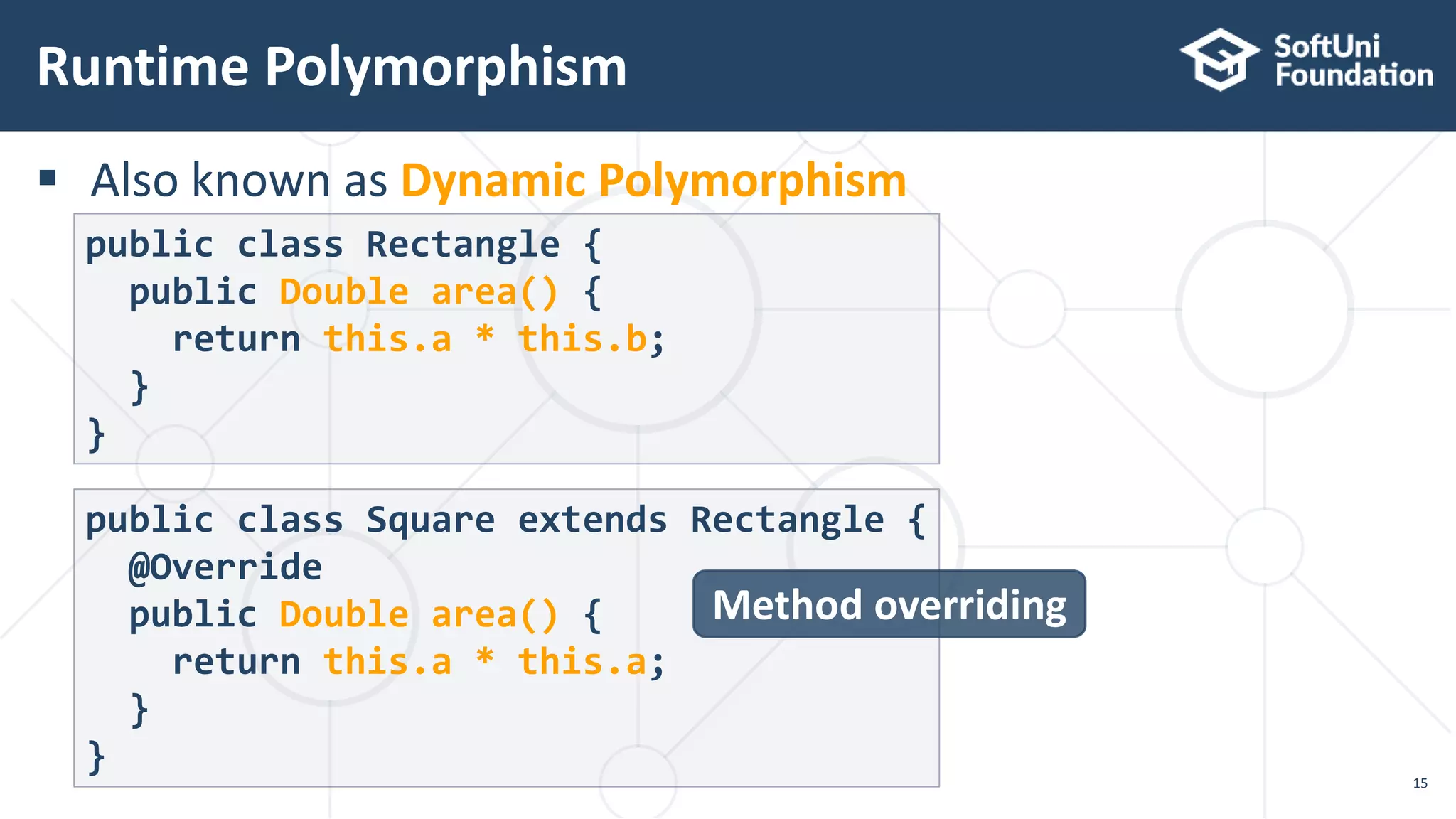
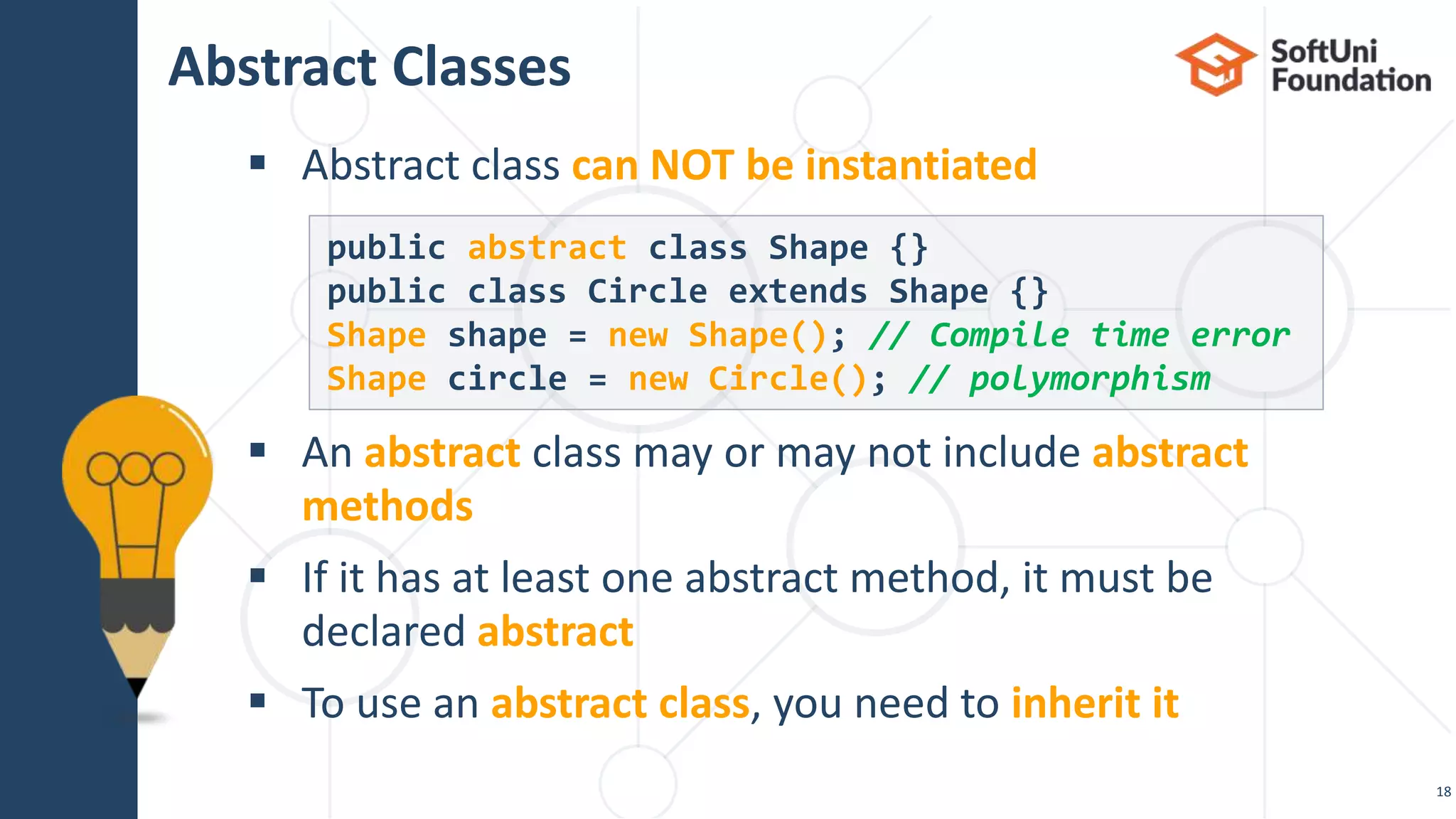
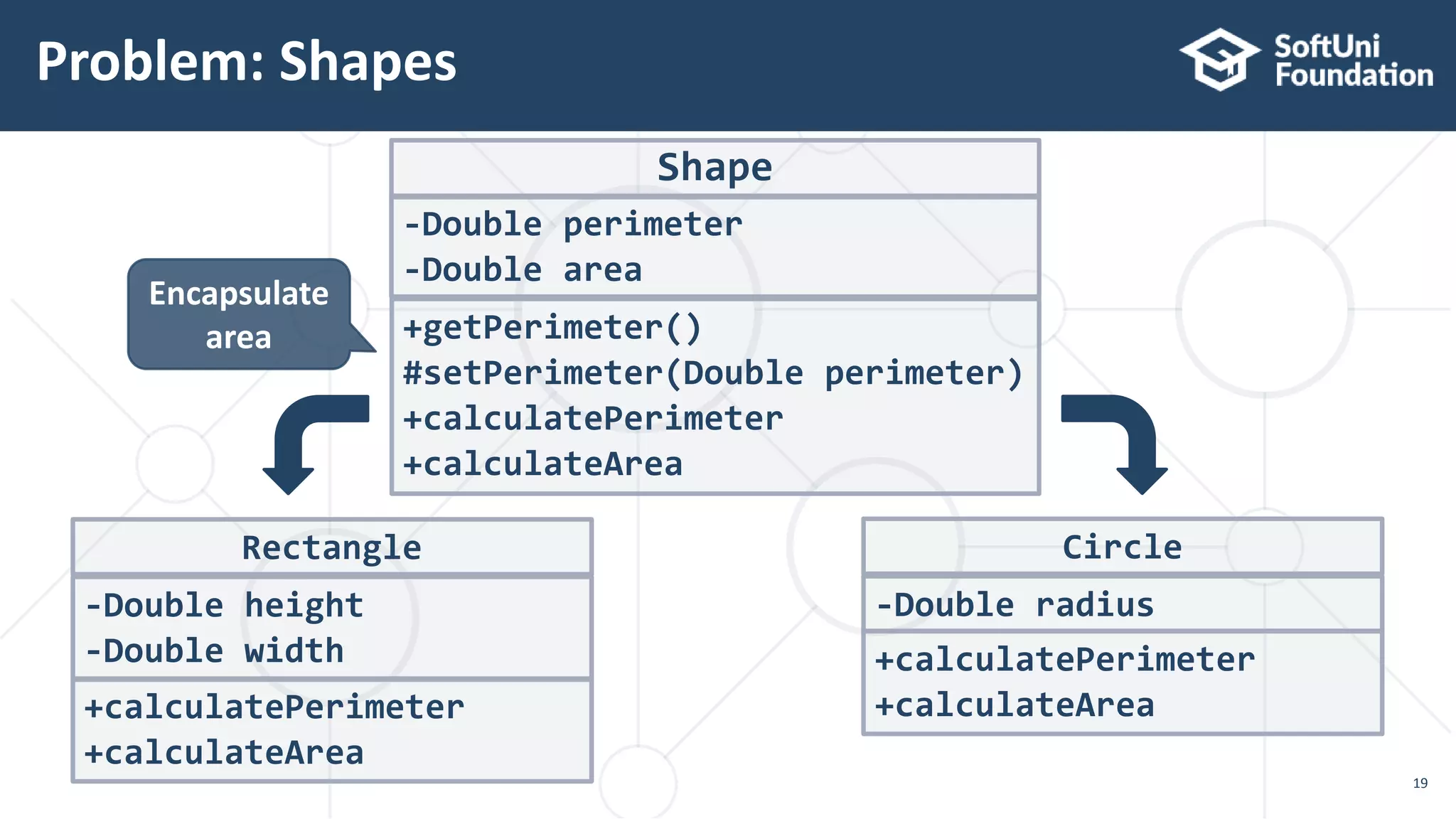
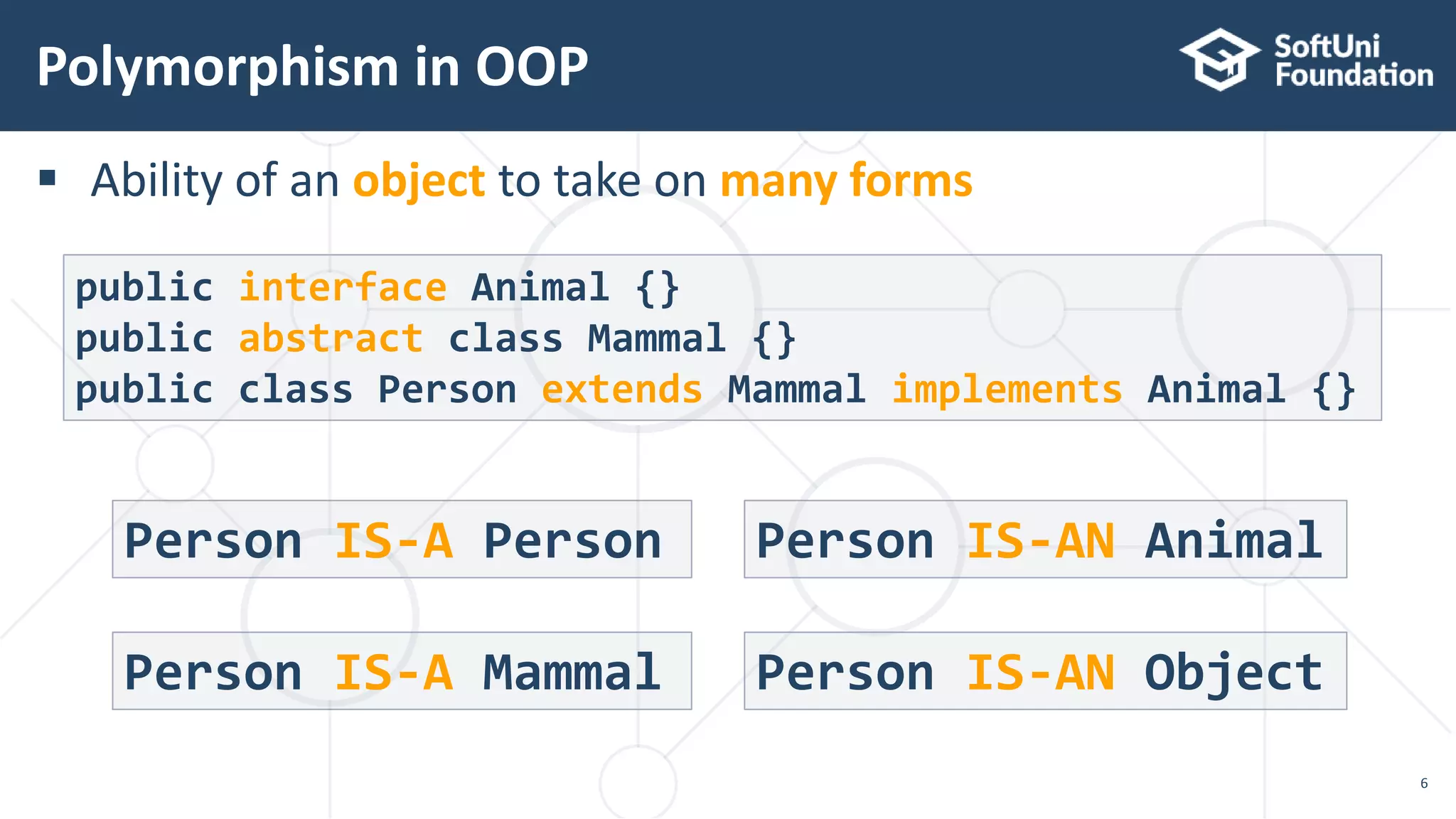
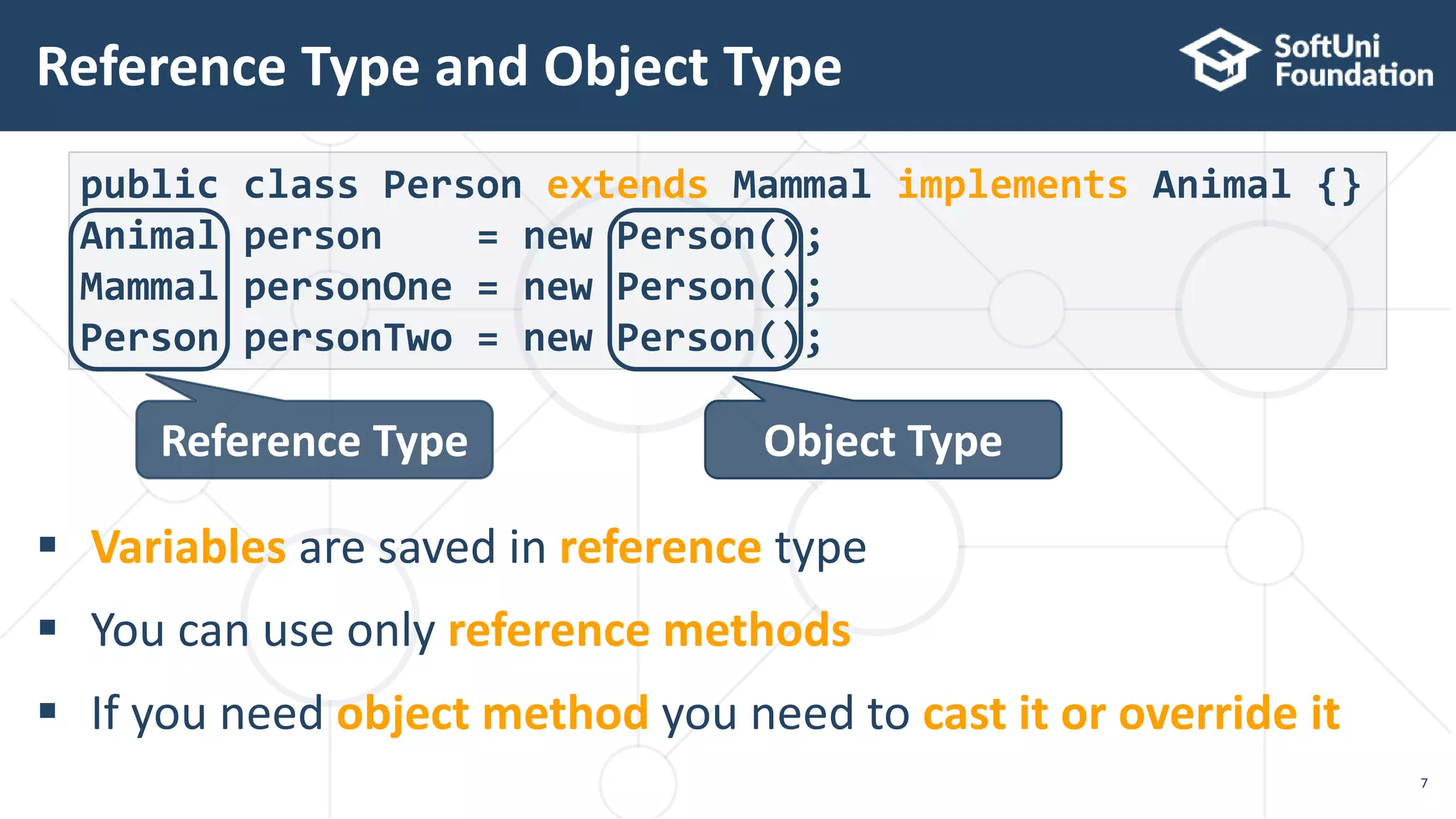
