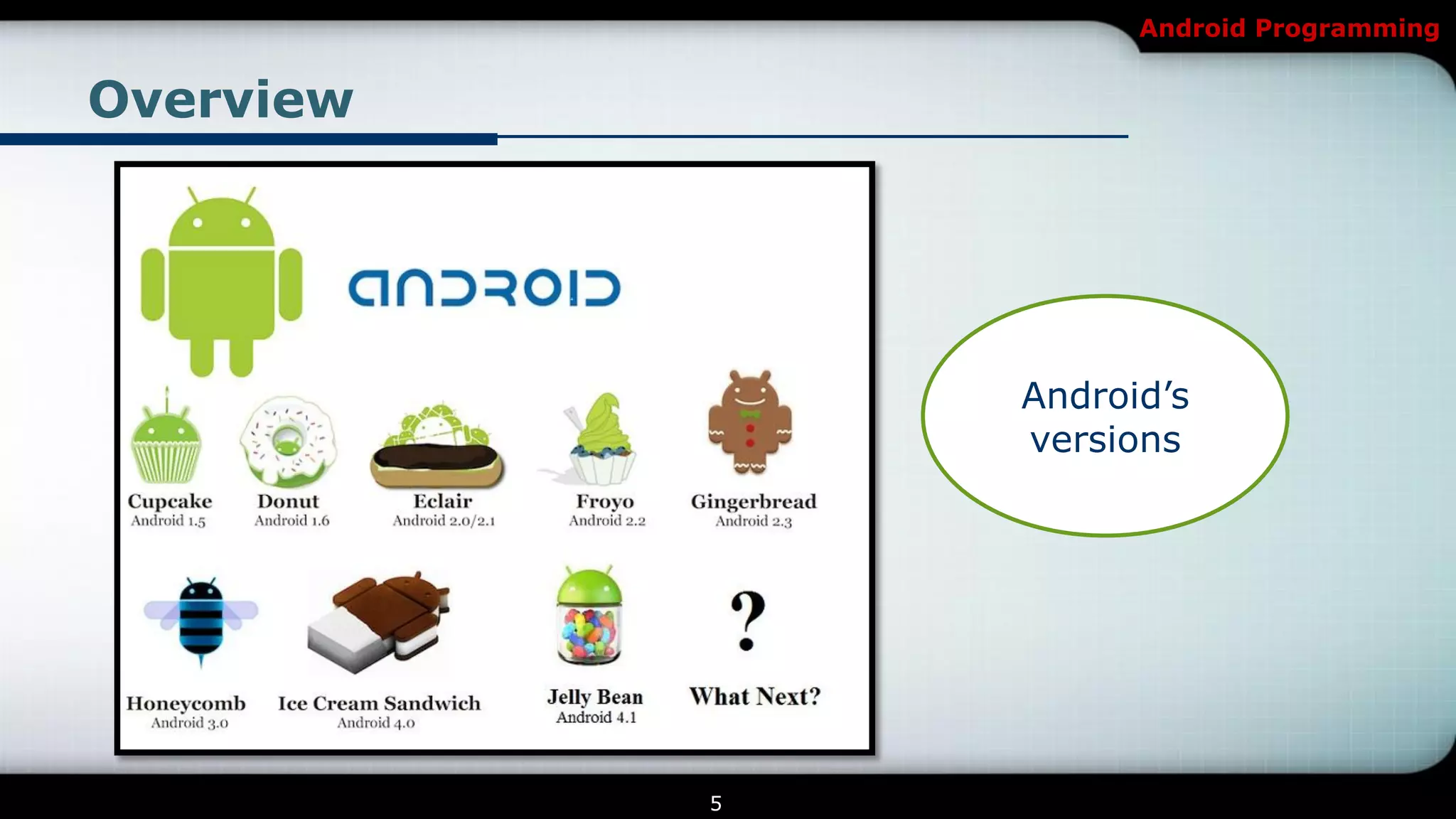
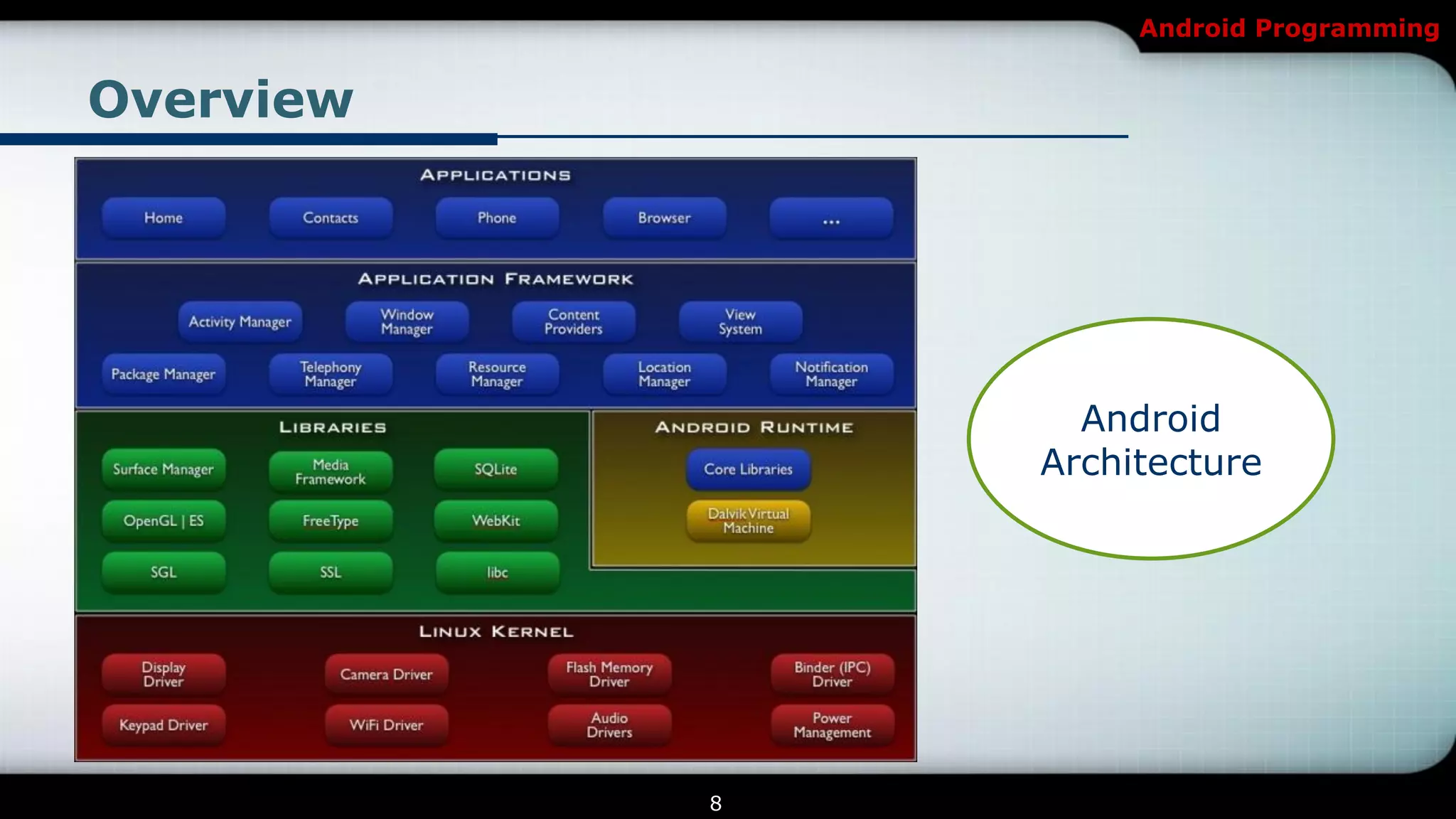
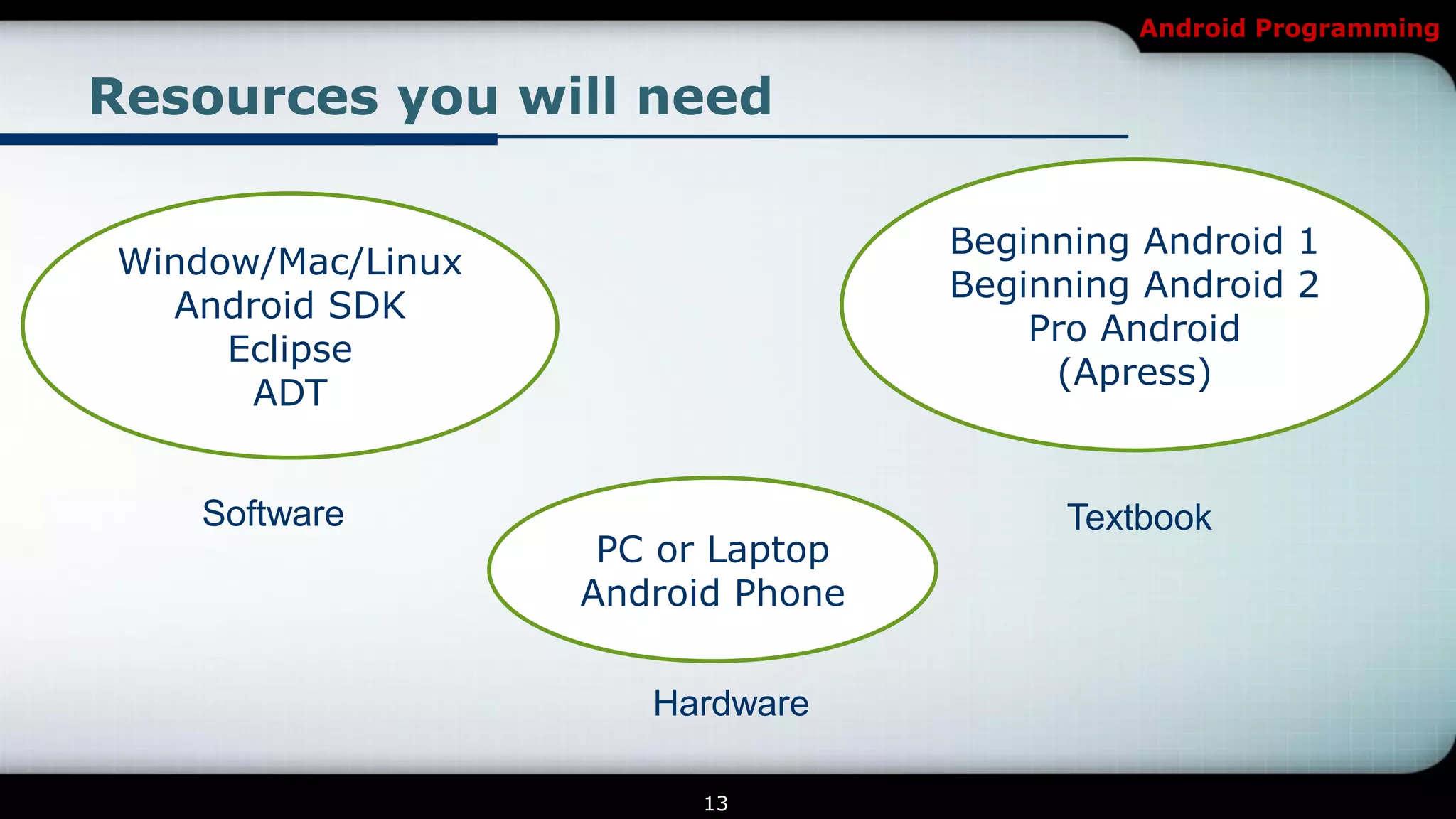
