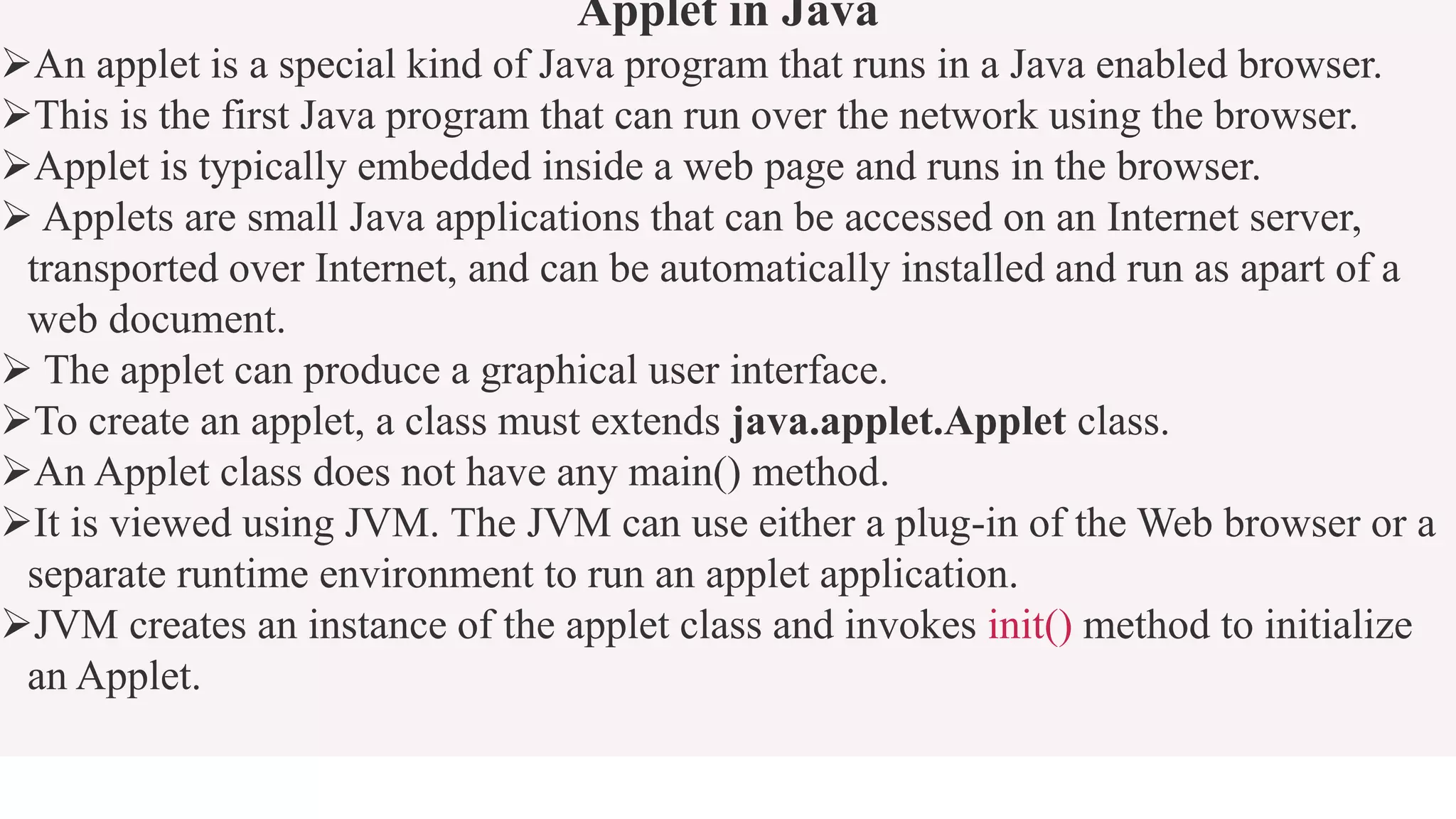
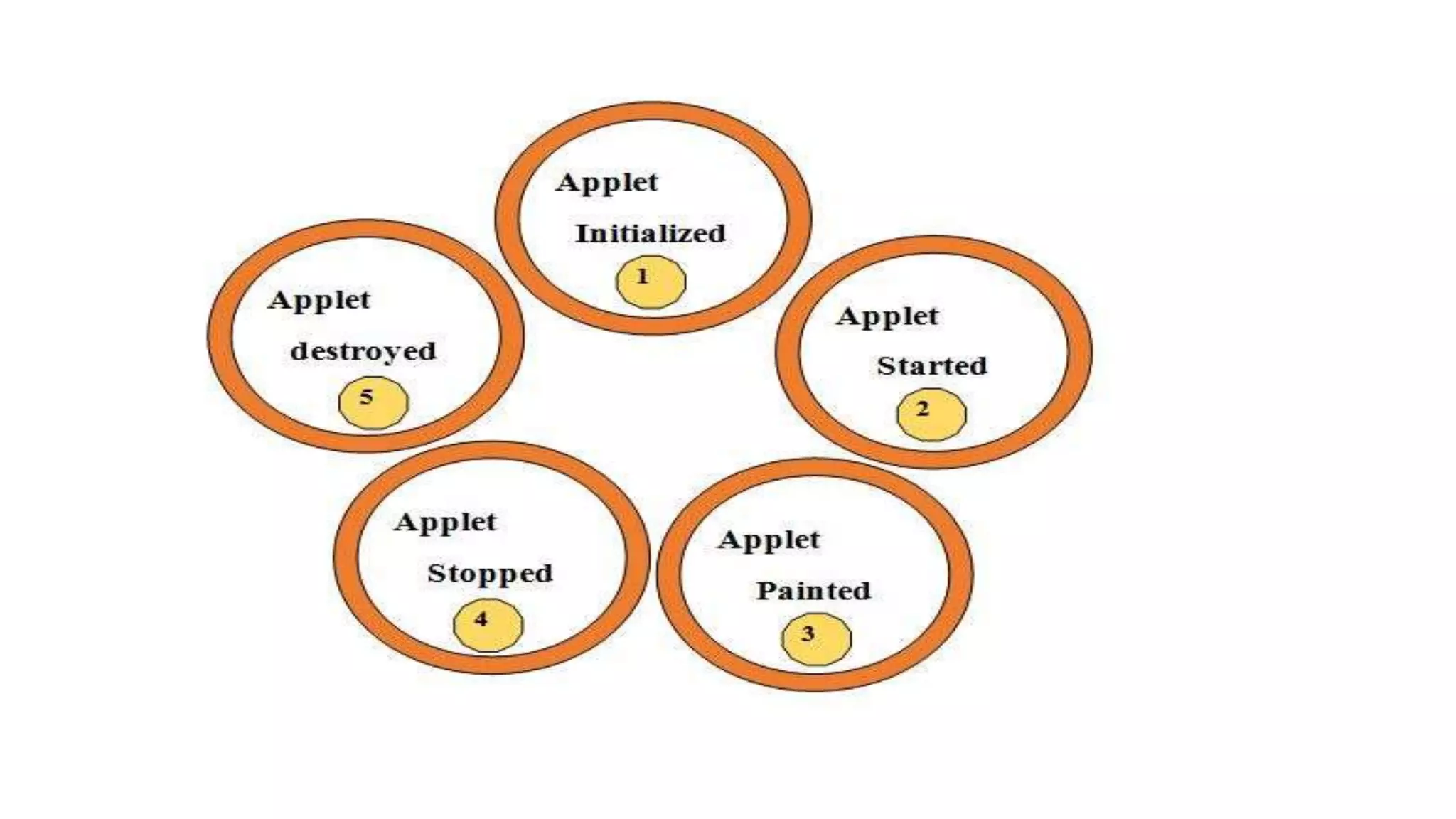
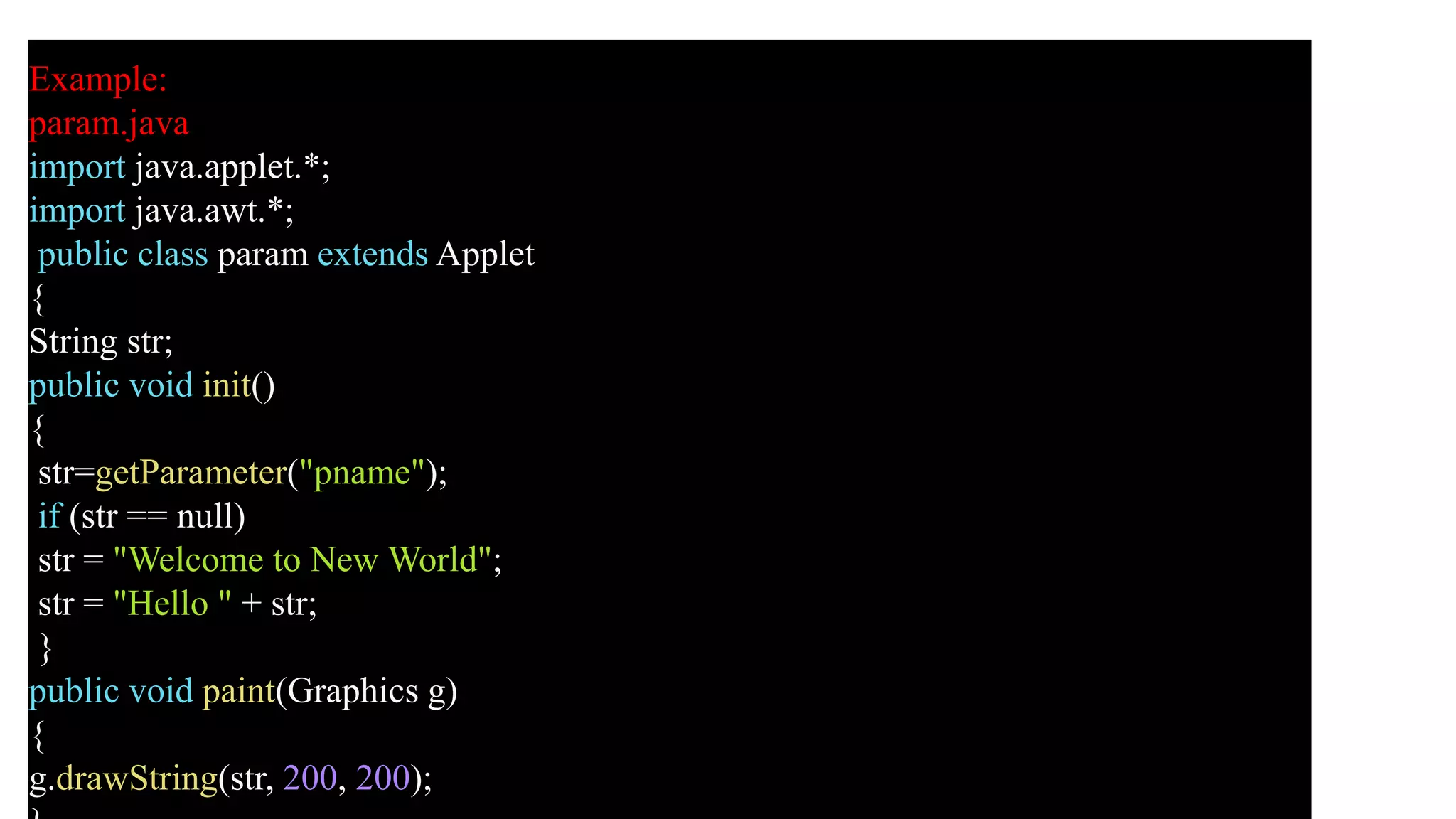
