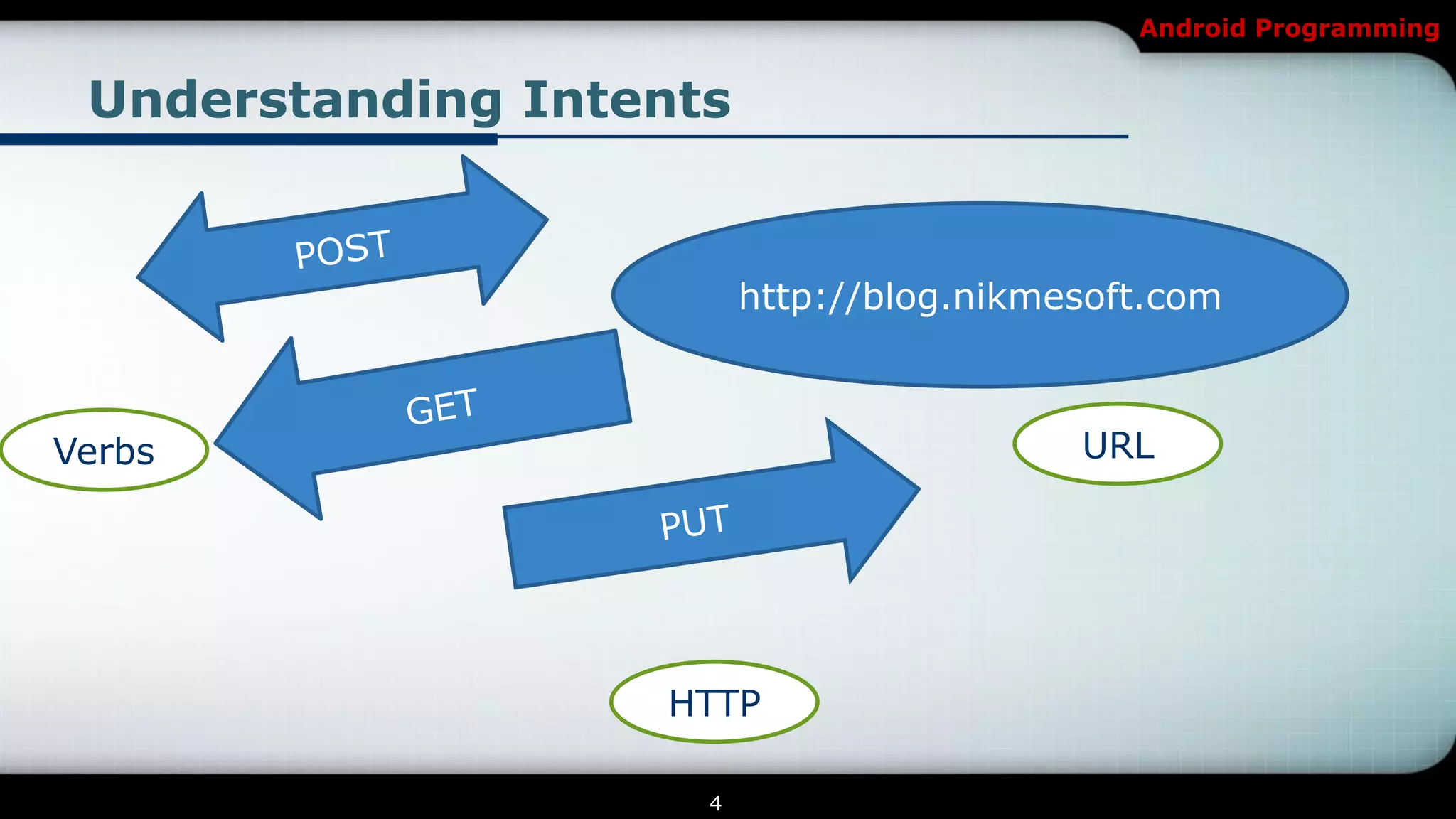
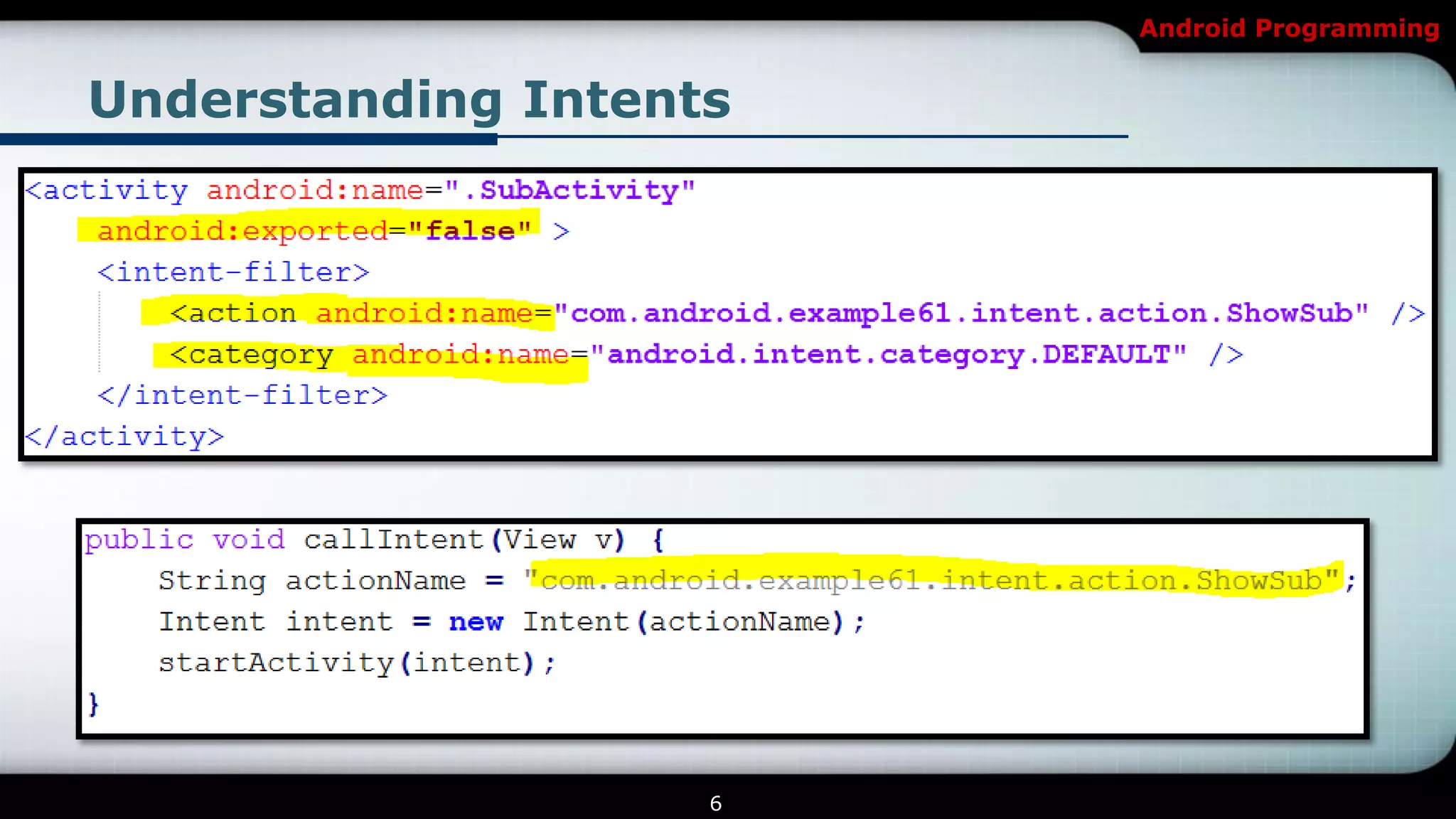
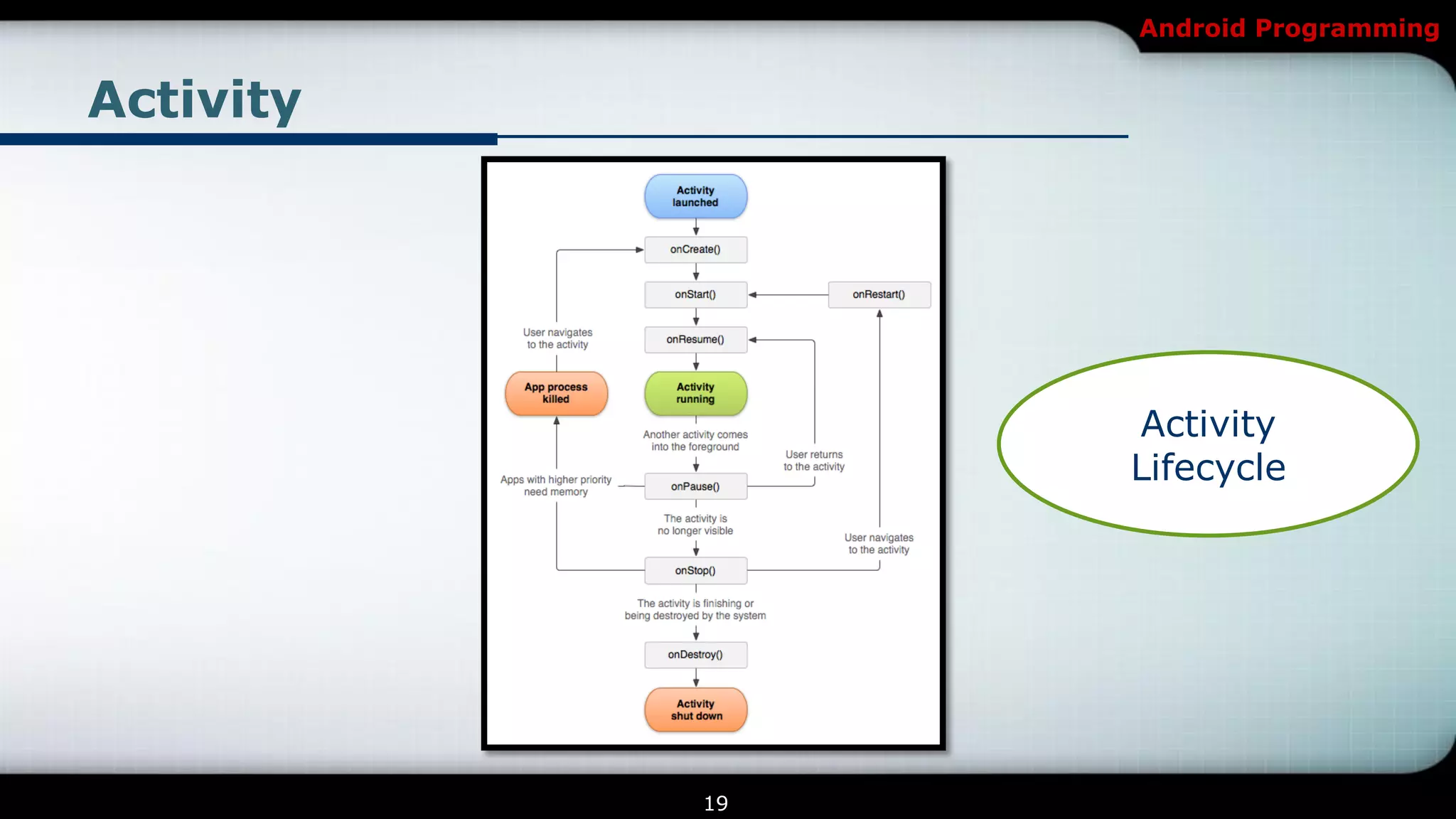
