On this page
- Invalid modules or themes
- The module or theme is missing
- The module or theme is incompatible with the installed version of Drupal
- The module or theme is incompatible with the installed version of PHP
- If none of the above options work you can use the missing module fixer
- Programmatically removing a missing theme or module
- Manually removing a missing theme or module
- Manually removing a missing theme
- Manually removing a missing module
- Removing abandoned settings from the database
Troubleshooting database updates
This documentation needs review. See "Help improve this page" in the sidebar.
Before you begin troubleshooting a database update issue, always back up both your database and codebase.
If there are any issues that prevent database updates from being run safely, update.php or drush updatedb will report an error.
Read the error message carefully to troubleshoot the issue.
Invalid modules or themes
In some cases, update.php may report that there are invalid modules or themes. This happens when a module or theme is listed in the core.extension.yml configuration file, but is either missing or incompatible with the site.
If the module listed is no longer wanted and you have access to Drush, the quickest solution is to run drush cedit core.extension - you can then delete the line containing the unwanted module.
Altenatively, enable devel module and on the administrative interface go to /devel/config, edit core.extension delete missing module entry. (from https://www.drupal.org/node/2487215)
When troubleshooting this issue, you should first check that you have not imported an incorrect version of core.extension.yml configuration. Then, troubleshoot further based on the specific message displayed. Re-run update.php once the issue is resolved.
The module or theme is missing
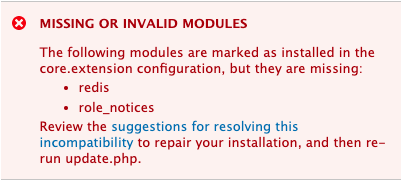
-
If
update.phpreports that a module or theme is missing and the correctcore.extension.ymlis in use, check to make sure the module or theme is present in the site's codebase.- For example, if a Drupal module is missing, look in
[site-root]/modulesand[site-root]/sites/all/modulesfor a folder that matches the missing module name.[site-root]/modulestakes precedence over[site-root]/sites/all/modules, but both are scanned for modules. - If update.php or drush updatedb complains about a missing Drupal theme, make sure that your themes folder e.g.
[site-root]/themesor[site-root]/themes/contribcontains a folder matching the missing theme.
- For example, if a Drupal module is missing, look in
-
If the folder is completely missing, search for the module on Drupal.org and try re-downloading it to your modules folder. Make sure to download a version that is compatible with your version of Drupal.
-
If the folder is present, it might be missing files or otherwise have damaged contents. You can also search for the module on Drupal.org and try re-downloading it in this case. Make sure to download a version that is compatible with your version of Drupal. Overwrite the existing folder with the newly downloaded version.
-
If the module was not downloaded from Drupal.org, try to locate its original source.
- If the module is specific to your site or application, try to locate its original version and re-add it to the modules folder.
- If the module was created by a third party, but is not hosted on Drupal.org (e.g., provided on GitHub), try to locate a valid version and re-download it.
-
As a last resort, if the original code of a module or theme cannot be located, you can remove the theme or module "manually" from your site's database. See section Manually removing a missing theme or module for details. Be aware that this could cause other fatal errors on the site.
-
Once the module is restored, re-run
update.phpordrush updatedb.
The module or theme is incompatible with the installed version of Drupal

-
If
update.phpreports that a module or theme is incompatible with the installed version of Drupal, you will need to either update Drupal, or update the module or theme. -
Then, check which version of the module or theme is installed by reading the
modules/modulename/modulename.info.ymlfile. You should see at least one of the following lines near the top of the file:-
core: 8.x core_version_requirement: ^8.8 || ^9This means the module is compatible with both Drupal 8.8+ and Drupal 9. The
core: 8.xkey is optional in this case and may or may not be present. (More information on thecore_version_requirementkey.) -
core_version_requirement: ^9This means the module is only compatible with Drupal 9. (More information on the
core_version_requirementkey.) -
core: 8.xThis means the module is only compatible with Drupal 8.
