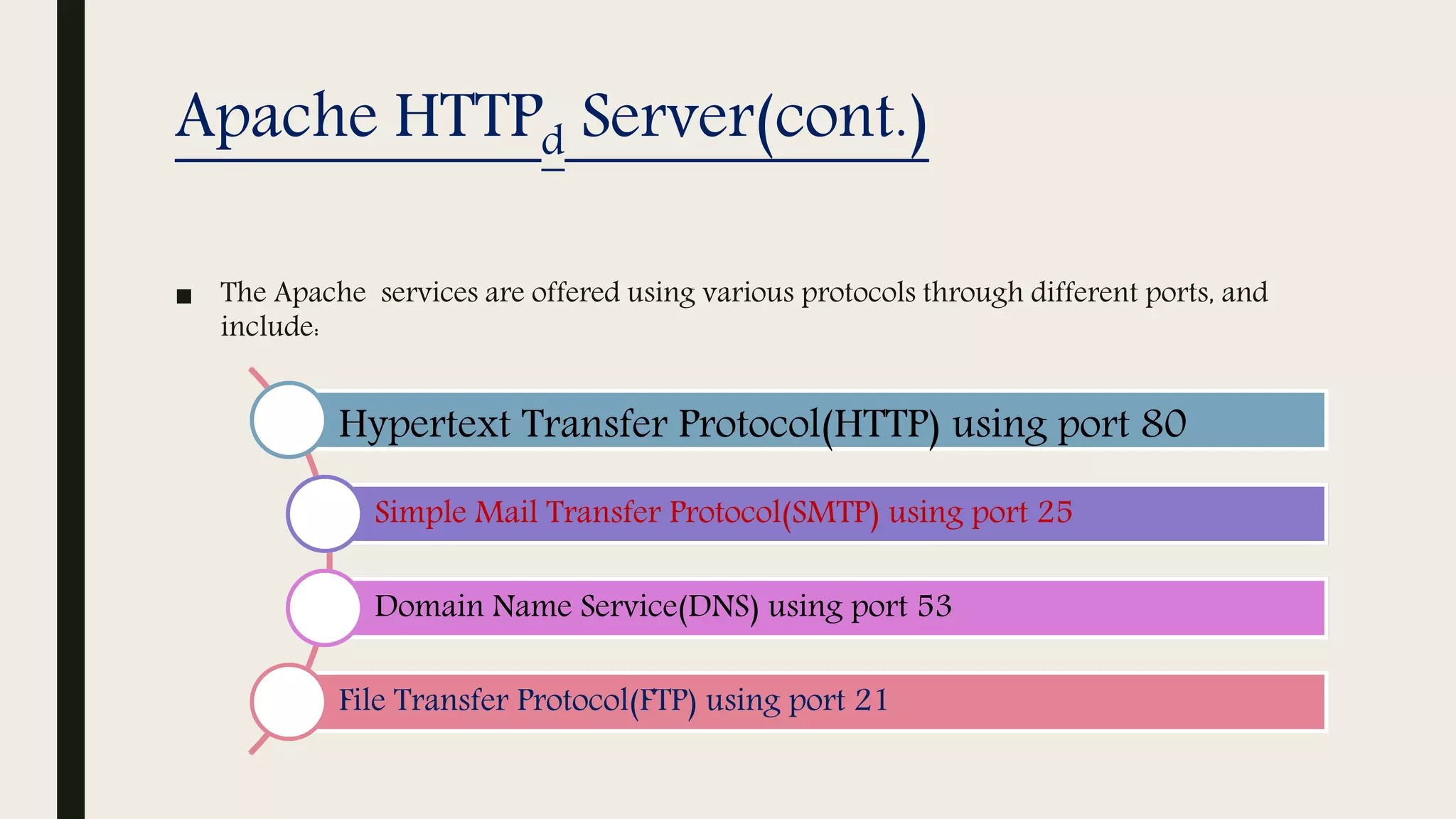
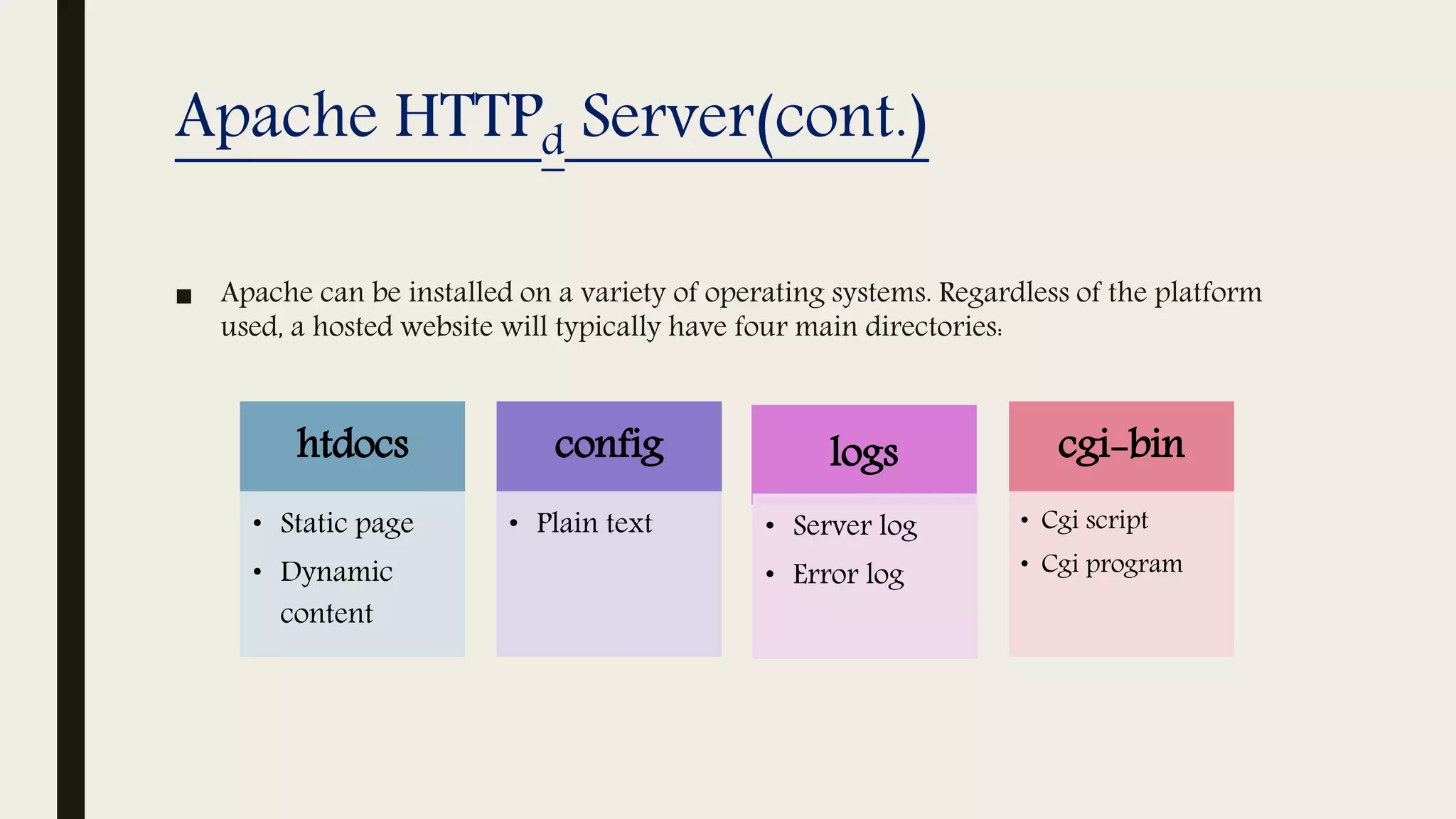
