Mining Sector Toolset
Prevent and Address Forced Labor in Your Company’s Supply Chains

Introduction & Framing
The minerals, metals, and products produced through mining are essential parts of the global economy and critical to a variety of industries, including energy technologies, defense, construction, transportation, agriculture, durable consumer goods, packaging, currency, and jewelry. While demand for minerals and mineral products – like lithium, cobalt, and nickel – are rapidly increasing, mining remains a highly hazardous sector that poses risks to workers, especially in smaller scale and informal operations, and includes high rates of injuries, fatalities, exposure to toxins, low pay, and lack of legal protections. Migrants, including children, who driven by poverty are especially vulnerable to exploitation, including human trafficking.
More on Mining:
Read the Sector Report: Human Trafficking and Other Labor Risks in the Mining Sector (2025).
Watch the Webinar: Responsible Sourcing in the Mining Sector (part one of the three-part series).
This tool provides an overview of the processes a company could implement to identify where risks of human trafficking, including forced labor, are present within its supply chains; to address identified issues; to implement enduring solutions; and to monitor supplier performance over time.
See the Supply Chain Due Diligence Process Flow, below.
A supply chain Code of Conduct establishes basic performance expectations for suppliers, agents, and subcontractors. It is important that your company sourcing policy or Code of Conduct explicitly prohibits forced labor and related human rights abuses and sets out clear protections for workers. The sample provisions in this tool can be used by mining companies and for the management of their on-site sub-contractors, services providers, and labor agents.
Benchmarks of good practice are the detailed performance standards of a Code of Conduct. They further clarify requirements for business partners and can be used to measure the labor and human rights performance of suppliers. The set of sample benchmarks is consistent with the sample Code of Conduct provisions listed in Tool 2 and can serve as a basis for establishing and monitoring key performance indicators.
Understanding the laws that govern the prevention and remediation of human trafficking, including forced labor, in a particular country can help mining companies assess where in their operations and supply chains there may be heightened risk of forced labor and provide insight into the operating environment that may contribute to such risks. In addition, it is helpful to understand whether the country has committed to any other frameworks, such as treaties, bilateral agreements, or conventions, that address factors that contribute to the risk of forced labor.
The purpose of a Supplier Agreement is to formally record the commitment of a supplier, contractor, subcontractor, or agent to conform to a customer’s Code of Conduct, contract terms and conditions, and applicable legal requirements. It can be a standalone document or included as an appendix to the contract. Contract terms and conditions covering the obligations of both the buyer and supplier are the legally enforceable requirements for suppliers to prevent human trafficking, including forced labor.
Supply chain mapping allows a company to trace the chain of custody — and points of accountability — to the farthest upstream levels of materials and services supply chains. With a complete understanding of its materials and labor supply chains, mining companies can identify, prioritize, prevent, and mitigate forced labor risks to workers they employ or that are employed by their subcontractors and suppliers.
The risks of human trafficking, including forced labor, can be mitigated by properly designed and implemented processes for recruitment, selection, and hiring of workers. Those risks are greater and more difficult to control when recruitment, selection, and hiring are outsourced to third-party recruitment and labor agents. Therefore, mining companies and their subcontractors and suppliers should, whenever possible, recruit, hire, and employ workers directly. When direct recruitment is not possible, companies must exercise careful due diligence in the screening and selection of recruitment agents to minimize the risk of forced labor because of fraudulent or misleading recruitment practices.
An important part of a due diligence systems approach to preventing forced labor and other supply chain human rights issues is to assess current and prospective subcontractors and suppliers for potential risks. This sample self-assessment tool can help identify potential forced labor risks in how a subcontractor or supplier recruits, selects, and hires workers, the supplier’s relationship with labor brokers, and how workers are managed.
The risks of human trafficking, including forced labor, in mining industry operations and supply chains can be controlled by properly designed and implemented processes for the recruitment, selection, and hiring of workers. Those risks are greater and more difficult to control when recruitment, selection, and hiring are outsourced to third-party labor agents. The risk increases when these responsibilities are passed to informal labor agents who gather workers through social and familial networks. Therefore, whenever possible, mining companies and their suppliers and on-site subcontractors should recruit, hire, and employ workers directly.
Migrants are a particularly vulnerable class of workers due to their non-local and often contingent status. They are frequently insecure socially and economically; may not speak local languages; may lack the social and legal protections local workers hold; and may be victims of human trafficking due to unethical recruitment and employment practices like indebtedness or lack of access to their identity documents. Because migrant workers are present throughout mining supply chains, companies should carefully plan worker interviews for the many different suppliers and services subcontractors used in a mining project.