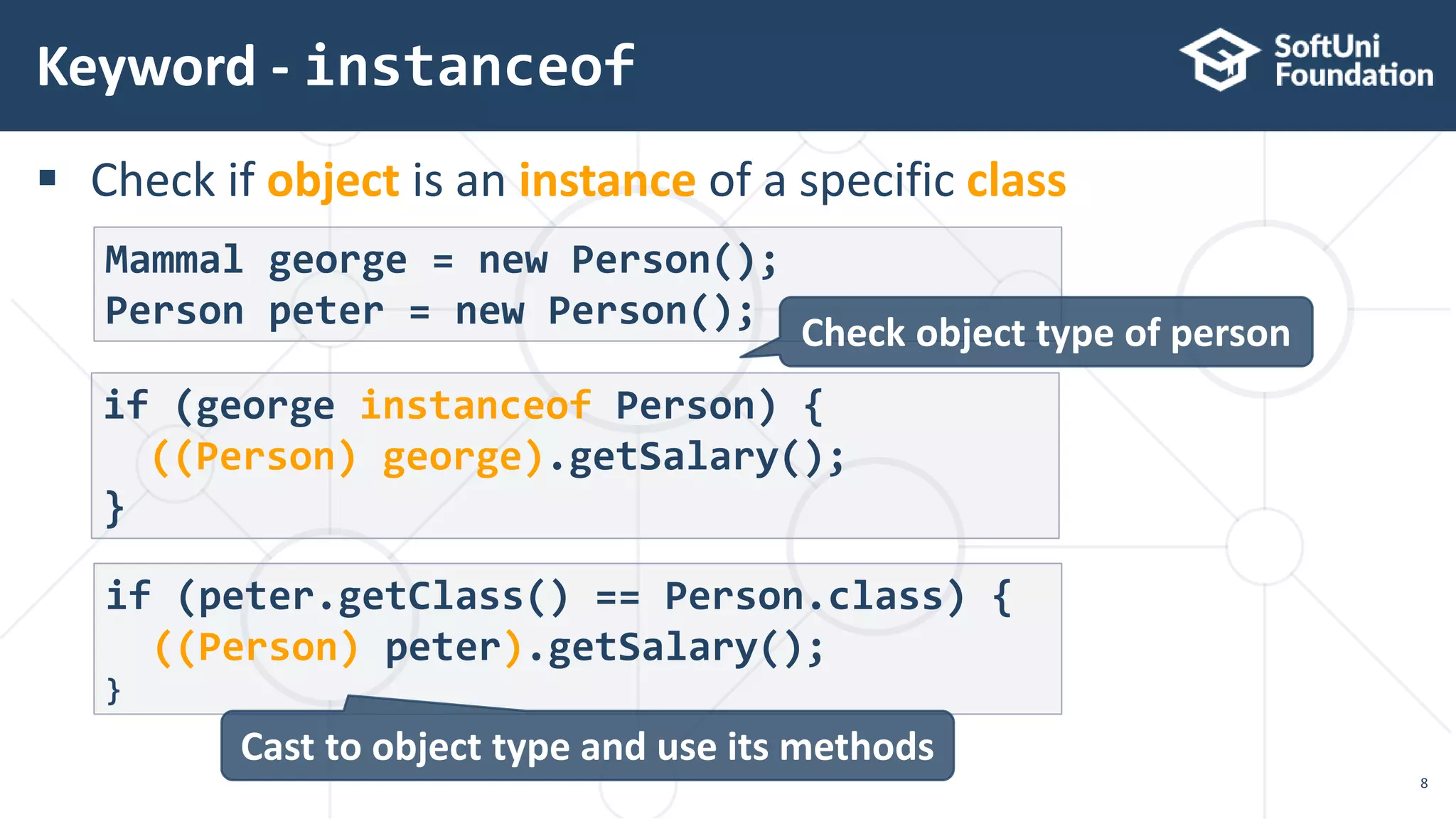
This document discusses polymorphism, abstract classes, and abstract methods. It defines polymorphism as an object's ability to take on many forms and describes how it allows reference variables to refer to objects of child classes. It also distinguishes between method overloading and overriding, and explains the rules for each. Abstract classes are introduced as classes that cannot be instantiated directly but can be inherited from, and it is noted they may or may not contain abstract methods.



