The Tulane National Biomedical Research Center drew national attention in 2015 when a deadly foreign-strain of bacteria escaped one of the center’s high-containment laboratories.
Funds for SNAP, WIC, and Head Start run out on Saturday, affecting over 1 million people in Georgia.
Trump’s budget bill slashes nearly 20% from SNAP through 2034. Separate from any temporary SNAP stoppages due to the federal shutdown, the law cuts off access for refugees and other immigrant groups who are in the country lawfully.
Also in the Global Health Checkup: Bird flu in Europe, Fiji free of trachoma, Rift Valley Fever in Senegal, and what happens when malaria aid is cut.
As CDC systems are dismantled, the idea of a coordinated national response to a health emergency seems as fictional as zombies themselves.
The Tulane National Biomedical Research Center drew national attention in 2015 when a deadly foreign-strain of bacteria escaped one of the center’s high-containment laboratories.
Funds for SNAP, WIC, and Head Start run out on Saturday, affecting over 1 million people in Georgia.
Trump’s budget bill slashes nearly 20% from SNAP through 2034. Separate from any temporary SNAP stoppages due to the federal shutdown, the law cuts off access for refugees and other immigrant groups who are in the country lawfully.
Also in the Global Health Checkup: Bird flu in Europe, Fiji free of trachoma, Rift Valley Fever in Senegal, and what happens when malaria aid is cut.
The discussion at the Brookings Institution in Washington, D.C., explored coverage of the outbreak's origin: Was it caused by an accident at a lab in Wuhan, China? Or an infected animal at a Wuhan market or in the wild?
Warning by European health agency about mpox strain notes locally spread cases in Spain, Italy, Portugal, the Netherlands, and California.
The state’s $7.75 billion poultry industry is one of the largest in the nation, so bird flu “poses a serious threat,” Georgia Agriculture Commissioner Tyler Harper said.
As CDC systems are dismantled, the idea of a coordinated national response to a health emergency seems as fictional as zombies themselves.
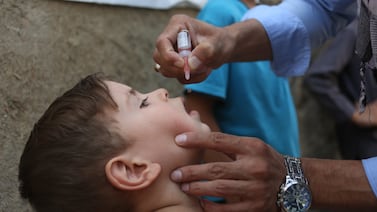
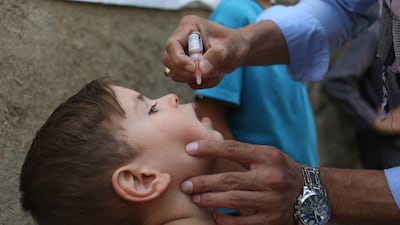
History shows that mandates increase the use of vaccines. Lower vaccination rates will mean increased rates of diseases like measles, hepatitis, meningitis, and pneumonia — and even the return of diphtheria and polio.
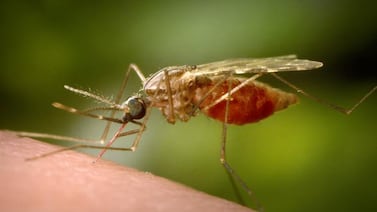
Public health team’s investigation suggests Tacoma-area woman is state’s first known locally acquired malaria infection.
Several New York neighborhoods are considered “food deserts” — where it’s difficult to buy healthy, nutritious food at an affordable price.
Also in the Global Health Checkup: Severe hunger, biodiversity loss, the global funding gap, and a tuberculosis comeback.
There’s a shortage of RNs across the U.S., with Georgia needing to train 772 more a year to keep up with projected demand. One nurse’s journey from Khartoum shows how foreign-trained nurses can help plug that gap.
The new cases are the first reported clade I infections in the United States that don’t involve international travel, the California Department of Public Health said.
Healthbeat is inviting New York’s public health community to step into the spotlight and share the stories that show why this work matters, in their own words.
A core part of the job will be appointing a commissioner to lead one of the largest public health agencies in the world and to set priorities on issues like chronic disease, mental health, overdose prevention, vaccines, and climate and emergency preparedness.
For the leaders of CARE, The Carter Center, The Task Force on Global Health, the CDC, and the CDC Foundation, the abrupt cuts have brought layoffs and challenges to fulfilling their mission.
New research, suspected cases in N.J., Washington this year raise concerns about local malaria infections.
Efforts to contain Ebola in the Democratic Republic of Congo may show that the WHO and Red Cross can rally new sources of emergency aid in absence of U.S. But is that a long-term solution?
More than 40% of adults are obese in some states. New report details U.S. obesity epidemic and makes policy recommendations amid federal cuts to public health.