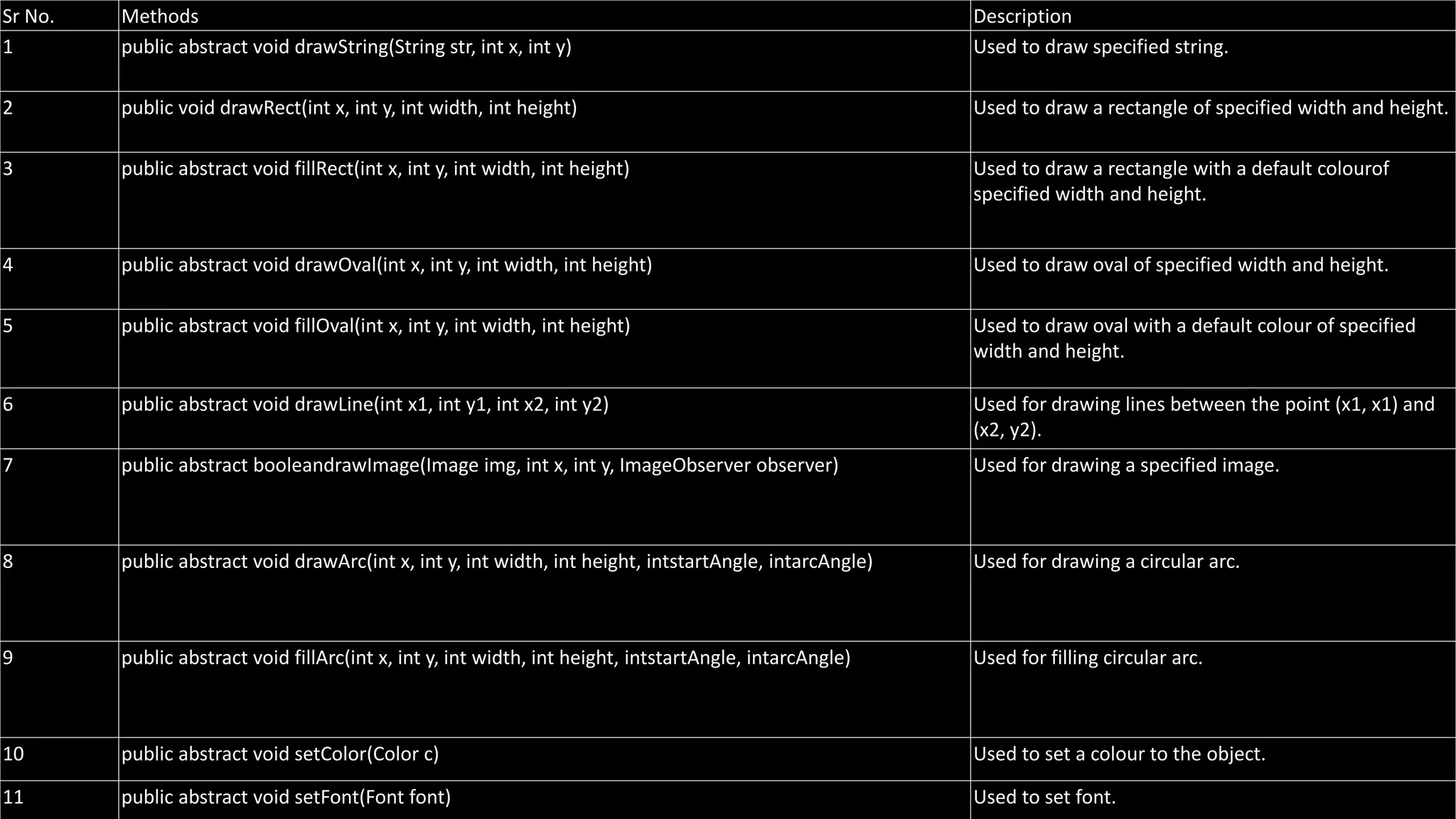
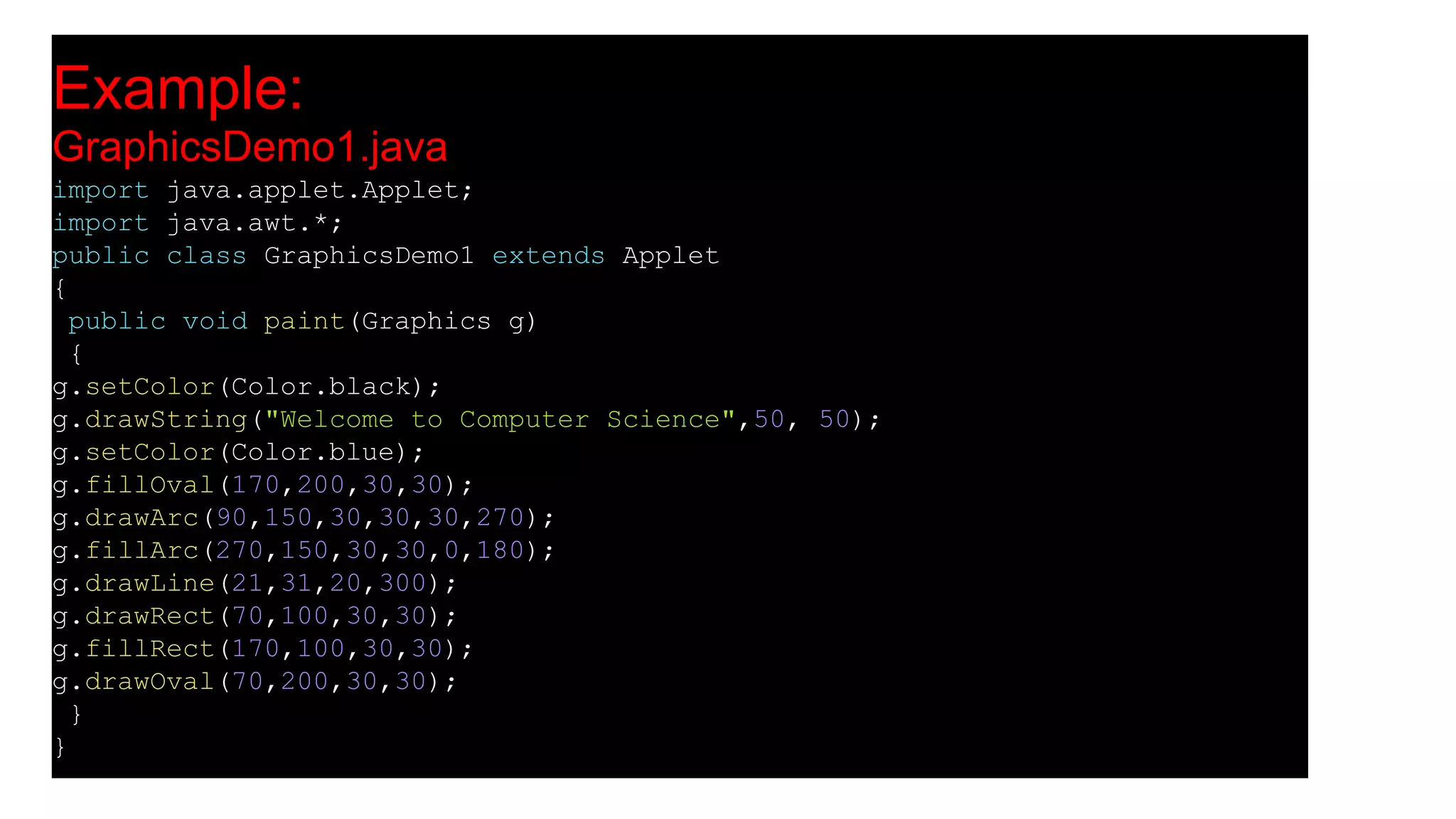
