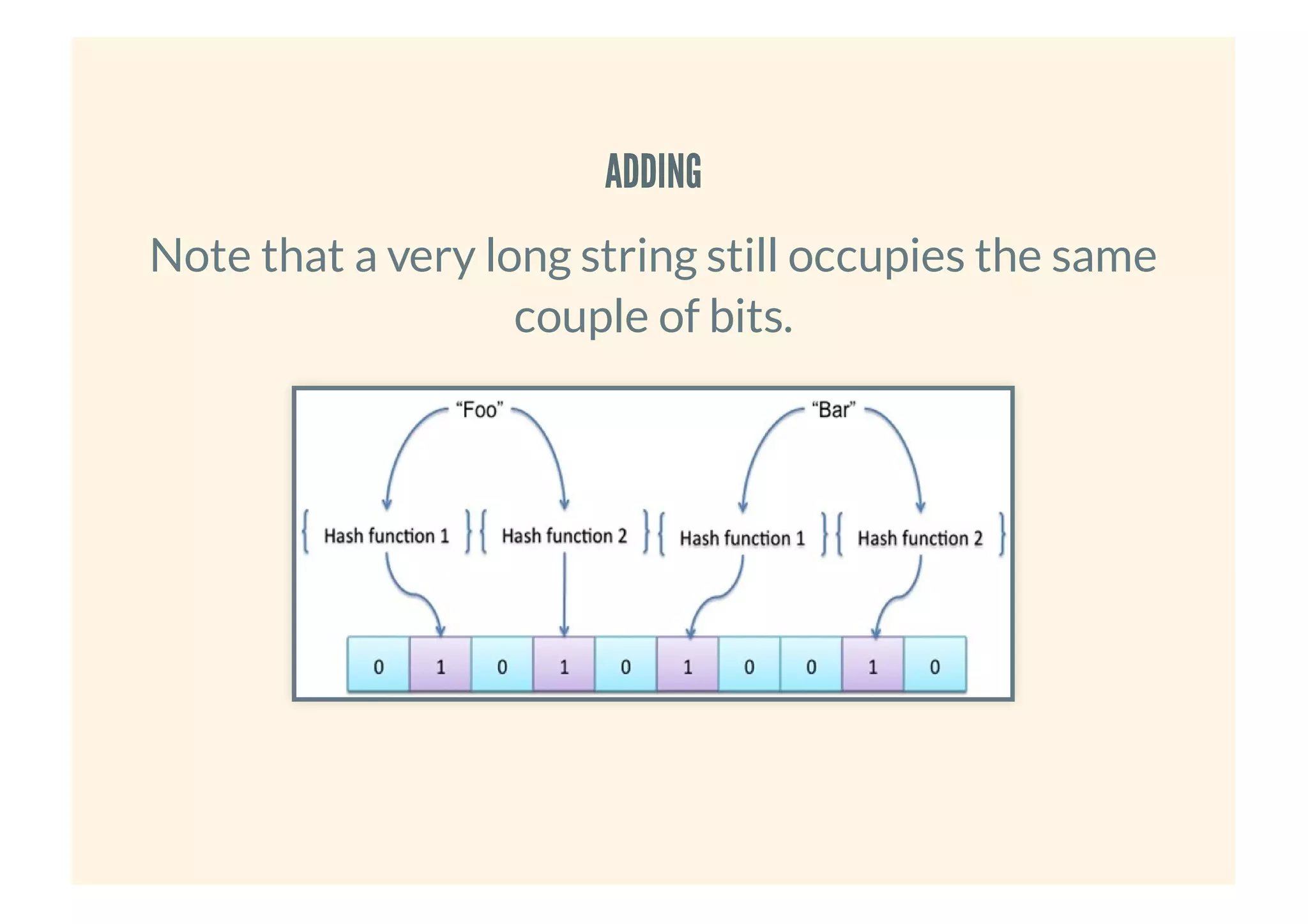
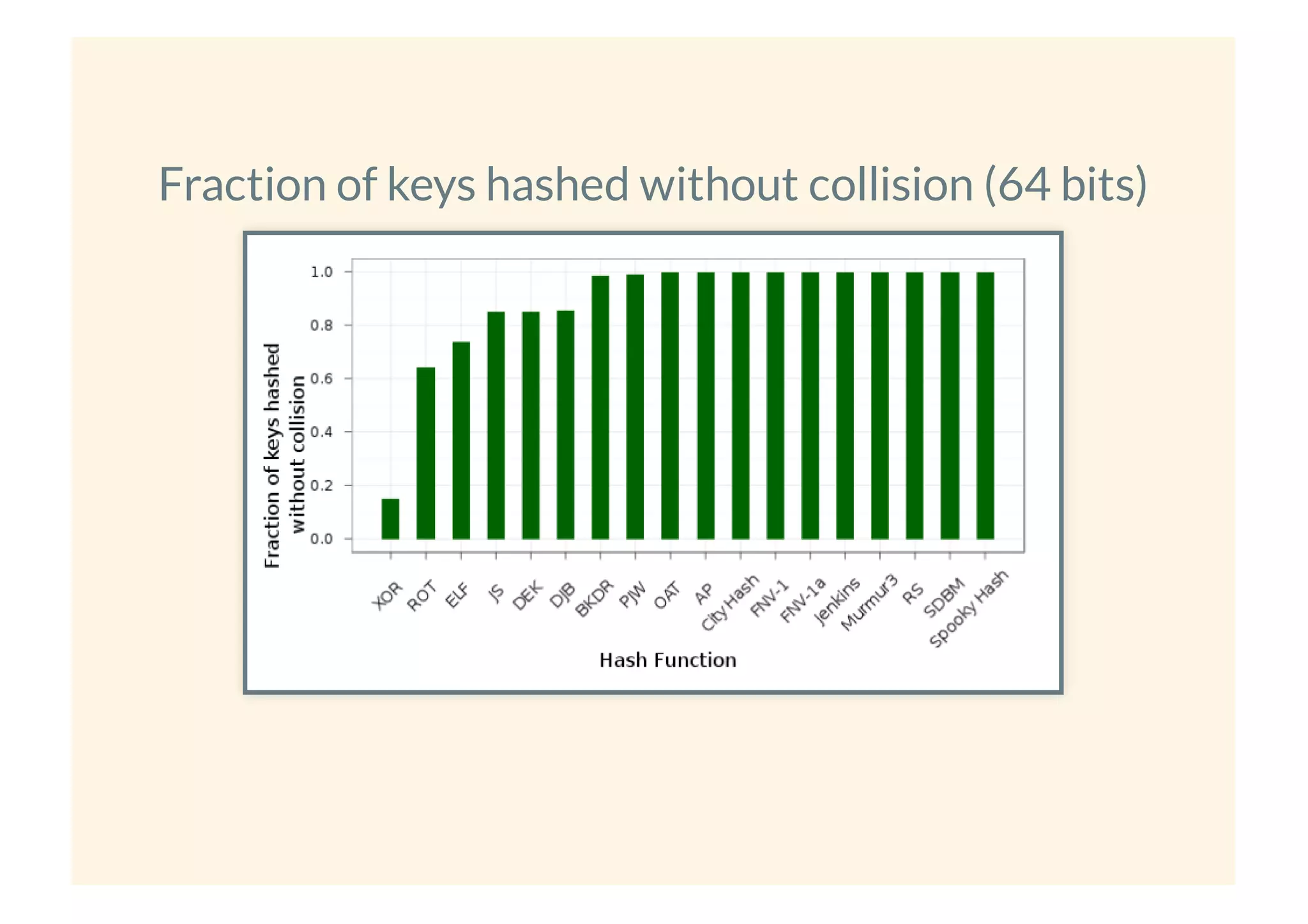
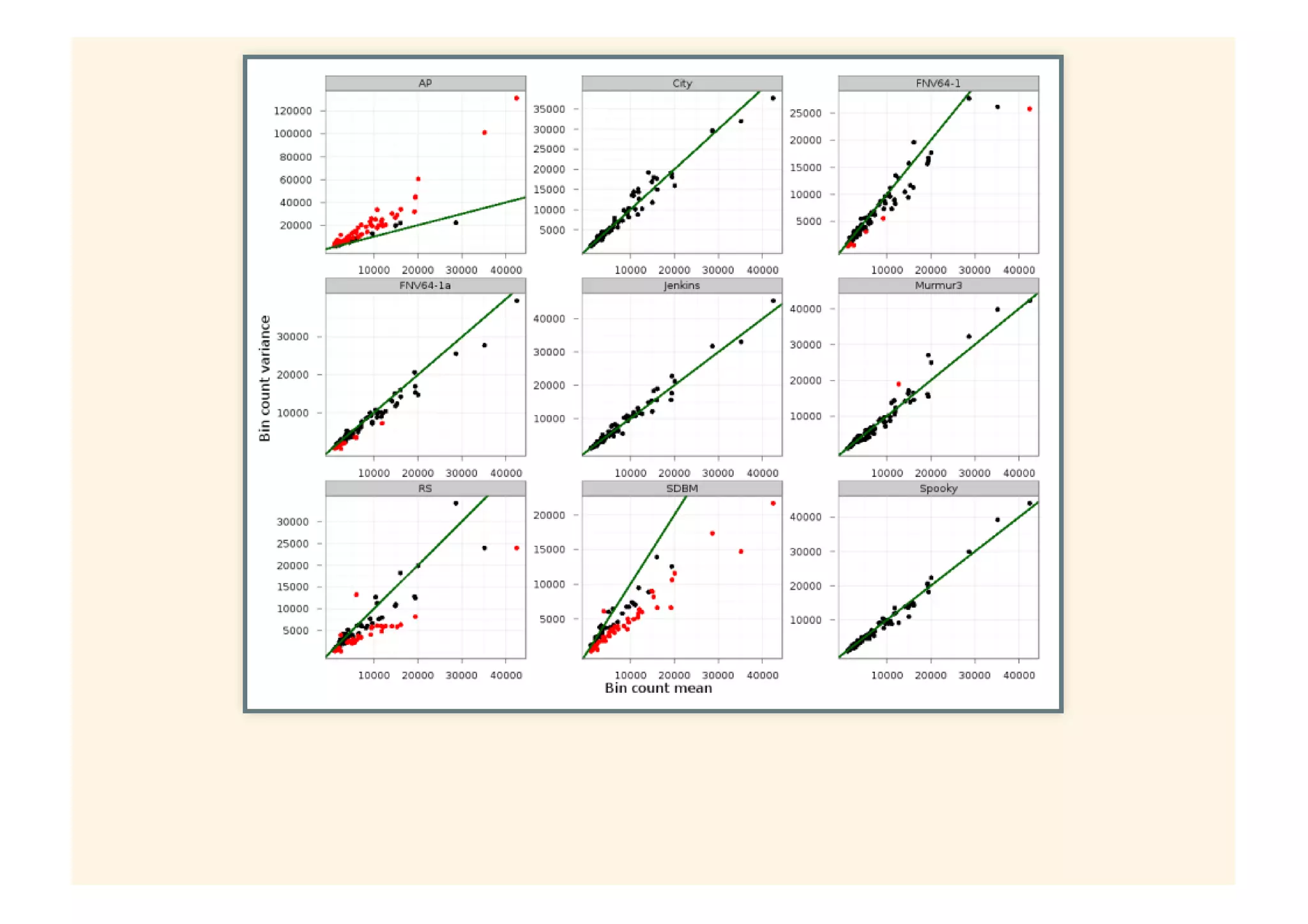
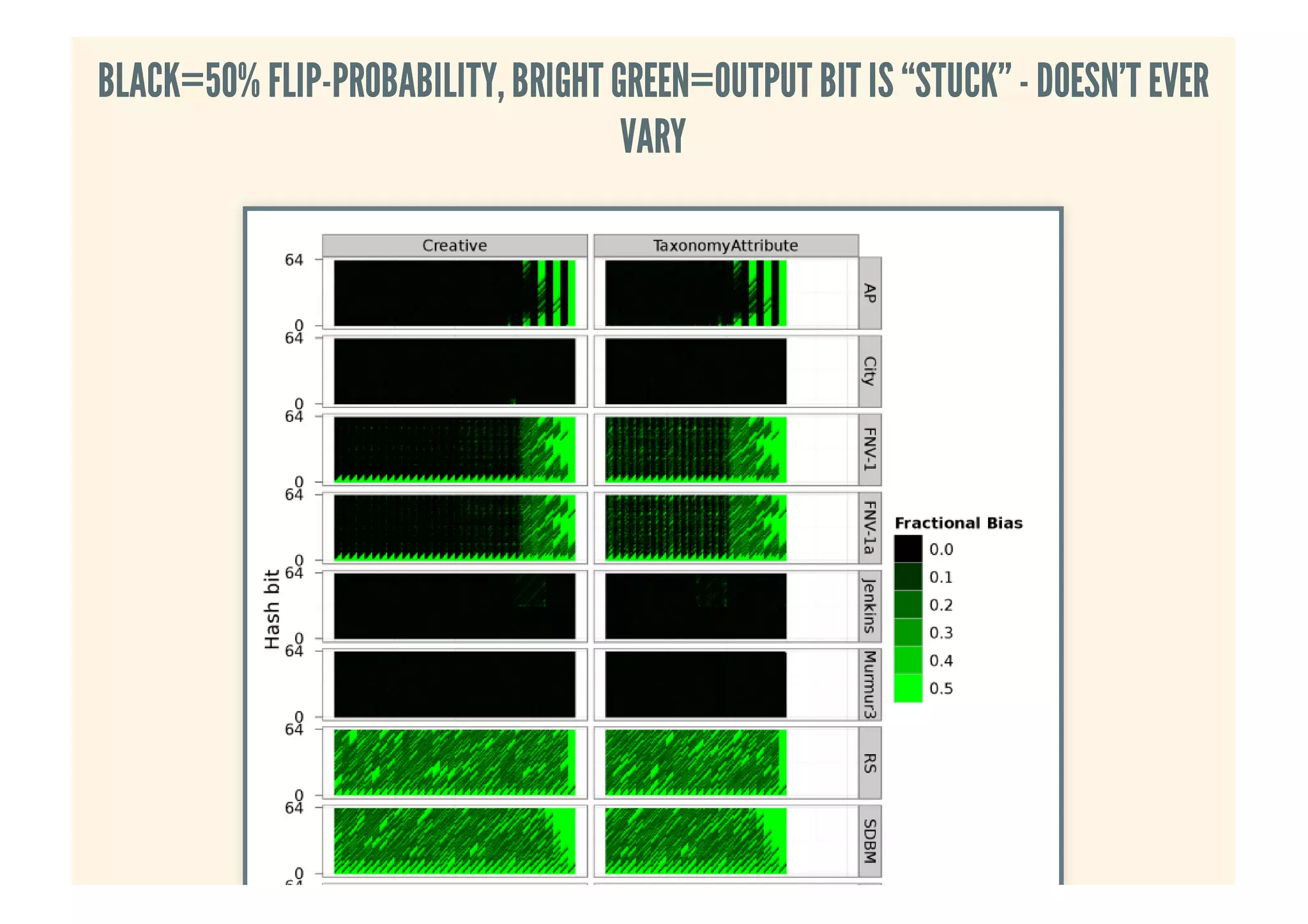
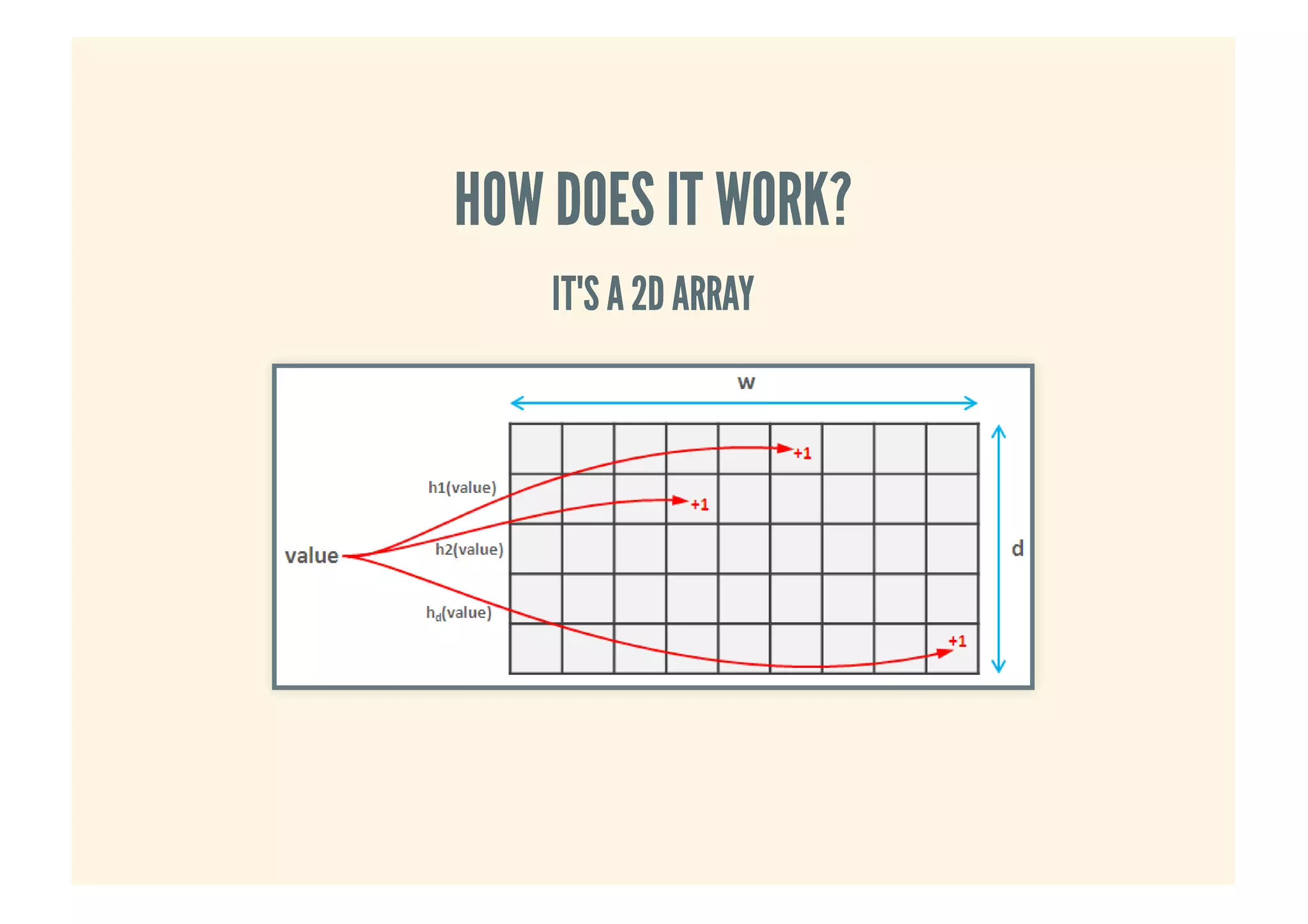
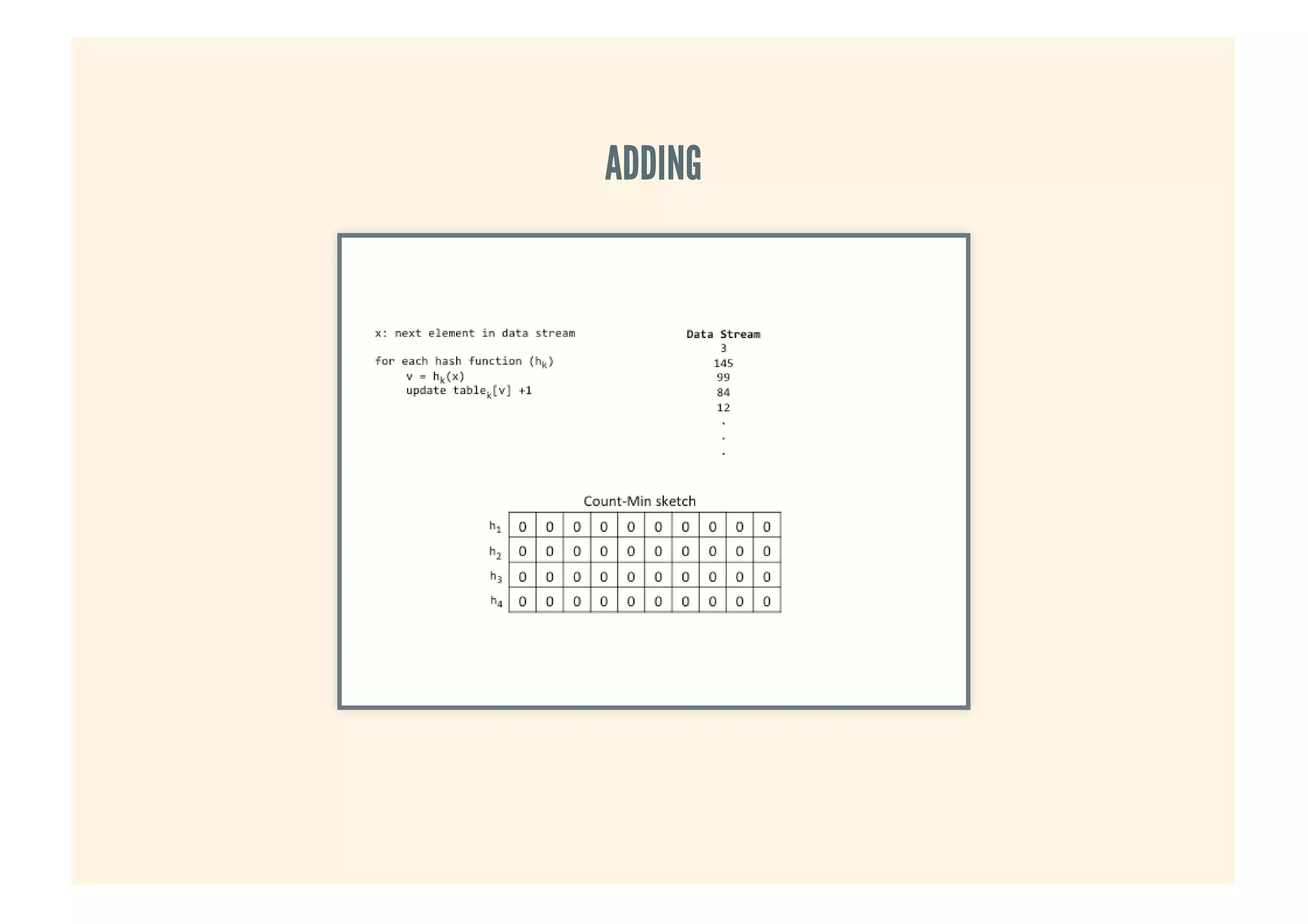
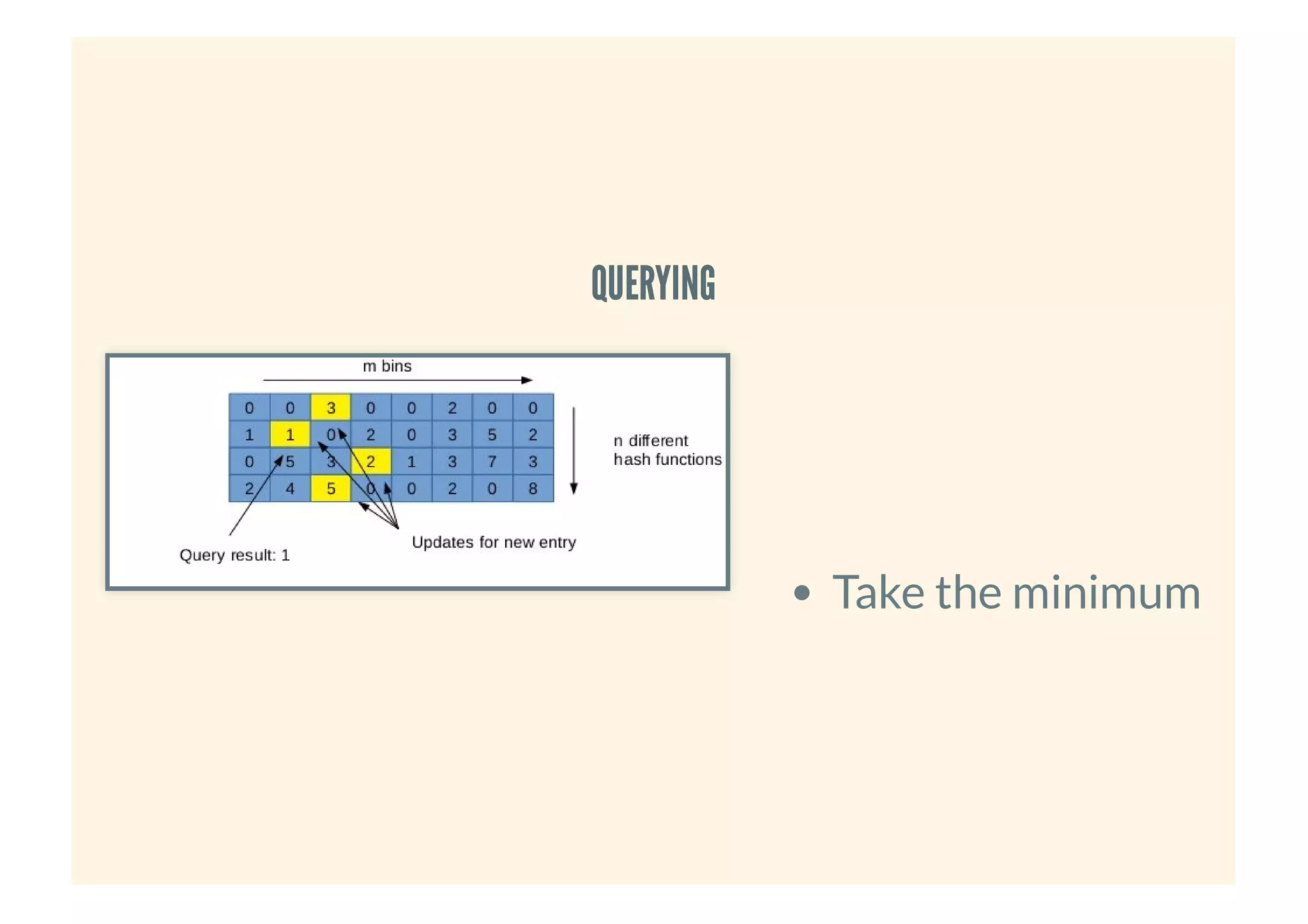
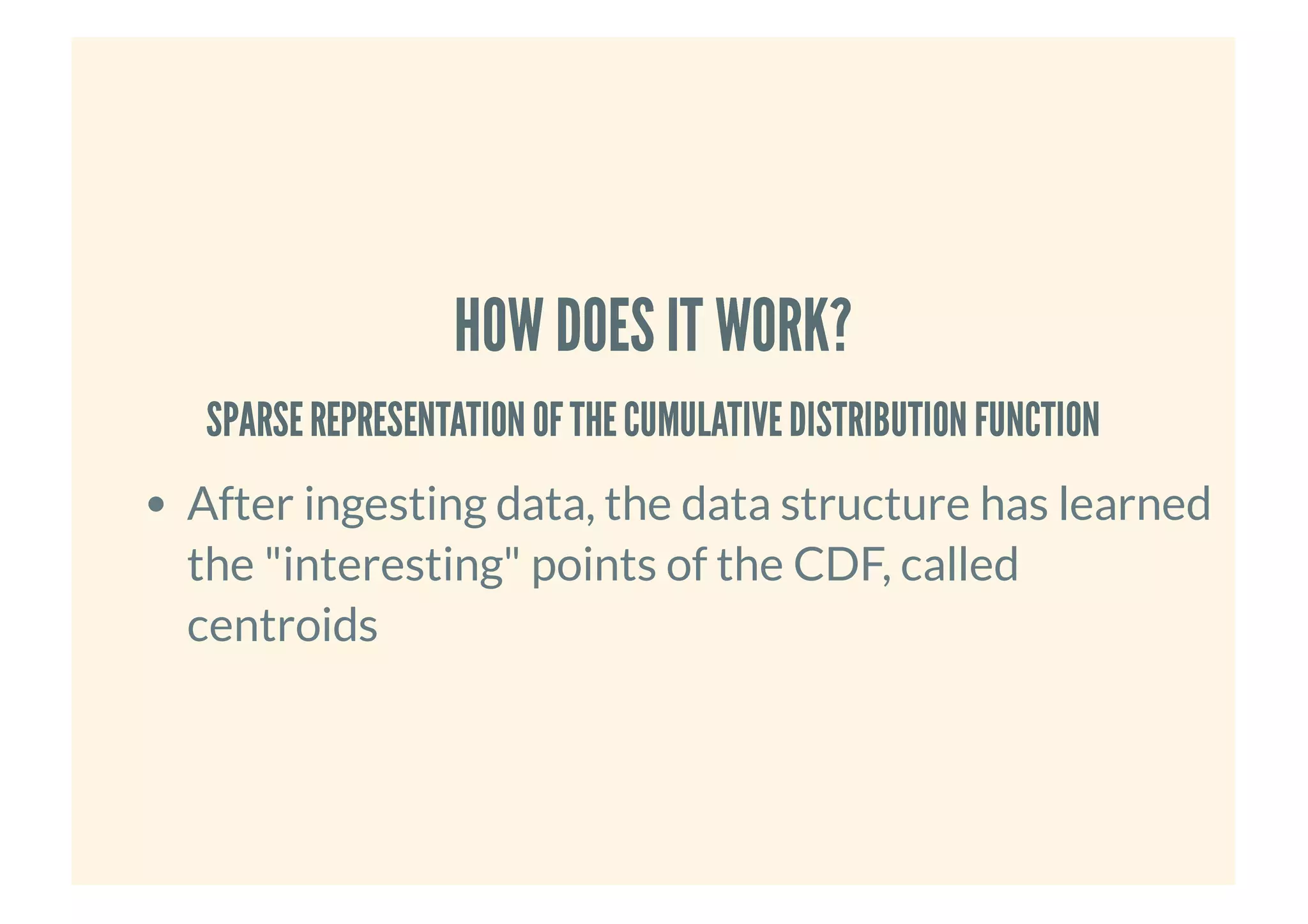
