The document is a detailed guide on string processing in Java, covering topics such as string manipulation, initialization, and methods for searching, replacing, and splitting strings. It also explains the use of the StringBuilder class for efficient string modification. Various examples and exercises are provided to illustrate the concepts discussed.



![ Initializing from a string literal:
Reading a string from the console:
Converting a string from and to a char array:
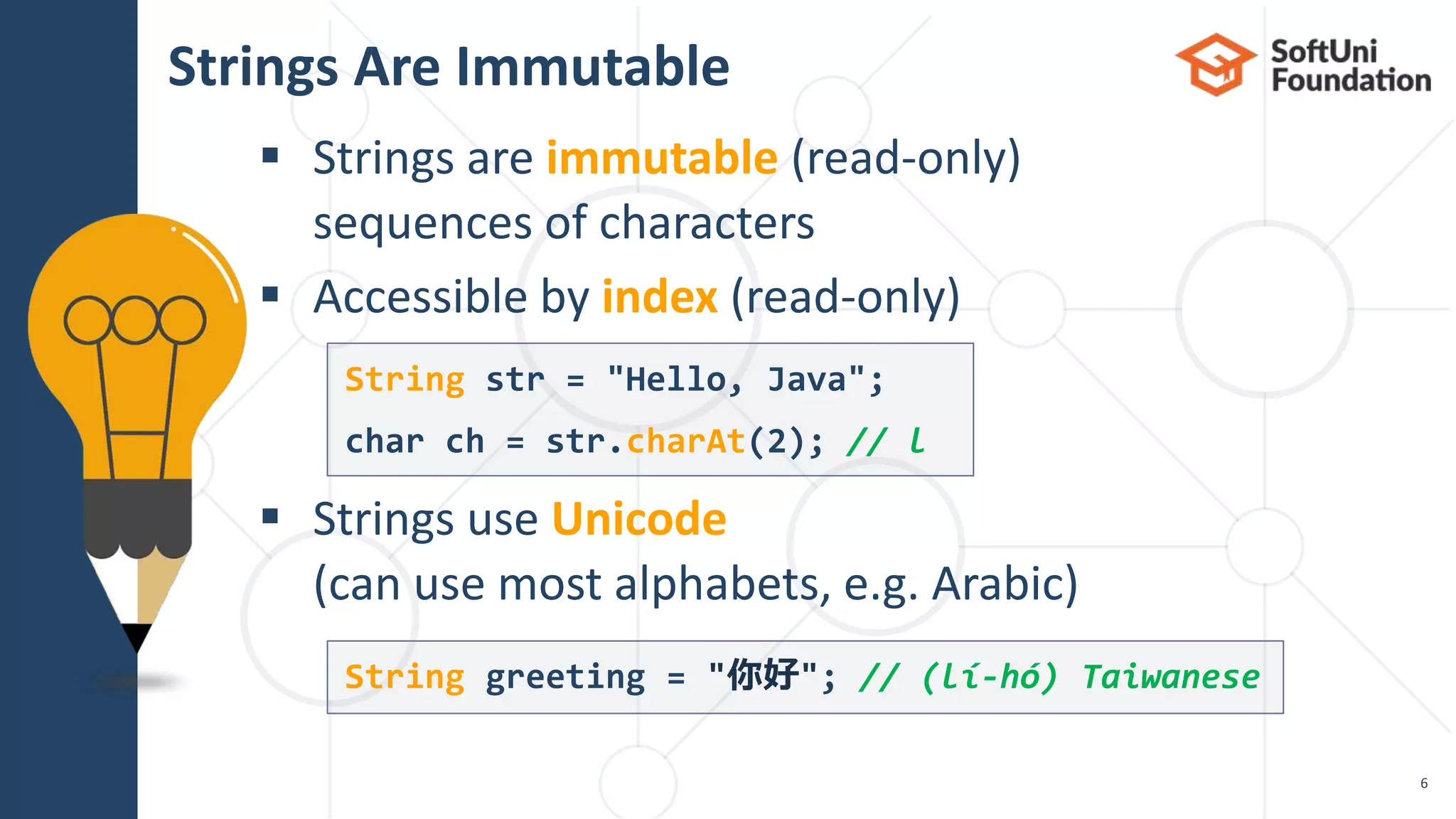
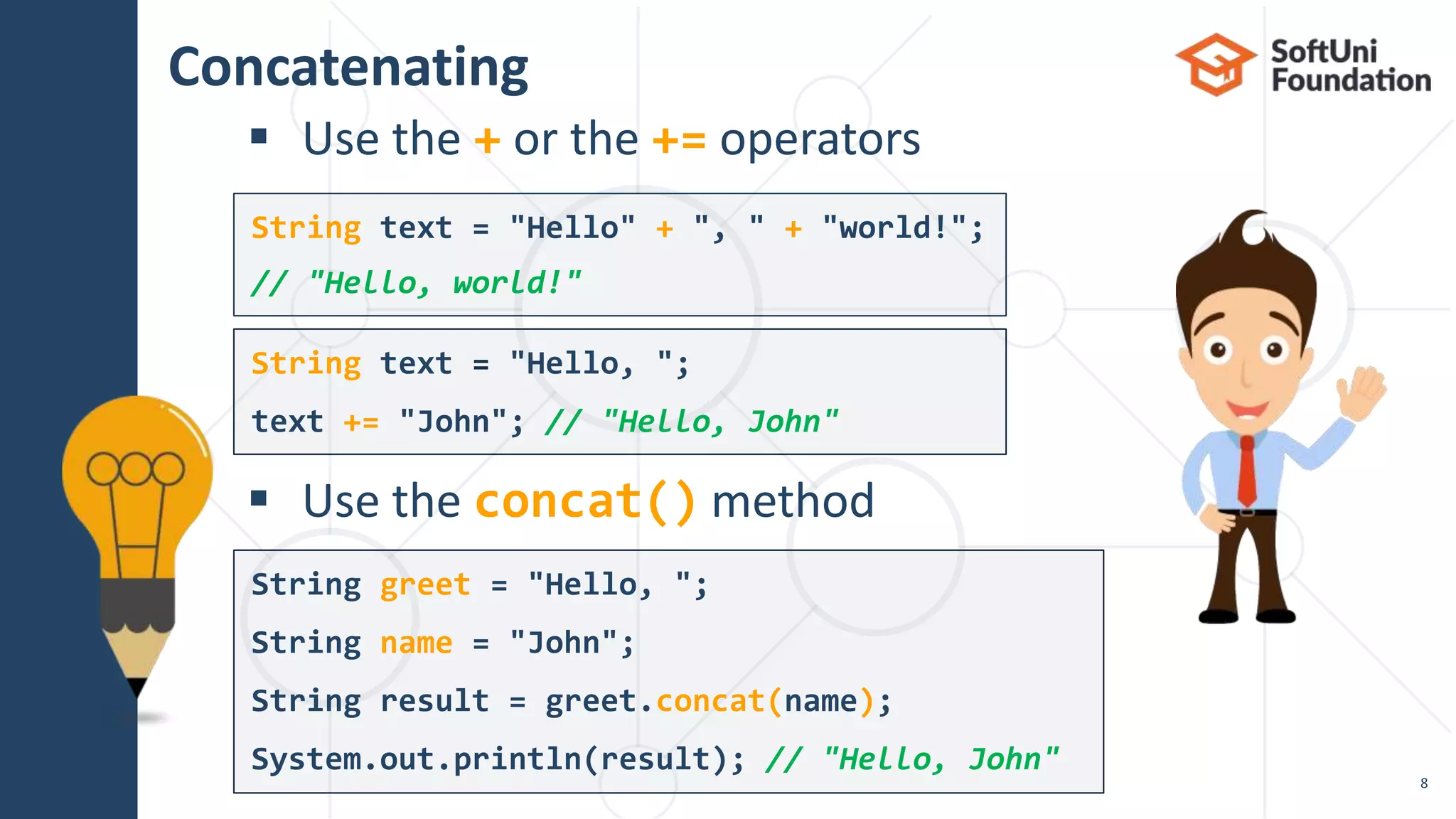
Initializing a String
7
String str = "Hello, Java";
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("Hi, " + name);
String str = new String(new char[] {'s', 't', 'r'});
char[] charArr = str.toCharArray();
// ['s', 't', 'r']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08-200321142801/75/13-Java-text-processing-7-2048.jpg)

