This document provides a summary of key Scala basics and comparisons to Java, including:
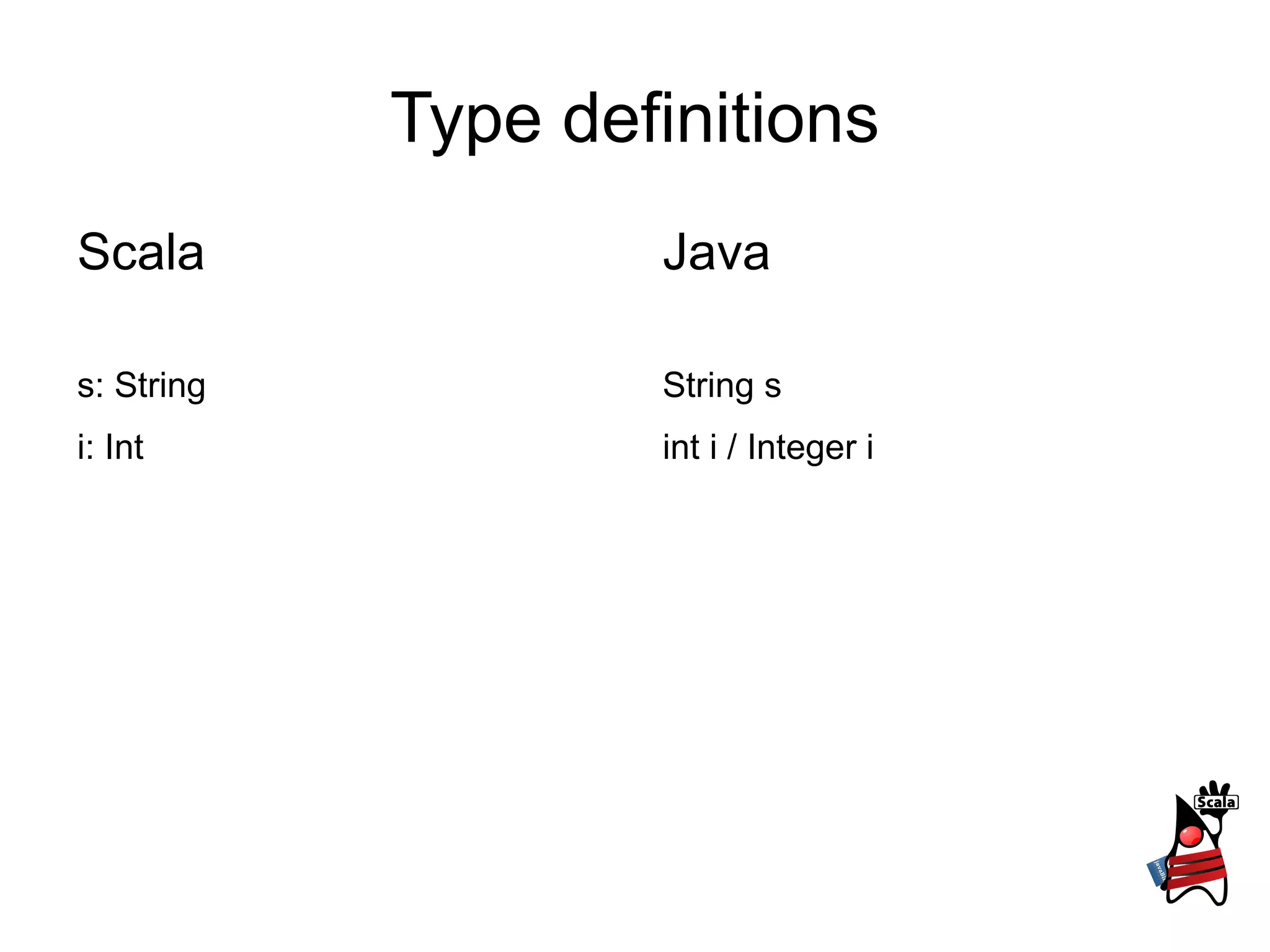
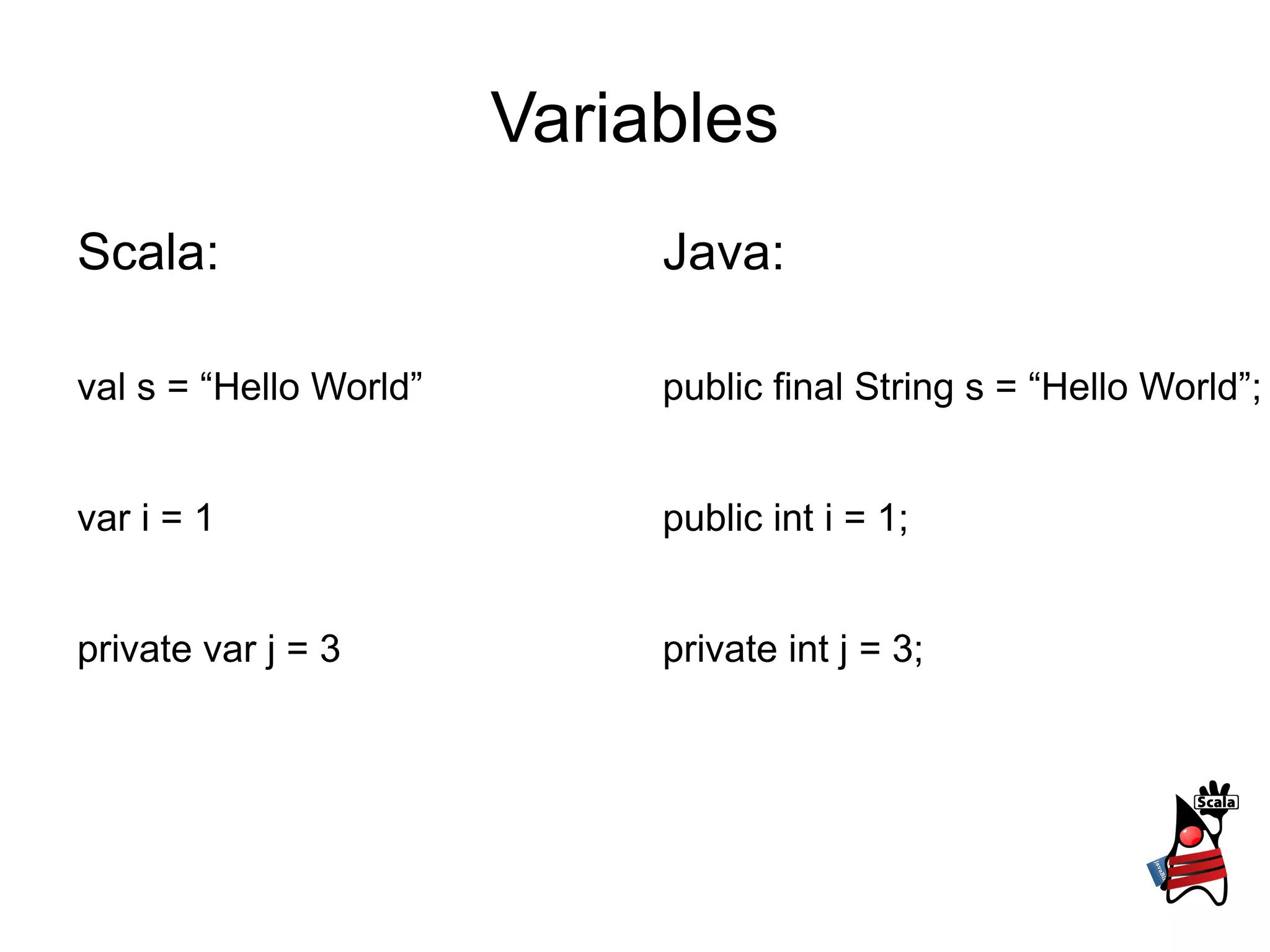
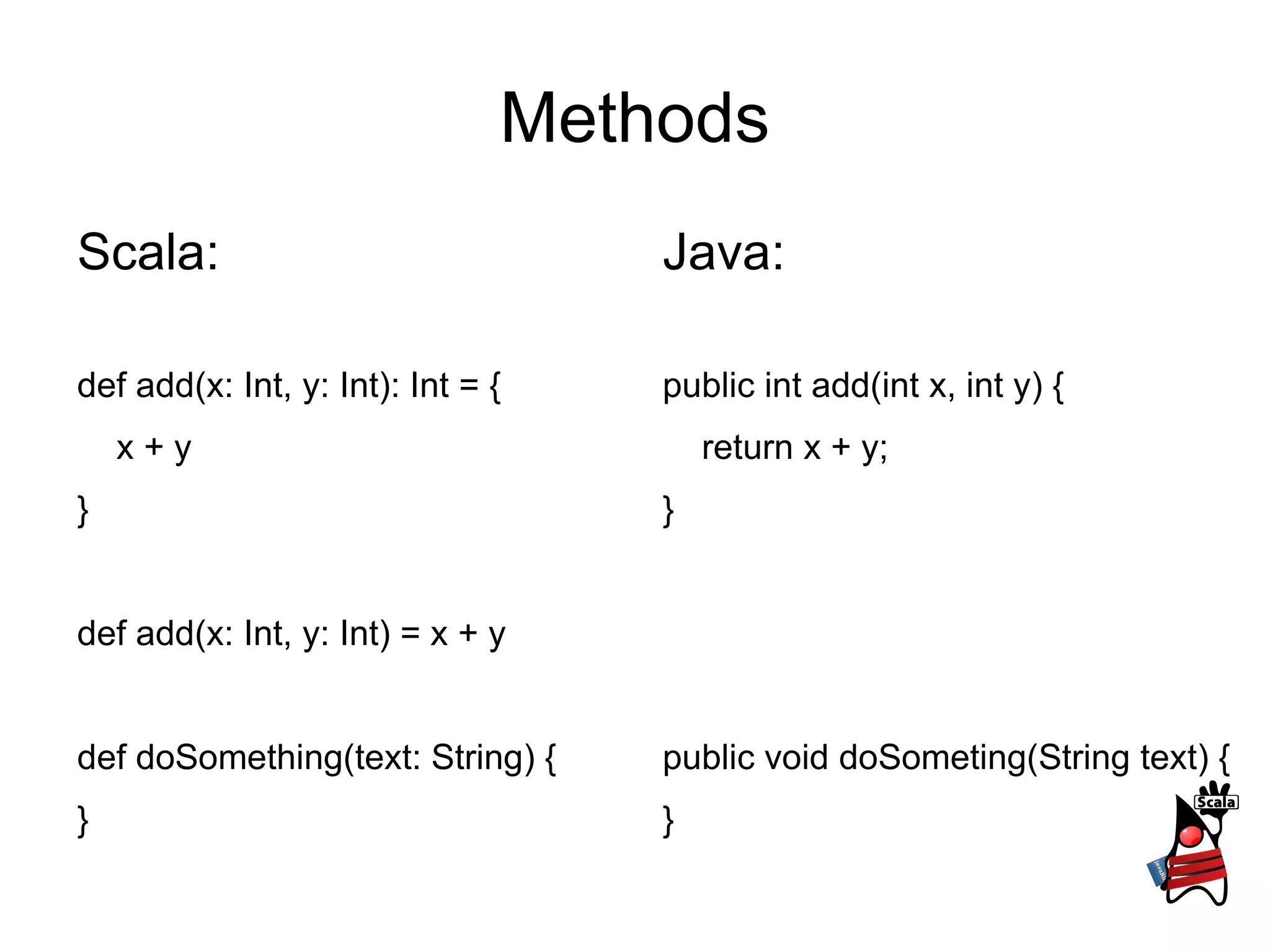