![ Runtime polymorphism
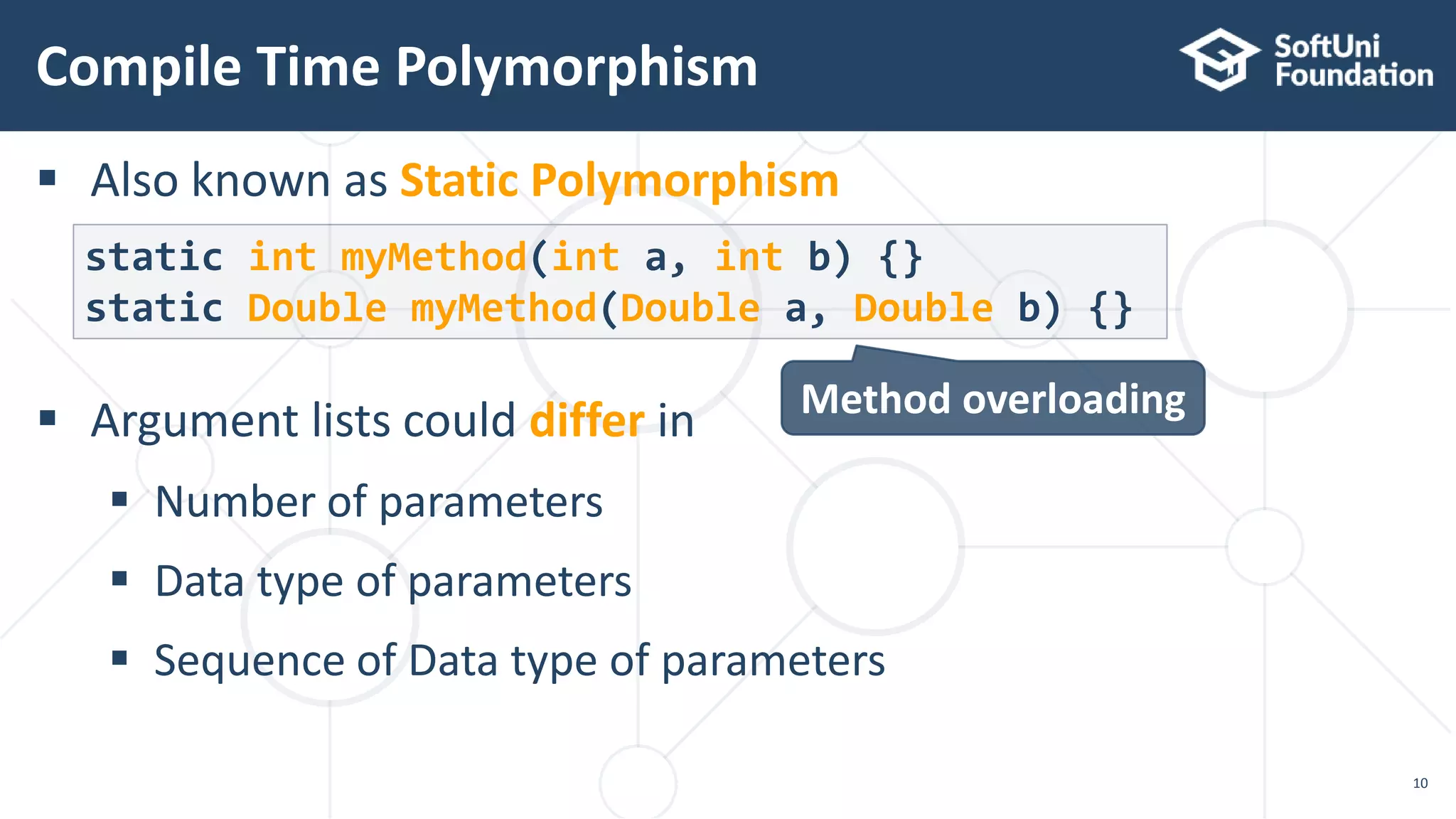
Compile time polymorphism
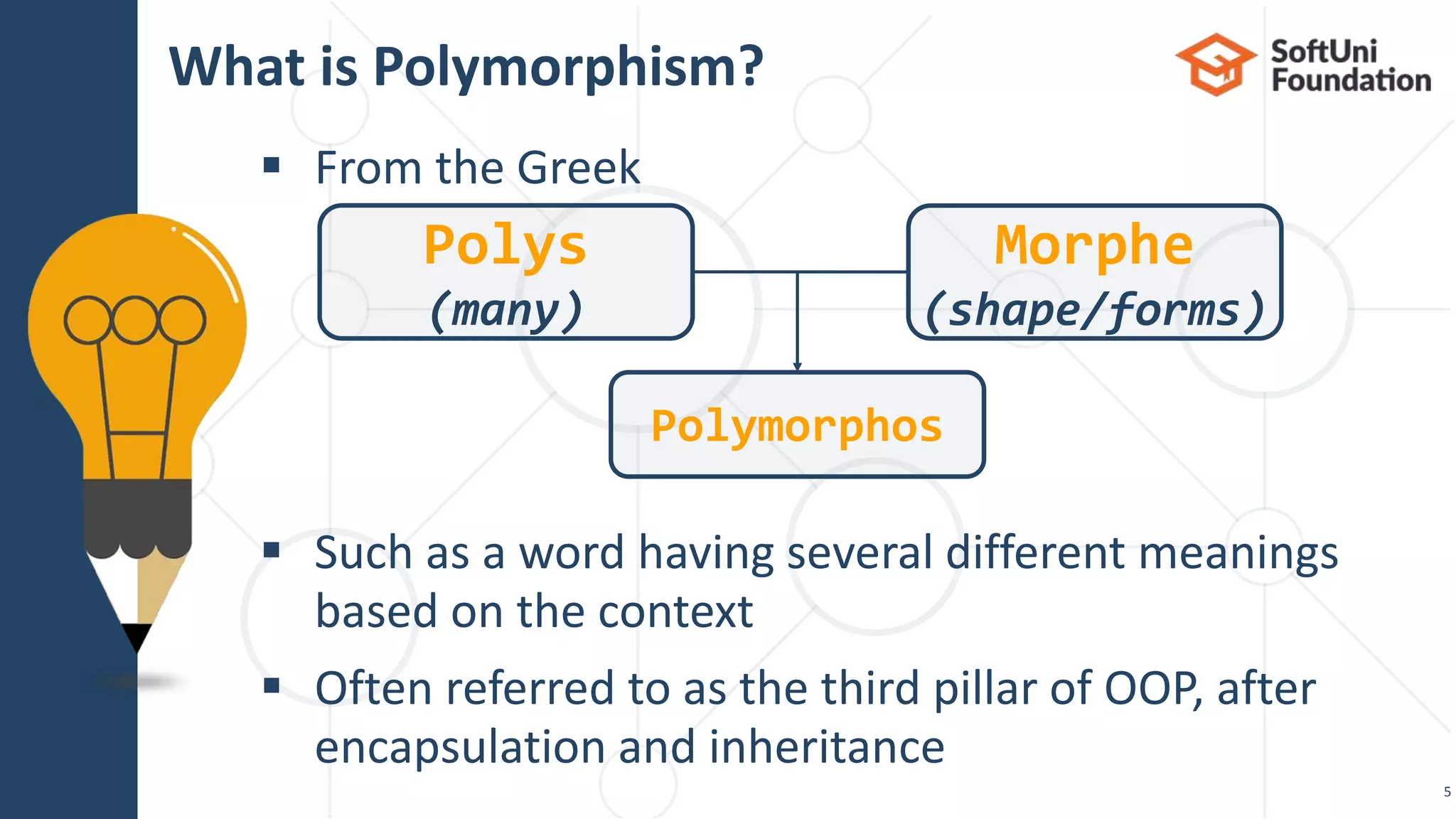
Types of Polymorphism
9
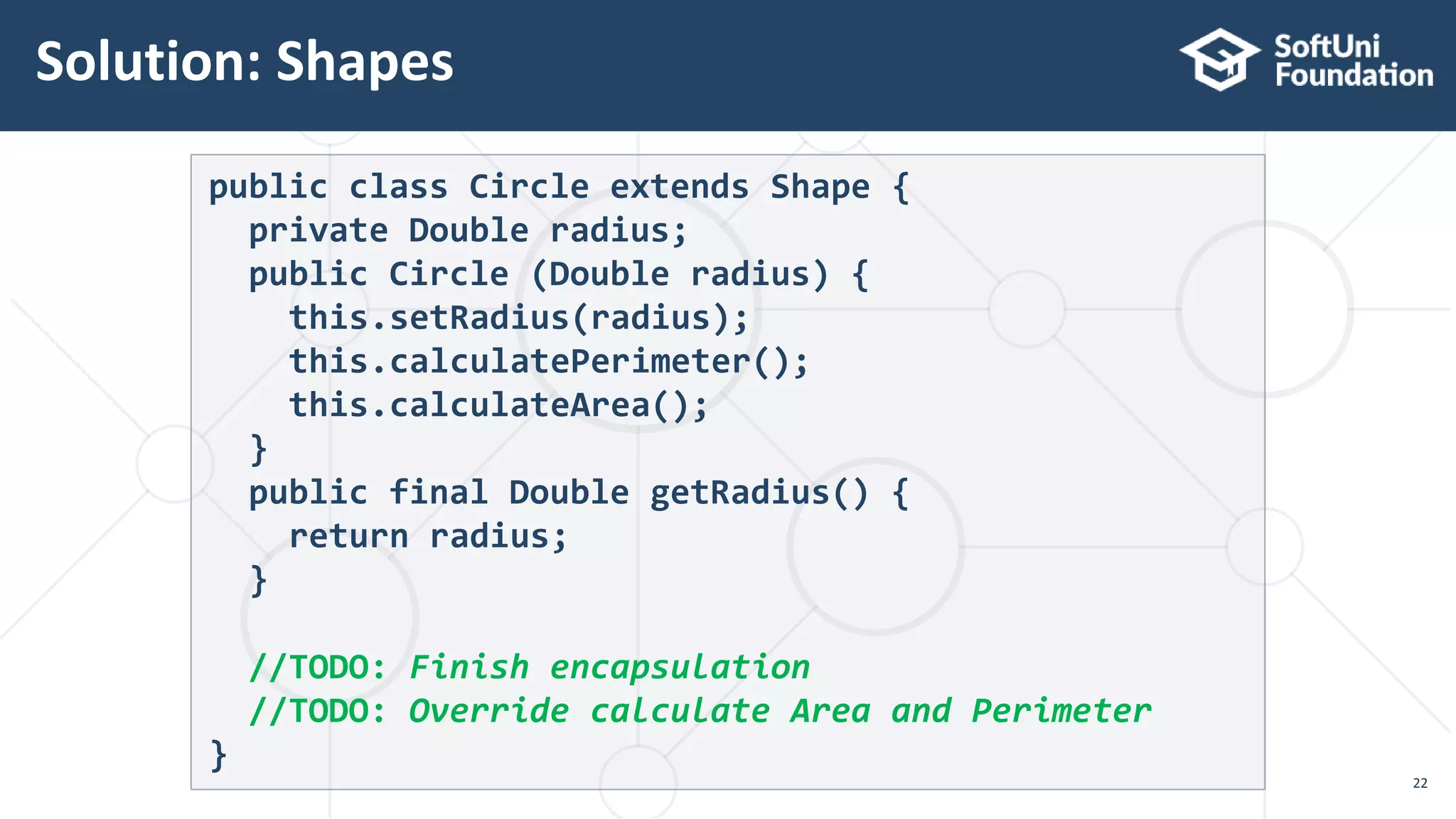
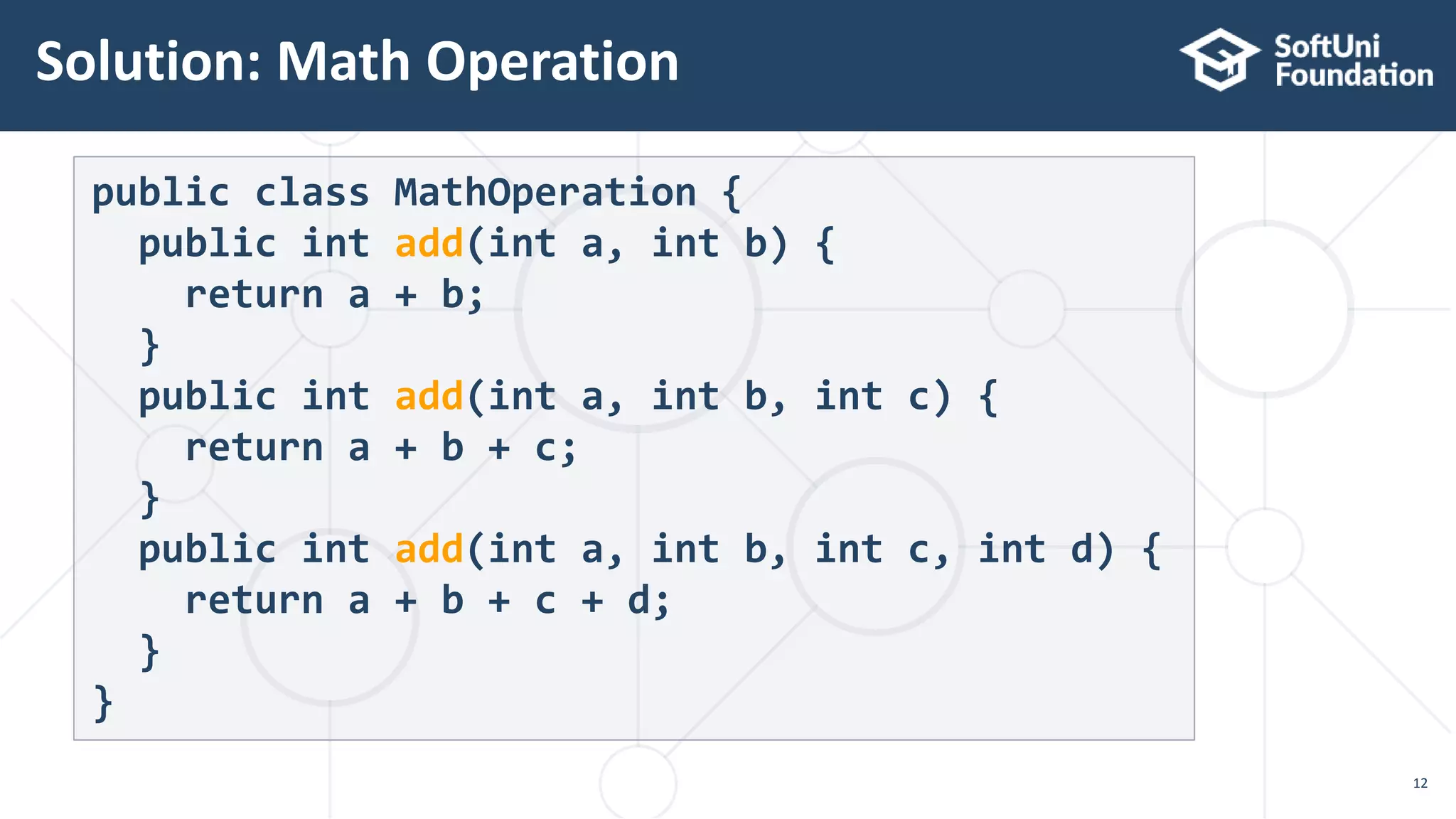
public class Shape {}
