On this page
- Overview of Drupal's Ajax API.
- Why Ajax?
- Methods for triggering Ajax requests
- Trigger Ajax request from a form
- Trigger Ajax request with a link
- Trigger Ajax request with a submit button
- Trigger Ajax request with custom code (Client JavaScript)
- Autocomplete on text fields
- Drupal Ajax Conventions
- Replacing markup
Basic Concepts
Overview of Drupal's Ajax API.
This page is based on the "Ajax API" documentation.
Why Ajax?
Ajax is the process of dynamically updating parts of a page's HTML based on data from the server without requiring full page refresh. You can find events triggering Ajax requests all over Drupal, for example when selecting Views filters, Views pagers or forms widgets like autocomplete fields.
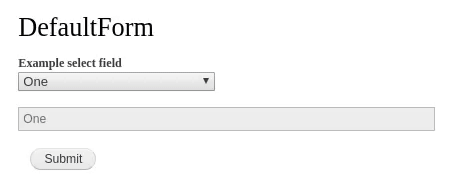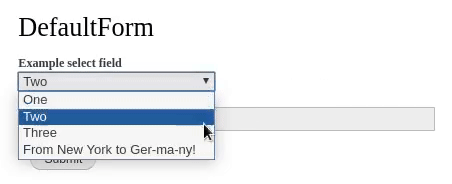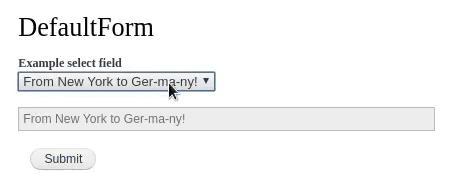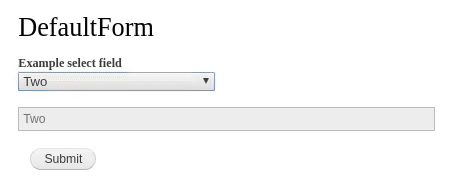
When a specified event takes place, like entering values in a textbox or clicking a button, a PHP callback is triggered. The callback function performs server-side logic and either
- returns updated markup to display new information on a page or form without a full page refresh, or
- executes JavaScript commands which can display dialog boxes, alter CSS on the page or execute custom JavaScript code.
Any valid DOM event can be used to trigger Ajax requests, simply omit the 'on' portion of the event. For example 'onclick' becomes 'click', 'onchange' is 'change'. Find example code on the Ajax Forms documentation page. Examples events:
- Clicking a button
- Pressing a key
- Entering values in a textbox
- Selecting a checkbox
- Moving the mouse
Methods for triggering Ajax requests
Trigger Ajax request from a form
Add an '#ajax' parameter with appropriate values to your form element.
See the AJAX Forms Documentation Page for details on triggering ajax and handling callbacks from a drupal form.
See also
Trigger Ajax request with a link
Add class 'use-ajax' to a link. The link will be loaded using an Ajax call. When using this method, the href of the link can contain '/nojs/' as part of the path. When Ajax JavaScript processes the page, it will convert this to '/ajax/'. The server is then able to easily tell if this request was made through an actual Ajax request or in a degraded state, and respond appropriately.
Assume there is custom controller route that returns a render array of markup, defined with the help of a MYMODULE.routing.yml file:
MYMODULE.test:
path: '/MYMODULE/test'
defaults:
_controller: 'Drupal\MYMODULE\Controller\ExampleController:testContent'
requirements:
_permission: 'access content'And a src/Controller/ExampleController.php file:
<?php
namespace Drupal\MYMODULE\Controller;
use Drupal\Core\Controller\ControllerBase;
class ExampleController extends ControllerBase {
public function testContent() {
$content = $this->t(__METHOD__);
$markup = [
'#type' => 'markup',
'#markup' => $content,
];
}
}
Here is a link that is part of a form and is able to trigger AJAX opening a modal dialog by use of 'use-ajax' class:
use Drupal\Component\Serialization\Json;
use Drupal\Core\Url;
$form['test_ajax_link'] = [
'#type' => 'link',
'#url' => Url::fromRoute('MYMODULE.test'),
'#title' => 'Click Me',
'#attributes' => [
'id' => 'my-dialog',
'class' => ['use-ajax'],
'data-dialog-type' => 'modal',
'data-dialog-options' => Json::encode([
'width' => 700,
'minHeight' => 500,
'title' => $this->t('This is a title'),
]),
],
];Trigger Ajax request with a submit button
Add class 'use-ajax-submit' to a submit button in a form. The form will then be submitted via Ajax to the path specified in the #action. Like the ajax-submit class on links, this path will have '/nojs/' replaced with '/ajax/' so that the submit handler can tell if the form was submitted in a degraded state or not.
// This should match with the HTTP verb of the route specified in $form['#action'].
$form['#method'] = 'GET';
// This route should return a Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\JsonResponse object
// so that the form could handle the result after submit.
$form['#action'] = \Drupal\Core\Url::fromRoute('MYMODULE.test')->toString();
// A HTML element that is part of the form where AJAX submit result could be inserted.
$form['result'] = [
'#markup' => '<div id="result"></div>',
];
// Makes AJAX request to $form['#action'] route aka `MYMODULE.test` route.
