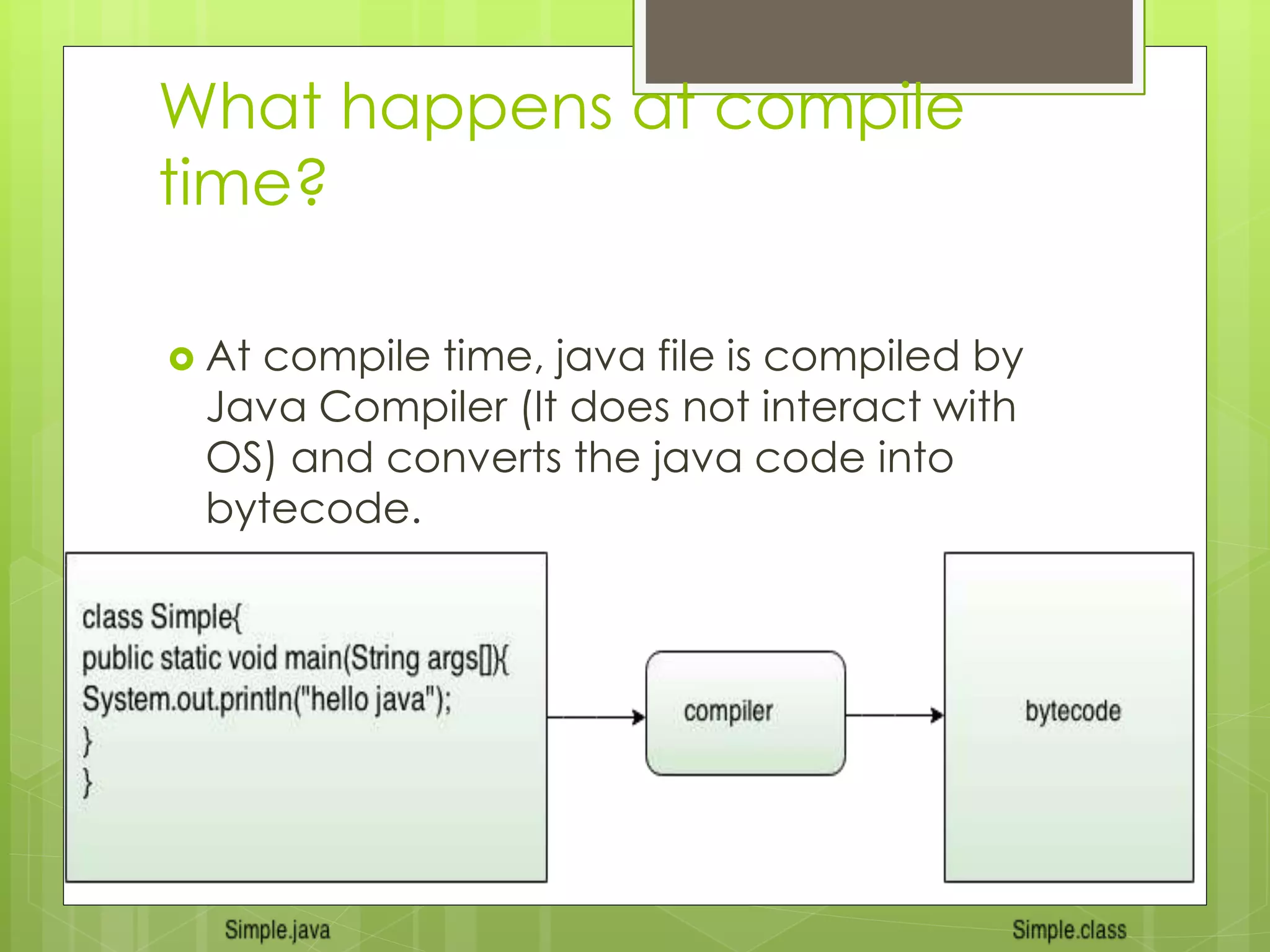
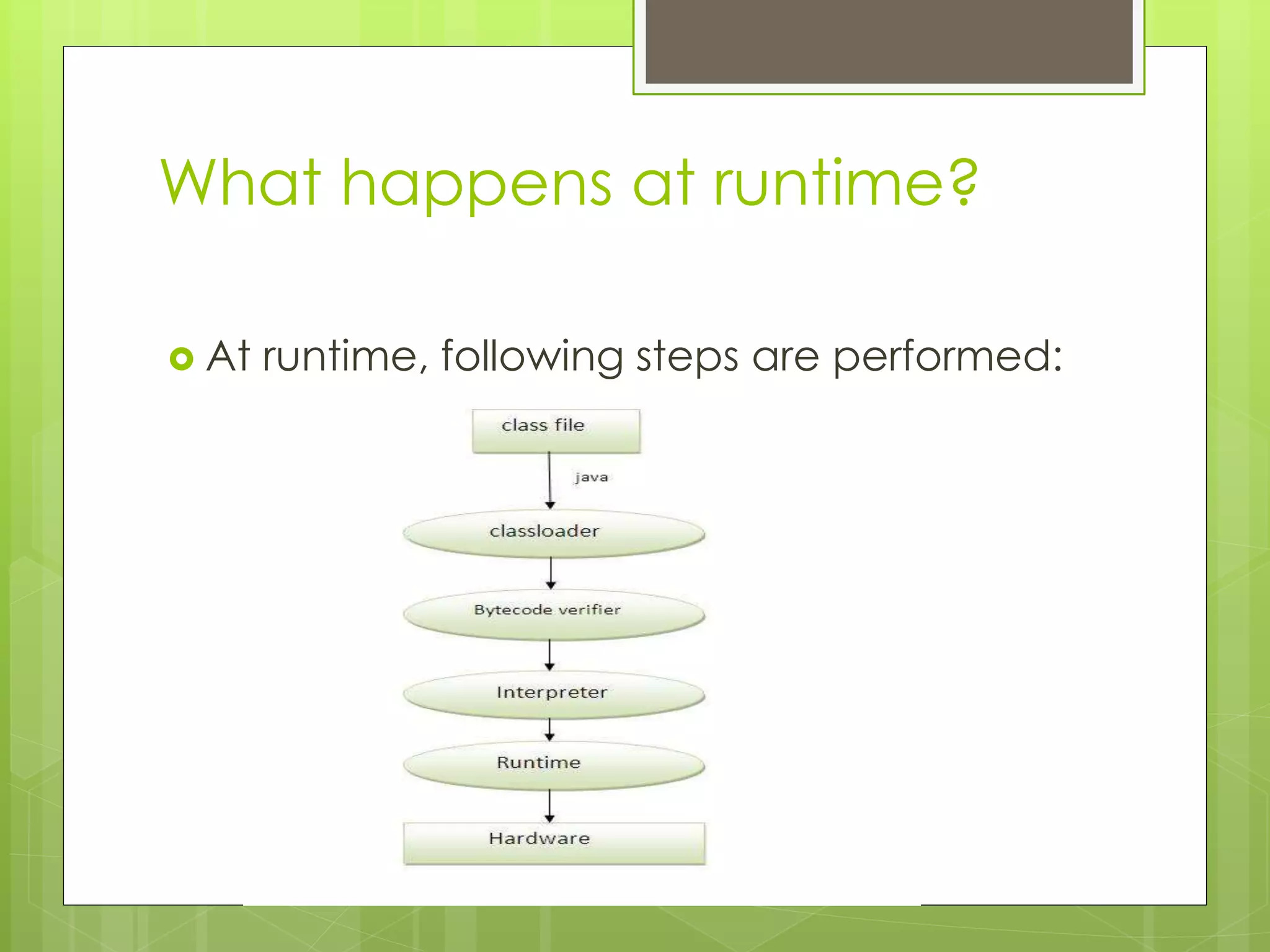
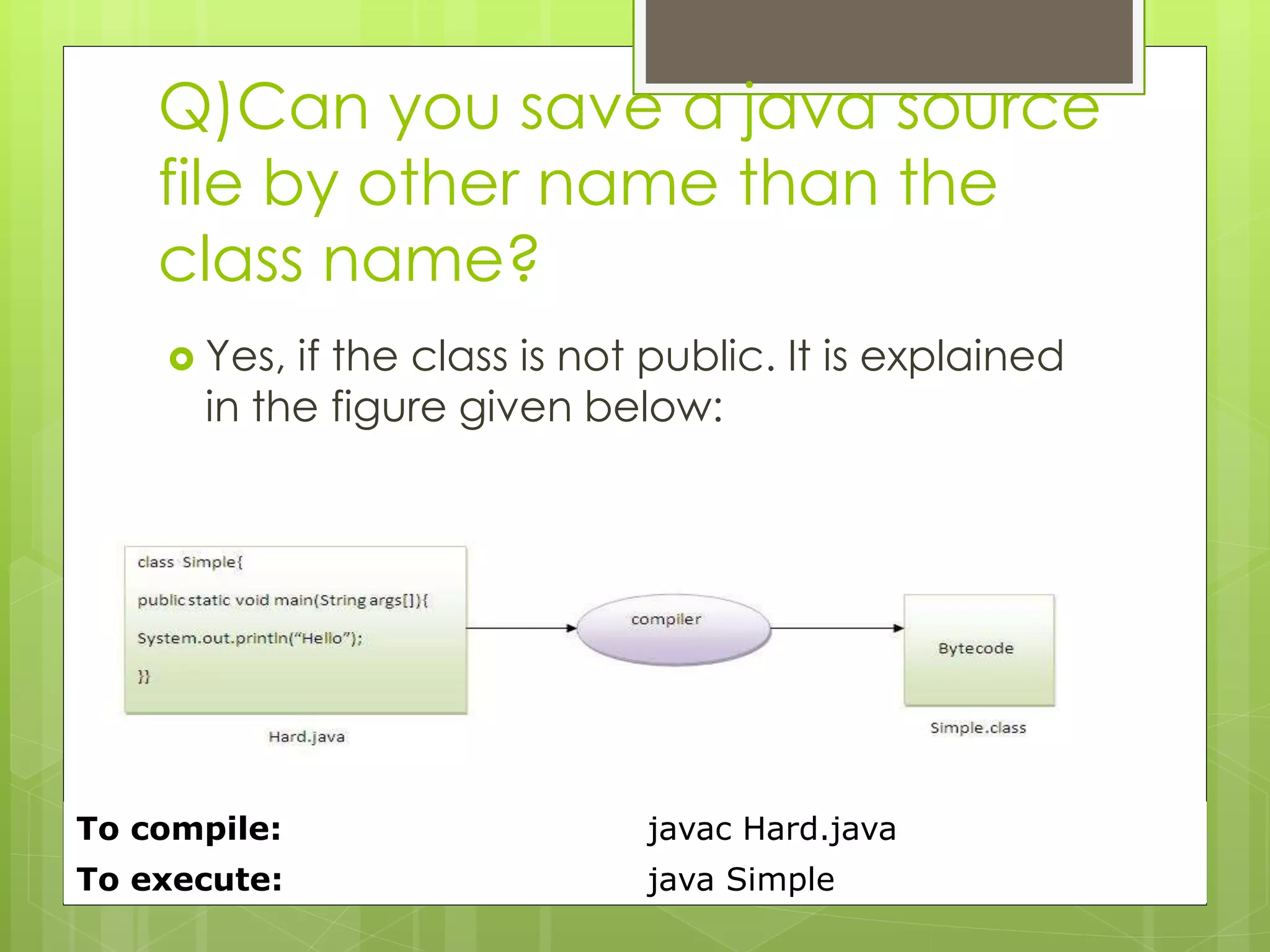
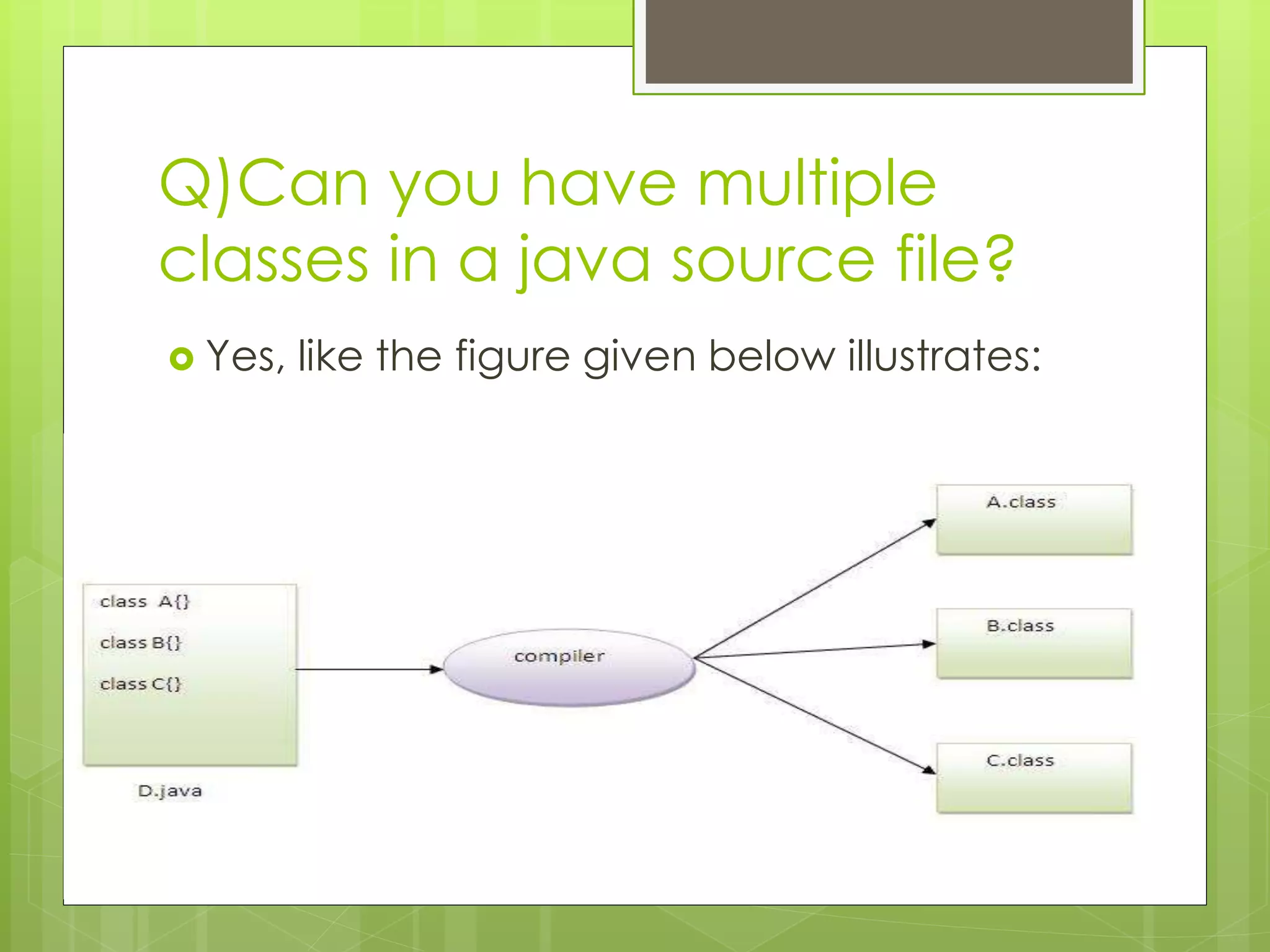