public class Circle extends Shape {}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Shape shape = new Circle();
}
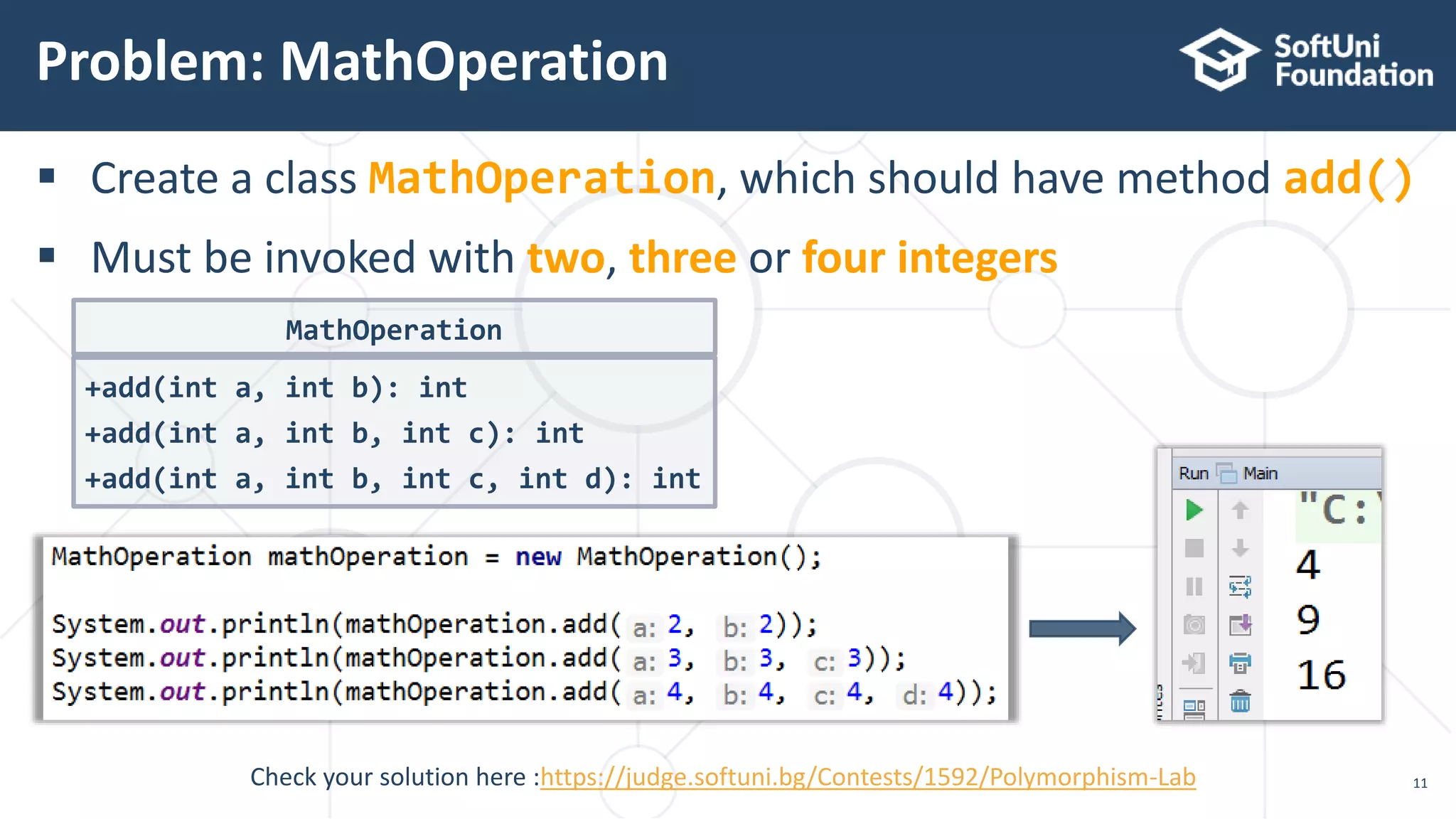
int sum(int a, int b, int c){}
double sum(Double a, Double b){}
Method
overloading
