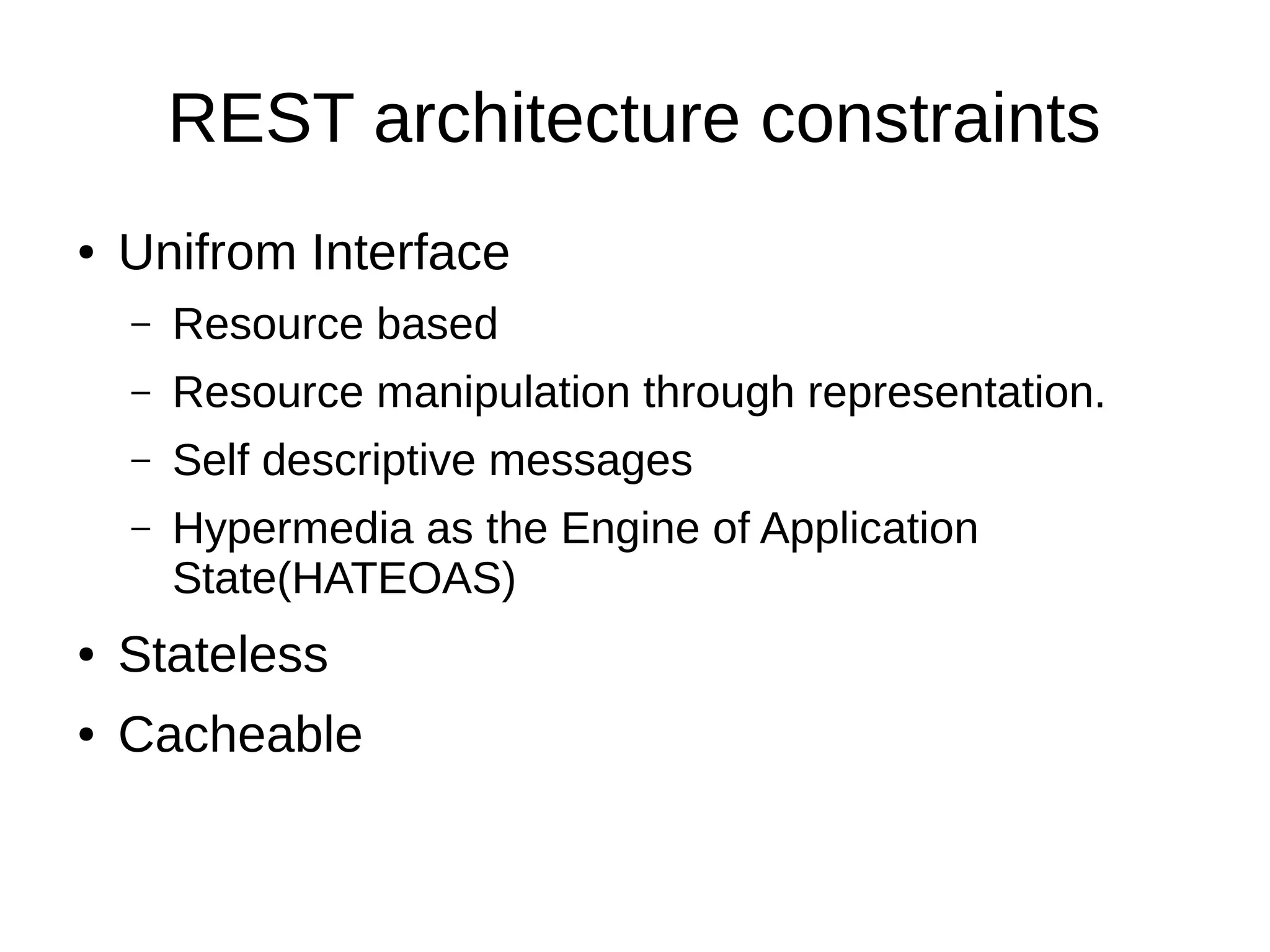
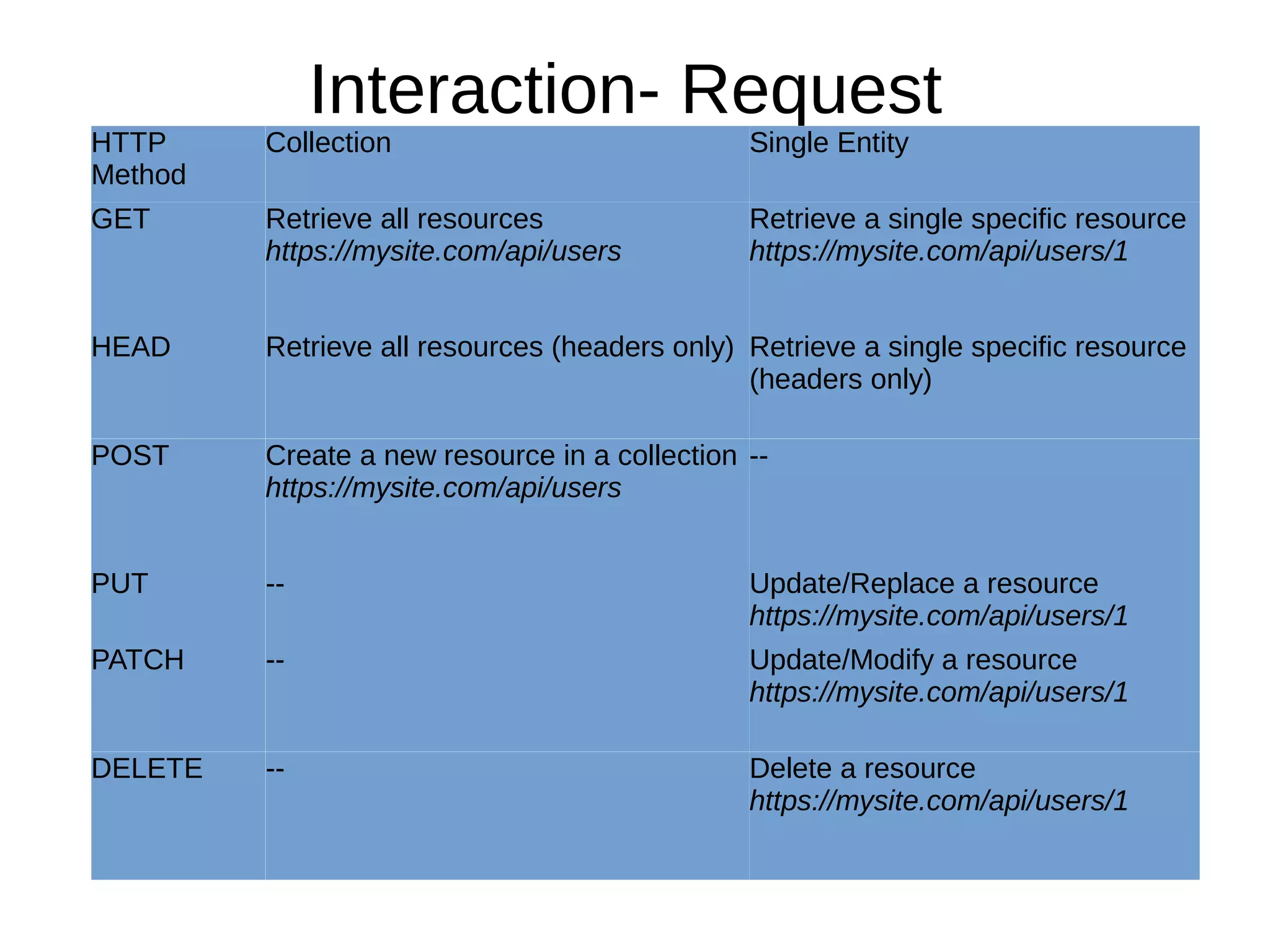
This document discusses REST APIs and how to attack them. It begins by explaining what REST APIs are and how they map CRUD operations to HTTP verbs like GET, POST, PUT, DELETE. It then covers REST architecture constraints like using resources and representations. The document outlines how to interact with APIs through requests and responses. It provides examples of enumeration, injection, authentication vulnerabilities and how to test authorization, rate limiting, SSL and information disclosure. It concludes with discussing cross-site request forgery attacks on REST APIs.