-
core: 7.xThis means the module is only compatible with Drupal 7.
-
-
If the version of Drupal core is too low for the installed module, download an update for Drupal core.
-
If the version of the module is too low for the version of Drupal core, download or install an updated version of the module.
-
If a compatible version of the module or core is not available, you may need to restore a previous version from backup.
-
Once compatible versions of both Drupal core and the module or theme are present in the codebase, re-run
update.php.
The module or theme is incompatible with the installed version of PHP

-
If the module or theme is incompatible with the installed version of PHP, look in the
modules/modulename/modulename.info.ymlfor a line like:php: 7.3 -
Option 1: Install a version of the module or theme that supports your site's PHP version.
-
Option 2: Change your site's PHP version to a version that is compatible with the module.
-
Once compatible versions of PHP and the affected module or theme are present in the codebase, re-run
update.php.
If none of the above options work you can use the missing module fixer
Note that the Module Missing Message Fixer can only automatically correct problems with missing or broken Drupal modules. If you run into problems with an unsupported or broken theme, you will have to use one of the manual approaches explained above.
https://www.drupal.org/project/module_missing_message_fixer
Programmatically removing a missing theme or module
After identifying which modules are missing, you can create an array with those modules and remove them from the config. See the example below:
- Create an array with the module machine name:
$modules_to_disable = ['module_name', 'other_module_name', 'another_module_name',];- Define which config you want to edit and load the existing configuration:
$config_name = 'core.extension';
$config = \Drupal::configFactory()->getEditable($config_name);- Get the current list of enabled modules
$enabled_modules = $config->get('module') ?? [];- Disable the specified modules
foreach ($modules_to_disable as $module) {
if (isset($enabled_modules[$module])) {
unset($enabled_modules[$module]);
}
} - Update the configuration with the new list of enabled modules
$config->set('module', $enabled_modules);
$config->save();We can add this to a HOOK_update_N and apply it with drush updb. There are many different ways to run this piece of code, like using drush ev or drush php
- Example of full code:
function MYMODULE_update_9001() {
$modules_to_disable = ['module_name', 'other_module_name', 'another_module_name',];
$config_name = 'core.extension';
// Load the existing configuration.
$config = \Drupal::configFactory()->getEditable($config_name);
// Get the current list of enabled modules.
$enabled_modules = $config->get('module') ?? [];
// Disable the specified modules.
foreach ($modules_to_disable as $module) {
if (isset($enabled_modules[$module])) {
unset($enabled_modules[$module]);
}
}
// Update the configuration with the new list of enabled modules.
$config->set('module', $enabled_modules);
$config->save();
}
Manually removing a missing theme or module
If for any reason, you can't get hold of a copy of a missing theme or module you can either manually remove that theme from the Drupal database or - as a less intrusive approach - create a dummy module or theme and use Drupal's built-in uninstall functions.
Basically, the same approach applies to modules and themes alike. The dummy is an "empty" module or theme with a system name that matches the missing package's system name. A problem with this approach is, that the dummy is missing the uninstall hooks of the original module or theme. This can lead to abandoned settings and other leftovers in your database. Usually, those settings can easily be found and removed from the database.
A real-world example with more details can be found in the article How to manually remove broken or missing Drupal modules from the database.
Manually removing a missing theme
- Start by identifying the missing theme's system name. The error messages from
update.phpordrush updatedbwill display the missing theme's system name. - Create a dummy theme named exactly like the original theme. To create a dummy theme you don't need more than a directory and the info.yml file. See Defining a theme with an .info.yml file for a complete guide.
- Visit
/admin/appearanceor rundrush pmlto check if Drupal recognizes the dummy theme. - Uninstall the theme via the UI or run
drush pmu your_dummy_theme_name. - Clear all caches.