![Joining Strings
String.join("", …) concatenates strings
Or an array/list of strings
Useful for repeating a string
10
String t = String.join("", "con", "ca", "ten", "ate");
// "concatenate"
String s = "abc";
String[] arr = new String[3];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = s; }
String repeated = String.join("", arr); // "abcabcabc"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08-200321142801/75/13-Java-text-processing-10-2048.jpg)
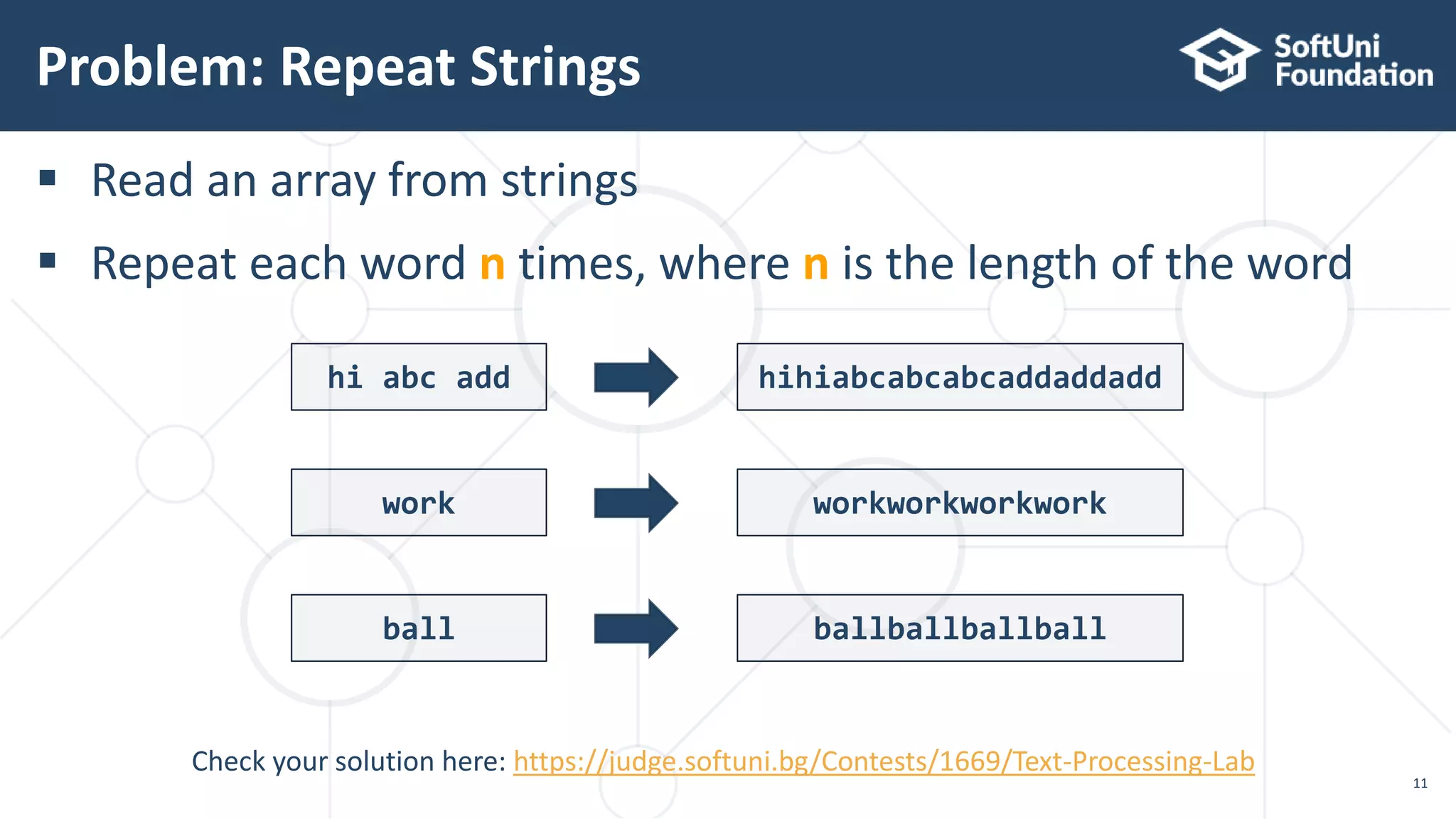
![Solution: Repeat Strings (1)
12
String[] words = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (String word : words) {
result.add(repeat(word, word.length()));
}
System.out.println(String.join("", result));
Check your solution here: https://judge.softuni.bg/Contests/1669/Text-Processing-Lab](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