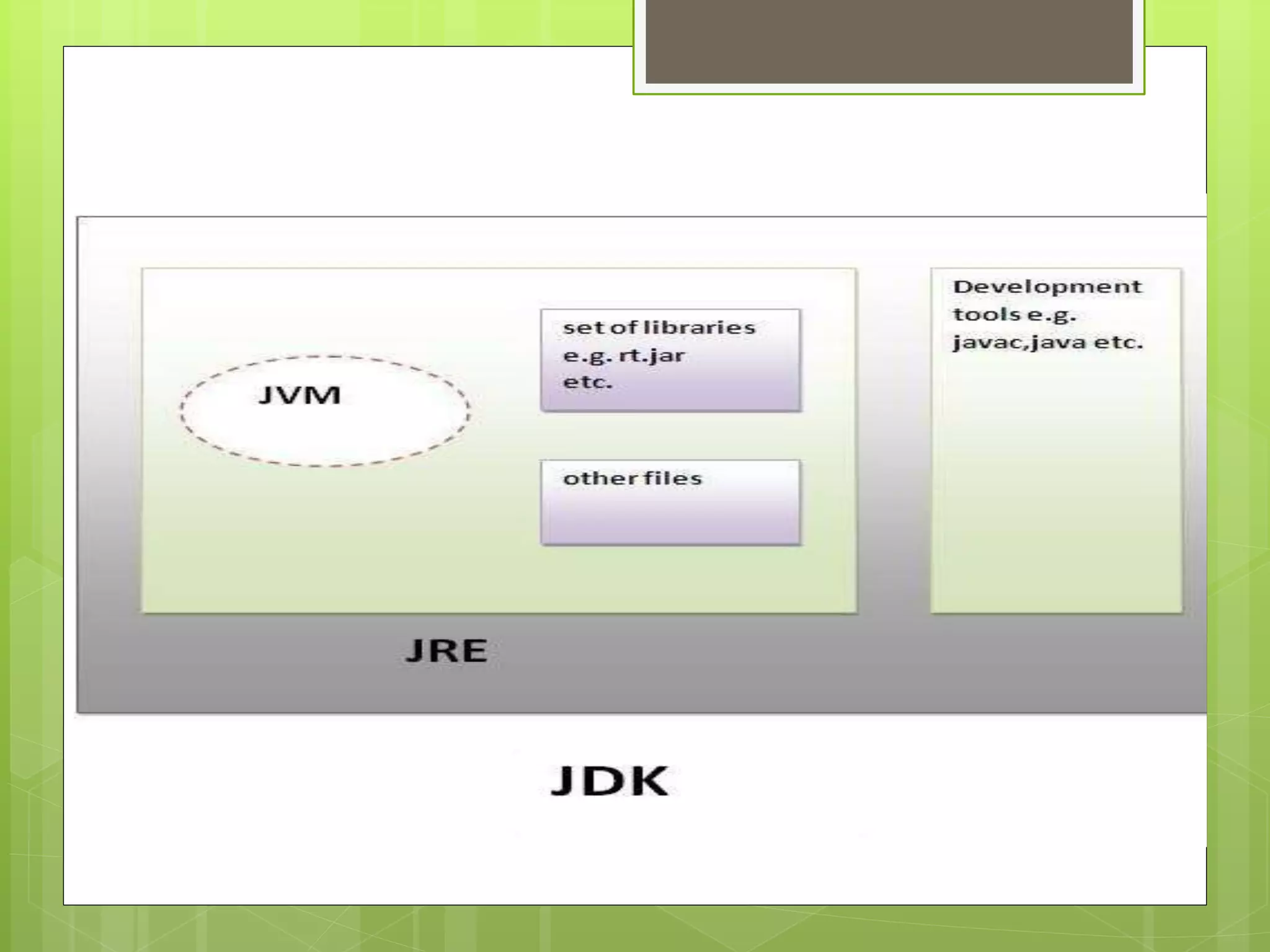
The document discusses the internal details of running a Java program. It explains that at compile time, the Java compiler converts Java code into bytecode. At runtime, the classloader loads the bytecode and the bytecode verifier checks for illegal code before the interpreter executes the instructions. It then addresses some questions about naming Java files and having multiple classes in a file. Finally, it defines the JVM, JRE, and JDK, explaining that the JVM executes bytecode, the JRE provides the runtime environment, and the JDK contains the JRE plus development tools.