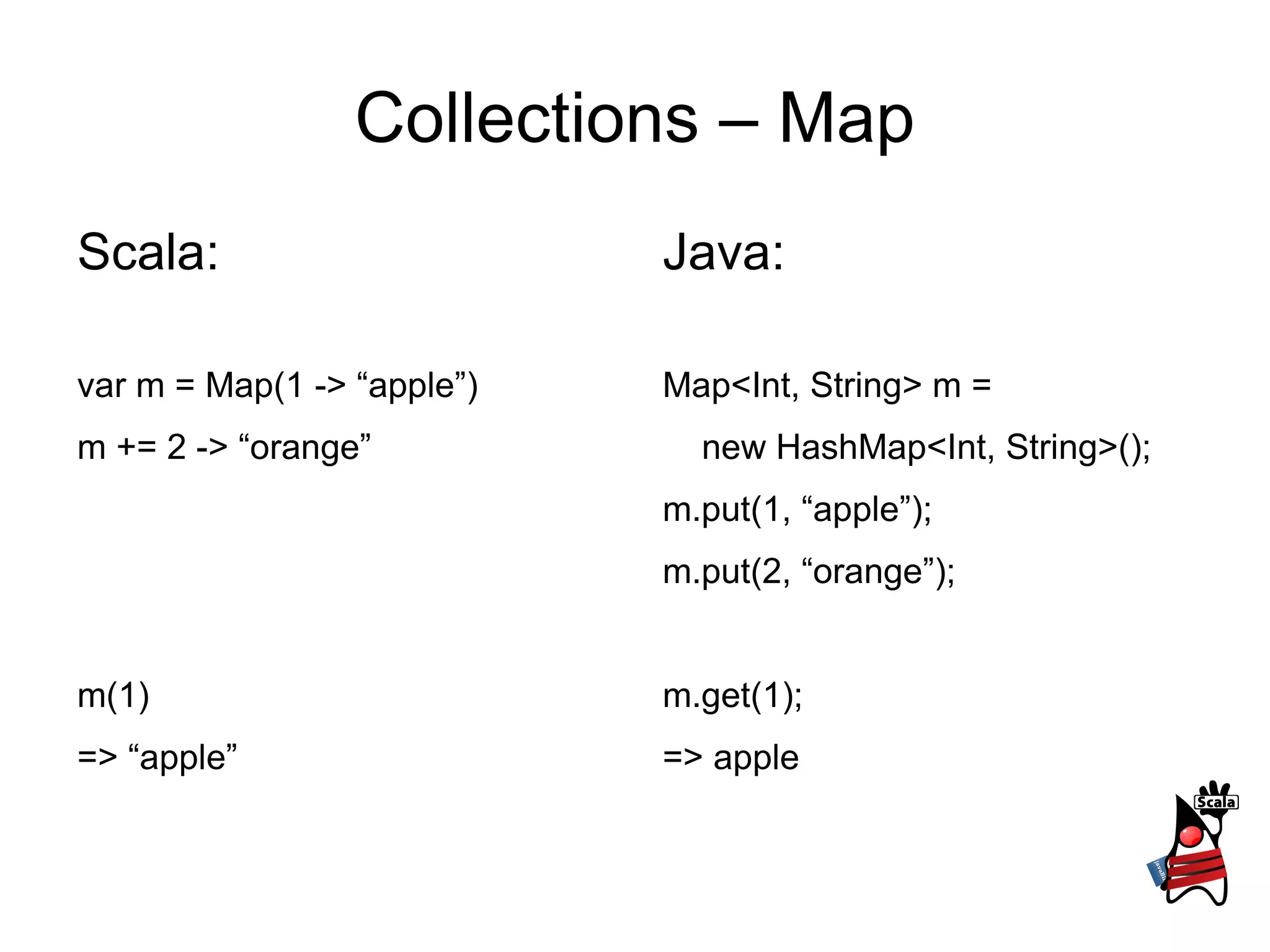
1) It describes type definitions, variables, methods and how they are defined in Scala versus Java. It also covers method invocation syntax differences.