08-200321142801/75/13-Java-text-processing-12-2048.jpg)
![static String repeat(String s, int repeatCount) {
String[] repeatArr = new String[repeatCount];
for (int i = 0; i < repeatCount; i++) {
repeatArr[i] = s;
}
return String.join("", repeatArr);
}
Solution: Repeat Strings (2)
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08-200321142801/75/13-Java-text-processing-13-2048.jpg)
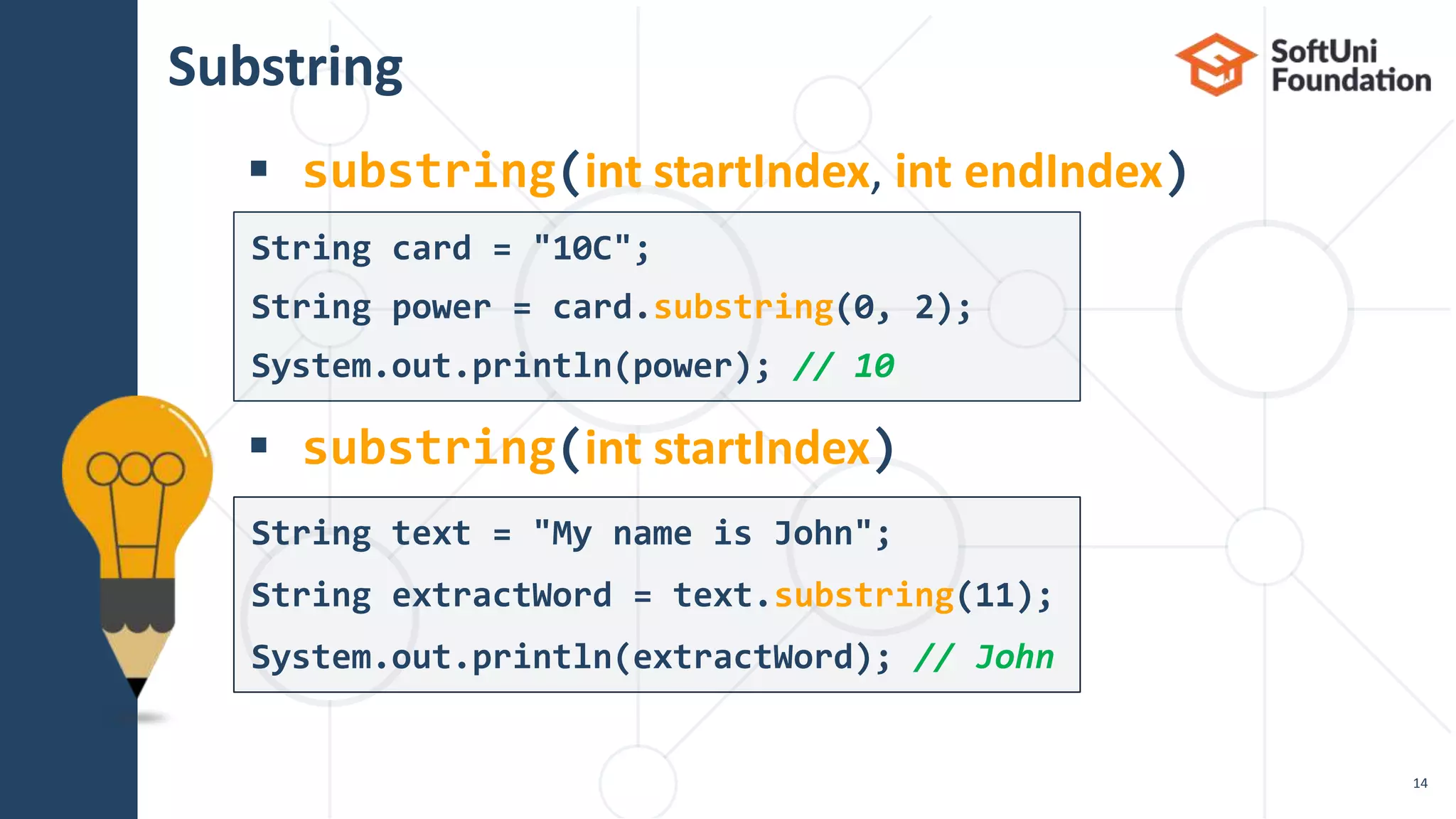