The problematic theme should be removed by then, but this approach can lead to abandoned settings and leftovers in your database. See Removing abandoned settings from the database.
Manually removing a missing module
If you have access to Drush, the quickest solution is to run drush cedit core.extension - you can then delete the line containing the unwanted module.
The approach of creating a dummy works for themes and modules alike. Still, removing modules straight from the database is a little less tricky, than removing a theme. If you feel comfortable with manipulating the database, skip the creation of a dummy and jump right to Removing abandoned settings from the database.
- Start by identifying the missing module's system name. The error messages from
update.phpordrush updatedbwill display the missing module's system name. - Create a dummy module named exactly like the original module. See Let Drupal know about your module with an .info.yml file for examples and details.
- Visit
/admin/modulesor rundrush pmlto check if Drupal recognizes the dummy module. - Uninstall the module via the UI
/admin/modules/uninstallor rundrush pmu your_dummy_module_name. - Clear all caches.
See Removing abandoned settings from the database to find out, how to remove abandoned settings of a manually removed module.
Removing abandoned settings from the database
Modules and themes can leave their traces in different tables. A good spot to find module leftovers is the tables
- config / config_export
- key_value
- locales_location / locales_source
- and sometimes the cache tables.
Use a tool like phpMyAdmin that allows searching through all tables of your database comfortably and removing rows that hold your module's or theme's system name.
In this example the missing module's system name is user_points.
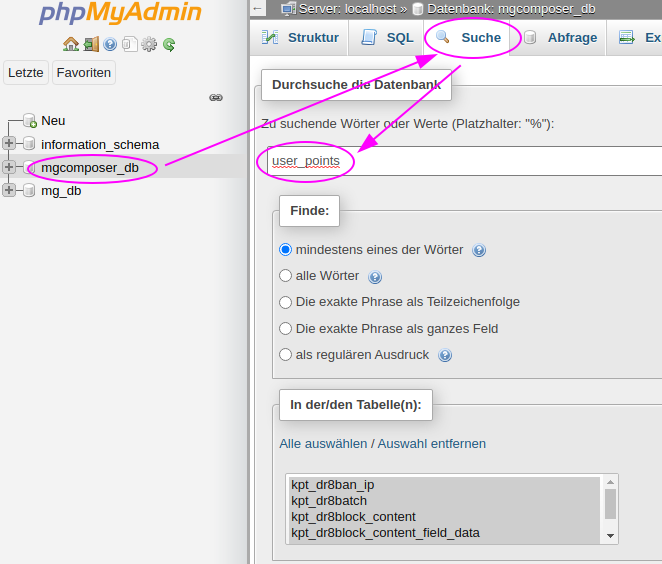
The search reveals some tables, that hold references to the user_point module. A click on the table name displays all matching rows.

Edit or remove the matching rows.

Make sure not to remove entries that store more than your missing module's configuration. E.g. in the table config the row with name core.extension stores settings in a BLOB. Don't remove the entire row, rather edit the BLOB in the data column and remove only traces of your missing module.
If you prefer working on the command line, in order to find references to missing or corrupted modules or themes, you could export your Drupal database drush sql-dump > mysite.sql and grep for the module's name grep module_system_name mysite.sql. If a match shows up, open the database dump in a text editor and search for the module's system name, to see which tables hold relicts of old modules. Then either manipulate the database dump and run drushsql:cli < mysite.sql or use drush sql:cli to edit or remove the rows.
Help improve this page
You can:
- Log in, click Edit, and edit this page
- Log in, click Discuss, update the Page status value, and suggest an improvement
- Log in and create a Documentation issue with your suggestion
 Still on Drupal 7? Security support for Drupal 7 ended on 5 January 2025. Please visit our Drupal 7 End of Life resources page to review all of your options.
Still on Drupal 7? Security support for Drupal 7 ended on 5 January 2025. Please visit our Drupal 7 End of Life resources page to review all of your options.