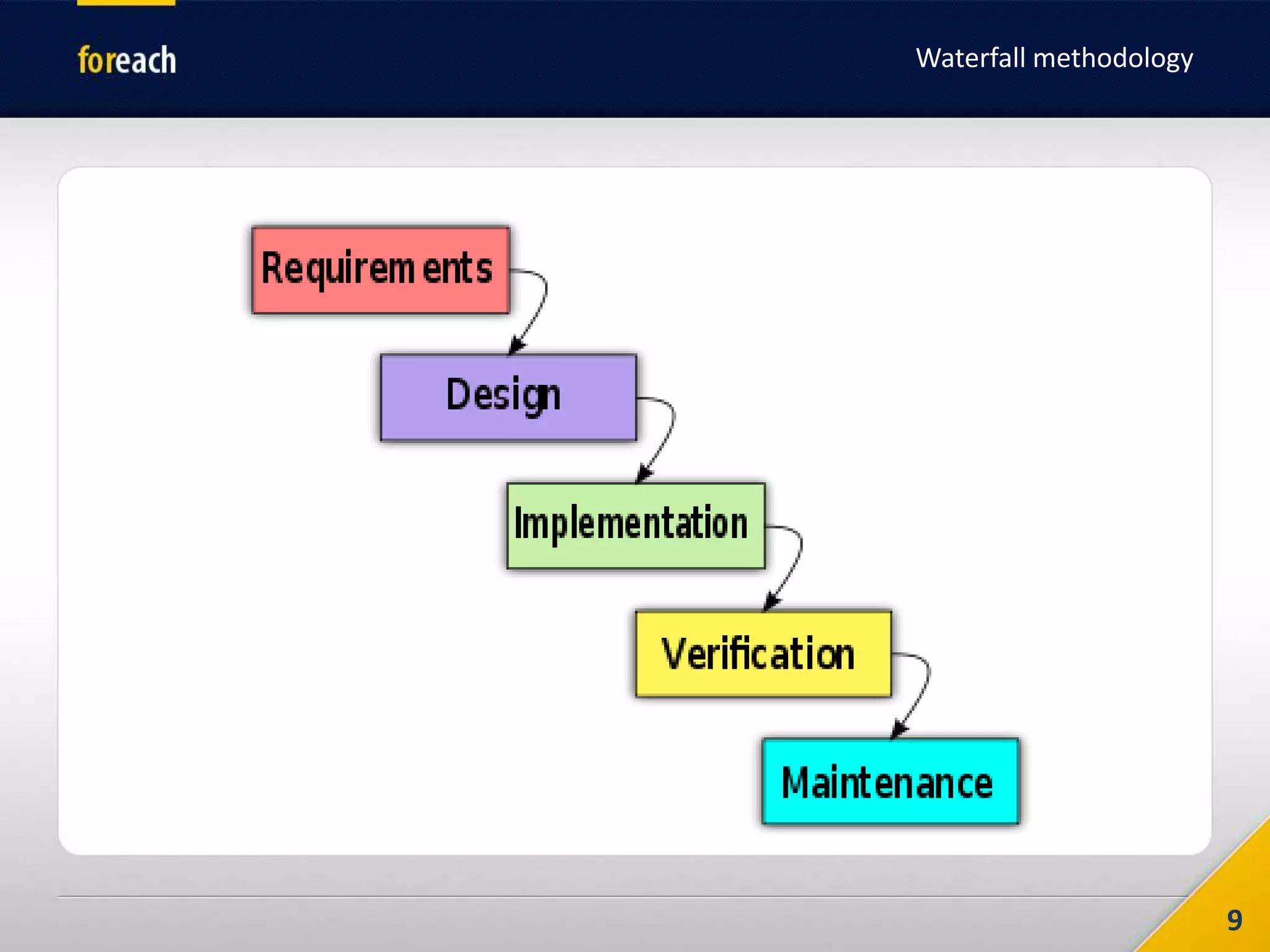
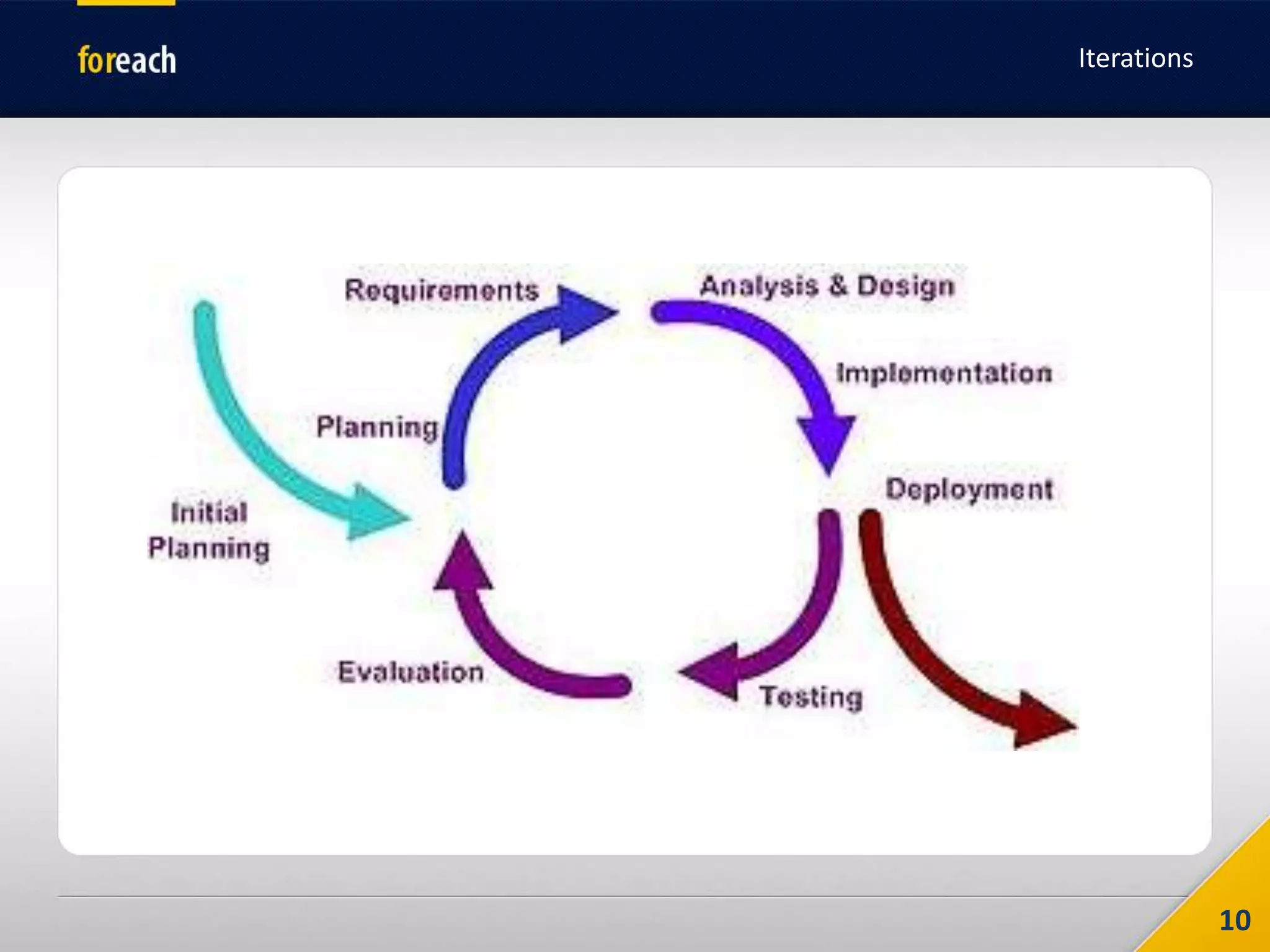
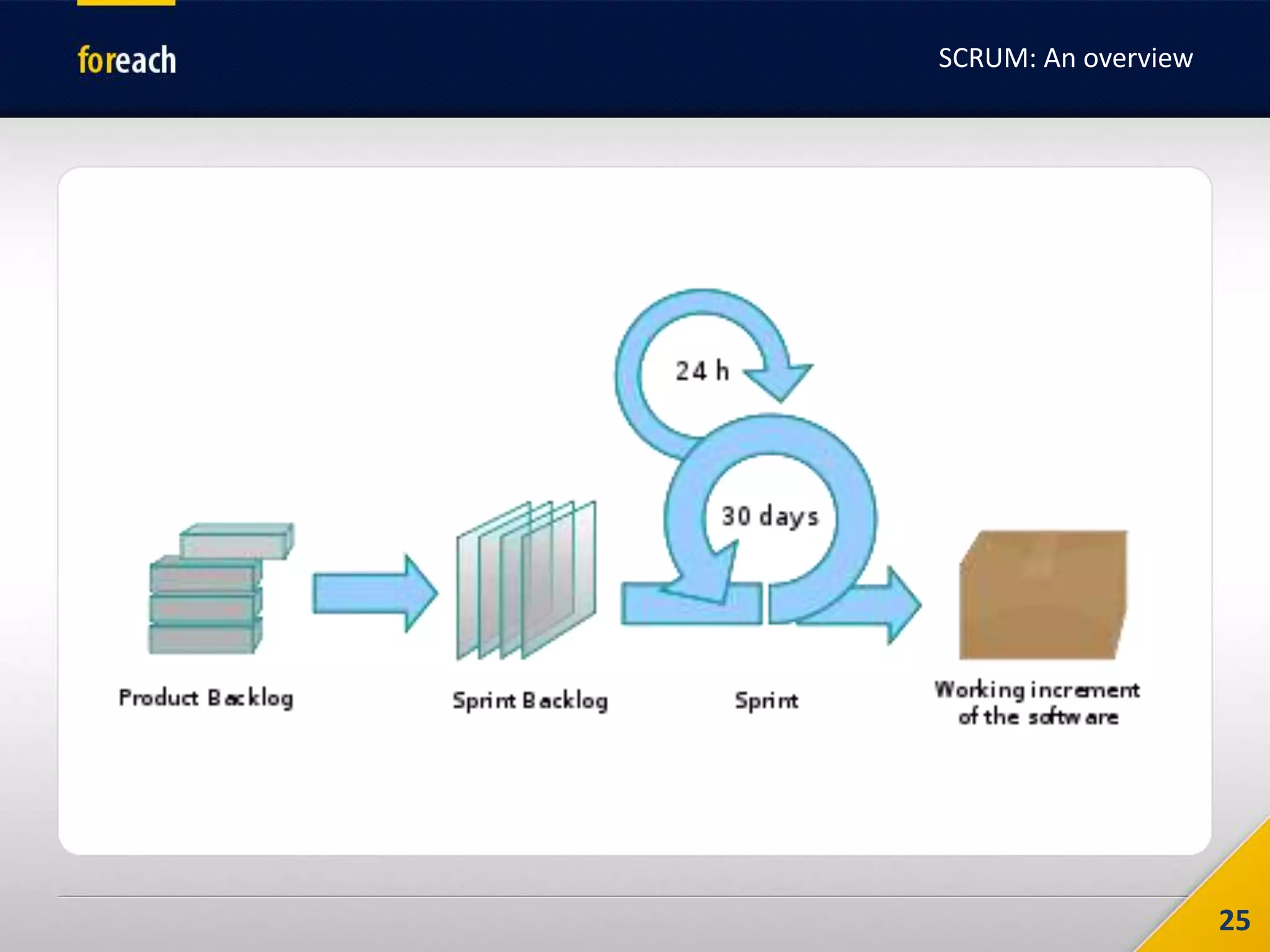