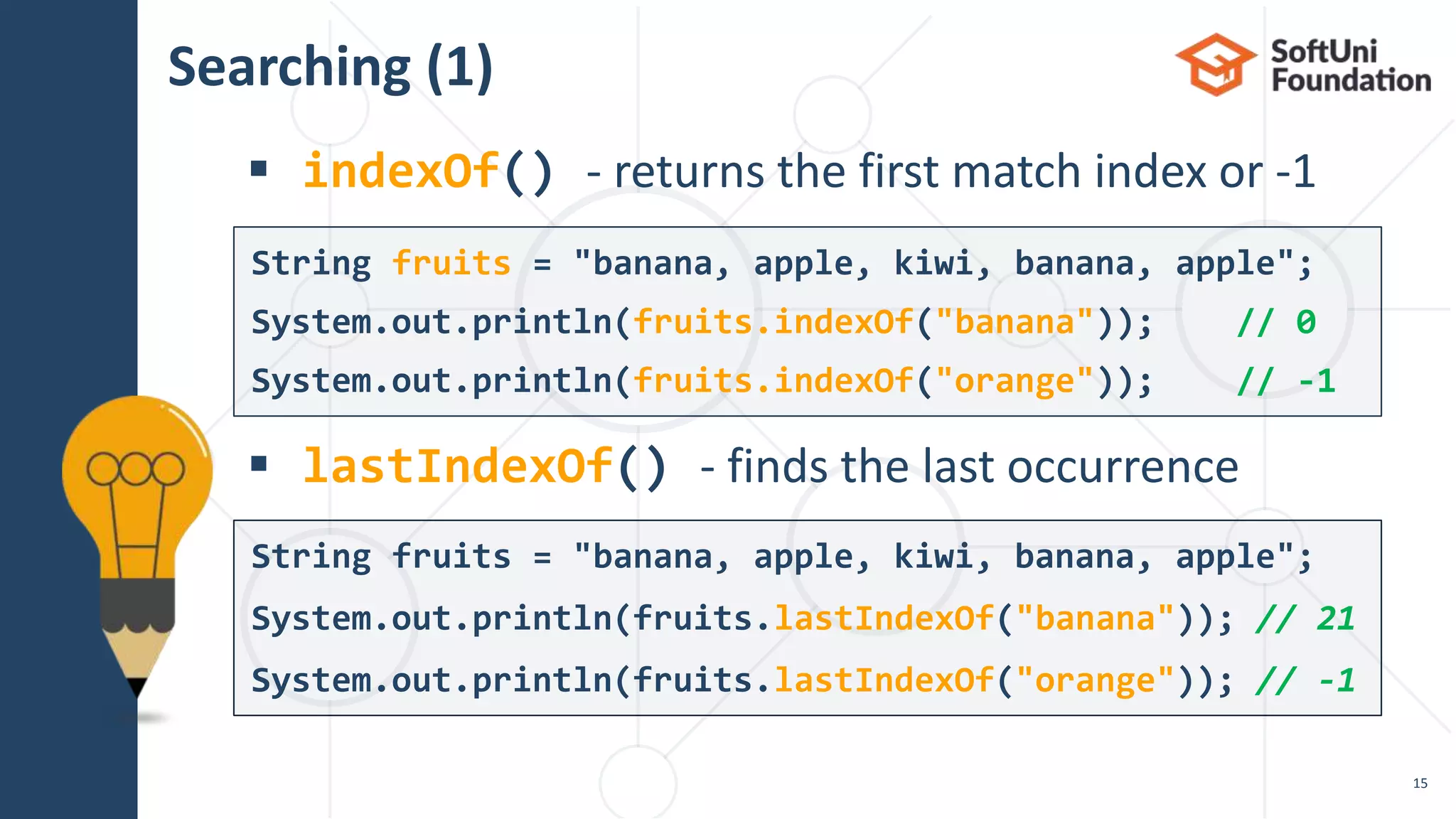

![Splitting
Split a string by given pattern
Split by multiple separators
19
String text = "Hello, I am John.";
String[] words = text.split("[, .]+");
// "Hello", "I", "am", "John"
String text = "Hello, john@softuni.bg, you have been
using john@softuni.bg in your registration";
String[] words = text.split(", ");
// words[]: "Hello", "john@softuni.bg","you have