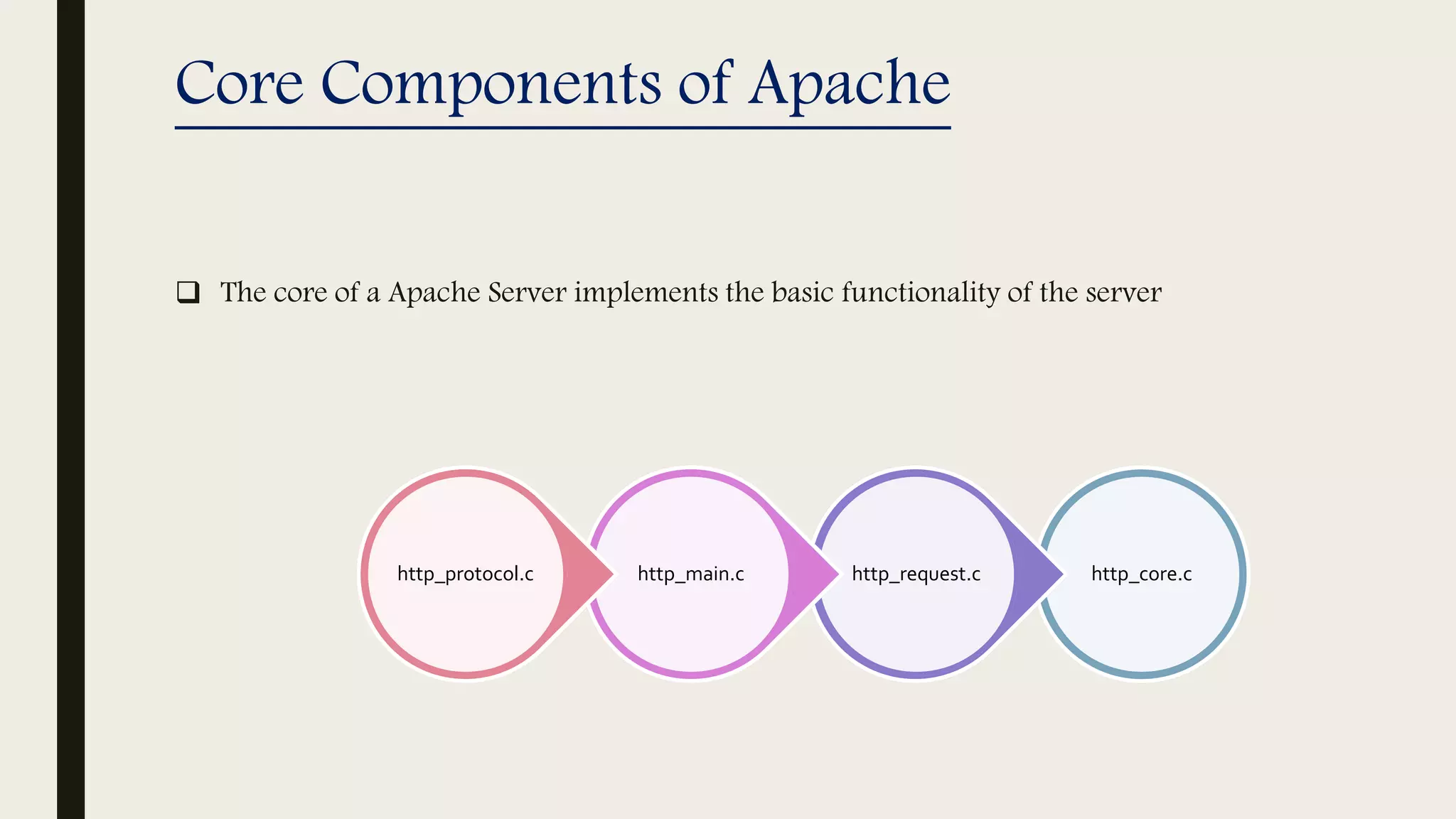
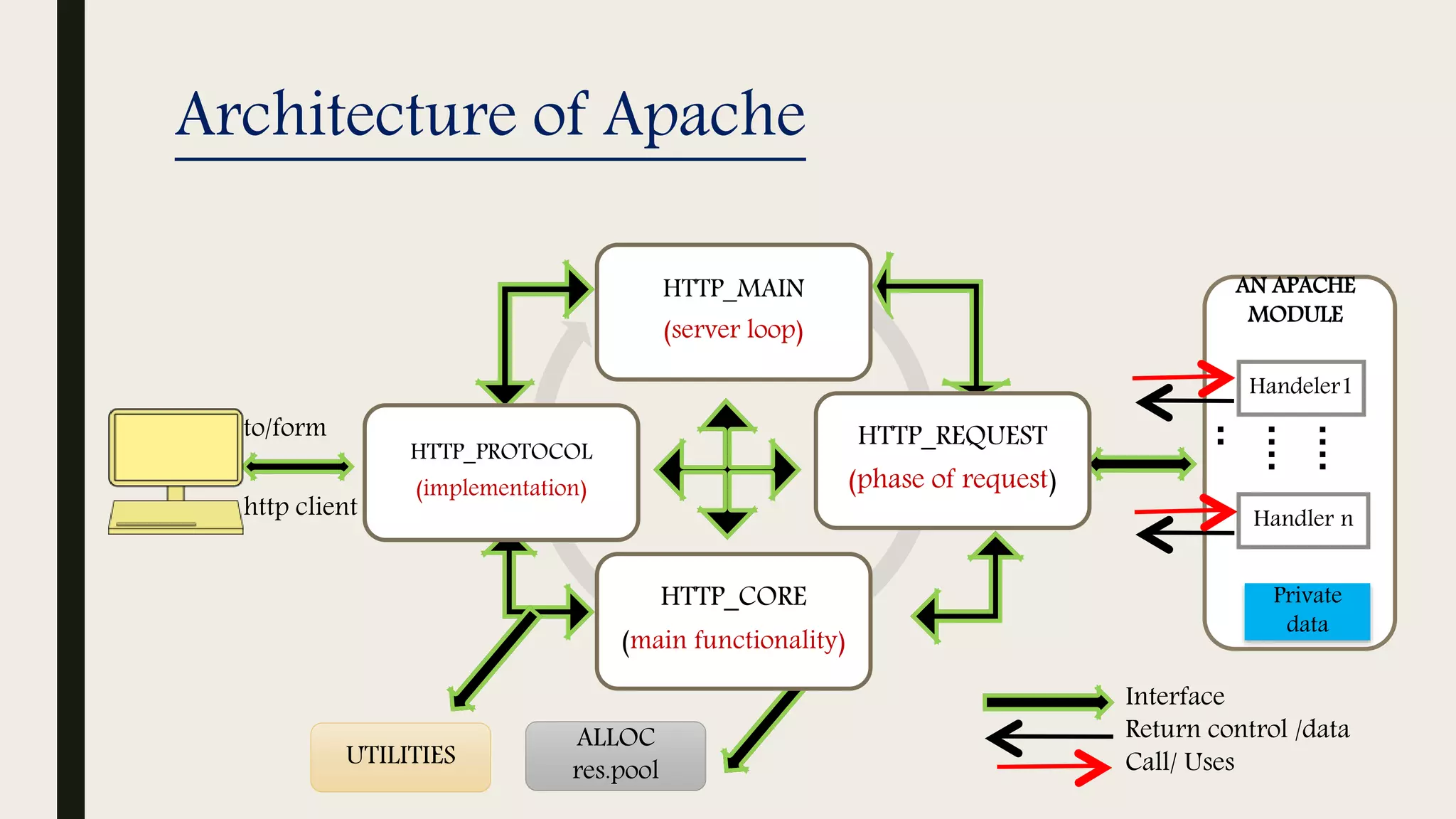
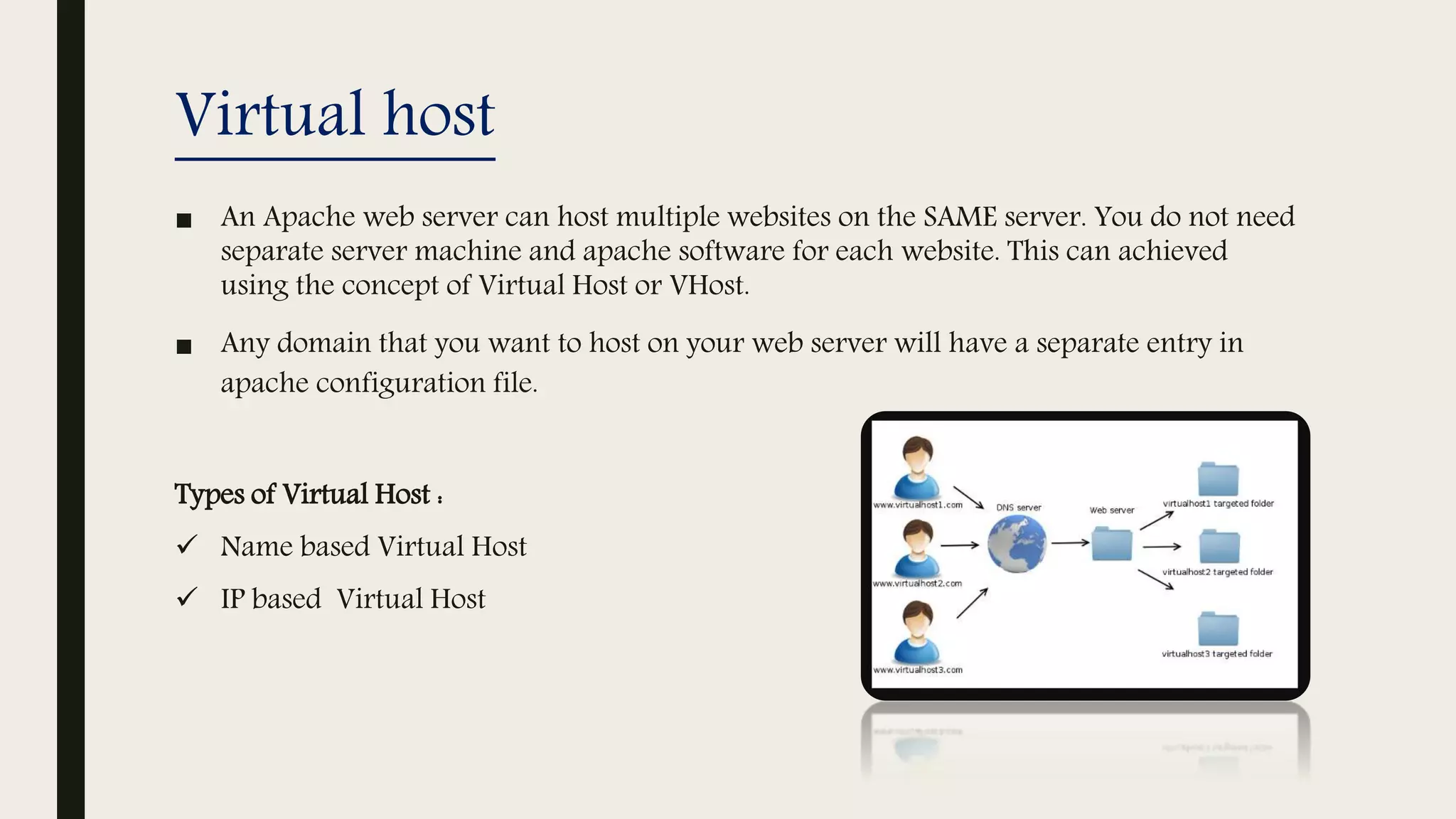