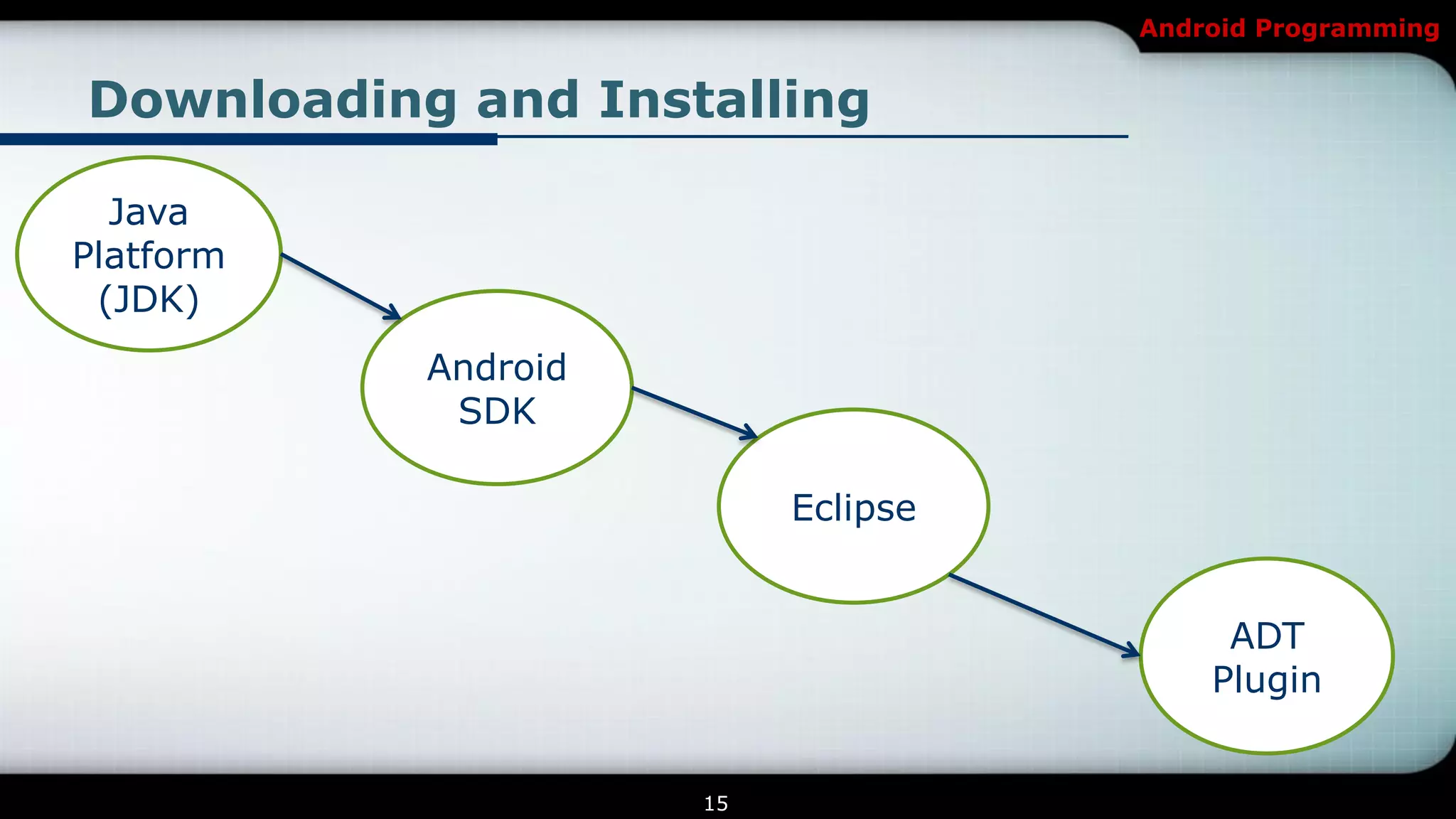
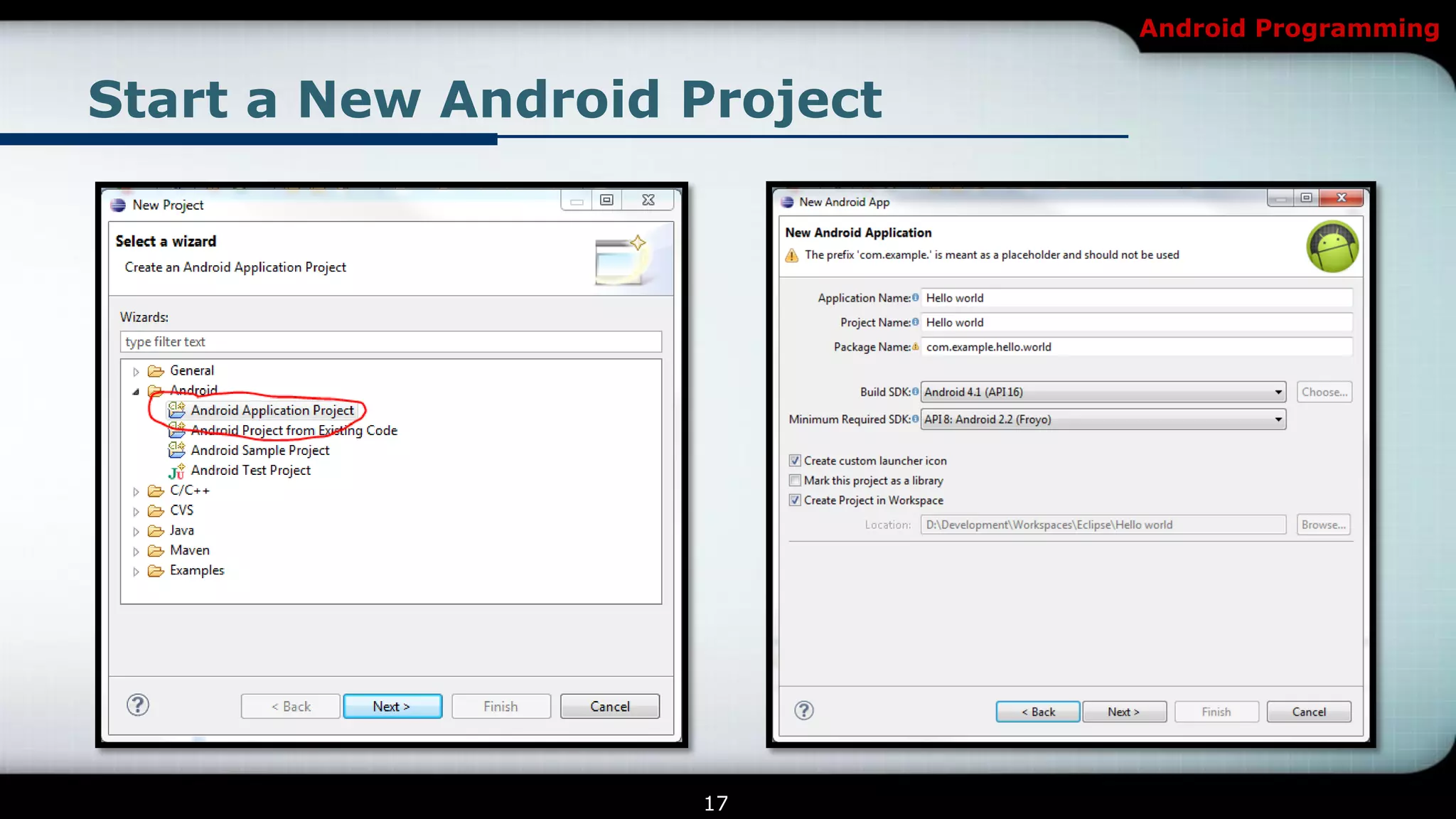