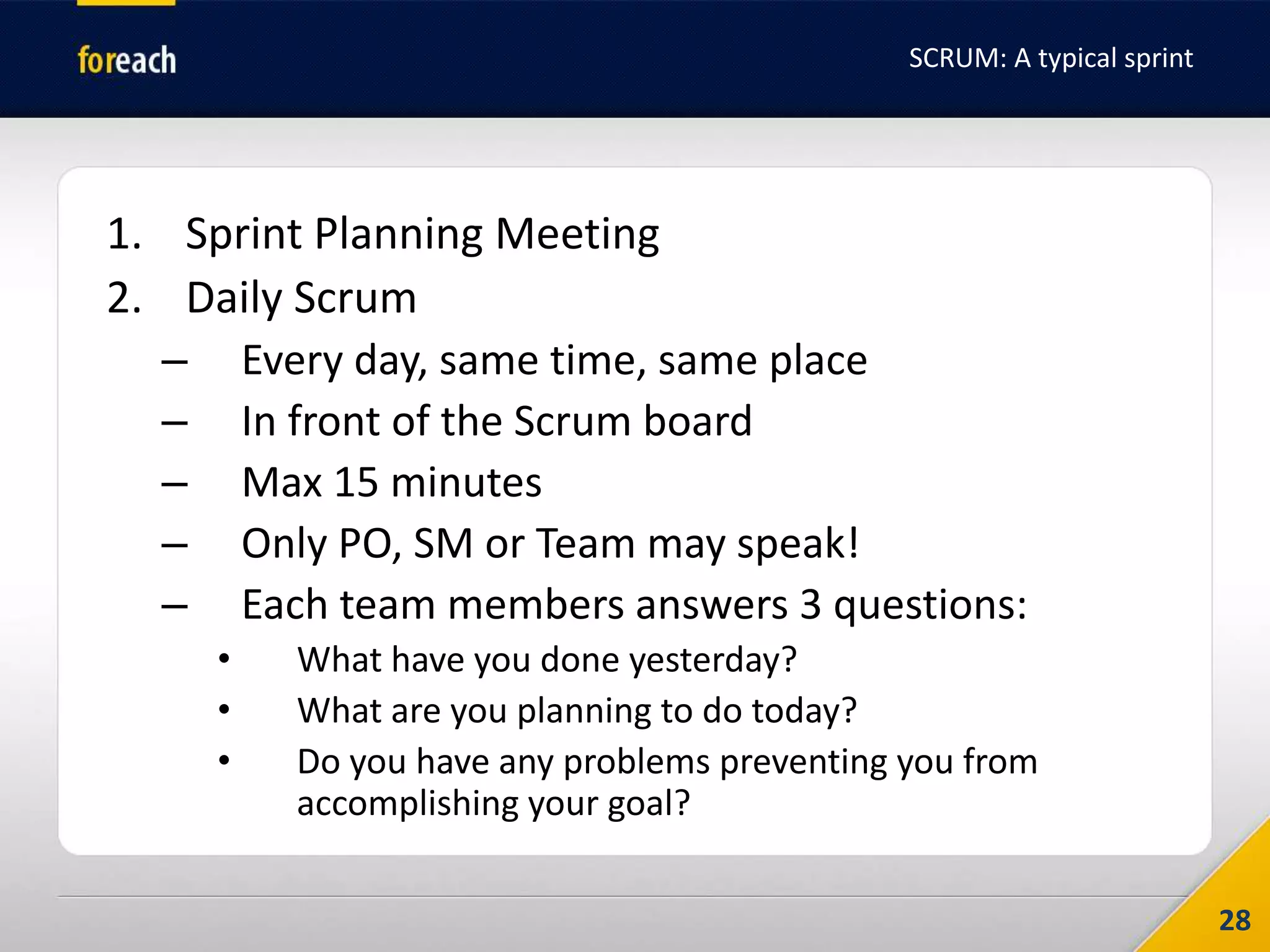
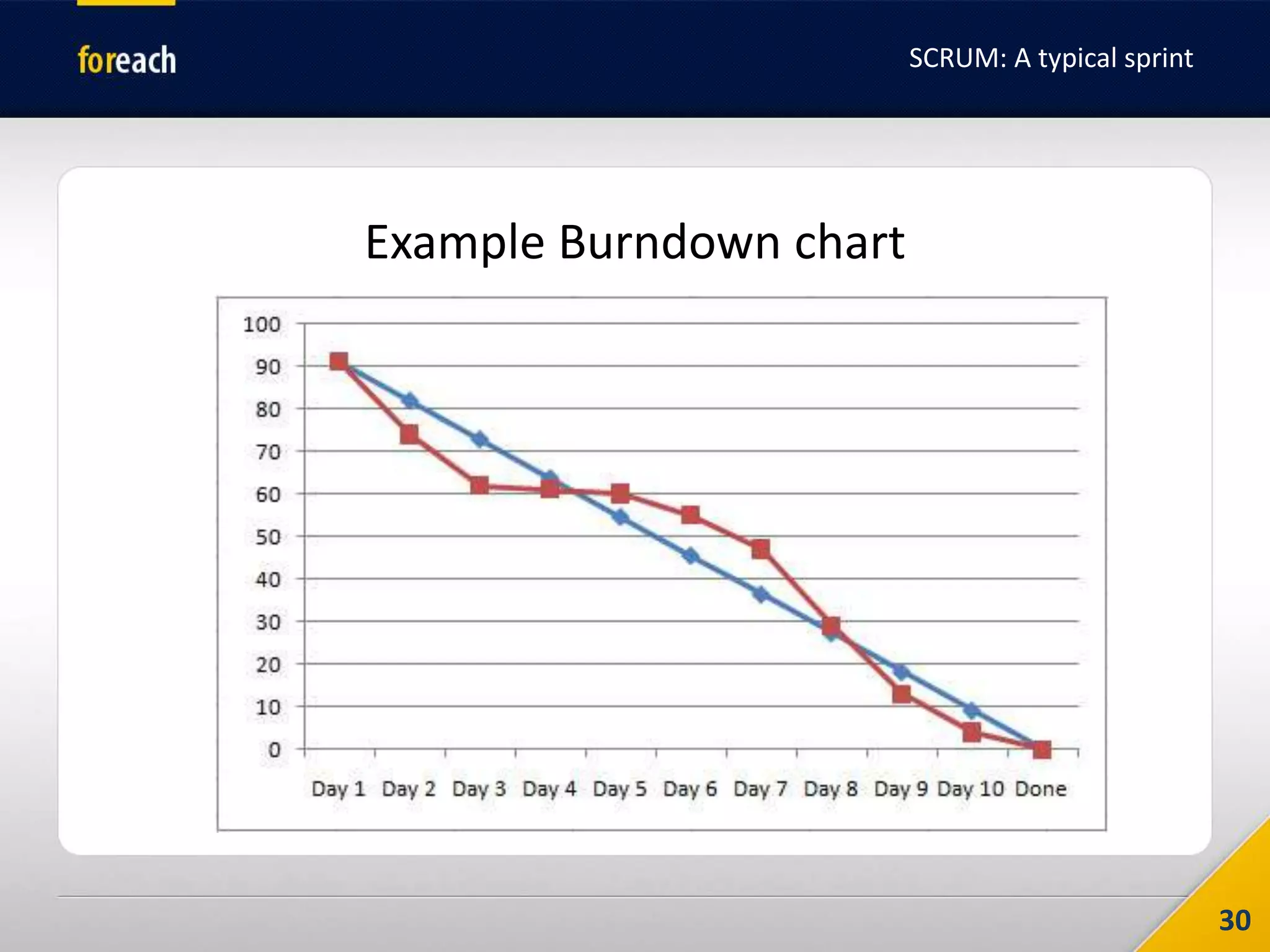
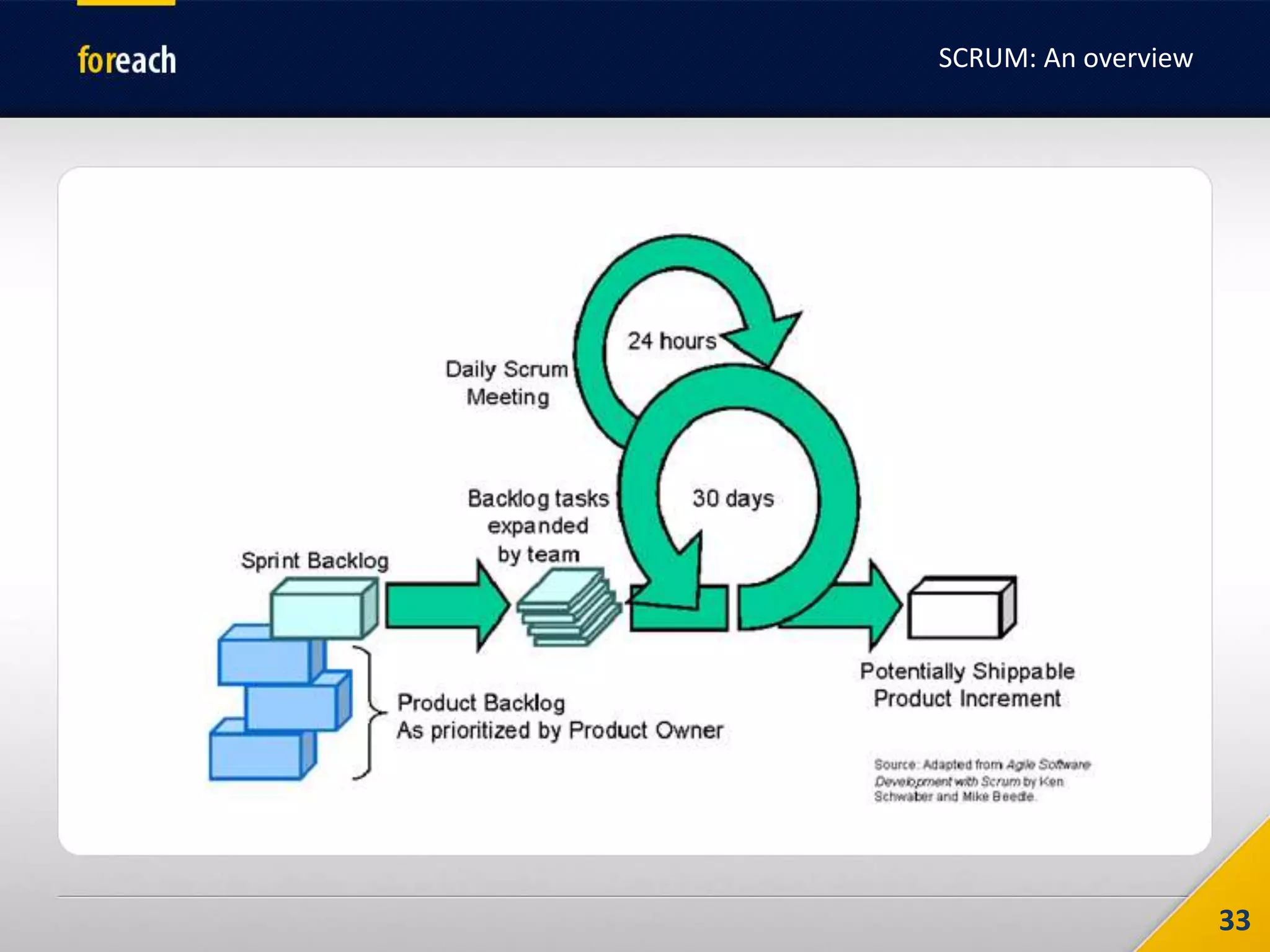
The document outlines the fundamentals of Agile development, focusing on the Agile Manifesto established in 2001 which emphasizes individuals, working software, customer collaboration, and adaptability to change. It covers methodologies such as Scrum and Kanban, highlighting roles, processes, and the importance of iterative development, planning, and user stories. Additionally, it emphasizes the need for self-discipline and commitment within teams to effectively implement Agile practices.