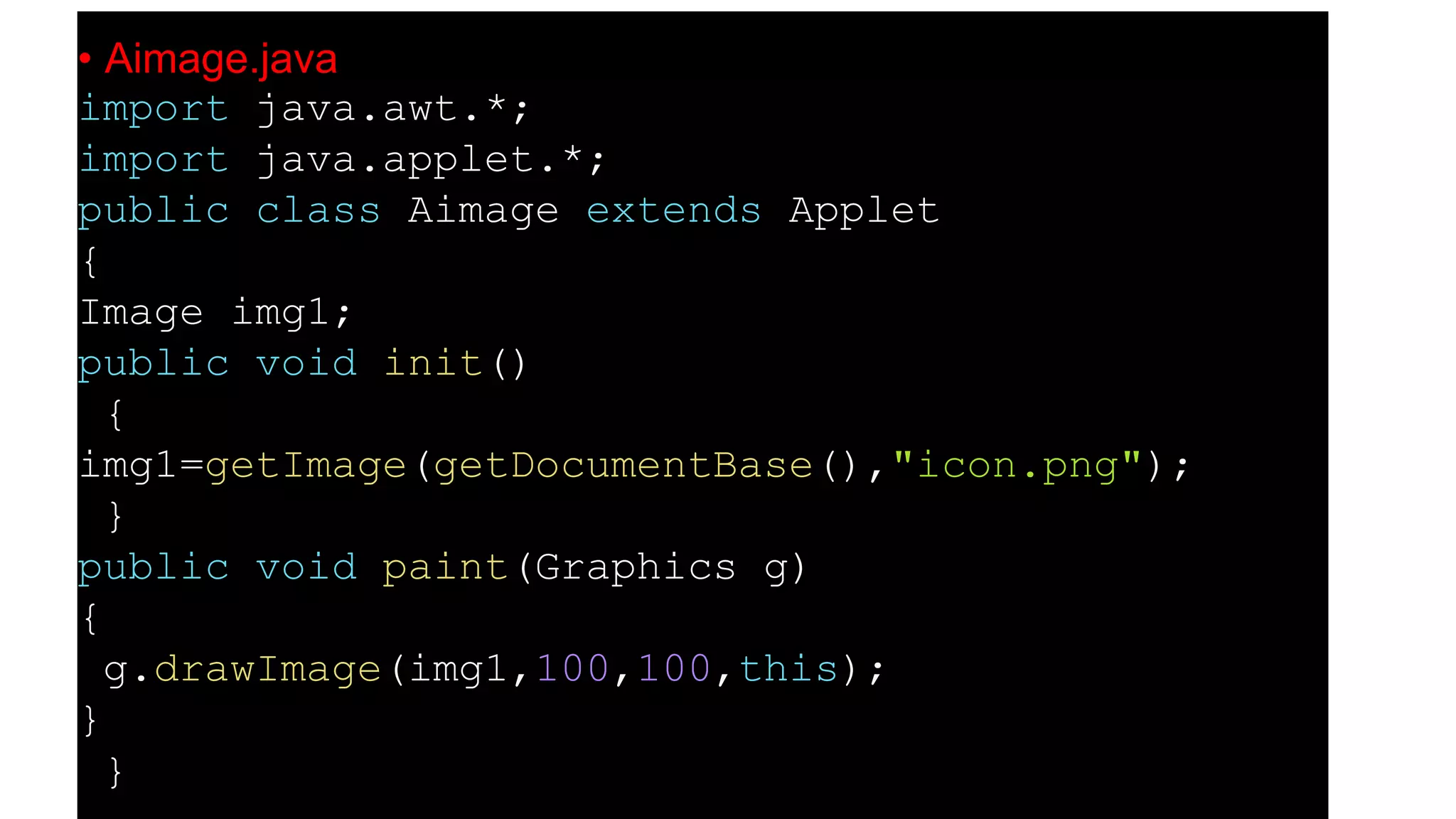
An applet is a Java program that runs in a web browser. It is embedded in an HTML page and runs in the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). To create an applet, a class must extend the Applet class. The applet lifecycle includes initialization, starting, painting, stopping, and destruction. Applets allow Java programs to be run from web pages and have graphical user interfaces.