This document provides an overview of probabilistic data structures. It describes how they trade accuracy for speed or space by providing approximate results. Specific probabilistic data structures covered include Bloom filters, count-min sketch, t-digest, and hyperloglog. Bloom filters are used for set membership tests and can return false positives but not false negatives. Count-min sketch counts frequencies/popular items with a two-dimensional array. T-digest approximates quantiles through a sparse representation of the cumulative distribution function. Hyperloglog estimates cardinality by observing leading zeros in binary representations.













































![BUCKETINGBUCKETING
number: 13,200,393
hash: 2,005,620,294
bits: [100010110101011001000110]
100010110101011001 000110
---------------|------
value index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-190918035040/75/An-introduction-to-probabilistic-data-structures-69-2048.jpg)
![BUCKETINGBUCKETING
number: 13,200,393
hash: 2,005,620,294
bits: [100010110101011001000110]
value: number of zeros +1 (rtl)
100010110101011001 000110
---------------|------
value index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-190918035040/75/An-introduction-to-probabilistic-data-structures-70-2048.jpg)
![BUCKETINGBUCKETING
number: 13,200,393
hash: 2,005,620,294
bits: [100010110101011001000110]
value: number of zeros +1 (rtl)
index: The lowest b bits used to determine the
index of the register whose value is to be updated.
(m=2b)
100010110101011001 000110
---------------|------
value index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-190918035040/75/An-introduction-to-probabilistic-data-structures-71-2048.jpg)
![BUCKETINGBUCKETING
number: 13,200,393
hash: 2,005,620,294
bits: [100010110101011001000110]
value: number of zeros +1 (rtl)
index: The lowest b bits used to determine the
index of the register whose value is to be updated.
(m=2b)
each bucket will serve as an "estimator"
100010110101011001 000110
---------------|------
value index](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/slides-190918035040/75/An-introduction-to-probabilistic-data-structures-72-2048.jpg)