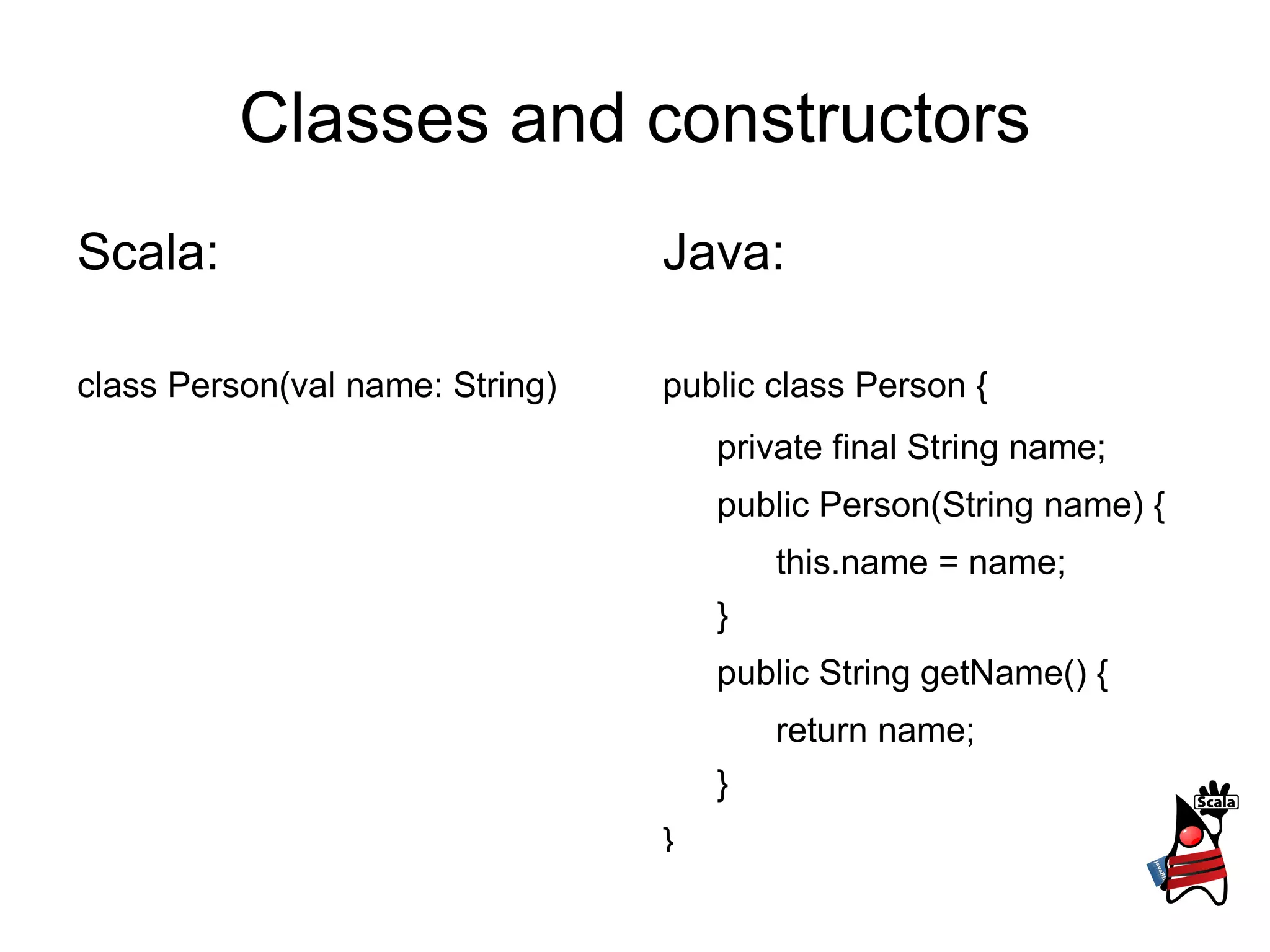
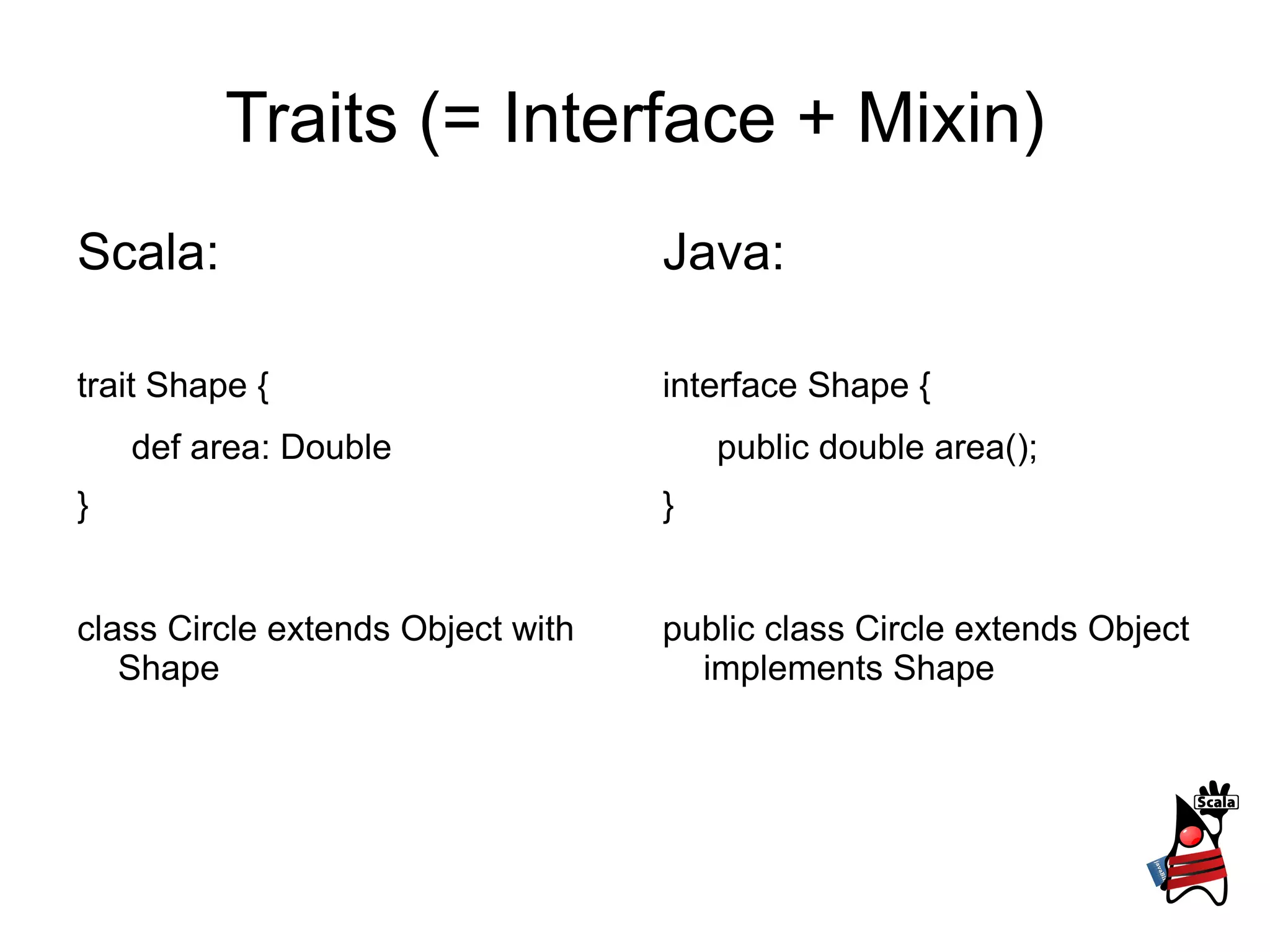
2) It explains classes and constructors, traits versus interfaces, and static methods in Scala versus Java.