been…"](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08-200321142801/75/13-Java-text-processing-19-2048.jpg)
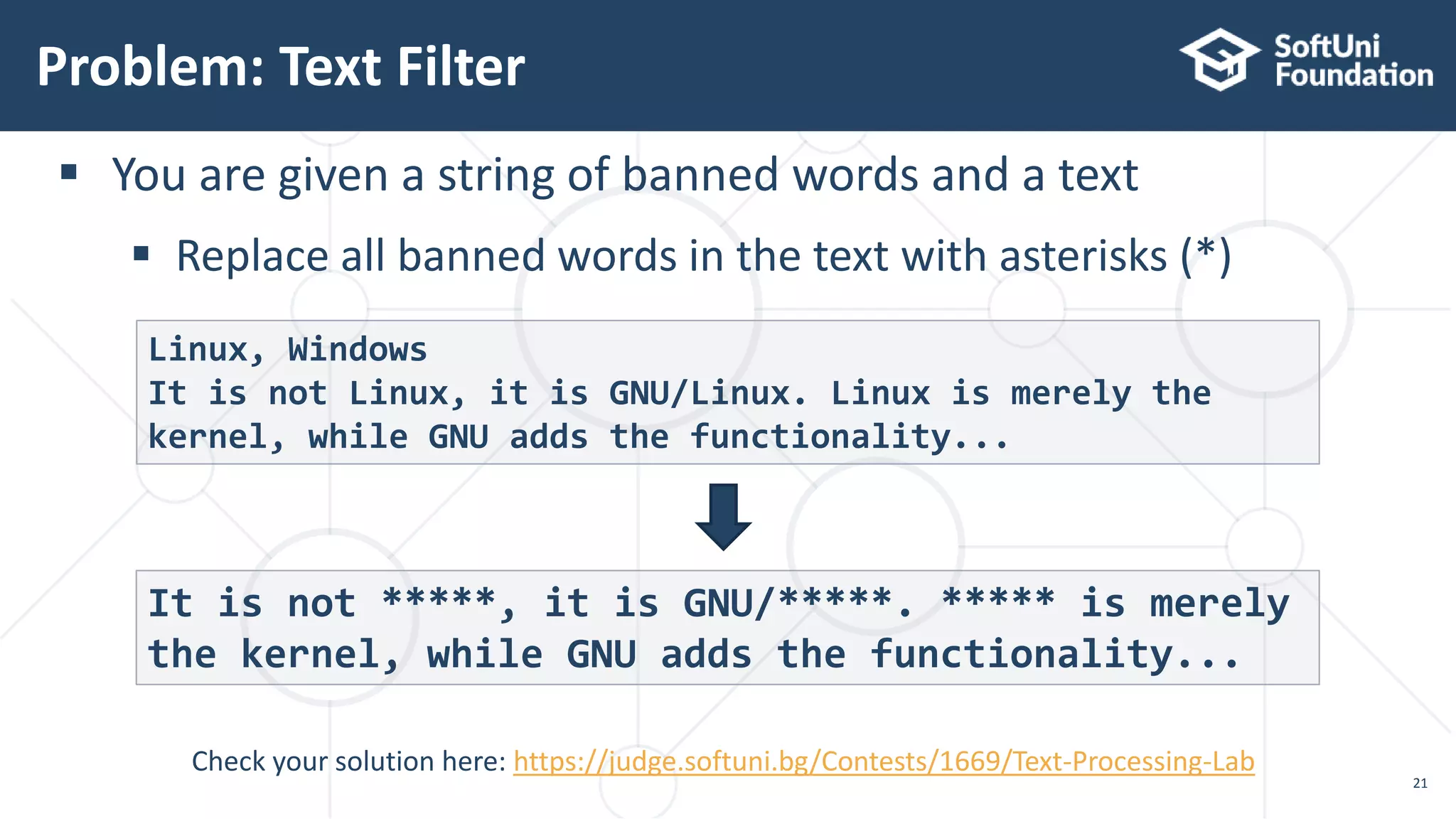
![Solution: Text Filter (1)
22
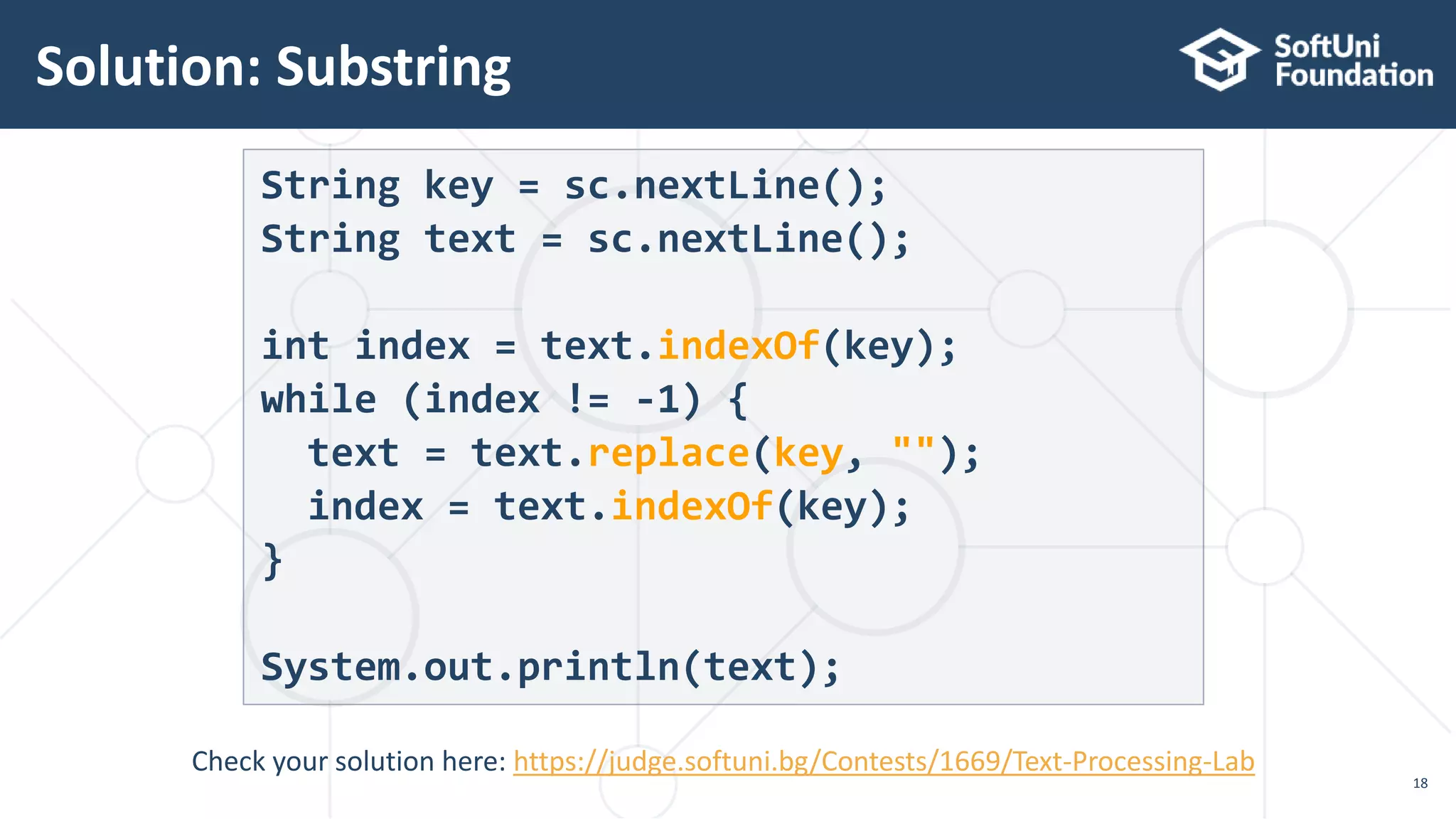
String[] banWords = sc.nextLine.split(", ");
String text = sc.nextLine();
for (String banWord : banWords) {
if (text.contains(banWord)) {
String replacement = repeatStr("*",
banWord.length());
text = text.replace(banWord, replacement);