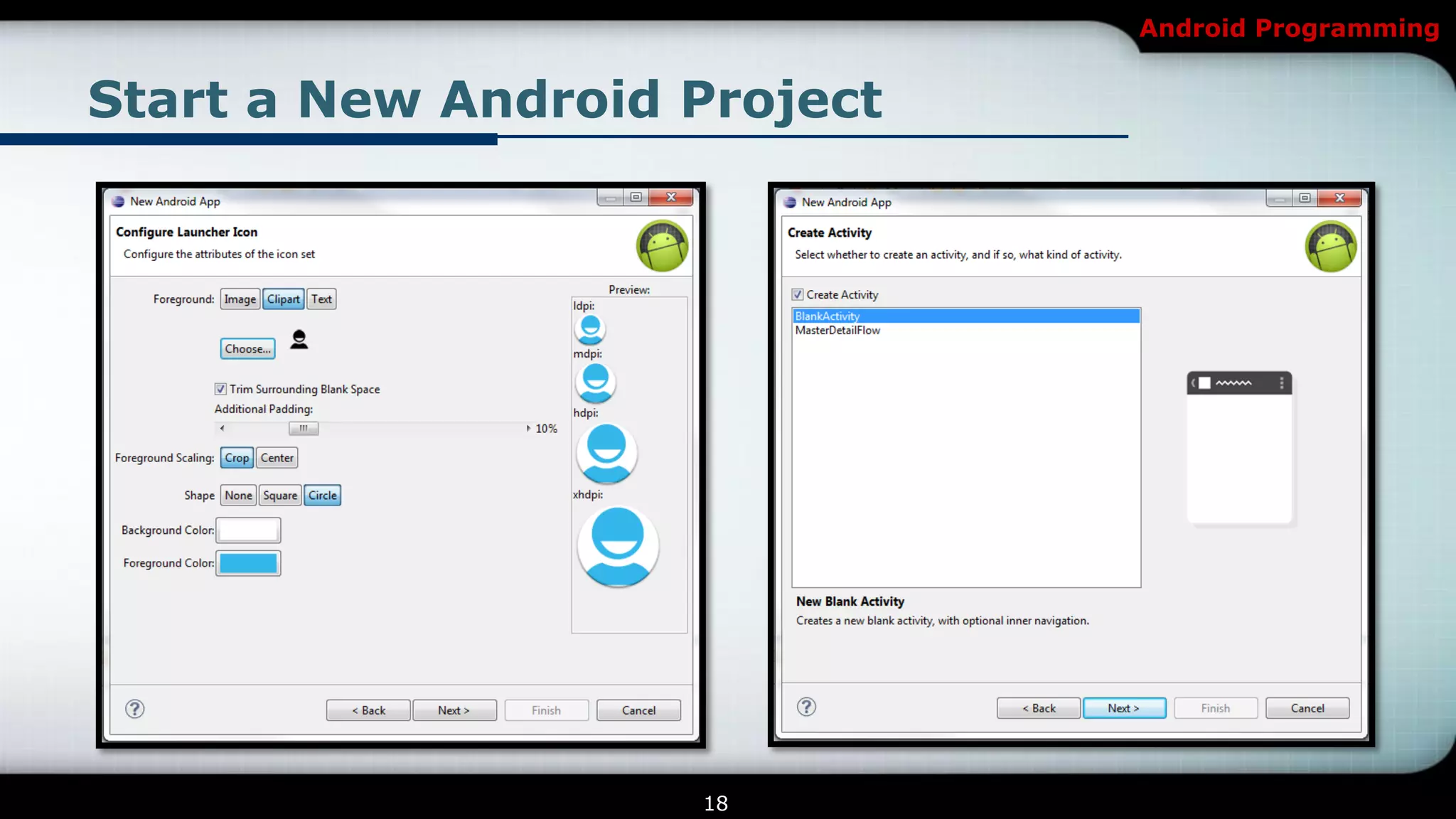
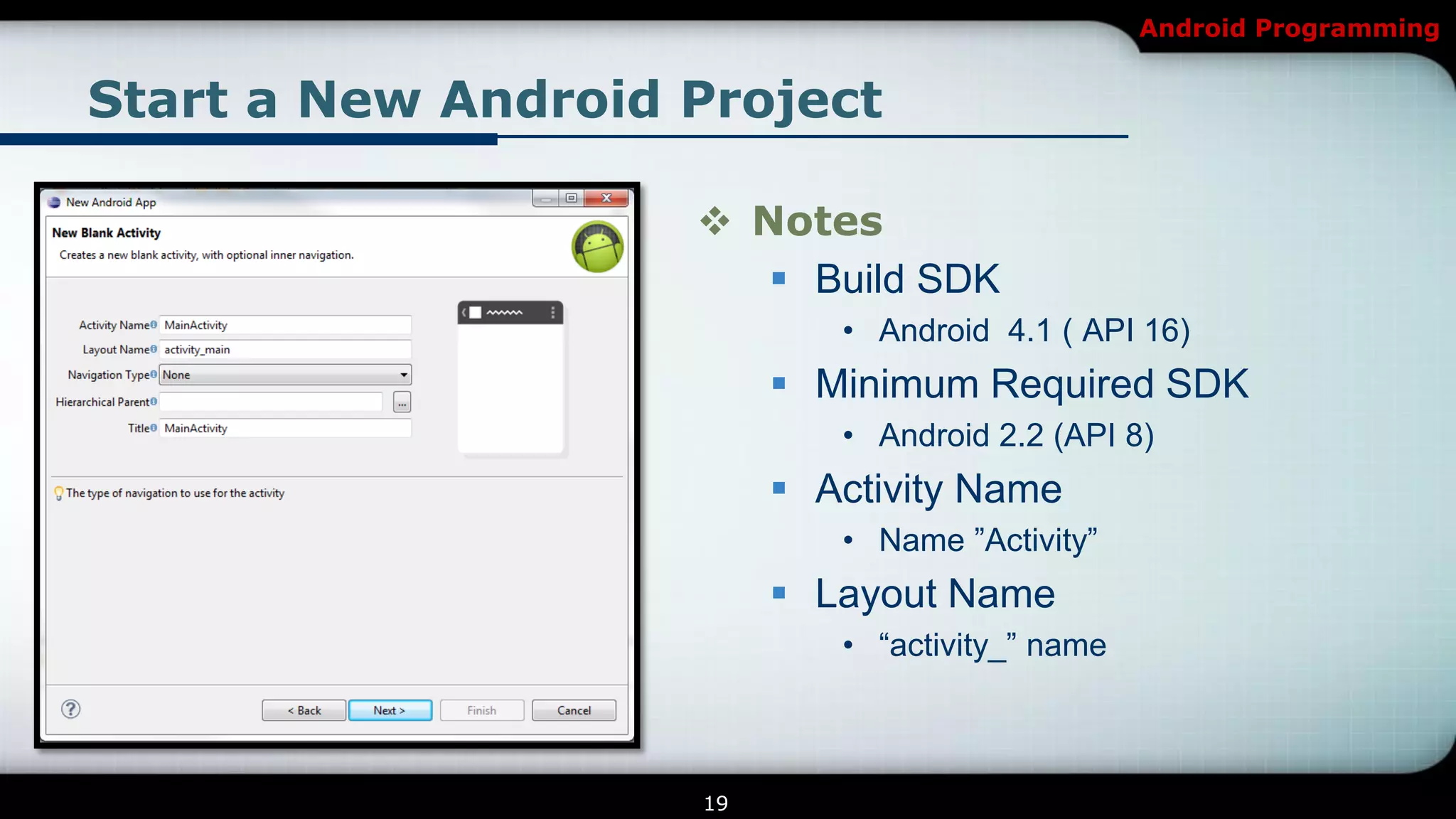
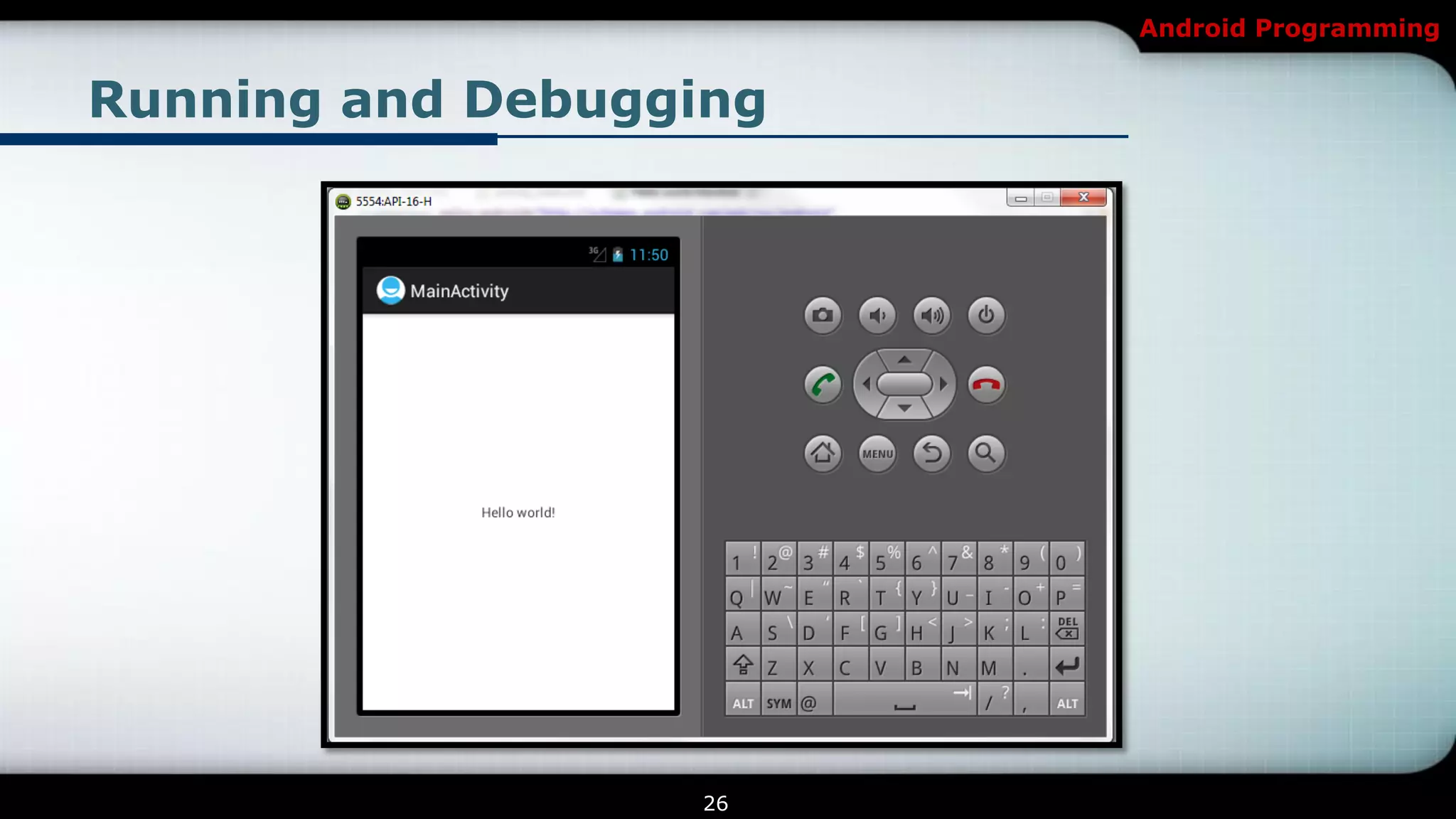
This document provides an introduction and overview of Android programming. It discusses what Android is, how it works, and its architecture. It also covers the Android SDK, Android Development Tools (ADT) plugin for Eclipse, and Android Native Development Kit (NDK). The document explains how to set up a development environment, start a new Android project, and run and debug apps. It provides details on project structure and outlines an example exercise to create login fields and buttons in an app.