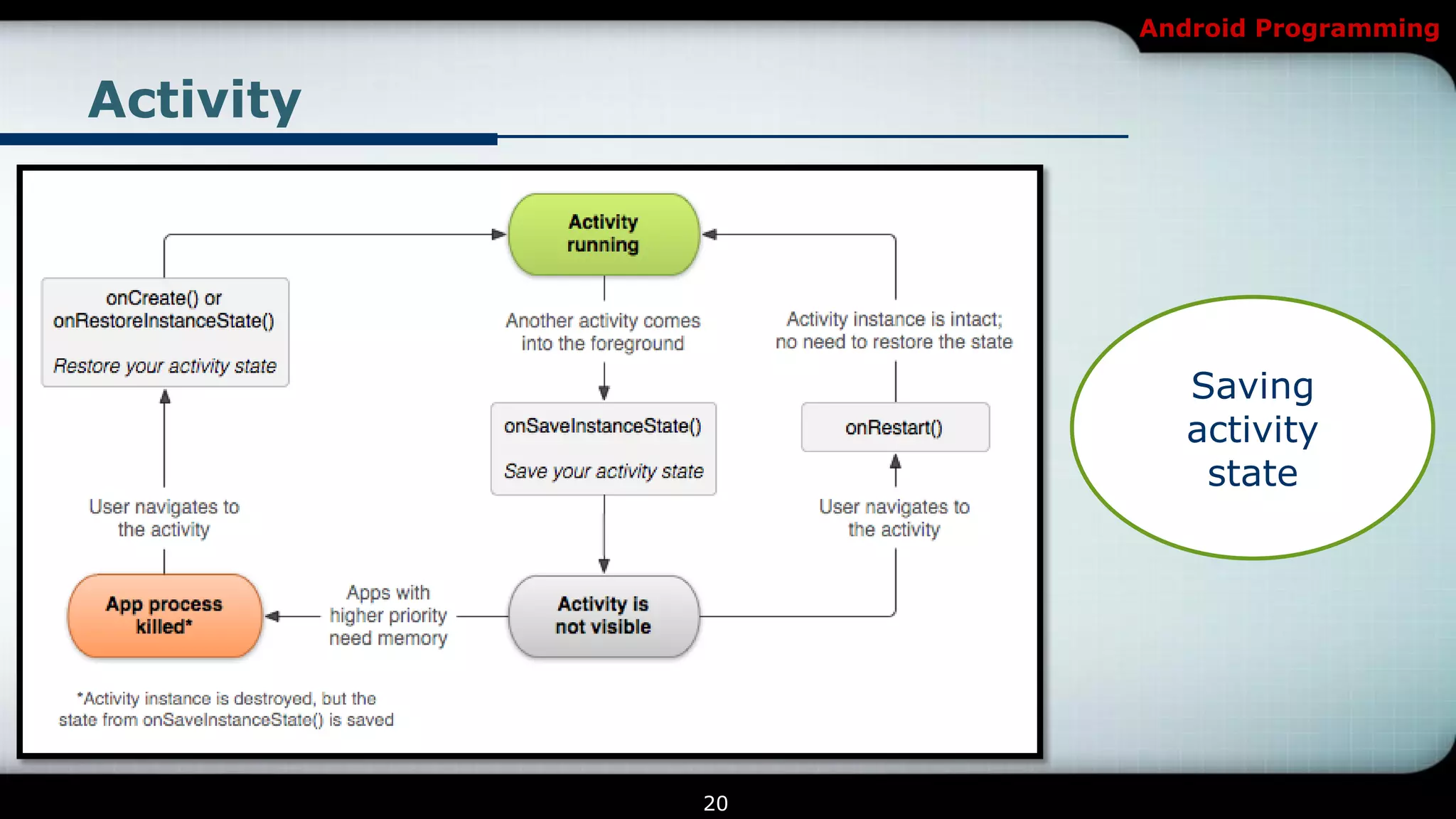
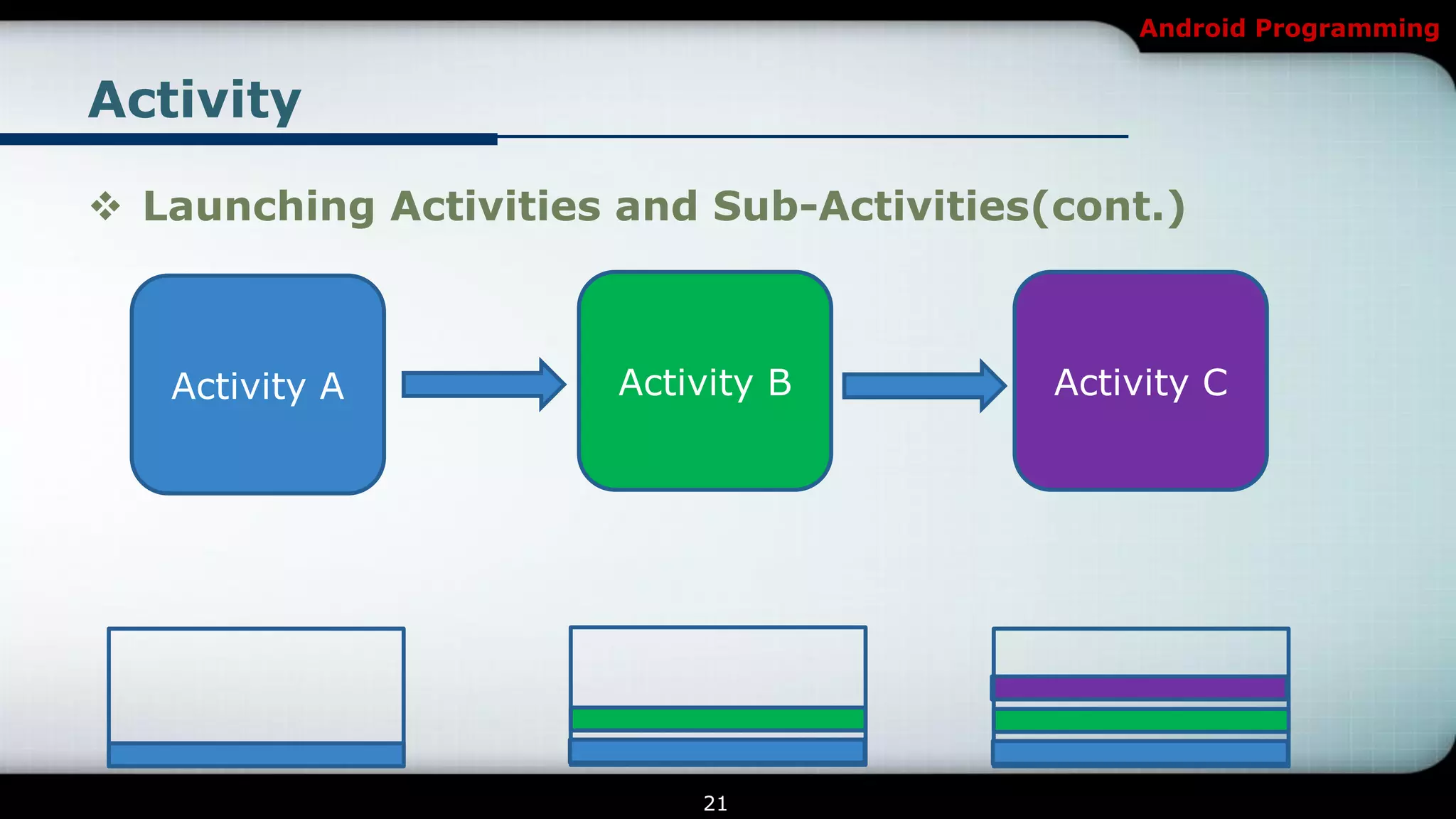