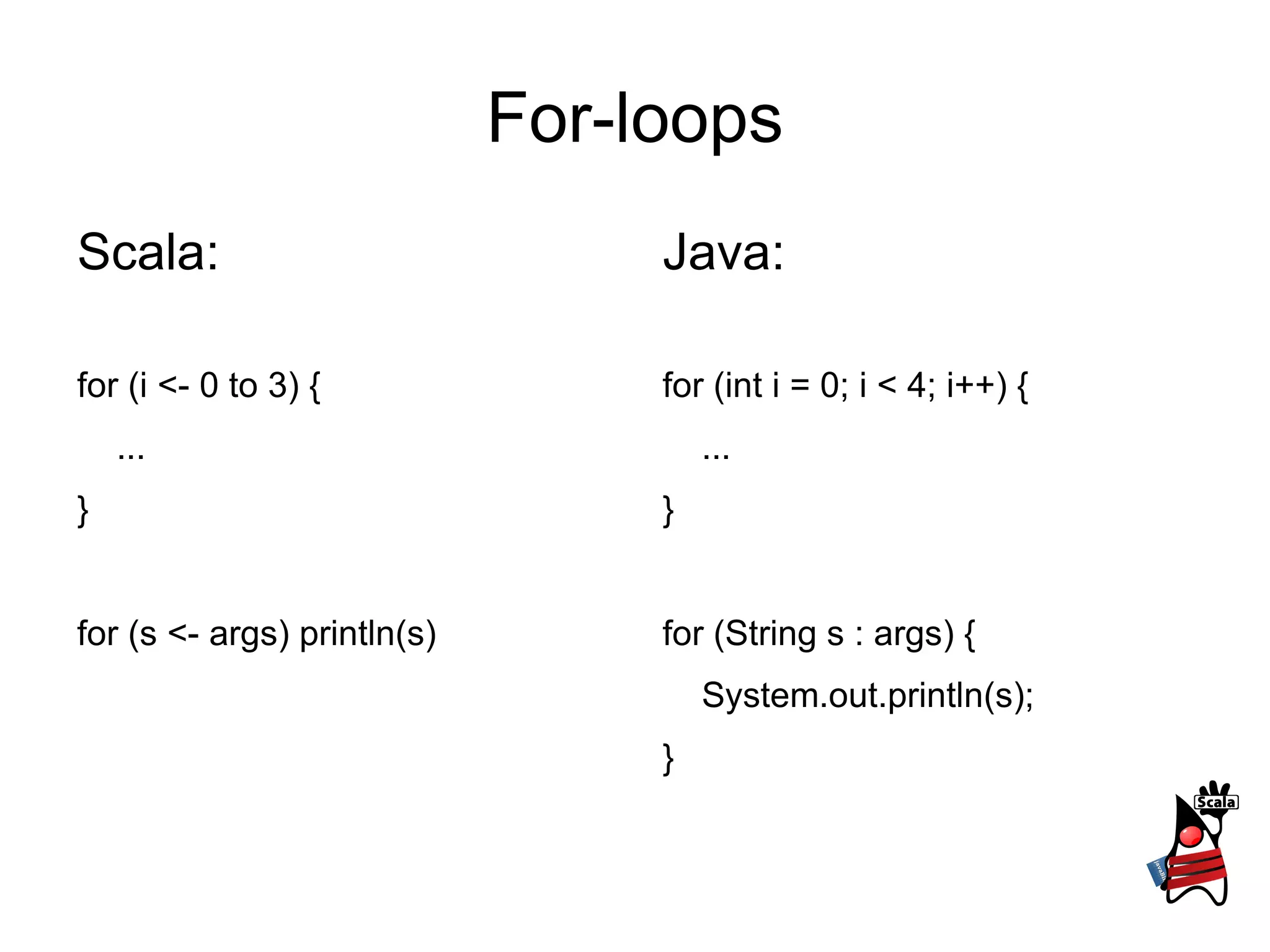
3) It provides examples of control structures like if/else, for loops, while loops and exceptions in both languages.




![No “static” in Scala Scala: object PersonUtil { val AgeLimit = 18 def countPersons(persons: List[Person]) = ... } Java: public class PersonUtil { public static final int AGE_LIMIT = 18; public static int countPersons(List<Person> persons) { ... } }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-2-scalabasics-100112145817-phpapp02/75/1-2-Scala-Basics-10-2048.jpg)



![Varargs def foo(values: String*){ } foo("bar", "baz") val arr = Array("bar", "baz") foo(arr: _*) public void foo(String... values){ } foo("bar", "baz"); String[] arr = new String[]{"bar", "baz"} foo(arr);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-2-scalabasics-100112145817-phpapp02/75/1-2-Scala-Basics-15-2048.jpg)


![Generics Scala: List[String] Java: List<String>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-2-scalabasics-100112145817-phpapp02/75/1-2-Scala-Basics-19-2048.jpg)
![Tuples Scala: val tuple: Tuple2[Int, String] = (1, “apple”) val quadruple = (2, “orange”, 0.5d, false) Java: Pair<Integer, String> tuple = new Pair<Integer, String>(1, “apple”) ... yeah right... ;-)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-2-scalabasics-100112145817-phpapp02/75/1-2-Scala-Basics-20-2048.jpg)