$form['submit'] = [
'#type' => 'submit',
'#value' => $this->t('Submit'),
'#attributes' => [
'class' => ['use-ajax-submit'],
],
];Here is how the MYMODULE.test controller route may look like:
<?php
namespace Drupal\MYMODULE\Controller;
use Drupal\Core\Controller\ControllerBase;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\JsonResponse;
class TestController extends ControllerBase {
// Perhaps tweak the route a bit so it has some parameters
// for the selector, the command, making this a bit more dynamic.
// For simplicity, hard-code them for now.
public function testContent() {
$content = $this->t(__METHOD__);
return new JsonResponse([
'command' => 'insert',
'selector' => '#result',
'data' => $content,
]);
}
}
Finally, a custom JS code to make use of the JsonResponse object. Don't forget to declare a library in MYMODULE.libraries.yml file and attach it to the form.
$form['#attached']['library'][] = 'MYMODULE/my_library';
(function ($) {
$(document).on('ajaxComplete', function (event, request, settings) {
if (!('responseJSON' in request)) {
return;
}
console.log(request.responseJSON);
const {command, selector, data} = request.responseJSON;
if (command === 'insert') {
$(selector).html(data);
}
});
})(jQuery);
Trigger Ajax request with custom code (Client JavaScript)
To trigger an Ajax request in custom JavaScript code on the client, you can find the related code in /misc/ajax.js Javascript file. The key API function is Drupal.ajax() - see its JSDoc below for more details.
To make a simple AJAX call to a URL (or probably your Drupal Ajax Command URL)
const ajax = Drupal.ajax({
url: '/your-ajax-url?_wrapper_format=drupal_ajax',
});
ajax.execute();More details and examples in the JSDoc:
/**
* Provides Ajax page updating via jQuery $.ajax.
*
* This function is designed to improve developer experience by wrapping the
* initialization of {@link Drupal.Ajax} objects and storing all created
* objects in the {@link Drupal.ajax.instances} array.
*
* @example
* Drupal.behaviors.myCustomAJAXStuff = {
* attach: function (context, settings) {
*
* var ajaxSettings = {
* url: 'my/url/path',
* // If the old version of Drupal.ajax() needs to be used those
* // properties can be added
* base: 'myBase',
* element: $(context).find('.someElement')
* };
*
* var myAjaxObject = Drupal.ajax(ajaxSettings);
*
* // Declare a new Ajax command specifically for this Ajax object.
* myAjaxObject.commands.insert = function (ajax, response, status) {
* $('#my-wrapper').append(response.data);
* alert('New content was appended to #my-wrapper');
* };
*
* // This command will remove this Ajax object from the page.
* myAjaxObject.commands.destroyObject = function (ajax, response, status) {
* Drupal.ajax.instances[this.instanceIndex] = null;
* };
*
* // Programmatically trigger the Ajax request.
* myAjaxObject.execute();
* }
* };
*
* @param {object} settings
* The settings object passed to {@link Drupal.Ajax} constructor.
* @param {string} [settings.base]
* Base is passed to {@link Drupal.Ajax} constructor as the 'base'
* parameter.
* @param {HTMLElement} [settings.element]
* Element parameter of {@link Drupal.Ajax} constructor, element on which
* event listeners will be bound.
*
* @return {Drupal.Ajax}
* The created Ajax object.
*
* @see Drupal.AjaxCommands
*/
Drupal.ajax = function (settings) {...}Autocomplete on text fields
Add property '#autocomplete_route_name' to a text field in a form. The route controller for this route must return an array of options for autocomplete, as a \Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\JsonResponse object. See the Routing topic for more information about routing.
It is worth checking out the Drupal\Core\Entity\Element\EntityAutocomplete element.
Do NOT attempt to set '#autocomplete_route_name' and '#autocomplete_route_parameters' by yourself because that is automatically handled by Drupal\Core\Entity\Element\EntityAutocomplete::processEntityAutocomplete() method which also updates the 'entity_autocomplete' keyvalue store for performance. If you set the '#autocomplete_*' manually, the keyvalue store never gets updated properly, which causes issue.
$form['test_autocomplete'] = [
'#type' => 'entity_autocomplete',
'#target_type' => 'node',
'#tags' => TRUE,
'#selection_handler' => 'default',
'#selection_settings' => [
'target_bundles' => ['article',],
],
'#autocreate' => [
'bundle' => 'article',
'uid' => 1,
],
];Also check out the linkit and dynamic_entity_reference contrib modules for more autocomplete examples.
Drupal Ajax Conventions
Replacing markup
It is best practice to use an element's id attribute to target it for replacement to avoid any chance of the wrong element or multiple elements being replaced unless that is specifically required. In order to maintain the replaceability of that element, the replacement render array or HTML markup should contain a wrapper element with the same id as the element that was being replaced.
When working with render arrays, if such a wrapper is not automatically included it is common practice to use the '#prefix' and '#suffix' render variables at the top level to provide one.
Help improve this page
You can:
- Log in, click Edit, and edit this page
- Log in, click Discuss, update the Page status value, and suggest an improvement
- Log in and create a Documentation issue with your suggestion
 Still on Drupal 7? Security support for Drupal 7 ended on 5 January 2025. Please visit our Drupal 7 End of Life resources page to review all of your options.
Still on Drupal 7? Security support for Drupal 7 ended on 5 January 2025. Please visit our Drupal 7 End of Life resources page to review all of your options.