Method
overriding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-200321145754/75/20-5-Java-polymorphism-9-2048.jpg)
![ Using of override method
Runtime Polymorphism
14
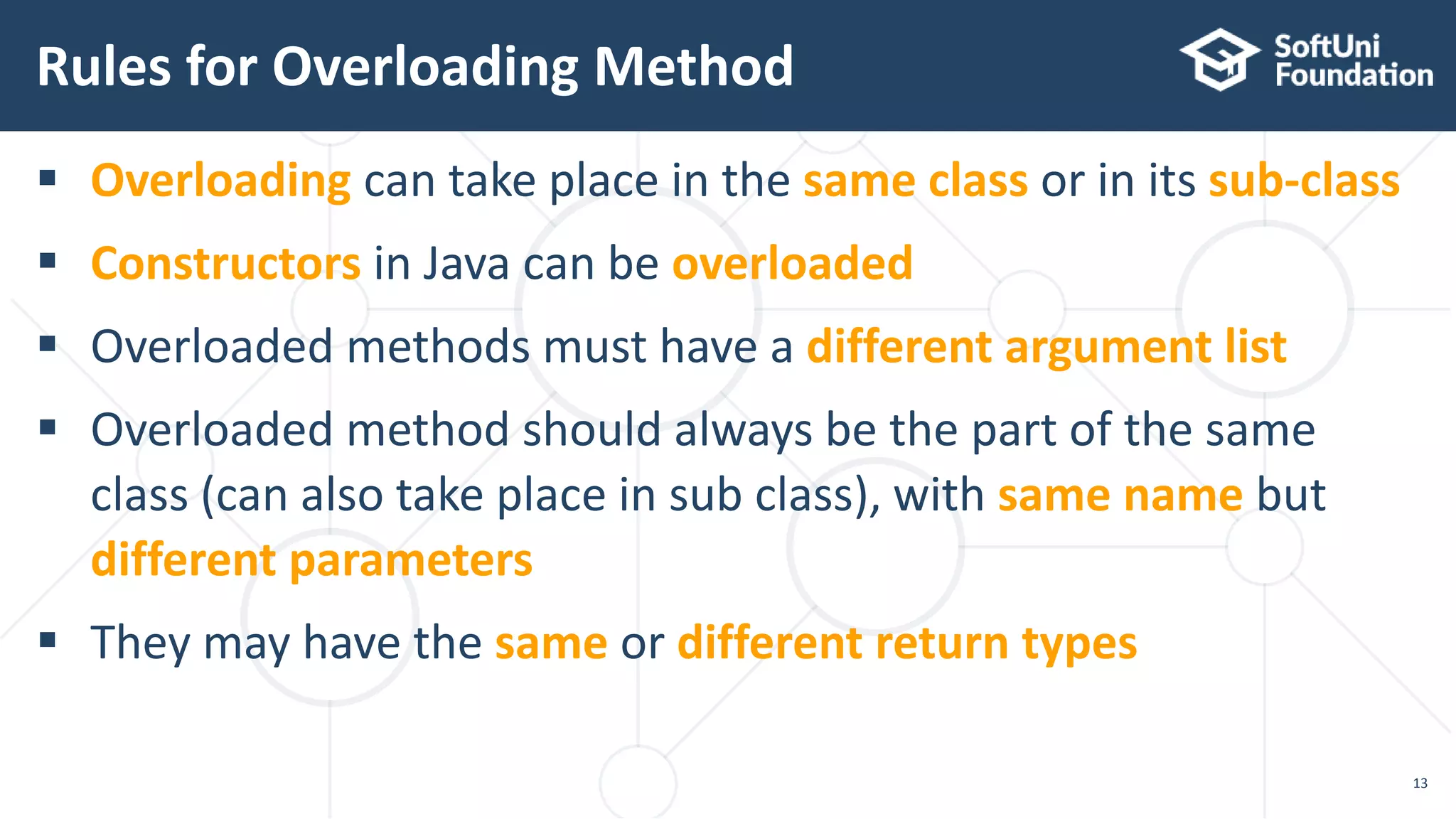
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(3.0, 4.0);
Rectangle square = new Square(4.0);
System.out.println(rect.area());
System.out.println(square.area());
}
Method
overriding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05-200321145754/75/20-5-Java-polymorphism-14-2048.jpg)