The ability for workers to gain awareness of and advocate for their rights, to discuss workplace issues of concern and interest, to have channels for individual and collective advocacy, and to communicate grievances, is essential to the prevention of trafficking in persons. It can also serve to provide companies with effective means for information exchange on workplace conditions and potential risk areas. In fact, workers themselves are often the best source of information regarding labor conditions.
This tool is specifically intended for use by companies that need to demonstrate compliance with the requirements of the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR): Combating Trafficking in Persons and submit certification 52.222-56 set forward by 52.222-50(h) and 22.1703(c).
Supply Chain Due Diligence Process
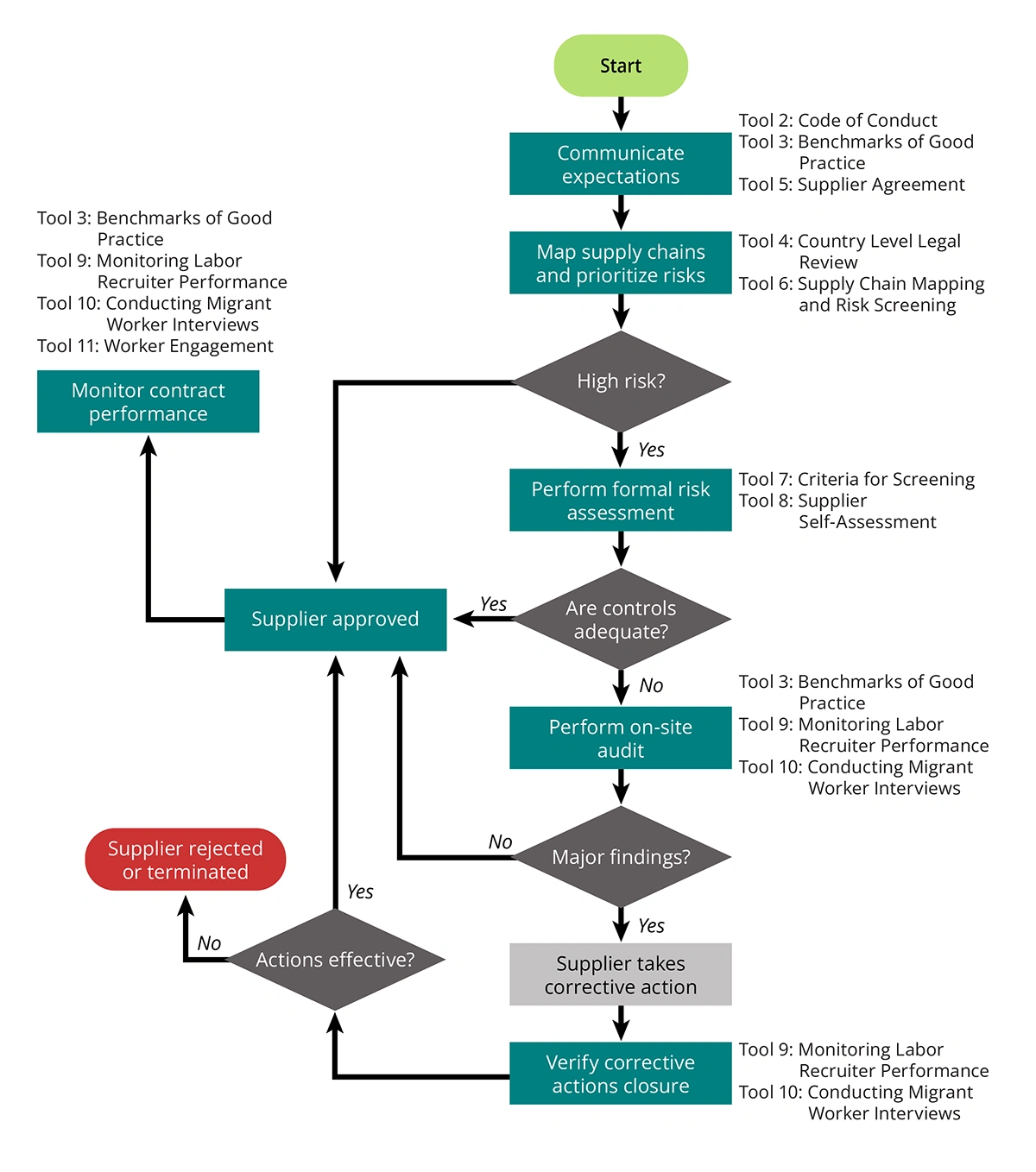
This flowchart is available for download in two formats:
Mining Toolset
Establish Policies and Performance Standards
Assess, Address, and Monitor
Compliance Plan
Dive deeper into forced labor case studies, compliance, and more in our Resource Library.