}
}
System.out.println(text);
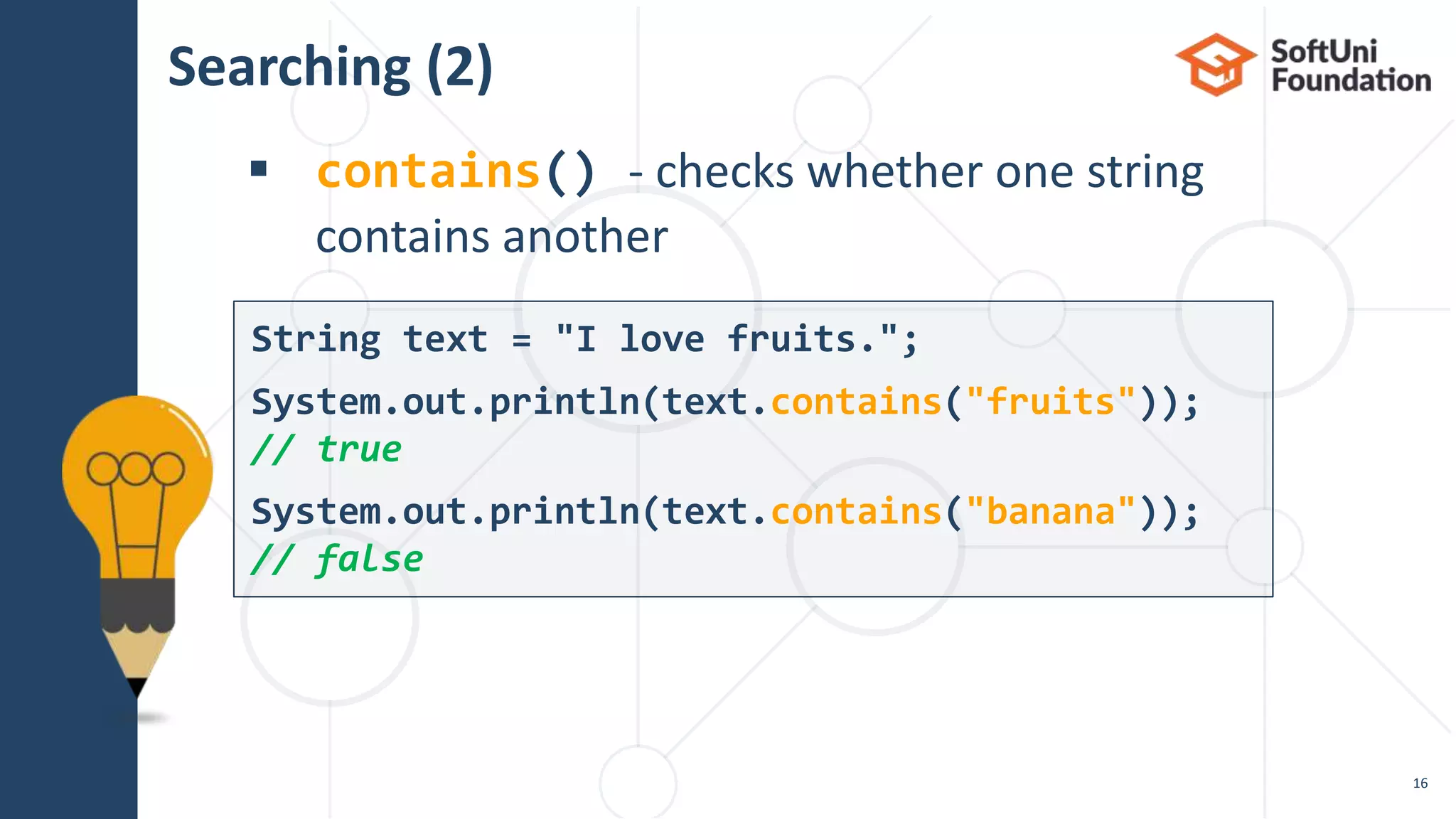
contains(…) checks if string
contains another string
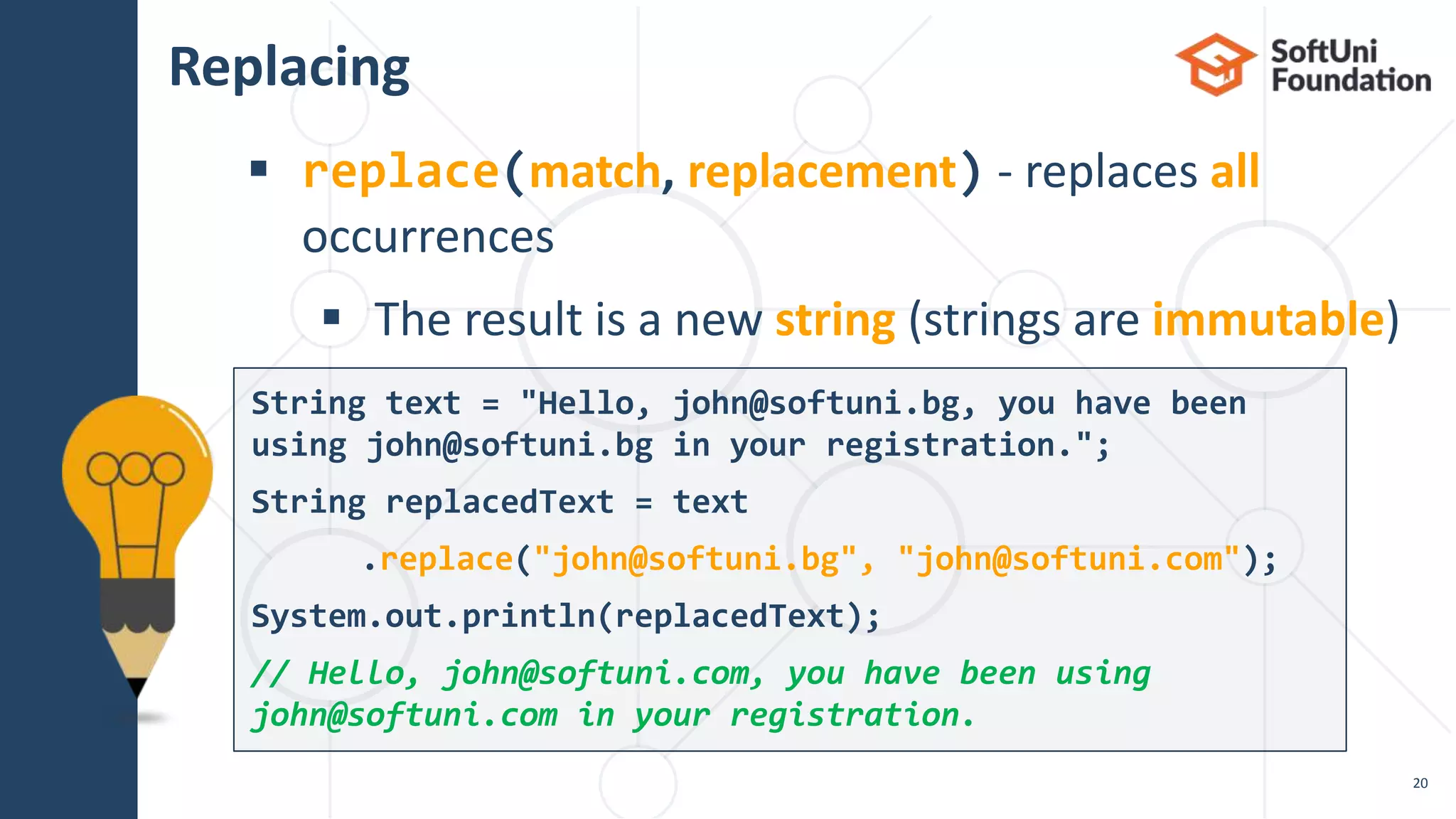
replace() a word with a sequence
of asterisks of the same length
Check your solution here: https://judge.softuni.bg/Contests/1669/Text-Processing-Lab](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/08-200321142801/75/13-Java-text-processing-22-2048.jpg)