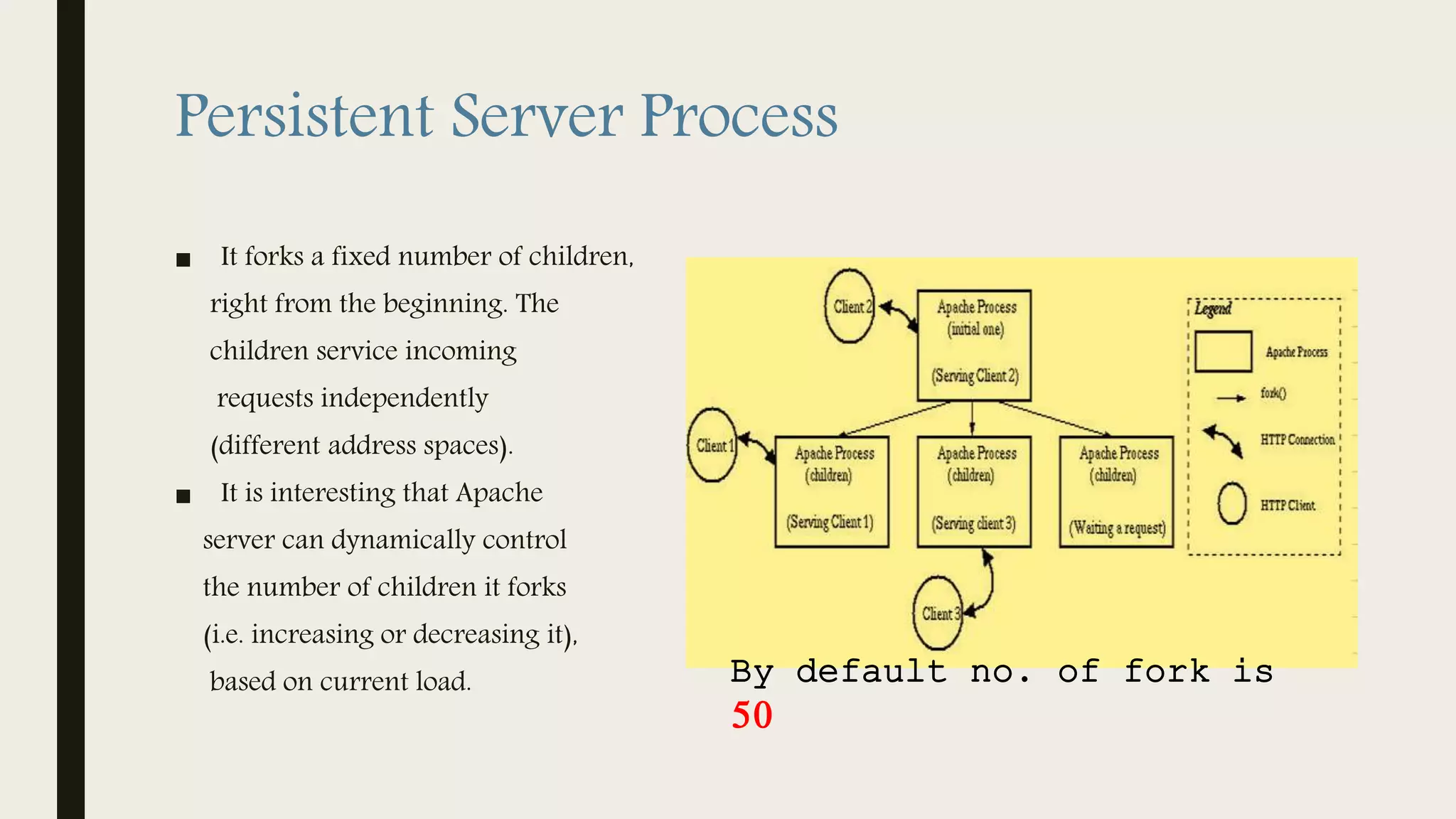
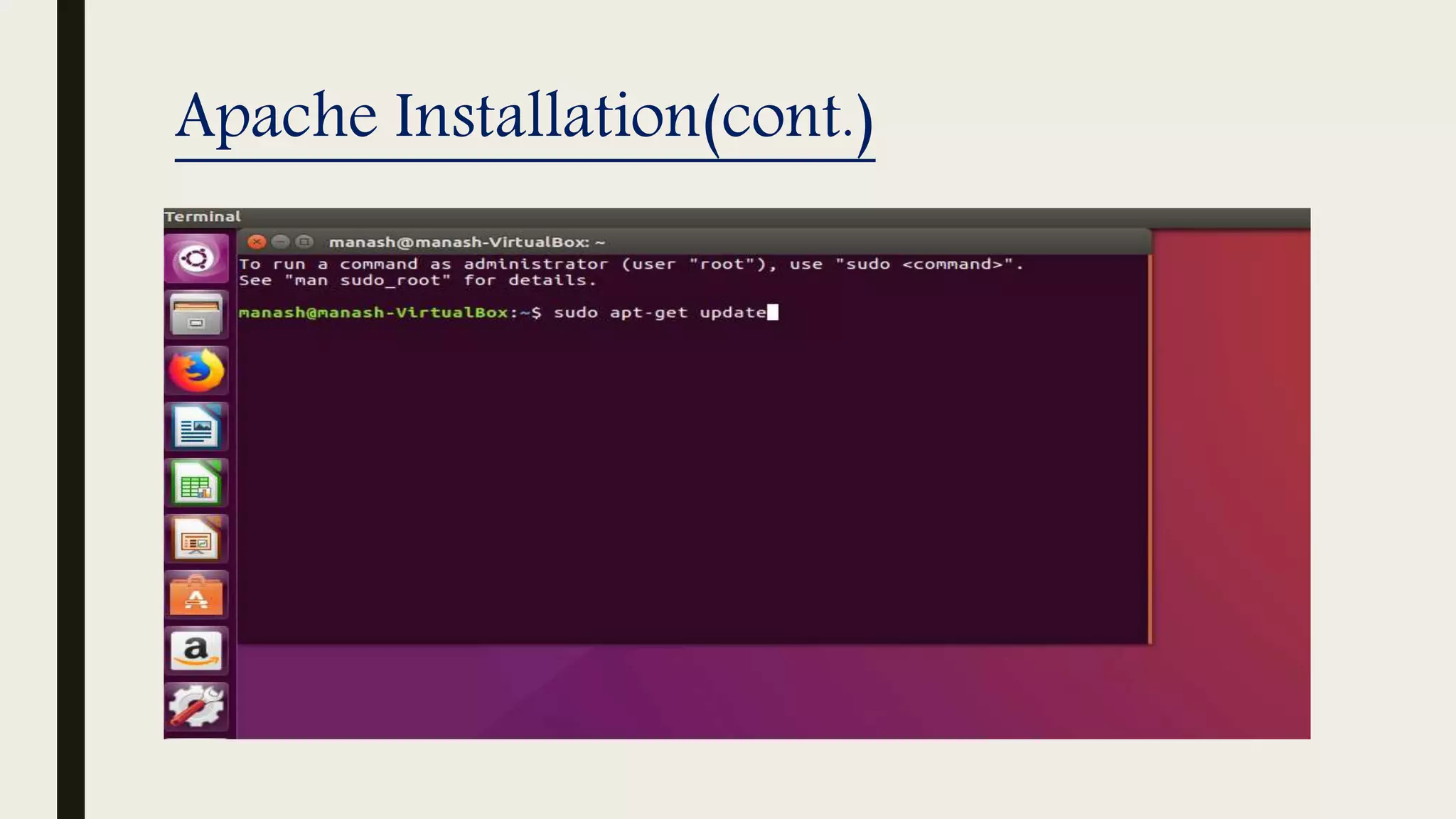