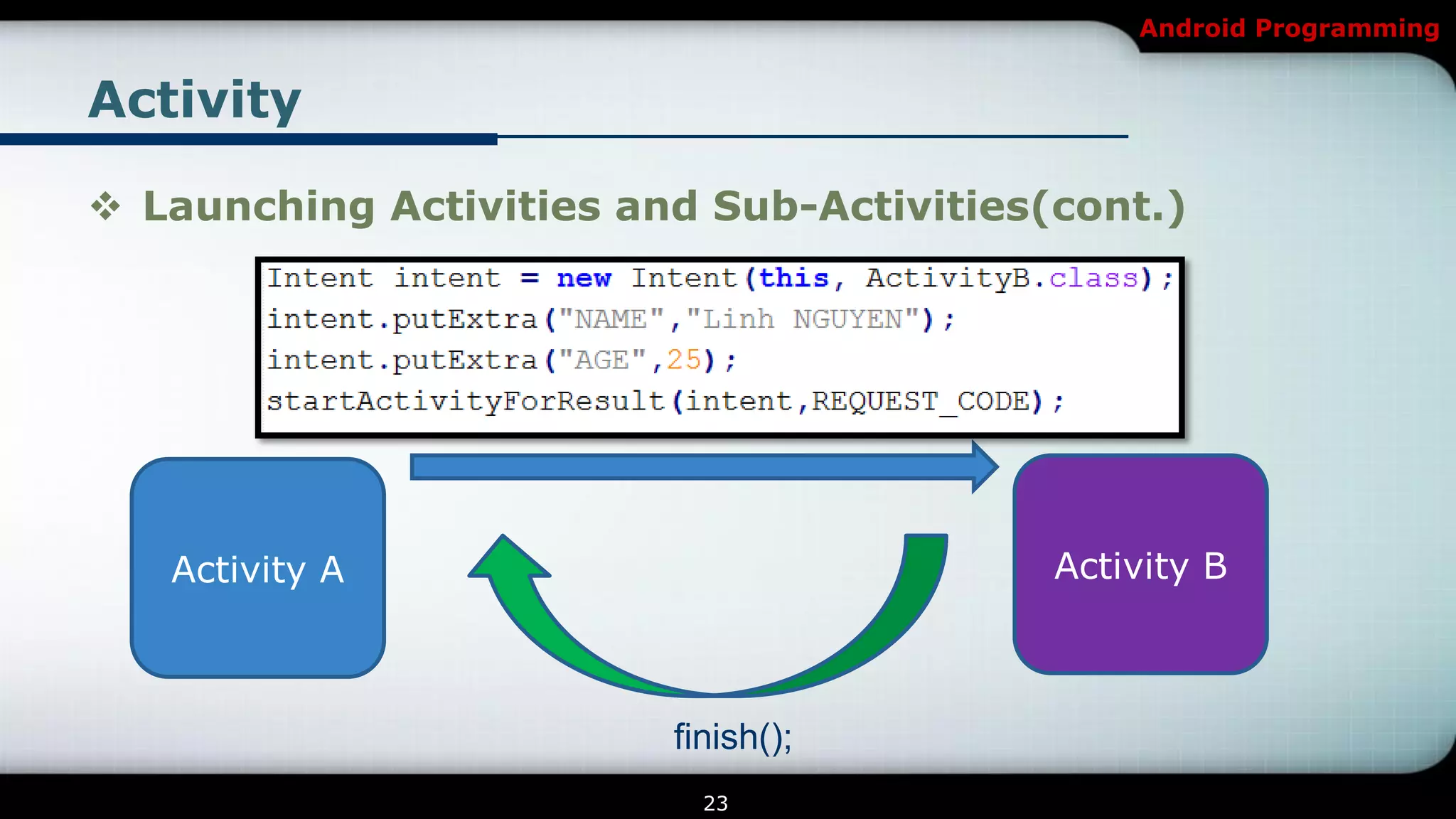
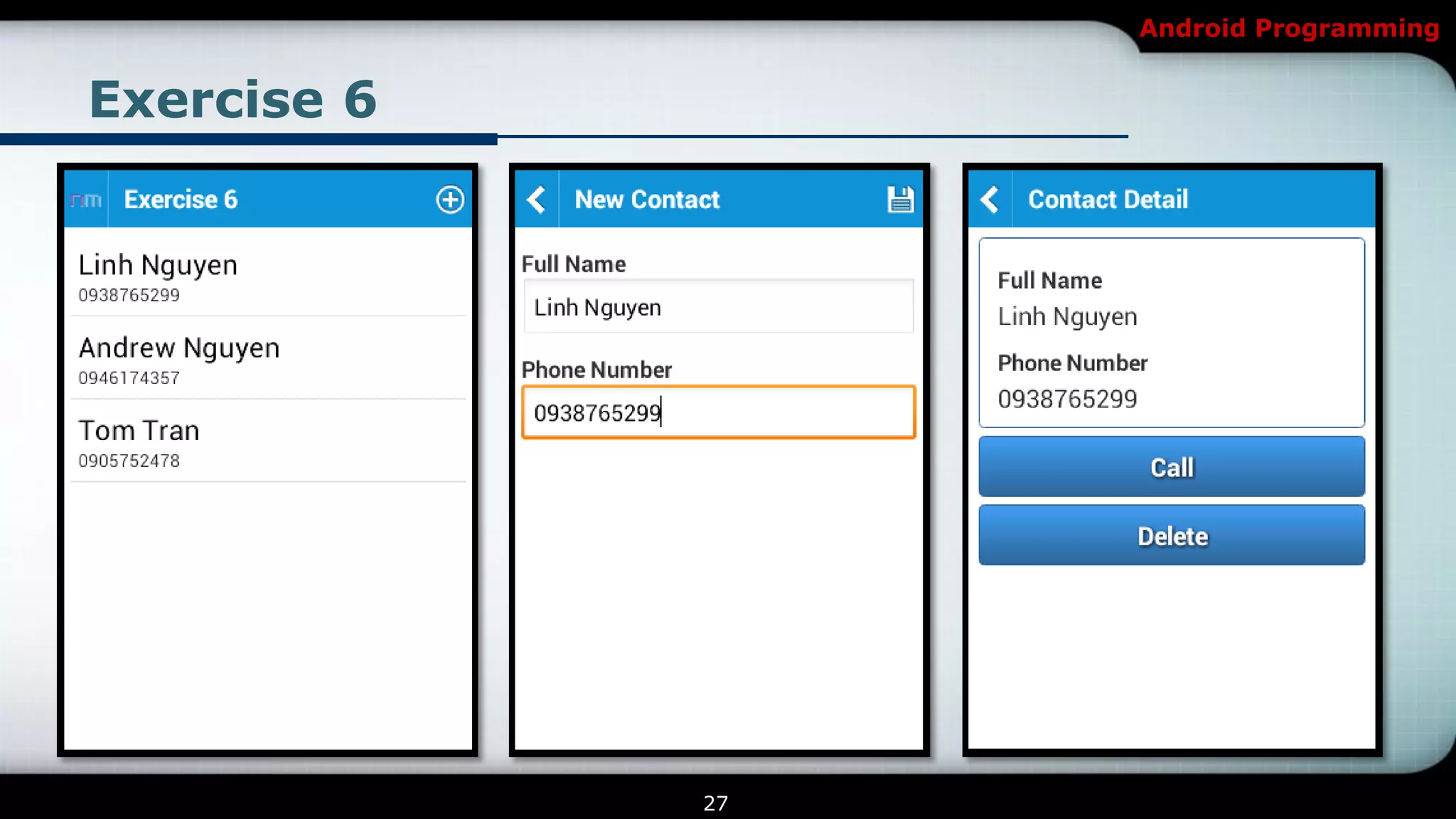
The document provides an overview of Android programming focusing on intents and activities, explaining how intents represent actions in Android, and how to use them to launch activities. It covers essential concepts such as exporting activities, using extras to pass information, and managing the activity lifecycle with specific method callbacks. Additionally, it discusses launching activities and sub-activities, including handling result codes and data returned from sub-activities.