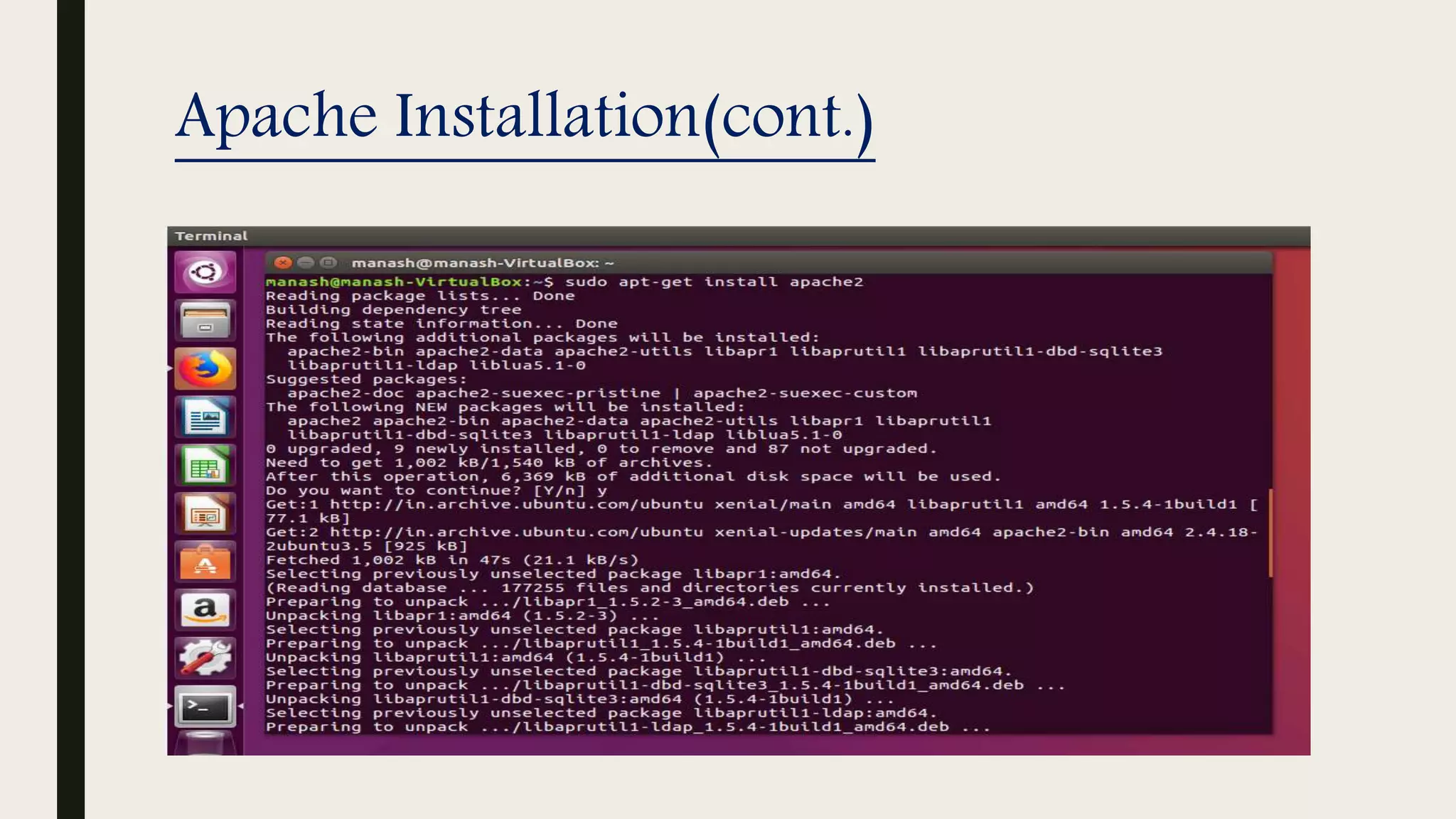
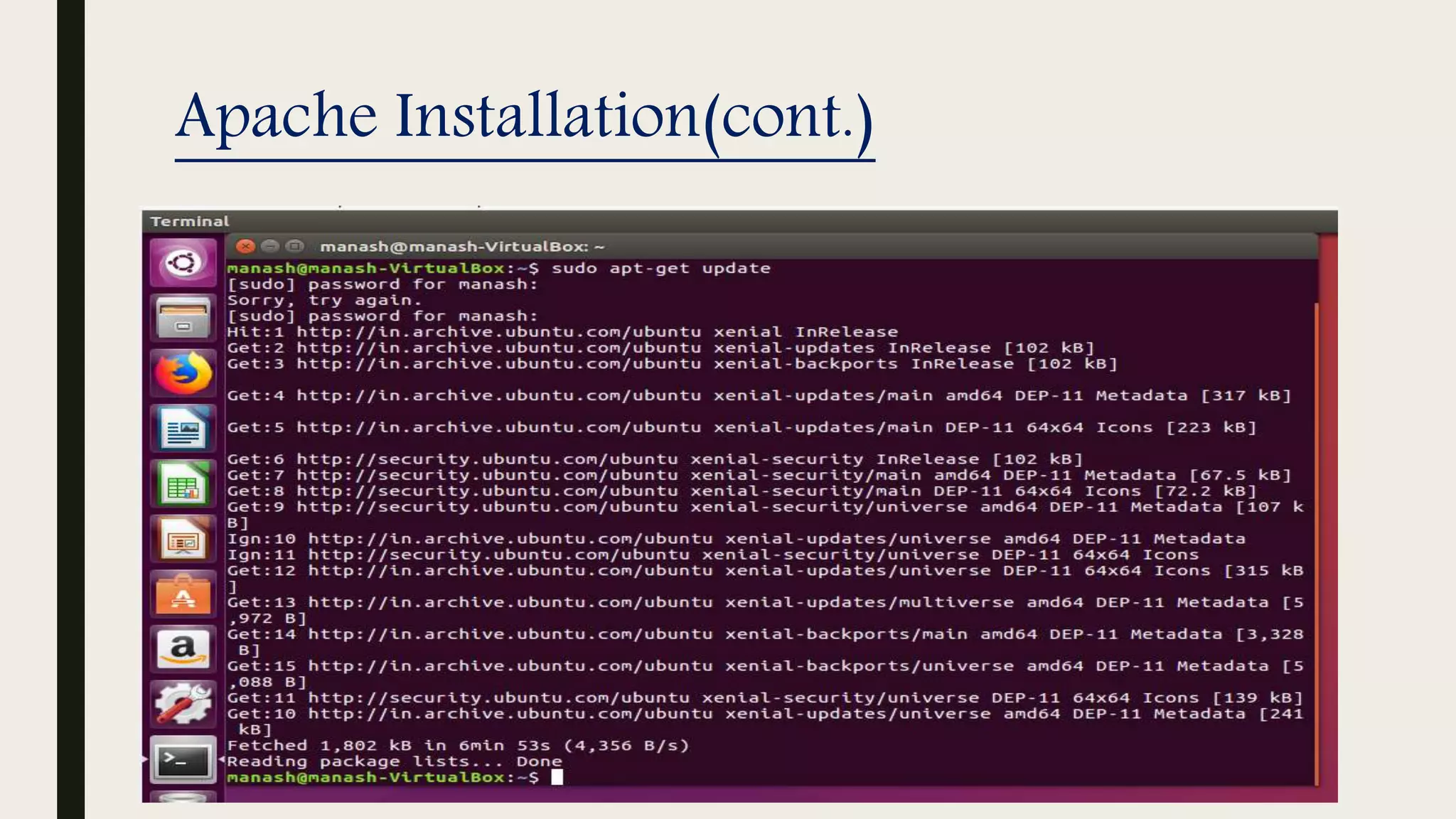
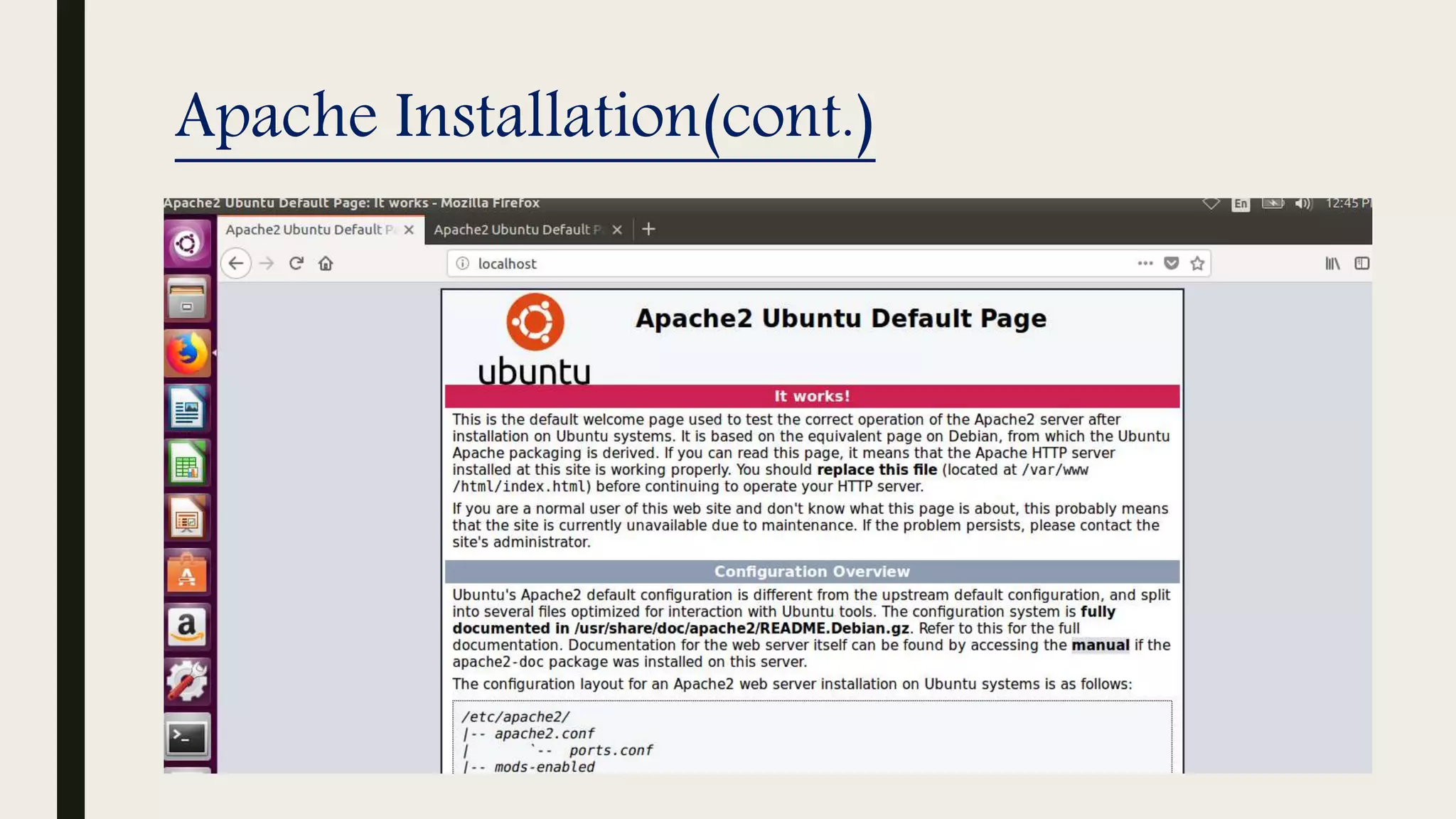
The document provides an introduction to Apache web services, detailing its history, architecture, and core components. It explains how the Apache HTTP server handles requests, supports multiple virtual hosts, and demonstrates concurrency through persistent server processes. Additionally, it includes installation instructions for Apache on Ubuntu and lists resources for further reference.